Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Release Notes for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a)
Available Languages
Table Of Contents
Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders
Cisco Nexus 2148T Fabric Extender
Cisco Nexus 2248TP Fabric Extender
Cisco Nexus 2232PP Fabric Extender
Cisco Nexus 2224TP Fabric Extender
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
Configuration Synchronization Enhancements
Role Based Access Control Support
SPAN Session Port Channel Enhancement
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) Features
Private VLANs over Port Channel and vPC Interfaces
Access control list (ACL) on a virtual terminal (VTY)
AAA Command Authorization with RBAC
Privilege Level Support for Authorization on TACACS+ Servers
Support for Type 2 vPC Consistency Checks
HTTP and HTTPS Enable and Disable
Increased Configuration Limits for the Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform Switch
Upgrading or Downgrading to a New Release
Supported Upgrade and Downgrade Paths
Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines
Upgrading the Power Sequencer on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020 Switches
Configuration Synchronization Limitation
Limitations on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020
SPAN Limitations on Fabric Extender Ports
Checkpoint and Configuration Rollback Limitation
Resolved Caveats—Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a)
Resolved Caveats—Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
Resolved CaveatsCisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)
Installation and Upgrade Guides
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series
and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Release Notes,
for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1),
and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a)
Release: 5.0(2)N2(1a) May 6, 2011Part Number: OL-22747-02 K0Current Release: Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a)Current Release: Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)Current Release: Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)This document describes the features, caveats, and limitations for Cisco Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches and the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders. Use this document in combination with documents listed in the "Related Documentation" section.

Note
Release notes are sometimes updated with new information about restrictions and caveats. See the following website for the most recent version of the Cisco Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series release notes: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/release/notes/Nexus_5000_Release_Notes.html

Note
Table 1 shows the online change history for this document.
Table 1 Online History Change
A0
October 15, 2010
Created release notes for Release 5.0(2)N1(1)
B0
December 20, 2010
Created release notes for Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
C0
January 26, 2011
Added resolved bugs for NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1).
Updated New Features sections.
Moved Configuration Synchronization Best Practices to the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Operations Guide.
Updated the Upgrading the Power Sequencer on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020 Switches section.
Added Configuration Synchronization Limitation and related caveats (CSCtl87260 and CSCtl87240) to the Open Caveats section.
Updated Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a) Supported Upgrades and Downgrades.
D0
March 17, 2011
Added Support for Type 2 vPC Consistency Checks.
Updated Limitations with Cisco Nexus 2148 Fabric Extender limitation.
E0
March 28, 2011
Updated Limitations with IGMP snooping limitation.
F0
May 6, 2011
Created release notes for NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1a)
G0
August 12, 2011
Updated Hardware Features to include statement about supported CNAs.
H0
September 12, 2011
I0
July 30, 2012
J0
September 20, 2012
Added Documentation Updates
K0
November 19, 2012
Revised the description of BPDU guard and filter in Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders.
Contents
This document includes the following sections:
•
Upgrading or Downgrading to a New Release
•
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
Introduction
The Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches comprise a family of line-rate, low-latency, lossless 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) switches for data center applications. The Cisco Nexus 5000 Series includes the Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform and the Cisco Nexus 5000 Platform switches.
The Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch hardware is described in the following topics:
Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) introduces the Cisco Nexus 5500 platform which extends the industry-leading versatility of the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series of purpose-built, 10-Gigabit Ethernet data center class switches and provides higher density, lower latency, and multilayer services. The Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform is well suited for enterprise-class data center server access layer deployments and smaller scale, mid-market data center aggregation deployments across a diverse set of physical, virtual, storage access, and high-performance compute data center environments. The first switch in this series is the Cisco Nexus 5548P Switch.
Cisco Nexus 5548P Switch
The Cisco Nexus 5548P Switch is the first switch in the Cisco Nexus 5500 platform. It is a one-rack-unit (1 RU), 10-Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) switch that offers up to 960-Gbps throughput and up to 48 ports. The switch has 32, 1/10-Gbps fixed Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+) Ethernet and FCoE ports and one expansion slot. As a top-of-rack switch, all the servers in the rack connect to the Cisco Nexus 5548P switch, and it connects to the LAN or SAN. It has the following features:
•
1 RU 1/10-Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE switch that offers up to 960-Gbps throughput.
•
32 fixed SFP+ port and up to 1 expansion module
•
Hardware that is capable of 1/10-Gigabit Ethernet
•
32,000 MAC address table entries
•
Low-latency cut-through design that provides predictable, consistent traffic latency regardless of packet size, traffic pattern, or enabled features on 10-Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
•
Line-rate traffic throughput on all ports
•
Extension through the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series
•
Cisco Nexus 5548P supports the following expansion modules:
–
16-port 1 and 10-Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE module
–
8-port 8/4/2/1-Gbps Fibre Channel plus 8-port 1- and 10-Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE module
Cisco Nexus 5000 Platform
The Cisco Nexus 5000 Platform includes the Cisco Nexus 2020 switch and the Nexus 5010 switch.
Cisco Nexus 5020 Switch
The Cisco Nexus 5020 is a 56-port switch. It is a two rack unit (2 RU), 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, FCoE, and Fibre Channel switch that provides 1.04 terabits per second (Tbps) throughput with very low latency.
It has the following features:
•
Forty fixed 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and FCoE Small Form Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+) ports. Sixteen of the forty fixed ports support both Gigabit Ethernet and 10-Gigabit Ethernet. The default is 10-Gigabit Ethernet.
•
Two expansion module slots that can be configured to support up to 12 additional 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and FCoE SFP+ ports, up to 16 Fibre Channel switch ports, or a combination of both.
•
Serial console port and an out-of-band 10/100/1000-Mbps Ethernet management port.
•
1+1 redundant, hot-pluggable power supplies.
•
4+1 redundant, hot-pluggable fan modules to provide highly reliable front-to-back cooling.
For additional information about the Cisco Nexus 5020 switch, see the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Hardware Installation Guide.
Cisco Nexus 5010 Switch
The Cisco Nexus 5010 is a 28-port switch. It is a 1 RU, 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, FCoE, and Fibre Channel switch that provides more than 500-Gbps throughput with very low latency. It has the following features:
•
Twenty fixed 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and FCoE SFP+ ports. Eight of the twenty fixed ports support Gigabit Ethernet and 10-Gigabit Ethernet speed.
•
One expansion module slot that can be configured to support up to 6 additional 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and FCoE SFP+ ports, up to 8 Fibre Channel switch ports, or a combination of 4 additional 10-Gigabit Ethernet, Cisco Data Center Ethernet, and FCoE SFP+ ports with 4 additional Fibre Channel switch ports.
•
Serial console port and an out-of-band 10/100/1000-Mbps Ethernet management port.
•
1+1 redundant, hot-pluggable power supplies.
•
1+1 redundant, hot-pluggable fan modules to provide highly reliable front-to-back cooling.
For additional information about the Cisco Nexus 5010 switch, see the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Hardware Installation Guide.

Note
The Cisco Nexus 5020 switch and the N5K-M1404 and N5K-M1600 gigabit expansion modules (GEMs) support Cisco NX-OS Release 4.0(0)N1(1) or later releases. The Cisco Nexus 5010 Platform switch and the N5K-M1008 GEM support Cisco NX-OS Release 4.0(1a)N1(1) or later releases. The N5K-M1060 8GFC GEM supports Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1(3)N2(1).
Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders
The Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender was first released in Release 4.0(1a)N2(1). It is a highly scalable and flexible server networking solution that works with the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches to provide high-density and low-cost connectivity for server aggregation.
Scaling across a multitude of 1-Gigabit Ethernet, 10-Gigabit Ethernet, unified fabric, rack, and blade server environments, the Fabric Extender is designed to simplify data center architecture and operations.
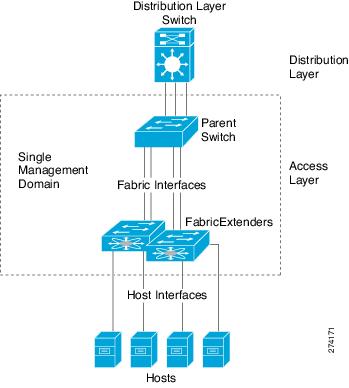
The Fabric Extender integrates with its parent switch, allowing zero-touch provisioning as well as automatic configuration. This integration allows large numbers of servers and hosts to be supported using the same feature set as the parent Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, including security and quality of service (QoS) configuration parameters, with a single point of management as shown in Figure 1. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is not required between the Fabric Extender and its parent switch, because the Fabric Extender and its parent switch allow you to enable a large multi-path, loop-free, active-active topology.
Because the Fabric Extender can connect to servers directly, by default, all Fabric Extender host ports are edge ports. In addition, BPDU guard is on by default and cannot be turned on. BPDU filter can be turned on or off.
Figure 1 Single Management Domain
This section describes the 2148T Fabric Extender. It includes the following topics:
•
Cisco Nexus 2148T Fabric Extender
•
Cisco Nexus 2248TP Fabric Extender
•
Cisco Nexus 2232PP Fabric Extender
•
Cisco Nexus 2224TP Fabric Extender
Cisco Nexus 2148T Fabric Extender
The first product in the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series is the Cisco Nexus 2148T Fabric Extender, a 1 RU chassis designed for rack mounting. The chassis supports redundant hot-swappable fans and power supplies.
The Cisco Nexus 2148T Fabric Extender forwards all traffic to a parent Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch over 10-Gigabit Ethernet fabric uplinks, allowing all traffic to be inspected by policies established on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. No software is included with the Cisco Nexus 2148T. Software is downloaded and upgraded from its parent Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch.
The Cisco Nexus 2148T has 48 1-Gigabit Ethernet host interfaces for its downlink connection to servers or hosts and 4 10-Gigabit Ethernet fabric interfaces with SFP+ interface adapters for its uplink connection to the parent switch.
Cisco Nexus 2248TP Fabric Extender
The Cisco Nexus 2248TP is a stackable 1 RU 450 mm deep switch that supports 48 1000-TX host ports and 4 10G SFP+ network ports. Both 100 Mbps and Gigabit Ethernet are supported on the 48 TX host ports.
Host ports can be configured in an EtherChannel as well as part of a vPC. It is typically used with the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. The Cisco Nexus 2248TP is managed and configured by the upstream switch. The Fabric Extender software is shipped with the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch software. The Fabric Extender downloads the software image from the switch in the same way that a module would download it from the supervisor in a modular chassis.
Cisco Nexus 2232PP Fabric Extender
The Cisco Nexus 2232PP is a stackable 1 RU 450 mm deep switch that supports 32 10G/1G SFP+ host ports and 8 10G SFP+ network ports. Host ports can be configured in an EtherChannel as well as part of a vPC. It is typically used with the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. The Cisco Nexus 2232PP is managed and configured by the upstream switch. The Fabric Extender software is shipped with the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch software. The Fabric Extender downloads the software image from the switch in the same way that a module would download it from the supervisor in a modular chassis.
Cisco Nexus 2224TP Fabric Extender
The Cisco Nexus 2224TP Fabric Extender is similar to the Cisco Nexus 2248T Fabric Extender but has 24 100/1000Base-T downlink ports, and 2 SFP+ uplink ports.
New and Changed Features
This section briefly describes the new features introduced in the Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) and Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1). This section includes the following topics:
•
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
•
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) Features
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
The Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) includes the following new or changed features:
•
Configuration Synchronization Enhancements
•
Role Based Access Control Support
•
SPAN Session Port Channel Enhancement
VTP Client/Server
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), VTP client/server modes are supported for VTP version 1 and 2. Prior to this release, VTP transparent was the only supported mode. This feature allows you to provision VLANs at a central point and distribute the VLAN database across a Layer 2 domain.
VE Ports
This feature allows you to build multi-hop FCoE fabrics by interconnecting multiple fiber channel forwarders by using the VE Port that functions as a Fiber Channel E-port running on top of a lossless Ethernet fabric.
