- Index
- New and Changed Information
- Preface
- Overview
- Configuring FIPS
- Configuring Users and Common Roles
- Configuring RADIUS and TACACS+
- Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 Access Control Lists
- Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates
- Configuring IPSec Network Security
- Configuring FC-SP and DHCHAP
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring Fabric Binding
- Configuring Cisco TrustSec Fibre Channel Link Encryption
Cisco Fabric Manager Security Configuration Guide
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- January 10, 2011
Chapter: Configuring Users and Common Roles
Configuring Users and Common Roles
The CLI and SNMP use common roles in all switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family. You can use the CLI to modify a role that was created using SNMP and vice versa.
Users, passwords, and roles for all CLI and SNMP users are the same. A user configured through the CLI can access the switch using SNMP (for example, the Fabric Manager or the Device Manager) and vice versa.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•![]() Recovering the Administrator Password
Recovering the Administrator Password
•![]() Configuring Cisco ACS Servers
Configuring Cisco ACS Servers
Role-Based Authorization
Switches in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family perform authentication based on roles. Role-based authorization limits access to switch operations by assigning users to roles. This kind of authentication restricts you to management operations based on the roles to which you have been added.
When you execute a command, perform command completion, or obtain context-sensitive help, the switch software allows the operation to progress if you have permission to access that command.
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Configuring Roles and Profiles
Configuring Roles and Profiles
•![]() About Rules and Features for Each Role
About Rules and Features for Each Role
•![]() Displaying Role-Based Information
Displaying Role-Based Information
About Roles
Each role can contain multiple users and each user can be part of multiple roles. For example, if role1 users are only allowed access to configuration commands, and role2 users are only allowed access to debug commands, then if Joe belongs to both role1 and role2, he can access configuration as well as debug commands.

Note ![]() If you belong to multiple roles, you can execute a union of all the commands permitted by these roles. Access to a command takes priority over being denied access to a command. For example, suppose you belong to a TechDocs group and you were denied access to configuration commands. However, you also belong to the engineering group and have access to configuration commands. In this case, you will have access to configuration commands.
If you belong to multiple roles, you can execute a union of all the commands permitted by these roles. Access to a command takes priority over being denied access to a command. For example, suppose you belong to a TechDocs group and you were denied access to configuration commands. However, you also belong to the engineering group and have access to configuration commands. In this case, you will have access to configuration commands.

Tip ![]() Any role, when created, does not allow access to the required commands immediately. The administrator must configure appropriate rules for each role to allow access to the required commands.
Any role, when created, does not allow access to the required commands immediately. The administrator must configure appropriate rules for each role to allow access to the required commands.
Configuring Roles and Profiles
To create an additional role or to modify the profile for an existing role using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
You see the information as shown in Figure 3-1
Figure 3-1 Roles Tab in Users and Roles Screen
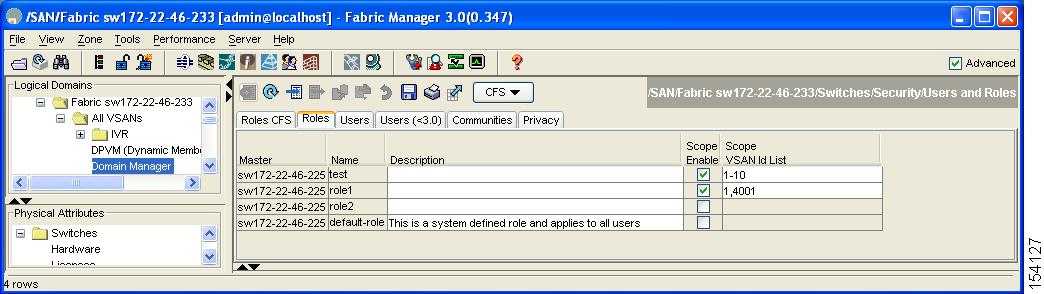
Step 2 ![]() Click Create Row to create a role in Fabric Manager.
Click Create Row to create a role in Fabric Manager.
You see the Create Roles dialog box in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Create Roles Dialog Box
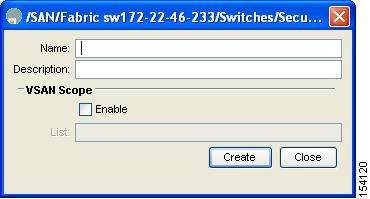
Step 3 ![]() Select the switches on which to configure a role.
Select the switches on which to configure a role.
Step 4 ![]() Enter the name of the role in the Name field.
Enter the name of the role in the Name field.
Step 5 ![]() Enter the description of the role in the Description field.
Enter the description of the role in the Description field.
Step 6 ![]() (Optional) Check the Enable check box to enable the VSAN scope and enter the list of VSANs in the Scope field to which you want to restrict this role.
(Optional) Check the Enable check box to enable the VSAN scope and enter the list of VSANs in the Scope field to which you want to restrict this role.
Step 7 ![]() Click Create to create the role, or click Close to close the Roles - Create dialog box without creating the common role.
Click Create to create the role, or click Close to close the Roles - Create dialog box without creating the common role.

Note ![]() Device Manager automatically creates six roles that are required for Device Manager to display a view of a switch. These roles are system, snmp, module, interface, hardware, and environment.
Device Manager automatically creates six roles that are required for Device Manager to display a view of a switch. These roles are system, snmp, module, interface, hardware, and environment.
Deleting Common Roles
To delete a common role using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the role you want to delete.
Click the role you want to delete.
Step 3 ![]() Click Delete Row to delete the common role.
Click Delete Row to delete the common role.
Step 4 ![]() Click Yes to confirm the deletion or No to cancel it.
Click Yes to confirm the deletion or No to cancel it.
About the VSAN Policy
Configuring the VSAN policy requires the ENTERPRISE_PKG license (For more information, see Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Licensing Guide).
You can configure a role so that it only allows tasks to be performed for a selected set of VSANs. By default, the VSAN policy for any role is permit, which allows tasks to be performed for all VSANs. You can configure a role that only allows tasks to be performed for a selected set of VSANs. To selectively allow VSANs for a role, set the VSAN policy to deny, and then set the configuration to permit or the appropriate VSANs.

