Zero Trust Microsegmentation-Agent and Agentless Workloads
Zero Trust Microsegmentation Journey
Secure Workload provides visibility into workload interactions, enabling automated policy recommendations tailored to the environment, providing flexibility to suit different business needs, and enabling secure migration to cloud and multi-cloud environments.
The Zero Trust microsegmentation journey in Cisco Secure Workload involves several key functions to restrict lateral movement to or from workloads and adopt a zero-trust security approach. With zero-trust microsegmentation, organizations can secure their applications and data centers by:
-
creating micro-perimeters at the workload level.
-
reducing the attack surface.
-
minimizing lateral movement and
-
identifying anomalous behaviors within the data center environment.

Traffic flow, package, and process visibility
Cisco Secure Workload employs both agent-based and agentless telemetry collection methods. With agent-based telemetry, the agent on the workload continuously monitors and reports on process activities, network flows, and vulnerabilities. The agents provide comprehensive visibility and control over the workload, therefore, enabling detailed forensic analysis and real-time monitoring. With agentless, it leverages the existing network infrastructure because workloads are dynamic and where administrative overhead needs to be minimized.
Both telemetry methods are designed to enhance security posture by providing insights into application behavior and potential vulnerabilities across the infrastructure.
In Cisco Secure Workload, there are two primary modes for traffic visibility: Detailed mode and Conversation mode, these two modes offer distinct features and levels of granularity in monitoring and analyzing network traffic.
To enable conversations mode, see the Flow Visibility Configuration section in: Software Agent Config.
The exact benefit gained by changing agents to report in conversation mode may vary due to multiple factors, including, but not limited to percentage of TCP flows, number of services listening on well-known service ports, and memory limitations at the agent.
After turning on conversations mode for some agents, there may be a mixture of conversations and flows in the observations on the Traffic Flow Search page.
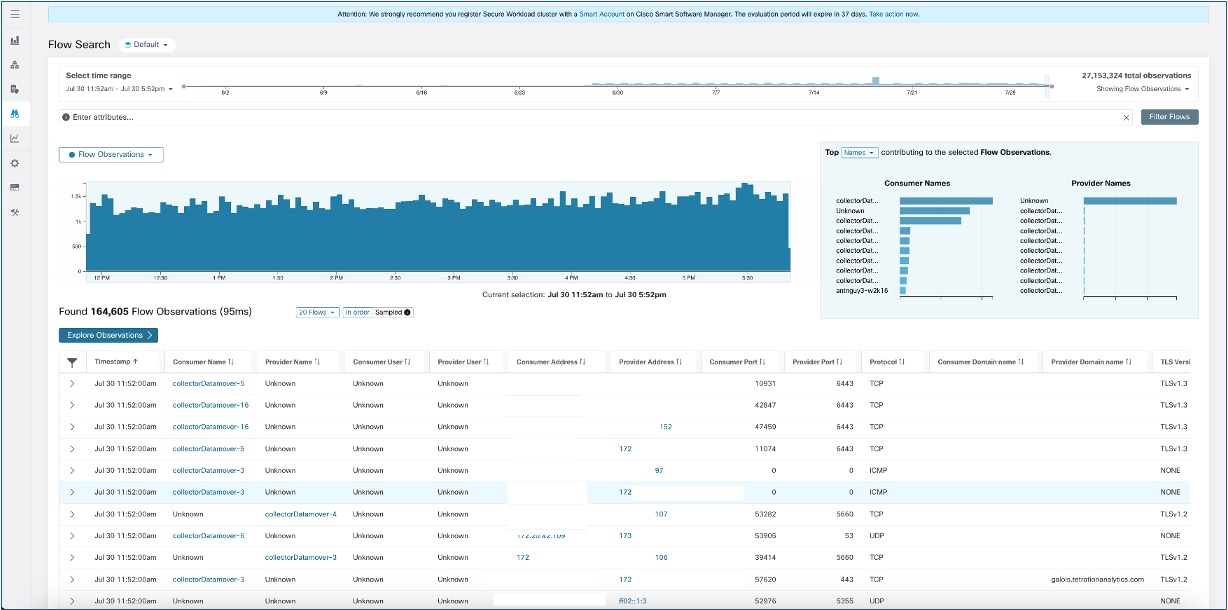
Contextual enrichment of ingested telemetry
Secure Workload provides comprehensive Zero Trust segmentation with detailed visibility at the flow, package, and processes through agents installed on hosts. This telemetry data is enriched with contextual labels from external systems—vCenter, Kubernetes, F5, Infoblox, DNS, and ServiceNow, enabling more precise policy generation.