The maximum distance between two Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches is 3000m for FCoE (lossless Ethernet) traffic. It can be enabled using the pause no-drop buffer-size buffer-size pause-threshold xoff-size resume-threshold xon-size command.
DHCP Snooping
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), DHCP snooping with option 82 is supported. DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and trusted DHCP servers. DHCP snooping is enabled on a per-VLAN basis
Configuration Synchronization Enhancements
Import running-config exclude interface Ethernet and RBAC support for configuration synchronization are supported.
Increased Distance
This software release supports up to 3 km between the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender and the upstream Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. The maximum distance between the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender and the upstream Nexus 5000 Series switch remains unchanged (300 m) for FCoE (lossless Ethernet) traffic.
vPC Enhancement Features
Several new features have been added to improve the resiliency and operation of vPC, such as the graceful consistency check, auto recovery, and per-VLAN consistency check.
Role Based Access Control Support
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), you can add, delete, or modify a switch profile configuration based on Role Based Access Control (RBAC) configurations.
Channel Group Force
The feature allows you to force the configuration of a LAN port to a channel group.
SPAN Session Port Channel Enhancement
When a port channel is the source interface in a SPAN session, the rx and tx option are now available for SPAN sessions.
For more information about the features listed, see the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series documentation listed in the"Related Documentation" section.
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) Features
This section includes the following topics:
Hardware Features
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) includes the following new or changed hardware features:
•
Support for the Cisco Nexus 5548P Platform switch which is a 1 RU chassis with 32 fixed ports and 1 expansion slot.
•
Support for the following modules:
–
16-port 1/10-Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE GEM
–
8-port 1/10-Gigabit Ethernet and FCoE plus an 8-port 8/4/2/1 native FC GEM
•
Support for Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders on the Cisco Nexus 5548 switch.
•
Support for 4000 VLANs per Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform switch.
•
Generation-1 (Pre-FIP) CNAs are supported on the Nexus 5000 Series; however, they are not supported on the Nexus 5500 Platform.
Software Features
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) includes the following new or changed software features:
•
Configuration Synchronization
•
Private VLANs over Port Channel and vPC Interfaces
•
Access control list (ACL) on a virtual terminal (VTY)
•
AAA Command Authorization with RBAC
•
Privilege Level Support for Authorization on TACACS+ Servers
•
Support for Type 2 vPC Consistency Checks
•
HTTP and HTTPS Enable and Disable
•
FCoE
•
SPAN
•
Increased Configuration Limits for the Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform Switch
Configuration Synchronization
Configuration synchronization (config-sync) allows you to make configuration changes on one switch and have the system automatically synchronize the switch's peers. This feature eliminates user errors and reduces the administrative overhead of having to configure both members of a virtual port channel (vPC) simultaneously.

CautionFor additional information and best practices that must be followed when using the configuration synchronization feature, see the "Configuration Synchronization Operations" chapter in the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Operations Guide at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/operations/n5k_ops_guide.html
Failure to do so may leave configurations in an inconsistent state.
Module Preprovisioning
Module preprovisioning allows you to preconfigure interfaces before inserting or attaching a module to a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. If a module goes offline, you can use preprovisioning to make changes to the interface configurations for the offline module. Preprovisioning allows you to synchronize the configuration for an interface that is online with one peer but offline with another peer.
Port profiles
A port profile is a container used to define a common set of network configuration commands for multiple interfaces. This feature enables you to define port configurations across a large number of ports.
Configuration Rollback
A configuration rollback provides the ability to revert a running configuration to a previously saved configuration snapshot or checkpoint.
Private VLANs over Port Channel and vPC Interfaces
This feature allows you to configure a promiscuous trunk (or isolated trunk) on port channel or vPC interfaces.
Access control list (ACL) on a virtual terminal (VTY)
This feature allows configuration of access control for the switch for a VTY, regardless of where the connection is established (mgmt0 or an external interface).
AAA Command Authorization with RBAC
Allows you to authorize every command that a user can execute.
Privilege Level Support for Authorization on TACACS+ Servers
This feature allows you to map the privilege levels configured on TACACS+ servers to user roles configured on Cisco NX-OS devices.
Support for Type 2 vPC Consistency Checks
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), the following QoS parameters support Type 2 vPC consistency checks:
•
Network QoS—MTU and Pause
•
Input Queuing —Bandwidth and Absolute Priority
•
Output Queuing—Bandwidth and Absolute Priority
When a Type 2 mismatch occurs, the vPC is not suspended. When a Type 1 mismatch occurs, the vPC is suspended.
HTTP and HTTPS Enable and Disable
This feature allows you to enable or disable HTTP or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS).
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS supports configurable buffer settings for no-drop classes for traffic and class-maps of type match-all for type qos policies.
Scaling
On the Cisco Nexus 5548 switch the following scaled-up configurations are supported: 4000 VLANs, 4000 IGMP groups and 16 Fabric Extenders.
FCoE
vFC interfaces now support trunking.
SPAN
The limit on number egress (TX) sources in a monitor session has been lifted. Port-channel interfaces can be configured as egress sources.
MIB Support
This release supports the CISCO-VTP-MIB and the CISCO-BRIDGE-MIB
Increased Configuration Limits for the Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform Switch
The Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform switch supports new configuration limits for VLANs, FEX, IGMP, MAC addresses, and logical ports.
For more information about the features listed, see the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series documentation listed in the"Related Documentation" section.
Upgrading or Downgrading to a New Release
This section describes the upgrade and downgrade paths that are supported for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a) on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. This section includes the following topics:
•
Supported Upgrade and Downgrade Paths
•
Upgrading the Power Sequencer on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020 Switches
Supported Upgrade and Downgrade Paths
Table 2 shows the upgrade and downgrade possibilities for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a):
Table 3 shows the upgrade and downgrade possibilities for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1):
Upgrade and Downgrade Guidelines
Use the following guidelines when upgrading or downgrading:
•
Upgrading to and from NX-OS Release 4.1(3) is disruptive.
•
Downgrading from NX-OS Release 5.0(2) to NX-OS Release 4.2(1) is disruptive.
•
Upgrading from NX-OS Release 4.2(1) to NX-OS Release 5.0(2) is a nondisruptive upgrade (ISSU).
•
Upgrading from a Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)-based release to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) and later releases is nondisruptive.
•
Downgrading from Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), or NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a) to a previous release is disruptive.
•
Beginning with Cisco NX-OS 5.0(2)N1(1), a disruptive upgrade occurs if the allowed VLAN list for MCT (vPC peer link) does not include the native VLAN, or if the FCoE feature is not enabled on the MCT native VLAN. The following message is displayed to indicate the disruptive upgrade:
"Allowed vlan list for MCT is not configured to include native vlan, or fcoe is enabled on MCT native vlan. Install needs to be disruptive"To perform a nondisruptive upgrade, configure the VLAN list to allow the default native VLAN on the MCT and do not enable the FCoE feature on the default native VLAN.
Upgrading the Power Sequencer on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020 Switches
Under certain conditions, a voltage spike that exceeds the system voltage guard band and glitch filter settings may result in a power cycle of the system mezzanine board which results in the failure of ports on the mezzanine board. To solve the issue, you need to upgrade to Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or a later release and makes sure that the power sequencer has been upgraded to v1.2 using the show version command. Follow the power sequencer upgrade procedure to upgrade the power sequencer to v1.2 and to workaround CSCsy21017 and CSCth33969.
If you upgrade the switch to Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or later release, but do not power cycle the switch following this procedure, even though the switch has instructions for the power sequencer upgrade, the power sequencer is not upgraded. The show version command output displays a v1.2 power sequencer, but that only indicates that the power sequencer upgrade instructions have been programmed. If you cannot confirm a power cycle, Cisco recommends that you perform a power off/on to ensure the power sequencer is upgraded.
To upgrade the power sequencer with Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or a later release, follow these steps:

Note
A power sequencer upgrade is not necessary if you already upgraded to an earlier version that includes the Power Sequencer v1.2, for example Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1).
Step 1
Download the kickstart and system image for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or a later release to the system.
Step 2
Enter the install all kickstart kickstart_url system system_url command to start the upgrade to Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or a later release. When prompted to confirm the upgrade, review the upgrade table and select y to proceed.
After completing the installation, the system reloads and displays the Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) or later release image.
Step 3
Repeat Step 2 to reinstall the Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image. During this process, the upgrade table displays the upgrade action for the power sequencer and then upgrades the power sequencer.
Step 4
After the installation is complete, power cycle the switch. The power sequencer is not updated until a power cycle is completed.
Step 5
After the system comes up, confirm that the power sequencer has been upgraded by issuing the show version command.The show version command only confirms if the power sequencer has the updated instructions. The upgrade does not take effect until the switch is power cycled.
Installing Expansion Modules
When you install an expansion module on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, use the show module command to check the status of the module installation in the system logs as follows:

Note
Hot swap expansion modules are not supported in Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) and earlier releases. Power down the switch before you insert or remove an expansion module.
e7-dut-1# show moduleMod Ports Module-Type Model Status--- ----- -------------------------------- ---------------------- ------------1 40 40x10GE/Supervisor N5K-C5020P-BF-XL-SU active *2 6 6x1/2/4/8G FC Module N5K-M1060 ok3 6 6x1/2/4/8G FC Module N5K-M1060 okMod Sw Hw World-Wide-Name(s) (WWN)--- -------------- ------ --------------------------------------------------1 4.1(3)N2(1) 1.2 --2 4.1(3)N2(1) 0.0 20:41:00:0d:ec:b4:6a:80 to 20:46:00:0d:ec:b4:6a:803 4.1(3)N2(1) 0.0 20:81:00:0d:ec:b4:6a:80 to 20:86:00:0d:ec:b4:6a:80Mod MAC-Address(es) Serial-Num--- -------------------------------------- ----------1 000d.ecb4.6a88 to 000d.ecb4.6aaf JAF1314AQHR2 000d.ecb4.6ab0 to 000d.ecb4.6ab7 JAF1325BBGE3 000d.ecb4.6ab8 to 000d.ecb4.6abf JAF1325BBJGIf the module is not seated properly, the following error message is displayed:
2009 Aug 3 23:45:16 Edge-2 %PFMA-2-MOD_INSERTION_FAILED: Module 2 insertion fai led. Module might not be seated properly. Please try removing the module and the n re-insert after five seconds or more.This example shows the output for the N55M16P expansion module:
Switch-1# show moduleMod Ports Module-Type Model Status--- ----- -------------------------------- ---------------------- ------------1 32 O2 32X10GE/Modular Supervisor N5K-C5548P-SUP active *2 16 O2 16X10GE Ethernet Module N51-M16EP okMod Sw Hw World-Wide-Name(s) (WWN)--- -------------- ------ --------------------------------------------------1 5.0(2u)N1(1u) 1.0 --2 5.0(2u)N1(1u) 1.0 --Mod MAC-Address(es) Serial-Num--- -------------------------------------- ----------1 0005.73a9.51e8 to 0005.73a9.51107 JAF1436ACQA2 badb.4243.5350 to badb.4243.535f JAF1432BCSPThis example shows the output for the N55M8P8FP expansion module:
Switch-1# show moduleMod Ports Module-Type Model Status--- ----- -------------------------------- ---------------------- ------------1 32 O2 32X10GE/Modular Supervisor N5K-C5548P-SUP active *2 16 O2 8X10GE + 8x1/2/4/8G FC Module N51-M8E8FP okMod Sw Hw World-Wide-Name(s) (WWN)--- -------------- ------ --------------------------------------------------1 5.0(2)N1(1) 1.0 --2 5.0(2)N1(1) 1.0 20:41:00:05:9b:23:40:c0 to 20:48:00:05:9b:23:40:c0Mod MAC-Address(es) Serial-Num--- -------------------------------------- ----------1 0005.9b23.40d0 to 0005.9b23.40ef JAF1421DKRS2 badb.414b.4245 to badb.414b.4254 JAF1432AKBEFor details, see the expansion modules section of the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform Hardware Installation Guide.