Note ![]() Users configured in roles where the VSAN policy is set to deny cannot modify the configuration for E ports. They can only modify the configuration for F or FL ports (depending on whether the configured rules allow such configuration to be made). This is to prevent such users from modifying configurations that may impact the core topology of the fabric.
Users configured in roles where the VSAN policy is set to deny cannot modify the configuration for E ports. They can only modify the configuration for F or FL ports (depending on whether the configured rules allow such configuration to be made). This is to prevent such users from modifying configurations that may impact the core topology of the fabric.

Tip ![]() Roles can be used to create VSAN administrators. Depending on the configured rules, these VSAN administrators can configure MDS features (for example, zone, fcdomain, or VSAN properties) for their VSANs without affecting other VSANs. Also, if the role permits operations in multiple VSANs, then the VSAN administrators can change VSAN membership of F or FL ports among these VSANs.
Roles can be used to create VSAN administrators. Depending on the configured rules, these VSAN administrators can configure MDS features (for example, zone, fcdomain, or VSAN properties) for their VSANs without affecting other VSANs. Also, if the role permits operations in multiple VSANs, then the VSAN administrators can change VSAN membership of F or FL ports among these VSANs.
Users belonging to roles in which the VSAN policy is set to deny are referred to as VSAN-restricted users.
Modifying the VSAN Policy
To modify the VSAN policy for an existing role using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Check the Scope Enable check box if you want to enable the VSAN scope and restrict this role to a subset of VSANs.
Check the Scope Enable check box if you want to enable the VSAN scope and restrict this role to a subset of VSANs.
Step 3 ![]() Enter the list of VSANs in the Scope VSAN Id List field that you want to restrict this role to.
Enter the list of VSANs in the Scope VSAN Id List field that you want to restrict this role to.
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click Undo Changes to discard any unsaved changes.
About Rules and Features for Each Role
Up to 16 rules can be configured for each role. These rules reflect what CLI commands are allowed. The user-specified rule number determines the order in which the rules are applied. For example, rule 1 is applied before rule 2, which is applied before rule 3, and so on. A user not belonging to the network-admin role cannot perform commands related to roles.
For example, if user A is permitted to perform all show CLI commands, user A cannot view the output of the show role CLI command if user A does not belong to the network-admin role.
A rule specifies operations that can be performed by a specific role. Each rule consists of a rule number, a rule type (permit or deny), a CLI command type (for example, config, clear, show, exec, debug), and an optional feature name (for example, FSPF, zone, VSAN, fcping, or interface).

Note ![]() In this case, exec CLI commands refer to all commands in the EXEC mode that do not fall in the show, debug, and clear CLI command categories.
In this case, exec CLI commands refer to all commands in the EXEC mode that do not fall in the show, debug, and clear CLI command categories.
Modifying Rules
To modify the rules for an existing role using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Click Security > Roles.
Click Security > Roles.
Step 2 ![]() You see the Common Roles dialog box shown in Figure 3-3.
You see the Common Roles dialog box shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Common Roles Dialog Box in Device Manager
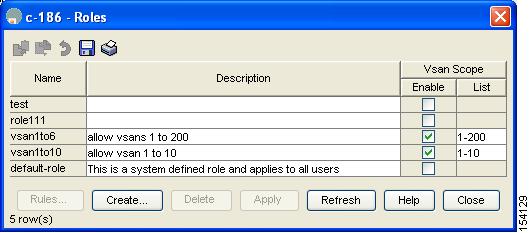
Step 3 ![]() Click the role for which you want to edit the rules.
Click the role for which you want to edit the rules.
Step 4 ![]() Click Rules to view the rules for the role.
Click Rules to view the rules for the role.
You see the Rules dialog box shown in Figure 3-4. It may take a few minutes to display.
Figure 3-4 Edit Common Role Rules Dialog Box
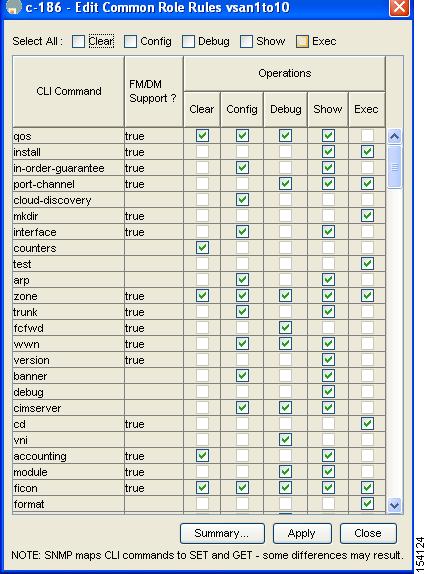
Step 5 ![]() Edit the rules you want to enable or disable for the common role.
Edit the rules you want to enable or disable for the common role.
Step 6 ![]() Click Apply to apply the new rules and close the Rules dialog box, or click Close to close the Rules dialog box without applying the rules.
Click Apply to apply the new rules and close the Rules dialog box, or click Close to close the Rules dialog box without applying the rules.
Rule 1 is applied first, which permits, for example, sangroup users access to all config CLI commands. Rule 2 is applied next, denying FSPF configuration to sangroup users. As a result, sangroup users can perform all other config CLI commands, except fspf CLI configuration commands.

