- Book Index
- Preface
- Product Overview
- Command-Line Interfaces
- Configuring the Switch for the First Time
- Administering the Switch
- Configuring the Cisco IOS In-Service Software Upgrade Process
- Configuring the Cisco IOS XE In Service Software Upgrade Process
- Configuring Interfaces
- Checking Port Status and Connectivity
- Configuring Supervisor Engine Redundancy Using RPR and SSO on Supervisor Engine 6-E and 6L-E
- Configuring Supervisor Engine Redundancy Using RPR and SSO on Supervisor Engine 7-E and 7L-E
- Configuring Cisco NSF with SSO Supervisor Engine Redundancy
- Environmental Monitoring and Power Management
- Configuring Power over Ethernet
- Configuring the Catalyst 4500 Series Switch with Cisco Network Assistant
- Configuring VLANs, VTP, and VMPS
- Configuring IP Unnumbered Interface
- Configuring Layer 2 Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring SmartPort Macros
- Configuring Auto SmartPort Macros
- Configuring STP and MST
- Configuring Flex Links and MAC Address-Table Move Update
- Configuring Resilient Ethernet Protocol
- Configuring Optional STP Features
- Configuring EtherChannel and Link State Tracking
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and Filtering
- Configuring IPv6 MLD Snooping
- Configuring 802.1Q Tunneling, VLAN Mapping, and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
- Configuring CDP
- Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Location Service
- Configuring UDLD
- Configuring Unidirectional Ethernet
- Configuring Layer 3 Interfaces
- Configuring Cisco Express Forwarding
- Configuring Unicast Reverse Path Forwarding
- Configuring IP Multicast
- Configuring ANCP Client
- Configuring Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
- Configuring Policy-Based Routing
- Configuring VRF-lite
- Configuring Quality of Service
- Configuring Voice Interfaces
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Configurig MACsec Encryption
- Configuring 802.1X Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring the PPPoE Intermediate Agent
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Control Plane Policing and Layer 2 Control Packet QoS
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard, and IPSG for Static Hosts
- Configuring Network Security with ACLs
- Support for IPv6
- Port Unicast and Multicast Flood Blocking
- Configuring Storm Control
- Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
- Configuring Wireshark
- Configuring Enhanced Object Tracking
- Configuring System Message Logging
- Configuring OBFL
- Configuring SNMP
- Configuring Netflow-lite
- Configuring Flexible NetFlow
- Configuring Ethernet OAM and CFM
- Configuring Y.1731 (AIS and RDI)
- Configuring Call Home
- Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLA Operations
- Configuring RMON
- Performing Diagnostics
- Configuring WCCP Version 2 Services
- Configuring MIB Support
- ROM Monitor
- Acronyms and Abbreviations
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Software Configuration Guide, Release IOS XE 3.3.0SG and IOS 15.1(1)SG
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- March 21, 2015
Chapter: Configuring Y.1731 (AIS and RDI)
Configuring Y.1731 (AIS and RDI)
The Catalyst 4500 series switch supports Y.1731 Ethernet Alarm Indication Signal function (ETH-AIS) and Ethernet Remote Defect Indication function (ETH-RDI) to provide fault and performance management for service providers in large networks. This chapter describes how to configure Y.1731 ETH-AIS and ETH-RDI.
This chapter contains these sections:
•![]() Displaying Y.1731 Information
Displaying Y.1731 Information
For complete command and configuration information for Y.1731, see the Cisco IOS feature module at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/cether/configuration/12-2sr/ce-cfm-y1731.html
AIS and RDI Terminology
About Y.1731
These sections contain conceptual information about Y.1731:
•![]() Ethernet Remote Defect Indication
Ethernet Remote Defect Indication
The advent of Ethernet as a metropolitan and WAN technology imposes a new set of Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) requirements on Ethernet's traditionally Enterprise-oriented functions. The expansion of this technology into the larger and more complex wider user base makes operational management of link uptime crucial. Isolating and responding to failures quickly directly affects the competitiveness of the service provider.
Server MEP
A Server MEP is a combined function of the server layer termination function and the server and ETH adaptation function. It issues frames with ETH-AIS information upon detecting a defect at the Server layer by the server layer termination function or the adaptation function.
A Virtual MEP represents the logical termination point of Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MAs defined at the link or transport layer. A server MEP runs or is defined at Maintenance Level -1. For example, you could associate an outward-facing Server MEP with each termination point of IEEE 802.3ah OAM, or with each termination point of MPLS PW OAM.