Limitations
This section describes the limitations for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), and NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a).
•
When upgrading from Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and earlier releases, to any release, the policy description is lost. This problem does not occur when upgrading from Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and later releases. After an upgrade, Cisco recommends that you reconfigure the policy description. For details, see CSCth14225.
•
Starting with Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1), LACP fast timers are supported. If you downgrade to an earlier release that does not support this feature, issuing the install all command displays the following warning:
"Configuration not supported - Lacp fast rate is enabled","Use \"lacp rate normal\" on those interfaces"Before downgrading to an earlier release, change the LACP rate to normal. If you ignore the warning and force the installation, then it is possible that the leftover LACP rate fast configuration would still be active with previous releases of software but the behavior would be unpredictable and link flap may occur. It is recommended that you change the LACP rate setting to normal. For details, see CSCth93787.
•
When an FC SPAN destination port is changed from SD to F mode and back to SD mode on a NPV switch, the port goes into an error-disabled state. Perform a shut/no-shut after the mode change recovers the port. This issue occurs only in NPV mode. For details, see CSCtf87701.
•
If you configure a Cisco Nexus 2248TP port to 100 Mbps instead of autonegotiation, autonegotiation does not occur, which is expected behavior. Both sides of the link should be configured to both hardwired speed or both autonegotiate.
no speed—Autonegotiates and advertises all speeds (only full duplex)
speed 1000—Autonegotiates only for a 802.3x pause
speed 100—Does not autonegotiate; pause cannot be advertised. The peer must be set to not autonegotiate and fix at 100 Mbps (similar to the N2248TP)
For details, see CSCte81998.
•
Given the implementation of a single CPU ISSU, the STP root on the PVST region with switches on an MST region is not supported. The PVST simulation on the boundary ports go into a PVST SIM inconsistent blocked state which breaks the STP active path. To workaround this issue, move all STP roots on the MST region. However, the workaround causes a nondisruptive ISSU to fail because Non-Edge Designated Forwarding Ports is required for an ISSU. For additional information, see CSCtf51577. For information topologies that a nondisruptive upgrade is supported, refer to the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Upgrade and Downgrade Guide.
•
IGMP queries sent in CSCtf94558 are group-specific queries that are sent with the destination IP/MAC address as the group's address.
GS queries are sent for IP address: 224.1.14.1 to 224.1.14.100 [0100.5E01.0E01 to 0100.5E01.0E64]
These are not link-local addresses. By default, they are not flooded by hardware into the VLAN. They are sent only to the ports that have joined this group.
This is expected behavior during an ISSU.
In another scenario, the IGMP global queries [dest IP 224.0.0.1] get flooded correctly in the VLAN.
Group-specific queries are not forwarded to ports other than the one that joined the group during ISSU. The reason to forward group-specific queries toward hosts is to avoid having them leave the group. However, if a group has not joined the group, then this is not an issue. If there is an interface that has joined the group, then the queries are expected to make it to the host. While the behavior is different when ISSU is not occurring, it is sufficient and works as expected and there is no impact to traffic. For details, see CSCtf94558.
•
The meaning of an MTU configuration has changed in Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and earlier releases. In releases earlier than Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1), the configured MTU included the Ethernet payload and Ethernet headers. In Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1), the configured MTU includes only the Ethernet payload and not the Ethernet headers. When upgrading or downgrading between Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and earlier releases, Cisco NX-OS automatically converts the configuration to address this semantic change by adding or subtracting 38 to the MTU to address the Ethernet header size.
In a vPC configuration, the MTU per class needs to be consistent on both switches in the vPC domain for the vPC peer-link to come up. When upgrading/downgrading a working vPC setup between pre-4.2(1)N1(1) and 4.2(1)N1(1) releases, the MTU is adjusted to make sure that the MCT peer-link always comes up.
However if you add a peer-link between two switches in a vPC domain that are identically configured (MTU in particular) with one switch running Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and another switch running an earlier release, then the vPC peer-link does not come up because the MTU is inconsistent between the two switches.
This is not an issue when upgrading or downgrading peer switches in a vPC domain; this is only an issue when adding a peer-link between two switches running Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and earlier releases that were not previously in the same vPC domain.
To resolve this issue, upgrade downgrade one switch to match the version on the other switch and reconfigure the MTU to be consistent on both sides. For details, see CSCtg27538.
•
The channel-group configuration is not applied to the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series downlink interface after downgrading to the Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1(3)N1(1) software. This issue occurs if the speed 1000 command is present under the context of the port channel. To workaround this issue, reconfigure the channel-group command after the system comes up and reapply the configuration from the saved configuration in the bootflash. For details, see CSCtc06276.
•
When a private VLAN port is configured as a TX (egress) SPAN source, the traffic seen at the SPAN destination port is marked with the VLAN of the ingressed frame. There is no workaround.
•
In large-scale configurations, some Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders may take up to 3 minutes to appear online after issuing the reload command. A configuration can be termed large scale when the maximum permissible Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders are connected to a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, and all host-facing ports are connected and each host-facing interface has a large configuration (that supports the maximum permissible ACEs per interface).
•
The Cisco Nexus 2000 Fabric Extender does not support PVLANs over VLAN trunks used to connect to another switch. The PVLAN trunks are used only on inter-switch links but the FEX ports are only meant to connect to servers. Because it is not a valid configuration to have an isolated secondary VLAN as part of a Fabric Extender port configured as a VLAN trunk, all frames on isolated secondary VLANs are pruned from going out to a FEX.
•
The Cisco Nexus 2148 Fabric Extender does not support frames with the dot1p vlan 0 tag.
•
Egress scheduling is not supported across the drop/no-drop class. Each Fabric Extender host port does not support simultaneous drop and no drop traffic. Each Fabric Extender host port can support drop or no drop traffic.
•
VACLs of more than one type on a single VLAN are unsupported. Cisco NX-OS software supports only a single type of VACL (either MAC, IPv4, or IPv6) applied on a VLAN. When a VACL is applied to a VLAN, it replaces the existing VACL if the new VACL is a different type. For instance, if a MAC VACL is configured on a VLAN and then an IPv6 VACL is configured on the same VLAN, the IPv6 VACL is applied and the MAC VACL is removed.
•
A MAC ACL is applied only on non-IP packets. Even if there is a match eth type = ipv4 statement in the MAC ACL, it does not match an IP packet. To avoid this situation, use IP ACLs to apply access control to IP traffic instead of using a MAC ACL that matches the EtherType to IPv4 or IPv6.
•
Multiple boot kickstart statements in the configuration are not supported.
•
If you remove an expansion module with Fibre Channel ports, and the cable is still attached, the following FCP_ERRFCP_PORT errors are displayed:
2008 May 14 15:55:43 switch %KERN-3-SYSTEM_MSG: FCP_ERRFCP_PORT: gat_fcp_isr_ip_fcmac_sync_intr@424, jiffies = 0x7add9a:Unknown intr src_id 42 - kernel2008 May 14 15:55:43 switch %KERN-3-SYSTEM_MSG: FCP_ERRFCP_PORT: gat_fcp_isr_ip_fcmac_sync_intr@424, jiffies = 0x7add9a:Unknown intr src_id 41 - kernelThese messages are informational only, and result in no loss of functionality.
IGMP Snooping Limitation
On the Cisco Nexus 5010 switch and the Cisco Nexus 5020 switch with a Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender (FEX) installed, unregistered IP multicast packets on one VLAN are forwarded to other VLANs where IGMP snooping is disabled. We recommend that you do not disable IGMP snooping on the Cisco Nexus 5010 switch and the Cisco Nexus 5020 switch. A static IGMP join can be configured for devices intended to receive IP multicast traffic but not to send IGMP join requests. This limitation applies to the Cisco Nexus 5010 switch and the Cisco Nexus 5020 switch only.
Configuration Synchronization Limitation
When you remove a switch profile using the no switch-profile name [all-config | local-config] command, the configuration in the switch profile is immediately removed from the running configuration. This disrupts the configurations that were present in the switch profile. For example, port channel and vPC configurations are disrupted. For current information about this issue, refer to CSCtl87240 and CSCtl87260.
Limitations on the Cisco Nexus 5010 and Cisco Nexus 5020
This section describes the limitations on the Cisco Nexus 5010 switch and the Cisco Nexus 5020 switch.
•
Traffic going out the Ethernet SPAN destination is always tagged. The SPAN destination can be in the access or trunk mode and frames on the SPAN source port can be tagged or untagged. Frames are always tagged internally as they travel through the system. Information about whether the frame was originally tagged or untagged, as it appeared in the SPAN source, is not preserved in the SPAN destination. The spanned traffic exiting the SPAN destination port always has the VLAN tag on it. The correct VLAN tag is applied on the frame as it goes out the SPAN destination. The only exception is if frames ingress on a SPAN source port on an invalid VLAN. In this case, vlan 0 is applied on a spanned frame.
•
Spanned FCoE frames do not preserve original SMAC and DMAC fields. The Ethernet header gets modified as the frame is spanned to the destination. The modified header fields are displayed when monitored on the SPAN destination.
•
The CoS value in spanned FCoE frames on the Ethernet SPAN destination port does not match with the CoS value in the SPAN FCoE source frame. The CoS value on the captured SPAN FCoE frame should be ignored.
•
The class-fcoe cannot be removed even if Fibre Channel is not enabled on a switch.
•
If a port drains traffic at a rate less than 100 Kbps, it is errdisabled in 10 seconds to avoid buffer exhaustion. However, if the drain rate is larger than 100 Kbps, the port may not be consistently errdisabled within 10 seconds which exhaust ingress buffers and discard frames. Use the shut command to disable the slow-draining port.
•
The multicast storm control functionality in the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series does not distinguish between IP, non-IP, registered, or unregistered multicast traffic. All multicast traffic is subject to a single-multicast storm control policer when configured.
SPAN Limitations on Fabric Extender Ports
This section describes the SPAN limitations on Fabric Extender ports.
•
Ports on a FEX can be configured as a tx-source in one session only.
If two ports on the same FEX are enabled to be tx-source, the ports need to be in the same session. If you configure a FEX port as a tx-source and another port belonging to the same FEX is already configured as a tx-source on a different SPAN session, then a error is displayed on the CLI.
In the following example, Interface Ethernet100/1/1 on a FEX 100 is already configured as a tx-source on SPAN session-1:
swor28(config-monitor)# show running-config monitorversion 4.0(1a)N2(1)monitor session 1source interface Ethernet100/1/1 txdestination interface Ethernet1/37no shutIf you add an interface Ethernet100/1/2 as a tx-source to a different SPAN session (session-2) the the following error is displayed:
swor28(config)# monitor session 2swor28(config-monitor)# source interface ethernet 100/1/2 txERROR: Eth100/1/2: Ports on a fex can be tx source in one session onlyswor28(config-monitor)#•
When a FEX port is configured as a tx-source, the multicast traffic on all VLANs for which the tx-source port is a member, is spanned. The FEX port sends out only multicast packets that are not filtered by IGMP snooping. For example, if FEX ports 100/1/1-12 are configured on VLAN 11 and the switch port 1/5 sends multicast traffic on VLAN 11 in a multicast group, and hosts connected to FEX ports 100/1/3-12 are interested in receiving that multicast traffic (through IGMP), then that multicast traffic goes out on FEX ports 100/1/3-12, but not on 100/1/1-2.
If you configure SPAN Tx on port 100/1/1, although the multicast traffic does not egress out of port 100/1/1, the SPAN destination does receive that multicast traffic, which is due to a design limitation.
•
When a FEX port is configured as both SPAN rx-source and tx-source, the broadcast, non-IGMP Layer-2 multicast, and unknown unicast frames originating from that port may be seen twice on the SPAN destination, once on the ingress and once on the egress path. On the egress path, the frames are filtered by the FEX to prevent them from going out on the same port on which they were received. For example, if FEX port 100/1/1 is configured on VLAN 11 and is also configured as SPAN rx-source and tx-source and a broadcast frame is received on that port, the SPAN destination recognizes two copies of the frame, even though the frame is not sent back on port 100/1/1.
