FlexPod Datacenter Base Manual Configuration with Cisco IMM and NetApp ONTAP
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback

![]()
In partnership with:

About the Cisco Validated Design Program
The Cisco Validated Design (CVD) program consists of systems and solutions designed, tested, and documented to facilitate faster, more reliable, and more predictable customer deployments. For more information, go to: http://www.cisco.com/go/designzone.
The FlexPod Datacenter solution is a validated design for deploying Cisco and NetApp technologies and products to build shared private and public cloud infrastructure. Cisco and NetApp have partnered to deliver a series of FlexPod solutions that enable strategic data center platforms. The success of the FlexPod solution is driven through its ability to evolve and incorporate both technology and product innovations in the areas of management, compute, storage, and networking. This document explains the deployment details of the base configuration of FlexPod Datacenter, setting up a configuration where bare metal OS or hypervisors can be layered on as tenants to support applications. Some of the key advantages of FlexPod Datacenter Base Configuration are:
● Consistent FlexPod Base Configuration: having a FlexPod Datacenter Base Configuration provides a consistent configuration that one or more of any bare metal OS or hypervisor can be layered on in a secure way to support one or more applications.
● Simpler and programmable infrastructure: the entire configuration can be configured using infrastructure as code delivered using Ansible.
● End-to-End 100Gbps Ethernet: utilizing the 5th Generation Cisco UCS VICs, the 5th Generation Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnect, and the Cisco UCSX-I-9108-100G Intelligent Fabric Module to deliver 100Gbps Ethernet from the server through the network to the storage.
● End-to-End 32Gbps Fibre Channel: utilizing the 5th Generation Cisco UCS VICs, the 5th Generation Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnect, and the Cisco UCSX-I-9108-100G Intelligent Fabric Module to deliver 32Gbps Ethernet from the server (via 100Gbps FCoE) through the network to the storage.
● Built for investment protections: design ready for future technologies such as liquid cooling and high-Wattage CPUs, CXL-ready.
In addition to the FlexPod-specific hardware and software innovations, the integration of the Cisco Intersight cloud platform with NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager, and Cisco Nexus and MDS switches delivers monitoring, orchestration, and workload optimization capabilities for different layers (storage and networking) of the FlexPod infrastructure. Implementation of this integration at this point in the deployment process would require Cisco Intersight Assist and NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager to be deployed outside of the FlexPod.
For information about the FlexPod design and deployment details, including the configuration of various elements of design and associated best practices, refer to Cisco Validated Designs for FlexPod, here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/design-zone/data-center-design-guides/flexpod-design-guides.html.
Solution Overview
This chapter contains the following:
● Audience
The intended audience of this document includes but is not limited to IT architects, sales engineers, field consultants, professional services, IT managers, partner engineering, and customers who want to take advantage of an infrastructure built to deliver IT efficiency and enable IT innovation.
This document provides deployment guidance around bringing up the base FlexPod Datacenter infrastructure. The base configuration involves basic configuration that connects the FlexPod devices to the network, then configuring the base network configuration of each component, preparing the FlexPod for layering on bare metal OS, hypervisors, and applications in a multi-tenant way. This document introduces various design elements and explains various considerations and best practices for a successful deployment.
The following design elements distinguish this version of FlexPod from previous models:
● Configuration of only the base FlexPod, which mainly involves connecting the FlexPod devices to the network, then configuring the base network configuration of each component.
● All future FlexPod solution documents will refer to this document for a consistent base setup and then layer on the solution bare metal OS, hypervisor, and/or applications in a multi-tenant fashion.
Deployment Hardware and Software
This chapter contains the following:
The FlexPod Datacenter with Cisco UCS and Cisco Intersight meets the following general design requirements:
● Resilient design across all layers of the infrastructure with no single point of failure
● Scalable design with the flexibility to add compute capacity, storage, or network bandwidth as needed
● Modular design that can be replicated to expand and grow as the needs of the business grow
● Flexible design that can support different models of various components with ease
● Simplified design with ability to integrate and automate with external automation tools
● Cloud-enabled design which can be configured, managed, and orchestrated from the cloud using GUI or APIs
To deliver a solution which meets all these design requirements, various solution components are connected and configured as covered in the upcoming sections.
The FlexPod Datacenter base configuration is built using the following hardware components:
● Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis with Cisco UCSX-I-9108-100G intelligent fabric modules (IFMs) and up to eight Cisco UCS X210C Compute Nodes
● Fifth-generation Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnects to support 100GbE, 25GbE, and 32GFC connectivity from various components
● Cisco UCS C-Series M7 rack mount servers
● High-speed Cisco NX-OS-based Nexus 93600CD-GX switching design to support 100GE and 400GE connectivity
● NetApp AFF C800 end-to-end NVMe storage with 25G or 100G Ethernet and (optional) 32G Fibre Channel connectivity
● Cisco MDS 9132T* switches to support Fibre Channel storage configuration
Note: * Cisco MDS 9132T and FC connectivity is not needed when implementing IP-based connectivity design supporting iSCSI boot from SAN, NFS, and NVMe-TCP.
The software components of this solution consist of:
● Cisco Intersight to deploy, maintain, and support the Cisco UCS server components
● Cisco Intersight SaaS platform to maintain and support the FlexPod components
● Cisco Intersight Assist Virtual Appliance to help connect NetApp ONTAP and Cisco Nexus and MDS switches with Cisco Intersight
● NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager to monitor and manage the storage and for NetApp ONTAP integration with Cisco Intersight
FlexPod Datacenter for IP-based Storage Access
Figure 1 shows various hardware components and the network connections for the IP-based FlexPod design.
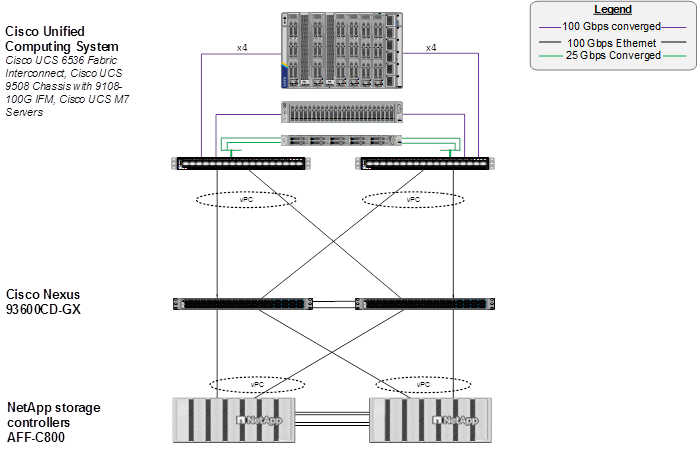
The reference hardware configuration includes:
● Two Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX Switches in Cisco NX-OS mode provide the switching fabric. Other Cisco Nexus Switches are also supported.
● Two Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnects (FI) provide the chassis connectivity. Two 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports from each FI, configured as a Port-Channel, are connected to each Nexus 93600CD-GX. 25 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity is also supported as well as earlier versions of the Cisco UCS FI.
● One Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis connects to fabric interconnects using Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-100G IFMs, where four 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports are used on each IOM to connect to the appropriate FI. If additional bandwidth is required, all eight 100G ports can be utilized. The Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-25G IFM is also supported with 25 Gigabit Ethernet Connectivity.
● One NetApp AFF C800 HA pair connects to the Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX Switches using two 100 GE ports from each controller configured as a Port-Channel. 25 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity is also supported as well as other NetApp AFF, ASA, and FAS storage controllers.
● One Cisco UCS C240 M7 rack mount server connects to the Fabric Interconnects using two 100 GE ports per server.
● One Cisco UCS C220 M7 rack mount server connects to the Fabric Interconnects using four 25 GE ports per server via breakout.
FlexPod Datacenter for FC-based Storage Access
Figure 2 shows various hardware components and the network connections for the FC-based FlexPod design.
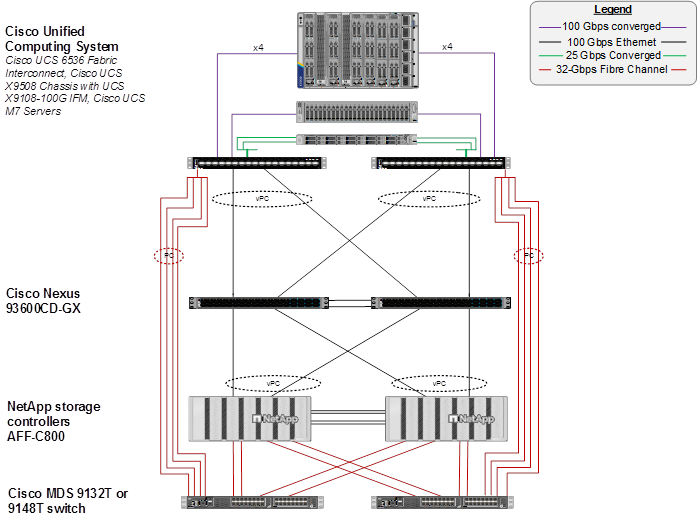
The reference hardware configuration includes:
● Two Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX Switches in Cisco NX-OS mode provide the switching fabric. Other Cisco Nexus Switches are also supported.
● Two Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnects (FI) provide the chassis connectivity. Two 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports from each FI, configured as a Port-Channel, are connected to each Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX. Four FC ports are connected to the Cisco MDS 9132T switches using 32-Gbps Fibre Channel connections via breakout configured as a single port channel for SAN connectivity. 25 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity and 16-Gbps Fibre Chanel connectivity is also supported as well as earlier versions of the Cisco UCS FI.
● One Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis connects to fabric interconnects using Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-100G IFMs, where four 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports are used on each IOM to connect to the appropriate FI. If additional bandwidth is required, all eight 100G ports can be utilized. The chassis to fabric interconnect connections are converged and carry both Ethernet and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE). The Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-25G IFM is also supported with 25 Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE Connectivity.
● One NetApp AFF C800 HA pair connects to the Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX Switches using two 100 GE ports from each controller configured as a Port-Channel. Two 32Gbps FC ports from each controller are connected to each Cisco MDS 9132T for SAN connectivity. 25 Gigabit Ethernet and 16-Gbps Fibre Channel connectivity is also supported as well as other NetApp AFF, ASA, and FAS storage controllers.
● One Cisco UCS C240 M7 Rack Mount Server connects to the Fabric Interconnects using two 100 GE ports per server. These connections are also converged and carry both Ethernet and FCoE.
● One Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Mount Server connects to the Fabric Interconnects using four 25 GE ports per server. These connections are also converged and carry both Ethernet and FCoE.
Note: The NetApp storage controller and disk shelves should be connected according to best practices for the specific storage controller and disk shelves. For disk shelf cabling, go to NetApp Support: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems/index.html
FlexPod Datacenter for FC-based Storage Access with Nexus SAN Switching
Figure 3 shows various hardware components and the network connections for the FC-based FlexPod design.

The reference hardware configuration includes:
● Two Cisco Nexus 93180YC-FX, 93360YC-FX2, or 9336C-FX2-E Switches in Cisco NX-OS mode provide the switching fabric for both LAN and SAN.
● Two Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnects (FI) provide the chassis connectivity. Two 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports from each FI, configured as a Port-Channel, are connected to each Nexus switch. Two 100G FCoE ports are connected to the Cisco Nexus switches configured as a single Ethernet port channel for SAN connectivity. 25 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity is also supported as well as earlier versions of the Cisco UCS FI.
● One Cisco UCS X9508 Chassis connects to fabric interconnects using Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-100G IFMs, where four 100 Gigabit Ethernet ports are used on each IOM to connect to the appropriate FI. If additional bandwidth is required, all eight 100G ports can be utilized. The chassis to fabric interconnect connections are converged and carry both Ethernet and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE). The Cisco UCS UCSX-I-9108-25G IFM is also supported with 25 Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE Connectivity.
● One NetApp AFF C800 HA pair connects to the Cisco Nexus Switches using two 100 GE ports from each controller configured as a Port-Channel. Two 32Gbps FC ports from each controller are connected to each Cisco Nexus switch for SAN connectivity (Cisco Nexus 9336C-FX2-E using breakout). 25 Gigabit Ethernet and 16-Gbps Fibre Channel connectivity is also supported as well as other NetApp AFF, ASA, and FAS storage controllers.
● One Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Mount Server connects to the Fabric Interconnects using two 100 GE ports per server. These connections are also converged and carry both Ethernet and FCoE.
● One Cisco UCS C220 M7 Rack Mount Server connects to the Fabric Interconnects four 25 GE ports per server. These connections are also converged and carry both Ethernet and FCoE.
Note: The NetApp storage controller and disk shelves should be connected according to best practices for the specific storage controller and disk shelves. For disk shelf cabling, refer to NetApp Support: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems/index.html
VLAN Configuration
Table 1 lists VLANs configured for setting up the FlexPod environment along with their usage.
| VLAN ID |
Name |
Usage |
IP Subnet used in this deployment |
| 2 |
Native-VLAN |
Use VLAN 2 as native VLAN instead of default VLAN (1). |
|
| 1020 |
OOB-MGMT-VLAN |
Out-of-band management VLAN to connect management ports for various devices |
10.102.0.0/24; GW: 10.102.0.254 |
Some of the key highlights of VLAN usage are as follows:
● VLAN 1020 allows you to manage and access out-of-band management interfaces of various devices.
Table 2 lists the VMs or bare metal servers necessary for deployment as outlined in this document.
| Virtual Machine Description |
VLAN |
IP Address |
Comments |
| FlexPod AD1 |
1021 |
10.102.1.151 |
Hosted on pre-existing management infrastructure |
| FlexPod AD2 |
1021 |
10.102.1.152 |
Hosted on pre-existing management infrastructure |
| FlexPod Ansible |
1021 |
10.102.1.14 |
Hosted on pre-existing management infrastructure |
| NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager |
1021 |
10.102.1.97 |
Hosted on pre-existing management infrastructure |
| Cisco Intersight Assist |
1021 |
10.102.1.96 |
Hosted on pre-existing management infrastructure |
| Nexus Dashboard Fabric Controller (NDFC)-SAN |
1021 and 1020 |
10.102.1.21 |
Hosted on a separate server on pre-existing management infrastructure |
Table 3 lists the software revisions for various components of the solution.
| Layer |
Device |
Image Bundle |
Comments |
| Compute |
Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect 6536 |
4.3(4.240066) |
|
|
|
Cisco UCS X9108-100G IFM |
4.3(4a) |
|
|
|
Cisco UCS X210C M7 |
5.2(2.240053) |
|
|
|
Cisco UCS C220/240 M7 |
4.3(4.240152) |
|
| Network |
Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX NX-OS |
10.3(4a)M |
|
| Cisco MDS 9132T |
9.3(2a) |
Requires SMART Licensing |
|
| Storage |
NetApp AFF C800 |
ONTAP 9.14.1 |
Latest patch release |
| Software |
Cisco Intersight Assist Appliance |
1.0.9-675 |
1.0.9-538 initially installed and then automatically upgraded |
| NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager |
9.14 |
|
The information in this section is provided as a reference for cabling the physical equipment in a FlexPod environment. To simplify cabling requirements, a cabling diagram was used.
The cabling diagram in this section contains the details for the prescribed and supported configuration of the NetApp AFF C800 running NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1.
Note: For any modifications of this prescribed architecture, consult the NetApp Interoperability Matrix Tool (IMT).
Note: This document assumes that out-of-band management ports are plugged into an existing management infrastructure at the deployment site. These interfaces will be used in various configuration steps.
Note: Be sure to use the cabling directions in this section as a guide.
The NetApp storage controller and disk shelves should be connected according to best practices for the specific storage controller and disk shelves. For disk shelf cabling, refer to NetApp Support.
Figure 4 details the cable connections used in the validation lab for the FlexPod topology based on the Cisco UCS 6536 fabric interconnect. Four 32Gb uplinks connect as port-channels from each Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect to the MDS switches, and a total of eight 32Gb links connect the MDS switches to the NetApp AFF controllers. Also, two 100Gb links connect each Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect to the Cisco Nexus Switches and each NetApp AFF controller to the Cisco Nexus Switches. Additional 1Gb management connections will be needed for an out-of-band network switch that sits apart from the FlexPod infrastructure. Each Cisco UCS fabric interconnect and Cisco Nexus switch is connected to the out-of-band network switch, and each AFF controller has a connection to the out-of-band network switch. Layer 3 network connectivity is required between the Out-of-Band (OOB) and In-Band (IB) Management Subnets. This cabling diagram includes both the FC-boot and iSCSI-boot configurations.
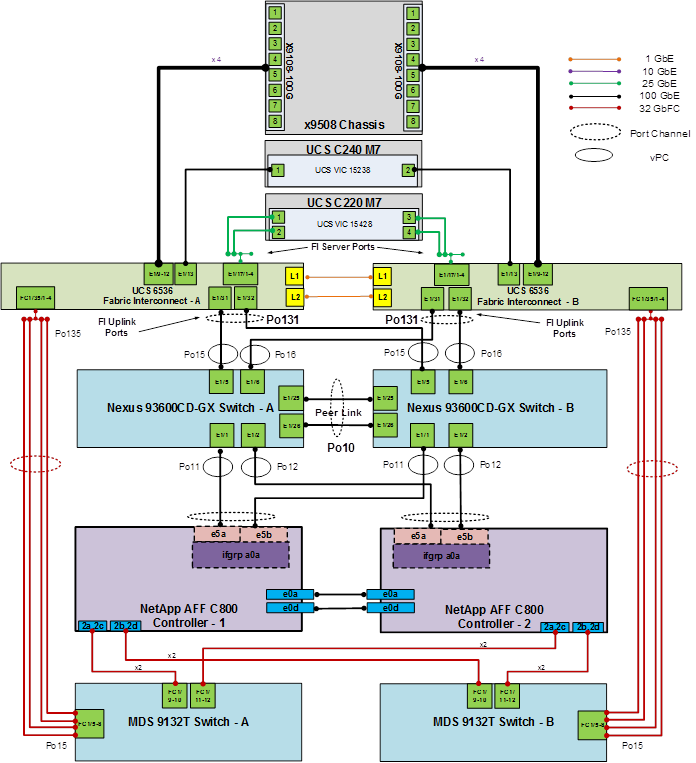
Network Switch Configuration
This chapter contains the following:
● Cisco Nexus Switch Manual Configuration
This chapter provides a detailed procedure for configuring the Cisco Nexus 93600CD-GX switches for use in a FlexPod environment.
Note: The following procedures describe how to configure the Cisco Nexus switches for use in a base FlexPod environment. This procedure assumes the use of Cisco Nexus 9000 10.3(4a)M.
● If using the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switches or other Cisco Nexus switches for both LAN and SAN switching, please refer to section FlexPod with Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Configuration in the Appendix.
● The following procedure includes the setup of NTP distribution on both the mgmt0 port and the in-band management VLAN. The interface-vlan feature and ntp commands are used to set this up. This procedure also assumes that the default VRF is used to route the in-band management VLAN.
● This procedure sets up and uplink virtual port channel (vPC) with the IB-MGMT and OOB-MGMT VLANs allowed.
● This validation assumes that both switches have been reset to factory defaults by using the “write erase” command followed by the “reload” command.
Follow the physical connectivity guidelines for FlexPod as explained in section FlexPod Cabling.
The following procedures describe this basic configuration of the Cisco Nexus switches for use in the FlexPod environment. This procedure assumes the use of Cisco Nexus 9000 10.3(4a)M, the Cisco suggested Nexus switch release at the time of this validation.
Procedure 1. Set Up Initial Configuration from a serial console
Set up the initial configuration for the Cisco Nexus A switch on <nexus-A-hostname>.
Step 1. Configure the switch.
Note: On initial boot, the NX-OS setup automatically starts and attempts to enter Power on Auto Provisioning.
