- Preface
- New and Changed Information
- Overview of Cisco Unified Computing System
- Overview of Cisco UCS Manager
- Overview of Cisco UCS Manager GUI
- Configuring the Fabric Interconnects
- Configuring Ports and Port Channels
- Configuring Communication Services
- Configuring Authentication
- Configuring Organizations
- Configuring Role-Based Access Control
- Configuring DNS Servers
- Configuring System-Related Policies
- Managing Licenses
- Managing Virtual Interfaces
- Registering Cisco UCS Domains with Cisco UCS Central
- LAN Uplinks Manager
- VLANs
- Configuring LAN Pin Groups
- Configuring MAC Pools
- Configuring Quality of Service
- Configuring Network-Related Policies
- Configuring Upstream Disjoint Layer-2 Networks
- Configuring Named VSANs
- Configuring SAN Pin Groups
- Configuring WWN Pools
- Configuring Storage-Related Policies
- Configuring Fibre Channel Zoning
- Configuring Server-Related Pools
- Setting the Management IP Address
- Configuring Server-Related Policies
- Configuring Server Boot
- Deferring Deployment of Service Profile Updates
- Service Profiles
- Configuring Storage Profiles
- Managing Power in Cisco UCS
- Managing Time Zones
- Managing the Chassis
- Managing Blade Servers
- Managing Rack-Mount Servers
- Starting the KVM Console
- CIMC Session Management
- Managing the I/O Modules
- Backing Up and Restoring the Configuration
- Recovering a Lost Password
Cisco UCS Manager GUI Configuration Guide, Release 2.2
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- June 5, 2015
Chapter: Configuring Ports and Port Channels
- Server and Uplink Ports on the 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect
- Unified Ports on the Fabric Interconnect
- Port Modes
- Port Types
- TCP and UDP Ports
- Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
- Guidelines for Configuring Unified Ports
- Cautions and Guidelines for Configuring Unified Uplink Ports and Unified Storage Ports
- Effect of Port Mode Changes on Data Traffic
- Configuring Port Modes for a 6248 Fabric Interconnect
- Configuring Port Modes for a 6296 Fabric Interconnect
- Configuring the Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
- Server Ports
- Uplink Ethernet Ports
- Reconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Enabling or Disabling a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Unconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Appliance Ports
- FCoE and Fibre Channel Storage Ports
- FC Links Rebalancing
- Configuring FC Uplink Ports
- FCoE Uplink Ports
- Unified Storage Ports
- Unified Uplink Ports
- Uplink Ethernet Port Channels
- Appliance Port Channels
- Creating a Threshold Condition
- Policy-Based Port Error Handling
- Fibre Channel Port Channels
- FCoE Port Channels
- Unified Uplink Port Channel
- Adapter Port Channels
- Fabric Port Channels
- Configuring Server Ports with the Internal Fabric Manager
Configuring Ports and Port Channels
This chapter includes the following sections:
- Server and Uplink Ports on the 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect
- Unified Ports on the Fabric Interconnect
- Server Ports
- Uplink Ethernet Ports
- Reconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Enabling or Disabling a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Unconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
- Appliance Ports
- FCoE and Fibre Channel Storage Ports
- FC Links Rebalancing
- Configuring FC Uplink Ports
- FCoE Uplink Ports
- Unified Storage Ports
- Unified Uplink Ports
- Uplink Ethernet Port Channels
- Appliance Port Channels
- Creating a Threshold Condition
- Policy-Based Port Error Handling
- Fibre Channel Port Channels
- FCoE Port Channels
- Unified Uplink Port Channel
- Adapter Port Channels
- Fabric Port Channels
- Configuring Server Ports with the Internal Fabric Manager
Server and Uplink Ports on the 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect
Each Cisco UCS 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect has a set of ports in a fixed port module that you can configure as either server ports or uplink Ethernet ports. These ports are not reserved. They cannot be used by a Cisco UCS domain until you configure them. You can add expansion modules to increase the number of uplink ports on the fabric interconnect or to add uplink Fibre Channel ports to the fabric interconnect.
 Note | When you configure a port on a fabric interconnect, the administrative state is automatically set to enabled. If the port is connected to another device, this may cause traffic disruption. You can disable the port after configuring it. |
You need to create LAN pin groups and SAN pin groups to pin traffic from servers to an uplink port.
 Note | Ports on the Cisco UCS 6100 Series Fabric Interconnect are not unified. For more information on Unified Ports, see Unified Ports. |
Each fabric interconnect can include the following port types:
- Server Ports
-
Server ports handle data traffic between the fabric interconnect and the adapter cards on the servers.
You can only configure server ports on the fixed port module. Expansion modules do not include server ports.
- Uplink Ethernet Ports
-
Uplink Ethernet ports handle Ethernet traffic between the fabric interconnect and the next layer of the network. All network-bound Ethernet traffic is pinned to one of these ports.
By default, Ethernet ports are unconfigured. However, you can configure them to function in the following ways: You can configure uplink Ethernet ports on either the fixed module or an expansion module.
- Uplink Fibre Channel Ports
-
Uplink Fibre Channel ports handle FCoE traffic between the fabric interconnect and the next layer of the storage area network. All network-bound FCoE traffic is pinned to one of these ports.
By default, Fibre Channel ports are uplink. However, you can configure them to function as Fibre Channel storage ports. This is useful in cases where Cisco UCS requires a connection to a Direct-Attached Storage (DAS) device.