•
A FEX port cannot be configured as a SPAN destination. Only a switch port can be configured and used as a SPAN destination.
Checkpoint and Configuration Rollback Limitation
When FCoE is enabled, the checkpoint and configuration rollback functionality is disabled.
Caveats
This section includes the following topics:
•
Resolved Caveats—Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
•
Resolved CaveatsCisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)
Open Caveats
This section lists the open caveats for the Cisco NX-OS 5.0(2)N2(1) release.
•
CSCtj13786
Symptom: On upgrade from the Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) to the Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1), igmp v3-groups might age out and the groups are flushed. Any data destined to these removed groups might be dropped during an ISSU. They resume when the ISSU is completed.
Workaround: There is no workaround when you upgrade from NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1). This is fixed in NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) and is not seen on upgrade from NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1).
•
CSCtk33187
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5500 may crash when an expansion module is removed from the switch and the expansion module has some fabric ports that are used for control traffic.
Workaround: Shut the fabric ports on the expansion module before removing the expansion module from the switch. Because expansion module itself is being removed, doing a "shut" on the fabric ports should not have any functional impact.
•
CSCtj66020
Symptom: After a downgrade from NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), channel-group config may be lost due to priority-flow-control config on a few ports.
Workaround: Although PFC mode auto is default, you need to config PFC mode 'auto' to Port channel members and then add it to the Port channel.
•
CSCtj85867
Symptom: The show running-config command does not show the switchport trunk allowed VLAN configuration for an interface. This happens when the interface inherits a port-profile and the allowed VLAN list that contains VLANs configured directly on interface are such that the number of contiguous VLAN ranges are greater than 64.
Workaround: Use show running-config expand-port-profile to get the effective configuration of the interface.
•
CSCtk08499
Symptom: On doing a snmpwalk of the vtp mib, the system becomes very slow and the VLAN manager hogs the cpu for several minutes. This happens when vtp is configured and an snmpwalk of the vtp mib is performed.
Workaround: Avoid doing snmpwalk on the vtp mib when the system is under load or when critical configuration changes need to be made.
•
CSCtj90485
Symptom: When 7m/10m Tyco cables are inserted into NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) based software, the following warning is displayed:
warning %ETHPORT-3-IF_NON_CISCO_TRANSCEIVER: Non-Cisco transceiver on interface Ethernet1/10 is detectedWorkaround: This is a harmless warning. There is no functionality that is affected.
•
CSCth83907
Symptom: This display issue is exhibited by port-profiles on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running the NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image. If a port-profile has switchport trunk allowed, VLAN commands and VLANs are added on the interface, and show running interface does not show the added VLANs. But show running interface <> expand-port-profile shows the right configuration.
port-profile type ethernet FEX-AA-trunk-portswitchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 101-400state enabledsw(config)# interface Ethernet 101/1/1sw(config-if)# inherit port-profile FEX-AA-trunk-portsw(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 601-603show running int eth 101/1/1 does not show vlan 601-603show running int eth 101/1/1 expand-port-profile has 101-400 as well as 601-603This occurs when an interface that inherits a port-profile has additional VLANs configured on the interface, in addition to the VLANs in the port-profile.
Workaround: None. This is only a display issue.
•
CSCth98138
Symptom: The VFC name in the output of show fc-port-security for some VFC interfaces is wrong. This occurs only with large vfc numbers. It does not happen with numbers like VFC311, VFC3102. and is observed with larger numbers like VFC6000.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti10941
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, the span mode is incorrectly shown in the show interface brief output.
monitor session 1source interface e1/22destination interface e1/9no shutinterface e1/9switchport mode trunkswitchport monitorr20-n5020-1(config-if)# show int bri-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface Vsan Admin Admin Status SFP Oper Oper PortMode Trunk Mode Speed ChannelMode (Gbps)-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Eth1/9 1 eth trunk up none 1000(D)This problem occurs when the span destination interface is configured in trunk mode. This problem is not seen when the interface is in access mode.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti14663
Symptom: The show diagnostic cli displays a pass status for fan and temperature sensors when it should have shown failed on hitting the alarms.
This occurs when major/minor alarms reach the threshold and you try to get information through the show diagnostic cli.
Workaround: Alarms or errors related to fan, temperature sensors do show up on the console and in syslog from pfm/nohms.The errors can be seen in show environment fan/show environment temperature.
•
CSCti15226
Symptom: On the Cisco Nexus 5500 platforms no error is thrown when you configure an acl based qos policy for class-fcoe. It happens when configured in the following order.
1.
qos policy with acl-based classification for class-fcoe.
2.
network-qos policy with class-fcoe.
3.
Apply policies at system qos level.
Workaround: Do not configure an acl based classification in class-fcoe.
•
CSCti19511
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch may not remove the router port immediately if the port is shut on the peer switch. The Show ip igmp snooping mrouter displays the port even though it is down. This happens when IGMP snooping has to be configured on the Nexus switch.
Workaround: The router port is removed after the querier timeout which is 5 minutes.
•
CSCti19892
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running the NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, switch-profile deletion cannot be interrupted with a Ctrl+C/Ctrl+Z operation when deleting a switch-profile.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti22121
Symptom: When you perform an lacp rate fast config on a vpc peer-link on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running a NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, unidirectional CFS peering is observed as follows:
Eth1-a# show vpc brief Legend: (*) - local vPC is down, forwarding via vPC peer-link vPC domain id : 1000 Peer status : peer adjacency formed ok vPC keep-alive status : peer is alive Eth1-b(config)# show vpc brief Legend: (*) - local vPC is down, forwarding via vPC peer-link vPC domain id : 1000 Peer status : peer link is down (vPC peer is not reachable over cfs) vPC keep-alive status : peer is aliveWorkaround: Perform a shut/no shut operation on the peer-link.
•
CSCti22294
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch may not forward the Mcast traffic on GEM ports after a reload/OIR of the GEM. The Show ip igmp snooping group cli may not show the GEM ports against the groups. This issue is observed if IGMP snooping is enabled onthe Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch.
Workaround: Statically configuring the groups again or apply any trigger (like port flap).
•
CSCti26220
Symptom: By default, on the Cisco Nexus 5500 platforms, there is a mechanism called slow port pruning that avoids drops for multicast traffic for uncongested ports when one of the receivers is slow. An example of this is the 1G. Traffic for for slow receivers is dropped in the fabric. However, there is no CLI command to indicate that such a drop has occurred. The drops occur for slow receivers of multicast traffic (like1G ports).
Workaround: If needed, slow port pruning can be turned off using the hardware multicast disable-slow-port-pruning command.
•
CSCti31594
Symptom: There are continuous stp disputes when 12K STP ports are configured with a hello time value 1.
Workaround: Avoid configuring hello time value as 1 and keep the default value.
•
CSCti34155
Symptom: The show running-config ipqos all command does not display complete default queuing-policy information.
Switch-1# show run ipqos allpolicy-map type queuing default-in-policypolicy-map type queuing default-out-policyWorkaround: Use following command to see the default queuing policy-maps.
show policy-map type queuing default-in-policyshow policy-map type queuing default-out-policy
•
CSCti40833
Symptom: Switch-profile session like Verify/Commit take long time before detecting a failure and returning the cli prompt in certain cases of peer becoming unresponsive while its still reachable over transport (CFSoIP) or in case of uni-directional failure (i.e. only one side sees peer becoming unreachable).
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti45602
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running an NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, if the offline interface configuration is made ahead of pre-provisioning configuration, commit may fail as the configuration is not applied on the peer switch. This happens when offline interfaces are configured ahead of pre-provisioning configuration and such configuration is synced to the peer.
Workaround: Configure pre-provisioning configuration ahead of interface configuration.
•
CSCti51365
Symptom: During ISSU, if NP port channels are flapped, the reason for downtime is displayed incorrectly, as follows:
NPV-switch# show int fc 2/1 fc2/1 is down (No operational members)Workaround: None. This is only a display issue. No functional impact
•
CSCti61513
Symptom: match ip rtp cannot be configured in a type qos class-map of type match-all.
Workaround: Configure match any classp-map.
•
CSCti63620
Symptom: For the config-sync feature, implicit configs generated on account of another configuration are not added into the data-structures maintained by the config-sync module. When this situation occurs, the import command may result in failure.
For example, consider member interfaces of a port channel. If a configuration is applied on the port channel, it could be implicitly updated on the member interfaces and could be reflected in the show running-config output of the member interface.
Workaround: This problem is generally encountered with the import command where the you can use the option import running-config. In this command all the commands that appear in the member interfaces are to be verified and committed to make it a part of switch-profile. Now if the implicit commands are not updated in the internal data-structures the import fails.
There two workarounds
a) The import command is generally used after a reload (or ISSU) in which case all the commands including the implicit ones are updated in the config-sync data-structures and hence this problem is not encountered.
b) Another work around is if reload or ISSU is not possible, a command called resync database can be used from within the switch-profile context to update the internal data-structures.
•
CSCti68764
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running an NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, The following commands are currently not supported under a switch-profile:
1.spanning-tree vlan <> priority <>2.spanning-tree vlan <> forward-time <>3.spanning-tree vlan <> hello-time <>4.spanning-tree vlan <> max-age <>5.spanning-tree vlan <> root primary | spanning-tree vlan <> root secondaryThis happens when a spanning tree configuration is made in a switch-profile.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti77835
Symptom: Rollback fails with following failure in rollback exec logs (show rollback log exec):
#Generating Rollback PatchExecuting Rollback Patch ========================================================`config t ` `no vlan 1, 100-199, 201-602`Error: Command is not mutually exclusive ========================================================Vlans are configured partially inside and outside the switch-profile.
Workaround: All Vlans should be configured either completely inside or outside the switch-profile.
•
CSCti82599
Symptom: Sometimes, SPAN stops working on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series.
Workaround: Flapping the SPAN destination again recovers the SPAN traffic
•
CSCti84186
Symptom: When an interface is pre-provisioned with non-default config, issuing a show running command with the all keyword at the end, default config is still displayed along with the newly configured non-default config. This can be confusing, as it would seem as if conflicting config is present. This is only a display issue, no functional impact. The default config is not actually applied. For example, if "switchport mode trunk" is configured on int eth 1/1, the following is seen for show run interface ethernet1/1: interface Ethernet1/1 switchport mode access switchport mode trunk This problem does not exist for a regular show running-config request, only when "all" is specified at the end. This happens when you configure any non-default config on a pre-provisioned interface, and issue a show run command with the all keyword.
Workaround: None. There is no behavioral impact. Seethe show running command without all.
•
CSCti86007
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running an NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, when a peer-link comes up and vPC ports are in the process of coming up, if the peer switch reboots, there is a small window where the vPC ports do not come up due to the peer-link being down.
Workaround: Perform a shut/no shut operation on the vPC ports.
•
CSCti86620
Symptom: When you configure the interface beacon and copy the config to startup-config 2 and reload the switch teh following message is displayed:
check interface LED ### Reproducibility reproducible ### Impact LED is not flashing after switch reload ### Expected Behavior LED should be flashingWorkaround: None.
•
CSCti86692
Symptom: The show interface <interface> may show an incorrect Last link flapped value at initialization.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti87532
Symptom: Rollback fails and output of show rollback log exec contains following:
......#Generating Rollback PatchExecuting Rollback Patch========================================================`config t ``policy-map type network-qos pu-ta2``class type network-qos class-fcoe``no pause no-drop buffer-size 152000 pause-threshold 150000 resume-threshold 40123`ERROR: can't modify pause parameter for class-fcoe========================================================......The pause no-drop config for class-fcoe differs between checkpointed configuration and running-configuration of the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch.
Workaround: Change the running configuration to make the pause no-drop configuration for class-fcoe same as the checkpointed configuration.
•
CSCti87913
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch may not be able to login any servers after following steps:
a.