Abort Power On Auto Provisioning [yes - continue with normal setup, skip - bypass password and basic configuration, no - continue with Power On Auto Provisioning] (yes/skip/no)[no]: yes
Disabling POAP.......Disabling POAP
poap: Rolling back, please wait... (This may take 5-15 minutes)
---- System Admin Account Setup ----
Do you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Enter the password for "admin": <password>
Confirm the password for "admin": <password>
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yes
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enter the switch name: <nexus-A-hostname>
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Mgmt0 IPv4 address: <nexus-A-out_of_band_mgmt0-ip>
Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <nexus-A-mgmt0-netmask>
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
IPv4 address of the default gateway: <nexus-A-mgmt0-gw>
Configure advanced IP options? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa) [rsa]: Enter
Number of rsa key bits <1024-2048> [1024]: Enter
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure default interface layer (L3/L2) [L2]: Enter
Configure default switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [noshut]: shut
Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: n
Configure CoPP system profile (strict/moderate/lenient/dense) [strict]: Enter
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Step 2. Review the configuration summary before enabling the configuration.
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Step 3. To set up the initial configuration of the Cisco Nexus B switch, repeat steps 1 and 2 with the appropriate host and IP address information.
Cisco Nexus Switch Manual Configuration
Procedure 1. Configure the Cisco Nexus switches from the management workstation
Step 1. Log into both Nexus switches as admin using ssh.
Step 2. Enable features on both Nexus switches.
config t
feature nxapi
feature udld
feature interface-vlan
feature lacp
feature vpc
feature lldp
Step 3. Set global configurations on both Nexus switches.
spanning-tree port type network default
spanning-tree port type edge bpduguard default
spanning-tree port type edge bpdufilter default
port-channel load-balance src-dst l4port
ntp server <global-ntp-server-ip> use-vrf management – Repeat this command to add additional NTP servers
clock timezone <timezone> <hour-offset> <minute-offset>
clock summer-time <timezone> <start-week> <start-day> <start-month> <start-time> <end-week> <end-day> <end-month> <end-time> <offset-minutes>
Note: It is important to configure the local time so that logging time alignment and any backup schedules are correct. For more information on configuring the timezone and daylight savings time or summer time, see the Cisco Nexus 9000 NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 10.3(x). Sample clock commands for the United States Eastern timezone are:
clock timezone EST -5 0
clock summer-time EDT 2 Sunday March 02:00 1 Sunday November 02:00 60
Step 4. Optionally enable NTP Distribution on both Nexus switches.
ntp master 3 – Set the stratum level appropriately
ntp peer <other-switch-mgmt-ip> use-vrf management
Step 5. Add the VLANs to both Nexus switches.
vlan <native-vlan-id>
name Native-Vlan
vlan <oob-mgmt-vlan-id>
name OOB-MGMT
Step 6. Add individual port descriptions for troubleshooting and enable UDLD for Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect interfaces to Cisco Nexus A.
interface Eth1/5
description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/31
udld enable
interface Eth1/6
description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/31
udld enable
interface Eth1/1
description <st-clustername>-01:e5a
interface Eth1/2
description <st-clustername>-02:e5a
interface Eth1/25
description <nexus-b-hostname>:1/25
interface Eth1/26
description <nexus-b-hostname>:1/26
interface Eth1/27
description Uplink-Switch
Note: For fibre optic connections to Cisco UCS systems (AOC or SFP-based), entering udld enable will result in a message stating that this command is not applicable to fiber ports. This message is expected.
Step 7. Add individual port descriptions for troubleshooting and enable UDLD for Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect interfaces to Cisco Nexus B.
interface Eth1/5
description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/32
udld enable
interface Eth1/6
description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/32
udld enable
interface Eth1/1
description <st-clustername>-01:e5b
interface Eth1/2
description <st-clustername>-02:e5b
interface Eth1/25
description <nexus-a-hostname>:1/25
interface Eth1/26
description <nexus-a-hostname>:1/26
interface Eth1/27
description Uplink-Switch
Step 8. Create the necessary port channels in both Nexus switches.
interface Po10
description vPC peer-link
interface Eth1/25-26
channel-group 10 mode active
no shutdown
interface Po11
description <st-clustername>-01
interface Eth1/1
channel-group 11 mode active
no shutdown
interface Po12
description <st-clustername>-02
interface Eth1/2
channel-group 12 mode active
no shutdown
interface Po15
description <ucs-domainname>-A
interface Eth1/5
channel-group 15 mode active
no shutdown
interface Po16
description <ucs-domainname>-B
interface Eth1/6
channel-group 16 mode active
no shutdown
interface Po127
description MGMT-Uplink
interface Eth1/27
channel-group 127 mode active
no shutdown
exit
copy run start
Step 9. Configure port channel parameters in both Nexus switches.
interface Po10
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <oob-mgmt-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type network
interface Po11
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
interface Po12
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
interface Po15
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <oob-mgmt-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
interface Po15
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <oob-mgmt-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
interface Po127
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <oob-mgmt-vlan-id>
spanning-tree port type network – This value could be type network or type normal
mtu 9216
exit
copy run start
Step 10. Configure virtual port channels (vPCs) in Cisco Nexus A.
vpc domain <nexus-vpc-domain-id>
role priority 10
peer-keepalive destination <nexus-B-mgmt0-ip> source <nexus-A-mgmt0-ip>
peer-switch
peer-gateway
auto-recovery
delay restore 150
ip arp synchronize
interface Po10
vpc peer-link
interface Po11
vpc 11
interface Po12
vpc 12
interface Po15
vpc 15
interface Po16
vpc 16
interface Po127
vpc 127
exit
copy run start
Step 11. Configure virtual port channels (vPCs) in Cisco Nexus B.
vpc domain <nexus-vpc-domain-id>
role priority 20
peer-keepalive destination <nexus-A-mgmt0-ip> source <nexus-B-mgmt0-ip>
peer-switch
peer-gateway
auto-recovery
delay restore 150
ip arp synchronize
interface Po10
vpc peer-link
interface Po11
vpc 11
interface Po12
vpc 12
interface Po15
vpc 15
interface Po16
vpc 16
interface Po127
vpc 127
exit
copy run start
Step 12. The following commands can be used to see the switch configuration and status.
show run
show vpc
show port-channel summary
show ntp peer-status
show cdp neighbors
show lldp neighbors
show run int
show int
show udld neighbors
show int status
NetApp ONTAP Storage Configuration
This chapter contains the following:
See the following section (NetApp Hardware Universe) for planning the physical location of the storage systems:
● Site Preparation
● System Connectivity Requirements
● Circuit Breaker, Power Outlet Balancing, System Cabinet Power Cord Plugs, and Console Pinout Requirements
● AFF Series Systems
NetApp Hardware Universe
The NetApp Hardware Universe (HWU) application provides supported hardware and software components for any specific ONTAP version. It also provides configuration information for all the NetApp storage appliances currently supported by ONTAP software and a table of component compatibilities.
To confirm that the hardware and software components that you would like to use are supported with the version of ONTAP that you plan to install, follow these steps at the NetApp Support site.
Procedure 1. Confirm hardware and software components
Step 1. Access the HWU application to view the System Configuration guides. Click the Products tab to select the Platforms menu to view the compatibility between different versions of the ONTAP software and the NetApp storage appliances with your desired specifications.
Step 2. Alternatively, to compare components by storage appliance, click Utilities and select Compare Storage Systems.
Controllers
Follow the physical installation procedures for the controllers found here: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems/index.html.
NetApp storage systems support a wide variety of disk shelves and disk drives. The complete list of disk shelves that are supported by the NetApp AFF C800 is available at the NetApp Support site.
When using SAS disk shelves with NetApp storage controllers, go to: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems/sas3/install-new-system.html for proper cabling guidelines.
When using NVMe drive shelves with NetApp storage controllers, go to: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap-systems/ns224/hot-add-shelf.html for installation and servicing guidelines.
Complete Configuration Worksheet
Before running the setup script, complete the Cluster setup worksheet in the NetApp ONTAP 9 Documentation Center. You must have access to the NetApp Support site to open the cluster setup worksheet.
Configure ONTAP Nodes
Before running the setup script, review the configuration worksheets in the Software setup section of the ONTAP 9 Documentation Center to learn about configuring ONTAP. Table 4 lists the information needed to configure two ONTAP nodes. Customize the cluster-detail values with the information applicable to your deployment.
Table 4. ONTAP Software Installation Prerequisites
| Cluster Detail |
Cluster Detail Value |
| Cluster node 01 IP address |
<node01-mgmt-ip> |
| Cluster node 01 netmask |
<node01-mgmt-mask> |
| Cluster node 01 gateway |
<node01-mgmt-gateway> |
| Cluster node 02 IP address |
<node02-mgmt-ip> |
| Cluster node 02 netmask |
<node02-mgmt-mask> |
| Cluster node 02 gateway |
<node02-mgmt-gateway> |
| ONTAP 9.14.1 URL (http server hosting ONTAP software) |
<url-boot-software> |
Procedure 1. Configure Node 01
Step 1. Connect to the storage system console port. You should see a Loader-A prompt. However, if the storage system is in a reboot loop, press Ctrl-C to exit the autoboot loop when the following message displays:
Starting AUTOBOOT press Ctrl-C to abort…
Step 2. Allow the system to boot up.
autoboot
Step 3. Press Ctrl-C when prompted.
Note: Use the latest NetApp ONTAP release patch. In this example, it is 9.14.1P2. If NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1P2 is not the version of the software being booted, continue with the following steps to install new software. If NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1P2 is the version being booted, select option 8 and y to reboot the node, then continue with section Set Up Node.
Step 4. To install new software, select option 7 from the menu.
Step 5. Enter y to continue the installation.
Step 6. Select e0M for the network port for the download.
Step 7. Enter n to skip the reboot.
Step 8. Select option 7 from the menu: Install new software first
Step 9. Enter y to continue the installation.
Step 10. Enter the IP address, netmask, and default gateway for e0M.
Enter the IP address for port e0M: <node01-mgmt-ip>
Enter the netmask for port e0M: <node01-mgmt-mask>
Enter the IP address of the default gateway: <node01-mgmt-gateway>
Step 11. Enter the URL where the software can be found.
Note: The e0M interface should be connected to the management network and the web server must be reachable (using ping) from node 01.
<url-boot-software>
Step 12. Press Enter for the user name, indicating no user name.
Step 13. Enter y to set the newly installed software as the default to be used for subsequent reboots.
Step 14. Enter y to reboot the node now.
Note: When installing new software, the system might perform firmware upgrades to the BIOS and adapter cards, causing reboots and possible stops at the Loader-A prompt. If these actions occur, the system might deviate from this procedure.
Note: During the ONTAP installation a prompt to reboot the node requests a Y/N response.
Step 15. Press Ctrl-C when the following message displays:
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu
Step 16. Select option 4 for Clean Configuration and Initialize All Disks.
Step 17. Enter y to zero disks, reset config, and install a new file system.
Step 18. Enter yes to erase all the data on the disks.
Note: When initialization and creation of root aggregate is complete, the storage system reboots. You can continue with the configuration of node 02 while the initialization and creation of the root aggregate for node 01 is in progress. For more information about root aggregate and disk partitioning, please refer to the following NetApp ONTAP documentation on root-data partitioning: https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap/concepts/root-data-partitioning-concept.html
Procedure 2. Configure Node 02
Step 1. Connect to the storage system console port. You should see a Loader-B prompt. However, if the storage system is in a reboot loop, press Ctrl-C to exit the autoboot loop when the following message displays:
Starting AUTOBOOT press Ctrl-C to abort…
Step 2. Allow the system to boot up.
autoboot
Step 3. Press Ctrl-C when prompted.
Note: If NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1P2 is not the version of the software being booted, continue with the following steps to install new software. If NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1P2 is the version being booted, select option 8 and y to reboot the node. Continue with section Set Up Node.
Step 4. To install new software, select option 7.
Step 5. Enter y to continue the installation.
Step 6. Select e0M for the network port you want to use for the download.
Step 7. Enter n to skip the reboot.
Step 8. Select option 7: Install new software first
Step 9. Enter y to continue the installation.
Step 10. Enter the IP address, netmask, and default gateway for e0M.
Enter the IP address for port e0M: <node02-mgmt-ip>
Enter the netmask for port e0M: <node02-mgmt-mask>
Enter the IP address of the default gateway: <node02-mgmt-gateway>
Step 11. Enter the URL where the software can be found.
Note: The web server must be reachable (ping) from node 02.
<url-boot-software>
Step 12. Press Enter for the username, indicating no username.
Step 13. Enter y to set the newly installed software as the default to be used for subsequent reboots.
Step 14. Enter y to reboot the node now.
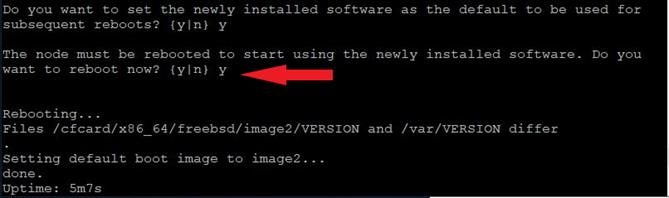
Note: When installing new software, the system might perform firmware upgrades to the BIOS and adapter cards, causing reboots and possible stops at the Loader-B prompt. If these actions occur, the system might deviate from this procedure.
Note: During the ONTAP installation a prompt to reboot the node requests a Y/N response.
Step 15. Press Ctrl-C when you see this message:
Press Ctrl-C for Boot Menu
Step 16. Select option 4 for Clean Configuration and Initialize All Disks.
Step 17. Enter y to zero disks, reset config, and install a new file system.
Step 18. Enter yes to erase all the data on the disks.
Note: When initialization and creation of root aggregate is complete, the storage system reboots. For more information about root aggregate and disk partitioning, please refer to the following ONTAP documentation on root-data partitioning. https://docs.netapp.com/us-en/ontap/concepts/root-data-partitioning-concept.html
Step 1. From a console port program attached to the storage controller A (node 01) console port, run the node setup script. This script appears when ONTAP 9.14.1 boots on the node for the first time.
Step 2. Follow the prompts to set up node 01.
Welcome to the cluster setup wizard.
You can enter the following commands at any time:
"help" or "?" - if you want to have a question clarified,
"back" - if you want to change previously answered questions, and
"exit" or "quit" - if you want to quit the setup wizard.
Any changes you made before quitting will be saved.
You can return to cluster setup at any time by typing “cluster setup”.
To accept a default or omit a question, do not enter a value.
This system will send event messages and weekly reports to NetApp Technical Support.
To disable this feature, enter "autosupport modify -support disable" within 24 hours.
Enabling AutoSupport can significantly speed problem determination and resolution should a problem occur on your system.
For further information on AutoSupport, see:
http://support.netapp.com/autosupport/
Type yes to confirm and continue {yes}: yes
Enter the node management interface port [e0M]: Enter
Enter the node management interface IP address: <node01-mgmt-ip>
Enter the node management interface netmask: <node01-mgmt-mask>
Enter the node management interface default gateway: <node01-mgmt-gateway>
A node management interface on port e0M with IP address <node01-mgmt-ip> has been created.
Use your web browser to complete cluster setup by accesing https://<node01-mgmt-ip>
Otherwise press Enter to complete cluster setup using the command line interface:
Step 3. To complete cluster setup, open a web browser and navigate to https://<node01-mgmt-ip>.
Table 5. Cluster Create in ONTAP Prerequisites
| Cluster Detail |
Cluster Detail Value |
| Cluster name |
<clustername> |
| Cluster Admin SVM |
<cluster-adm-svm> |
| Infrastructure Data SVM |
<infra-data-svm> |
| ONTAP base license |
<cluster-base-license-key> |
| Cluster management IP address |
<clustermgmt-ip> |
| Cluster management netmask |
<clustermgmt-mask> |
| Cluster management gateway |
<clustermgmt-gateway> |
| Cluster node 01 IP address |
<node01-mgmt-ip> |
| Cluster node 01 netmask |
<node01-mgmt-mask> |
| Cluster node 01 gateway |
<node01-mgmt-gateway> |
| Cluster node 02 IP address |
<node02-mgmt-ip> |
| Cluster node 02 netmask |
<node02-mgmt-mask> |
| Cluster node 02 gateway |
<node02-mgmt-gateway> |
| Node 01 service processor IP address |
<node01-sp-ip> |
| Node 01 service processor network mask |
<node01-sp-mask> |
| Node 01 service processor gateway |
<node01-sp-gateway> |
| Node 02 service processor IP address |
<node02-sp-ip> |
| Node 02 service processor network mask |
<node02-sp-mask> |
| Node 02 service processor gateway |
<node02-sp-gateway> |
| Node 01 node name |
<st-node01> |
| Node 02 node name |
<st-node02> |
| DNS domain name |
<dns-domain-name> |
| DNS server IP address |
<dns-ip> |
| NTP server A IP address |
<switch-a-ntp-ip> |
| NTP server B IP address |
<switch-b-ntp-ip> |
| SNMPv3 User |
<snmp-v3-usr> |
| SNMPv3 Authentication Protocol |
<snmp-v3-auth-proto> |
| SNMPv3 Privacy Protocol |
<snmpv3-priv-proto> |
Note: Cluster setup can also be performed using the CLI. This document describes the cluster setup using the NetApp ONTAP System Manager guided setup.
Step 4. Complete the required information on the Initialize Storage System screen:
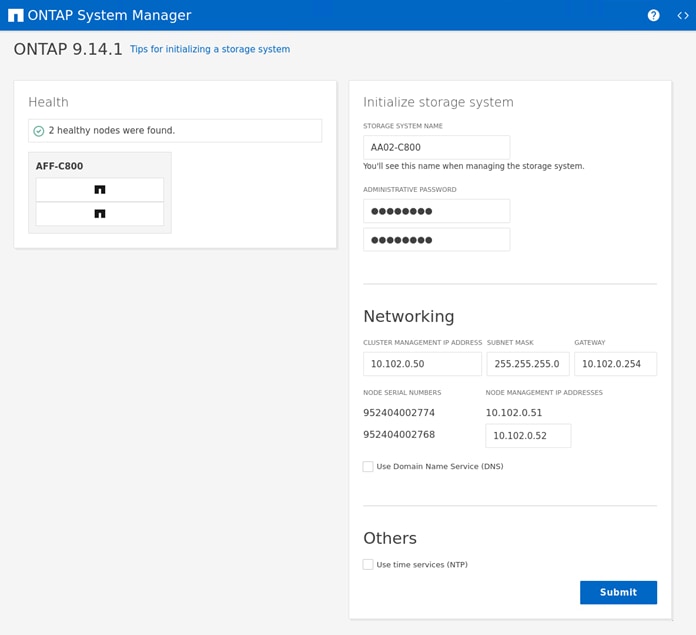
Step 5. In the Cluster Screen:
a. Enter the cluster name and administrator password.
b. Complete the Networking information for the cluster and each node.
c. Check the box for Use Domain Name Service (DNS) and enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers in a comma separated list.
d. Check the box for Use time services (NTP) and enter the IP addresses of the time servers in a comma separated list.
Note: The nodes should be discovered automatically; if they are not, Refresh the browser page. By default, the cluster interfaces are created on all the new factory shipping storage controllers.
Note: If all the nodes are not discovered, then configure the cluster using the command line.
Note: The node management interface can be on the same subnet as the cluster management interface, or it can be on a different subnet. In this document, we assume that it is on the same subnet.
Step 6. Click Submit.
Note: A few minutes will pass while the cluster is configured. When prompted, login to NetApp ONTAP System Manager to continue the cluster configuration.
Procedure 4. Manual ONTAP Storage Configuration – Base Config
Step 1. From the Dashboard click the CLUSTER menu on the left and select Overview.
Step 2. Click the More ellipsis button in the Overview pane at the top right of the screen and select Edit.
