|
TCP state bypass
|
8.2(1)
|
This feature was introduced. The following command was
introduced: set connection
advanced-options tcp-state-bypass.
|
|
Connection timeout for all protocols
|
8.2(2)
|
The idle timeout was changed to apply to all protocols, not just
TCP.
The following command was
modified:
set connection timeout
|
|
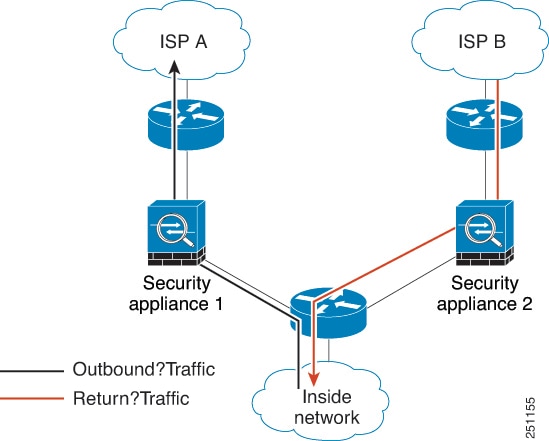
Timeout for connections using a backup static route
|
8.2(5)/8.4(2)
|
When multiple static routes exist to a network with different
metrics, the ASA uses the one with the best metric at the time of connection
creation. If a better route becomes available, then this timeout lets
connections be closed so a connection can be reestablished to use the better
route. The default is 0 (the connection never times out). To take advantage of
this feature, change the timeout to a new value.
We modified the following
command:
timeout floating-conn.
|
|
Configurable timeout for PAT xlate
|
8.4(3)
|
When a PAT xlate times out (by default after 30 seconds), and
the ASA reuses the port for a new translation, some upstream routers might
reject the new connection because the previous connection might still be open
on the upstream device. The PAT xlate timeout is now configurable, to a value
between 30 seconds and 5 minutes.
We introduced the following
command:
timeout pat-xlate.
This feature is not available
in 8.5(1) or 8.6(1).
|
|
Increased maximum connection limits for service policy rules
|
9.0(1)
|
The maximum number of connections for service policy rules was
increased from 65535 to 2000000.
We modified the following
commands:
set connection conn-max,
set connection embryonic-conn-max,
set connection per-client-embryonic-max,
set connection per-client-max.
|
|
Decreased the half-closed timeout minimum value to 30 seconds
|
9.1(2)
|
The half-closed timeout minimum value for both the global
timeout and connection timeout was lowered from 5 minutes to 30 seconds to
provide better DoS protection.
We modified the following
commands:
set connection timeout half-closed,
timeout half-closed.
|
|
Connection
holddown timeout for route convergence.
|
9.4(3)
9.6(2)
|
You can
now configure how long the system should maintain a connection when the route
used by the connection no longer exists or is inactive. If the route does not
become active within this holddown period, the connection is freed. You can
reduce the holddown timer to make route convergence happen more quickly.
However, the 15 second default is appropriate for most networks to prevent
route flapping.
We added the following command:
timeout
conn-holddown .
|
|
SCTP idle
timeout and SCTP state bypass
|
9.5(2)
|
You can
set an idle timeout for SCTP connections. You can also enable SCTP state bypass
to turn off SCTP stateful inspection on a class of traffic.
We added or modified the following commands:
timeout sctp ,
set connection
advanced-options sctp-state-bypass .
|
|
Flow
offload for the ASA on the
Firepower 9300.
|
9.5(2.1)
|
You can
identify flows that should be offloaded from the ASA and switched directly in
the NIC (on the
Firepower 9300).
This provides improved performance for large data flows in data centers.
This
feature requires FXOS 1.1.3.
We added or modified the following commands:
clear
flow-offload ,
flow-offload
enable ,
set-connection
advanced-options flow-offload ,
show conn
detail ,
show
flow-offload .
|
|
Flow
offload support for the ASA on the
Firepower 4100 series.
|
9.6(1)
|
You can
identify flows that should be offloaded from the ASA and switched directly in
the NIC for the
Firepower 4100 series.
This
feature requires
FXOS 1.1.4.
There are
no new commands or ASDM screens for this feature.
|
|
Flow
offload support for multicast connections in transparent mode.
|
9.6(2)
|
You can
now offload multicast connections to be switched directly in the NIC on
transparent mode Firepower 4100 and 9300 series devices. Multicast offload is
available for bridge groups that contain two and only two interfaces.
