- Preface
- Documentation Roadmap
- Chapter 1, Install the Cisco ONS 15454, ONS 15454 M2, and ONS 15454 M6 Shelf
- Chapter 2, Install the Control Cards
- Chapter 3, Connect the PC and Log into the GUI
- Chapter 4, Turn Up a Node
- Chapter 5, Perform Node Acceptance Tests
- Chapter 6, Provision Transponder and Muxponder Cards
- Chapter 7, Turn Up a Network
- Chapter 8, Create Circuits and Provisionable Patchcords
- Chapter 9, Monitor Performance
- Chapter 10, Manage Alarms
- Chapter 11, Manage the Node
- Chapter 12, Change DWDM Card Settings
- Chapter 13, Upgrade, Add, and Remove Cards and Nodes
- Chapter 14, Maintain the Node
- Appendix A, CTC Information and Shortcuts
- Appendix B, Configuring GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Provision Transponder and Muxponder Cards
This chapter explains how to provision transponder (TXP), muxponder (MXP), Xponder (GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE), and ADM-10G cards. The provisioning must be performed before you provision the dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) network and create circuits.

Note![]() The procedures and tasks described in this chapter for the Cisco ONS 15454 platform is applicable to the Cisco ONS 15454 M2 and Cisco ONS 15454 M6 platforms, unless noted otherwise.
The procedures and tasks described in this chapter for the Cisco ONS 15454 platform is applicable to the Cisco ONS 15454 M2 and Cisco ONS 15454 M6 platforms, unless noted otherwise.

Note![]() Unless otherwise specified, “ONS 15454” refers to both ANSI and ETSI shelf assemblies.
Unless otherwise specified, “ONS 15454” refers to both ANSI and ETSI shelf assemblies.
Before You Begin
Before performing any of the following procedures, investigate all alarms and clear any trouble conditions. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Troubleshooting Guide as necessary.