Alarm Indication Signal
ETH-AIS allows you to suppress alarms when defects are detected at the server (sub) layer. Because of STP's ability to restore, you would not expect to apply ETH-AIS in the STP environments. For the Catalyst 4500 Metro switch, an administrator can enable and disable AIS in the STP environment.
You can enable or disable transmission of frames with ETH-AIS information on an MEP (or on a Server MEP).
You also can issue frames with ETH-AIS information at the client Maintenance Level by a MEP, including a Server MEP upon detecting defect conditions.
The defect conditions may include:
•![]() Signal fail conditions with ETH-CC enabled
Signal fail conditions with ETH-CC enabled
•![]() AIS condition with ETH-CC disabled
AIS condition with ETH-CC disabled
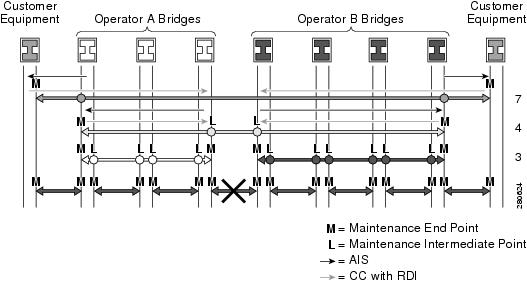
For multipoint ETH connectivity, a MEP cannot determine the specific server (sub) layer entity that has encountered defect conditions upon receiving a frame with ETH-AIS information. More importantly, it cannot determine the associated subset of its peer MEPs for which it should suppress alarms because the received ETH-AIS information does not contain that information. When a MEP receives a frame with ETH-AIS information, it suppresses alarms for all peer MEPs whether there is still connectivity or not.
For a point-to-point ETH connection, however, a MEP has only one peer MEP. There is no ambiguity regarding the peer MEP for which it should suppress alarms when it receives the ETH-AIS information.
Only a MEP, including a Server MEP, is configured to issue frames with ETH-AIS information. Once the MEP detects a defect condition, it immediately starts transmitting periodic frames with ETH-AIS information at a configured client maintenance level. We send the AIS frames at a configured MIP level for an interface. A MEP continues to transmit periodic frames with ETH-AIS information until the defect condition is removed. Upon receiving a frame with ETH-AIS information, a MEP detects AIS condition and suppresses loss of continuity alarms associated with all its peer MEPs. A MEP resumes loss of continuity alarm generation upon detecting loss of continuity defect conditions in the absence of AIS condition.
Ethernet Remote Defect Indication
A MEP can use ETH-RDI to notify its peer MEPs that it detects a defect condition. ETH-RDI is used only when ETH-CC transmission is enabled.
ETH-RDI has the following two applications:
•![]() Single-ended fault management—The receiving MEP detects an RDI defect condition, which is correlated with other defect conditions in this MEP and may cause a fault. The absence of received ETH-RDI information in a single MEP indicates the absence of defects in the entire maintenance.
Single-ended fault management—The receiving MEP detects an RDI defect condition, which is correlated with other defect conditions in this MEP and may cause a fault. The absence of received ETH-RDI information in a single MEP indicates the absence of defects in the entire maintenance.
•![]() Contribution to far-end performance monitoring— It reflects a defect condition in the far-end which serves as input to the performance monitoring process.
Contribution to far-end performance monitoring— It reflects a defect condition in the far-end which serves as input to the performance monitoring process.
A MEP that is in a defect condition transmits frames with ETH-RDI information. A MEP, upon receiving frames with ETH-RDI information, determines that its peer MEP has encountered a defect condition. For multipoint ETH connectivity, however, a MEP, upon receiving frames with ETH-RDI information, cannot determine the associated subset of its peer MEPs with which the MEP transmitting RDI information encounters defect conditions. it is because the transmitting MEP itself does not always have that information.
Figure 64-1 Generating and Propagating AIS Messages Upon a Defect (Link Fail)
Configuring Y.1731

Note ![]() Y.1731 is enabled by default.
Y.1731 is enabled by default.
These sections are included:
•![]() Y.1731 Configuration Guidelines
Y.1731 Configuration Guidelines
•![]() Clearing MEP from the AIS Defect Condition
Clearing MEP from the AIS Defect Condition
•![]() Clearing SMEP from the AIS Defect Condition
Clearing SMEP from the AIS Defect Condition
Y.1731 Configuration Guidelines
Configuration guidelines and restrictions for Y.1731 include the following:
•![]() Because of STP's restoration capability, do not expect ETH-AIS to be applied in the STP environments.
