Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Cisco CBS Series Switch. The Cisco CBS Series Switches combine powerful network performance and reliability with a complete suite of network features that you need for a solid business network. These expandable Gigabit Ethernet switches, with Gigabit or 10-Gigabit uplinks, provide multiple management options, rich security capabilities, and Layer-3 static routing features far beyond those of an unmanaged or consumer-grade switch, at a lower cost than fully managed switches.
Before You Begin
Before you begin installing your device, ensure that the following items are available:
-
RJ-45 Ethernet cables for connecting network devices. A category 6a and higher cable is required for 10G ports; a category 5e and higher cable is required for all other ports.
-
Tools for installing the hardware.
-
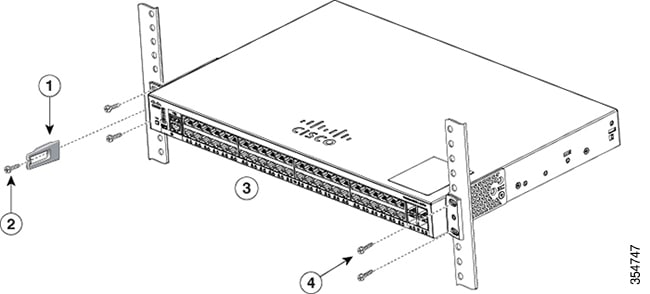
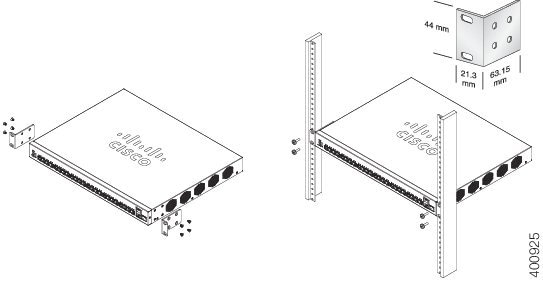
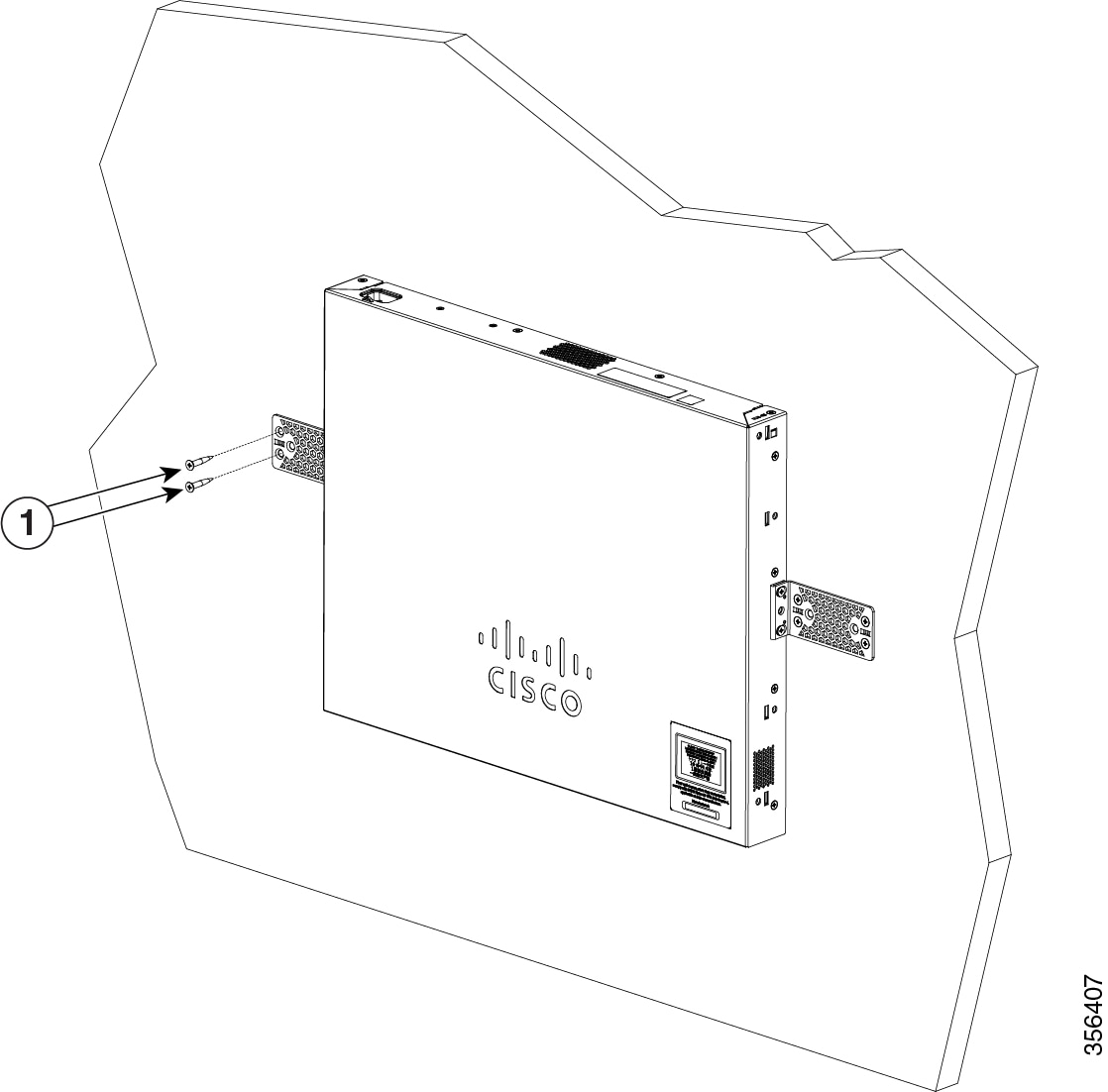
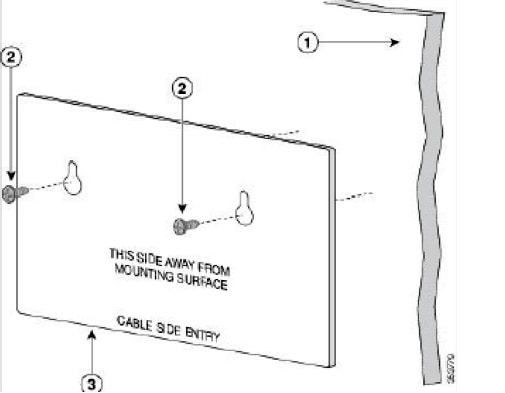
