Introduction to Hotspot 2.0
The Hotspot 2.0 feature enables IEEE 802.11 devices to interwork with external networks. The interworking service aids network discovery and selection, enabling information transfer from external networks. It provides information to the stations about the networks before association.
Interworking not only helps users within the home, enterprise, and public access domains, but also assists manufacturers and operators to provide common components and services for IEEE 802.11 customers. These services are configured on a per-WLAN basis on the Cisco Wireless Controller (controller).
Hotspot 2.0, also known as HS2 and Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint, is based on the IEEE 802.11u and Wi-Fi Alliance Hotspot 2.0 standards. It seeks to provide better bandwidth and services-on-demand to end users. The Hotspot 2.0 feature allows mobile devices to join a Wi-Fi network automatically, including during roaming, when the devices enter the Hotspot 2.0 area.
The Hotspot 2.0 feature has four distinct parts:
-
Hotspot 2.0 Beacon Advertisement: Allows a mobile device to discover Hotspot 2.0-compatible and 802.11u-compatible WLANs.
-
Access Network Query Protocol (ANQP) Queries: Sends queries about the networks from IEEE 802.11 devices, such as network type (private or public); connectivity type (local network, internet connection, and so on), or the network providers supported by a given network.
-
Online Sign-up: Allows a mobile device to obtain credentials to authenticate itself with the Hotspot 2.0 or WLAN.
-
Authentication and Session Management: Provides authentication (802.1x) and management of the STA session (session expiration, extension, and so on).
In order to mark a WLAN as Hotspot 2.0-compatible, the 802.11u-mandated information element and the Hotspot 2.0 information element is added to the basic service set (BSS) beacon advertised by the corresponding AP, and in WLAN probe responses.
 Note |
The Hotspot 2.0 feature supports only local mode or FlexConnect mode (central switching and central authentication). FlexConnect local switching is only supported when the Open Roaming configuration template is set up using the wireless hotspot anqp-server server-name type open-roaming command. If the configuration diverges from this template, FlexConnect local switching will not be supported. |
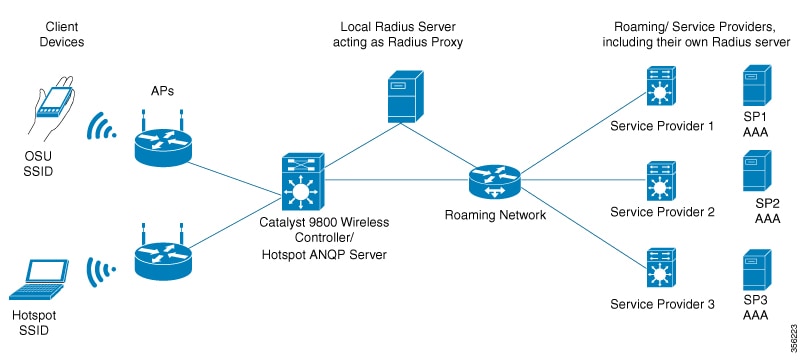
The following figure shows a standard deployment of the Hotspot 2.0 network architecture:
 Feedback
Feedback