You can only configure uplink Fibre Channel ports on an expansion module. The fixed module does not include uplink Fibre Channel ports.
Unified Ports on the Fabric Interconnect
Unified ports are ports on the fabric interconnect that can be configured to carry either Ethernet or Fibre Channel traffic. These ports are not reserved. A Cisco UCS domain cannot use these ports until you configure them.
 Note | When you configure a port on a fabric interconnect, the administrative state is automatically set to enabled. If the port is connected to another device, this may cause traffic disruption. You can disable the port after configuring it. |
Configurable beacon LEDs indicate which unified ports are configured for the selected port mode.
- Port Modes
- Port Types
- TCP and UDP Ports
- Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
- Guidelines for Configuring Unified Ports
- Cautions and Guidelines for Configuring Unified Uplink Ports and Unified Storage Ports
- Effect of Port Mode Changes on Data Traffic
- Configuring Port Modes for a 6248 Fabric Interconnect
- Configuring Port Modes for a 6296 Fabric Interconnect
- Configuring the Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
Port Modes
The port mode determines whether a unified port on the fabric interconnect is configured to carry Ethernet or Fibre Channel traffic. You configure the port mode in Cisco UCS Manager. However, the fabric interconnect does not automatically discover the port mode.
Changing the port mode deletes the existing port configuration and replaces it with a new logical port. Any objects associated with that port configuration, such as VLANs and VSANS, are also removed. There is no restriction on the number of times you can change the port mode for a unified port.
Port Types
The port type defines the type of traffic carried over a unified port connection.
By default, unified ports changed to Ethernet port mode are set to the Ethernet uplink port type. Unified ports changed to Fibre Channel port mode are set to the Fibre Channel uplink port type. You cannot unconfigure Fibre Channel ports.
Changing the port type does not require a reboot.
Ethernet Port Mode
When you set the port mode to Ethernet, you can configure the following port types:
-
Server ports
-
Ethernet uplink ports
-
Ethernet port channel members
-
FCoE ports
-
Appliance ports
-
Appliance port channel members
-
SPAN destination ports
-
SPAN source ports

Note
For SPAN source ports, configure one of the port types and then configure the port as SPAN source.
Fibre Channel Port Mode
When you set the port mode to Fibre Channel, you can configure the following port types:
TCP and UDP Ports
|
Port |
Interface |
Protocol |
Traffic type |
Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
23 |
CLI |
Telnet |
TCP |
Cisco UCS Manager CLI access |
|
22 |
CLI |
SSH |
TCP |
Cisco UCS Manager CLI access |
|
443 |
Static HTML |
HTTPS |
TCP |
Cisco UCS Manager login page access |
|
80 |
Static HTML |
HTTP |
TCP |
Client download |
|
443 |
XML |
HTTPS |
TCP |
Cisco UCS Manager XML API access |
|
80 |
XML |
HTTP |
TCP |
Ports used by Cisco UCS Manager GUI and third party management stations. |
|
23 |
Serial-over-LAN |
Telnet |
TCP |
COM1 port access on a specified server |
|
22 |
Serial-over-LAN |
SSH |
TCP |
COM1 port access on a specified server |
|
161 |
SNMP |
SNMP |
UDP |
SNMP MIBs exposed for monitoring |
|
623 |
IPMI-over-LAN |
RMCP |
UDP |
IPMI access to BMCs |
|
2068 |
KVM |
Avocent Video Session |
TCP |
Data path for the BMCs |
|
843 |
xmlPolicy |
|
TCP |
Adobe port used by KVM launcher |
|
5988 |
CIM XML |
|
TCP |
Send CIM messages over HTTP |
|
Port |
Service |
Protocol |
Traffic type |
Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1812 |
AAA |
RADIUS |
UDP |
AAA server authentication requests |
|
1813 |
AAA |
RADIUS |
UDP |
AAA server authentication requests |
|
49 |
AAA |
TACACS |
TCP |
AAA server authentication requests |
|
389 |
AAA |
LDAP |
UDP |
|
|
123 |
Time Sync |
NTP |
UDP |
Synchronize the time with global time servers |
|
162 |
SNMP Traps |
SNMP |
UDP |
Send traps to a remote network management system. |
|
25 |
Call Home |
SMTP |
TCP |
Email-based and web-based notifications for critical system events |
|
514 |
Syslog |
SYSLOG |
UDP |
Cisco UCS Manager generated Syslog messages |
|
53 |
Name resolution |
DNS |
UDP |
DNS queries |
|
69 |
TFTP |
TFTP |
UDP |
File transfers |
|
115 |
SFTP |
SFTP |
TCP |
File transfers |
|
20-21 |
FTP |
FTP |
TCP |
File transfers |
|
21 |
SCP |
SCP |
TCP |
File transfers |
Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
Each port on the 6200 series fabric interconnect has a corresponding beacon LED. When the Beacon LED property is configured, the beacon LEDs illuminate, showing you which ports are configured in a given port mode.
You can configure the Beacon LED property to show you which ports are grouped in one port mode: either Ethernet or Fibre Channel. By default, the Beacon LED property is set to Off.
 Note | For unified ports on the expansion module, you can reset the Beacon LED property to the default value of Off during expansion module reboot. |
Guidelines for Configuring Unified Ports
Consider the following guidelines and restrictions when configuring unified ports:
Hardware and Software Requirements
Unified ports are supported on the 6200 series fabric interconnect with Cisco UCS Manager, version 2.0.