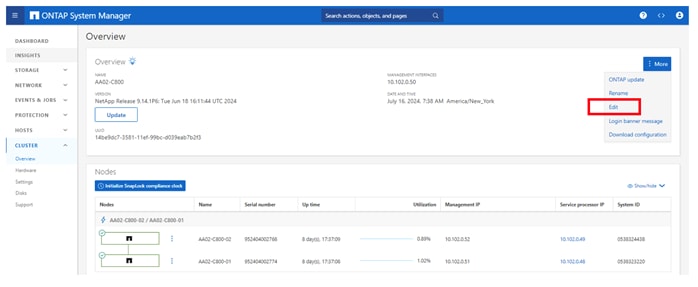
Step 3. Add additional cluster configuration details and click Save to make the changes persistent:
a. Cluster location
b. DNS domain name
c. DNS server IP addresses
d. NTP server IP addresses
Note: DNS and NTP server IP addresses can be added individually or with a comma separated list on a single line.
Note: For redundancy and best service NetApp recommends that you associate at least three NTP servers with the cluster. Otherwise, you will observe an alert/warning in AIQUM stating “NTP Server Count is Low.”
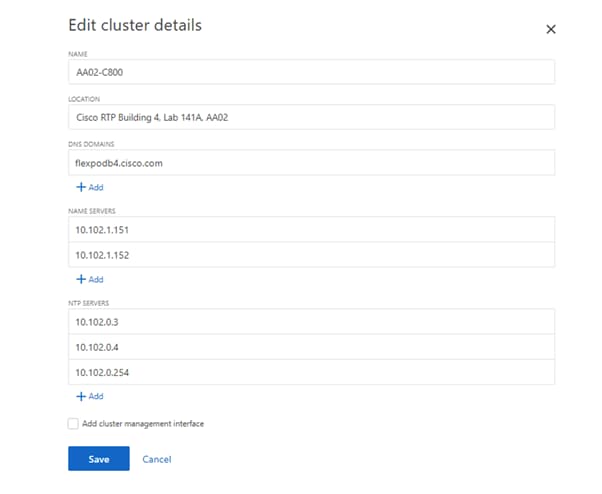
Step 4. Click Save to make the changes persistent.
Step 5. Select the Settings menu under the CLUSTER menu.
Step 6. If AutoSupport was not configured during the initial setup, click the ellipsis in the AutoSupport tile and select More options.
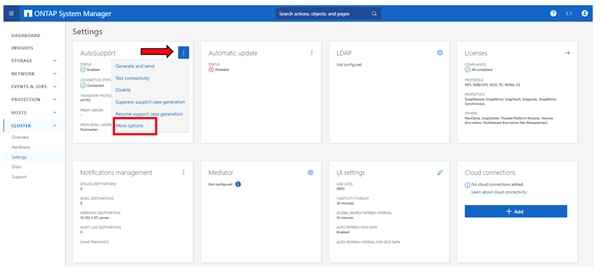
Step 7. To enable AutoSupport click the slider.
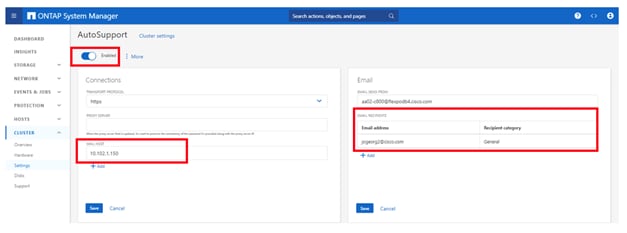
Step 8. In the Connections tile to the left, click Edit to change the transport protocol, add a proxy server address and a mail host as needed.
Step 9. Click Save to enable the changes.
Step 10. In the Email tile to the right, click Edit and enter the desired email information:
a. Email send from address
b. Email recipient addresses
c. Recipient category
Step 11. Click Save when complete.
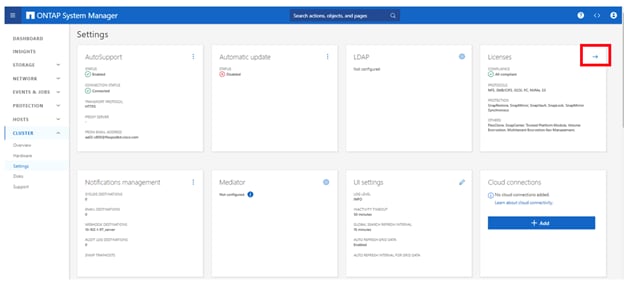
Step 12. Select CLUSTER > Settings at the top left of the page to return to the cluster settings page.
Step 13. Locate the Licenses tile on the right and click the detail arrow.
Step 14. Click Add to add the desired licenses to the cluster. Select Browse and choose the NetApp License File you downloaded.
Step 15. Click Add when complete.
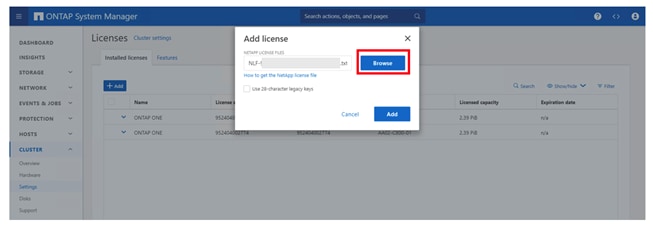
Step 16. If you have license keys you want to add, select Use 28-character legacy keys and enter the keys.
Note: NetApp ONTAP 9.10.1 and later for FAS/AFF storage systems uses a new file-based licensing solution to enable per-node NetApp ONTAP features. The new license key format is referred to as a NetApp License File, or NLF. For more information, go to: NetApp ONTAP 9.10.1 and later Licensing Overview - NetApp Knowledge Base.
Step 17. Configure storage aggregates by selecting the STORAGE menu on the left and selecting Tiers.
Step 18. Click Add local tier and allow NetApp ONTAP System Manager to recommend a storage aggregate configuration.
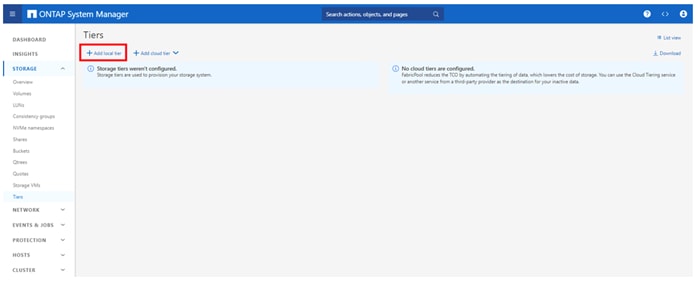
Step 19. NetApp ONTAP will use best practices to recommend an aggregate layout. Click the Recommendation details link to view the aggregate information.
Step 20. Optionally, enable NetApp Aggregate Encryption (NAE) by checking the box for Configure Onboard Key Manager for encryption.
Step 21. Enter and confirm the passphrase and save it in a secure location for future use.
Step 22. Click Save to make the configuration persistent.
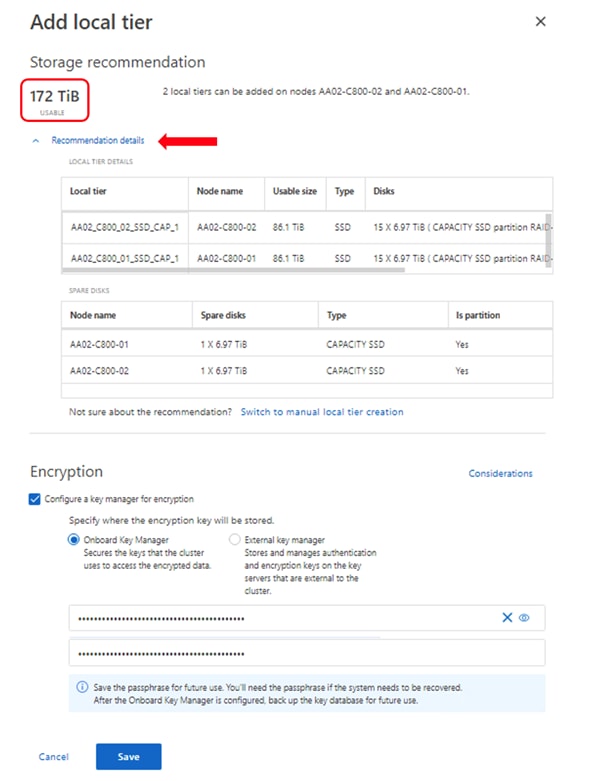
Note: Aggregate encryption may not be supported for all deployments. Please review the NetApp Encryption Power Guide and the Security Hardening Guide for NetApp ONTAP 9 (TR-4569) to help determine if aggregate encryption is right for your environment.
Procedure 5. Log into the Cluster
Step 1. Open an SSH connection to either the cluster IP or the host name.
Step 2. Log into the admin user with the password you provided earlier.
Procedure 6. Verify Storage Failover
Step 1. Verify the status of the storage failover.
storage failover show
Note: Both <st-node01> and <st-node02> must be capable of performing a takeover. Continue with step 2 if the nodes can perform a takeover.
Step 2. Enable failover on one of the two nodes if it was not completed during the installation.
storage failover modify -node <st-node01> -enabled true
Note: Enabling failover on one node enables it for both nodes.
Step 3. Verify the HA status for a two-node cluster.
Note: This step is not applicable for clusters with more than two nodes.
cluster ha show
Step 4. If HA is not configured use the below commands. Only enable HA mode for two-node clusters. Do not run this command for clusters with more than two nodes because it causes problems with failover.
cluster ha modify -configured true
Do you want to continue? {y|n}: y
Procedure 7. Set Auto-Revert Parameter on Cluster Management Interface
Step 1. Run the following command:
network interface modify -vserver <clustername> -lif cluster_mgmt_lif -auto-revert true
Note: A storage virtual machine (SVM) is referred to as a Vserver or vserver in the GUI and CLI.
Procedure 8. Zero All Spare Disks
Step 1. To zero all spare disks in the cluster, run the following command:
disk zerospares
Note: Advanced Data Partitioning creates a root partition and two data partitions on each SSD drive in an AFF configuration. Disk auto-assign should have assigned one data partition to each node in an HA pair. If a different disk assignment is required, disk auto-assignment must be disabled on both nodes in the HA pair by running the disk option modify command. Spare partitions can then be moved from one node to another by running the disk removeowner and disk assign commands.
Procedure 9. Set Up Service Processor Network Interface
Step 1. To assign a static IPv4 address to the Service Processor on each node, run the following commands:
system service-processor network modify –node <st-node01> -address-family IPv4 –enable true –dhcp none –ip-address <node01-sp-ip> -netmask <node01-sp-mask> -gateway <node01-sp-gateway>
system service-processor network modify –node <st-node02> -address-family IPv4 –enable true –dhcp none –ip-address <node02-sp-ip> -netmask <node02-sp-mask> -gateway <node02-sp-gateway>
Note: The Service Processor IP addresses should be in the same subnet as the node management IP addresses.
Procedure 10. Create Manual Provisioned Data Aggregates (Optional)
An aggregate containing the root volume is created during the NetApp ONTAP setup process. To manually create additional data aggregates, determine the aggregate name, the node on which to create it, and the number of disks it should contain. Options for disk class include solid-state, performance, capacity, array, and archive.
Step 1. Run the following command to get the disk class information from ONTAP storage system:
storage disk show -fields class
Step 2. To create data aggregates, run the following commands:
storage aggregate create -aggregate <aggr1_node01> -node <st-node01> -diskcount <num-disks> -diskclass solid-state
storage aggregate create -aggregate <aggr1_node02> -node <st-node02> -diskcount <num-disks> -diskclass solid-state
Note: Customers should have the minimum number of hot spare disks for the recommended hot spare disk partitions for their aggregate.
Note: For all-flash aggregates, you should have a minimum of one hot spare disk or disk partition. For non-flash homogenous aggregates, you should have a minimum of two hot spare disks or disk partitions. For Flash Pool aggregates, you should have a minimum of two hot spare disks or disk partitions for each disk type.
Note: In an AFF configuration with a small number of SSDs, you might want to create an aggregate with all, but one remaining disk (spare) assigned to the controller.
Note: The aggregate cannot be created until disk zeroing completes. Run the storage aggregate show command to display the aggregate creation status. Do not proceed until both aggr1_node01 and aggr1_node02 are online.
Procedure 11. Remove Default Broadcast Domains
By default, all network ports are included in separate default broadcast domain. Network ports used for data services (for example, e5a, e5b, and so on) should be removed from their default broadcast domain and that broadcast domain should be deleted.
Step 1. To perform this task, run the following commands:
network port broadcast-domain delete -broadcast-domain <Default-N> -ipspace Default
network port broadcast-domain show
Note: Delete the Default broadcast domains with Network ports (Default-1, Default-2, and so on). This does not include Cluster ports and management ports.
Procedure 12. Disable Flow Control on 25/100GbE Data Ports
Step 1. Run the following command to configure the ports on node 01:
network port modify -node <st-node01> -port e5a,e5b -flowcontrol-admin none
Step 2. Run the following command to configure the ports on node 02:
network port modify -node <st-node02> -port e5a,e5b -flowcontrol-admin none
Note: Disable flow control only on ports that are used for data traffic.
Procedure 13. Disable Auto-Negotiate on Fibre Channel Ports (Required only for FC configuration)
Step 1. Disable each FC adapter in the controllers with the fcp adapter modify command.
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2a –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2b –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2c –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2d –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2a –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2b –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2c –status-admin down
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2d –status-admin down
Step 2. Set the desired speed on the adapter and return it to the online state.
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2a -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2b -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2c -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node01> -adapter 2d -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2a -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2b -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2c -speed 32 -status-admin up
fcp adapter modify -node <st-node02> -adapter 2d -speed 32 -status-admin up
Procedure 14. Enable Cisco Discovery Protocol
Step 1. To enable the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) on the NetApp storage controllers, run the following command:
node run -node * options cdpd.enable on
Procedure 15. Enable Link-layer Discovery Protocol on all Ethernet Ports
Step 1. Enable LLDP on all ports of all nodes in the cluster:
node run -node * options lldp.enable on
Procedure 16. Configure Timezone
To configure time synchronization on the cluster, follow these steps:
Step 1. Set the time zone for the cluster.
timezone -timezone <timezone>
Note: For example, in the eastern United States, the time zone is America/New_York.
Procedure 17. Configure login banner for the NetApp ONTAP Cluster
Step 1. To create login banner for the NetApp ONTAP cluster, run the following command:
security login banner modify -message "Access restricted to authorized users" -vserver <clustername>
Note: If the login banner for the ONTAP cluster is not configured, users will observe a warning in AIQUM stating “Login Banner Disabled.”
Procedure 18. Remove insecure ciphers from the NetApp ONTAP Cluster
Step 1. Ciphers with the suffix CBC are considered insecure. To remove the CBC ciphers, run the following NetApp ONTAP command:
security ssh remove -vserver <clustername> -ciphers aes256-cbc,aes192-cbc,aes128-cbc,3des-cbc
Note: If the users do not perform the above task, they will see a warning in AIQUM saying “SSH is using insecure ciphers.”
Procedure 19. Enable FIPS Mode on the NetApp ONTAP Cluster
NetApp ONTAP is compliant in the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 for all SSL connections. When SSL FIPS mode is enabled, SSL communication from NetApp ONTAP to external client or server components outside of NetApp ONTAP will use FIPS compliant crypto for SSL.
Step 1. To enable FIPS mode on the NetApp ONTAP cluster, run the following commands:
set -privilege advanced
security config modify -interface SSL -is-fips-enabled true
Note: If you are running NetApp ONTAP 9.8 or earlier manually reboot each node in the cluster one by one. Beginning with NetApp ONTAP 9.9.1, rebooting is not required.
Note: If FIPS is not enabled on the NetApp ONTAP cluster, the users will observe a warning in AIQUM stating “FIPS Mode Disabled.”
Note: When FIPS mode is enabled, there are related security practices that will be enforced:
◦ Transport Layer Security v1.1 (TLSv1.1) is disabled, and only TLS v1.2 and TLS v1.3 remain enabled.
◦ SNMP users or SNMP traphosts that are non-compliant to FIPS will be deleted automatically.
◦ An SNMPv1 user, SNMPv2c user or SNMPv3 user (with none or MD5 as authentication protocol or none or DES as encryption protocol or both) is non-compliant to FIPS.
◦ An SNMPv1 traphost or SNMPv3 traphost (configured with an SNMPv3 user non-compliant to FIPS) is non-compliant to FIPS.
Procedure 20. Configure Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Step 1. Configure basic SNMP information, such as the location and contact. When polled, this information is visible as the sysLocation and sysContact variables in SNMP.
snmp contact <snmp-contact>
snmp location <snmp-location>
snmp init 1
options snmp.enable on
Step 2. Configure SNMP traps to send to remote hosts, such as an Active IQ Unified Manager server or another fault management system.
Note: This step works when FIPS mode is disabled on the cluster as an SNMPv1 traphost or SNMPv3 traphost (configured with an SNMPv3 user non-compliant to FIPS) is non-compliant to FIPS.
snmp traphost add <oncommand-um-server-fqdn>
Step 3. Configure SNMP community.
Note: This step works when FIPS mode is disabled as SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c users are non-compliant to FIPS.
system snmp community add -type ro -community-name <snmp-community> -vserver <clustername>
Note: In new installations of NetApp ONTAP, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c are disabled by default. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c are enabled after you create an SNMP community.
Note: NetApp ONTAP supports read-only communities.
Procedure 21. Configure SNMPv3 Access
SNMPv3 offers advanced security by using encryption and passphrases. The SNMPv3 users can run SNMP utilities from the traphost using the authentication and privacy settings that they specify.
Note: SNMPv3 user (with none or MD5 as authentication protocol or none or DES as encryption protocol or both) is non-compliant to FIPS. So, when FIPS mode is enabled on the cluster, below are the supported/compliant options for authentication and privacy protocols:
◦ Authentication protocol: sha, sha2-256
◦ Privacy protocol: aes128
Step 1. To configure SNMPv3 access, run the following commands:
security login create -user-or-group-name <<snmp-v3-usr>> -application snmp -authentication-method usm
Enter the authoritative entity's EngineID [local EngineID]:
Which authentication protocol do you want to choose (none, md5, sha, sha2-256) [none]: <<snmp-v3-auth-proto>>
Enter the authentication protocol password (minimum 8 characters long):
Enter the authentication protocol password again:
Which privacy protocol do you want to choose (none, des, aes128) [none]: <<snmpv3-priv-proto>>
Enter privacy protocol password (minimum 8 characters long):
Enter privacy protocol password again:
Note: See the SNMP Configuration Express Guide for additional information when configuring SNMPv3 security users.
Procedure 22. Create Interface Groups
Step 1. To create the LACP interface groups for the 100GbE data interfaces, run the following commands:
network port ifgrp create -node <st-node01> -ifgrp a0a -distr-func port -mode multimode_lacp
network port ifgrp add-port -node <st-node01> -ifgrp a0a -port e5a
network port ifgrp add-port -node <st-node01> -ifgrp a0a -port e5b
network port ifgrp create -node <st-node02> -ifgrp a0a -distr-func port -mode multimode_lacp
network port ifgrp add-port -node <st-node02> -ifgrp a0a -port e5a
network port ifgrp add-port -node <st-node02> -ifgrp a0a -port e5b
Procedure 23. Change MTU on Interface Groups
Step 1. To change the MTU size on the base interface-group ports, run the following commands:
network port modify –node <st-node01> -port a0a –mtu 9000
network port modify –node <st-node02> -port a0a –mtu 9000
Procedure 24. Configure AutoSupport (using ONTAP CLI)
If AutoSupport was not configured previously via System Manager, then perform this step.