This section lists the chapter procedures (NTPs). Turn to a procedure for applicable tasks (DLPs).
1.![]() G128 Manage Pluggable Port Modules—Complete this procedure to provision a multirate pluggable port module (PPM), provision or change the optical line rate of a PPM, or delete a PPM. PPMs provide the fiber interface to the TXP, MXP, and ADM-10G cards. With the exception of the TXP_MR_10G card, all TXPs, MXPs, and ADM-10G cards accept PPMs.
G128 Manage Pluggable Port Modules—Complete this procedure to provision a multirate pluggable port module (PPM), provision or change the optical line rate of a PPM, or delete a PPM. PPMs provide the fiber interface to the TXP, MXP, and ADM-10G cards. With the exception of the TXP_MR_10G card, all TXPs, MXPs, and ADM-10G cards accept PPMs.
2.![]() G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group—As needed, complete this procedure for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards that will be protected with Y-cable protection.
G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group—As needed, complete this procedure for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards that will be protected with Y-cable protection.
3.![]() G199 Create a Splitter Protection Group for the OTU2_XP Card—As needed, complete this procedure to create a splitter protection group for an OTU2_XP card.
G199 Create a Splitter Protection Group for the OTU2_XP Card—As needed, complete this procedure to create a splitter protection group for an OTU2_XP card.
4.![]() G198 Create 1+1 Protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards—As needed, complete this procedure to create 1+1 protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G198 Create 1+1 Protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards—As needed, complete this procedure to create 1+1 protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
5.![]() G98 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
G98 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
6.![]() G96 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards.
G96 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards.
7.![]() NTP-G292 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds, page 6-72—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards.
NTP-G292 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds, page 6-72—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards.
8.![]() G170 Provision the ADM-10G Card Peer Group, Ethernet Settings, Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to provision the transmission settings for ADM-10G cards.
G170 Provision the ADM-10G Card Peer Group, Ethernet Settings, Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to provision the transmission settings for ADM-10G cards.
9.![]() G333 Add an ADM-10G card to an Existing Topology—As needed, complete this procedure to add an ADM-10G card to an existing topology.
G333 Add an ADM-10G card to an Existing Topology—As needed, complete this procedure to add an ADM-10G card to an existing topology.
10.![]() G97 Modify the 4x2.5G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C cards.
G97 Modify the 4x2.5G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C cards.
11.![]() G99 Modify the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
G99 Modify the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
12.![]() G148 Modify the 10G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards.
G148 Modify the 10G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards.
13.![]() G293 Modify the 40G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards.
G293 Modify the 40G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards.
14.![]() G281 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Channel Group Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the channel group settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G281 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Channel Group Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the channel group settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
15.![]() G283 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card CFM Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the CFM settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G283 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card CFM Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the CFM settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
16.![]() G285 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card EFM Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the EFM settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G285 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card EFM Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the EFM settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
17.![]() G287 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card REP Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the REP settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G287 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card REP Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the REP settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
18.![]() G165 Modify the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE Cards Ethernet Parameters, Line Settings, and PM Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
G165 Modify the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE Cards Ethernet Parameters, Line Settings, and PM Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
19.![]() G314 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card on a FAPS Ring—As needed, complete this procedure to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card on a FAPS Ring.
G314 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card on a FAPS Ring—As needed, complete this procedure to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card on a FAPS Ring.
20.![]() G197 Provision the OTU2_XP Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for OTU2_XP cards.
G197 Provision the OTU2_XP Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds—As needed, complete this procedure to change the transmission settings for OTU2_XP cards.
21.![]() G162 Change the ALS Maintenance Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the automatic laser shutdown settings for a TXP or MXP card.
G162 Change the ALS Maintenance Settings—As needed, complete this procedure to change the automatic laser shutdown settings for a TXP or MXP card.
22.![]() G192 Force FPGA Update—As needed, complete this procedure to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards.
G192 Force FPGA Update—As needed, complete this procedure to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards.
23.![]() G196 Force FPGA Update When the Card is Part of a Protection Group—As needed, complete this procedure to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards when the card is part of a protection group.
G196 Force FPGA Update When the Card is Part of a Protection Group—As needed, complete this procedure to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards when the card is part of a protection group.
24.![]() G232 Enabling Error Decorrelator—As needed, complete this procedure to enable error decorrelator on a TXP_MR_10EX_C, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card.
G232 Enabling Error Decorrelator—As needed, complete this procedure to enable error decorrelator on a TXP_MR_10EX_C, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card.

Note![]() Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM supports IBM's 5G DDR (Double Data Rate) InfiniBand1 interfaces.
Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM supports IBM's 5G DDR (Double Data Rate) InfiniBand1 interfaces.
NTP-G128 Manage Pluggable Port Modules
Complete this procedure to provision a multirate PPM, provision the optical line rate of a multirate PPM, or delete a single-rate or multirate PPM. |
|

Note![]() If a single-rate PPM is installed, the PPM screen will autoprovision and no further steps are necessary.
If a single-rate PPM is installed, the PPM screen will autoprovision and no further steps are necessary.