Because of STP's restoration capability, do not expect ETH-AIS to be applied in the STP environments.
•![]() AIS is enabled by default on a CFM maintenance domain. The following section illustrates the commands you can use to disable AIS on a maintenance domain. Likewise, RDI is a flag bit in the CC message. Provided CC transmission is enabled, the present RDI flag of the CC message is set to true or false.
AIS is enabled by default on a CFM maintenance domain. The following section illustrates the commands you can use to disable AIS on a maintenance domain. Likewise, RDI is a flag bit in the CC message. Provided CC transmission is enabled, the present RDI flag of the CC message is set to true or false.
Configuring AIS Parameters
To set the parameters for AIS, perform this task:
Use the no versions of the commands to remove the configuration or return to the default configurations.
Clearing MEP from the AIS Defect Condition
To clear the MEP, enter one of the following commands:
Switch# clear ethernet cfm ais domain domain name mpid local mpid vlan vlan#
Switch# clear ethernet cfm ais domain domain name mpid local mpid evc evc_name
Clearing SMEP from the AIS Defect Condition
To clear the CSMP, enter one of the following commands:
Switch# clear ethernet cfm ais link-status interface interface_name
Switch# clear ethernet cfm error

Note ![]() This operation also clears all error conditions including AIS.
This operation also clears all error conditions including AIS.
Displaying Y.1731 Information
To display Y.1731 information, you can use the following commands (Table 64-1).
This example shows how to track the RDI defect and to verify the configuration parameters:
Switch# show ethernet cfm main local detail
MEP Settings:
-------------
MPID: 1109
DomainName: PROVIDER_DOMAIN
Level: 4
Direction: I
EVC: evc_1
Interface: Gi3/1
CC-Status: Enabled
MAC: 001b.d550.91fd
Defect Condition: No Defect
presentRDI: FALSE (RDI defect is NOT present)
AIS-Status: Enabled
AIS Period: 60000(ms)
AIS Expiry Threshold: 3.5
Level to transmit AIS: Default
Suppress Alarm configuration: Enabled
Suppressing Alarms: No
MIP Settings:
-------------
Level Type Port MAC
7 MIP Gi3/1 001b.d550.91fd
4 MIP Te1/2 001b.d550.91fd
Switch#
*Feb 18 05:40:35.659: %ETHER_CFM-6-ENTER_AIS: local mep with mpid 1109 level 4 id 100 dir I Interface GigabitEthernet3/1 enters AIS defect condition (gi3/2 enters AIS state)
Switch# show ethernet cfm main local detail
MEP Settings:
-------------
MPID: 1109
DomainName: PROVIDER_DOMAIN
Level: 4
Direction: I
EVC: evc_1
Interface: Gi3/1
CC-Status: Enabled
MAC: 001b.d550.91fd
Defect Condition: AIS
presentRDI: TRUE (RDI defect IS present)
AIS-Status: Enabled
AIS Period: 60000(ms)
AIS Expiry Threshold: 3.5
Level to transmit AIS: Default
Suppress Alarm configuration: Enabled
Suppressing Alarms: Yes
MIP Settings:
-------------
Level Type Port MAC
7 MIP Gi3/1 001b.d550.91fd
4 MIP Te1/2 001b.d550.91fd
Switch# show ethernet cfm error
Level Vlan MPID Remote MAC Reason Service ID
4 100 2101 001d.4566.aa3d 0 lifetime TLV customerX
4 100 - 001b.d550.91fd Receive AIS customerX
Switch#
*Feb 18 05:51:08.567: %ETHER_CFM-6-EXIT_AIS: local mep with mpid 1109 level 4 id 100 dir I Interface GigabitEthernet3/1 exited AIS defect condition (gi3/1 exits AIS state)
Switch# show ethernet cfm main local detail
MEP Settings:
-------------
MPID: 1109
DomainName: PROVIDER_DOMAIN
Level: 4
Direction: I
EVC: evc_1
Interface: Gi3/1
CC-Status: Enabled
MAC: 001b.d550.91fd
Defect Condition: No Defect
presentRDI: FALSE (RDI defect is not present anymore)
AIS-Status: Enabled
AIS Period: 60000(ms)
AIS Expiry Threshold: 3.5
Level to transmit AIS: Default
Suppress Alarm configuration: Enabled
Suppressing Alarms: No
MIP Settings:
-------------
Level Type Port MAC
7 MIP Gi3/1 001b.d550.91fd
4 MIP Te1/2 001b.d550.91fd
Switch#
 Feedback
Feedback