Step 1. NetApp AutoSupport sends support summary information to NetApp through HTTPS. To configure AutoSupport using command-line interface, run the following command:
system node autosupport modify -node * -state enable –mail-hosts <mailhost> -from <from-email-address> -to <to-email-address> -transport https -support enable
Cisco Intersight Managed Mode Configuration
This chapter contains the following:
● Set up Cisco Intersight Managed Mode on Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects
● Set up Cisco Intersight Account
● Set up Cisco Intersight Licensing
● Set Up Cisco Intersight Resource Group
● Set Up Cisco Intersight Organization
● Claim Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects in Cisco Intersight
● Verify Addition of Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects to Cisco Intersight
● Upgrade Fabric Interconnect Firmware using Cisco Intersight
● Configure a Cisco UCS Domain Profile
● Create and Apply VLAN Policy
● Create and Apply VSAN Policy (FC configuration only)
● Configure FC Port Channel (FC configuration only)
● Port Configuration for Fabric Interconnect B
● Configure Network Connectivity Policy
● Summary
● Deploy the Cisco UCS Domain Profile
● Verify Cisco UCS Domain Profile Deployment
● Configure a Cisco UCS Chassis Profile
● UCS Chassis Profile General Configuration
● Cisco UCS Chassis Assignment
● Create and Apply Power Policy
● Create and Apply Thermal Policy
● Complete UCS Chassis Profile and Deploy
The Cisco Intersight platform is a management solution delivered as a service with embedded analytics for Cisco and third-party IT infrastructures. The Cisco Intersight Managed Mode (also referred to as Cisco IMM or Intersight Managed Mode) is an architecture that manages Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS) fabric interconnect–attached systems through a Redfish-based standard model. Cisco Intersight managed mode standardizes both policy and operation management for Cisco UCS C-Series M7 and Cisco UCS X210c M7 compute nodes used in this deployment guide.
Cisco UCS B-Series M6 servers, connected and managed through Cisco UCS FIs, are also supported by IMM. For a complete list of supported platforms, go to: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/unified_computing/Intersight/b_Intersight_Managed_Mode_Configuration_Guide/b_intersight_managed_mode_guide_chapter_01010.html
Procedure 1. Set up Cisco Intersight Managed Mode on Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects
The Cisco UCS fabric interconnects need to be set up to support Cisco Intersight Managed Mode. When converting an existing pair of Cisco UCS fabric interconnects from Cisco UCS Manager mode to Intersight Managed Mode (IMM), first erase the configuration and reboot your system.
Note: Converting fabric interconnects to Cisco Intersight managed mode is a disruptive process, and configuration information will be lost. You are encouraged to make a backup of their existing configuration.
Step 1. Configure Fabric Interconnect A (FI-A). On the Basic System Configuration Dialog screen, set the management mode to Intersight. The remaining settings are similar to those for the Cisco UCS Manager Managed mode (UCSM-Managed).
Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect A
To configure the Cisco UCS for use in a FlexPod environment in IMM, follow these steps:
1. Connect to the console port on the first Cisco UCS fabric interconnect.
Enter the configuration method. (console/gui) ? console
Enter the management mode. (ucsm/intersight)? intersight
The Fabric interconnect will be configured in the intersight managed mode. Choose (y/n) to proceed: y
Enforce strong password? (y/n) [y]: Enter
Enter the password for "admin": <password>
Confirm the password for "admin": <password>
Enter the switch fabric (A/B) []: A
Enter the system name: <ucs-cluster-name>
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IP address : <ucsa-mgmt-ip>
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask : <ucs-mgmt-mask>
IPv4 address of the default gateway : <ucs-mgmt-gateway>
DNS IP address : <dns-server-1-ip>
Configure the default domain name? (yes/no) [n]: y
Default domain name : <ad-dns-domain-name>
Following configurations will be applied:
Management Mode=intersight
Switch Fabric=A
System Name=<ucs-cluster-name>
Enforced Strong Password=yes
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IP Address=<ucsa-mgmt-ip>
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IP Netmask=<ucs-mgmt-mask>
Default Gateway=<ucs-mgmt-gateway>
DNS Server=<dns-server-1-ip>
Domain Name=<ad-dns-domain-name>
Apply and save the configuration (select 'no' if you want to re-enter)? (yes/no): yes
Step 2. After applying the settings, make sure you can ping the fabric interconnect management IP address. When Fabric Interconnect A is correctly set up and is available, Fabric Interconnect B will automatically discover Fabric Interconnect A during its setup process as shown in the next step.
Step 3. Configure Fabric Interconnect B (FI-B). For the configuration method, select console. Fabric Interconnect B will detect the presence of Fabric Interconnect A and will prompt you to enter the admin password for Fabric Interconnect A. Provide the management IP address for Fabric Interconnect B and apply the configuration.
Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnect B
Enter the configuration method. (console/gui) ? console
Installer has detected the presence of a peer Fabric interconnect. This Fabric interconnect will be added to the cluster. Continue (y/n) ? y
Enter the admin password of the peer Fabric interconnect: <password>
Connecting to peer Fabric interconnect... done
Retrieving config from peer Fabric interconnect... done
Peer Fabric interconnect Mgmt0 IPv4 Address: <ucsa-mgmt-ip>
Peer Fabric interconnect Mgmt0 IPv4 Netmask: <ucs-mgmt-mask>
Peer FI is IPv4 Cluster enabled. Please Provide Local Fabric Interconnect Mgmt0 IPv4 Address
Physical Switch Mgmt0 IP address : <ucsb-mgmt-ip>
Local fabric interconnect model <fi-model>
Peer fabric interconnect is compatible with the local fabric interconnect. Continuing with the installer...
Apply and save the configuration (select 'no' if you want to re-enter)? (yes/no): yes
Procedure 2. Set up Cisco Intersight Account
Step 1. Go to https://intersight.com and click Create an account. Complete the log in process.
Step 2. Select the appropriate Region and click Next.
Step 3. Read and accept the license agreement. Click Next.
Step 4. Provide an Account Name and click Create.
With a successful creation of the Intersight account, the following page will be displayed:
Note: You can also choose to add the Cisco UCS FIs to an existing Cisco Intersight account.
Procedure 3. Set up Cisco Intersight Licensing
Note: When setting up a new Cisco Intersight account (as explained in this document), the account needs to be enabled for Cisco Smart Software Licensing.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Smart Licensing portal: https://software.cisco.com/software/smart-licensing/alerts.
Step 2. Verify that the correct virtual account is selected.
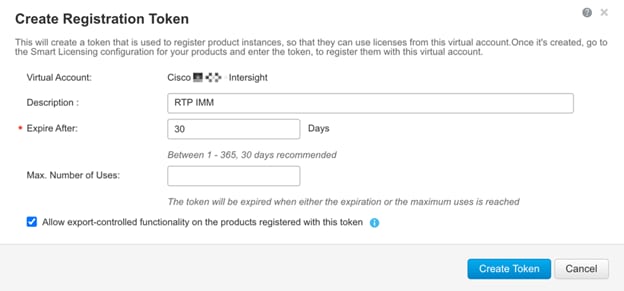
Step 3. Under Inventory > General, click New Token to generate a new token for product registration.
Step 4. Fill in the form and click Create Token. Copy this newly created token.
Step 5. In Cisco Intersight, if you created a new account, click Register Smart Licensing.
Step 6. Enter the copied token from the Cisco Smart Licensing portal. Click Next.
Step 7. With Enable Subscription Information selected, click Next. In the popup, click Allow.
Step 8. Select the products, you wish to enable (minimally Infrastructure Service). Use the pulldown to select the licenses or your Default Tier (for example, Advantage for all).
Step 9. Select Set Default Tier to all existing servers.
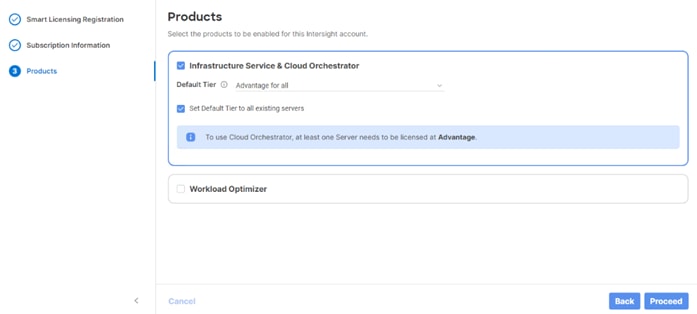
Step 10. Click Proceed then click Confirm.
Step 11. When the registration is successful, a Meet Intersight window will appear. Click Let’s Go to review the latest Intersight features or click Skip.
Procedure 4. Set Up Cisco Intersight Resource Group
In this procedure, a Cisco Intersight resource group is created where resources such as targets will be logically grouped. In this deployment, a single resource group is created to host all the resources, but you can choose to create multiple resource groups for granular control of the resources.
Step 1. Log into Cisco Intersight.
Step 2. Select System. On the left, click Settings (the gear icon).
Step 3. Click Resource Groups in the middle panel.
Step 4. Click + Create Resource Group in the top-right corner.
Step 5. Provide a name for the Resource Group (for example, AA02-rg).
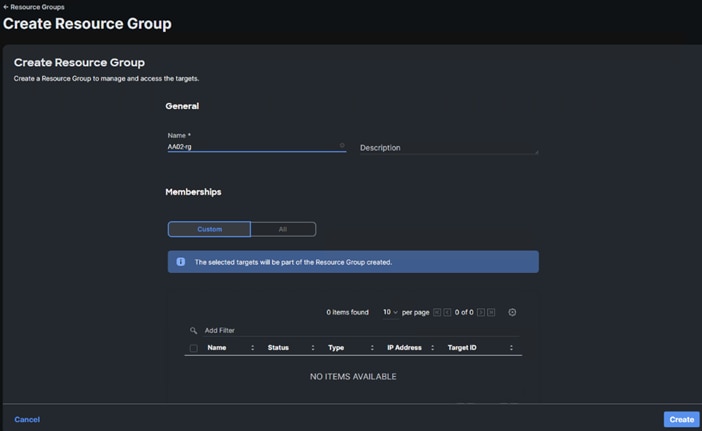
Step 6. Under Memberships, select Custom.
Step 7. Click Create.
Procedure 5. Set Up Cisco Intersight Organization
In this procedure, an Intersight organization is created where all Cisco Intersight Managed Mode configurations including policies are defined.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. Select System. On the left, click Settings (the gear icon).
Step 3. Click Organizations in the middle panel.
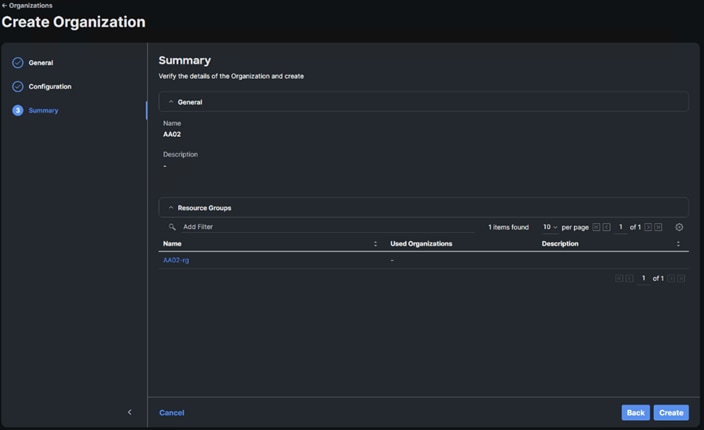
Step 4. Click + Create Organization in the top-right corner.
Step 5. Provide a name for the organization (for example, AA02), optionally select Share Resources with Other Organizations, and click Next.
Step 6. Select the Resource Group created in the last step (for example, AA02-rg) and click Next.
Step 7. Click Create.
Procedure 6. Claim Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects in Cisco Intersight
Make sure the initial configuration for the fabric interconnects has been completed. Log into the Fabric Interconnect A Device Console using a web browser to capture the Cisco Intersight connectivity information.
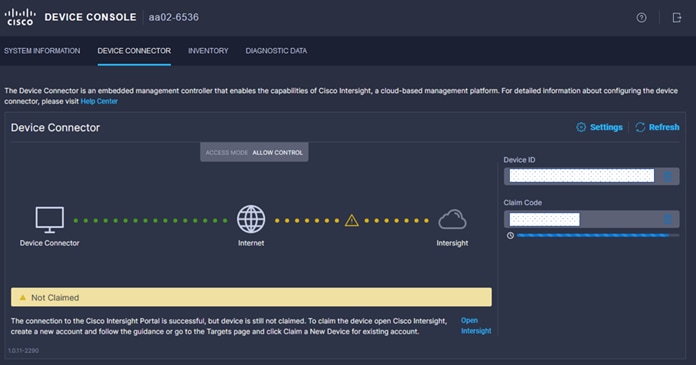
Step 1. Use the management IP address of Fabric Interconnect A to access the device from a web browser and the previously configured admin password to log into the device.
Step 2. Under DEVICE CONNECTOR, the current device status will show “Not claimed.” Note or copy, the Device ID, and Claim Code information for claiming the device in Cisco Intersight.
Step 3. Log into Cisco Intersight.
Step 4. Select System. On the left, click Admin > Targets.
Step 5. Click Claim a New Target.
Step 6. Select Cisco UCS Domain (Intersight Managed) and click Start.
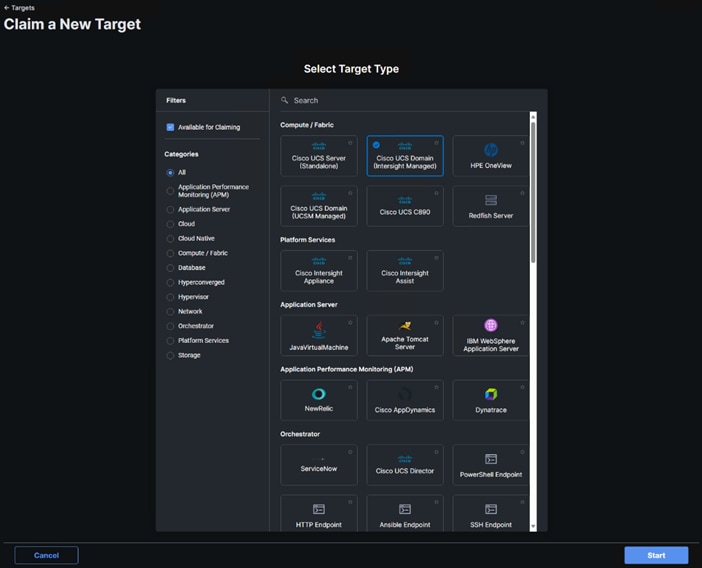
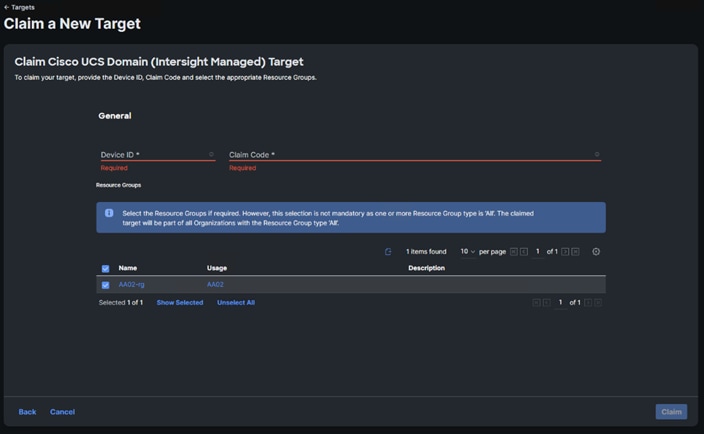
Step 7. Copy and paste the Device ID and Claim from the Cisco UCS FI to Intersight.
Step 8. Select the previously created Resource Group and click Claim.
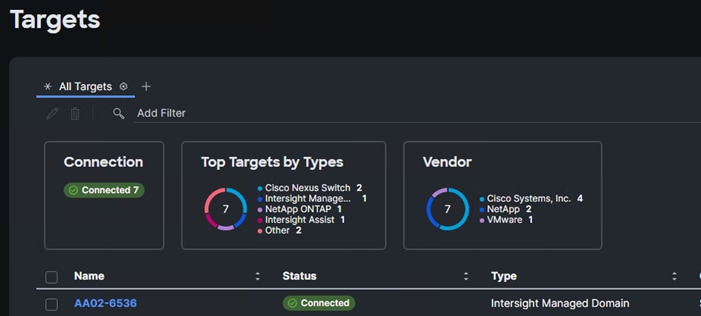
With a successful device claim, Cisco UCS FI should appear as a target in Cisco Intersight as shown below:
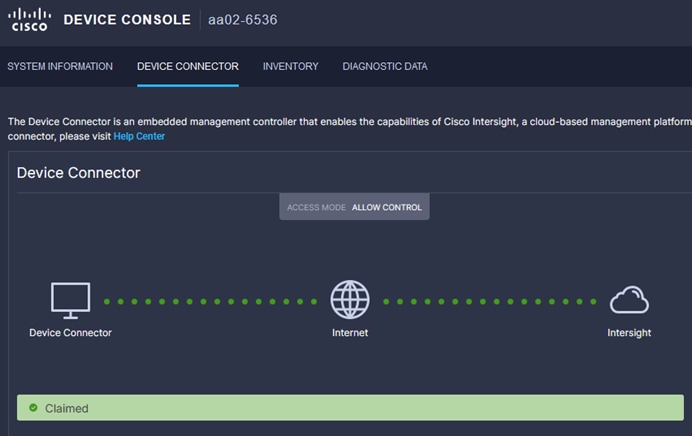
Procedure 7. Verify Addition of Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects to Cisco Intersight
Step 1. Log into the web GUI of the Cisco UCS fabric interconnect and click the browser refresh button.
The fabric interconnect status should now be set to Claimed.
Procedure 8. Upgrade Fabric Interconnect Firmware using Cisco Intersight
If your Cisco UCS 6536 Fabric Interconnects are not already running firmware release 4.3(3.24007) (NX-OS version 9.3(5)I43(3a)), upgrade them to 4.3(3.24007) or later.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select Infrastructure Service and then select Fabric Interconnects under Operate on the left.
Step 3. Click the ellipses “…” at the end of the row for either of the Fabric Interconnects and select Upgrade Firmware.
Step 4. Click Start.
Step 5. Verify the Fabric Interconnect information and click Next.
Step 6. Enable Advanced Mode using the toggle switch and uncheck Fabric Interconnect Traffic Evacuation.
Step 7. Select 4.3(3.24007) release or later from the list and click Next.
Step 8. Verify the information and click Upgrade to start the upgrade process.
Step 9. Watch the Request panel of the main Intersight screen as the system will ask for user permission before upgrading each FI. Click on the Circle with Arrow and follow the prompts on screen to grant permission.
Step 10. Wait for both the FIs to successfully upgrade.
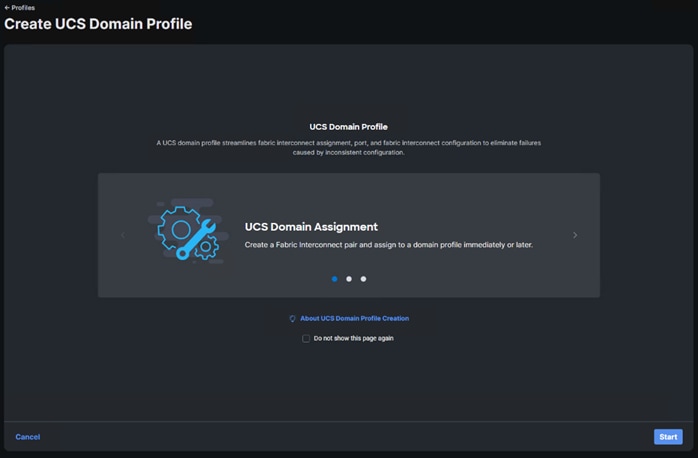
Procedure 9. Configure a Cisco UCS Domain Profile
Note: A Cisco UCS domain profile configures a fabric interconnect pair through reusable policies, allows configuration of the ports and port channels, and configures the VLANs and VSANs in the network. It defines the characteristics of and configured ports on fabric interconnects. The domain-related policies can be attached to the profile either at the time of creation or later. One Cisco UCS domain profile can be assigned to one fabric interconnect domain.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select Infrastructure Service and then under Configure select Profiles.