Note ![]() The order of rule placement is important. If you had swapped these two rules and issued the deny config feature fspf rule first and issued the permit config rule next, you would be allowing all sangroup users to perform all configuration commands because the second rule globally overrode the first rule.
The order of rule placement is important. If you had swapped these two rules and issued the deny config feature fspf rule first and issued the permit config rule next, you would be allowing all sangroup users to perform all configuration commands because the second rule globally overrode the first rule.
Displaying Role-Based Information
The rules are displayed by rule number and are based on each role. All roles are displayed if the role name is not specified.
To view rules for a role using Device Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Click Security > Roles.
Click Security > Roles.
You see the Roles dialog box.
Step 2 ![]() Select a role name and click Rules.
Select a role name and click Rules.
You see the Rules dialog box.
Step 3 ![]() Click Summary to get a summarized view of the rules configured for this role.
Click Summary to get a summarized view of the rules configured for this role.
Role Distributions
Role-based configurations use the Cisco Fabric Services (CFS) infrastructure to enable efficient database management, and to provide a single point of configuration for the entire fabric.
The following configurations are distributed:
•![]() Role names and descriptions
Role names and descriptions
•![]() List of rules for the roles
List of rules for the roles
•![]() VSAN policy and the list of permitted VSANs
VSAN policy and the list of permitted VSANs
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Displaying Roles When Distribution is Enabled
Displaying Roles When Distribution is Enabled
About Role Databases
Role-based configurations use two databases to accept and implement configurations.
•![]() Configuration database—The running database currently enforced by the fabric.
Configuration database—The running database currently enforced by the fabric.
•![]() Pending database—Your subsequent configuration changes are stored in the pending database. If you modify the configuration, you need to commit or discard the pending database changes to the configuration database. The fabric remains locked during this period. Changes to the pending database are not reflected in the configuration database until you commit the changes.
Pending database—Your subsequent configuration changes are stored in the pending database. If you modify the configuration, you need to commit or discard the pending database changes to the configuration database. The fabric remains locked during this period. Changes to the pending database are not reflected in the configuration database until you commit the changes.
Locking the Fabric
The first action that modifies the database creates the pending database and locks the feature in the entire fabric. Once you lock the fabric, the following situations apply:
•![]() No other user can make any configuration changes to this feature.
No other user can make any configuration changes to this feature.
•![]() A copy of the configuration database becomes the pending database along with the first change.
A copy of the configuration database becomes the pending database along with the first change.
Committing the Changes
If you commit the changes made to the pending database, the configuration is committed to all the switches in the fabric. On a successful commit, the configuration change is applied throughout the fabric and the lock is released. The configuration database now contains the committed changes and the pending database is now cleared.
To commit role-based configuration changes using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
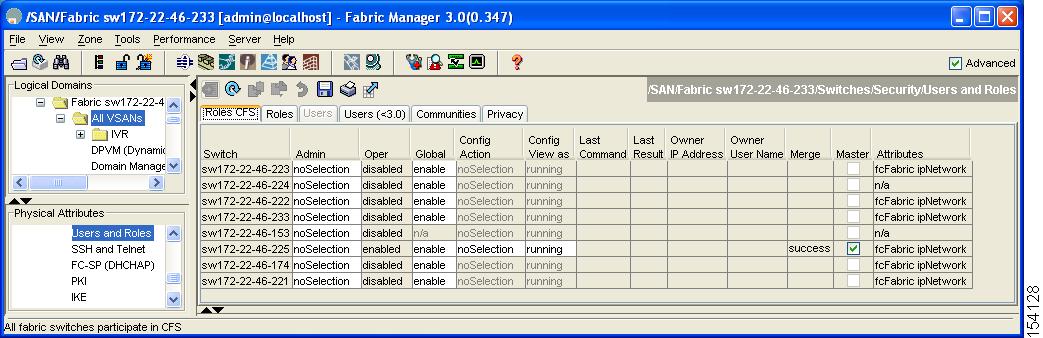
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
You see the screen shown in Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 Roles CFS Tab
Step 2 ![]() Set the Global drop-down menu to enable to enable CFS.
Set the Global drop-down menu to enable to enable CFS.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Step 4 ![]() Set the Config Action drop-down menu to commit to commit the roles using CFS.
Set the Config Action drop-down menu to commit to commit the roles using CFS.
Step 5 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Discarding the Changes
If you discard (abort) the changes made to the pending database, the configuration database remains unaffected and the lock is released.
To discard role-based configuration changes using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Set the Config Action drop-down menu to abort to discard any uncommitted changes.
Set the Config Action drop-down menu to abort to discard any uncommitted changes.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Enabling Distribution
To enable role-based configuration distribution using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Set the Global drop-down menu to enable to enable CFS distribution.
Set the Global drop-down menu to enable to enable CFS distribution.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Clearing Sessions
To forcibly clear the existing role session in the fabric using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Set the Config Action drop-down menu to clear to clear the pending database.
Set the Config Action drop-down menu to clear to clear the pending database.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.

Note ![]() Any changes in the pending database are lost when you clear a session.
Any changes in the pending database are lost when you clear a session.
Database Merge Guidelines
Fabric merge does not modify the role database on a switch. If two fabrics merge, and the fabrics have different role databases, the software generates an alert message.
•![]() Verify that the role database is identical on all switches in the entire fabric.
Verify that the role database is identical on all switches in the entire fabric.
•![]() Be sure to edit the role database on any switch to the desired database and then commit it. This synchronizes the role databases on all the switches in the fabric.
Be sure to edit the role database on any switch to the desired database and then commit it. This synchronizes the role databases on all the switches in the fabric.
Displaying Roles When Distribution is Enabled
When you enable distribution for roles, you can view either the pending role database (the database before it is distributed) or the running database.
To view the roles using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane (see Figure 3-6).
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Roles CFS tab in the Information pane (see Figure 3-6).
Figure 3-6 Roles CFS Tab