Secure Workload automatically discovers segmentation policies based on the contextually enriched network flows and other telemetry data, ensuring consistent policy orchestration across various workload types, including bare-metal, virtual machines, and containers (Kubernetes). This capability extends to multiple cloud platforms, with Secure Workload supporting AWS, Azure, and GCP through agentless methods that leverage cloud-native security control, such as AWS security groups, Azure network security groups, and GCP's native network firewall. By integrating with Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), Secure Workload enhances user and device context, allowing for more granular policy enforcement. With Secure Workload, you can implement Zero Trust principles by automatically discovering and enforcing microsegmentation policies tailored to your specific application environments, thereby reducing the attack surface and mitigating risks associated with lateral movement.
Automatically discover segmentation policies
Secure Workload derives microsegmentation policies by analyzing application communication patterns and dependencies using machine learning techniques.
Secure Workload collects enriched telemetry data from software agents running on workloads or agentless sources—cloud flow logs, NetFlow, and NSEL logs. This provides comprehensive visibility into application interactions.
Machine learning algorithms analyze the collected telemetry data to identify application clusters and dependencies. This allows Secure Workload to automatically discover application communication patterns. Based on the discovered communication patterns, Secure Workload generates microsegmentation policies tailored to specific workloads. These policies are designed to restrict application access and enforce segmentation across data centers and multi-cloud environments. The generated policies are continuously validated against live traffic using machine learning. This ensures the policies remain effective and relevant as application behaviors evolve.
Secure Workload automatically updates the policies in real-time to keep pace with changes in the application landscape and cloud infrastructure updates. By leveraging machine learning to analyze application interactions, Secure Workload automatically derives microsegmentation policies that enables organizations to implement zero trust security and minimize the attack surface without manual policy management.
Consistent policy orchestration across workloads
Secure Workload provides consistent policy orchestration across cloud providers, AWS, Azure, and GCP. By leveraging contextual awareness through cloud tags and metadata, these capabilities ensure that security policies are applied uniformly, regardless of the underlying cloud infrastructure. This approach allows for agentless enforcement, utilizing built-in security controls, such as security groups in AWS, network security groups in Azure, and GCP's native network firewall. This level of consistency and adaptability helps organizations mitigate risks, reduce complexity, and streamline security management across their cloud-based workloads.
Audience
The intended audience for this use case includes:
-
Site Administrators
-
IT Administrators
-
Network or Cloud Security Engineers
Network Topology
With comprehensive visibility into every workload interaction and powerful AI or ML driven automation, Secure workload prevents lateral movement by reducing the attack surface, identifies workload behavior anomalies, helps rapidly remediate threats, and continuously monitors compliance.
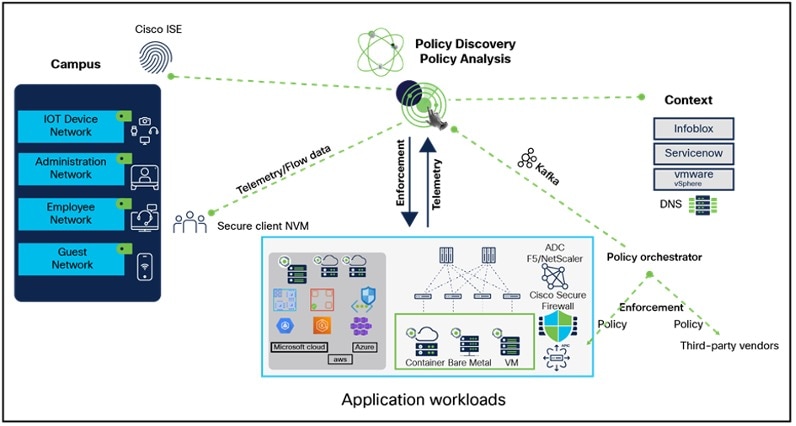
Zero Trust Microsegmentation
Business Scenario
A Financial organization is experiencing a significant increase in east-west traffic within the data center and between distributed systems, primarily due to the adoption of cloud technologies and the rise of remote work.