Step 3. In the main window, select UCS Domain Profiles and click Create UCS Domain Profile.
Step 4. From the Create UCS Domain Profile screen, click Start.
Procedure 10. General Configuration
Step 1. Select the organization from the drop-down list (for example, AA02).
Step 2. Provide a name for the domain profile (for example, AA02-6536-Domain-Profile).
Step 3. Provide an optional Description.
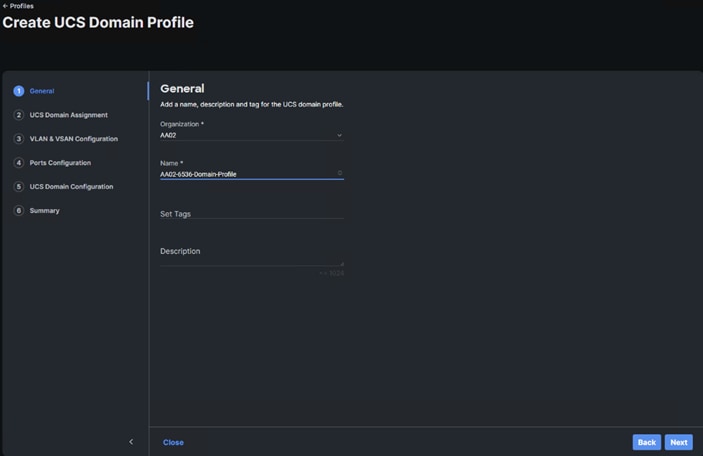
Step 4. Click Next.
Procedure 11. Cisco UCS Domain Assignment
Step 1. Assign the Cisco UCS domain to this new domain profile by clicking Assign Now and selecting the previously added Cisco UCS domain (for example, AA02-6536).
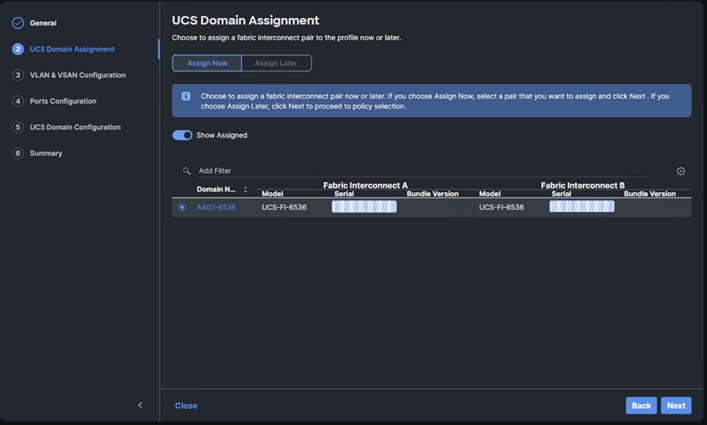
Step 2. Click Next.
In this procedure, a single VLAN policy is created for both fabric interconnects and two individual VSAN policies are created because the VSAN IDs are unique for each fabric interconnect.
Procedure 1. Create and Apply VLAN Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to VLAN Configuration under Fabric Interconnect A.
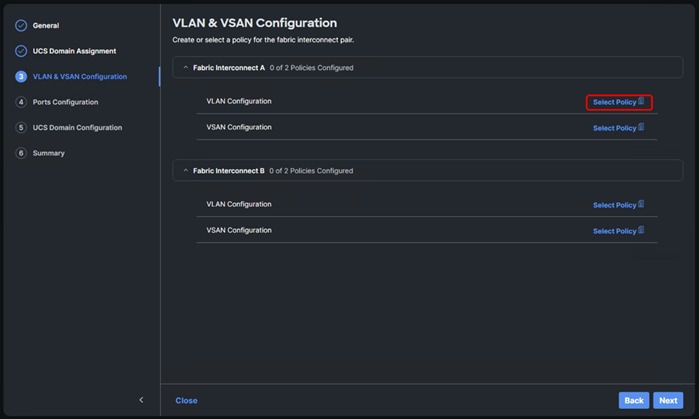
Step 2. In the pane on the right, click Create New.
Step 3. Verify the correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-6536-VLAN).
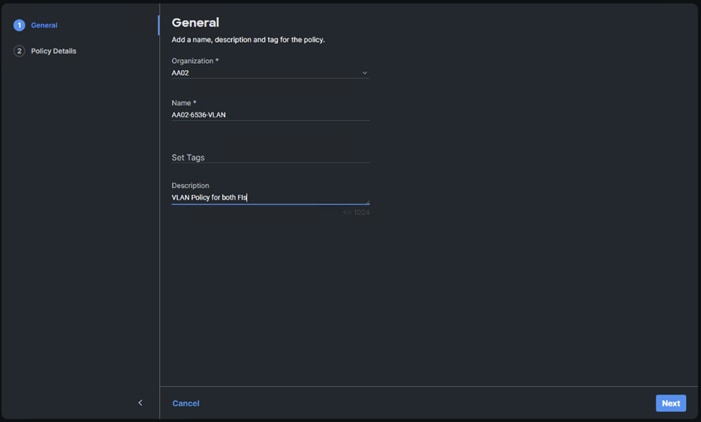
Step 4. Click Next.
Step 5. Click Add VLANs.
Step 6. Provide a name and VLAN ID for the native VLAN.
Step 7. Make sure Auto Allow On Uplinks is enabled.
Step 8. To create the required Multicast policy, under Multicast, click Select Policy.
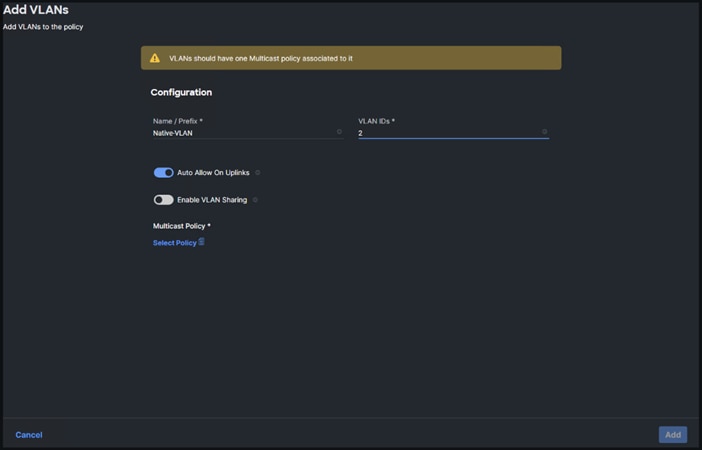
Step 9. In the window on the right, click Create New to create a new Multicast Policy.
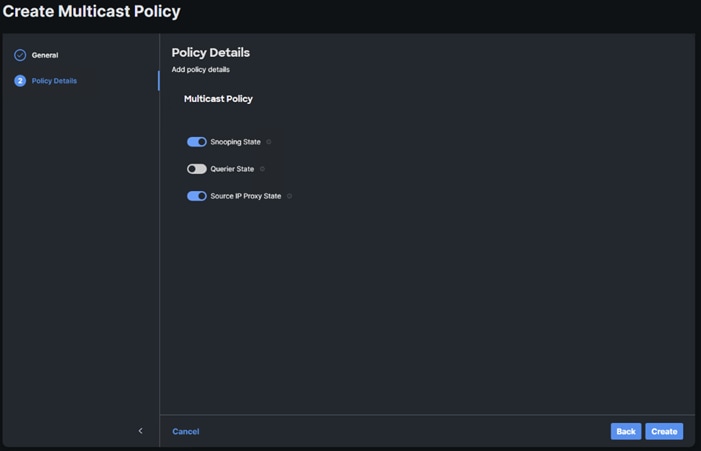
Step 10. Provide a Name for the Multicast Policy (for example, AA02-MCAST).
Step 11. Provide an optional Description and click Next.
Step 12. Leave the default settings and click Create.
Step 13. Click Add VLANs to add the VLAN.
Step 14. Select Set Native VLAN ID and enter the VLAN number (for example, 2) under VLAN ID.
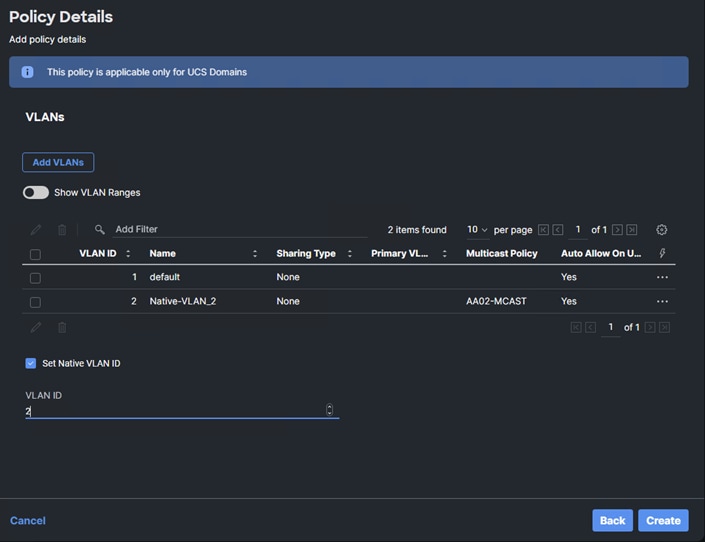
Step 15. Add the OOB-MGMT VLAN by clicking Add VLANs and entering the OOB-MGMT VLAN name and VLAN id. Reuse the previously created multicast policy for this VLAN.
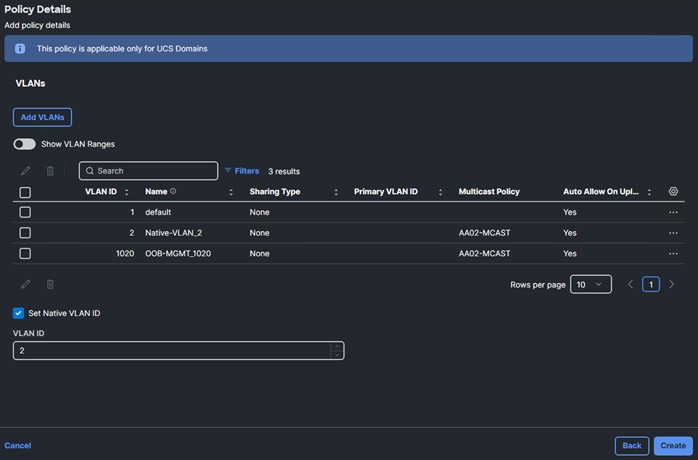
Step 16. Click Create to finish creating the VLAN policy and associated VLANs.
Step 17. Click Select Policy next to VLAN Configuration for Fabric Interconnect B and select the same VLAN policy.
Procedure 2. Create and Apply VSAN Policy (FC/FCoE configuration only)
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to VSAN Configuration under Fabric Interconnect A and click Create New.
Step 2. Verify the correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-6536-VSAN-Pol-A).
Note: A separate VSAN-Policy is created for each fabric interconnect.
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 4. Optional: enable Uplink Trunking.

Step 5. Click Add VSAN and provide a name (for example, VSAN-A), VSAN ID (for example, 101), and associated Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) VLAN ID (for example, 101) for SAN A.
Step 6. Set VLAN Scope as Uplink.
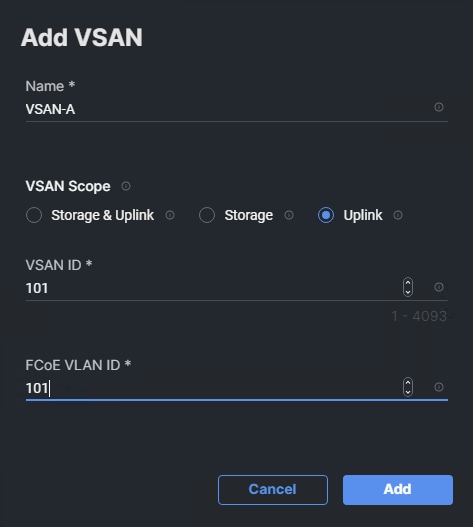
Step 7. Click Add.
Step 8. Click Create to finish creating VSAN policy for fabric A.
Step 9. Repeat steps 1 - 8 to create a new VSAN policy for SAN-B. Name the policy to identify the SAN-B configuration (for example, AA02-6536-VSAN-Pol-B) and use appropriate VSAN and FCoE VLAN (for example, 102).
Step 10. Verify that a common VLAN policy and two unique VSAN policies are associated with the two fabric interconnects.
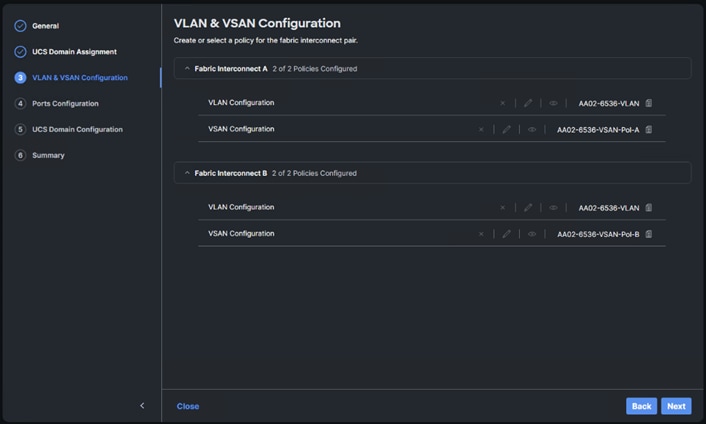
Step 11. Click Next.
Procedure 3. Ports Configuration
Step 1. Click Select Policy for Fabric Interconnect A.
Step 2. Click Create New in the pane on the right to define a new port configuration policy.
Note: Use two separate port policies for the fabric interconnects. Using separate policies provide flexibility when port configuration (port numbers or speed) differs between the two FIs. When configuring Fibre Channel, two port policies are required because each fabric interconnect uses a unique Fibre Channel VSAN ID.
Step 3. Verify correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-6536-PortPol-A). Select the UCS-FI-6536 Switch Model.
Step 4. Click Next.
Step 5. Move the slider to set up unified ports. In this deployment, the last two ports were selected as Fibre Channel ports as 4x32G breakouts. Click Next.
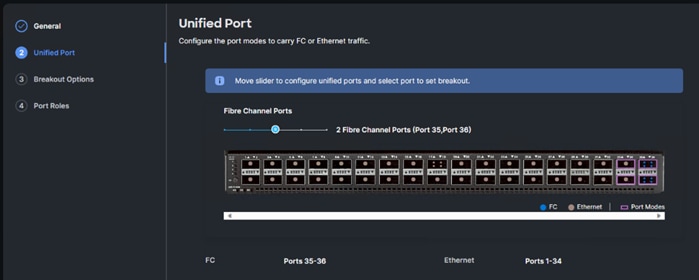
Step 6. If any ethernet ports need to be configured as breakouts, either 4x25G or 4x10G, for connecting Cisco UCS C-Series servers or a Cisco UCS 5108 chassis, configure them here. In the list, select the checkbox next to any ports that need to be configured as breakout or select the ports on the graphic. When all ports are selected, click Configure.
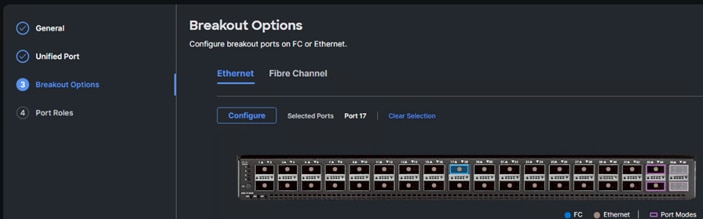
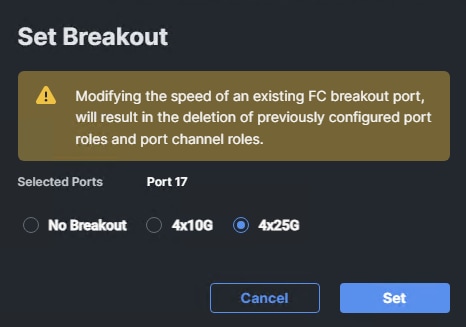
Step 7. In the Set Breakout popup, select either 4x10G or 4x25G and click Set.
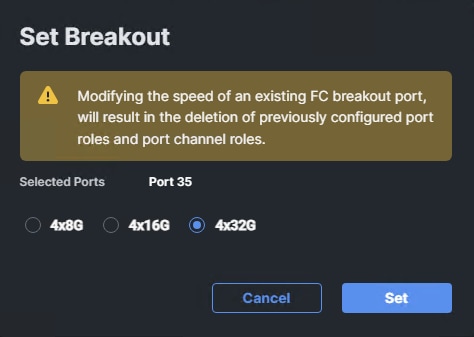
Step 8. Under Breakout Options, select Fibre Channel. Select any ports that need the speed changed from 16G to 32G and click Configure.
Step 9. In the Set Breakout popup, select 4x32G and click Set.
Step 10. Click Next.
Step 11. From the list, check the box next to any ports that need to be configured as server ports, including ports connected to chassis or Cisco UCS C-Series servers. Ports can also be selected on the graphic. When all ports are selected, click Configure. Breakout and non-breakout ports cannot be configured together. If you need to configure breakout and non-breakout ports, do this configuration in two steps.
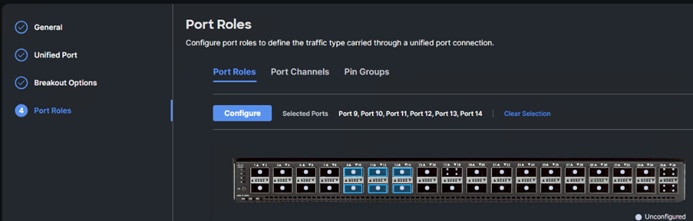
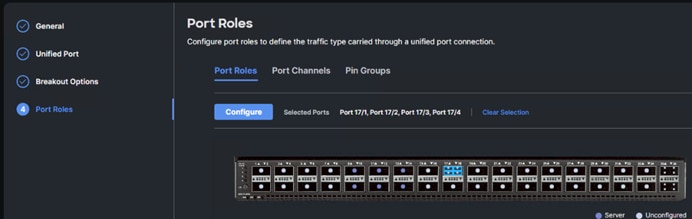
Step 12. From the drop-down list, select Server as the role. Also, unless you are using a Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX23 as a FEX, leave Auto Negotiation enabled. If you need to do manual number of chassis or Cisco UCS C-Series Servers, enable Manual Chassis/Server Numbering.
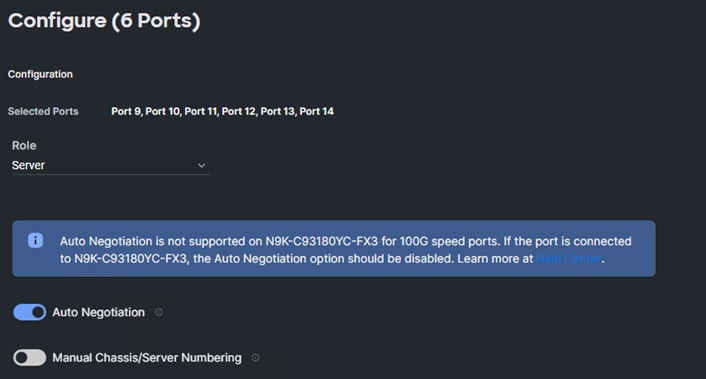
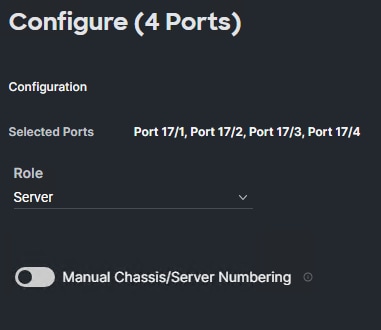
Step 13. Click Save.