Step 2 ![]() Set the Config View As drop-down value to pending to view the pending database or set the Config View drop-down menu to running to view the running database.
Set the Config View As drop-down value to pending to view the pending database or set the Config View drop-down menu to running to view the running database.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
User Accounts
Every Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch user has the account information stored by the system. Your authentication information, user name, user password, password expiration date, and role membership are stored in your user profile.
The tasks explained in this section enable you to create users and modify the profile of an existing user. These tasks are restricted to privileged users as determined by your administrator.
The password should have the strong characteristics, such as the following:
•![]() Are at least eight characters long
Are at least eight characters long
•![]() Not contain many consecutive characters (such as "abcd")
Not contain many consecutive characters (such as "abcd")
•![]() Not contain many repeating characters (such as "aaabbb")
Not contain many repeating characters (such as "aaabbb")
•![]() Not contain dictionary words
Not contain dictionary words
•![]() Contain both upper- and lowercase characters
Contain both upper- and lowercase characters
•![]() Contain numbers
Contain numbers
The following are examples of strong passwords:
•![]() If2CoM18
If2CoM18
•![]() 2004AsdfLkj30
2004AsdfLkj30
•![]() Cb1955S21
Cb1955S21

Note ![]() Clear test passwords can only contain alphanumeric characters. Special characters such as the dollar sign ($) or the percent sign (%) are not allowed.
Clear test passwords can only contain alphanumeric characters. Special characters such as the dollar sign ($) or the percent sign (%) are not allowed.
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() Displaying User Account Information
Displaying User Account Information
Creating Users Guidelines
The passphrase specified in the snmp-server user option and the password specified username option are synchronized .
By default, the user account does not expire unless you explicitly configure it to expire. The expire option determines the date on which the user account is disabled. The date is specified in the YYYY-MM-DD format.
When creating users, note the following guidelines:
•![]() The following words are reserved and cannot be used to configure users: bin, daemon, adm, lp, sync, shutdown, halt, mail, news, uucp, operator, games, gopher, ftp, nobody, nscd, mailnull, rpc, rpcuser, xfs, gdm, mtsuser, ftpuser, man, and sys.
The following words are reserved and cannot be used to configure users: bin, daemon, adm, lp, sync, shutdown, halt, mail, news, uucp, operator, games, gopher, ftp, nobody, nscd, mailnull, rpc, rpcuser, xfs, gdm, mtsuser, ftpuser, man, and sys.
•![]() User passwords are not displayed in the switch configuration file.
User passwords are not displayed in the switch configuration file.
•![]() If a password is trivial (short, easy-to-decipher), your password configuration is rejected. Be sure to configure a strong password as shown in the sample configuration. Passwords are case-sensitive. "admin" is no longer the default password for any Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch. You must explicitly configure a strong password.
If a password is trivial (short, easy-to-decipher), your password configuration is rejected. Be sure to configure a strong password as shown in the sample configuration. Passwords are case-sensitive. "admin" is no longer the default password for any Cisco MDS 9000 Family switch. You must explicitly configure a strong password.

Configuring Users
To configure a new user or to modify the profile of an existing user using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
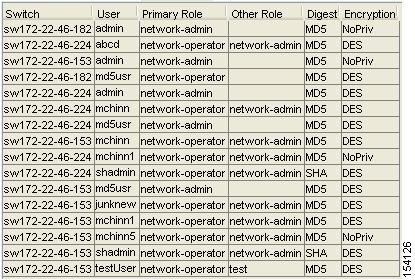
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users like the one in Figure 3-7.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users like the one in Figure 3-7.
Figure 3-7 Users Listed under the Users Tab
Step 2 ![]() Click Create Row.
Click Create Row.
You see the Create Users dialog box shown in Figure 3-8.
Figure 3-8 Create Users Dialog Box
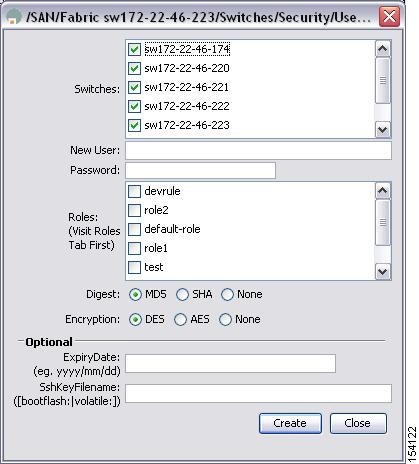
Step 3 ![]() (Optional) Alter the Switches check boxes to specify one or more switches.
(Optional) Alter the Switches check boxes to specify one or more switches.
Step 4 ![]() Enter the user name in the New User field.
Enter the user name in the New User field.
Step 5 ![]() Select a role from the Role drop-down menu. You can also enter a new role name in the field if you do not want to select one from the drop-down menu. If you do this, go back and configure this role appropriately (see the "User Accounts" section).
Select a role from the Role drop-down menu. You can also enter a new role name in the field if you do not want to select one from the drop-down menu. If you do this, go back and configure this role appropriately (see the "User Accounts" section).
Step 6 ![]() Enter the password for the user in the New Password and Confirm Password fields. Enter the same new password in the New Password and Confirm Password fields.
Enter the password for the user in the New Password and Confirm Password fields. Enter the same new password in the New Password and Confirm Password fields.
Step 7 ![]() Check the Privacy check box and complete the password fields to encrypt management traffic.
Check the Privacy check box and complete the password fields to encrypt management traffic.
Step 8 ![]() Click Create to create the entry or click Close to discard any unsaved changes and close the dialog box.
Click Create to create the entry or click Close to discard any unsaved changes and close the dialog box.
Changing Administrator Password Using Fabric Manager
To change the administrator password in Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Click the Open tab in the control panel.
Click the Open tab in the control panel.
Step 2 ![]() Choose the password field to change the password for an already existing user for the fabric.
Choose the password field to change the password for an already existing user for the fabric.
Step 3 ![]() Click Open to open the fabric.
Click Open to open the fabric.