Unified ports are not supported on 6100 series fabric interconnects, even if they are running Cisco UCS Manager, version 2.0.
Port Mode Placement
Because the Cisco UCS Manager GUI interface uses a slider to configure the port mode for unified ports on a fixed or expansion module, it automatically enforces the following restrictions which limits how port modes can be assigned to unified ports. When using the Cisco UCS Manager CLI interface, these restrictions are enforced when you commit the transaction to the system configuration. If the port mode configuration violates any of the following restrictions, the Cisco UCS Manager CLI displays an error:
-
Ethernet ports must be grouped together in a block. For each module (fixed or expansion), the Ethernet port block must start with the first port and end with an even numbered port.
-
Fibre Channel ports must be grouped together in a block. For each module (fixed or expansion), the first port in the Fibre Channel port block must follow the last Ethernet port and extend to include the rest of the ports in the module. For configurations that include only Fibre Channel ports, the Fibre Channel block must start with the first port on the fixed or expansion module.
-
Alternating Ethernet and Fibre Channel ports is not supported on a single module.
Example of a valid configuration— Might include unified ports 1–16 on the fixed module configured in Ethernet port mode and ports 17–32 in Fibre Channel port mode. On the expansion module you could configure ports 1–4 in Ethernet port mode and then configure ports 5–16 in Fibre Channel mode. The rule about alternating Ethernet and Fibre Channel port types is not violated because this port arrangement complies with the rules on each individual module.
Example of an invalid configuration— Might include a block of Fibre Channel ports starting with port 16. Because each block of ports has to start with an odd-numbered port, you would have to start the block with port 17.
 Note | The total number of uplink Ethernet ports and uplink Ethernet port channel members that can be configured on each fabric interconnect is limited to 31. This limitation includes uplink Ethernet ports and uplink Ethernet port channel members configured on the expansion module. |
Cautions and Guidelines for Configuring Unified Uplink Ports and Unified Storage Ports
The following are cautions and guidelines to follow while working with unified uplink ports and unified storage ports:
-
In an unified uplink port, if you enable one component as a SPAN source, the other component will automatically become a SPAN source.

Note
If you create or delete a SPAN source under the Ethernet uplink port, Cisco UCS Manager automatically creates or deletes a SPAN source under the FCoE uplink port. The same happens when you create a SPAN source on the FCOE uplink port.
-
You must configure a non default native VLAN on FCoE and unified uplink ports. This VLAN is not used for any traffic. Cisco UCS Manager will reuse an existing fcoe-storage-native-vlan for this purpose. This fcoe-storage-native-vlan will be used as a native VLAN on FCoE and unified uplinks.
-
In an unified uplink port, if you do not specify a non default VLAN for the Ethernet uplink port the fcoe-storage-native-vlan will be assigned as the native VLAN on the unified uplink port. If the Ethernet port has a non default native VLAN specified as native VLAN, this will be assigned as the native VLAN for unified uplink port.
-
When you create or delete a member port under an Ethernet port channel, Cisco UCS Manager automatically creates or deletes the member port under FCoE port channel. The same happens when you create or delete a member port in FCoE port channel.
-
When you configure an Ethernet port as a standalone port, such as server port, Ethernet uplink, FCoE uplink or FCoE storage and make it as a member port for an Ethernet or FCOE port channel, Cisco UCS Manager automatically makes this port as a member of both Ethernet and FCoE port channels.
-
When you remove the membership for a member port from being a member of server uplink, Ethernet uplink, FCoE uplink or FCoE storage, Cisco UCS Manager deletes the corresponding members ports from Ethernet port channel and FCoE port channel and creates a new standalone port.
-
If you downgrade Cisco UCS Manager from release 2.1 to any of the prior releases, all unified uplink ports and port channels will be converted to Ethernet ports and Ethernet port channels when the downgrade is complete. Similarly, all the unified storage ports will be converted to appliance ports.
-
For unified uplink ports and unified storage ports, when you create two interfaces, only one license is checked out. As long as either interface is enabled, the license remains checked out. The license will be released only if both the interfaces are disabled for a unified uplink port or a unified storage port.
-
Cisco UCS 6100 series fabric interconnect switch can only support 1VF or 1VF-PO facing same downstream NPV switch.
Effect of Port Mode Changes on Data Traffic
Port mode changes can cause an interruption to the data traffic for the Cisco UCS domain. The length of the interruption and the traffic that is affected depend upon the configuration of the Cisco UCS domain and the module on which you made the port mode changes.
 Tip | To minimize the traffic disruption during system changes, form a Fibre Channel uplink port-channel across the fixed and expansion modules. |
Impact of Port Mode Changes on an Expansion Module
After you make port mode changes on an expansion module, the module reboots. All traffic through ports on the expansion module is interrupted for approximately one minute while the module reboots.
Impact of Port Mode Changes on the Fixed Module in a Cluster Configuration
A cluster configuration has two fabric interconnects. After you make port changes to the fixed module, the fabric interconnect reboots. The impact on the data traffic depends upon whether or not you have configured the server vNICs to failover to the other fabric interconnect when one fails.
If you change the port modes on the expansion module of one fabric interconnect and then wait for that to reboot before changing the port modes on the second fabric interconnect, the following occurs:
-
With server vNIC failover, traffic fails over to the other fabric interconnect and no interruption occurs.
