Cisco NCS 560-4 Router Features
-
Fully redundant and centralized forwarding
-
Six Interface Module (IM) slots
-
Aggregate backplane capacity of 1.8Tbps
-
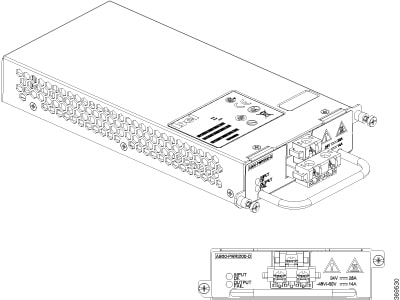
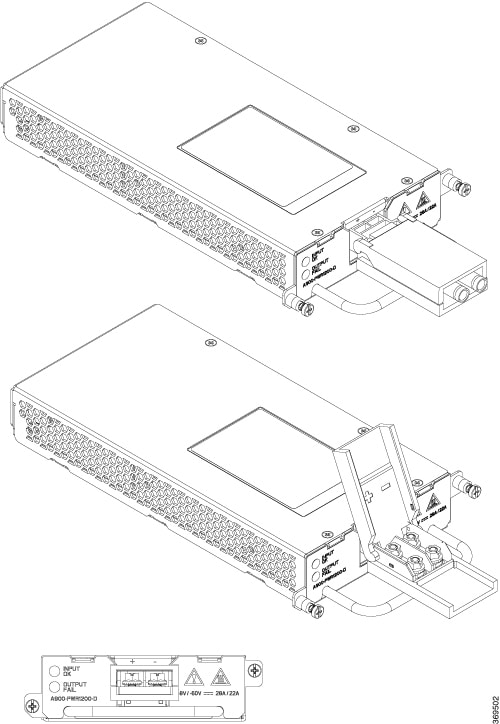
Support for 1:1 and 2:1 power supply redundancy configurations, capable of delivering approximately 1.5KW to the router
-
Three fan trays working in pull-mode and drawing air from right to left
The image below illustrates the Cisco NCS 560-4 Router chassis design.
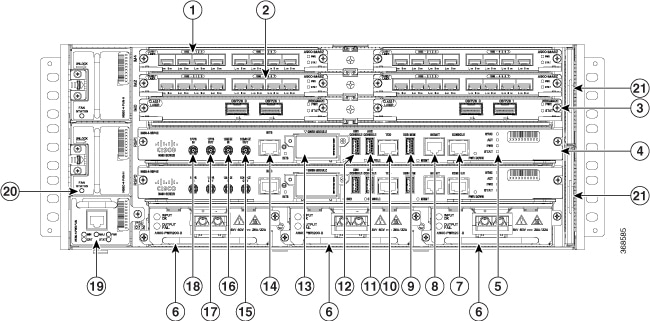
|
1 |
Interface module slot |
2 |
Interface module slot |
|
3 |
Interface module slot |
4 |
Route Switch Processor (N560-4-RSP4E or N560-4-RSP4) |
|
5 |
System LEDs |
6 |
Power Supplies (three) |
|
7 |
RJ-45 Console |
8 |
Management Port |
|
9 |
USB memory port |
10 |
Time of day timing (ToD) port |
|
11 |
Auxiliary console |
12 |
USB console |
|
13 |
GNSS module |
14 |
BITS timing port |
|
15 |
10 MHz Out |
16 |
10 MHz In |
|
17 |
1PPS Out |
18 |
1PPS In |
|
19 |
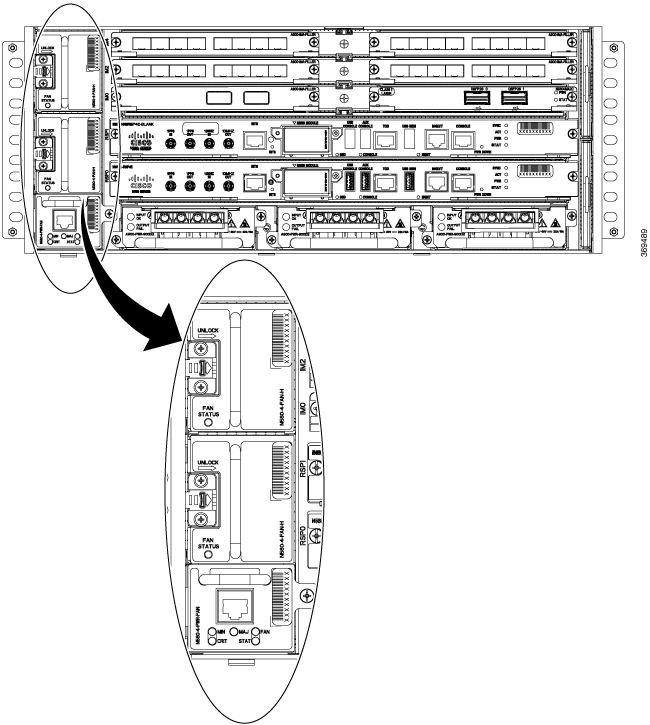
Master fan tray |
20 |
Slave fan tray |
|
21 |
Fan Filters |
— |
— |
The cabling for all interfaces (power, data and control) are on the front side of the chassis. The chassis grounding point is located on the rear side of the chassis.
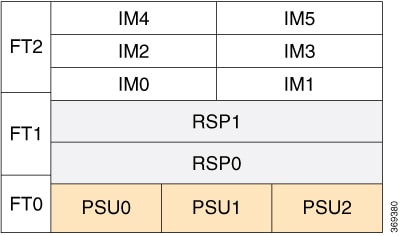
The following image illustrates the slot numbering scheme for the FRUs in Cisco NCS 560-4 router in case of single width IMs.


 Feedback
Feedback