Note![]() When you autoprovision a PPM, initial alarm and TCA defaults are supplied by Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) depending on your port and rate selections and the type of PPM. These default values can be changed after you install the PPM.
When you autoprovision a PPM, initial alarm and TCA defaults are supplied by Cisco Transport Controller (CTC) depending on your port and rate selections and the type of PPM. These default values can be changed after you install the PPM.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC to log into an ONS 15454 on the network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC to log into an ONS 15454 on the network. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
a.![]() Verify that the alarm filter is not turned on. See the G128 Disable Alarm Filtering as necessary.
Verify that the alarm filter is not turned on. See the G128 Disable Alarm Filtering as necessary.
b.![]() Verify that no unexplained conditions appear. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Troubleshooting Guide.
Verify that no unexplained conditions appear. If unexplained conditions appear, resolve them before continuing. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Troubleshooting Guide.
Step 3![]() If you are provisioning a MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card, complete the G235 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 4
If you are provisioning a MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card, complete the G235 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 4
Step 4![]() If you are provisioning a MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card, complete the G332 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Port Mode. If not, continue with Step 5.
If you are provisioning a MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card, complete the G332 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Port Mode. If not, continue with Step 5.
Step 5![]() If you are provisioning a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 6.
If you are provisioning a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 6.
Step 6![]() If you are provisioning a OTU2_XP card, complete the G452 Change the OTU2_XP Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 7.
If you are provisioning a OTU2_XP card, complete the G452 Change the OTU2_XP Card Mode. If not, continue with Step 7.
Step 7![]() If you are provisioning a PPM on an ADM-10G card, complete the G411 Provision an ADM-10G PPM and Port. If not, continue with Step 8.
If you are provisioning a PPM on an ADM-10G card, complete the G411 Provision an ADM-10G PPM and Port. If not, continue with Step 8.
Step 8![]() Complete the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP ports with multirate PPMs. If you already preprovisioned the multirate PPM (G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot), skip this step and continue with Step 9.
Complete the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP ports with multirate PPMs. If you already preprovisioned the multirate PPM (G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot), skip this step and continue with Step 9.
Step 9![]() If you are provisioning an IBM ETR_CLO (External Time Reference – Control Link Oscillator) or InterSystem Coupling Link (ISC) service on the PPM, complete G274 Verify Topologies for ETR_CLO and ISC Services. Otherwise, continue with Step 10.
If you are provisioning an IBM ETR_CLO (External Time Reference – Control Link Oscillator) or InterSystem Coupling Link (ISC) service on the PPM, complete G274 Verify Topologies for ETR_CLO and ISC Services. Otherwise, continue with Step 10.
Step 10![]() Complete the G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate to assign a line rate to a TXP, MXP, or OTU2_XP port after the PPM is provisioned. (This task is not performed for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.)
Complete the G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate to assign a line rate to a TXP, MXP, or OTU2_XP port after the PPM is provisioned. (This task is not performed for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.)
Step 11![]() If you need to delete a PPM at any point in this procedure, complete the G280 Delete a PPM.
If you need to delete a PPM at any point in this procedure, complete the G280 Delete a PPM.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G235 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Mode
This task changes the card mode for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. The card mode determines which PPMs can be provisioned for the card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Locate the Trunk port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If the service state is correct, continue with Step 6. If not, complete the following steps:
Locate the Trunk port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If the service state is correct, continue with Step 6. If not, complete the following steps:
a.![]() Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs.
Step 5![]() Locate the Trunk port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If the service state is correct, continue with Step 6. If not, complete the following steps:
Locate the Trunk port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If the service state is correct, continue with Step 6. If not, complete the following steps:
a.![]() Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Step 6![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 7![]() Change the Card Mode as needed:
Change the Card Mode as needed:
- FC-GE—Choose this option if you will provision any of the following PPM port rates: FC1G (Ports 1-1 and 2-1 only), FC2G (Port 1-1 only), FICON1G (Ports 1-1 and 2-1 only), FICON2G (Port 1-1 only), and ONE_GE (Ports 1-1 through 8-1).
- Mixed—Choose this option if you will provision any of the following PPM port rates: FC1G and ONE_GE (Port 1–1 only), ESCON (Ports 5–1 through 8-1 only)
- ESCON—Choose this option if you will provision the ESCON PPM on Ports 1-1 through 8-1.