-
Without server vNIC failover, all data traffic through the fabric interconnect on which you changed the port modes is interrupted for approximately eight minutes while the fabric interconnect reboots.
If you change the port modes on the fixed modules of both fabric interconnects simultaneously, all data traffic through the fabric interconnects are interrupted for approximately eight minutes while the fabric interconnects reboot.
Impact of Port Mode Changes on the Fixed Module in a Standalone Configuration
A standalone configuration has only one fabric interconnect. After you make port changes to the fixed module, the fabric interconnect reboots. All data traffic through the fabric interconnect is interrupted for approximately eight minutes while the fabric interconnect reboots.
Configuring Port Modes for a 6248 Fabric Interconnect
 Caution | Changing the port mode on either module can cause an interruption in data traffic because changes to the fixed module require a reboot of the fabric interconnect and changes on an expansion module require a reboot of that module . If the Cisco UCS domain has a cluster configuration that is set up for high availability and servers with service profiles that are configured for failover, traffic fails over to the other fabric interconnect and data traffic is not interrupted when the port mode is changed on the fixed module. |
What to Do Next
Configure the port types for the ports. You can right-click on any port in the module display above the slider and configure that port for an available port type.
Configuring Port Modes for a 6296 Fabric Interconnect
 Caution | Changing the port mode on either module can cause an interruption in data traffic because changes to the fixed module require a reboot of the fabric interconnect and changes on an expansion module require a reboot of that module . If the Cisco UCS domain has a cluster configuration that is set up for high availability and servers with service profiles that are configured for failover, traffic fails over to the other fabric interconnect and data traffic is not interrupted when the port mode is changed on the fixed module. |
Configuring the Beacon LEDs for Unified Ports
Complete the following task for each module for which you want to configure beacon LEDs.
Server Ports
Configuring Server Ports
All of the port types listed are configurable on both the fixed and expansion module, including server ports, which are not configurable on the 6100 series fabric interconnect expansion module, but are configurable on the 6200 series fabric interconnect expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring ports. You can also configure ports from a right-click menu or in the LAN Uplinks Manager.
Uplink Ethernet Ports
Configuring Uplink Ethernet Ports
You can configure uplink Ethernet ports on either the fixed module or an expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring uplink Ethernet ports. You can also configure uplink Ethernet ports from a right-click menu.
What to Do Next
If desired, change the properties for the default flow control policy and admin speed of the uplink Ethernet port.
Changing the Properties of an Uplink Ethernet Port
Reconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
Example: Reconfiguring an Uplink Ethernet Port as a Server Port
Enabling or Disabling a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
After you enable or disable a port on a fabric interconnect, wait for at least 1 minute before you re-acknowledge the chassis. If you re-acknowledge the chassis too soon, the pinning of server traffic from the chassis might not get updated with the changes to the port that you enabled or disabled.
You can enable or disable a port only when it is configured. If the port is unconfigured, the enable disable option is not active.
Unconfiguring a Port on a Fabric Interconnect
Appliance Ports
 Note | When you create a new appliance VLAN, its IEEE VLAN ID is not added to the LAN Cloud. Therefore, appliance ports that are configured with the new VLAN remain down, by default, due to a pinning failure. To bring up these appliance ports, you have to configure a VLAN in the LAN Cloud with the same IEEE VLAN ID. |
Cisco UCS Manager supports up to four appliance ports per fabric interconnect.
Configuring an Appliance Port
You can configure Appliance ports on either the fixed module or an expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring appliance ports. You can also configure appliance ports from the General tab for the port.
 Note | If you configure an appliance port when the uplink port is down, Cisco UCS Manager may display an error message stating that the appliance port has failed. This message is controlled by the Action on Uplink Fail option in the associated Network Control Policy. For details about this option, see Network Control Policy. |
Modifying the Properties of an Appliance Port
FCoE and Fibre Channel Storage Ports
Configuring an FCoE Storage Port
You can configure FCoE storage ports on either the fixed module or an expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring FCoE storage ports. You can also configure FCoE storage ports from the General tab for the port.
The Fibre Channel switching mode must be set to Switching for these ports to be valid. The storage ports cannot function in end-host mode.
Configuring a Fibre Channel Storage Port
This task describes only one method of configuring FC storage ports. You can also configure FC storage ports from the General tab for the port.
The Fibre Channel switching mode must be set to Switching for these ports to be valid. The storage ports cannot function in end-host mode.
Restoring an Uplink Fibre Channel Port
This task describes only one method of restoring an FC storage port to function as an uplink FC port. You can also reconfigure FC storage ports from the General tab for the port.
FC Links Rebalancing
The FC uplinks balance automatically when FC Port Channels are utilized. To create FC Port Channels, refer to Creating an Uplink Fibre Channel Port Channel.
For the FC uplinks that are not members of the Port Channels (Individual ISLs), load balancing is done according to the FC uplinks balancing algorithm. For a vHBA of a host or service profile to choose an available FC uplink, when FC uplink trunking is disabled, the uplink and vHBA must belong to the same VSAN
This process continues for all the other vHBAs. The algorithm also considers other parameters such as pre-fip/fip adapters and number of flogis. You may not see the least-used component when there are less than six flogis.
After a port configuration or any other uplink state changes, if the traffic passing through the FC uplinks is no longer balanced, you can re-balance the traffic by resetting the vHBA(s) on each adapter and allow the load balancing algorithm to evaluate for the current state of the FC uplinks.