Step 14. Configure the Ethernet uplink port channel by selecting Port Channels in the main pane and then clicking Create Port Channel.
Step 15. Select Ethernet Uplink Port Channel as the role, provide a port-channel ID (for example, 131), and select a value for Admin Speed from drop-down list (for example, Auto).
Note: You can create the Ethernet Network Group, Flow Control, Link Aggregation for defining disjoint Layer-2 domain or fine tune port-channel parameters. These policies were not used in this deployment and system default values were utilized.
Step 16. Under Link Control, click Select Policy then click Create New.
Step 17. Verify the correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-UDLD-Link-Control). Click Next.
Step 18. Leave the default values selected and click Create.
Step 19. Scroll down and select uplink ports from the list of available ports (for example, port 31 and 32)
Step 20. Click Save.
Procedure 4. Configure FC Port Channel (FC configuration only)
Note: FC uplink port channels are only needed when configuring FC SAN and can be skipped for IP-only (iSCSI) storage access. If configuring 100G or 25G FCoE port channels, skip to the next Procedure.
Step 1. Configure a Fibre Channel Port Channel by selecting the Port Channel in the main pane again and clicking Create Port Channel.
Step 2. From the Role drop-down list, select FC Uplink Port Channel.
Step 3. Provide a port-channel ID (for example, 135), select a value for Admin Speed (for example, 32Gbps), and provide a VSAN ID (for example, 101).
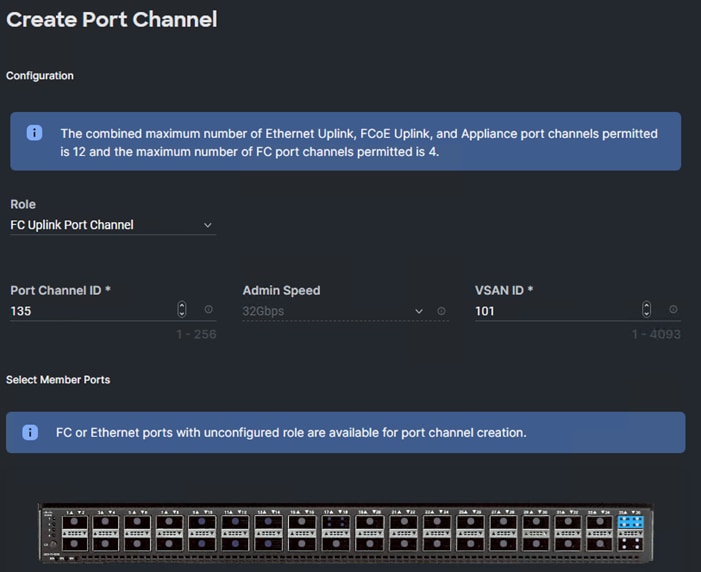
Step 4. Select ports (for example, 35/1,35/2,35/3,35/4).
Step 5. Click Save.
Step 6. Verify the port-channel IDs and ports after both the Ethernet uplink port channel and the Fibre Channel uplink port channel have been created.
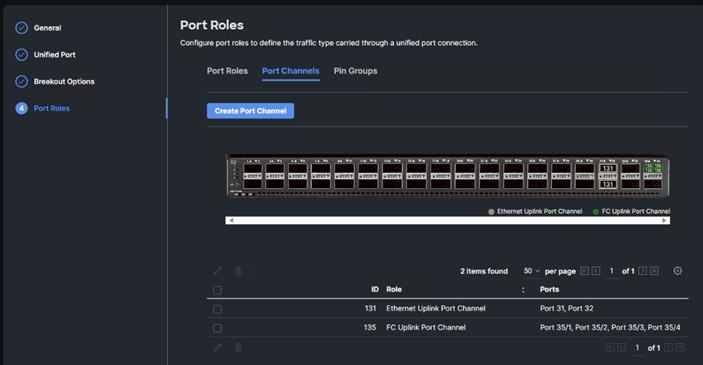
Step 7. Click Save to create the port policy for Fabric Interconnect A.
Note: Use the summary screen to verify that the ports were selected and configured correctly.
Procedure 5. Configure FCoE Port Channel (FCoE Uplink configuration only)
Note: FCoE uplink port channels are only needed when configuring FC SAN and can be skipped for IP-only (iSCSI) storage access.
Step 1. Configure a FCoE Port Channel by selecting the Port Channel in the main pane again and clicking Create Port Channel.
Step 2. From the Role drop-down list, select FCoE Uplink Port Channel.
Step 3. Provide a port-channel ID (for example, 127) and leave Admin Speed set to Auto.
Step 4. Select the <Prefix>-Link-Control-UDLD Link Control policy.
Step 5. Select ports (for example, 27,28).
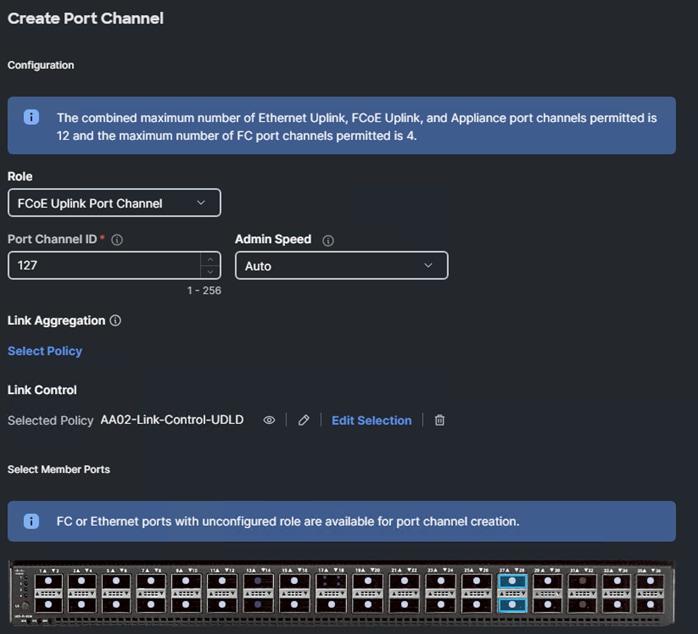
Step 6. Click Save.
Step 7. Verify the port-channel IDs and ports after both the Ethernet uplink port channel and the FCoE Uplink Channel have been created.
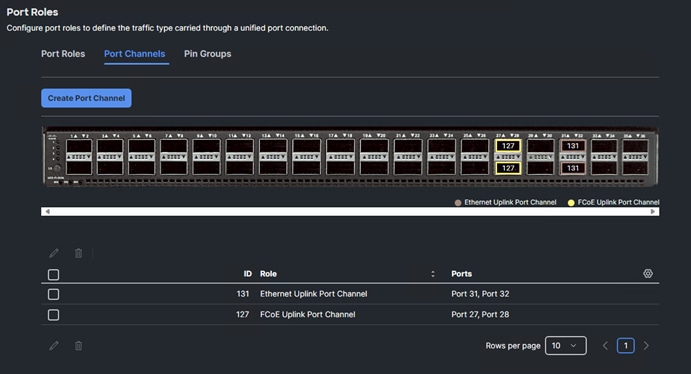
Step 8. Click Save to create the port policy for Fabric Interconnect A.
Note: Use the summary screen to verify that the ports were selected and configured correctly.
Procedure 6. Port Configuration for Fabric Interconnect B
Step 1. Repeat the steps in Ports Configuration and Configure FC Port Channel to create the port policy for Fabric Interconnect B including the Ethernet port-channel and the FC/FCoE port-channel (if configuring SAN). Use the following values for various parameters:
● Name of the port policy: AA02-PortPol-B
● Ethernet port-Channel ID: 131
● FC port-channel ID: 135
● FCoE port-channel ID: 127
● FC VSAN ID: 102
Step 2. When the port configuration for both fabric interconnects is complete and looks good, click Next.
Procedure 7. UCS Domain Configuration
Under UCS domain configuration, additional policies can be configured to setup NTP, Syslog, DNS settings, SNMP, QoS and UCS operating mode (end host or switch mode). For this deployment, four policies (NTP, Network Connectivity, SNMP, and System QoS) will be configured, as shown below:
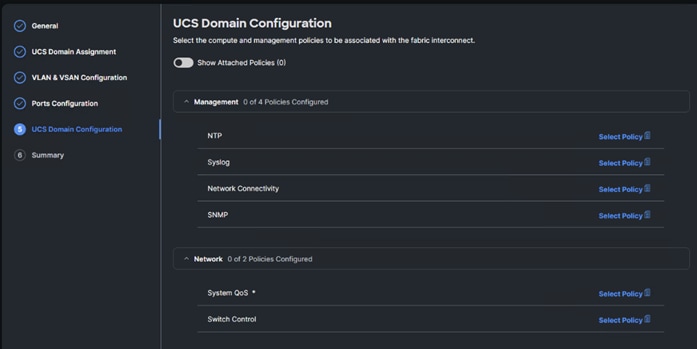
Procedure 8. Configure NTP Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to NTP and then, in the pane on the right, click Create New.
Step 2. Verify correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-NTP).
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 4. Enable NTP, provide the first NTP server IP address, and select the time zone from the drop-down list.
Step 5. Add a second NTP server by clicking + next to the first NTP server IP address.
Note: The NTP server IP addresses should be Nexus switch management IPs. NTP distribution was configured in the Cisco Nexus switches.
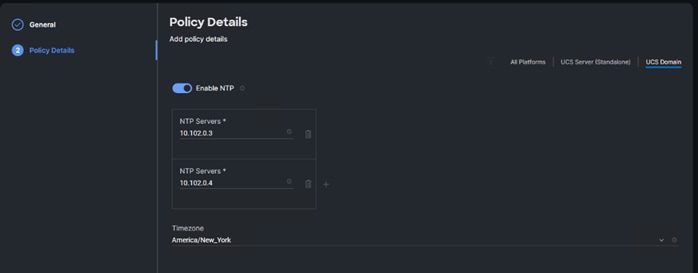
Step 6. Click Create.
Procedure 9. Configure Network Connectivity Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to Network Connectivity and then, in the pane on the right, click Create New.
Step 2. Verify correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-NetConn).
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 4. Provide DNS server IP addresses for Cisco UCS (for example, 10.102.1.151 and 10.102.1.152).
Step 5. Click Create.
Procedure 10. Configure SNMP Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to SNMP and then, in the pane on the right, click Create New.
Step 2. Verify correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-SNMP).
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 4. Provide a System Contact email address, a System Location, and optional Community Strings.
Step 5. Under SNMP Users, click Add SNMP User.
Step 6. This user id will be used for Cisco DCNM SAN to query the UCS Fabric Interconnects. Fill in a user name (for example, snmpadmin), Auth Type SHA, an Auth Password with confirmation, Privacy Type AES, and a Privacy Password with confirmation. Click Add.
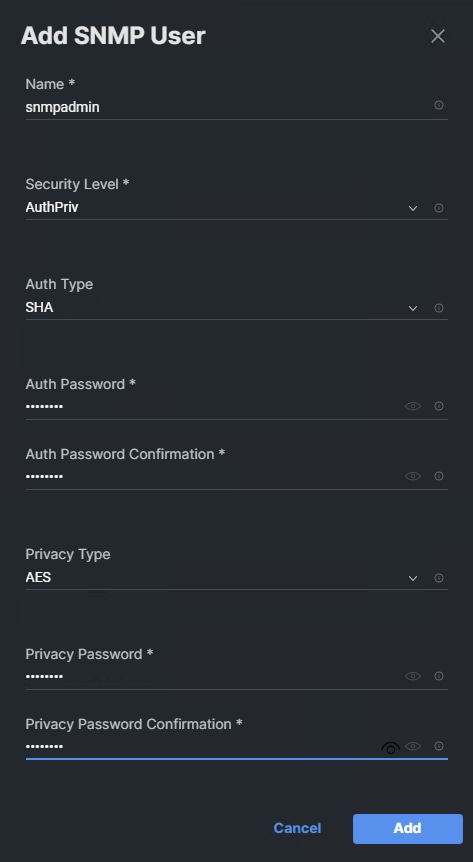
Step 7. Optional: Add an SNMP Trap Destination (for example, the DCNM SAN IP Address). If the SNMP Trap Destination is V2, you must add Trap Community String.
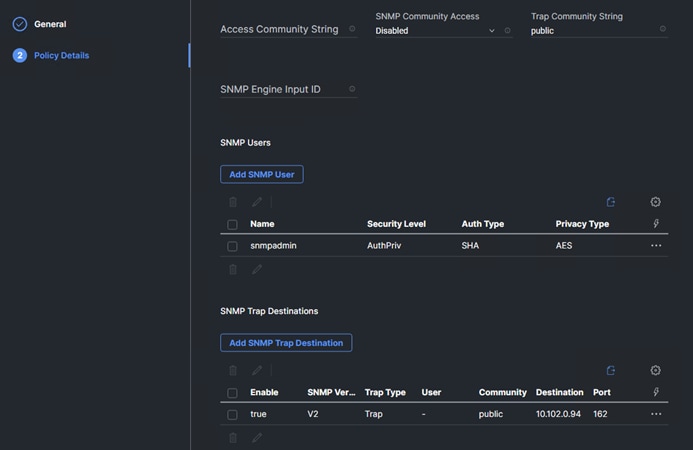
Step 8. Click Create.
Procedure 11. Configure System QoS Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to System QoS* and in the pane on the right, click Create New.
Step 2. Verify correct organization is selected from the drop-down list (for example, AA02) and provide a name for the policy (for example, AA02-QoS).
Step 3. Click Next.
Step 4. Change the MTU for Best Effort class to 9216.
Step 5. Keep the default selections or change the parameters if necessary.
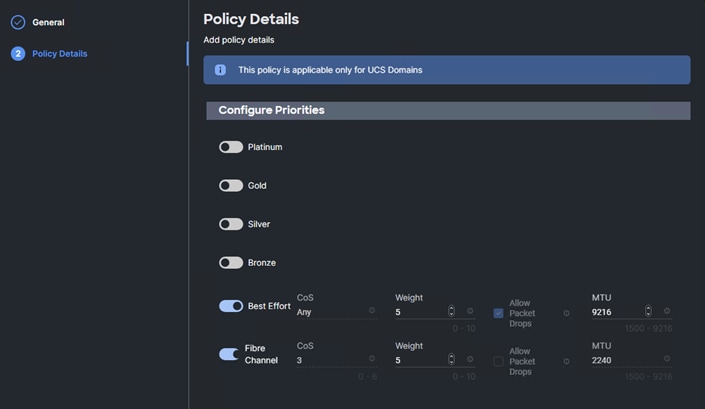
Step 6. Click Create.
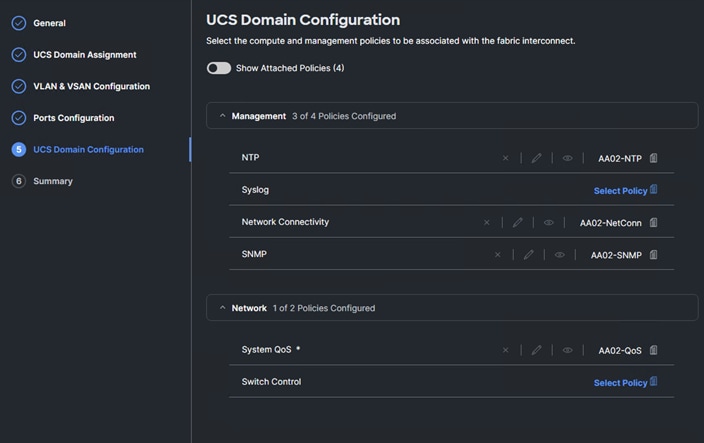
Step 7. Click Next.
Step 1. Verify all the settings including the fabric interconnect settings, by expanding the settings and make sure that the configuration is correct.
Procedure 13. Deploy the Cisco UCS Domain Profile
Step 1. From the UCS domain profile Summary view, click Deploy.
Step 2. Acknowledge any warnings and click Deploy again.
Note: The system will take some time to validate and configure the settings on the fabric interconnects. Log into the fabric interconnect serial console servers to see when the Cisco UCS fabric interconnects have finished configuration and are successfully rebooted.
Procedure 14. Verify Cisco UCS Domain Profile Deployment
When the Cisco UCS domain profile has been successfully deployed, the Cisco UCS chassis and the blades should be successfully discovered.
Note: It takes a while to discover the blades and rackmounts for the first time. Watch the number of outstanding requests in Cisco Intersight.
Step 1. Log into Cisco Intersight. Under Infrastructure Service > Configure > Profiles > UCS Domain Profiles, verify that the domain profile has been successfully deployed.
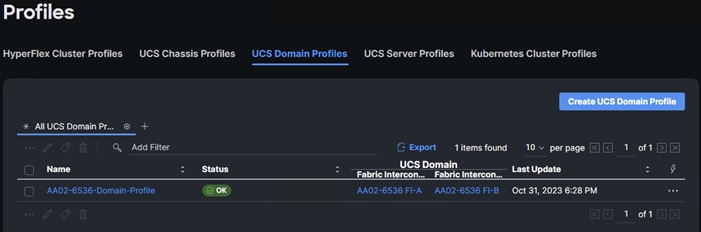
Step 2. Verify that the chassis (either UCSX-9508 or UCS 5108 chassis) has been discovered and is visible under Infrastructure Service > Operate > Chassis.
Step 3. Verify that the servers have been successfully discovered and are visible under Infrastructure Service > Operate > Servers.
Procedure 15. Configure a Cisco UCS Chassis Profile
Note: A Cisco UCS chassis profile configures either a UCS X9508 or UCS 5108 chassis through reusable policies. It defines the characteristics of power distribution and fan configuration in the chassis. One Cisco UCS chassis profile can be assigned to one chassis.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select Infrastructure Service, then under Configure select Profiles.
Step 3. In the main window, select UCS Chassis Profiles and click Create UCS Chassis Profile.
Step 4. From the Create UCS Chassis Profile screen, click Start.
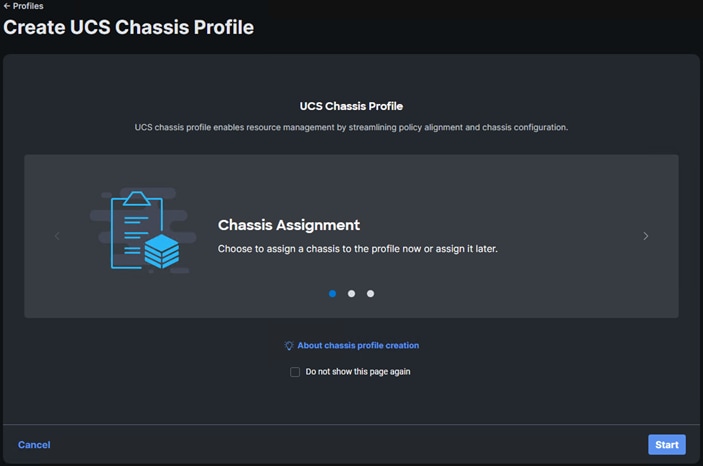
Procedure 16. UCS Chassis Profile General Configuration
Step 1. Select the organization from the drop-down list (for example, AA02).
Step 2. Provide a name for the domain profile (for example, AA02-6536-1-Chassis-Profile).
Step 3. Provide an optional Description.
