Overview of URL Filtering
The URL Filtering feature enables the user to provide controlled access to Internet websites by configuring the URL-based policies and filters on the device.
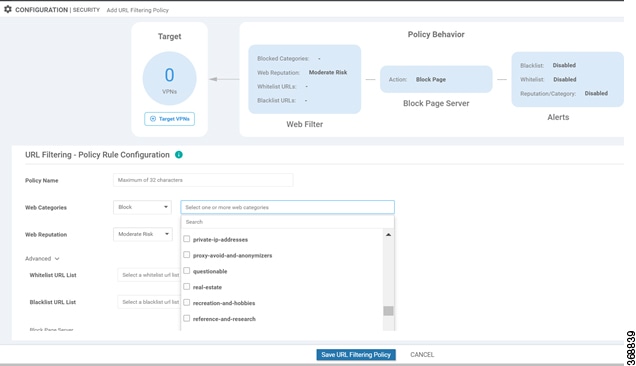
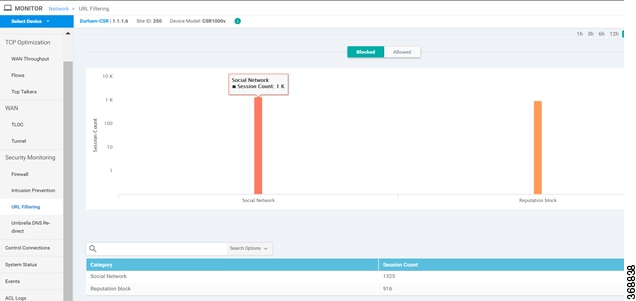
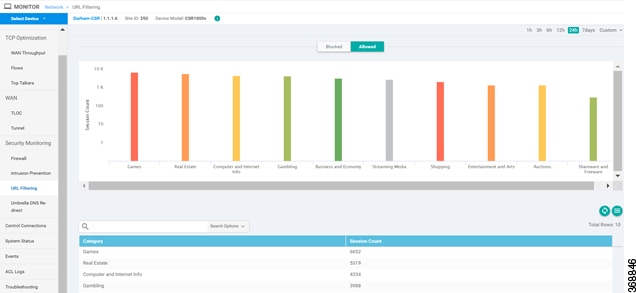
The URL Filtering feature allows a user to control access to Internet websites by permitting or denying access to specific websites based on the category, reputation, or URL. For example, when a client sends a HTTP/HTTP(s) request through the router, the HTTP/HTTP(s) traffic is inspected based on the URL Filtering policies (allowed list/ blocked list, Category, and Reputation). If the HTTP/HTTP(s) request matches the blocked list, the HTTP(s) request is blocked by an inline block page response. If the HTTP/HTTP(s) request matches the allowed list, the traffic is allowed without further URL Filtering inspection.
For HTTPS traffic, the inline block page is not be displayed. URL Filtering will not decode any encoded URL before performing a lookup.
When there is no alloweed list or blocked list configured on the device, based on the category and reputation of the URL, traffic is allowed or blocked using a block page. For HTTP(s), a block page is not displayed and the traffic is dropped.
Filtering Options
The URL Filtering allows you to filter traffic using the following options:
Category-Based Filtering
 Note |
By default, vManage does not download the URL database from the cloud. To enable the URL database download, you must set the Resource Profile to High in the Feature Template. |
If configured, vManage downloads the URL database from the cloud. After the full database is downloaded from the cloud, if there are any updates to the existing database, the incremental updates will be automatically downloaded every 15 minutes. The complete database size is approximately 440 MB and the downloaded database should always synchronize with the cloud. The database will be invalid if the connection to the cloud is lost for more than 24 hours. The default URL category/reputation database only has a few IP address based records. The category/reputation look up occurs only when the host portion of the URL has the domain name.
If the device does not get the database updates from the cloud, vManage ensures that the traffic designated for URL Filtering is not dropped.
 Note |
The URL Filtering database is periodically updated from the cloud in every 15 minutes. |
Reputation-Based Filtering
In addition to category-based filtering, you can also filter based on the reputation of the URL. Each URL has a reputation score associated with it. The reputation score range is from 0-100 and it is categorized as:
-
High risk: Reputation score of 0 to 20
-
Suspicious: Reputation score of 21 to 40
-
Moderate risk: Reputation score of 41 to 60
-
Low risk: Reputation score of 61 to 80
-
Trustworthy: Reputation score of 81 to 100
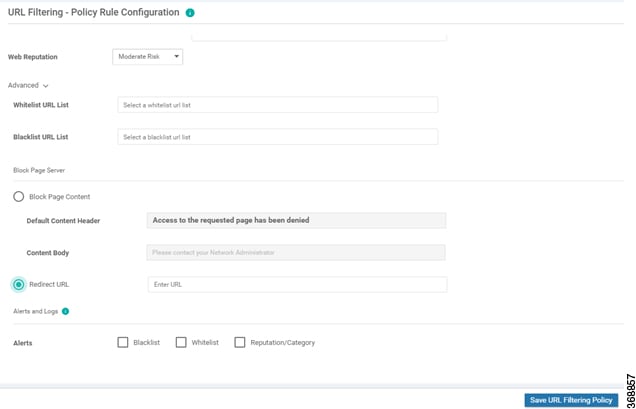
When you configure a web reputation in vManage, you are setting a reputation threshold. Any URL that is below the threshold is blocked by URL filtering. For example, if you set the web reputation to Moderate Risk in vManage, any URL that has a reputation score below than and equal to 60 is blocked.
Based on the reputation score of a URL and the configuration, a URL is either blocked or allowed.
List-based Filtering
List-based filtering allows the user to control access by permitting or denying access based on allowed or blocked lists. Here are some important points to note regarding these lists:
-
URLs that are allowed are not subjected to any category-based filtering (even if they are configured).
-
If the same item is configured under both the allowed and blocked list, the traffic is allowed.
-
If the traffic does not match either the allowed or blocked lists, then it is subjected to category-based and reputation-based filtering (if configured).
-
A user may consider using a combination of allowed and blocked pattern lists to design the filters. For example, if you want to allow www\.foo\.com but also want to block other URLs such as www\.foo\.abc and www\.foo\.xyz, you can configure www\.foo\.com in the allowed list and www\.foo\. in the blocked list.
 Feedback
Feedback