Prerequisites for Using Cisco Unified SRST Gateways as a Multicast MOH Resource
-
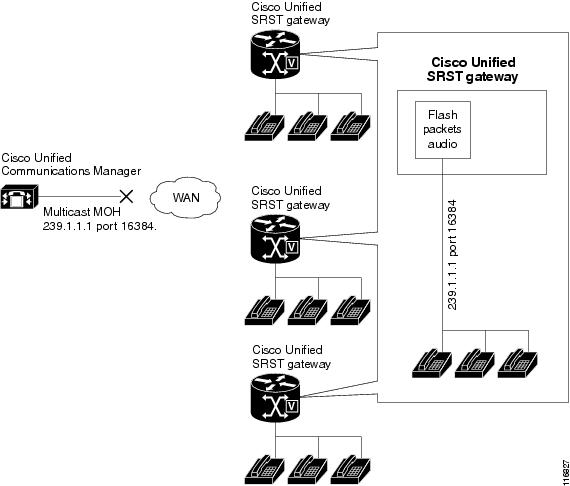
Multicast MOH for H.323 and MGCP is supported on Cisco Unified CM 3.1.1 and higher versions.
-
Cisco Unified CM must be configured as follows:
-
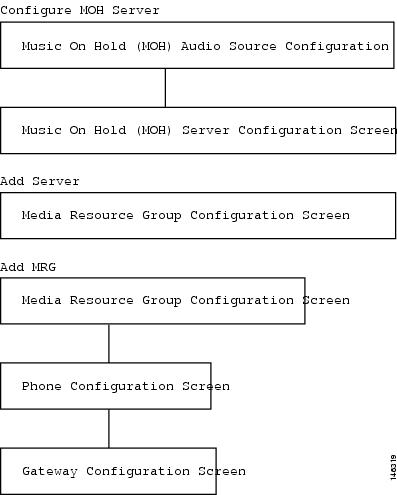
With multicast MOH enabled.
-
With Media Resource Groups (MRGs) and Media Resource Group Lists (MRGLs) controlling which devices receive multicast MOH and which devices receive unicast MOH.
-
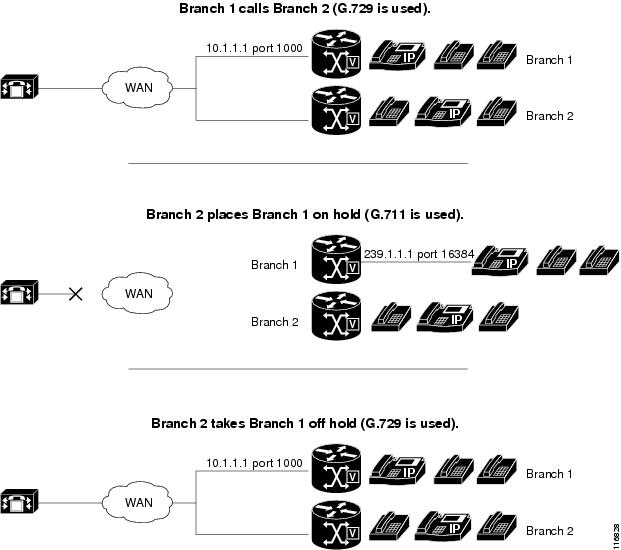
With Cisco Unified CM regions assigned so that G.711 is used whenever a Cisco Unified SRST multicast MOH resource is invoked.
-
-
The Cisco Unified SRST gateways must run on Cisco Unified SRST 3.0 on Cisco IOS Release 12.2(15)ZJ2 or a later release.
-
Cisco Unified SRST must be registered to Cisco Unified CM using protocol such as H.323, MGCP, or SIP.
-
For branches that do not run Cisco Unified SRST, Cisco Unified CM multicast MOH packets must cross the WAN. To accomplish this, you must have multicast routing enabled in your network. For more information about multicast routing, see the “IP Multicast” section of Cisco IOS IP Configuration Guide, Release 12.4T.
-
With Cisco IOS earlier than 12.3(14)T, configure Cisco Unified SRST as your MGCP gateway’s fallback mode using the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp and call application alternate commands. With Cisco IOS releases after 12.3(14)T, the ccm-manager fallback-mgcp and service commands must be configured. Configuring these two commands allows Cisco Unified SRST to assume control over the voice port and over call processing on the MGCP gateway. A complete configuration describing setting up Cisco Unified SRST as your fallback mode is shown in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration Guide, Release 5.1(3) Survivable Remote Site Telephony Configuration.



 Feedback
Feedback