Configuring FC Uplink Ports
You can configure FC Uplink port on either a fixed module or an expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring FC Uplink ports. You can also configure FC uplink ports from a right-click menu for the port.
FCoE Uplink Ports
FCoE uplink ports are physical Ethernet interfaces between the fabric interconnects and the upstream Ethernet switch, used for carrying FCoE traffic. With this support the same physical Ethernet port can carry both Ethernet traffic and Fibre Channel traffic.
FCoE uplink ports connect to upstream Ethernet switches using the FCoE protocol for Fibre Channel traffic. This allows both the Fibre Channel traffic and Ethernet traffic to flow on the same physical Ethernet link.
 Note | FCoE uplinks and unified uplinks enable the multi-hop FCoE feature, by extending the unified fabric up to the distribution layer switch. |
You can configure the same Ethernet port as any of the following:
Configuring FCoE Uplink Ports
You can configure FCoE Uplink port on either a fixed module or an expansion module.
This task describes only one method of configuring FCoE Uplink ports. You can also configure FCoE uplink ports from a right-click menu or from the General tab for the port.
Unified Storage Ports
Unified storage involves configuring the same physical port as both an Ethernet storage interface and an FCoE storage interface. You can configure any appliance port or FCoE storage port as a unified storage port, on either a fixed module or an expansion module. To configure a unified storage port, you must have the fabric interconnect in Fibre Channel switching mode.
In a unified storage port, you can enable or disable individual FCoE storage or appliance interfaces.
-
In an unified storage port, if you do not specify a non-default VLAN for the appliance port, the FCoE-storage-native-vlan will be assigned as the native VLAN on the unified storage port. If the appliance port has a non-default native VLAN specified as native VLAN, this will be assigned as the native VLAN for the unified storage port.
-
When you enable or disable the appliance interface, the corresponding physical port is enabled or disabled. So when you disable the appliance interface in unified storage, even if the FCoE storage is enabled, it goes down with the physical port.
-
When you enable or disable the FCoE storage interface, the corresponding VFC is enabled or disabled. So when the FCoE storage interface is disabled in a unified storage port, the appliance interface will continue to function normally.
Configuring an Appliance Port as a Unified Storage Port
You can configure a unified storage port either from an appliance port or an FCoE storage port. You can also configure the unified storage port from an unconfigured port. If you start from an unconfigured port, you will assign either appliance or FCoE storage configuration to the port and then add another configuration to enable it as a unified storage port.
Make sure the FI is in FC switching mode.
Unconfiguring a Unified Storage Port
You can unconfigure and remove both configurations from the unified connect port. Or you can unconfigure either one of them and retain the other one on the port.
Unified Uplink Ports
When you configure an Ethernet uplink and an FCoE uplink on the same physical Ethernet port, it is called a unified uplink port. You can individually enable or disable either the FCoE or Ethernet interfaces independently.
-
Enabling or disabling the FCoE uplink results in the corresponding VFC being enabled or disabled.
-
Enabling or disabling an Ethernet uplink results in the corresponding physical port being enabled or disabled.
If you disable an Ethernet uplink, it disables the underlying physical port in a unified uplink. Therefore, even when the FCoE uplink is enabled, the FCoE uplink also goes down. But if you disable an FCoE uplink, only the VFC goes down. If the Ethernet uplink is enabled, it can still function properly in the unified uplink port.
Configuring Unified Uplink Ports
You can configure the unified uplink port from either one of the following:
This process describes one method to configure an unified uplink port from an existing FCoE uplink port. You can configure the unified uplink port on either a fixed module or an expansion module. suppress ucs-mini
Unconfiguring Unified Uplink Port
You can unconfigure and remove both configurations from the unified uplink port. Or you can unconfigure either one of the FCoE or Ethernet port configuration and retain the other one on the port.
Uplink Ethernet Port Channels
An uplink Ethernet port channel allows you to group several physical uplink Ethernet ports (link aggregation) to create one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed connectivity. In Cisco UCS Manager, you create a port channel first and then add uplink Ethernet ports to the port channel. You can add up to 16 uplink Ethernet ports to a port channel.
 Note | Cisco UCS uses Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), not Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP), to group the uplink Ethernet ports into a port channel. If the ports on the upstream switch are not configured for LACP, the fabric interconnects treat all ports in an uplink Ethernet port channel as individual ports, and therefore forward packets. |
- Creating an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
- Enabling an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
- Disabling an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
- Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
- Deleting an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
Creating an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
Enabling an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect that includes the port channel you want to enable. |
| Step 4 | Expand the Port Channels node. |
| Step 5 | Right-click the port channel you want to enable and choose Enable Port Channel. |
| Step 6 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
Disabling an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Click the port channel to which you want to add or remove ports. |
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. |
| Step 5 | In the Actions area, click Add Ports. |
| Step 6 | In the
Add Ports
dialog box, do one of the following:
|
| Step 7 | Click OK. |
Deleting an Uplink Ethernet Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect where you want to delete the port channel. |
| Step 4 | Click the Port Channels node. |
| Step 5 | In the General tab for the Port Channels node, choose the port channel you want to delete. |
| Step 6 | Right-click the port channel and choose Delete. |
Appliance Port Channels
An appliance port channel allows you to group several physical appliance ports to create one logical Ethernet storage link for the purpose of providing fault-tolerance and high-speed connectivity. In Cisco UCS Manager, you create a port channel first and then add appliance ports to the port channel. You can add up to eight appliance ports to a port channel.
