- Preface
- Using the Command-Line Interface
-
- IP Multicast Routing Technology Overview
- Configuring IGMP
- Configuring IGMP Proxy
- Constraining IP Multicast in Switched Ethernet
- Configuring PIM
- Configuring PIM MIB Extension for IP Multicast
- Configuring MSDP
- Configuring Wireless Multicast
- Configuring SSM
- Configuring Basic IP Multicast Routing
- Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
- IP Multicast Optimization: Optimizing PIM Sparse Mode in a Large IP Multicast Deployment
- IP Multicast Optimization: Multicast Subsecond Convergence
- IP Multicast Optimization: IP Multicast Load Splitting across Equal-Cost Paths
- IP Multicast Optimization: SSM Channel Based Filtering for Multicast
- IP Multicast Optimization: PIM Dense Mode State Refresh
- IP Multicast Optimization: IGMP State Limit
-
- Configuring the Device for Access Point Discovery
- Configuring Data Encryption
- Configuring Retransmission Interval and Retry Count
- Configuring Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
- Configuring Authentication for Access Points
- Converting Autonomous Access Points to Lightweight Mode
- Using Cisco Workgroup Bridges
- Configuring Probe Request Forwarding
- Optimizing RFID Tracking
- Configuring Country Codes
- Configuring Link Latency
- Configuring Power over Ethernet
-
- Preventing Unauthorized Access
- Controlling Switch Access with Passwords and Privilege Levels
- Configuring TACACS+
- Configuring RADIUS
- Configuring Kerberos
- Configuring Local Authentication and Authorization
- Configuring Secure Shell (SSH)
- X.509v3 Certificates for SSH Authentication
- Configuring Secure Socket Layer HTTP
- Configuring IPv4 ACLs
- Configuring IPv6 ACLs
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring IP Source Guard
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
- Configuring IEEE 802.1x Port-Based Authentication
- Configuring Web-Based Authentication
- Configuring Port-Based Traffic Control
- Configuring IPv6 First Hop Security
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec
- Configuring Control Plane Policing
- Configuring Wireless Guest Access
- Managing Rogue Devices
- Classifying Rogue Access Points
- Configuring wIPS
- Configuring Intrusion Detection System
-
- Administering the Switch
- Performing Device Setup Configuration
- Configuring Right-To-Use Licenses
- Configuring Administrator Usernames and Passwords
- Configuring 802.11 parameters and Band Selection
- Configuring Aggressive Load Balancing
- Configuring Client Roaming
- Configuring Application Visibility and Control
- Configuring Voice and Video Parameters
- Configuring RFID Tag Tracking
- Configuring Location Settings
- Cisco Hyperlocation
- Monitoring Flow Control
- Configuring SDM Templates
- Configuring System Message Logs
- Configuring Online Diagnostics
- Managing Configuration Files
- Configuration Replace and Configuration Rollback
- Working with the Flash File System
- Upgrading the Switch Software
- Conditional Debug and Radioactive Tracing
- Troubleshooting the Software Configuration
Configuring IPv6 WLAN Security
Restrictions for IPv6 WLAN Security
RADIUS Server Support
-
If multiple RADIUS servers are configured for redundancy, the user database must be identical in all the servers for the backup to work properly.
Radius ACS Support
-
You must configure RADIUS on both your Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) and your device
-
RADIUS is supported on Cisco Secure ACS version 3.2 and later releases.
Information About IPv6 WLAN Security
Information About RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) is a client/server protocol that provides centralized security for users attempting to gain management access to a network. It serves as a back-end database similar to Local EAP and provides authentication and accounting services.
-
Authentication—The process of verifying users when they attempt to log into the device
Users must enter a valid username and password for the device to authenticate users to the RADIUS server. If multiple databases are configured, then specify the sequence in which the backend database must be tried.
-
Accounting— The process of recording user actions and changes.
Whenever a user successfully executes an action, the RADIUS accounting server logs the changed attributes, the user ID of the person who made the change, the remote host where the user is logged in, the date and time when the command was executed, the authorization level of the user, and a description of the action performed and the values provided. If the RADIUS accounting server is unreachable, the users can continue their sessions uninterrupted.
User Datagram Protocol— RADIUS uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for its transport. It maintains a database and listens on UDP port 1812 for incoming authentication requests and UDP port 1813 for incoming accounting requests. The device, which requires access control, acts as the client and requests AAA services from the server. The traffic between the device and the server is encrypted by an algorithm defined in the protocol and a shared secret key configured on both devices.
Configures multiple RADIUS accounting and authentication servers. For example, you can have one central RADIUS authentication server but several RADIUS accounting servers in different regions. If you configure multiple servers of the same type and the first one fails or becomes unreachable, the controller automatically tries the second one, then the third one if necessary, and so on.
When RADIUS method is configured for the WLAN, the device will use the RADIUS method configured for the WLAN. When the WLAN is configured to use local EAP, the RADIUS method configured on the WLAN points to Local. The WLAN must also be configured with the name of the local EAP profile to use.
If no RADIUS method is configured in the WLAN, the device will use the default RADIUS method defined in global mode.
Information About Local EAP
Local EAP is an authentication method that allows users and wireless clients to be authenticated locally. It is designed for use in remote offices that maintain connectivity to wireless clients when the back-end system is disrupted or the external authentication server goes down. When you enable local EAP, the device serves as the authentication server and the local user database, which removes dependence on an external authentication server. Local EAP retrieves user credentials from the local user database or the LDAP back-end database to authenticate users. Local EAP supports LEAP, EAP-FAST, EAP-TLS, PEAPv0/MSCHAPv2, and PEAPv1/GTC authentication between the controller and wireless clients.
Without an EAP profile name being provided, or if a name was provided for an EAP profile that does not exist, then EAP by default allows no EAP method for local authentication.
 Note |
The LDAP back-end database supports these local EAP methods: EAP-TLS, EAP-FAST/GTC, and PEAPv1/GTC. LEAP, EAP-FAST/MSCHAPv2, and PEAPv0. MSCHAPv2 is supported only if the LDAP server is set up to return a clear-text password. |
 Note |
Device support Local EAP authentication against external LDAP databases such as Microsoft Active Directory and Novell’s eDirectory. For more information about configuring the controller for Local EAP authentication against Novell’s eDirectory, see the Configure Unified Wireless Network for Authentication Against Novell's eDirectory Database whitepaper. |
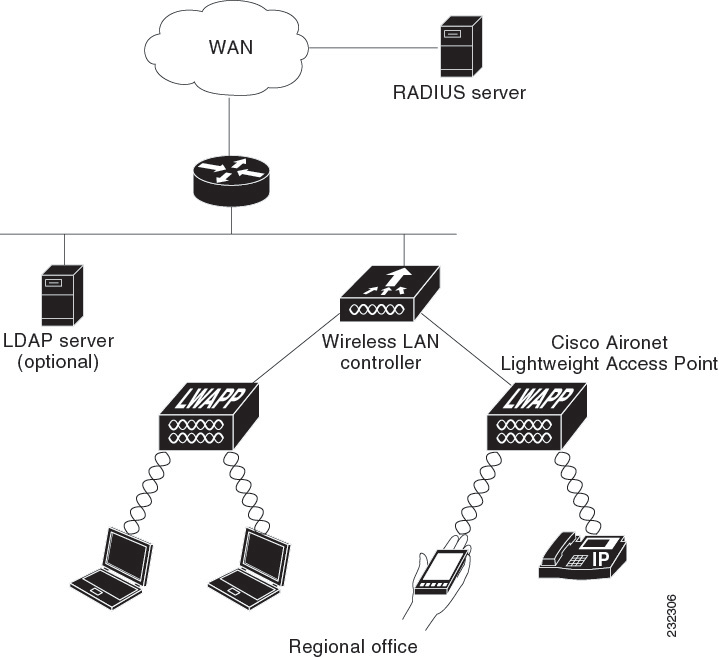
How to Configure IPv6 WLAN Security
Configuring Local Authentication
Creating a Local User
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
username aaa_test Example: |
Creates a username. |
| Step 3 |
password 0 aaa_test Example: |
Assigns a password for the username. |
| Step 4 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# username aaa_test password 0 aaa_test
Device(config)# endCreating an Client VLAN and Interface
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
vlan Example: |
Creates a VLAN. |
| Step 3 |
exit Example: |
Exits VLAN configuration mode. |
| Step 4 |
interface vlan vlan_ID Example: |
Associates the VLAN to an interface. |
| Step 5 |
ip address Example: |
Assigns an IP address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 6 |
ipv6 address Example: |
Assigns an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 7 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Example
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# vlan 137
Device(config-vlan)#exit
Device(config)#interface vlan 137
Device(config-if)#ip address 10.7.137.10 255.255.255.0
Device(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8::20:1/64
Device(config-if)#endConfiguring a EAP Profile
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
eap profile name Example: |
Creates a EAP profile. |
| Step 2 |
method leap Example: |
Configures EAP-LEAP method on the profile. |
| Step 3 |
method tls Example: |
Configures EAP-TLS method on the profile. |
| Step 4 |
method peap Example: |