Performing an ISSU to Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) from a previous release with feature fcoe configuration enabled.
b.
Disabling feature fcoe and then re-enabling feature fcoe.
c.
Copying all the feature fcoe configurations back.
Workaround: The recommended step after issuing the no feature fcoe command to reload the switch. Subsequently feature fcoe can be re-enabled and configurations copied without facing this issue.
•
CSCti92741
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, show port-resources module x may display incorrect information for Total bandwidth and Total shared bandwidth.
Workaround: None. It is a display issue with no impact on functionality.
•
CSCti97003
Symptom: Rollback fails and output of show rollback log exec contains following:
......--------------------------------------------------------------------------------`config sync ``no switch-profile ta1 all-config`--------------------------------------------------------------------------------time: Thu, 19:20:04 16 Sep 2010Status: (null)Verification successful...Proceeding to delete switch-profile. This might take a while depending on amount of configuration under a switch-profile.Please avoid other configuration changes during this time.Deletion of switch profile failed......Workaround: As a best configuration practice with switch-profile, if a policy-map is configured inside switch-profile then it is referred only inside switch-profile. Similarly, if a policy map is configured outside the switch-profile then it is not referred inside switch-profile.
•
CSCti99872
Symptom: After ISSU, if an existing vsan is deleted and recreated, then the vfcs on that vsan goes into to an error disabled state.
Workaround: Perform a shut/no shut of the vfc to help it recover.
•
CSCtj05044
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, IGMP groups are not relearnt after VLAN deletion and addition on a VLAN which is SPAN source. The VLAN has to be configured as a SPAN source on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch.
Workaround: Avoid using the VLAN as a SPAN source.
•
CSCtj10460
Symptom: Deletion of switch-profile fails when switch-profile contains port channel definitions and some interfaces are members of the port channel. This happens when switch profile contains configurations imported from a running-config.
Workaround: Execute resync-database command and then delete the switch-profile.
•
CSCtj13786
•
CSCtj16996
Symptom: Rollback fails and output for show rollback log exec contains following:

Note
This example features feature vpc as an example. The failed configuration is different for other conditional features:
......========================================================`config sync ``switch-profile Test`Switch-Profile started, Profile ID is 1`interface port-channel100``switchport mode trunk`Syntax error while parsing 'vpc peer-link'========================================================......Workaround: Prior to rollback, you should configure the conditional feature (feature vpc in this case). In case of feature vpc, you should also configure vpc domain and peer-keepalive.
•
CSCtj19861
Symptoms a Cisco Nexus 5548 switch, in NPV mode, performing a shut on a non-trunking san-port channel uplink takes more than 30 seconds (the CLI is not responsive for 30 seconds).
Workaround: None. There is no functionality impact.
•
CSCtj22747
Symptom: When you pre-provision a module and insert an incompatible module and then later fix the configuration and provision a new module, and the module does not come online, the module needs to be pre-provisioned and replaced with a different type of module.
Workaround: Physically remove and re-insert the module.
•
CSCtj23007
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running an NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) image, multiple checkpoints with same name could get created. This problem is seen only when checkpoint names are 31 character long.
Workaround: The checkpoint names used must be less than 31 character long.
•
CSCtj26673
Symptom: Import verification may not work for certain class configurations that are implicitly generated on configuring policy-maps of type network-qos and queuing.
Workaround: Use resync-database command to resynchronize the config-sync database with system configuration and then issue the verify/commit in import mode again.
•
CSCtj26863
Symptom: If the eth1/39 is up with traffic running and you configure a channel-group command under the eth1/39, it displays junk values after the port channel is created.
Eugene1(config-monitor)# show interface port-channel 1port-channel1 is upinput rate 1.22 Gbps, 2.36 Mpps; output rate 867.62 Mbps, 1.69 MppsRX18446743955409989970 unicast packets 18446744035193376576 multicast packets 0 broadcast packets18446743916893814929 input packets 18446733960470130948 bytes0 jumbo packets 0 storm suppression packets0 runts 0 giants 0 CRC 0 no buffer0 input error 0 short frame 0 overrun 0 underrun 0 ignored0 watchdog 0 bad etype drop 0 bad proto drop 0 if down drop0 input with dribble 0 input discard0 Rx pauseTX18446743955125934157 unicast packets 18446744073706175895 multicast packets 0 broadcast packets18446743955122558435 output packets 18446736484122209748 bytes0 jumbo packets0 output errors 0 collision 0 deferred 0 late collision0 lost carrier 0 no carrier 0 babble0 Tx pause1 interface resetsThis happens when show int po 1 counters shows huge counter values when an interface with running traffic is added to the port channel. And this happens to a newly created port channel that does not have any members to begin with.
Workaround: Use the clear counters command.
•
CSCtj27113
Symptom: When the UDLD feature is turned on and LACP rate fast is configured on an MCT unified port on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series or a Cisco Nexus 5500 switch, the MCT port may go to UDLD empty echo and turn error disabled.
Workaround: Enable error recovery on the MCT unified port.
•
CSCtj27689
Symptom: If there are 10 or more discontinuous VLAN-ranges created on the switch or configured under any of the trunk interfaces, then forwarding(fwm) service can crash on Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running versions 4.2(1)N1(1) or 4.2(1)N2(1). This leads to reloading of the box.

Note
The actual number of VLAN ranges allowed could be slightly more than 10 depending on actual VLAN values used while defining ranges. If this configuration of 10 or more discontinuous VLAN-ranges is present in a start-up config, then it could lead to continuous reload of the box due to fwm service crash each time.
There are two different conditions when this issue can be seen:
a.
When 10 or more discontinuous VLAN ranges are configured under any of the trunk interfaces using allowed vlan list command
E.g.
interface Ethernet2/4switchport mode trunkswitchport trunk allowed vlan 221-226,237-242,253-258,269-274switchport trunk allowed vlan add 285-290,301-306,317-322,333-338switchport trunk allowed vlan add 349-354,365-370,381-386,397-402switchport trunk allowed vlan add 413-418,429-434,445-450,461-466........b.
VLANs created on the switch themselves comprise of 10 or more discontinuous ranges.
vlan 1,101-103,127-129,153-154,160-161,167-168,174-175,181-182,188-189,195-196,202-203,209- 222,237-238,253-254,269-270,285-286,301-302,317-318,333-334,349-350,365-366,381-382,39 7-398,413-414,429-430,445-446,461-462,477-478........
Workaround: - Allowed VLAN list configured under any of the trunk interfaces should comprise of less than 10 discontinuous VLAN-ranges.
- VLANs created on the switch should comprise of less than 10 discontinuous ranges.
- If this configuration of 10 or more discontinuous VLAN-ranges is already present in start-up config from earlier releases, then 'write erase' is required by breaking into kickstart prompt.
•
CSCtj29477
Symptom: When the UDLD feature is turned on, Cisco Nexus 5000 Series vPC unified port may be error disabled due to UDLD Empty echo upon MCT flap. Another similar symptom is the other switch that is connected to the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series.
Workaround: Enable error recovery on both the MCT and vPC port.
•
CSCtj34994
•
CSCtj42415
Symptom: When a Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender port that is a member of more than 2000 VLANs is configured as a TX span source, the following syslog error is printed:
%$ VDC-1 %$ %FWM-2-FWM_SPAN_EGR_MCAST_ERROR: FwM SPAN fex source programming has failed. Error: Fex Po/interfaces should be part of < 2000 vlans to be a monitor source.Workaround: Once VLAN membership for the FEX port is brought down to a reasonable number, the issue can be cleared by either performing a shut/no shut of the monitor session or removing the Fabrix Extender port as SPAN src and adding it back
•
CSCtj44387
Symptom: On the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches, performing snmpwalk on a BRIDGE-MIB when the vpc peer-link is going down, causes high cpu utilization. This may result in some processes crashing.
Workaround: A BRIDGE-MIB should not be used under stressful conditions.
•
CSCtj53287
Symptom: On the Cisco Nexus 5500 platform, due to a limitation Fibre channel ports cannot be configured as RX sources in a monitor session. The following sources are blocked in the CLI as a result of the above limitation:
–
Fibre channel ports: fc x/y
–
SAN port channels: san-port-channel x
–
VSAN: vsan x
This limitation does not apply to FCoE VLAN and VFC interfaces. FC and SAN port channel interfaces can be configured as TX sources with no issue.
Workaround: Configure the egress points of Fibre channel traffic as SPAN sources on the Cisco Nexus 5548 switch.
•
CSCth69160
Symptom: The SVI on secondary VLAN does not work.
Workaround: Assign SVI to non Private VLANs
•
CSCti11823
Symptom: The Cisco NX-OS version 4.2(1)N1() supports only 10 Gigabit Ethernet on the Nexus 2232 host ports. If the administrator plugs in 1Gig SFPs on Nexus 2232 host ports with Cisco NX-OS 4.2(1)N1(1) running, the SFP validation fails, the LED blinks amber and the interface shows LinkNotConnected. The administrator performs an ISSU from Cisco NX-OS 4.2(1)N1(1) to Cisco NX-OS 4.2(1)N2(1) and the Cisco NX-OS 4.2(1)N2(1) version supports Gigabit Ethernet on Cisco Nexus 2232 host ports. After ISSU, if the administrator configures speed 1000 on the interface with Gigabit Ethernet SFP plugged in, the Gigabit Ethernet interface comes up (traffic flows) but the Gigabit Ethernet port LED continues to blink amber. The LED should be green after and ISSU to the Cisco NX-OS version 4.2(1)N2(1) and configuration of speed 1000.
Workaround:Unplug and re-plug SFP and the LED turns green.
•
CSCtc62994
Symptom: With combining RBAC roles (multiple roles assigned to the same user account), interface policies in those roles do not work on per role basis. In the example shown in this bug, user lan-admin is assigned to the following 3 roles: LAN-admin, LAN-admin-ETH and LAN-admin-no.
Roles LAN-admin and LAN-admin-no include eth1/1 in their interface policy permit list and both deny the shutdown command under their permitted interfaces.
Roles LAN-admin-ETH excludes eth1/1 from its interface policy permit-list and permits the shutdown command under its permitted interfaces.
When all 3 roles are assigned to the user, lan-admin, the user should not be allowed to shutdown interface eth1/1 but it currently can.
Workaround: Do not configure multiple roles for the same user account
•
CSCtd31131
Symptom: If you change PVLAN configuration as follows very rapidly (less than 5 seconds between any two commands), then the interface may end up in an err-disabled state.
DUT2(config-vlan)# vlan 421DUT2(config-vlan)# private-vlan communityDUT2(config-vlan)# private-vlan isolatedDUT2(config-vlan)# private-vlan communityDUT2(config-vlan)# private-vlan isolatedWorkaround: Shut the interface, followed by no shut if the interface recovers properly.
•
CSCtf32340
Symptom: When you change the VSAN or Interface Scope of an existing Role via DM, a This entry already exists error dialog is shown and the change is not applied
Workaround: Use the CLI to make the scope changes for the existing role.
•
CSCtf79253
Symptom: This is the case of having an STP topology with parallel links (there is a loop) on the secondary switch with a path cost for the non-vpc ports is smaller than the vpc ports. Therefore, peer-link would end up being blocked by STP. In this case, transient traffic loop could be formed.
Workaround: Recommended best practice topology for deployment does not have parallel links to vPCs that have their cost tweaked to be higher than vPCs. By default all vPC links have preferred (smaller) cost over non vPC links.
•
CSCtf98638
Symptom: The message "%SYSMGR-5-SUBPROC_KILLED "System Manager (core-client) (PID 7679) hasn't caught signal 9 (no core)." is printed when the system is rebooting after an install.