- Creating an Appliance Port Channel
- Enabling an Appliance Port Channel
- Disabling an Appliance Port Channel
- Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from an Appliance Port Channel
- Deleting an Appliance Port Channel
Creating an Appliance Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. | ||
| Step 2 | Expand . | ||
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect where you want to add the port channel. | ||
| Step 4 | Right-click the Port Channels node and choose Create Port Channel. | ||
| Step 5 | In the
Set Port
Channel Name
panel of the
Create Port Channel wizard, complete the
required fields to specify the identity and other properties of the port
channel.
You can create a LAN pin group, network control policy, and flow control policy from this panel. | ||
| Step 6 | In the
VLANs area, specify the
Port Mode and other information for the VLANs.
You can create a VLAN from this panel. | ||
| Step 7 | (Optional) If you want to add an endpoint, check the Ethernet Target Endpoint check box specify the name and MAC address. | ||
| Step 8 | Click Next. | ||
| Step 9 | In the
Add Ports
panel of the
Create
Port Channel wizard, specify the ports that you want to add.
| ||
| Step 10 | Click Finish. |
Enabling an Appliance Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect that includes the port channel you want to enable. |
| Step 4 | Expand the Port Channels node. |
| Step 5 | Right-click the port channel you want to enable and choose Enable Port Channel. |
| Step 6 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
Disabling an Appliance Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect that includes the port channel you want to disable. |
| Step 4 | Expand the Port Channels node. |
| Step 5 | Right-click the port channel you want to disable and choose Disable Port Channel. |
| Step 6 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from an Appliance Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Click the port channel to which you want to add or remove ports. |
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. |
| Step 5 | In the Actions area, click Add Ports. |
| Step 6 | In the
Add Ports
dialog box, do one of the following:
|
| Step 7 | Click OK. |
Deleting an Appliance Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric interconnect that includes the port channel you want to delete. |
| Step 4 | Expand the Port Channels node. |
| Step 5 | Right-click the port channel you want to enable and choose Delete. |
| Step 6 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
Creating a Threshold Condition
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click the Admin tab. |
| Step 2 | In the Admin tab, expand . |
| Step 3 | Click Create Threshold Class. |
| Step 4 | In the Choose Statistics Class screen of the Create Threshold Class wizard, choose NI Ether Error Stats statistics class to monitor the network interface ports for which you want to configure a custom threshold from the Stat Class drop-down list. |
| Step 5 | Click Next. |
| Step 6 | In the
Threshold
Definitions screen of the
Create
Threshold Class
wizard, click
Add.
The Create Threshold Definition dialog box opens. |
Monitoring a Fabric Port
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click Equipment. | ||||||||||
| Step 2 | On the Equipment tab, expand . | ||||||||||
| Step 3 | Click the fabric port that you want to monitor. | ||||||||||
| Step 4 | Click one of the
following tabs to view the status of the fabric:
|
Policy-Based Port Error Handling
If Cisco UCS Manager detects any errors on active NI ports, and if the error-disable feature is enabled, Cisco UCS Manager automatically disables the respective FI port that is connected to the NI port that had errors. When a FI port is error disabled, it is effectively shut down and no traffic is sent or received on that port.
The error-disable function serves two purposes:
-
It lets you know which FI port is error-disabled and that the connected NI Port has errors.
-
It eliminates the possibility that this port can cause other ports, which are connected to the same Chassis/FEX, to fail. Such a failure can occur when the NI port has errors, which can ultimately cause serious network issues. The error-disable function helps prevent these situations.
Configuring Error-Based Action
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click the Admin tab. |
| Step 2 | In the Admin tab, expand . |
| Step 3 | Select a delta property. |
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. |
| Step 5 | To enable error disable on the FI port, check the Disable FI port when fault is raised check box. |
| Step 6 | To enable auto recovery, in the Enable Auto Recovery field, select Enable. |
| Step 7 | To specify the time after which the port can automatically be re-enabled, in the Time (in minutes) field, type the time in minutes. |
| Step 8 | Click Save Changes. |
Fibre Channel Port Channels
A Fibre Channel port channel allows you to group several physical Fibre Channel ports (link aggregation) to create one logical Fibre Channel link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed connectivity. In Cisco UCS Manager, you create a port channel first and then add Fibre Channel ports to the port channel.
 Note | Fibre Channel port channels are not compatible with non-Cisco technology. |
You can create up to four Fibre Channel port channels in each Cisco UCS domain with Cisco UCS 6200 and 6300 Series fabric interconnects. Each Fibre Channel port channel can include a maximum of 16 uplink Fibre Channel ports.
You can create up to two Fibre Channel port channels in each Cisco UCS domain with Cisco UCS 6324 fabric interconnects. Each Fibre Channel port channel can include a maximum of four uplink Fibre Channel ports.
Ensure that the Fibre Channel port channel on the upstream NPIV switch is configured with its channel mode as active. If both the member port(s) and peer port(s) do not have the same channel mode configured, the port channel will not come up. When the channel mode is configured as active, the member ports initiate port channel protocol negotiation with the peer port(s) regardless of the channel group mode of the peer port. If the peer port, while configured in a channel group, does not support the port channel protocol, or responds with a nonnegotiable status, it defaults to the On mode behavior. The active port channel mode allows automatic recovery without explicitly enabling and disabling the port channel member ports at either end.