Note ![]() New password will be saved after the fabric is open. The user name and password fields are editable in the Fabric tab only after you unmanage the fabric.
New password will be saved after the fabric is open. The user name and password fields are editable in the Fabric tab only after you unmanage the fabric.
Deleting a User
To delete a user using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see a list of users.
Step 2 ![]() Click the name of the user you want to delete.
Click the name of the user you want to delete.
Step 3 ![]() Click Delete Row to delete the selected user.
Click Delete Row to delete the selected user.
Step 4 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Click Apply Changes to save this change.
Displaying User Account Information
To display configured information about user accounts using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane.
Expand Security and then select Users and Roles in the Physical Attributes pane.
Step 2 ![]() Click the Users tab. You see the list of SNMP users shown in Figure 3-9 in the Information pane.
Click the Users tab. You see the list of SNMP users shown in Figure 3-9 in the Information pane.
Figure 3-9 Users Listed under the Users Tab

SSH Services
The Telnet service is enabled by default on all Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches. Before enabling the SSH service, generate a server key pair (see the "Generating the SSH Server Key Pair" section).
This section includes the following topics:
•![]() About the SSH Server Key Pair
About the SSH Server Key Pair
•![]() Generating the SSH Server Key Pair
Generating the SSH Server Key Pair
•![]() Overwriting a Generated Key Pair
Overwriting a Generated Key Pair
•![]() Enabling SSH or Telnet Service
Enabling SSH or Telnet Service
•![]() SSH Authentication Using Digital Certificates
SSH Authentication Using Digital Certificates
About SSH
SSH provides secure communications to the Cisco NX-OS CLI. You can use SSH keys for the following SSH options:
•![]() SSH1
SSH1
•![]() SSH2 using RSA
SSH2 using RSA
•![]() SSH2 using DSA
SSH2 using DSA
About the SSH Server Key Pair
Be sure to have an SSH server key pair with the appropriate version before enabling the SSH service. Generate the SSH server key pair according to the SSH client version used. The number of bits specified for each key pair ranges from 768 to 2048.
The SSH service accepts three types of key pairs for use by SSH versions 1 and 2.
•![]() The rsa1 option generates the RSA1 key pair for the SSH version 1 protocol.
The rsa1 option generates the RSA1 key pair for the SSH version 1 protocol.
•![]() The dsa option generates the DSA key pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.
The dsa option generates the DSA key pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.
•![]() The rsa option generates the RSA key pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.
The rsa option generates the RSA key pair for the SSH version 2 protocol.

Caution
Generating the SSH Server Key Pair
To generate the SSH server key pair, follow these steps:
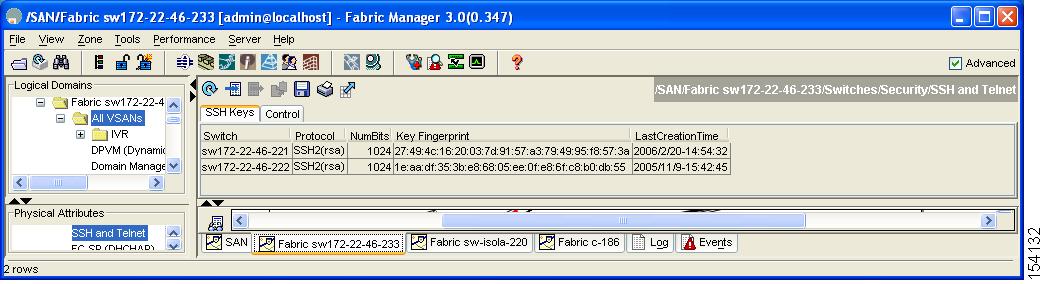
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
You see the configuration shown in Figure 3-10 in the Information pane.
Figure 3-10 SSH and Telnet Configuration
Step 2 ![]() Click Create Row.
Click Create Row.
You see the SSH and Telnet Key Create dialog box shown in Figure 3-11.
Figure 3-11 Create SSH and Telnet Dialog Box
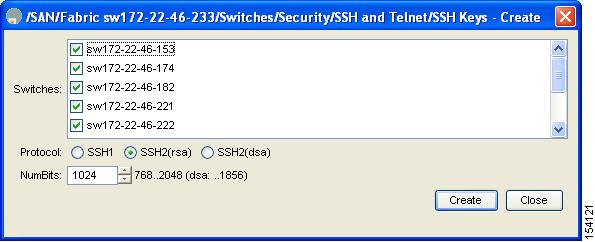
Step 3 ![]() Check the switches you want to assign to this SSH key pair.
Check the switches you want to assign to this SSH key pair.
Step 4 ![]() Choose the key pair option type from the listed Protocols. The listed protocols are SSH1, SSH2(rsa), and SSH2(dsa).
Choose the key pair option type from the listed Protocols. The listed protocols are SSH1, SSH2(rsa), and SSH2(dsa).
Step 5 ![]() Set the number of bits that will be used to generate the key pairs in the NumBits drop-down menu.
Set the number of bits that will be used to generate the key pairs in the NumBits drop-down menu.
Step 6 ![]() Click Create to generate these keys or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.
Click Create to generate these keys or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.