Freeing memory in the file system.2010 Apr 1 08:39:09 SW2-5020-ANIL %$ VDC-1 %$ %CALLHOME-2-EVENT: SW_CRASH cimxmlserver in slot 1 crashed with crash type : stateful crash[####################] 100% -- SUCCESSLoading images into memory.[####################] 100% -- SUCCESSSaving supervisor runtime state.Apr 1 08:39:18 %SYSMGR-5-SUBPROC_KILLED "System Manager (core-client)" (PID 7679) hasn't caught signal 9 (no core).[####################] 100% -- SUCCESSWorkaround: There is no functional impact. Ignore the message
•
CSCtg33706
Symptom: Debug LACP is not available on the Fabric Extender ports
Workaround: Use LACP event histories etc. on the Fabric Extender. Other show commands should also help with debug information.
•
CSCtd15304
Symptom: When you perform a Cisco Nexus 5000 series switch software install using the Fabric Manager, the Success Reset status message is shown just before the switch reboots.
Workaround: To determine the status of the software install, do the following:
–
Close the wizard and go to the main FM screen
–
Click on the Rediscover...button in the toolbar and wait for the rediscovery to complete. Once the rediscovery is complete, you may encounter either of the scenarios:
•
If the topology shows the switch with a cross, the switch is rebooting/down. Wait for some time and repeat the second step again.
If the topology shows the switch as discovered/managed, select the corresponding fabric tree node from the Logical Domains tree. In the right hand side panel, under the Switches tab information about the switches along with their current versions is displayed. Use this to confirm the status of the software install.
•
CSCtd70554
Symptom: When you downgrade from the Cisco NX-OS Releases 4.1(3)N2(1) or 4.1(3)N2(1a) to the Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1(3)N1(1) or 4.1(3)N1(1a), the feature fc-port-security command does not get converted to feature port-security. As a result, the FC port security configuration gets lost and remains disabled.
Workaround: After the downgrade to Cisco NX-OS Releases 4.1(3)N1(1) or 4.1(3)N1(1a), re-enable the FC port security feature by executing the command feature port-security.
•
CSCta77490
Symptom: When the type of a pVLAN is toggled from being a regular VLAN to a pVLAN and back to regular VLAN in very small interval of time, the type change fails.
Workaround: Issue the type change commands with a 5 seconds gap in between.
•
CSCtb34546
Symptom: When a PACL with deny ip any any is applied on mgmt0, CFS discovery gets stuck.
ip access-list ip110 deny ip any anyApplying such a ACL on the mgmt0
int mgmt 0ip access-group ip1 inwould cause this issue.
Workaround: Remove the deny ip any any rule from the PACL applied on mgmt0 interface.
•
CSCtb61197
Symptom: When a port channel provisioning fails because the system has reached the limit of number of port channels supported, output of show san-portchannel continues to display the port channel as present but down. The port channel is seen as down even if the member interface is operationally up because it could not be provisioned correctly due to resource limitation.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCtc44231
Symptom: LACP port channel doesn't come up. A VLAN is deleted from the switch which is also configured as native VLAN for the lacp port channel.
Workaround: Create the VLAN or remove the native VLAN config from the lacp port channel.
•
CSCtc77180
Symptom: Ports are error disabled with error Ethernet interface not present if feature fcoe is enabled immediately after the switch prompt comes up on bootup.
Workaround: Enable feature fcoe after confirming that the interfaces are displayed in the output of show interface brief.
•
CSCtb58641
Symptom: If a mac-address moves from an isolated host port to a promiscuous trunk port, in certain conditions, the mac-address is never cleared from the system.
Workaround: None
•
CSCtc36397
Symptom: Changing the role-priority and flapping the peer-link does not change the roles of the vPC peers. This happens when one of the switch has its role as Operational primary due to an earlier reload of the primary switch.
Workaround: None
•
CSCtb84512
Symptom: In mixed span mode where ethernet port channel, vfc and FC ports are span sources and ethernet interface is a span destination, vfc flap causes the traffic coming in on ethernet port channel to be not spanned.
Workaround: Remove and add span source command for the ethernet port channel.
•
CSCtb94310d
Symptom: With a san port channel as the source and ethernet interface as the destination, removing the channel-group config from the san port channel member causes monitor session to go to error state.
Workaround: Unconfigure and reconfigure the monitor session.
•
CSCtb53820
Symptom: After save and reload with a monitor session configuration where source is a vsan and destination is an fc port, the monitor session goes to error state.
Workaround: Unconfigure and reconfigure the monitor session.
•
CSCtc04213
Symptom: Vlan related configurations do not get applied on a range of interfaces. This issue may occur when you try to configure a VLAN configuration on a range of interfaces in a way that the number of interfaces being configured at a time is greater than 192. As a result, even though the VLAN configuration command returns with no errors on the console, the VLANs do not get applied to the interfaces. You can confirm this by running the cli, show system internal ethpm info interface one of affected
Workaround: Select a smaller range of interfaces to apply the VLAN configuration to.
•
CSCsz82199
Symptom: You cannot enable std.pause on a port channel interface connected between two Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches. Enable std.pause between two Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches and configure std.pause in the hardware.
Workaround: None
•
CSCsv39939
Symptom: Incorrect values are displayed for interface capabilities for ports for Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric extenders connected to a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. In particular, the number of input and output queues for the ports are displayed as zero instead of two.
Workaround: This is a display issue and does not impact functionality.
•
CSCsz81365
Symptom: SPAN session should stop reflecting packets as soon as mapping is removed.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCta04383
Symptom: When you install a new image from one of two vPC switches, the vPC switch gets upgraded. Also, each of the connected Fabric Extenders update their firmware with the new version, but continue to run the current version and stay connected to the other vPC switch. When you reload the upgraded switch, but revert back to the older version of software on the switch, both the vPC switches and all the Fabric Extenders run the older version of software. However, the Fabric Extenders have the more recent version of software in the firmware. When the Fabric Extenders reload there is loss of connectivity with the hosts.
Workaround: Reinstall the older version of software from either of the two switches while the Fabric Extenders are connected to that switch.
•
CSCsx35870
Symptom: The CLI times out when a large number of VLANs are created and deleted followed by PVLAN creation and deletion. The system indicates that the Ethernet Port Manager (ethpm) has timed out to communicate with the SPAN manager or PVLAN manager. As a result, some of the PVLAN interfaces are error disabled.
Workaround: Perform shut and no shut on the error disabled interfaces.
•
CSCsx59489
Symptom: Call home notifications for events generated when both a switch and a Fabric Extender are rebooting may contain a timestamp of January 1 1970 as shown in the following example:
System Notification from sample-system - environment:minor - 1970-01-01 00:00:00 GMT+0000The most likely scenario where this would occur is after a power failure or after issuing the reload all command. The event is generated before the Fabric Extender connects with the switch and before the local time is updated for the Fabric Extender.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsx80279
Symptom: When traffic is sent at line rate as a single burst, all addresses are not learned when egress interfaces are FEX facing ports. This problem does not occur if sustained traffic is sent for more than 0.4 seconds.
Workaround: Resending the unlearned MAC addresses would render them relearned.
•
CSCsy99816
Symptom: When a Cisco Nexus 2000 Fabric Extender is already online and a fabric interface that is not part of a port channel is configured with a serial number that does not match that of the FEX, the fabric interface is brought down, and show interface fex does not display the reason for being down.
Workaround: None. This is a display issue.
•
CSCsy02439
Symptom: Under some circumstances, the FC MAC driver displays the following error message:
%KERN-3-SYSTEM_MSG: FCP_ERRFCP_PORT: gat_fcp_isr_ip_fcmac_sync_intr@424, jiffies = 0x1c422:Unknown intr src_id 41 - kernelThe error message is when an unused interrupt in the MAC fires. The error message does not indicate any functional problem.
Workaround: None
•
CSCsx68778
Symptom: You cannot configure commands under the interface range
Workaround: Configure command sunder HIF ports of one FEX at a time.
•
CSCsx40562
Symptom: ACL drop traffic with 802.1p cos values greater than 3 may not get spanned if all four user qos classes are not configured in system qos service-policy configuration.e
Workaround: Configure all four user qos classes (except class-default and class-fcoe) under system qos service-policy to span all ACL drop traffic.
•
CSCsv93263
Symptom: Cisco NX-OS does not provide offline configuration support. The creation of a FEX interface depends on the FEX coming online after a fabric interface configuration. When you restore configuration from a file, there period when FEX interfaces are not yet created but interface configuration is applied and fails. (See also CSCsw21301)
Workaround: If system configuration is to be restored from a configuration file (copied locally or through tftp), you can separate the FEX interface part of the configuration (if any) into a different file. Copy the main file first, then wait for FEX to come online, and then copy the separate FEX interface configuration file. Alternately, you can copy twice.
•
CSCsv81694
Symptom: The auto learn static MAC entry is removed if the port on which the same MAC address is dynamically learned is flapped. The static MAC address is removed from the software as well as the hardware.
Workaround: Re-add the static MAC entry through the CLI.
•
CSCsv56881
Symptom: Each Switched Virtual Interface (SVI) for inband management must be configured with a different IP address. IPv6 has an error check feature. When an administrator enters a duplicate IPv6 address across two SVIs, the software fails the command due to the duplicate address. A similar error check should exist for IPv4 address configuration on SVIs. ( See also CSCsx60187)
Workaround: Do not configure duplicated IPv4 or IPv6 addresses.
•
CSCsv02866
Symptom: The command show interface ethernet transceiver details may show invalid calibration for DOM-supported 1 G SFP.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsv00989
Symptom: The show interface ethernet transceiver details command may show all zero values for a DOM-capable 1 G SFP.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsu77946
Symptom: Within a configuration session, when you enable statistics on the PACL add more than 252 ACES to the ACL, and apply it to an interface, an error message is generated as the statistics counter is exhausted. Even if you try to remove the statistics keyword, it does not get removed. The result is that the ACL cannot be applied to the interface. This problem occurs only with a configuration session, and only after a configuration failure.
Workaround: Reduce the size of the ACL (fewer than 252 ACES) and re-apply the ACL to an interface. The statistics keyword remains and consumes hardware resources.
•
CSCsv19979
Symptom: Any FC port set to SD mode does not come up until the speed is configured manually. The port goes into the error disabled state and the only way to bring it online as SD is to manually set the speed 2 G or 4 G.
Workaround: Configure the speed manually to 2 G or 4 G.
•
CSCsr20499
Symptom: When you restore a configuration to running-config from a configuration file, ACL manager may leak memory. The size of the leak is related to the size of ACL configurations and the number of times the restoration occurs. The switch may reboot if the ACL configuration is very large and the restoration occurs too many times.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsq64251
Symptom: TACACS+ fails if the user name input at login initiates a directed request authentication. The syntax to authenticate a directed request to a switch is username@(IP address or name of TACACS+ server).
Workaround: Use RADIUS for directed request authentication.
•
CSCsq76688
Symptom: The neighboring device for the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is not removed after shutting down the port for CDP hold time interval.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsr28868
Symptom: When the Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) feature is disabled, any untagged Ethernet packet with 00 00 in the Ethertype/length field is treated as an invalid packet and is forwarded out with a bad Ethernet CRC.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsr35452
Symptom: When the ntp peer command is configured on the MDS fabric and is distributed using CFS, the Nexus 5000 Series switch appends an incorrect VRF name AC to the command instead of VRF management.
Workaround: Use the ntp server command to synchronize time across the fabric.
•
CSCsr36661
Symptom: When IGMP group membership is statically configured with private VLAN (PVLAN) host ports, the hardware gets programmed correctly. However, the membership information is not programmed for PVLAN host ports after the switch is reloaded.
Workaround: Delete and add the private VLAN association once again
•
CSCsr68690
Symptom: When an egress SPAN is configured on a port transmitting jumbo or large frames, the spanned frames are truncated to 2384 bytes.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsl21529
Symptom: An incorrect MTU value is displayed in the show interface command output. The Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch only supports class-based MTU. Per-interface level MTU configuration is not supported. The switch supports jumbo frames by default. However, the show interface command output currently displays an incorrect MTU value of 1500 bytes.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsm03765
Symptom: The Set operation on the CISCO-IP-IF-MIB is not supported. You cannot set the mgmt0 IP address using SNMP.