This example shows how to configure channel mode as active:
switch(config)# int po114 switch(config-if)# channel mode active
- Creating an Uplink Fibre Channel Port Channel
- Enabling a Fibre Channel Port Channel
- Disabling a Fibre Channel Port Channel
- Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from a Fibre Channel Port Channel
- Modifying the Properties of a Fibre Channel Port Channel
- Deleting a Fibre Channel Port Channel
Creating an Uplink Fibre Channel Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click SAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric where you want to create the port channel. |
| Step 4 | Right-click the FC Port Channels node and choose Create Port Channel. |
| Step 5 | In the Set Port Channel Name panel, specify the ID and name, then click Next. |
| Step 6 | In the Add Ports panel, specify the port channel admin speed, and add ports to the port channel. |
| Step 7 | Click Finish. |
Enabling a Fibre Channel Port Channel
Disabling a Fibre Channel Port Channel
Adding Ports to and Removing Ports from a Fibre Channel Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click SAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Click the port channel to which you want to add or remove ports. |
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. |
| Step 5 | In the Actions area, click Add Ports. |
| Step 6 | In the
Add Ports
dialog box, do one of the following:
|
| Step 7 | Click OK. |
Modifying the Properties of a Fibre Channel Port Channel
 Note | If you are connecting two Fibre Channel port channels, the admin speed for both port channels must match for the link to operate. If the admin speed for one or both of the Fibre Channel port channels is set to auto, Cisco UCS adjusts the admin speed automatically. |
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click SAN. | ||||||||
| Step 2 | Expand . | ||||||||
| Step 3 | Click the port channel that you want to modify. | ||||||||
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. | ||||||||
| Step 5 | In the Properties area, change the values in one or more of the following fields:
| ||||||||
| Step 6 | Click Save Changes. |
Deleting a Fibre Channel Port Channel
FCoE Port Channels
An FCoE port channel allows you to group several physical FCoE ports to create one logical FCoE port channel. At a physical level, the FCoE port channel carries FCoE traffic over an Ethernet port channel. So an FCoE port channel with a set of members is essentially an ethernet port channel with the same members. This Ethernet port channel is used as a physical transport for FCoE traffic.
For each FCoE port channel, Cisco UCS Manager creates a VFC internally and binds it to an Ethernet port channel. FCoE traffic received from the hosts is sent over the VFC the same way as the FCoE traffic is sent over Fibre Channel uplinks.
Creating an FCoE Port Channel
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click SAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the node for the fabric where you want to create the port channel. |
| Step 4 | Right-click the FCoE Port Channels node and choose Create FCoE Port Channel. |
| Step 5 | In the Set Port Channel Name panel of the Create FCoE Port Channel wizard, specify the ID and name, then click Next. |
| Step 6 | In the Add Ports panel of the Create FCoE Port Channel wizard, specify the ports that you want to add. |
| Step 7 | Click Finish. |
Deleting an FCoE Port Channel
Unified Uplink Port Channel
When you create an Ethernet port channel and an FCoE port channel with the same ID, it is called a unified uplink port channel. When the unified port channel is created, a physical Ethernet port channel and a VFC are created on the fabric interconnect with the specified members. The physical Ethernet port channel is used to carry both Ethernet and FCoE traffic. The VFC binds FCoE traffic to the Ethernet port channel.
The following rules will apply to the member port sets of the unified uplink port channel:
-
The Ethernet port channel and FCoE port channel on the same ID, must have the same set of member ports.
-
When you add a member port channel to the Ethernet port channel, Cisco UCS Manager adds the same port channel to FCoE port channel as well. Similarly, adding a member to the FCoE port channel adds the member port to the Ethernet port channel.
-
When you delete a member port from one of the port channels, Cisco UCS Manager automatically deletes the member port from the other port channel.
If you disable an Ethernet uplink port channel, it disables the underlying physical port channel in a unified uplink port channel. Therefore, even when the FCoE uplink is enabled, the FCoE uplink port channel also goes down. If you disable an FCoE uplink port channel, only the VFC goes down. If the Ethernet uplink port channel is enabled, it can still function properly in the unified uplink port channel.
Adapter Port Channels
An adapter port channel groups into one logical link all the physical links going from a Cisco UCS Virtual Interface Card (VIC) into an I/O.
Adapter port channels are created and managed internally by Cisco UCS Manager when it detects that the correct hardware is present. Adapter port channels cannot be configured manually. Adapter port channels are viewable using the Cisco UCS Manager GUI or the Cisco UCS Manager CLI.
Viewing Adapter Port Channels
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click Equipment. |
| Step 2 | On the Equipment tab, expand |
| Step 3 | Click the adapter for which you want to view the adapter port channels. |
| Step 4 | In the Work pane, click the DCE Interfaces tab. |
| Step 5 | To view details of the adapter port channel, click the link in the Port Channel column. |
Fabric Port Channels
Fabric port channels allow you to group several of the physical links from an IOM to a fabric interconnect into one logical link for redundancy and bandwidth sharing. As long as one link in the fabric port channel remains active, the fabric port channel continues to operate.
If the correct hardware is connected, fabric port channels are created by Cisco UCS Manager in the following ways:
During chassis discovery according to the settings configured in the chassis discovery policy.
After chassis discovery according to the settings configured in the chassis connectivity policy for a specific chassis.