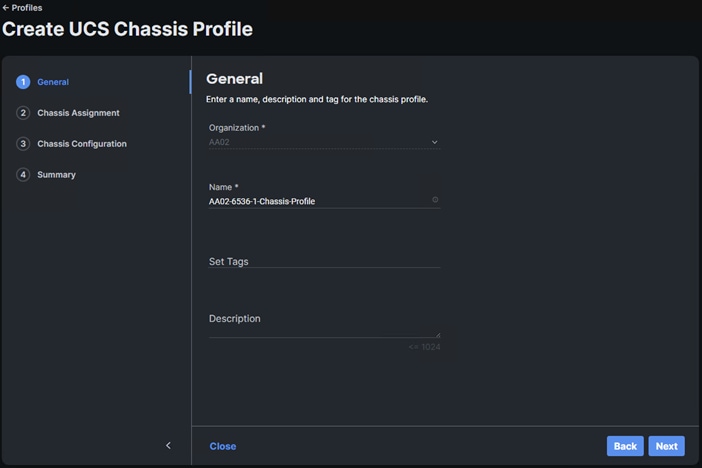
Step 4. Click Next.
Procedure 17. Cisco UCS Chassis Assignment
Step 1. Assign the Cisco UCS chassis to this new chassis profile by clicking Assign Now and selecting a Cisco UCS chassis (for example, AA02-6536-1).
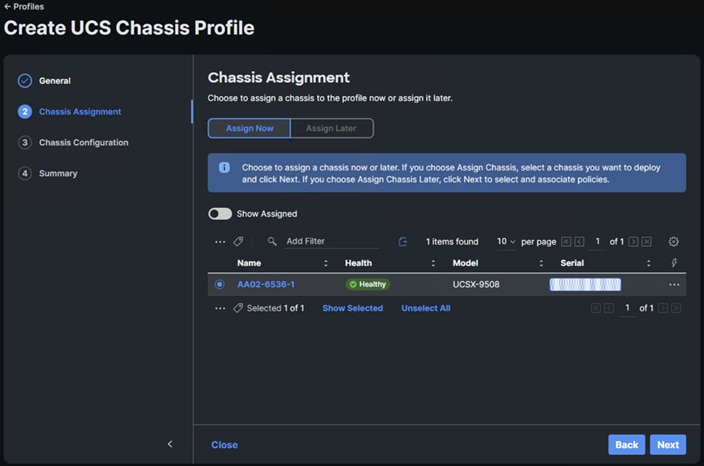
Step 2. Click Next.
Procedure 18. Create and Apply Power Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to Power.
Step 2. Click Create New to create a new policy.
Step 3. Make sure the correct Organization (for example, AA02) is selected.
Step 4. Enter a Name for the policy (for example, AA02-Chassis-Server-Power). Optionally, enter a Description.
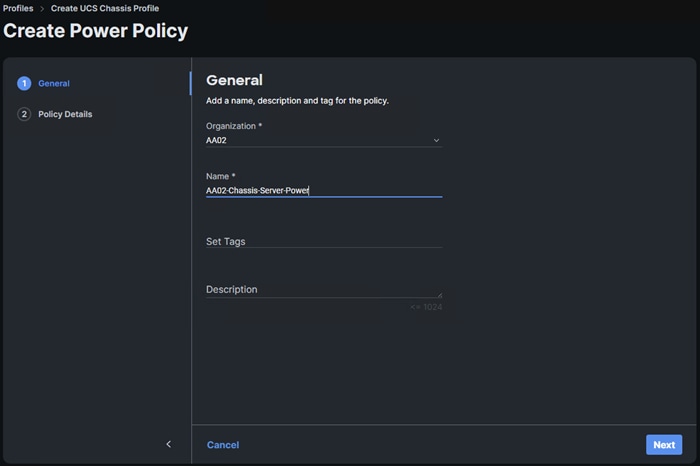
Step 5. Click Next.
Step 6. Select All Platforms. It is recommended to leave all settings at their defaults, but the settings can be adjusted later according to performance and sustainability requirements.
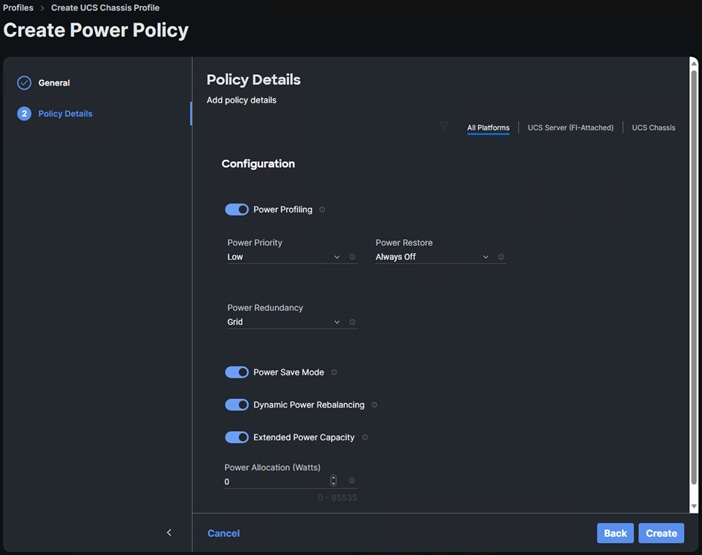
Step 7. Click Create to create the power policy.
Procedure 19. Create and Apply Thermal Policy
Step 1. Click Select Policy next to Thermal.
Step 2. Click Create New to create a new policy.
Step 3. Make sure the correct Organization (for example, AA02) is selected.
Step 4. Enter a Name for the policy (for example, AA02-Chassis-Thermal). Optionally, enter a Description.
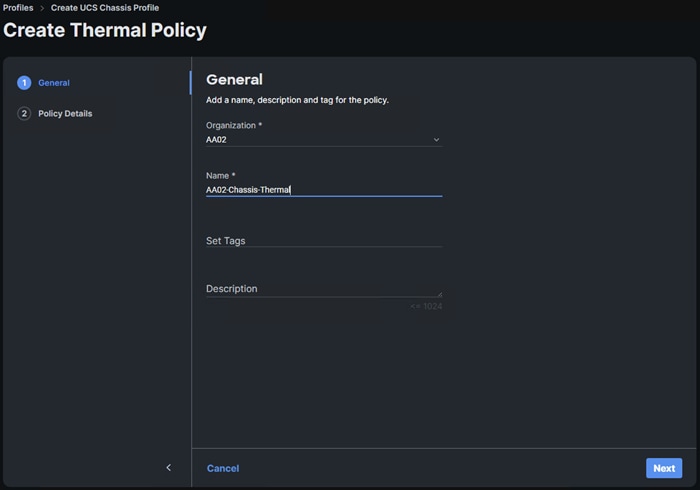
Step 5. Click Next.
Note: It is recommended to leave all settings at their defaults, but the settings can be adjusted later according to performance and sustainability requirements.
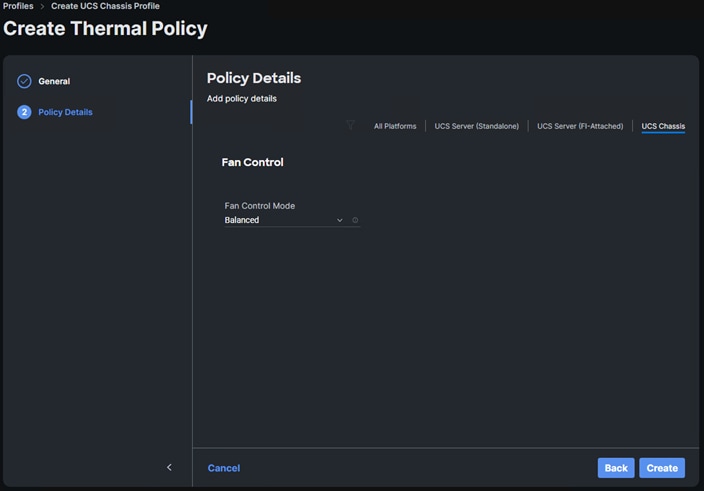
Step 6. Click Create to create the thermal policy.
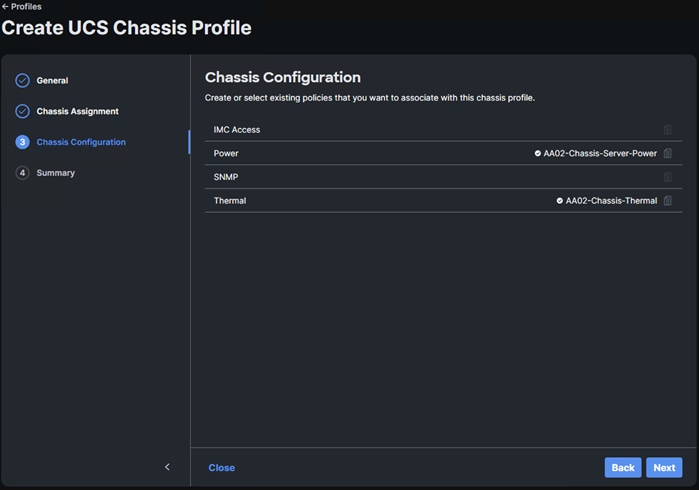
Step 7. Click Next.
Procedure 20. Complete UCS Chassis Profile and Deploy
Step 1. Review the UCS Chassis Profile Summary and click Deploy. Click Deploy again to deploy the profile.
When deployment is complete, the profile Status will show OK.
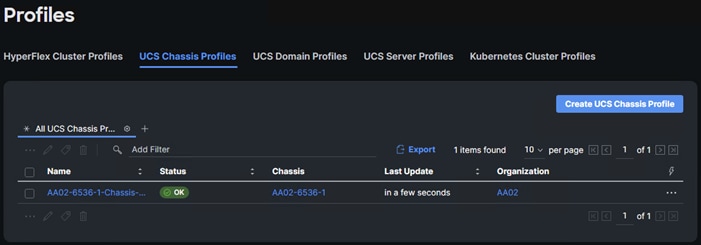
Note: This set of procedures can be used to create profiles for additional chassis. In these additional chassis profiles, the power and thermal policies can be reused as needed.
This chapter contains the following:
This chapter explains how to configure the Cisco MDS 9000s for use in a FlexPod environment. The configuration covered in this section is only needed when configuring Fibre Channel and FC-NVMe storage access.
Note: If FC connectivity is not required in the FlexPod deployment, this section can be skipped.
Note: If the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switches are being used for SAN switching in this FlexPod Deployment, refer to section FlexPod with Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Configuration – Part 2 in the Appendix of this document.
Follow the physical connectivity guidelines for FlexPod as explained in Physical Topology section.
The following procedures describe how to configure the Cisco MDS switches for use in a base FlexPod environment. This procedure assumes you are using the Cisco MDS 9132T with NX-OS 9.3(2a).
Procedure 1. Set up Cisco MDS 9132T A and 9132T B
Note: On initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start and attempt to enter Power on Auto Provisioning. Enter y to get to the System Admin Account Setup.
Step 1. Configure the switch using the command line:
---- System Admin Account Setup ----
Do you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Enter the password for "admin": <password>
Confirm the password for "admin": <password>
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yes
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enter the switch name : <mds-A-hostname>
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Mgmt0 IPv4 address : <mds-A-mgmt0-ip>
Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask : <mds-A-mgmt0-netmask>
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
IPv4 address of the default gateway : <mds-A-mgmt0-gw>
Configure advanced IP options? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa) [rsa]: Enter
Number of rsa key bits <1024-2048> [1024]: Enter
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure congestion/no_credit drop for fc interfaces? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Enter the type of drop to configure congestion/no_credit drop? (con/no) [c]: Enter
Enter milliseconds in multiples of 10 for congestion-drop for logical-type edge
in range (<200-500>/default), where default is 500. [d]: Enter
Enable the http-server? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Configure clock? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure timezone? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure summertime? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure default switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [shut]: Enter
Configure default switchport trunk mode (on/off/auto) [on]: auto
Configure default switchport port mode F (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure default zone policy (permit/deny) [deny]: Enter
Enable full zoneset distribution? (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure default zone mode (basic/enhanced) [basic]: Enter
Step 2. Review the configuration.
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Procedure 2. FlexPod Cisco MDS Switch Manual Configuration
Step 1. Connect to both Cisco MDS switches with the admin user using ssh.
Step 2. Configure features on both MDS switches.
configure terminal
feature nxapi
feature npiv
feature fport-channel-trunk
Step 3. Configure NTP servers and local time configuration. It is important to configure the local time so that logging time alignment and any backup schedules are correct. For more information on configuring the timezone and daylight savings time or summertime, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 9.x.
ntp server <nexus-A-mgmt0-ip>
ntp server <nexus-B-mgmt0-ip>
clock timezone <timezone> <hour-offset> <minute-offset>
clock summer-time <timezone> <start-week> <start-day> <start-month> <start-time> <end-week> <end-day> <end-month> <end-time> <offset-minutes>
copy running-config startup-config
Sample clock commands for the United States Eastern timezone are:
clock timezone EST -5 0
clock summer-time EDT 2 Sunday March 02:00 1 Sunday November 02:00 60
copy running-config startup-config
Step 4. Configure individual ports on Cisco MDS A.
interface fc1/1
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2a
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/2
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2a
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/3
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2c
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/4
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2c
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/5
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/1
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/6
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/2
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/7
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/3
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/8
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/4
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface port-channel15
channel mode active
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-a-id>
switchport description <ucs-clustername>-A
switchport speed 32000
no shutdown
exit
Note: If VSAN trunking is not being used between the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects and the MDS switches, do not enter “switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-a-id>” for interface port-channel15. Also, the default setting of the switchport trunk mode auto is being used for the port channel.
Step 5. Configure individual ports on Cisco MDS B.
interface fc1/1
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2b
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/2
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2b
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/3
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2d
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/4
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2d
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/5
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/1
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/6
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/2
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/7
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/3
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/8
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/4
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface port-channel15
channel mode active
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-b-id>
switchport description <ucs-clustername>-B
switchport speed 32000
no shutdown
exit
Note: If VSAN trunking is not being used between the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects and the MDS switches, do not enter “switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-B-id>” for interface port-channel15. Also, the default setting of the switchport trunk mode auto is being used for the port channel.
Step 6. Create and configure the Fabric-A VSAN.
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id>
vsan <vsan-a-id> name FlexPod-Fabric-A
exit
zone smart-zoning enable vsan <vsan-a-id>
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/1
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/2
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/3
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/4
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface port-channel15
exit
copy r s
Step 7. Create and configure the Fabric-B VSAN.
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id>
vsan <vsan-b-id> name FlexPod-Fabric-B
exit
zone smart-zoning enable vsan <vsan-b-id>
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/1
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/2
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/3
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/4
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface port-channel15
exit
copy r s
Step 8. Smart licensing should be setup in the MDS switches. For more information see: Cisco MDS 9000 Series Licensing Guide, Release 9.x.
Claim Targets to Cisco Intersight
This chapter contains the following:
● Claim NetApp ONTAP Storage Targets
● Claim Cisco Nexus Switch Targets
● Claim Cisco MDS Switch Targets
If you have a management pod capable of running virtual machines, you can install Cisco Intersight Assist and NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager (AIQUM) and integrate a number of the FlexPod components to Cisco Intersight as targets. You will first need to install, claim, and configure the Intersight Assist appliance using the installation instructions found in the Cisco Intersight Virtual Appliance and Intersight Assist Getting Started Guide, 1.0.9 - Cisco. When the Assist is claimed to Intersight, you can then begin claiming targets through the Assist.
Procedure 1. Claim NetApp ONTAP Storage Targets
NetApp ONTAP Storage Targets can be claimed through Intersight Assist and NetApp AIQUM. NetApp AIQUM can be installed on VMware from OVA, on Microsoft Windows, or on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. Install AIQUM with instructions from https://mysupport.netapp.com and configure AIQUM, making sure to enable the API Gateway feature in AIQUM and adding any NetApp ONTAP clusters in the FlexPod to AIQUM.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select System, then select Targets. Select Claim a New Target.
Step 3. Under Select Target Type, scroll down and select NetApp Active IQ Unified Manager and click Start.
Step 4. Make sure the correct Cisco Assist is selected and enter the AIQUM Hostname/IP Address or FQDN and then the username and password used to configure AIQUM. Click Claim.
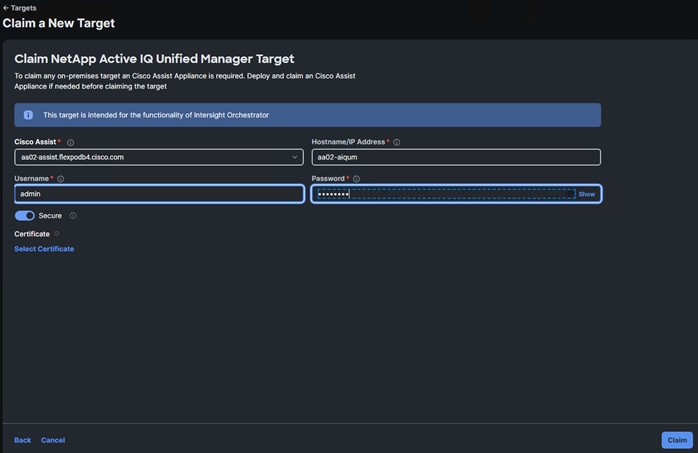
Step 5. When the target is successfully claimed, from the drop-down list select Infrastructure Service. Select Storage. The NetApp storage cluster(s) configured in NetApp AIQUM appear in the list.
Procedure 2. Claim Cisco Nexus Switch Targets
A Cisco Nexus switch can be claimed two ways in Cisco Intersight. The first type of claim is using the switch’s native device connector and is used for the Intersight Connected TAC feature. The second type of claim utilizes Cisco Assist, provides inventory, and alerts information, and allows Intersight Cloud Orchestrator (ICO) workflows to be run on the switch.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select System, then select Targets. Select Claim a New Target.
Step 3. Under Select Target Type, select Cisco Nexus Switch and click Start.
Step 4. To claim the switch for the Intersight Connected TAC feature, leave Claim Target selected and open a ssh connection to the switch. Once connected to the switch, type the following commands:
show system device-connector claim-info
Step 5. Use the switch SerialNumber to fill in the Intersight Device ID field and the switch SecurityToken to fill in the Intersight Claim Code field. Select the appropriate Resource Group(s) and click Claim.
Step 6. To claim the switch for inventory and alerts information and for ICO workflows, select Claim a New Target.
Step 7. Under Select Target Type, select Cisco Nexus Switch and click Start.
Step 8. Select Claim Target with Cisco Assist. Make sure the correct Cisco Assist is selected and enter the switch’s Hostname/IP Address or FQDN and then an administrator user id and password for the switch. Click Claim.
Step 9. It is not an issue to claim a switch both ways. Repeat steps 1 - 8 to claim all Nexus switches into Cisco Intersight.
Procedure 3. Claim Cisco MDS Switch Targets
A Cisco MDS switch can also be claimed two ways in Cisco Intersight. The first type of claim is using the switch’s native device connector and is used for the Intersight Connected TAC feature. The second type of claim utilizes Cisco Assist, provides inventory, and alerts information, and allows Intersight Cloud Orchestrator (ICO) workflows to be run on the switch. The second type of claim is currently in Tech Preview.
Step 1. Log into the Cisco Intersight portal.
Step 2. From the drop-down list, select System, then select Targets. Select Claim a New Target.
Step 3. Under Select Target Type, select Cisco MDS Switch and click Start.
Step 4. To claim the switch for the Intersight Connected TAC feature, leave Claim Target selected and open a ssh connection to the switch. Once connected to the switch, type the following commands:
show intersight claim-info
Step 5. Use the switch SerialNumber to fill in the Intersight Device ID field and the switch SecurityToken to fill in the Intersight Claim Code field. Select the appropriate Resource Group(s) and click Claim.
Step 6. To claim the switch for inventory and alerts information and for ICO workflows, select Claim a New Target.
Step 7. Under Select Target Type, select Cisco MDS Switch and click Start.
Step 8. Select Claim Target with Cisco Assist. Make sure the correct Cisco Assist is selected and enter the switch’s Hostname/IP Address or FQDN, Port 8443, and then an administrator user id and password for the switch. Click Claim.
Step 9. It is not an issue to claim a switch both ways. Repeat steps 1 - 8 to claim all MDS switches into Cisco Intersight.
