Cisco HCM-F Application Node Overview
The following figure illustrates the architecture of Cisco HCM-F Application Node.
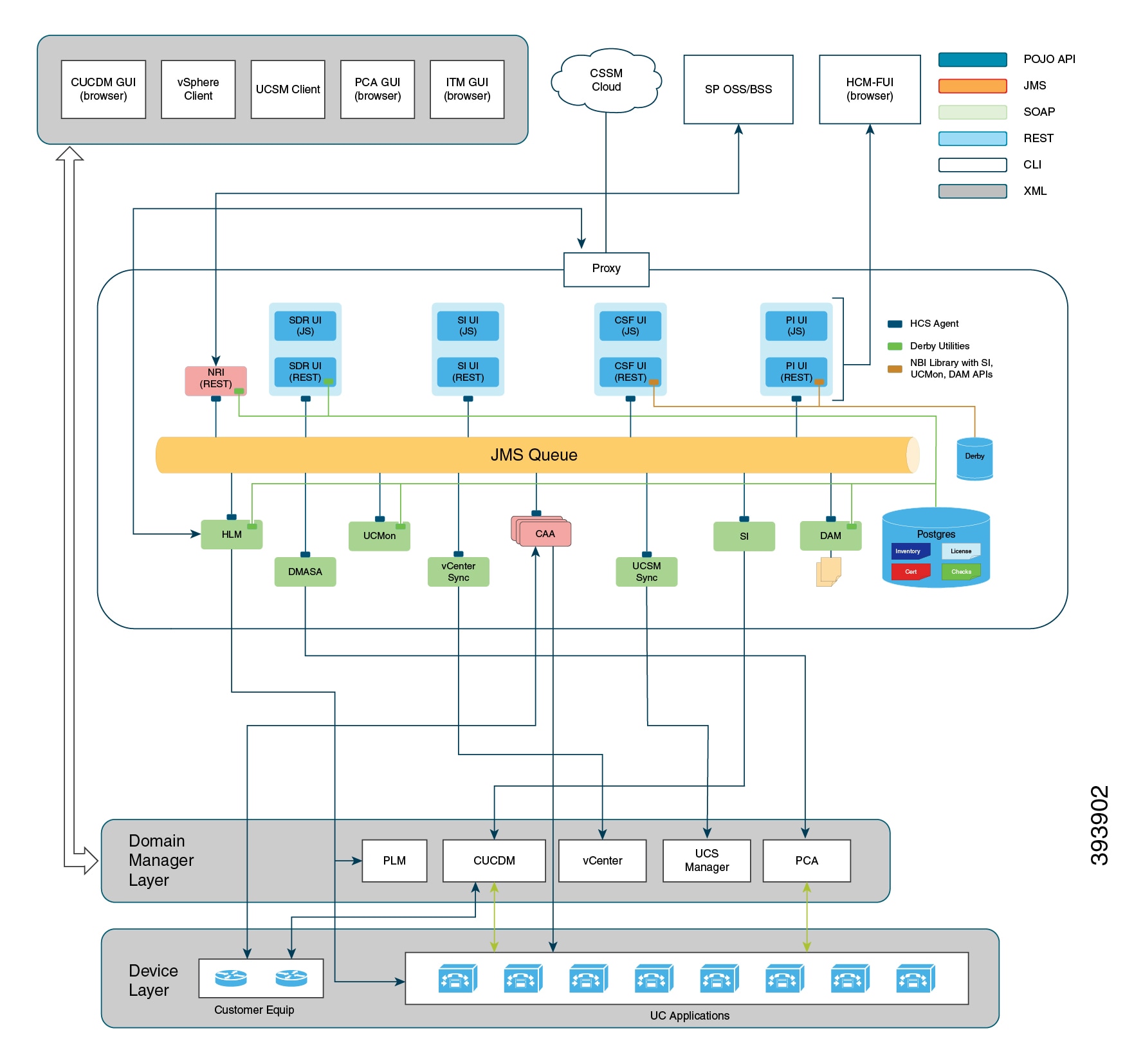
Cisco HCM-F Application Node delivers the following main functions and services:
-
Centralized database for the Cisco HCS solution: the Shared Data Repository (SDR)
-
Synchronization of the SDR with domain managers: Multiple synchronization services populate the SDR and keep it updated when configuration changes are applied through these domain managers. The following services populate and update the SDR:
-
CUCDMSync service updates the SDR when configuration changes are applied through the Cisco Unified Communications Domain Manager.
-
VCenterSync service updates the SDR when configuration changes are applied through vCenter.
-
HCS UCSMSync service monitors configuration data of Cisco UCS Managers and maintains synchronization between the Cisco HCS Shared Data Repository.
-
-
North Bound Interface (NBI): Populates and updates SDR.
-
Cisco HCM-F Administrative UI: Allows configuration of Cisco HCM-F services.
-
Services for automatic configuration of the Prime Collaboration Assurance (PCA):
-
HCS Fulfillment service
-
HCS DMA-SA service

Note
Based on data that is extracted from the SDR, the services work together to automatically configure the PCA to monitor Unified Communications Applications and customer equipment.
-
HCS Provisioning Adapter Service

Note
Fulfillment and Cisco HCS CAA CUCM Service work together to automatically configure Cisco Unified Communications Manager applications with the data required for those applications to be monitored by PCA. Other applications such as Cisco Unity Connection and Cisco Unified Communications Manager IM and Presence Service must be manually configured to be monitored by PCA.
-
-
HCS License Manager (HLM) service: Manages licenses for UC applications.
-
HCS Northbound Interface (NBI) API service: Provides an interface to the service provider BSS or OSS through a SOAP web services interface.
-
UC Monitor: Exposes REST API to trigger the checks. On receiving the JMS message, UC Monitor fetches the cluster type from SDR and validates the checks present in the message if they match with the cluster type or not. If match is not found, then UC Monitor responds with an error.
-
DAM: Data Access Manager is an auto start service in HCM-F which exposes functionality to store data from UC Monitor.
-
Cisco Application Adapter Service: Cisco Application Adapter (CAA) is the adapter that communicates with all UC apps and expressway services.
-
Service Inventory: Provides the service provider with reports on customers, subscribers, and devices. Service provider may use these reports to audit customer admin provisioning, and generate billing reports and change reports for their customers, based on MACD operations.
 Feedback
Feedback