Note ![]() 1856 DSA NumberKeys are not supported by switches that running Cisco MDS NX-OS software version 4.1(1) and later.
1856 DSA NumberKeys are not supported by switches that running Cisco MDS NX-OS software version 4.1(1) and later.
Overwriting a Generated Key Pair
If the SSH key pair option is already generated for the required version, you can force the switch to overwrite the previously generated key pair.
To overwrite a previously generated key pair using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
You see the configuration in the Information pane.
Step 2 ![]() Highlight the key that you want to overwrite and click Delete Row.
Highlight the key that you want to overwrite and click Delete Row.
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click the Undo Changes to discard unsaved changes.
Click Apply Changes to save these changes or click the Undo Changes to discard unsaved changes.
Step 4 ![]() Click the Create Row.
Click the Create Row.
You see the SSH and Telnet Key Create dialog box.
Step 5 ![]() Check the switches you want to assign this SSH key pair.
Check the switches you want to assign this SSH key pair.
Step 6 ![]() Choose the key pair option type from the Protocols radio buttons.
Choose the key pair option type from the Protocols radio buttons.
Step 7 ![]() Set the number of bits that will be used to generate the key pairs in the NumBits drop-down menu.
Set the number of bits that will be used to generate the key pairs in the NumBits drop-down menu.
Step 8 ![]() Click Create to generate these keys or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.
Click Create to generate these keys or click Close to discard any unsaved changes.
Enabling SSH or Telnet Service
By default, the SSH service is disabled. Fabric Manager enables SSH automatically when you configure it.
To enable or disable SSH using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
Expand Switches > Security and then select SSH and Telnet.
Step 2 ![]() Select the Control tab and check an SSH check box or Telnet check box for each switch as shown in Figure 3-12.
Select the Control tab and check an SSH check box or Telnet check box for each switch as shown in Figure 3-12.
Figure 3-12 Control Tab under SSH and Telnet
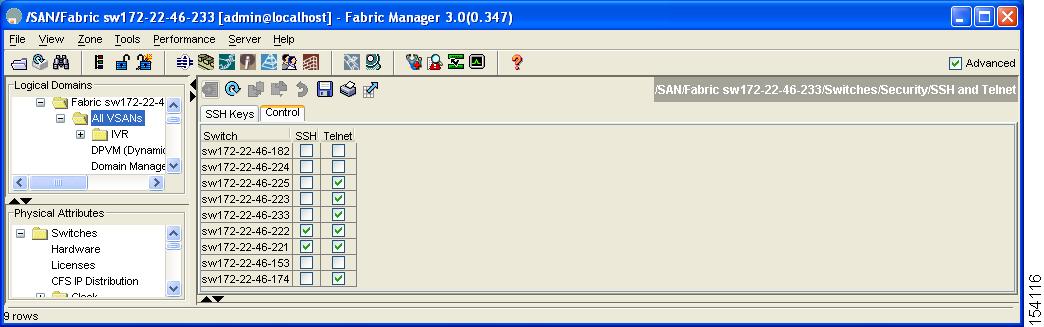
Step 3 ![]() Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard unsaved changes.
Click Apply Changes to save this change or click Undo Changes to discard unsaved changes.

Note ![]() If you are logging in to a switch through SSH and you have issued the aaa authentication login default none CLI command, you must enter one or more key strokes to log in. If you press the Enter key without entering at least one keystroke, your log in will be rejected.
If you are logging in to a switch through SSH and you have issued the aaa authentication login default none CLI command, you must enter one or more key strokes to log in. If you press the Enter key without entering at least one keystroke, your log in will be rejected.
SSH Authentication Using Digital Certificates
SSH authentication on the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches provide X.509 digital certificate support for host authentication. An X.509 digital certificate is a data item that vouches for the origin and integrity of a message. It contains encryption keys for secured communications and is "signed" by a trusted certification authority (CA) to verify the identity of the presenter. The X.509 digital certificate support provides either DSA or RSA algorithms for authentication.
The certificate infrastructure uses the first certificate that supports the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and is returned by the security infrastructure, either through query or notification. Verification of certificates is successful if the certificates are from any of the trusted CAs.
You can configure your switch for either SSH authentication using an X.509 certificate or SSH authentication using a Public Key Certificate, but not both. If either of them is configured and the authentication fails, you will be prompted for a password.
For more information on CAs and digital certificates, see Chapter 6, "Configuring Certificate Authorities and Digital Certificates."
Creating or Updating Users
Only the network-admin users are allowed to modify other user's privlieges.
To configure a new user or to modify the profile of an existing user using Fabric Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1 ![]() Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see the user information.
Expand Switches > Security and then select Users and Roles from the Physical Attributes pane. Click the Users tab in the Information pane to see the user information.
Step 2 ![]() Click Create Row to create a user.
Click Create Row to create a user.
You see the Create Users dialog box.
Step 3 ![]() Select the switches to which this user will be allowed access.
Select the switches to which this user will be allowed access.
Step 4 ![]() Assign a new user name and password.
Assign a new user name and password.

Note ![]() User account names must contain non-numeric characters.
User account names must contain non-numeric characters.
Step 5 ![]() Select the roles that you want to assign to this new user.
Select the roles that you want to assign to this new user.
Step 6 ![]() Select the digest and encryption for the user that you are creating or updating.
Select the digest and encryption for the user that you are creating or updating.
Step 7 ![]() (Optional) Enter an expiry date and an SSH file name for the user.
(Optional) Enter an expiry date and an SSH file name for the user.
Step 8 ![]() Click Create to create the user or Close to discard the changes.
Click Create to create the user or Close to discard the changes.
Recovering the Administrator Password
You can recover the administrator password using one of two methods:
•![]() From the CLI with a user name that has network-admin privileges.
From the CLI with a user name that has network-admin privileges.
•![]() Power cycling the switch.
Power cycling the switch.