John George, Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco Systems, Inc.
John has been involved in designing, developing, validating, and supporting the FlexPod Converged Infrastructure since it was developed 13 years ago. Before his role with FlexPod, he supported and administered a large worldwide training network and VPN infrastructure. John holds a master’s degree in Computer Engineering from Clemson University.
Kamini Singh, Technical Marketing Engineer, Hybrid Cloud Infra & OEM Solutions, NetApp
Kamini Singh is a Technical Marketing engineer at NetApp. She has around five years of experience in data center infrastructure solutions. Kamini focuses on FlexPod hybrid cloud infrastructure solution design, implementation, validation, automation, and sales enablement. Kamini holds a bachelor’s degree in Electronics and Communication and a master’s degree in Communication Systems.
Acknowledgements
For their support and contribution to the design, validation, and creation of this Cisco Validated Design, the authors would like to thank:
● Haseeb Niazi, Principal Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco Systems, Inc.
● Paniraja Koppa, Technical Marketing Engineer, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Appendix
This appendix contains the following:
● FlexPod with Cisco Nexus SAN Switching Configuration – Part 1
● FlexPod with Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Configuration – Part 2
Note: The features and functionality explained in this Appendix are optional configurations which can be helpful in configuring and managing the FlexPod deployment.
FlexPod with Cisco Nexus SAN Switching Configuration – Part 1
If the Cisco Nexus switches are to be used for both LAN and SAN switching in the FlexPod configuration, either an automated configuration with Ansible or a manual configuration can be done. For either configuration method, the following base switch setup must be done manually. Figure 5 shows the validation lab cabling for this setup.
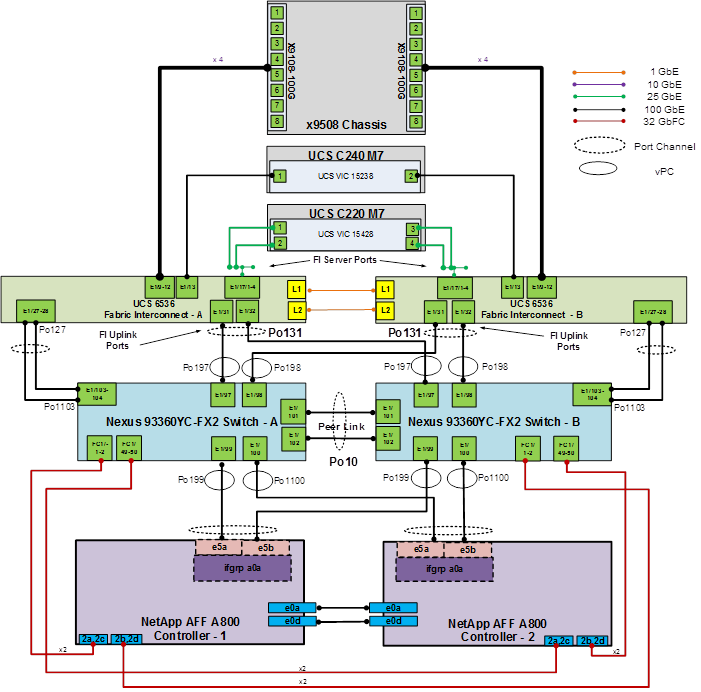
FlexPod Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Base Configuration
The following procedures describe how to configure the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switches for use in a base FlexPod environment that uses the switches for both LAN and SAN switching. This procedure assumes you’re using Cisco Nexus 9000 10.3(4a)M. This procedure also assumes that you have created an FCoE Uplink Port Channel on the appropriate ports in the Cisco UCS IMM Port Policies for each UCS fabric interconnect.
Procedure 1. Set Up Initial Configuration in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 A
Step 1. Configure the switch:
Note: On initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start and attempt to enter Power on Auto Provisioning.
Abort Power On Auto Provisioning [yes - continue with normal setup, skip - bypass password and basic configuration, no - continue with Power On Auto Provisioning] (yes/skip/no)[no]: yes
Disabling POAP.......Disabling POAP
poap: Rolling back, please wait... (This may take 5-15 minutes)
---- System Admin Account Setup ----
Do you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Enter the password for "admin": <password>
Confirm the password for "admin": <password>
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yes
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enter the switch name: <nexus-A-hostname>
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Mgmt0 IPv4 address: <nexus-A-mgmt0-ip>
Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <nexus-A-mgmt0-netmask>
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
IPv4 address of the default gateway: <nexus-A-mgmt0-gw>
Configure advanced IP options? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa) [rsa]: Enter
Number of rsa key bits <1024-2048> [1024]: Enter
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure default interface layer (L3/L2) [L2]: Enter
Configure default switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [noshut]: shut
Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure default physical FC switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [shut]: Enter
Configure default switchport trunk mode (on/off/auto) [on]: auto
Configure default zone policy (permit/deny) [deny]: Enter
Enable full zoneset distribution? (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure CoPP system profile (strict/moderate/lenient/dense) [strict]: Enter
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Step 2. Review the configuration summary before enabling the configuration:
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Procedure 2. Set Up Initial Configuration in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 B
Step 1. Configure the switch:
Note: On initial boot and connection to the serial or console port of the switch, the NX-OS setup should automatically start and attempt to enter Power on Auto Provisioning.
Abort Power On Auto Provisioning [yes - continue with normal setup, skip - bypass password and basic configuration, no - continue with Power On Auto Provisioning] (yes/skip/no)[no]: yes
Disabling POAP.......Disabling POAP
poap: Rolling back, please wait... (This may take 5-15 minutes)
---- System Admin Account Setup ----
Do you want to enforce secure password standard (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Enter the password for "admin": <password>
Confirm the password for "admin": <password>
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): yes
Create another login account (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-only SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure read-write SNMP community string (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enter the switch name: <nexus-B-hostname>
Continue with Out-of-band (mgmt0) management configuration? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Mgmt0 IPv4 address: <nexus-B-mgmt0-ip>
Mgmt0 IPv4 netmask: <nexus-B-mgmt0-netmask>
Configure the default gateway? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
IPv4 address of the default gateway: <nexus-B-mgmt0-gw>
Configure advanced IP options? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the telnet service? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Enable the ssh service? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Type of ssh key you would like to generate (dsa/rsa) [rsa]: Enter
Number of rsa key bits <1024-2048> [1024]: Enter
Configure the ntp server? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Configure default interface layer (L3/L2) [L2]: Enter
Configure default switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [noshut]: shut
Enter basic FC configurations (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure default physical FC switchport interface state (shut/noshut) [shut]: Enter
Configure default switchport trunk mode (on/off/auto) [on]: auto
Configure default zone policy (permit/deny) [deny]: Enter
Enable full zoneset distribution? (yes/no) [n]: y
Configure CoPP system profile (strict/moderate/lenient/dense) [strict]: Enter
Would you like to edit the configuration? (yes/no) [n]: Enter
Step 2. Review the configuration summary before enabling the configuration:
Use this configuration and save it? (yes/no) [y]: Enter
Note: SAN switching requires both the SAN_ENTERPRISE_PKG and FC_PORT_ACTIVATION_PKG licenses. Ensure these licenses are installed on each Nexus switch.
Note: This section is structured as a green field switch setup. If existing switches that are switching active traffic are being setup, execute this procedure down through Perform TCAM Carving and Configure Unified Ports in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX22 A and B first on one switch and then when that is completed, execute on the other switch.
Procedure 3. Install feature-set fcoe in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 A and B
Step 1. Run the following commands to set global configurations:
config t
install feature-set fcoe
feature-set fcoe
system default switchport trunk mode auto
system default switchport mode F
Note: These steps are provided in case the basic FC configurations were not configured in the switch setup script de-tailed in the previous section.
Procedure 4. Set System-Wide QoS Configurations in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 A and B
Step 1. Run the following commands to set global configurations:
config t
system qos
service-policy type queuing input default-fcoe-in-que-policy
service-policy type queuing output default-fcoe-8q-out-policy
service-policy type network-qos default-fcoe-8q-nq-policy
copy run start
Procedure 5. Perform TCAM Carving and Configure Unified Ports (UP) in Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 A and B
Note: SAN switching requires TCAM carving for lossless fibre channel no-drop support. Also, unified ports need to be converted to fc ports.
Note: On the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2, UP ports are converted to FC in groups of 4 in columns, for example, 1,2,49,50.
Step 1. Run the following commands:
hardware access-list tcam region ing-racl 1536
hardware access-list tcam region ing-ifacl 256
hardware access-list tcam region ing-redirect 256
slot 1
port 1-4,49-52 type fc
copy running-config startup-config
reload
This command will reboot the system. (y/n)? [n] y
Step 2. After the switch reboots, log back in as admin. Run the following commands:
show hardware access-list tcam region |i i ing-racl
show hardware access-list tcam region |i i ing-ifacl
show hardware access-list tcam region |i i ing-redirect
show int status
FlexPod Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Ethernet Switching Automated Configuration
For the automated configuration of the Ethernet part of the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switches when using the switches for SAN switching, once the base configuration is set, return to Ansible Nexus Switch Configuration, and execute from there.
FlexPod with Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 SAN Switching Configuration – Part 2
Note: If the Cisco Nexus 93360YC-FX2 switch is being used for SAN Switching, this section should be completed in place of the Cisco MDS section of this document.
Procedure 1. FlexPod Cisco MDS Switch Manual Configuration
Step 1. Connect to both Cisco MDS switches with the admin user using ssh.
Step 2. Configure features on both MDS switches.
configure terminal
feature nxapi
feature npiv
feature fport-channel-trunk
Step 3. Configure NTP servers and local time configuration. It is important to configure the local time so that logging time alignment and any backup schedules are correct. For more information on configuring the timezone and daylight savings time or summertime, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Series Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 9.x.
ntp server <nexus-A-mgmt0-ip>
ntp server <nexus-B-mgmt0-ip>
clock timezone <timezone> <hour-offset> <minute-offset>
clock summer-time <timezone> <start-week> <start-day> <start-month> <start-time> <end-week> <end-day> <end-month> <end-time> <offset-minutes>
copy running-config startup-config
Sample clock commands for the United States Eastern timezone are:
clock timezone EST -5 0
clock summer-time EDT 2 Sunday March 02:00 1 Sunday November 02:00 60
copy running-config startup-config
Step 4. Configure storage individual ports on Cisco MDS A and add to VSAN database.
interface fc1/1
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2a
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/2
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2a
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/49
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2c
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/50
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2c
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id>
vsan <vsan-a-id> name FlexPod-Fabric-A
exit
zone smart-zoning enable vsan <vsan-a-id>
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/1
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/2
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/3
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface fc1/4
exit
Note: If VSAN trunking is not being used between the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects and the MDS switches, do not enter “switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-a-id>” for interface port-channel15. Also, the default setting of the switchport trunk mode auto is being used for the port channel.
Step 5. Configure storage individual ports on Cisco MDS B.
interface fc1/1
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2b
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/2
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2b
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/49
switchport description <st-clustername>-01:2d
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/50
switchport description <st-clustername>-02:2d
switchport speed 32000
switchport trunk mode off
no shutdown
exit
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id>
vsan <vsan-b-id> name FlexPod-Fabric-B
exit
zone smart-zoning enable vsan <vsan-a-id>
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/1
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/2
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/3
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface fc1/4
exit
Note: If VSAN trunking is not being used between the Cisco UCS Fabric Interconnects and the MDS switches, do not enter “switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-B-id>” for interface port-channel15. Also, the default setting of the switchport trunk mode auto is being used for the port channel.
Step 6. If configuring FC links between the Cisco UCS FIs and Cisco Nexus SAN switches, configure the following in Cisco Nexus A.
interface fc1/3
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/1
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/4
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/2
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/51
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/3
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/52
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:1/35/4
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface san-port-channel13
channel mode active
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-a-id>
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A
switchport speed 32000
no shutdown
exit
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface san-port-channel13
exit
copy r s
Step 7. If configuring FC links between the Cisco UCS FIs and Cisco Nexus SAN switches, configure the following in Cisco Nexus B.
interface fc1/3
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/1
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/4
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/2
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/51
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/3
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface fc1/52
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:1/35/4
channel-group 15
no shutdown
exit
interface san-port-channel13
channel mode active
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-B-id>
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B
switchport speed 32000
no shutdown
exit
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface san-port-channel13
exit
copy r s
Step 8. If configuring FCoE links between the Cisco UCS FIs and Cisco Nexus SAN switches, configure the following in Cisco Nexus A.
vlan <vsan-a-id>
name FCoE-VLAN
fcoe vsan <vsan-a-id>
int eth1/103
description <ucs-domainname>-A:Eth1/27
int eth1/104
description <ucs-domainname>-A:Eth1/28
int eth1/103-104
channel-group 1103 mode active
no shutdown
int po1103
description <ucs-domainname>-A:FCoE
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <vsan-a-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input default-fcoe-in-policy
int vfc1103
bind interface port-channel1103
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-a-id>
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-A:FCoE
switchport trunk mode on
vsan database
vsan <vsan-a-id> interface vfc1103
exit
copy r s
Step 9. If configuring FCoE links between the Cisco UCS FIs and Cisco Nexus SAN switches, configure the following in Cisco Nexus B.
vlan <vsan-b-id>
name FCoE-VLAN
fcoe vsan <vsan-b-id>
int eth1/103
description <ucs-domainname>-B:Eth1/27
int eth1/104
description <ucs-domainname>-B:Eth1/28
int eth1/103-104
channel-group 1103 mode active
no shutdown
int po1103
description <ucs-domainname>-B:FCoE
switchport mode trunk
switchport trunk native vlan <native-vlan-id>
switchport trunk allowed vlan <vsan-b-id>
spanning-tree port type edge trunk
mtu 9216
service-policy type qos input default-fcoe-in-policy
int vfc1103
bind interface port-channel1103
switchport trunk allowed vsan <vsan-b-id>
switchport description <ucs-domainname>-B:FCoE
switchport trunk mode on
vsan database
vsan <vsan-b-id> interface vfc1103
exit
copy r s
Procedure 2. Switch Testing Commands
Step 1. The following commands can be used to check for correct switch configuration:
Note: Some of these commands need to run after further configuration of the FlexPod components are complete to see complete results.
show run
show run int
show int
show int status
show int brief
show flogi database
show device-alias database
show zone
show zoneset
show zoneset active
Procedure 1. Cisco Nexus and MDS Backups
The configuration of the Cisco Nexus 9000 and Cisco MDS 9132T switches can be backed up manually at any time with the copy command, but automated backups can be enabled using the NX-OS feature scheduler.
An example of setting up automated configuration backups of one of the NX-OS switches is shown below:
config t
feature scheduler
scheduler logfile size 1024
scheduler job name backup-cfg
copy running-config tftp://<server-ip>/$(SWITCHNAME)-cfg.$(TIMESTAMP) vrf management
exit
scheduler schedule name daily
job name backup-cfg
time daily 2:00
end
Note: Using “vrf management” in the copy command is only needed when Mgmt0 interface is part of VRF management. “vrf management is not needed in Cisco MDS switches.
Step 1. Verify the scheduler job has been correctly setup using following command(s):
show scheduler job
Job Name: backup-cfg
--------------------
copy running-config tftp://10.1.156.150/$(SWITCHNAME)-cfg.$(TIMESTAMP) vrf management
==============================================================================
show scheduler schedule
Schedule Name : daily
---------------------------
User Name : admin
Schedule Type : Run every day at 2 Hrs 0 Mins
Last Execution Time : Yet to be executed
-----------------------------------------------
Job Name Last Execution Status
-----------------------------------------------
backup-cfg -NA-
==============================================================================
The documentation for the feature scheduler can be found here: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/dcn/nx-os/nexus9000/102x/configuration/system-management/cisco-nexus-9000-series-nx-os-system-management-configuration-guide-102x/m-configuring-the-scheduler-10x.html
Procedure 2. NetApp ONTAP Configuration Backup
The configuration backup files of the NetApp ONTAP cluster and nodes are automatically created according to the following schedules:
● Every 8 hours
● Daily
● Weekly
At each of these times, a node configuration backup file is created on each healthy node in the cluster. All of these node configuration backup files are then collected in a single cluster configuration backup file along with the replicated cluster configuration and saved on one or more nodes in the cluster.
An example of viewing the ONTAP cluster configuration backup files is shown below:
AA16-A400::> set advanced
Warning: These advanced commands are potentially dangerous; use them only when directed to do so by NetApp personnel.
Do you want to continue? {y|n}: y
AA16-A400::*> row 0
(rows)
AA16-A400::*> system configuration backup show
Node Backup Name Time Size
--------- ----------------------------------------- ------------------ -----
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.8hour.2023-08-31.18_15_00.7z 08/31 18:15:00 34.60MB
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.8hour.2023-09-01.02_15_00.7z 09/01 02:15:00 35.65MB
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.8hour.2023-09-01.10_15_00.7z 09/01 10:15:00 36.05MB
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.daily.2023-08-31.00_10_01.7z 08/31 00:10:01 34.87MB
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.daily.2023-09-01.00_10_01.7z 09/01 00:10:01 35.09MB
AA16-A400-01 AA16-A400.weekly.2023-08-27.00_15_00.7z 08/27 00:15:00 23.50MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.8hour.2023-09-01.02_15_00.7z 09/01 02:15:00 35.65MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.8hour.2023-09-01.10_15_00.7z 09/01 10:15:00 36.05MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.daily.2023-08-30.00_10_00.7z 08/30 00:10:00 32.69MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.daily.2023-08-31.00_10_01.7z 08/31 00:10:01 34.87MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.daily.2023-09-01.00_10_01.7z 09/01 00:10:01 35.09MB
AA16-A400-02 AA16-A400.weekly.2023-08-27.00_15_00.7z 08/27 00:15:00 23.50MB
12 entries were displayed.
AA16-A400::*> set admin
AA16-A400::>
You can use the system configuration backup settings commands to manage configuration backup schedules and specify a remote URL (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, or TFTP ) where the configuration backup files will be uploaded in addition to the default locations in the cluster.
An example of setting up an automated ONTAP cluster configuration backup upload destination using TFTP is shown below:
AA16-A400::> set advanced
Warning: These advanced commands are potentially dangerous; use them only when directed to do so by NetApp personnel.
Do you want to continue? {y|n}: y
AA16-A400::*> system configuration backup setting modify -destination tftp://10.1.156.150/ONTAP
AA16-A400::*> system configuration backup setting show
Backup Destination URL Username
-------------------------------------------------- -------------
tftp://10.1.156.150/ONTAP
AA16-A400::*> set admin
AA16-A400::>
For comments and suggestions about this guide and related guides, join the discussion on Cisco Community at https://cs.co/en-cvds.
CVD Program
ALL DESIGNS, SPECIFICATIONS, STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS (COLLECTIVELY, "DESIGNS") IN THIS MANUAL ARE PRESENTED "AS IS," WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND ITS SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE. IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE DESIGNS, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
THE DESIGNS ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF THE DESIGNS. THE DESIGNS DO NOT CONSTITUTE THE TECHNICAL OR OTHER PROFESSIONAL ADVICE OF CISCO, ITS SUPPLIERS OR PARTNERS. USERS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TECHNICAL ADVISORS BEFORE IMPLE-MENTING THE DESIGNS. RESULTS MAY VARY DEPENDING ON FACTORS NOT TESTED BY CISCO.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unified Computing System (Cisco UCS), Cisco UCS B-Series Blade Servers, Cisco UCS C-Series Rack Servers, Cisco UCS S-Series Storage Servers, Cisco UCS X-Series, Cisco UCS Manager, Cisco UCS Management Software, Cisco Unified Fabric, Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure, Cisco Nexus 9000 Series, Cisco Nexus 7000 Series. Cisco Prime Data Center Network Manager, Cisco NX-OS Software, Cisco MDS Series, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trade-marks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries. (LDW_P1)
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
 Feedback
Feedback