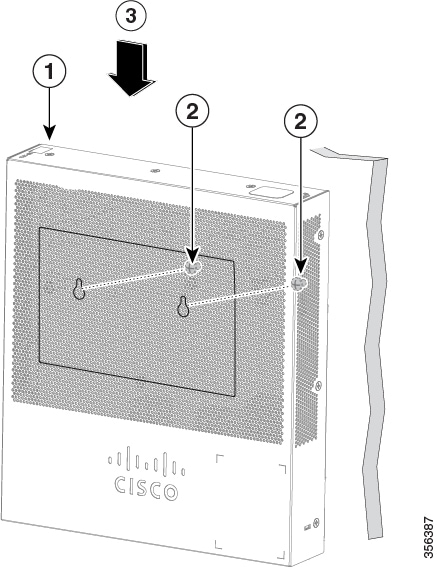
The rack-mount kit packed with the switch contains four rubber feet for desktop placement, and two brackets and twelve screws for rack mounting.
-
If the supplied screws are lost, use replacement screws in the following size:
-
Diameter of the screw head: 6.9 mm
-
Length of the face of the screw head to the base of screw: 5.9 mm
-
Shaft diameter: 3.94 mm
-

Warning
To prevent airflow restriction, allow clearance around the ventilation openings to be at least 3 inches (7.6 cm).
-
-
A computer to manage the device either via the console port or via the web-based interface. for web-based interface the computer needs to support one of the following browsers:
-
Microsoft Edge
-
Firefox (version 82 or 81 or higher)
-
Chrome (version 86 or 85 or higher)
-
Safari over MAC (version 14.0 and higher)
-
 Warning |
Suitable for installation in information Technology Rooms in accordance with Article 645 of the national Electric Code and NFPA 75. |




 Feedback
Feedback