Note ![]() To recover an administrator's password, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Security Configuration Guide.
To recover an administrator's password, refer to the Cisco MDS 9000 Family NX-OS Security Configuration Guide.
Configuring Cisco ACS Servers
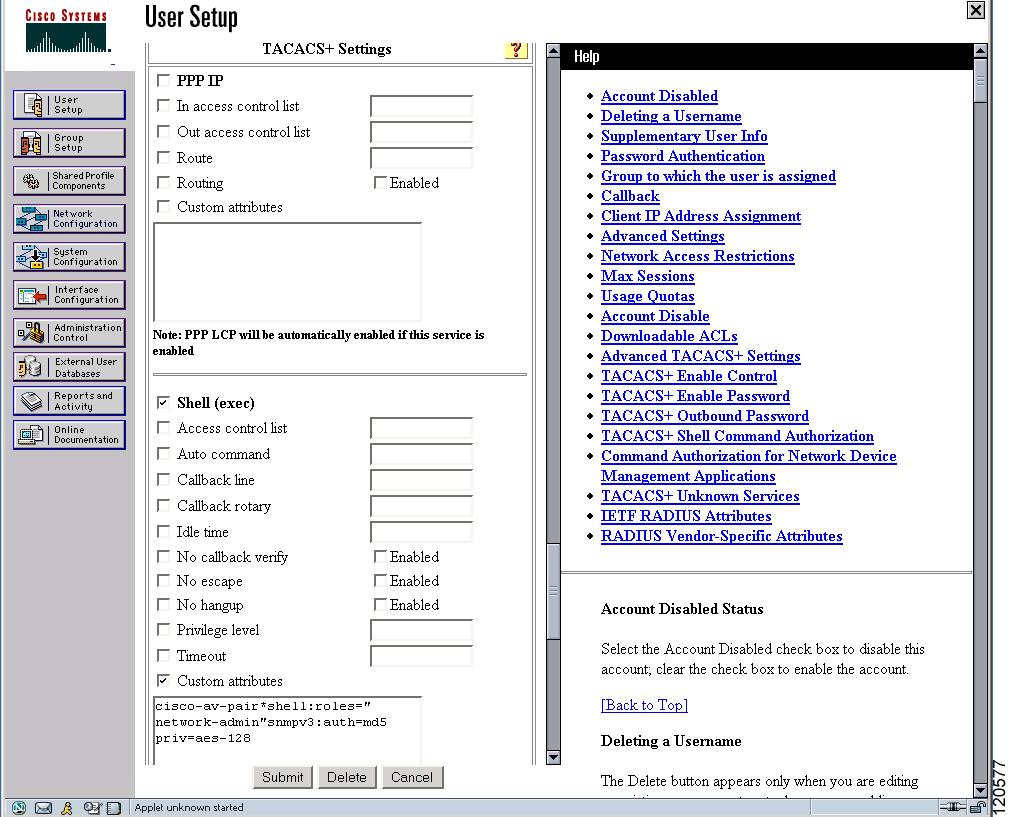
The Cisco Access Control Server (ACS) uses TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols to provide AAA services that ensure a secure environment. When using the AAA server, user management is normally done using Cisco ACS. Figure 3-13, Figure 3-14, Figure 3-15, and Figure 3-16 display ACS server user setup configurations for network-admin roles and multiple roles using either TACACS+ or RADIUS.