Workaround: Use the CLI to set the mgmt0 IP address.
•
CSCsm16222
Symptom: CFS does not support roles configuration distribution. Enter the show cfs application command to see the registered applications.
Workaround: Any features not registered with CFS need to be configured locally on the switch.
•
CSCsl73766
Symptom: CFS does not support RADIUS configuration distribution. Enter the show cfs application command to see the registered applications.
Workaround: Any features not registered with CFS need to be configured locally on the switch.
•
CSCso25966
Symptom: When an LACP port channel is configured between Catalyst 6500 and Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches, and the configurations on both sides of the port channel do not match, the Catalyst 6500 LACP ports may change to the errordisable state.
Workaround: Fix the configuration to make it consistent on both peer switches of the port channel, and perform a shut and no shut operation on the Catalyst 6500 port channel interface.
•
CSCso27446
Symptom: When a shutdown command is issued to the mgmt0 interface on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, the link never goes down and the remote end does not indicate that the link is down.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCso46345
Symptom: The current version of NX-OS software running on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches does not support Brocade i10K interop mode 4. The i10k v9.2.0.8 is supported by MDS in SAN-OS 3.2(2c), and 3.2(3) with interop mode 1 and 4.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCso74872
Symptom: When two SNMP walks are started simultaneously, one of them may fail with the following error:
OID not increasingThis problem does not occur with a single SNMP walk.
Workaround: This is not a permanent failure. Restart the walk to resolve the issue as long as there is no other SNMP walk in progress.
•
CSCso84269
Symptom: Occasionally, when reload is executed after bootup, and there has been no configuration change, the switch displays the following warning:
'WARNING: There is unsaved configuration!!!'Workaround: Enter the copy running startup command.
•
CSCsq10026
Symptom: When the small form-factor pluggable (SFP) is not in the Ethernet port, the show interface command output displays a bandwidth of 1 Gbps. When the SFP is plugged in, the bandwidth is displayed correctly (10 Gbps).
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsq35527
Symptom: When IGMP snooping is enabled on a switch, and the switch is the STP root and an STP topology change occurs, the IP multicast traffic may take a long time to converge. During this time, the IP multicast traffic may get affected.
Workaround: Configure a shorter query interval on the IGMP router to reduce the time it takes for ip-multicast traffic to converge in this topology.
•
CSCsq35728
Symptom: When a SAN port channel is created, the following syslog message is displayed:
2008 May 20 06:09:13 switch %PORT_CHANNEL-3-MSG_SEND_FAILURE: failed to send MAP_PARAM_FROM_CHANNEL to sap 45: Broken pipe"There is no functionality loss and this message can be ignored.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCso01268
Symptom: The following error message is displayed when a module is hot-swapped out:
2005 Jan 1 00:08:23 switch %KERN-4-SYSTEM_MSG: SI-VDC map entry <0, 0x0> does not exist! - kernel"There is no functionality loss and the message can be ignored.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsq57558
Symptom: Enhanced Inter Switch Link (EISL) encapsulation is not supported on a Fibre Channel SPAN destination port. When EISL encapsulation is configured on the SPAN destination (SD) port, a VFT header is added to the packets going out of the SD port. The VFT header has VSAN information that helps distinguish traffic for various VSANs. This applies to any Fibre Channel SPAN source. By default, EISL encap is not added and packets are sent out without a VFT header, and independent of the type of SPAN source port. For a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, the switchport encap EISL command does not have any effect.
Workaround: Use the Ethernet SPAN destination port to SPAN Fibre Channel traffic. FCoE packets going out of the Ethernet SPAN destination port contain VSAN information in the Ethernet VLAN tag.
•
CSCsq90423
Symptom: EISL encapsulation is not supported on Fibre Channel SPAN destination port in NPV mode. When EISL encapsulation is configured on the SPAN destination (SD) port, a VFT header is added to the packets going out of the SD port. The VFT header has VSAN information, which helps distinguish traffic for various VSANs. This applies to any Fibre Channel SPAN source. By default, EISL encapsulation is not added and packets are sent out without a VFT header, and independent of the type of SPAN source port. For a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, the switchport encap EISL command does not have any effect.
Workaround: Use the Ethernet SPAN destination port to SPAN Fibre Channel traffic. FCoE packet going out of the Ethernet SPAN destination port contain VSAN information in the Ethernet VLAN tag.
•
CSCsv93922
Symptom: If the modulo(%) operator is used in a Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender description the show fex <fex-id> command brings up the following error message
ERROR: bad format: non escaped % not followed by 's'.Workaround: Remove the modulo(%) operator from the Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender description
•
CSCsv95478
Symptom:The Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender pinning redistribute command does not wait for user prompt with a yes or no operation.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCsv15775
Symptom: When priority tagged frames are received on Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender ports, they are dropped and not forward on the native or default VLAN of the port. The MAC addresses are not learned.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCtl87240
Symptom: Switch profile commands are removed from the running configuration when the switch profile is deleted. This occurs when you issue the no switch-profile name all-config | local-config command.
Workaround: Make a backup copy of the running configuration before deleting the switch profile and restore your startup configuration after the switch profile has been deleted. To restore the startup configuration, use the copy startup-config running-config command.
•
CSCtl87260
Symptom: Removing a switch profile from a configuration disrupts some configurations that were present in the running configuration, for example port channel and vPC configurations. This occurs when you issue the no switch-profile name all-config | local-config command.
Workaround: Make a backup copy of the running configuration before deleting the switch profile and restore your startup configuration after the switch profile has been deleted. To restore the startup configuration, use the copy startup-config running-config command.
Resolved Caveats—Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a)
Table 4 lists the caveats that are resolved in Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1a). The caveats may be open in previous Cisco NX-OS releases.
Resolved Caveats—Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1)
This section lists the resolved caveats for this release.
The caveats in this section are resolved in Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N2(1) but may be open in previous Cisco NX-OS releases.
•
CSCtk03738
Symptom: On Cisco Nexus 2000 Fabric Extenders, multicast packets are forwarded on multiple FEX ports.
Workaround: Enable IGMP snooping, then use static IGMP entries to add multicast receivers to the switch MAC table if the host is unable to send an IGMP group membership report. Alternatively, upgrade the host application to support the IGMP protocol so it can automatically send IGMP join/leave reports without a static configuration on the switch.
•
CSCtk33187
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform switch may fail when an expansion module is removed from the switch and the expansion module has fabric ports that are used for control traffic.
Workaround: Before removing the expansion module from the switch, use the show fex detail command to display the fabric ports that are used for control traffic then use the shut command to shut down the fabric ports. Because the expansion module is removed, using the shut command on the fabric ports should not have any functional impact.
•
CSCth47056
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), switch-profiles that are created by one user cannot be modified by an another user. The following error is displayed when a different user tries to modify the switch-profile.
N5k(config-sync)# switch-profile SYNCError: Session is owned by another userWorkaround: Modify the switch-profile by logging in as the user who initially created the switch-profile.
•
CSCtk37139
Symptom: CDP syslog message (add and remove) are logged at level 6. This issue logged to change the Sev level from 6 to 5. Not from 2 to 5.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti87650
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000, the output of the command "show interface fc<x/y> capabilities" may indicate that "Class 2 sequential delivery" and "BB state change notification" are supported when in fact they are not supported. The command "show interface fc<x/y> capabilities" has to be executed.
Workaround: None.It is a display issue which should be ignored.
•
CSCtj27662
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5548 iIn NPV mode, TNP ports may take more than a minute to come up the first time after a reload.Switch has to be Nexus 5548 and NPV should be enabled.
Workaround:This happens only the first time after reload. No workaround is available.
•
CSCtj50241
Symptom: With NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), when a VFC interface is shut down, in addition to the FIP Clear Virtual Link message, FCOE-LOGO is sent to the CNA. Some CNA vendors may have problems processing the FCOE LOGO. As a result, the VFC interface may not come back after a no-shut.
Workaround: Flap the ethernet interface that the VFC interface is bound to.
•
CSCti84496
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, running NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), the following is observed with igmp snooping.
Switch# sh ip igmp snooping vlan 3001IGMP Snooping information for vlan 3001IGMP snooping enabledOptimised Multicast Flood (OMF) disabledIGMP querier noneSwitch-querier disabledIGMPv3 Explicit tracking enabled <<<<<<< EHT enabled for the vlanIGMPv2 Fast leave disabledIGMPv1/v2 Report suppression enabledIGMPv3 Report suppression disabledLink Local Groups suppression enabledRouter port detection using PIM Hellos, IGMP QueriesNumber of router-ports: 2Number of groups: 10VLAN vPC function enabledActive ports:Po10 Po1011 Po1012 Po1031Po1111 Po1112 Po1131 Po1931Po4000 Eth1/2 Eth101/1/1 Eth101/1/16Eth113/1/1 Eth113/1/16 Eth103/1/1 Eth103/1/16Eth111/1/1 Eth111/1/16 Eth193/1/1 Eth193/1/16Switch#Switch# sh ip igmp snooping explicit-trackingIGMPv3 Snooping Explicit-tracking informationVlan Source/GroupIntf Reporter Uptime Last-Join Expires3001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.1Eth101/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:33 00:00:03 00:04:163001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.1Eth111/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:22 00:00:02 00:04:173001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.2Eth101/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:32 00:00:02 00:04:173001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.2Eth111/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:21 00:00:01 00:04:183001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.3Eth101/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:31 00:00:01 00:04:183001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.3Eth111/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:20 0.158710 00:04:193001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.4Eth101/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:30 0.743343 00:04:193001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.4Eth111/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:19 00:00:09 00:04:103001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.5Eth101/1/130.1.1.1 00:08:29 00:00:09 00:04:103001 100.1.1.1 /237.1.0.5Switch# sh ip igmp snooping explicit-tracking vlan 3001 <<<<<<<<<<<<<<< No infowhen specific VLAN is usedIGMPv3 Snooping Explicit-tracking informationVlan Source/GroupIntf Reporter Uptime Last-Join ExpiresSwitch#This occurs when the command is issued for a specific VLAN.
Workaround: None
•
CSCti87650
Symptom:On a Cisco Nexus 5000, the output of the command "show interface fc<x/y> capabilities" may indicate that "Class 2 sequential delivery" and "BB state change notification" are supported when in fact they are not supported. The command "show interface fc<x/y> capabilities" has to be executed
Workaround: This issue is resolved..
Workaround: No workaround is available. It's just a display issue which should be ignored.
•
CSCti91712
Symptom: Nexus 5000 implementation of igmp snooping needs to be consistent with Nexus 7000
Workaround: None
•
CSCtj10418
Symptom: When peer Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switches are configured with switch-profile for configuration sync functionality, and merge for the first time, merge fails if the switch-profile configuration between the peer switches do not match.
Workaround: After a merge failure, correct the offending configuration before issuing a commit.
•
CSCtj24599
Symptom: Deleting a switch-profile using 'no switch-profile local-config | all-config' doesn't removes the configuration applied under switch-profile. The issue has been sporadically seen on 5548 which has dual core CPU.
Workaround:The leftover configuration needs to be manually removed.
•
CSCtj27351
Symptom: Sometimes "show switch-profile <name> status" or "show switch-profile <name> status commit" displays error message in truncated form.
switch(config-sync-sp)# show switch-profile test statusswitch-profile : test----------------------------------------------------------
Start-time: 876054 usecs after Fri Oct 15 05:30:35 2010End-time: 939787 usecs after Fri Oct 15 05:30:54 2010Profile-Revision: 16Session-type: CommitSession-subtype: -Peer-triggered: NoProfile-status: Commit FailedLocal information:----------------Status: Commit FailureError(s):Failed command(s):interface Ethernet1/12inherit port-profile xERROR: Operation Inherit Interface failednfiguring active mode << Error message truncated here.Peer information:----------------IP-address: 10.65.121.100Sync-status: In Sync.Status: Commit FailureError(s):Failed command(s):interface Ethernet1/12Syntax error while parsing ' inherit port-profile x'This occurs when switch-profile buffer contains port-profile configuration and the following commit fails due to port-profile config and ppm returns error.