Configures PEAP method on the profile. |
| Step 5 |
method mschapv2 Example: |
Configures EAP-MSCHAPV2 method on the profile. |
| Step 6 |
method md5 Example: |
Configures EAP-MD5 method on the profile. |
| Step 7 |
method gtc Example: |
Configures EAP-GTC method on the profile. |
| Step 8 |
method fast profile my-fast Example: |
Creates a EAP profile named my-fast. |
| Step 9 |
description my_localeap profile Example: |
Provides a description for the local profile. |
| Step 10 |
exit Example: |
Exits the eap-profile configuration mode. |
| Step 11 |
eap method fast profile myFast Example: |
Configures the EAP method profile. |
| Step 12 |
authority-id [identity|information] Example: |
Configure the authority ID and information for the EAP method profile. |
| Step 13 |
local-key 0 key-name Example: |
Configures the local server key. |
| Step 14 |
pac-password 0 password Example: |
Configures the PAC password for manual PAC provisioning. |
| Step 15 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Example
Device(config)#eap profile wcm_eap_prof
Device(config-eap-profile)#method leap
Device(config-eap-profile)#method tls
Device(config-eap-profile)#method peap
Device(config-eap-profile)#method mschapv2
Device(config-eap-profile)#method md5
Device(config-eap-profile)#method gtc
Device(config-eap-profile)#eap method fast profile my-fast
Device (config-eap-profile)#description my_local eap profile
Device(config-eap-profile)# exit
Device (config)# eap method fast profile myFast
Device(config-eap-method-profile)#authority-id identity my_identity
Device(config-eap-method-profile)#authority-id information my_information
Device(config-eap-method-profile)#local-key 0 test
Device(config-eap-method-profile)#pac-password 0 test
Device(config-eap-method-profile)# endCreating a Local Authentication Model
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
aaa new-model Example: |
Creates a AAA authentication model. |
| Step 2 |
authentication dot1x default local Example: |
Implies that the dot1x must use the default local RADIUS when no other method is found. |
| Step 3 |
dot1x method_list local Example: |
Assigns the local authentication for wcm_local method list. |
| Step 4 |
aaa authentication dot1x dot1x_name local Example: |
Configures the local authentication for the dot1x method. |
| Step 5 |
aaa authorization credential-download name local Example: |
Configures local database to download EAP credentials from Local/RADIUS/LDAP. |
| Step 6 |
aaa local authentication auth-name authorization authorization-name Example: |
Selects local authentication and authorization. |
| Step 7 |
session ID Example: |
Configures a session ID for AAA. |
| Step 8 |
dot1x system-auth-control Example: |
Enables dot.1x system authentication control. |
Example
Device(config)# aaa new-model
Device(config)# aaa authentication dot1x default local
Device(config)# aaa authentication dot1x wcm-local local
Device(config)# aaa authentication dot1x aaa_auth local
Device(config)# aaa authorization credential-download wcm_author local
Device(config)# aaa local authentication wcm_local authorization wcm_author
Device(config)# aaa session-id common
Device(config)# dot1x system-auth-controlCreating a Client WLAN
 Note |
This example uses 802.1x with dynamic WEP. You can use any other security mechanism supported by the wireless client and configurable on the device |
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
wlan wlan name <identifier> SSID Example: |
Creates a WLAN. |
| Step 3 |
broadcast-ssid Example: |
Configures to broadcast the SSID on a WLAN. |
| Step 4 |
no security wpa Example: |
Disables the wpa for WLAN to enable 802.1x. |
| Step 5 |
security dot1x Example: |
Configures the 802.1x encryption security for the WLAN. |
| Step 6 |
security dot1x authentication-list wcm-local Example: |
Configures the server group mapping to the WLAN for dot1x authentication. |
| Step 7 |
local-auth wcm_eap_prof Example: |
Configures the eap profile on the WLAN for local authentication. |
| Step 8 |
client vlan 137 Example: |
Associates the VLAN to a WLAN. |
| Step 9 |
no shutdown Example: |
Enables the WLAN. |
| Step 10 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Example
Device# config terminal
Device(config)#wlan wlanProfileName 1 ngwcSSID
Device(config-wlan)#broadcast-ssid
Device(config-wlan)#no security wpa
Device(config-wlan)#security dot1x
Device(config-wlan)#security dot1x authentication-list wcm-local
Device (config-wlan)# local-auth wcm_eap_prof
Device(config-wlan)#client vlan 137
Device(config-wlan)#no shutdown
Device(config-wlan)#end
Device# Configuring Local Authentication with WPA2+AES
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
aaa new model Example: |
Creates a AAA authentication model. |
| Step 3 |
dot1x system-auth-control Example: |
Enables dot1x system authentication control. |
| Step 4 |
aaa authentication dot1x default local Example: |
Configures the local authentication for the default dot1x method. |
| Step 5 |
aaa local authorization credential-download default local Example: |
Configures default database to download EAP credentials from local server. |
| Step 6 |
aaa local authentication default authorization default Example: |
Selects the default local authentication and authorization. |
| Step 7 |
eap profile wcm_eap_profile Example: |
Creates an EAP profile. |
| Step 8 |
method leap Example: |
Configures EAP-LEAP method on the profile. |
| Step 9 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# aaa new-model
Device(config)# dot1x system-auth-control
Device(config)# aaa authentication dot1x default local
Device(config)# aaa authorization credential-download default local
Device(config)# aaa local authentication default authorization default
Device(config)#eap profile wcm_eap_profile
Device(config)# method leap
Device(config)# endCreating Client VLAN for WPA2+AES
Create a VLAN for the WPA2+AES type of local authentication. This VLAN is later mapped to a WLAN.
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
vlan vlan_ID Example: |
Creates a VLAN. |
| Step 3 |
exit Example: |
Exits from the VLAN mode. |
| Step 4 |
interface vlan vlan_ID Example: |
Associates the VLAN to the interface. |
| Step 5 |
ip address Example: |
Assigns IP address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 6 |
ipv6 address Example: |
Assigns IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 7 |
exit Example: |
Exits from the interface mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# vlan105
Device (config-vlan)# exit
Device (config)# interface vlan 105
Device(config-if)#ip address 10.8.105.10 255.255.255.0
Device(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8::10:1/64
Device(config-if)#exit
Device(config)#Creating WLAN for WPA2+AES
Create a WLAN and map it to the client VLAN created for WPA2+AES.
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
wlan wpas2-aes-wlan 1 wpas2-aes-wlan Example: |
Creates a WLAN. |
| Step 3 |
client vlan 105 Example: |
Maps the WLAN to the client VLAN. |
| Step 4 |
local-auth wcm_eap_profile Example: |
Creates and sets the EAP profile on the WLAN. |
| Step 5 |
security dot1x authentication-list default Example: |
Uses the default dot1x authentication list. |
| Step 6 |
no shutdown Example: |
Enables the WLAN. |
| Step 7 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)#wlan wpa2-aes-wlan 1 wpa2-aes-wlan
Device(config-wlan)#client vlan 105
Device(config-wlan)#local-auth wcm_eap_profile
Device(config-wlan)#security dot1x authentication-list default
Device(config-wlan)#no shutdown
Device(config-wlan)# exitConfiguring External RADIUS Server
Configuring RADIUS Authentication Server Host
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
radius server One Example: |
Creates a radius server. |
| Step 3 |
address ipv4 address auth-port auth_port_number acct-port acct_port_number Example: |
Configures the IPv4 address for the radius server. |
| Step 4 |
address ipv6 address auth-port auth_port_number acct-port acct_port_number Example: |
|
| Step 5 |
key 0cisco Example: |
exit |
| Step 6 |
Example: |
Exits from the radius server mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device (config)# radius server One
Device (config-radius-server)# address ipv4 10.10.10.10 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
Device (config-radius-server)# address ipv6 2001:db8::25:2 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
Device (config-radius-server)# key 0 cisco
Device (config-radius-server)#exit
Configuring RADIUS Authentication Server Group
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
aaa new-model Example: |
Creates a AAA authentication model. |
| Step 3 |
aaa group server radius wcm_rad Example: |
Creates an radius server-group. |
