Stateful Firewall on Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches
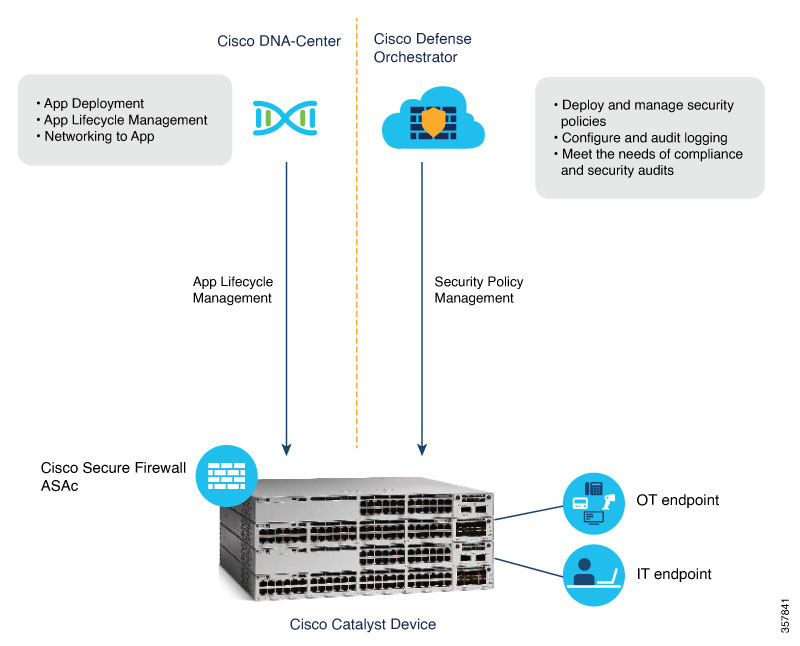
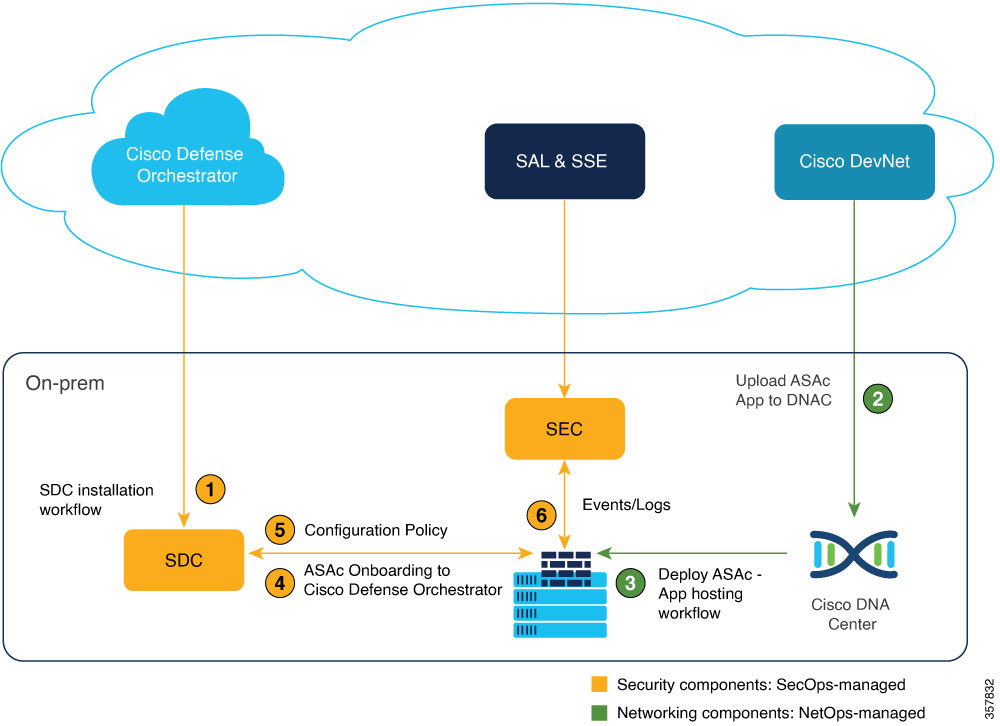
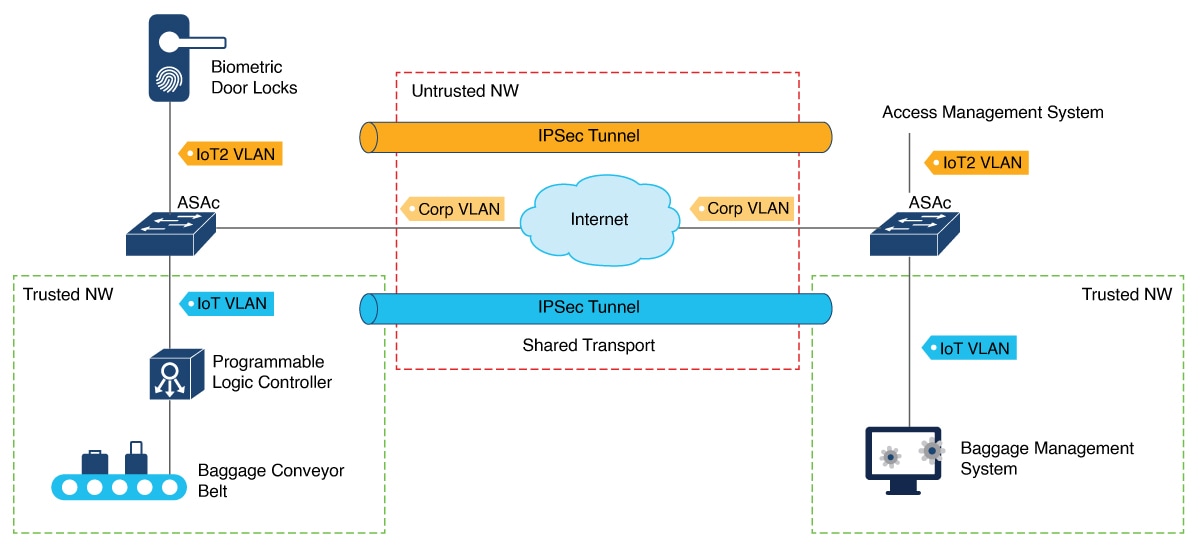
Application hosting on Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches is integrated with the Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance (ASAc) for the stateful inspection of traffic in a network without changing the network architecture. The app-hosting infrastructure on these Catalyst switches can seamlessly add the ASAc instances to the existing network by using USB SSD to host ASAc on Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches.
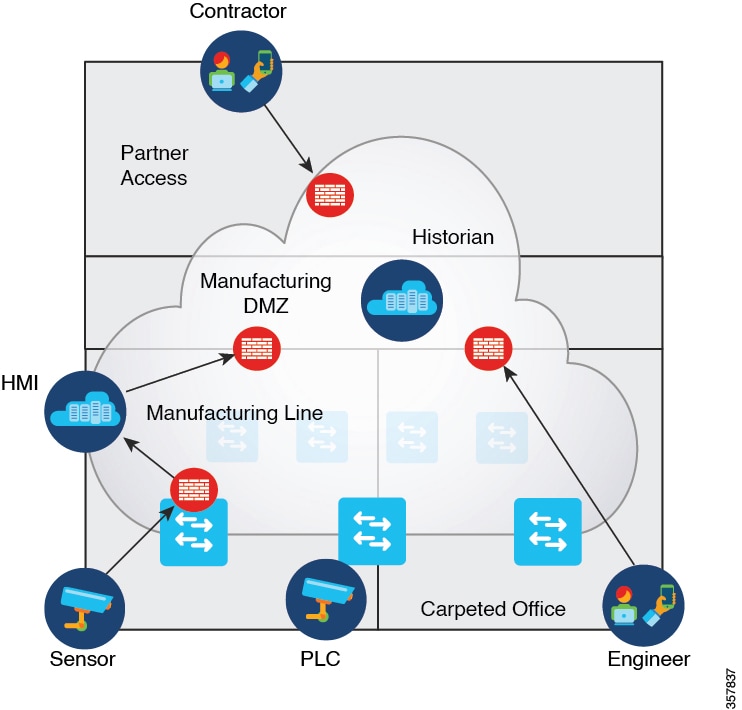
Previously, operational technology (OT) systems were isolated from external networks, making them less vulnerable to cyber threats. With Industry 4.0, digital transformation and smart manufacturing have accelerated the convergence of information technology (IT) and OT networks in the process industry. While this integration can bring significant benefits, such as, increased efficiency, improved visibility, and better decision-making, it can also increase the risk of cyberattacks.
IoT (Internet of Things) devices and sensors are proliferating into IT networks, and these devices are managed under a single IT network infrastructure to build smarter and safer work spaces. However; these IoT devices introduce several security threats to IT networks because these devices often have limited processing power and memory, making it challenging to implement robust security features, and most of these devices are not up to date on security updates. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to pivot from compromised IoT devices to critical systems and data.