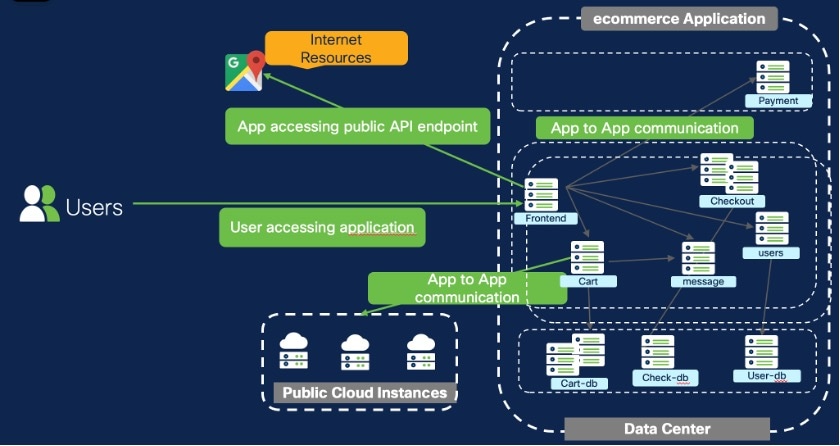
This has made it increasingly challenging to defend the network perimeter using traditional security models. The organization has identified the need to enhance its security posture, protect resources and control access based on user identity, roles, and context.
Microsegmentation and Zero Trust
Microsegmentation is the foundation for implementing a zero-trust security model for application workloads in the data center and cloud. The intent of microsegmentation in Cisco Secure Workload is to allow only the traffic your organization needs and block all other traffic. With microsegmentation, you can, therefore, optimize network connectivity, ensure data security, and streamline network administration.
Cisco Secure Workload offers zero trust microsegmentation through agent-based and agentless approaches. Agent-based solutions provide granular control over workloads, while agentless solutions leverage network traffic analysis for policy enforcement, ensuring comprehensive security across hybrid multicloud environments.
Agent-based and agentless microsegmentation are two approaches that can help businesses address the challenges posed by traffic surges.
Secure Workload Agent-Based Microsegmentation
Secure Workload agent-based solution provides visibility, microsegmentation, and zero-trust security and therefore ensures comprehensive protection and threat detection for workloads, containers, on-premises, and cloud environments.
Agent-based segmentation involves deploying software agents on individual workloads or endpoints within the network. This method offers the advantage of creating secure zones and enforcing tight access controls, thereby reducing the attack surface and improving breach containment.These agents monitor and enforce network security policies, ensuring secure communication between segmented areas.
Agent-based segmentation is suited that require:
-
Granular Control: Agent-based segmentation offers granular control over individual workloads and endpoints, allowing for more precise security policies.
-
Dynamic Segmentation: As new workloads are added or removed, agents can automatically adjust security policies, ensuring consistent protection.
-
Vulnerability Detection and Security: The agents enhance security by detecting vulnerabilities on the host systems, enabling organizations to identify potential risks and incorporate this information into their microsegmentation policies.
-
Process Visibility and Security: Agent-based microsegmentation provides in-depth visibility into running processes on the hosts, allows creation of granular policies that restrict access based on specific processes or user-process associations.
The following procedure describes the process of installing agents, gathering labels, and creating a scope hierarchy to microsegment your organization’s workloads.
Procedure
Step 1 | Gather the IP addresses of workloads on your network. Choose a single application that you can focus on. |
Step 2 | Install agents on supported bare metal or virtual workloads to gather process, package and flow data, which is used by Secure Workload to suggest relevant policies. To do this: For more information, see Deploy Software Agents. For more information, see Scopes and Inventory. |
Step 3 | Create a basic scope hierarchy for your internal organization, data centers, and preproduction environments.
For more information, see Scopes and Inventory. |
Step 4 | Set up common policies to allow access from all internal workloads to your NTP, DNS, and or Active Directory servers. Deny access from all hosts outside your organization to hosts inside your network unless explicitly permitted. For example, you might want to allow access from all internal workloads to your NTP server, and deny all external traffic, or deny access from all non-internal hosts unless explicitly permitted. Policies can be absolute, meaning that they cannot be overridden by more specific policies, or default, where they can be overridden by more specific policies. Manually create policies that apply across your network. For more information, see Manually Create Policies. Secure Workload has policy templates that make policy creation easier. For more information, see Policy Templates. |
Step 5 | Create a scope for your applications that you want to apply policies. For more information, see Scopes and Inventory. |
Step 6 | Create a workspace for each scope for which you want to create policies. The workspace is where you manage policies for the workloads in that scope. For more information, see Workspaces. |
Step 7 | Create a workspace for the application scope to manage the policies. Automatically discover policies in workspaces associated with lower-level scopes. For more information, see Discover Policies Automatically and the subtopics. |
Step 8 | To automatically discover policies based on existing traffic patterns, see Automatic Policy Discovery. Secure Workload analyzes traffic between workloads, groups workloads based on their behavior, and suggests a set of policies that are intended to allow the traffic that your organization needs, so you can block all other traffic. Analysis of more data flow over a longer time period leads to more accurate policy suggestions. Review and analyze the suggested policies. For more information, see Review Automatically Discovered Policies and Live Policy Analysis, and the subtopics. |
Step 9 | To ensure that the suggested policies have the intended effects (and not have any unintended effects) before the policies are enforced, iteratively discover policies as needed. For more information, see Live Policy Analysis and Iteratively Revise Policies and the subtopics. |
Step 10 | When you are ready, enforce policies. After you have determined that the policies associated with a workspace (and hence, the associated scope) are appropriate and will block unwanted traffic while not interrupting essential services, you can enforce those policies. Enforce policies both in the workspace and in the agent configuration. For more information, see Enforce Policies. |
Secure Workload Agentless Microsegmentation
Agentless segmentation does not require software agents to be installed on individual workloads or endpoints. In such scenarios, Secure Workload is configured with cloud connectors, Secure Firewall Management Center (FMC), or load balancers, F5 or Citrix and the telemetry data is collected from them.
Agentless segmantation has the following benefits:
-
Reduced Overhead: Agentless segmentation eliminates the need to install and maintain software agents on every workload or endpoint, reducing overhead and complexity.
-
Compatibility: Agentless segmentation can be more compatible with legacy systems and devices that cannot support software agents.
There are multiple ways to achieve agentless microsegmentation in Cisco Secure Workload:
-
Configure cloud connectors and enforce policies using the cloud-native network security groups.
-
Configure a firewall management center instance with Secure Workload and enforce policies on workloads using the firewall threat defense devices.
