About the DHCP Relay Agent
DHCP Relay Agent
You can configure the device to run a DHCP relay agent, which forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. This feature is useful when clients and servers are not on the same physical subnet. Relay agents receive DHCP messages and then generate a new DHCP message to send out on another interface. The relay agent sets the gateway address (giaddr field of the DHCP packet) and, if configured, adds the relay agent information option (Option 82) in the packet and forwards it to the DHCP server. The reply from the server is forwarded back to the client after removing Option 82.
After you enable Option 82, the device uses the binary ifindex format by default. If needed, you can change the Option 82 setting to use an encoded string format instead.
 Note |
When the device relays a DHCP request that already includes Option 82 information, the device forwards the request with the original Option 82 information without altering it. |
DHCP Relay Agent Option 82
You can enable the device to insert and remove Option 82 information on DHCP packets that are forwarded by the relay agent.
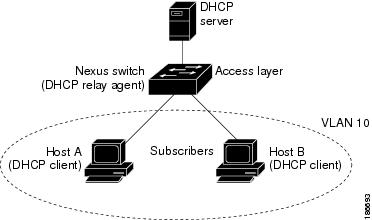
This figure shows an example of a metropolitan Ethernet network in which a centralized DHCP server assigns IP addresses to subscribers connected to the device at the access layer. Because the DHCP clients and their associated DHCP server do not reside on the same IP network or subnet, a DHCP relay agent is configured with a helper address to enable broadcast forwarding and to transfer DHCP messages between the clients and the server.
When you enable Option 82 for the DHCP relay agent on the Cisco NX-OS device, the following sequence of events occurs:
-
The host (DHCP client) generates a DHCP request and broadcasts it on the network.
-
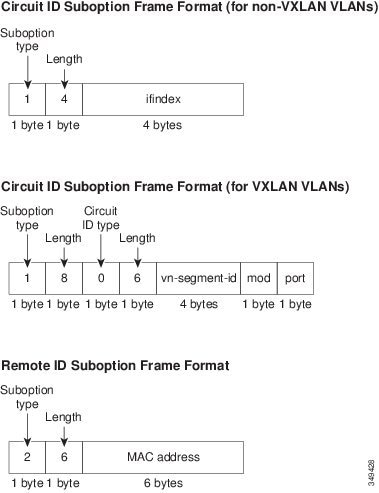
When the Cisco NX-OS device receives the DHCP request, it adds the Option 82 information in the packet. The Option 82 information contains the device MAC address (the remote ID suboption) and the port identifier ifindex (for non-VXLAN VLANs) or vn-segment-id-mod-port (for VXLAN VLANs), from which the packet is received (the circuit ID suboption). In DHCP relay, the circuit ID is filled with the ifindex of the SVI or Layer 3 interface on which DHCP relay is configured.
-
The device adds the IP address of the relay agent to the DHCP packet.
-
The device forwards the DHCP request that includes the Option 82 field to the DHCP server.
-
The DHCP server receives the packet. If the server is Option 82 capable, it can use the remote ID, the circuit ID, or both to assign IP addresses and implement policies, such as restricting the number of IP addresses that can be assigned to a single remote ID or circuit ID. The DHCP server echoes the Option 82 field in the DHCP reply.
-
The DHCP server unicasts the reply to the Cisco NX-OS device if the request was relayed to the server by the device. The Cisco NX-OS device verifies that it originally inserted the Option 82 data by inspecting the remote ID and possibly the circuit ID fields. The Cisco NX-OS device removes the Option 82 field and forwards the packet to the interface that connects to the DHCP client that sent the DHCP request.
This figure shows the packet formats for the circuit ID suboption and the remote ID suboption.
VRF Support for the DHCP Relay Agent
You can configure the DHCP relay agent to forward DHCP broadcast messages from clients in a virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) instance to DHCP servers in a different VRF. By using a single DHCP server to provide DHCP support to clients in multiple VRFs, you can conserve IP addresses by using a single IP address pool rather than one for each VRF. For general information about VRFs, see the Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide.
Enabling VRF support for the DHCP relay agent requires that you enable Option 82 for the DHCP relay agent.
If a DHCP request arrives on an interface that you have configured with a DHCP relay address and VRF information and the address of the DCHP server belongs to a network on an interface that is a member of a different VRF, the device inserts Option 82 information in the request and forwards it to the DHCP server in the server VRF. The Option 82 information includes the following:
- VPN identifier
-
Name of the VRF that the interface that receives the DHCP request is a member of.
- Link selection
-
Subnet address of the interface that receives the DHCP request. When DHCP smart relay is enabled, the link selection is filled with the subnet of the active giaddr.
- Server identifier override
-
IP address of the interface that receives the DHCP request. When DHCP smart relay is enabled, the server identifier is filled with the active giaddr.
 Note |
The DHCP server must support the VPN identifier, link selection, and server identifier override options. |
When the device receives the DHCP response message, it strips off the Option 82 information and forwards the response to the DHCP client in the client VRF.
DHCP Smart Relay Agent
When the DHCP relay agent receives broadcast DHCP request packets from a host, it sets giaddr to the primary address of the inbound interface and forwards the packets to the server. The server allocates IP addresses from the giaddr subnet pool until the pool is exhausted and ignores further requests.
You can configure the DHCP smart relay agent to allocate IP addresses from the secondary IP address subnet pool if the first subnet pool is exhausted or the server ignores further requests. This enhancement is useful if the number of hosts is greater than the number of IP addresses in the pool or if multiple subnets are configured on an interface using secondary addresses.
 Feedback
Feedback