Overview of G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection
The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection feature implements protection switching mechanisms for Ethernet layer ring topologies. This feature uses the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol version 1, defined in ITU-T G.8032, to provide protection for Ethernet traffic in a ring topology with non-Cisco devices.
Ring Protection Links
An Ethernet ring consists of multiple Ethernet ring nodes. Each Ethernet ring node is connected to adjacent Ethernet ring nodes using two independent ring links. A ring link prohibits the formation of loops that affect the network. The Ethernet ring uses a specific link to protect the entire Ethernet ring. This specific link is known as the Ring Protection Link (RPL). A ring link is bound by two adjacent Ethernet ring nodes and a port for a ring link (also known as a ring port). There must be at least two Ethernet ring nodes in an Ethernet ring.
ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching Functionality
The Ethernet ring protection functionality includes the following:
-
Loop avoidance
-
The use of learning, forwarding, and Filtering Database (FDB) mechanisms
Loop avoidance in an Ethernet ring is achieved by ensuring traffic flows continuously through all links except the Ring Protection Link (RPL).
Here is a list of RPL types (or RPL nodes) and their functions:
-
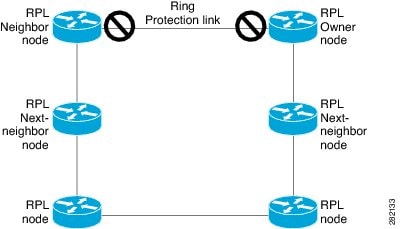
RPL owner—Responsible for blocking traffic over the RPL to prevent loops in the Ethernet traffic. There can be only one RPL owner in a ring.
-
RPL neighbor node—An Ethernet ring node adjacent to the RPL. It is responsible for blocking its end of the RPL under normal conditions. This node type is optional and prevents RPL usage when protected.
-
RPL next-neighbor node—Next-neighbor node is an Ethernet ring node adjacent to an RPL owner node or RPL neighbor node. It is mainly used for FDB flush optimization on the ring. This node is also optional.
The figure illustrates the G.8032 Ethernet ring topology.
R-APS Control Messages
Nodes on the ring use control messages called Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) messages to coordinate switching the ring protection link (RPL) on and off. A failure along the ring triggers a R-APS Signal Failure (R-APS SF) message in both directions of the nodes adjacent to the failed link after they have blocked the port facing the failed link. Upon receipt of this message, the RPL owner unblocks the RPL port.
 Note |
A single link failure in the ring ensures a loop-free topology. |
CFM Protocols and Link Failures
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) and line status messages are used to detect ring link and node failure. During the recovery phase, when the failed link is restored, the nodes adjacent to the restored link send Ring Automatic Protection Switching (R-APS) No Request (R-APS NR) messages. Upon obtaining this message, the ring protection link (RPL) owner blocks the RPL port and sends two messages: R-APS NR and R-APS RPL (R-APS NR, RB). These messages cause all other nodes, other than the RPL owner in the ring, to unblock all blocked ports. The Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol works for both unidirectional failure and multiple link failure scenarios in a ring topology.
 Note |
The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol uses CFM Continuity Check Messages (CCMs) at an interval of 3.3 milliseconds (ms). At this interval (which is supported only on selected platforms), SONET-like switching time performance and loop-free traffic can be achieved. |
When you enable CFM, the G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection feature ensures recovery times of less than 50 milliseconds. This is achieved by managing the forwarding state of each ring port, preventing loops, and maintaining connectivity in the event of a failure.
 Note |
This feature can operate without CFM; however, performance of less than 50 milliseconds is not guaranteed without it. |
G.8032 ERP Timers
The G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection (ERP) protocol specifies the use of different timers to avoid race conditions and unnecessary switching operations:
-
Delay timers—Used by the Ring Protection Link (RPL) owner to verify that the network has stabilized before blocking the RPL. Note the following points about delay timers.
-
After a signal failure (SF) condition, a Wait-to-Restore (WTR) timer is used to verify that the SF is not intermittent.
-
The WTR timer can be configured by the operator. The default time interval is 5 minutes; the time interval ranges from 1 to 12 minutes.
-
After a force switch (FS) or a manual switch (MS) command is issued, a Wait-to-Block (WTB) timer is used to verify that no background condition exists.

Note
The WTB timer interval may be shorter than the WTR timer interval.
-
-
Guard timer—Used by all nodes when changing state; the guard timer blocks latent outdated messages from causing unnecessary state changes. The guard timer can be configured. The default time interval is 500 ms; the time interval ranges from 10 to 2000 ms.
-
Hold-off timers—Used by the underlying Ethernet layer to filter out intermittent link faults. The hold-off timer can be configured. The default time interval is 0 seconds; the time interval ranges from 0 to 10 seconds. Faults are reported to the ring protection mechanism only if this timer expires.
 Feedback
Feedback