SRST Overview
Cisco Unified SRST provides Cisco Unified CM with fallback support for Cisco Unified IP phones that are attached to a Cisco router on your local network. Cisco Unified SRST enables routers to provide call-handling support for Cisco Unified IP phones when they lose connection to remote primary, secondary, or tertiary Cisco Unified CM installations or when the WAN connection is down.
Cisco Unified CM supports Cisco Unified IP phones at remote sites attached to Cisco multiservice routers across the WAN. Before Cisco Unified SRST, when the WAN connection between a router and the Cisco Unified CM failed or when connectivity with Cisco Unified CM was lost for some reason, Cisco Unified IP phones on the network became unusable for the duration of the failure. Cisco Unified SRST overcomes this problem and ensures that the Cisco Unified IP phones offer continuous (although minimal) service by providing call-handling support for Cisco Unified IP phones directly from the Cisco Unified SRST router. The system automatically detects a failure and uses Simple Network Auto Provisioning (SNAP) technology to autoconfigure the branch office router to provide call processing for Cisco Unified IP phones that are registered with the router. When the WAN link or connection to the primary Cisco Unified CM is restored, call handling reverts to the primary Cisco Unified CM.
When Cisco Unified IP phones lose contact with primary, secondary, and tertiary Cisco Unified CM, they must establish a connection to a local Cisco Unified SRST router to sustain the call-processing capability necessary to place and receive calls. The Cisco Unified IP phone retains the IP address of the local Cisco Unified SRST router as a default router in the Network Configuration area of the Settings menu. The Settings menu supports a maximum of five default router entries; however, Cisco Unified CM accommodates a maximum of three entries. When a secondary Cisco Unified CM is not available on the network, the local Cisco Unified SRST Router's IP address is retained as the standby connection for Cisco Unified CM during normal operation.
 Note |
Cisco Unified CM fallback mode telephone service is available only to those Cisco Unified IP phones that are supported by a Cisco Unified SRST router. Other Cisco Unified IP phones on the network remain out of service until they re-establish a connection with their primary, secondary, or tertiary Cisco Unified CM. |
How Fallback Occurs
Typically, it takes three times the keepalive period for a phone to discover that its connection to Cisco Unified CM has failed. The default keepalive period is 30 seconds. If the phone has an active standby connection established with a Cisco Unified SRST router, the fallback process takes 10 to 20 seconds after connection with Cisco Unified CM is lost. An active standby connection to a Cisco Unified SRST router exists only if the phone has the location of a single Cisco Unified CM in its Unified Communications Manager list. Otherwise, the phone activates a standby connection to its secondary Cisco Unified CM.
If a Cisco Unified IP phone has multiple Cisco Unified CM in its Cisco Unified CM list, it progresses through its list of secondary and tertiary Cisco Unified CM before attempting to connect with its local Cisco Unified SRST router. Therefore, the time that passes before the Cisco Unified IP phone eventually establishes a connection with the Cisco Unified SRST router increases with each attempt to contact to a Cisco Unified CM. If each attempt to connect to a Cisco Unified CM takes about 1 minute, the Cisco Unified IP phone in question could remain offline for 3 minutes or more following a WAN link failure.
 Note |
|
Resumption of Primary Call Control
While in Cisco Unified CM fallback mode, Cisco Unified IP phones periodically attempt to re-establish a connection with Cisco Unified CM at the central office. Generally, the default time that Cisco Unified IP phones wait before attempting to re-establish a connection to a remote Cisco Unified CM is 120 seconds. The time can be changed in Cisco Unified CM by editing the Connection Monitor Duration parameter. See the "Configure SRST” chapter of the System Configuration Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager. A manual reboot can immediately reconnect Cisco Unified IP phones to Cisco Unified CM.
When a connection is re-established with Cisco Unified CM, Cisco Unified IP phones automatically cancel their registration with the Cisco Unified SRST Router. However, if a WAN link is unstable, Cisco Unified IP phones can bounce between Cisco Unified CM and Cisco Unified SRST. A Cisco Unified IP phone cannot re-establish a connection with the primary Cisco Unified CM at the central office if it is currently engaged in an active call.
Supported Call Combinations
Cisco Unified SRST supports the following call combinations:
-
SIP phone to SIP phone
-
SIP phone to SCCP phone
-
SIP phone to PSTN/router voice-port
-
SIP phone to WAN VoIP using SIP
-
SCCP phone to SIP phone
-
SCCP phone to SCCP phone
-
SCCP phone to PSTN/router voice-port
-
SCCP phone to WAN VoIP using SIP or H.323
The following figure shows a remote site that connects to primary call control over a WAN IP connection. In this example, the WAN is down, making primary call control impossible to reach via IP networks. The SRST router acts as a fallback server, providing backup call control for IP Phones at the remote site, which can still use the PSTN for external calls, and for calls to phones that still register to the primary site.
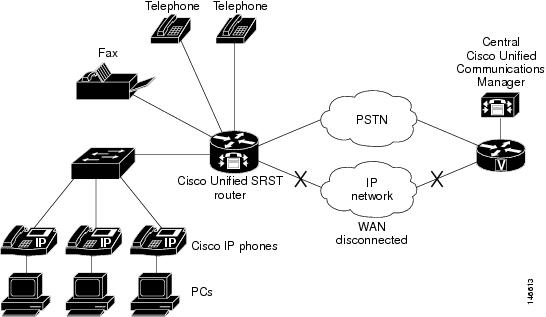
Figure 1: Branch Office Cisco Unified IP Phones Connected to a Remote Central Cisco Unified Communications Manage Operating in SRST Mode
 Feedback
Feedback