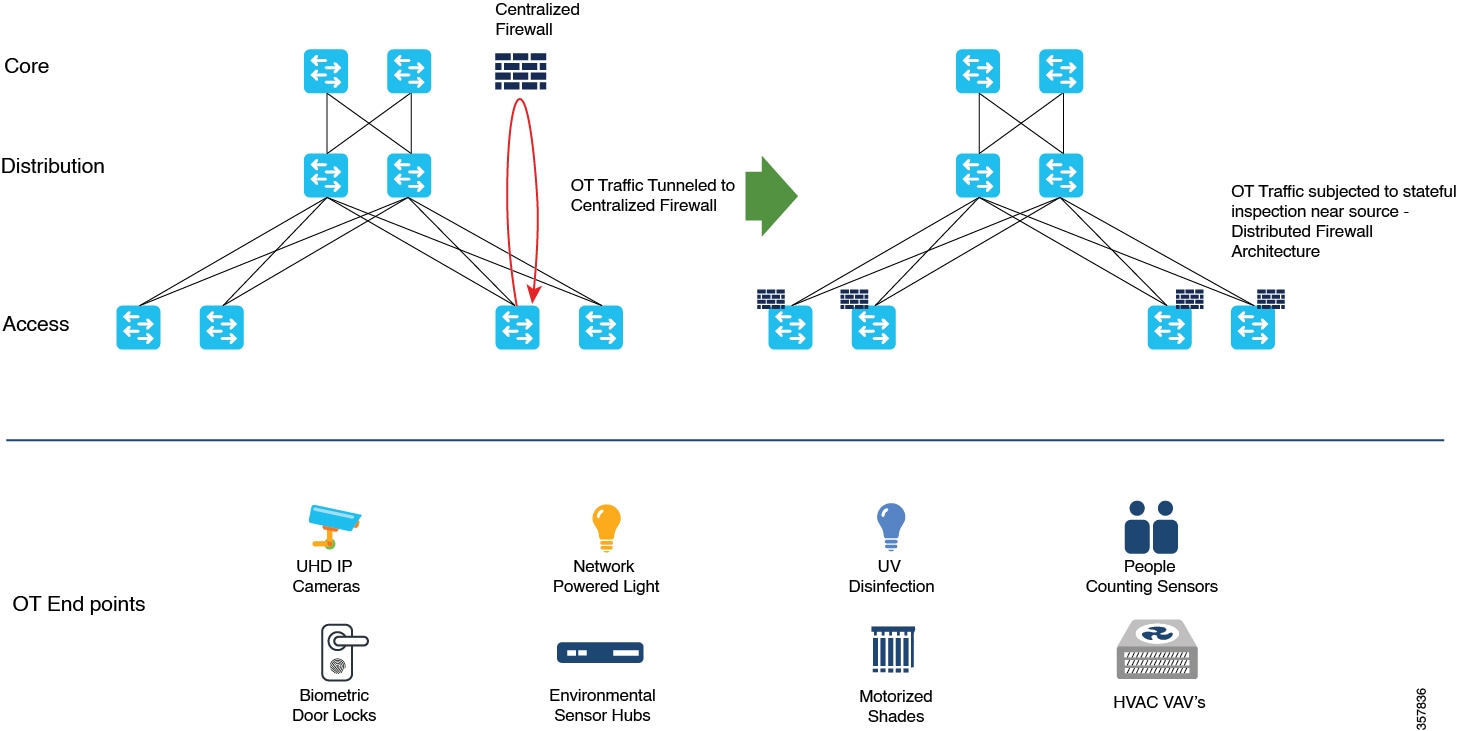
By hosting the containerized Secure Firewall ASA on Catalyst 9300 Series Switches, organizations can benefit from enhanced security and simplified network deployment. This solution not only reduces the complexity of steering the traffic to centralized firewalls using complex tunnels, but also eliminates the need for additional hardware.
Positioning the firewall services nearer to the source provides a cost-effective and highly efficient way of securing IT-OT converged networks. It also minimizes the latency for time-sensitive SOS applications, by enforcing the policies near the source, where the devices connect to the network.
The redundant links and power supplies of the Catalyst 9300 Series Switches are leveraged by the virtual firewall instances that are hosted on these switches, thereby reducing the need for additional servers and physical firewall appliances, saving on rack space, cooling requirements, and operational costs.
By leveraging these capabilities, organizations can simplify their network design, reduce costs, and improve their security posture.

 Feedback
Feedback