Cisco Cyber Vision Docker Compose Creation
The Cisco Cyber Vision Docker Sensor deployment requires two steps:
-
Compose file generation.
-
Container creation.
Procedure
|
Step 1 |
If it’s not already done, create some new deployment tokens. See Create Deployment Tokens from Cisco Cyber Vision Administration Guide. |
||
|
Step 2 |
From the main menu, choose Admin > Sensors > Sensor Explorer. |
||
|
Step 3 |
Click New sensor. |
||
|
Step 4 |
Click Docker sensors from the drop-down list. |
||
|
Step 5 |
Fill in the details in the Sensor Application page. |
||
|
Step 6 |
Click Next. The Capture Configuration page appears. |
||
|
Step 7 |
Fill out the Capture Configuration form with the capture interface configuration.
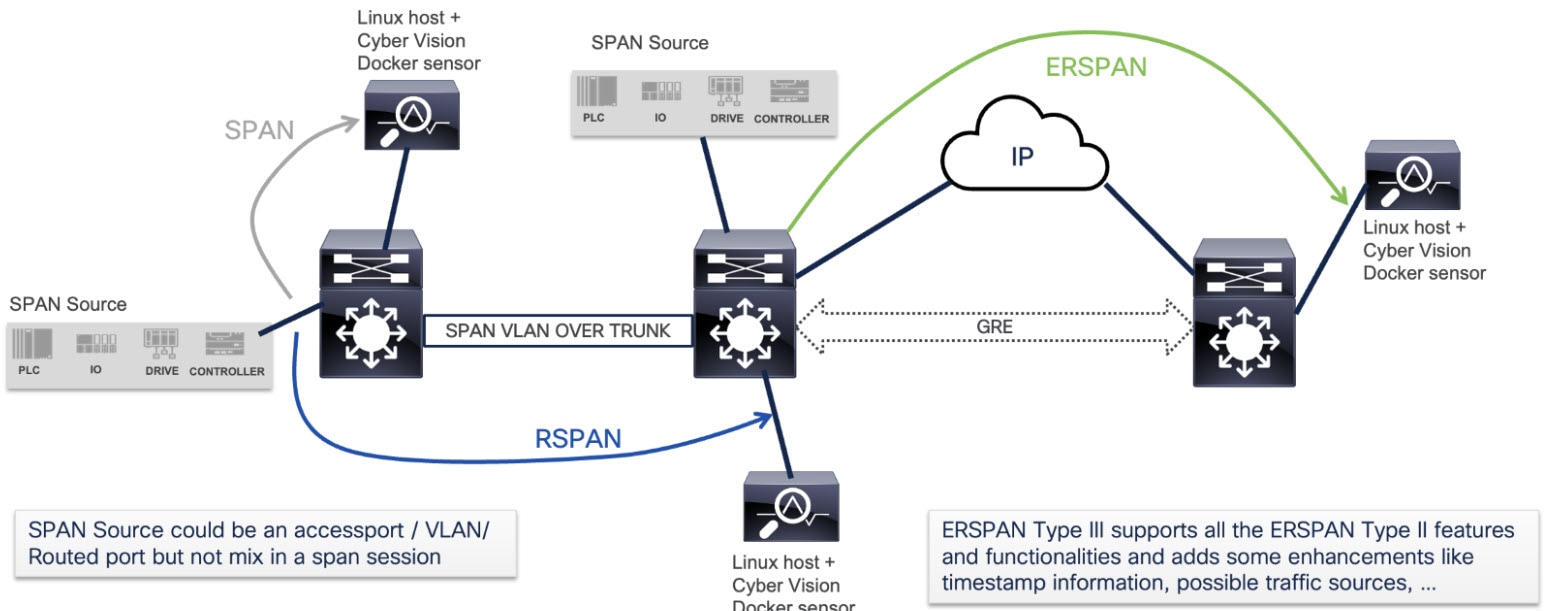 |
||
|
Step 8 |
Click Continue with interfaces. The Active Discovery page appears. |
||
|
Step 9 |
Fill in the details on the Active Discovery page.
|
||
|
Step 10 |
Click Continue with target interface. The Docker Compose page appears. |
||
|
Step 11 |
The Docker Compose page provides the compose file needed to deploy sensor applications. Users need to download or copy it and add the file to their Linux system where Docker is running. 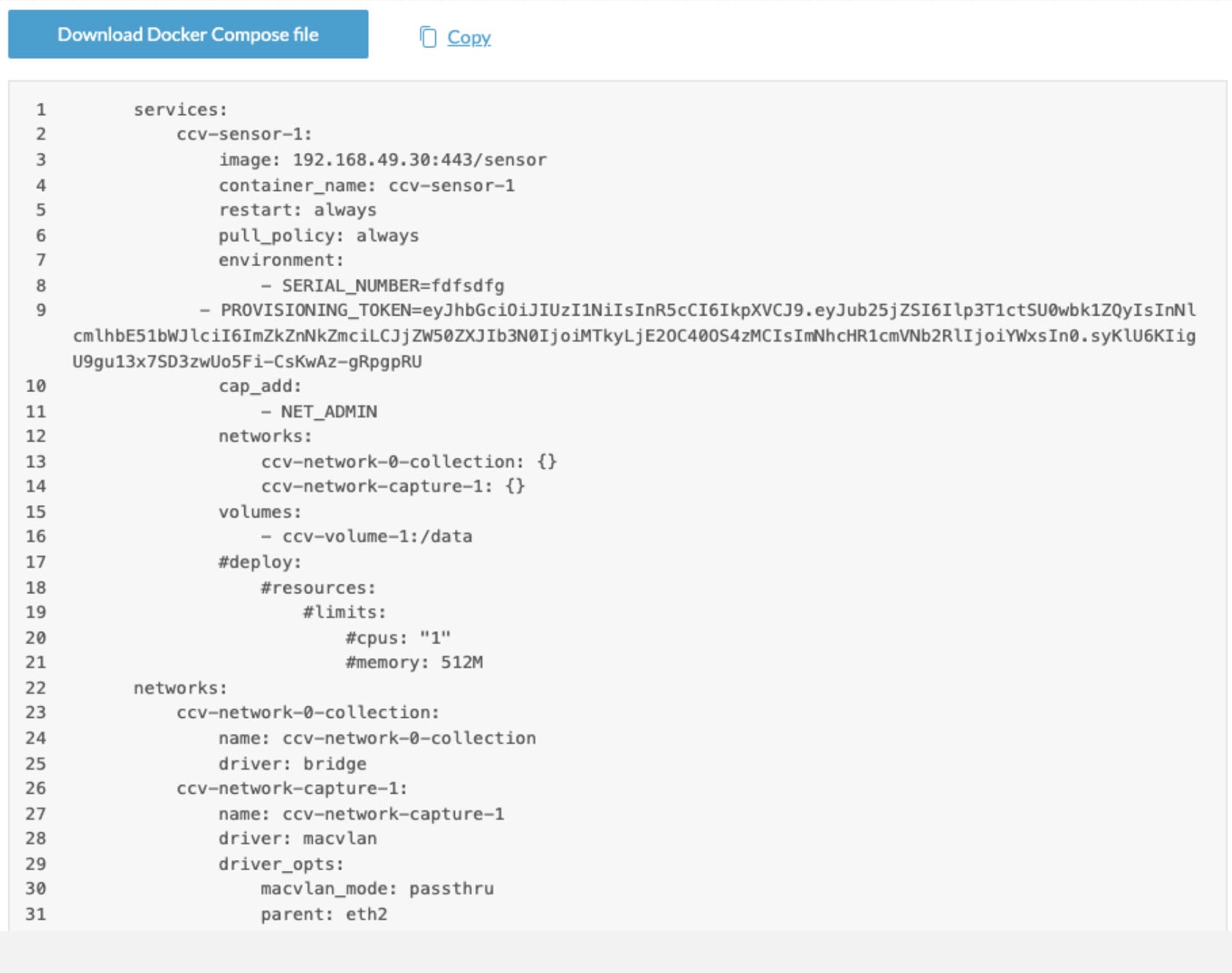 |
 Feedback
Feedback