For each IOM there is a single fabric port channel. Each uplink connecting an IOM to a fabric interconnect can be configured as a discrete link or included in the port channel, but an uplink cannot belong to more than one fabric port channel. For example, if a chassis with two IOMs is discovered and the chassis discovery policy is configured to create fabric port channels, Cisco UCS Manager creates two separate fabric port channels: one for the uplinks connecting IOM-1 and another for the uplinks connecting IOM-2. No other chassis can join these fabric port channels. Similarly, uplinks belonging to the fabric port channel for IOM-1 cannot join the fabric port channel for IOM-2.
- Load Balancing Over Ports
- Cabling Considerations for Fabric Port Channels
- Configuring a Fabric Port Channel
- Viewing Fabric Port Channels
- Enabling or Disabling a Fabric Port Channel Member Port
Load Balancing Over Ports
Load balancing traffic among ports between IOMs and fabric interconnects uses the following criteria for hashing.
-
For Ethernet traffic:
Layer 2 source and destination address
Layer 3 source and destination address
Layer 4 source and destination ports
-
For FCoE traffic:
Layer 2 source and destination address
Source and destination IDs (SID and DID) and Originator Exchange ID (OXID)
In this example, a 2200 Series IOM module is verified by connecting iom X (where X is the chassis number).
show platform software fwmctrl nifport (....) Hash Parameters: l2_da: 1 l2_sa: 1 l2_vlan: 0 l3_da: 1 l3_sa: 1 l4_da: 1 l4_sa: 1 FCoE l2_da: 1 l2_sa: 1 l2_vlan: 0 FCoE l3_did: 1 l3_sid: 1 l3_oxid: 1
Cabling Considerations for Fabric Port Channels
When you configure the links between the Cisco UCS 2200 Series FEX and a Cisco UCS 6200 series fabric interconnect in fabric port channel mode, the available virtual interface namespace (VIF) on the adapter varies depending on where the FEX uplinks are connected to the fabric interconnect ports.
Inside the 6248 fabric interconnect there are six sets of eight contiguous ports, with each set of ports managed by a single chip. When all uplinks from an FEX are connected to a set of ports managed by a single chip, Cisco UCS Manager maximizes the number of VIFs used in service profiles deployed on the blades in the chassis. If uplink connections from an IOM are distributed across ports managed by separate chips, the VIF count is decreased.
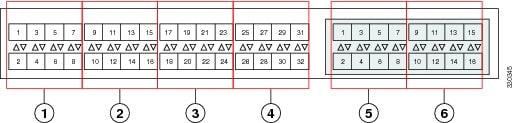
 Caution | Adding a second link to a fabric-port-channel port group is disruptive and will automatically increase the available amount of VIF namespace from 63 to 118. Adding further links is not disruptive and the VIF namespace stays at 118. |
 Caution | Linking a chassis to two fabric-port-channel port groups does not affect the VIF namespace unless it is manually acknowledged. The VIF namespace is then automatically set to the smaller size fabric port-channel port group usage (either 63 or 118 VIFs) of the two groups. |
For high availability cluster-mode applications, we strongly recommend symmetric cabling configurations. If the cabling is asymmetric, the maximum number of VIFs available is the smaller of the two cabling configurations.
For more information on the maximum number of VIFs for your Cisco UCS environment, see the Configuration Limits document for your hardware and software configuration.
Configuring a Fabric Port Channel
| Step 1 | To include all links from the IOM to the fabric interconnect in a fabric port channel during chassis discovery, set the link grouping preference in the chassis discovery policy to port channel. |
| Step 2 | To include links from individual chassis in a fabric port channel during chassis discovery, set the link grouping preference in the chassis connectivity policy to port channel. |
| Step 3 | After chassis discovery, enable or disable additional fabric port channel member ports. |
What to Do Next
To add or remove chassis links from a fabric port channel after making a change to the chassis discovery policy or the chassis connectivity policy, reacknowledge the chassis. Chassis reacknowledgement is not required to enable or disable chassis member ports from a fabric port channel
Viewing Fabric Port Channels
Enabling or Disabling a Fabric Port Channel Member Port
| Step 1 | In the Navigation pane, click LAN. |
| Step 2 | Expand . |
| Step 3 | Expand the port channel for which you want to enable or disable a member port. |
| Step 4 | Click the ethernet interface for the member port you want to enable or disable. |
| Step 5 | In the Work pane, click the General tab. |
| Step 6 | In the Actions area, click one of the following: |
| Step 7 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
Configuring Server Ports with the Internal Fabric Manager
Internal Fabric Manager
The Internal Fabric Manager provides a single interface where you can configure server ports for a fabric interconnect in a Cisco UCS domain. The Internal Fabric Manager is accessible from the General tab for that fabric interconnect.
Some of the configuration that you can do in the Internal Fabric Manager can also be done in nodes on the Equipment tab, on the LAN tab, or in the LAN Uplinks Manager.
Launching the Internal Fabric Manager
Configuring a Server Port with the Internal Fabric Manager
| Step 1 | In the Internal Fabric Manager, click the down arrows to expand the Unconfigured Ports area. |
| Step 2 | Right-click the port that you want to configure and choose Configure as Server Port. |
| Step 3 | If a confirmation dialog box displays, click Yes. |
| Step 4 | If you complete all of the tasks in the Internal Fabric Manager, click OK. |
 Feedback
Feedback