| Step 4 |
server <ip address>auth-port 1812acct-port 1813 Example: |
Adds servers to the radius group created in Step 3. Configures the UDP port for RADIUS accounting server and authentication server. |
| Step 5 |
aaa authentication dot1x method_list group wcm_rad Example: |
Maps the method list to the radius group. |
| Step 6 |
dot1x system-auth-control Example: |
Enables the system authorization control for the radius group. |
| Step 7 |
aaa session-id common Example: |
Ensures that all session IDs information sent out, from the radius group, for a given call are identical. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# aaa new-model
Device(config)# aaa group server radius wcm_rad
Device(config-sg-radius)# server One auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
Device(config-sg-radius)# server Two auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
Device(config-sg-radius)# server Three auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
Device(config)# aaa authentication dot1x method_list group wcm_rad
Device(config)# dot1x system-auth-control
Device(config)# aaa session-id common
Device(config)#Creating a Client VLAN
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
vlan 137 Example: |
Creates a VLAN and associate it to the interface. |
| Step 3 |
exit Example: |
Exits from the VLAN mode. |
| Step 4 |
interface vlan 137 Example: |
Assigns a VLAN to an interface. |
| Step 5 |
ip address 10.7.137.10 255.255.255.0 Example: |
Assigns an IPv4 address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 6 |
ipv6 address 2001:db8::30:1/64 Example: |
Assigns an IPv6 address to the VLAN interface. |
| Step 7 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit global configuration mode. |
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)# vlan137
Device(config-vlan)# exit
Device(config)# interface vlan137
Device(config-if)# ip address 10.7.137.10 255.255.255.0
Device(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8::30:1/64
Device(config-if)# end
Creating 802.1x WLAN Using an External RADIUS Server
Procedure
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: |
Enters global command mode. |
| Step 2 |
wlan ngwc-1x<ssid> ngwc-1x Example: |
Creates a new WLAN for 802.1x authentication. |
| Step 3 |
broadcast-ssid Example: |
Configures to broadcast the SSID on WLAN. |
| Step 4 |
no security wpa Example: |
Disables the WPA for WLAN to enable 802.1x. |
| Step 5 |
security dot1x Example: |
Configures the 802.1x encryption security for the WLAN. |
| Step 6 |
security dot1x authentication-list wcm-rad Example: |
Configures the server group mapping to the WLAN for dot1x authentication. |
| Step 7 |
client vlan 137 Example: |
Associates the VLAN to a WLAN. |
| Step 8 |
no shutdown Example: |
Enables the WLAN. |
| Step 9 |
end Example: |
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. Alternatively, you can also press Ctrl-Z to exit the global configuration mode. |
Example
Device# configure terminal
Device(config)#wlan ngwc_8021x 2 ngwc_8021x
Device(config-wlan)# broadcast-ssid
Device(config-wlan)# no security wpa
Device(config-wlan)# security dot1x
Device(config-wlan)# security dot1x authentication-list wcm-rad
Device(config-wlan)# client vlan 137
Device(config-wlan)# no shutdown
Device(config-wlan)# endAdditional References
Related Documents
| Related Topic | Document Title |
|---|---|
| IPv6 command reference | IPv6 Command Reference (Catalyst 3650 Switches) |
| WLAN command reference | WLAN Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches) |
| WLAN configuration | WLAN Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches) |
Error Message Decoder
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
To help you research and resolve system error messages in this release, use the Error Message Decoder tool. |
https://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Errordecoder/index.cgi |
MIBs
| MIB | MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| All supported MIBs for this release. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
Technical Assistance
| Description | Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for IPv6 WLAN Security
|
Feature |
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|---|
|
IPv6 WLAN Security Functionality |
Cisco IOS XE 3.3SECisco IOS XE 3.3SE |
This feature was introduced. |
 Feedback
Feedback