Workaround: None.There is no functionality impact and only the display issue in show command output.
•
CSCtj27662
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5548 iIn NPV mode, TNP ports may take more than a minute to come up the first time after a reload. The switch has to be Nexus 5548 and NPV should be enabled.
Workaround: None. This happens only the first time after reload.
•
CSCtj29657
Symptom: System does not throw an error when two classes are configured as priority in switch-port profile, it throws an error when user configures in config-terminal.
Workaround:Don't configure two classes as priority in switch-port profile.
•
CSCtj31760
Symptom: If the beacon is enabled on the interface and the switch is reloaded, the interface beacon stops blinking even though the running configurations shows it as enabled.The beacon needs to be configured at interface level configuration and a reload needs to be done
Workaround:Disable and re-enable the beacon configuration on the interface to enable the port beacon.
•
CSCtj39025
Symptom: After upgrading to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch, if the partner side of the LACP port channel is configured as lacp rate fast and there are more than 10 ports connected through a Cisco Nexus 2148 Fabric Extender, these ports flap periodically. The partner side of the LACP port channel is configured as lacp rate fast. The Cisco Nexus 2148 image is upgraded through ISSU.
Workaround: Reload Cisco Nexus 2148 Fabric Extender or configure the 10 or less ports at a time on the partner.
•
CSCtj40413
Symptom: When checkpoints are deleted using the clear checkpoint database command, subsequent verify/commit operation from switch-profile fails with the following error:
Failed: Rollback in progress.Workaround: Delete every checkpoint file individually using the no checkpoint <name> command and create another checkpoint after using the clear checkpoint database command.
•
CSCtj46045
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series may crash when the Fabric Extender (chassis) IDs for 2 Fabric Extenders are exchanged.
Workaround: Perform a shut on the fabric ports of the Fabric Extenders before exchanging the Fabric Extender IDs and perform a no shut after the Fabric Extender IDs are exchanged.
•
CSCtj46688
Symptom: Very short power cuts / fluctuations on the power grid in the DC may trigger a reload of the FEX. However, in certain situations the FEX does not reboot. It remains "stuck" and the blue locater led stays on. This occurs when the reload is triggered by very short power cut / fluctuations. (typically seen when no UPS is used
Workaround: Turn off the power to the FEX for five seconds and power it back up.
•
CSCtj56177
Symptom: After a downgrade from Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) to a Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1(3)N1 or Release 4.1(3)N2 , class-ip-multicast or class-all-flood is lost from type qos policymaps. This causes all traffic mapped to such classes to be classified to other classes in the type qos policymap. This occurs only when the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch is downgraded from Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) to Cisco NX-OS Release 4.1(3)N1 or Release 4.1(3)N2.
Workaround: Reconfigure class-ip-multicast and class-all-flood classes in the type qos policy-maps after downgrading to the Cisco NX-OS 4.1(3)N based releases
•
CSCtj65732
Symptom: Peer keep-alive syslog messages are missing.
Workaround: None
•
CSCtj71171
Symptom: Upgrade from Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1) to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) failing. N5K stuck in a boot loop. The service "port-profile" is causing the reload. This occurs when the Found Banner motd not being left justified.
Workaround: 1) Ensure that the banner motd text is left aligned with no preceding spaces.
Example:
banner motd #No Unauthorized Access#Remove the preceding spaces to become left-aligned:
banner motd #No Unauthorized Access#2) Downgrade to Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1) and remove the Banner. Then retry the upgrade to NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1).
3) Perform a 'write erase', after which the device wont be in a boot loop. You can then paste your configuration back - however be sure to either remove the banner motd text or modify it to become left-aligned.
•
CSCtj77234
Symptom: The command "enable" is not available after rebooting the switch even though "feature privilege" appears in the configuration. This has been observed on NX-OS 5.0.2 and 5.0.3 on both Nexus 5000 and Nexus 7000.
Workaround: Remove and re-add "feature privilege".
•
CSCtj86759
Symptom:
Nexus5000 do not see LLDP neighbour that do use Organization specific unknown TLV. Those LLDP packet should be accepted even if some TLV's are unknown.
LLDP packets are dropped with totla unrecognized TLV error :
(config)# sh lldp traffic int ethernet 1/16LLDP interface traffic statistics:Total frames transmitted: 11473Total entries aged: 0*Total frames received: 11323*Total frames received in error: 0*Total frames discarded: 11323*Total unrecognized TLVs: 11323Workaround: None
•
CSCtj88849
Symptom:
When a VLAN is simultaneously added to the vpc peer-link and other vpc ports it does not pass traffic, suspended by a vpc.
Example:
Port-channel 100 is configured as a vpc peer-link and port-channel 101-102 areconfigured as vpcsSwitch(config)# interface Port-channel 100-102Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 123VLAN 123 may not become operational on port channels 101 and 102.
Workaround:
1) As a best practice, the VLAN needs to be operational on the vpc peer-link first before it can brought on vpc ports. In the above example, the configuration needs to be broken up in to three steps.
Configure the vpc peer-link
Switch(config)# interface Port-channel 100Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 123Check the status on vpc peer-link
Ensure vlan 123 is operational on vpc peer-link using "show vpc"Configure the vpc ports
Switch(config)# interface Port-channel 101-102Switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan add 1232) Remove and re-add the VLAN to the nexus 5000 pair.
switch(config)#no vlan 123switch(config)#vlan 123Resolved CaveatsCisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)
This section lists the resolved caveats for this release.
•
CSCte95521
Symptom: When both vPC peer switches are powered down and only one is brought back up, the ports are in suspended mode.
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti03176
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch fails in fcoe_mgr when attempting to bind a vFC interface to an Ethernet interface. This can occur when an RBAC role is created for a SAN administrator without access to the vFC interfaces.
Workaround: Avoid conflicting role assignments in user accounts, or, for the san-admin role, add permissions for interface vfc1-8192 as shown in the following example:
role name san-admindescription SAN/FC/FCoE Administratorvlan policy denypermit vlan 200-200interface policy denypermit interface fc1/1-4permit interface Ethernet1/1-20permit interface vfc1-8192•
CSCti23241
Symptom: The spanning tree TCN counters return to zero after 59:59:59
Workaround: None.
•
CSCti38091
Symptom: If a release prior to the Cisco NX-OS 5.0(2)N1(1) release has virtual FC interfaces in the down state, when you upgrade to Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1), such virtual FC interfaces may become error disabled.
Workaround: This feature is designed for FCoE software starting Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) onwards
•
CSCti38455
Symptom:The DWRR scheduling on the Cisco Nexus 2248 and Cisco Nexus 2232 Fabric Extenders is not accurate. As a result, the class of traffic that presents more traffic is given a larger share of the bandwidth.
Workaround: Strict priority scheduling can be used (enter the priority keyword in the queuing policy command) to provide scheduling precedence.
•
CSCti62723
Symptom: An inconsistent MST spanning tree status exists between the vPC primary and secondary switches. This can occur with recent MST configuration changes when manually shutting vPC member ports or when the vPC secondary switch reloads.
Workaround: Perform a shut/no shut on affected vPC member ports on the primary switch.
•
CSCti76612
Symptom: Slow throughput is observed for FCoE and FC traffic from a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch when using port 4 of the N5K-M1060 FC module in a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch. Poor performance is seen even on other Fiber Channel interfaces if port 4 is part of a SAN port channel.
Workaround: Do not use port 4 in the N5K-M1060 FC module. This issue is resolved in NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1).
•
CSCti87640
Symptom: On a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1) or earlier releases, FEX Active-Active interfaces may remain in the down or not connected state after repeated interface resets in a short duration of time. This occurs when a Cisco Nexus 2148 Fabric Extender or Nexus 2248 Fabric Extender is in an Active/Active topology and the high debounce timer is configured on the FEX interfaces.
Workaround: Issue a shut/no shut on the interface. This is resolved in NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) and later releases.
•
CSCti92608 N5k:
Symptom: In a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1) or NX-OS Release 5.2(1)N1(1), after an ISSU upgrade, newly configured vFCs do not come up for CNA's connected to a Cisco Nexus 2232 Fabric Extender or Ethernet expansion module.
This can occur when an ISSU upgrade is performed on a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch and after the switch comes up, FCoE is configured on the Cisco Nexus 2232 Fabric Extender and/or the Ethernet expansion module interfaces which were in a down or not connected state before the upgrade.
Workaround: Reload the Cisco Nexus 2232 Fabric Extender or the Ethernet expansion module. This issue is fixed in NX-OS 5.0(2)N1(1)and later releases.
•
CSCti96718
Symptom: a Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch running NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N2(1) might fail if a connected FEX does not come online.
Workaround: Make sure the FEX connected to the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch is configured correctly and comes online, or, do not do any SNMPget operations on the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch which is connected to a FEX that is not coming online.
•
CSCth18541 802.3
Symptom: The show interface Ex/y flowcontrol counters increment when receiving PFC Pause frames This can occur when working with Gen 1 CNA's.
Workaround: This issue is resolved.
Workaround: For a differientiated count of 802.3 Pause frames vs. PFC Pause frames, use the show hardware internal gatos port e1/3 | beg MAC command:
n5kswitch# show hardware internal gatos port e1/3 | beg MACRX_PKT_802.3x_PAUSE | 0x4bfaccRX_PKT_PER_PRIORITY_PAUSE | 0xc6758daRX_PKT_802.3x_PAUSE | 0x4bfaccRX_PKT_PER_PRIORITY_PAUSE | 0xc67b8e3•
CSCth81348
Symptom: A port fails and goes into the "Internal-Fail errDisable" state. This occurs when cable is removed from a server that is connected to a Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender interface which is part of a vPC.
Workaround: Reload the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch.
•
CSCtj44836
Symptom: A Cisco Nexus 5000 Series switch can fail in an LACP process associated with a memory leak in the LACP process. This can occur when running an LACP port channel on the switch.
Workaround: Disable LACP temporarily. This issue is fixed in NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)and later releases.
•
CSCtk15683
Symptom: Multiple multicast streams hash to a single member of a 4-port port channel which causes interface oversubscription and traffic drops. This issue is rare when there are more multicast streams, more fan out, and lower traffice rate.
Workaround: None.
Documentation Updates
Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1) supports the BRIDGE-MIB topologychange and newRoot, but the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide for Release 5.0(2)N1(1) cannot be updated to reflect this information.
Use the following commands to enable these traps:
•
snmp-server enable traps bridge newroot command
•
snmp-server enable traps bridge topologychange command
Related Documentation
Documentation for Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switches and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps9670/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
The following are related Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender documents:
Release Notes
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Release Notes
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch Release Notes
Configuration Guides
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Configuration Limits for Cisco NX-OS Release 5.0(2)N1(1)
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Configuration Limits for Cisco NX-OS Release 4.2(1)N1(1) and Release 4.2(1)N2(1)
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Fibre Channel over Ethernet Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Quality of Service Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS SAN Switching Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Security Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switch NX-OS Software Configuration Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Fabric Manager Configuration Guide, Release 3.4(1a)
Cisco Nexus 7000 Series NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide, Release 4.2
Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender Software Configuration Guide
Maintain and Operate Guides
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Operations Guide
Installation and Upgrade Guides
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 5500 Platform Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series NX-OS Software Upgrade and Downgrade Guide, Release 4.2(1)N1(1)
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Switches and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extenders
Licensing Guide
Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide
Command References
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series Command Reference
Technical References
Cisco Nexus 5000 Series and Cisco Nexus 2000 Series Fabric Extender MIBs Reference
Error and System Messages
Cisco NX-OS System Messages Reference
Troubleshooting Guide
Cisco Nexus 5000 Troubleshooting Guide
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What's New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently supports RSS Version 2.0.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
©2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback