Connector and Cable Specifications
Connector Specifications
10/100 and 10/100/1000 Ports
The 10/100 and 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports on switches use RJ-45 connectors and Ethernet pinouts with internal crossovers. Figure B-1 and Figure B-2 show the pinouts.
Figure B-1 10/100 Port Pinouts
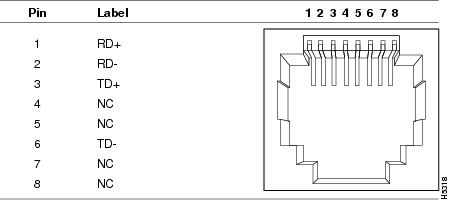
Figure B-2 10/100/1000 Port Pinouts
SFP Module Connectors
Figure B-3 Fiber-Optic SFP Module LC Connector
 |
Warning |
Dual-Purpose Ports
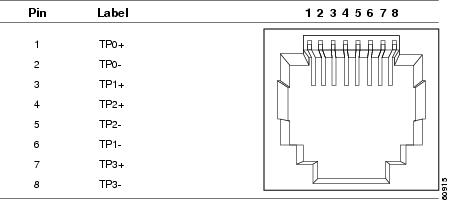
The 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports on the dual-purpose ports use RJ-45 connectors.
Figure B-4 10/100/1000 Port Pinouts

Cables and Adapters
SFP Module Cables
Each port must match the wave-length specifications on each end of the cable, and for reliable communications, the cable must not exceed the allowable length. Copper 1000BASE-T SFP transceivers use standard four twisted-pair, Category 5 (or greater) cable at lengths up to 328 feet (100 meters).
|
|
(nanometers) |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1000BASE-LX/LH |
1310 |
MMF2 |
62.5/125 |
500 |
1804 feet (550 m) |
1000BASE-SX |
850 |
MMF |
62.5/125 |
160 |
722 feet (220 m) |
1000BASE-ZX |
1550 |
SMF |
G.6522 |
— |
43.4 to 62 miles |
1000BASE-BX10-U |
1310 TX |
SMF |
G.6522 |
— |
32,810 feet (10 km) |
1000BASE-BX10-D |
1490 TX |
SMF |
G.6524 |
— |
32,810 feet (10 km) |
100BASE-FX (GLC-FE-100FX) |
1310 |
MMF |
50/125 |
500 |
6,562 feet (2 km) |
100BASE-LX (GLC-FE-100LX) |
1310 |
SMF |
G.6522 |
— |
32,810 feet (10 km) |
100BASE-BX (GLC-FE-100BX-D |
1310 TX |
SMF |
G.6522 |
— |
32,810 feet (10 km) |
CWDM |
1470, 1490, 1510, 1530, 1550, 1570, 1590, 1610 |
SMF |
G.6522 |
— |
62 miles (100 km) |
1 Modal bandwidth applies only to multimode fiber. 2 A mode-conditioning patch cord is required. Using an ordinary patch cord with MMF, 1000BASE-LX/LH SFP modules, and a short link distance can cause transceiver saturation, resulting in an elevated bit error rate (BER). When using the LX/LH SFP module with 62.5-micron diameter MMF, you must also install a mode-conditioning patch cord between the SFP module and the MMF cable on both the sending and receiving ends of the link. The mode-conditioning patch cord is required for link distances greater than 984 feet (300 m). 3 1000BASE-ZX SFP modules can send data up to 62 miles (100 km) by using dispersion-shifted SMF or low-attenuation SMF; the distance depends on the fiber quality, the number of splices, and the connectors. 4 A mode-field diameter/cladding diameter = 9 micrometers/125 micrometers. |

Note ![]() When the fiber-optic cable span is less than 15.43 miles (25 km), insert a 5-decibel (dB) or 10-dB inline optical attenuator between the fiber-optic cable plant and the receiving port on the 1000BASE-ZX SFP module.
When the fiber-optic cable span is less than 15.43 miles (25 km), insert a 5-decibel (dB) or 10-dB inline optical attenuator between the fiber-optic cable plant and the receiving port on the 1000BASE-ZX SFP module.
Cable Pinouts
Figure B-5 Two Twisted-Pair Straight-Through Cable Schematic for 10/100 Ports
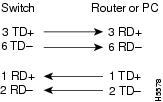
Figure B-6 Two Twisted-Pair Crossover Cable Schematic for 10/100 Ports
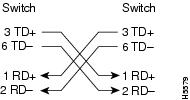
Figure B-7 Four Twisted-Pair Straight-Through Cable Schematic for 1000BASE-T Ports
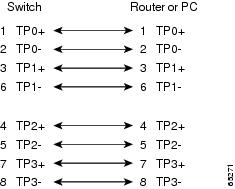
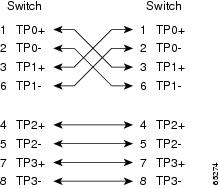
Figure B-8 Four Twisted-Pair Crossover Cable Schematics for 1000BASE-T Ports
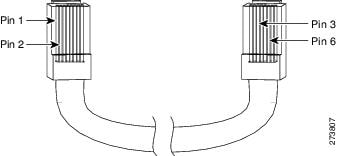
To identify a crossover cable, hold the cable ends side-by-side, with the tab at the back. The wire connected to pin 1 on the left end should be the same color as the wire connected to pin 3 on the right end. The wire connected to pin 2 on the left end should be the same color as the wire connected to pin 6 on the right end.
Figure B-9 Identifying a Crossover Cable
Console Port Adapter Pinouts
The console port uses an 8-pin RJ-45 connector, which is described in Table B-2 and Table B-3. If you did not order a console cable, you need to provide an RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable to connect the switch console port to a PC console port. You need to provide an RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter if you want to connect the switch console port to a terminal. You can order an adapter (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=). For console port and adapter pinout information, see Table B-2 and Table B-3.
Table B-2 lists the pinouts for the console port, the RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable, and the console device.
Table B-3 lists the pinouts for the switch console port, RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter, and the console device.

Note ![]() The RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter is not supplied with the switch. You can order this adapter from Cisco (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=).
The RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter is not supplied with the switch. You can order this adapter from Cisco (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=).
 Feedback
Feedback