Note ![]() Each role specified in the cisco-av-pair must exist in the MDS, or the user will have the network-operator role.
Each role specified in the cisco-av-pair must exist in the MDS, or the user will have the network-operator role.
Figure 3-13 Configuring the Network-admin Role When Using RADIUS
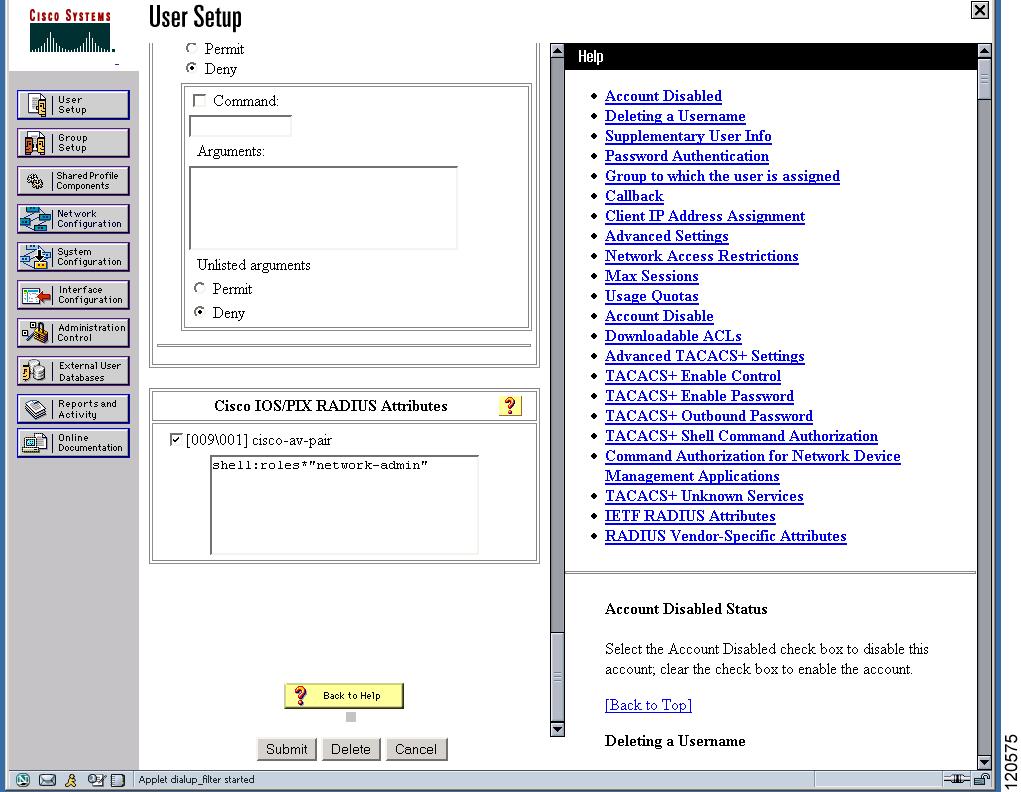
Figure 3-14 Configuring Multiple Roles with SNMPv3 Attributes When Using RADIUS
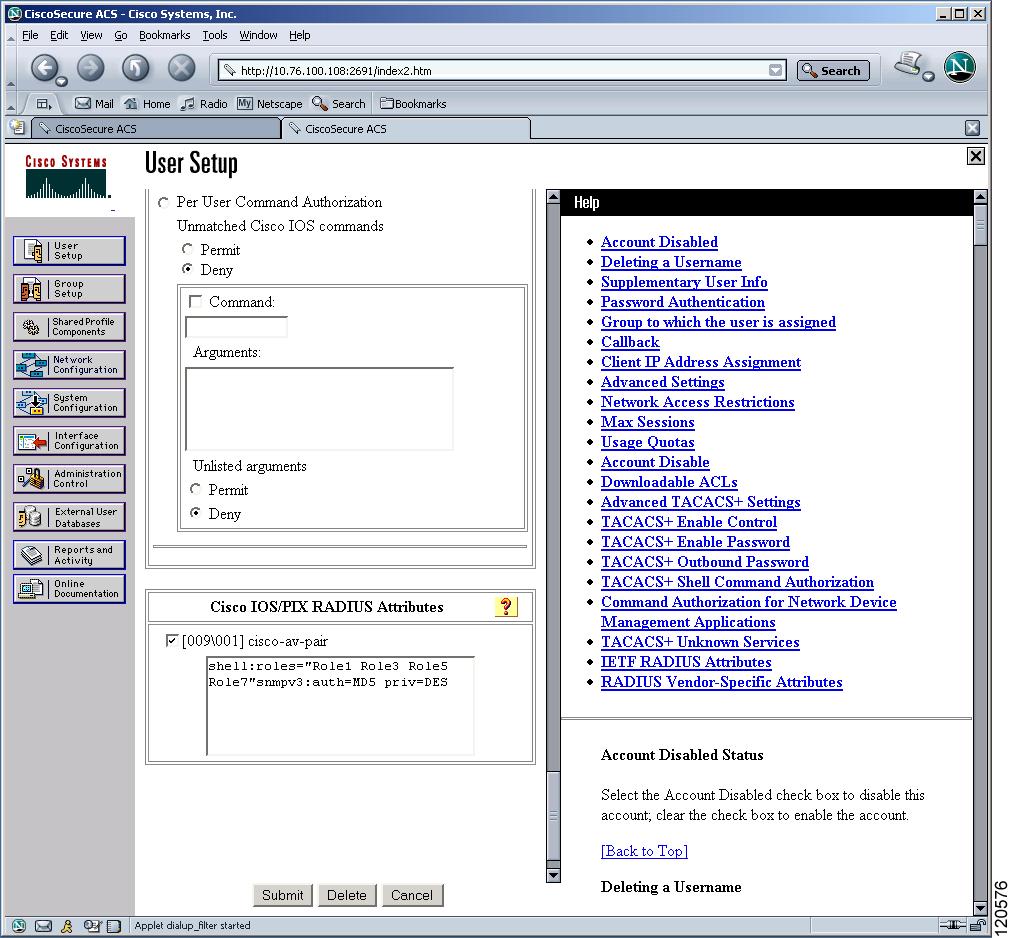
Figure 3-15 Configuring the network-admin Role with SNMPv3 Attributes When Using TACACS+
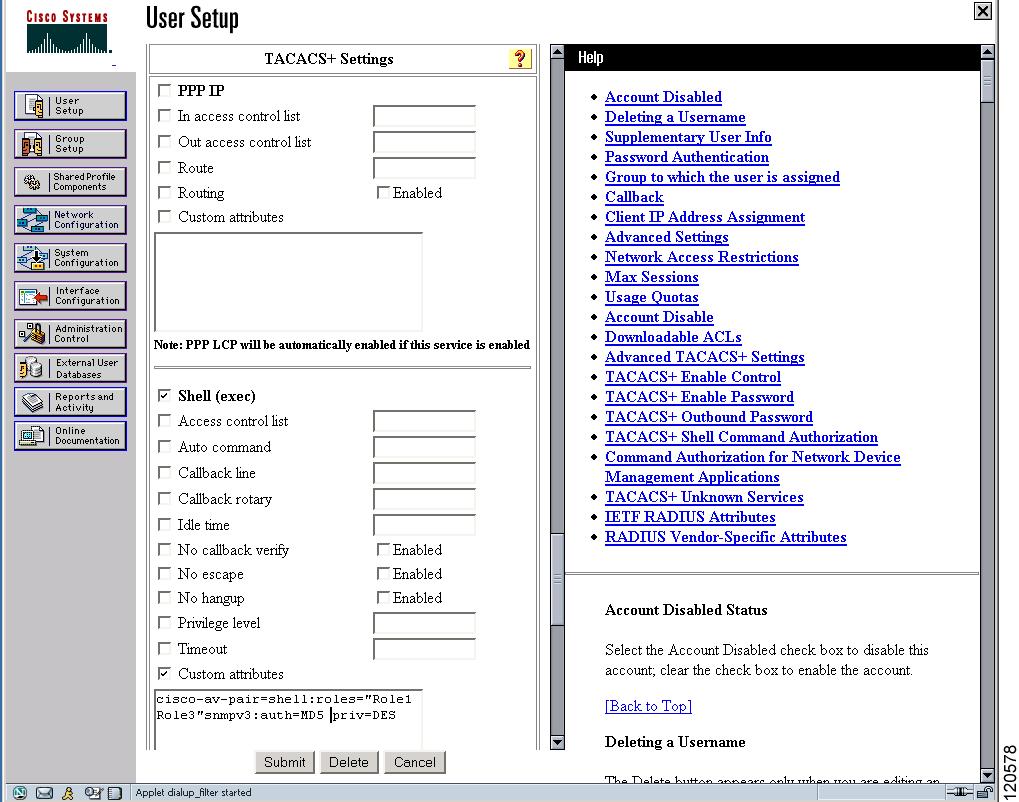
Figure 3-16 Configuring Multiple Roles with SNMPv3 Attributes When Using TACACS+
Default Settings
Table 3-1 lists the default settings for all switch security features in any switch.
 Feedback
Feedback