-
Configure F5 or Citrix load balancers and enforce policies using these load balancers.
Configure AWS Cloud Connector
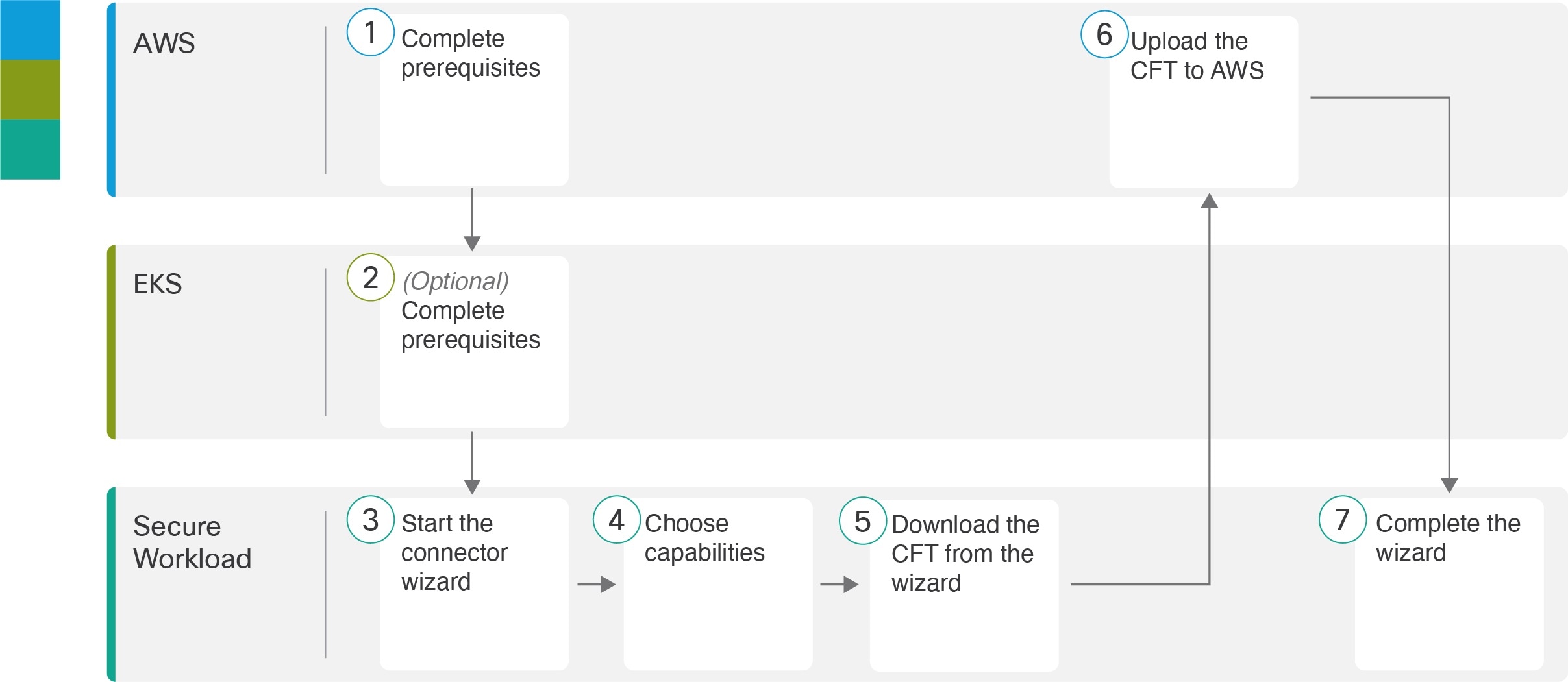
The following procedure describes the process of configuring AWS cloud connector to microsegment your organization’s workloads.
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Ensure that the following prerequisites are met before configuring an AWS cloud connector in Secure Workload:
For more information, see Requirements and Prerequisites for AWS. |
|
|
If you have enabled the Kubernetes option, see Requirements and Prerequisites for EKS. |
|
|
From the navigation pane, choose , and then click Generate Template. |
|
|
Choose the capabilities for the selected AWS user. |
|
|
A CloudFormation Template (CFT) is generated based on the capabilities you choose. |
|
|
|
Upload the generated CFT template in your AWS CloudFormation to create the policy for the user. For more information, see Steps 1 to 7 in Configure new AWS Connector. |
|
|
After uploading the CFT template on the AWS account, complete the remaining steps in the Secure Workload wizard to configure the AWS cloud connector. For more information, see Steps 8 to 16 in Configure new AWS Connector. |
Enforce Policies in Workspaces and Software Agents
Cisco Secure Workload enforces policies on workloads and applications through a comprehensive approach that involves managing policies across various scopes, including creating, analyzing, and enforcing policies within workspaces.
For agents, Secure Workload offers deployment options for various platforms, including Linux and Windows, with specific requirements for installation and configuration.
By leveraging these features, Secure Workload ensures that policies are effectively enforced across workloads and applications, providing a robust security posture for hybrid multicloud environments.
To enforce policies, perform these steps:
Enable Policy Enforcement
Procedure
Step 1 | From the navigation pane, choose . |
Step 2 | You can enforce policies for one scope or for multiple scopes at the same time. For more information, see Enable Policy Enforcement. |
Step 3 | On the final page of the wizard, click Accept and Enforce to push new firewall rules to the assets that are affected by policies in this workspace. A label flag is created at the time of enforcement: |
For more information, see the following sections:
Conclusion
Zero trust microsegmentation stands out as the ultimate safeguard for workloads and applications by providing granular control over access and security measures. This approach ensures that policies are applied at a fine-grained level, down to individual workloads, preventing lateral movement within networks and securing dynamic environments effectively. By combining the principles of zero trust with microsegmentation, organizations can establish robust defenses that protect against sophisticated cyber threats, reduce attack surfaces, and maintain the integrity of their data and applications across diverse environments. In essence, zero trust microsegmentation offers a comprehensive and proactive security solution tailored to the modern threat landscape.
Full Cisco Trademarks with Software License
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB's public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies of this document are considered uncontrolled. See the current online version for the latest version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses and phone numbers are listed on the Cisco website at www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/legal/trademarks.html. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1721R)