There are
no new commands or ASDM screens for this feature.
|
|
Changes in
TCP option handling.
|
9.6(2)
|
You can
now specify actions for the TCP MSS and MD5 options in a packet’s TCP header
when configuring a TCP map. In addition, the default handling of the MSS,
timestamp, window-size, and selective-ack options has changed. Previously,
these options were allowed, even if there were more than one option of a given
type in the header. Now, packets are dropped by default if they contain more
than one option of a given type. For example, previously a packet with 2
timestamp options would be allowed, now it will be dropped.
You can
configure a TCP map to allow multiple options of the same type for MD5, MSS,
selective-ack, timestamp, and window-size. For the MD5 option, the previous
default was to clear the option, whereas the default now is to allow it. You
can also drop packets that contain the MD5 option. For the MSS option, you can
set the maximum segment size in the TCP map (per traffic class). The default
for all other TCP options remains the same: they are cleared.
We modified the following command:
timeout igp
stale-route .
|
|
Stale
route timeout for interior gateway protocols
|
9.7(1)
|
You can
now configure the timeout for removing stale routes for interior gateway
protocols such as OSPF.
We added the following command:
timeout igp
stale-route .
|
|
Global
timeout for ICMP errors
|
9.8(1)
|
You can
now set the idle time before the ASA removes an ICMP connection after receiving
an ICMP echo-reply packet. When this timeout is disabled (the default), and you
enable ICMP inspection, then the ASA removes the ICMP connection as soon as an
echo-reply is received; thus any ICMP errors that are generated for the (now
closed) connection are dropped. This timeout delays the removal of ICMP
connections so you can receive important ICMP errors.
We added the following command:
timeout
icmp-error
|
|
Default idle timeout for TCP state bypass
|
9.10(1)
|
The default idle timeout for TCP state bypass connections is
now 2 minutes instead of 1 hour.
|
|
Initiator and responder information for Dead Connection Detection (DCD), and DCD support in a cluster.
|
9.13(1)
|
If you enable Dead Connection Detection (DCD), you can use the show conn detail command to get information about the initiator and responder. Dead Connection Detection allows you to maintain an inactive
connection, and the show conn output tells you how often the endpoints have been probed. In addition, DCD is now supported in a cluster.
New/Modified commands: show conn (output only).
|
|
Configure the maximum segment size (MSS) for embryonic
connections.
|
9.16(1)
|
You can configure a service policy to set the server maximum segment
size (MSS) for SYN-cookie generation for embryonic connections upon
reaching the embryonic connections limit. This is meaningful for
service policies where you are also setting embryonic connection
maximums.
New or changed commands: set connection
syn-cookie-mss .
|
|
IPsec flow offload.
|
9.18(1)
|
On the Secure Firewall 3100, IPsec flows are offloaded by default. After the initial setup of
an IPsec site-to-site VPN or remote access VPN security association
(SA), IPsec connections are offloaded to the field-programmable gate
array (FPGA) in the device, which should improve device
performance.
We added the following commands: clear
flow-offload-ipsec ,
flow-offload-ipsec ,
show flow-offload-ipsec
|
|
DTLS Crypto Acceleration
|
9.22(1)
|
Cisco Secure Firewall 4200 and 3100 series support DTLS cryptographic
acceleration. The hardware performs DTLS encryption and decryption,
and improves the throughput of the DTLS-encrypted and DTLS-decrypted
traffic. The hardware also performs optimization of the
egress-encrypted packets to improve latency.
New/Modified commands:
flow-offload-dtls ,
flow-offload-dtls
egress-optimization
|
|
Flow offload is enabled by default for the Secure Firewall
3100/4200
|
9.23(1)
|
Flow offload is now enabled by default.
Added/modified commands: flow-offload
enable .
|
|
Cluster redirect: flow offload support for the Secure Firewall 4200 asymmetric cluster traffic
|
9.23(1)
|
For asymmetric flows, cluster redirect lets the forwarding node
offload flows to hardware. This feature is enabled by default.
When traffic for an existing flow is sent to a different node, then
that traffic is redirected to the owner node over the cluster
control link. Because asymmetric flows can create a lot of traffic
on the cluster control link, letting the forwarder offload these
flows can improve performance.
Added/modified commands: flow-offload
cluster-redirect , show
conn , show flow-offload
flow , show flow-offload flow
protocol ,show flow-offload
info .
|
|
IPsec flow offload for traffic on the cluster control link on the Secure Firewall 4200 in distributed site-to-site VPN mode
|
9.23(1)
|
For asymmetric flows in distributed site-to-site VPN mode, IPsec flow
offload now lets the flow owner decrypt IPsec traffic in hardware
that was forwarded over the cluster control link. This feature is
not configurable and is always available when you enable IPsec flow
offload.
Added/modified commands:
flow-offload-ipsec ,
show crypto ipsec sa detail .
|


 Feedback
Feedback