Note![]() The Provisioning > Card tab also has the display-only Tunable Wavelengths field. This field shows the supported wavelengths of the trunk port after the card is installed in the format:
The Provisioning > Card tab also has the display-only Tunable Wavelengths field. This field shows the supported wavelengths of the trunk port after the card is installed in the format:
first wavelength-last wavelength-frequency spacing-number of supported wavelengths.
For example, 1529.55nm-1561.83nm-50gHz-82.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G332 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Port Mode
This task changes the port mode for the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C muxponder cards. The port mode determines which PPMs can be provisioned on the ports. |
|

Note![]() The MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards have two port mode groups, one for Ports 1 through 4, and the second for Ports 5 through 8. To change the port mode, all ports within the selected port group must be in OOS (out-of-service) service state. Ports in the second port group do not need to be in OOS service state if you are not changing the port mode for the second port group. Before you change the port mode, you must also ensure that any PPM port rate provisioned for the selected port group is deleted (see G280 Delete a PPM).
The MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards have two port mode groups, one for Ports 1 through 4, and the second for Ports 5 through 8. To change the port mode, all ports within the selected port group must be in OOS (out-of-service) service state. Ports in the second port group do not need to be in OOS service state if you are not changing the port mode for the second port group. Before you change the port mode, you must also ensure that any PPM port rate provisioned for the selected port group is deleted (see G280 Delete a PPM).
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the port mode.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the port mode.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Change the port mode as described in Table 6-1 .
Change the port mode as described in Table 6-1 .

Note![]() The PPM port rates are provisioned in the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM.
The PPM port rates are provisioned in the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM.

Note![]() The Provisioning > Cards tab also has a display-only Tunable Wavelengths field which shows the wavelengths supported by the card. If a MXP_MR_10DME_C card is installed, the 32 C-band wavelengths appear. If the MXP_MR_10DME_L card is installed, the 32 L-band wavelengths appear. If the MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card is installed, the 82 C-band wavelengths appear.
The Provisioning > Cards tab also has a display-only Tunable Wavelengths field which shows the wavelengths supported by the card. If a MXP_MR_10DME_C card is installed, the 32 C-band wavelengths appear. If the MXP_MR_10DME_L card is installed, the 32 L-band wavelengths appear. If the MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card is installed, the 82 C-band wavelengths appear.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).

Note![]() Loopbacks on MXP-MR-10DME are not applicable when Fiber Channel switches are present.
Loopbacks on MXP-MR-10DME are not applicable when Fiber Channel switches are present.

Note![]() If the Fiber Channel switch version is not present then the Distance Extension settings are not supported.
If the Fiber Channel switch version is not present then the Distance Extension settings are not supported.
DLP-G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the card mode.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the card mode.
Step 2![]() In card view, click Provisioning > Ether Ports > Ports.
In card view, click Provisioning > Ether Ports > Ports.
Step 3![]() Verify that any provisioned client or trunk ports have an OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state in the Service State column. If so, continue with Step 4
Verify that any provisioned client or trunk ports have an OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state in the Service State column. If so, continue with Step 4![]() . If not, complete the following substeps.
. If not, complete the following substeps.
a.![]() For the first port that is not out of service, in the Admin State column, choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI).
For the first port that is not out of service, in the Admin State column, choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI).
b.![]() Repeat Step a for each port that is not out of service.
Repeat Step a for each port that is not out of service.
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 5![]() Choose one of the card modes shown in Table 6-2 .
Choose one of the card modes shown in Table 6-2 .
The GE-XP and GE-XPE cards operating in 10GE MXP mode and configured for 100% traffic flow, do not drop frames when up to nine ports are in use. However, when all the ten ports are in use, some frames are dropped. When the tenth port is to be used, configure the Committed Info Rate (CIR) at 55% on any one of the ports. For more information about configuring the CIR, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 6![]() Click Apply, then click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Click Apply, then click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G411 Provision an ADM-10G PPM and Port
This task provisions a fixed-rate PPM and port on an ADM-10G PPM card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to provision PPM settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to provision PPM settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
Step 5![]() Click OK. The newly created PPM appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Click OK. The newly created PPM appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Step 6![]() In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Ports dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Ports dialog box appears.
Step 7![]() In the Create Ports dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create Ports dialog box, complete the following:
–![]() Ports 1 - 8 can only be OC-3, OC-12, or ONE_GE
Ports 1 - 8 can only be OC-3, OC-12, or ONE_GE
–![]() Ports 9 - 12 can on be OC-3 or OC-12
Ports 9 - 12 can on be OC-3 or OC-12
–![]() Ports 13 - 16 can only be OC-3, OC-12, or OC-48
Ports 13 - 16 can only be OC-3, OC-12, or OC-48
Step 8![]() Click OK. The newly created port appears in the Pluggable Ports area. The port type you provisioned is listed
Click OK. The newly created port appears in the Pluggable Ports area. The port type you provisioned is listed![]() in the Rate column.
in the Rate column.
Step 9![]() If you want to provision a PPM or another port, repeat Steps 4 through 8 .
If you want to provision a PPM or another port, repeat Steps 4 through 8 .
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G452 Change the OTU2_XP Card Mode
This task changes the OTU2_XP card mode. The card mode determines which PPMs can be provisioned for the card. |
|

Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the card mode.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the card mode.
Step 2![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tab.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tab.
Step 3![]() Verify that all provisioned client or trunk ports have an OOS-MA, DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled, disabled (ETSI) service state in the Service State column. If so, continue with Step 4
Verify that all provisioned client or trunk ports have an OOS-MA, DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled, disabled (ETSI) service state in the Service State column. If so, continue with Step 4![]() . If not, complete the following substeps
. If not, complete the following substeps![]() .
.
a.![]() For the first port that is not out of service, in the Admin State column, choose OOS, DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked, disabled (ETSI).
For the first port that is not out of service, in the Admin State column, choose OOS, DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked, disabled (ETSI).
b.![]() Repeat Step a for each port that is not out of service.
Repeat Step a for each port that is not out of service.
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tab.
Click the Provisioning > Card tab.
Step 5![]() Change the Card Configuration as needed:
Change the Card Configuration as needed:
- Transponder —Choose this option to provision the OTU2_XP card as a transponder. Port pairs 1-3 and 2-4 are both configured as transponders. This is the default card configuration.
- Standard Regen —Choose this option to provision the OTU2_XP card as a standard regenerator (with E-FEC only on one port). Port pairs 1-3 and 2-4 are both configured as regenerators.
- Enhanced FEC —Choose this option to provision the OTU2_XP card as an E-FEC regenerator (with E-FEC on two ports). Port pair 3-4 is configured as enhanced regenerator. Ports 1 and 2 are not used.
- Mixed —Choose this option to provision the OTU2_XP card as a transponder and a standard regenerator (mixed configuration). One of the port pair (1-3 or 2-4) is configured as a transponder and the other port pair as a standard regenerator.
- 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy— Choose this option to provision the OTU2_XP card to enable the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy conversion. Port pair 1-3 supports LAN Phy to WAN Phy conversion. Port pair 2-4 can be configured either as a transponder or a standard regenerator.

Note![]() If you revert to the previous release (release earlier than 9.10), be sure to disable the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy conversion feature. If you do not disable the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy feature, an error message stating that the user needs to disable 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy feature before reverting to the previous release is displayed.
If you revert to the previous release (release earlier than 9.10), be sure to disable the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy conversion feature. If you do not disable the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy feature, an error message stating that the user needs to disable 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy feature before reverting to the previous release is displayed.

Note![]() Table 6-140 lists the Ethernet variables supported on Ports 1 and 3 of the OTU2_XP card that has the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy enabled. When the card is in the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode, no 10G FC RMONS are supported on Ports 2 and 4.
Table 6-140 lists the Ethernet variables supported on Ports 1 and 3 of the OTU2_XP card that has the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy enabled. When the card is in the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode, no 10G FC RMONS are supported on Ports 2 and 4.
For more information on OTU2_XP card configuration rules, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual .
Step 6![]() Click Apply. Then click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Click Apply. Then click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G277 Provision a Multirate PPM
This task provisions a multirate PPM on a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card. |
|

Note![]() If the PPM was preprovisioned using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot this task is unnecessary, unless the PPM has an Out-of-Service and Autonomous Management, Unassigned (OOS-AUMA,UAS) (ANSI) or unlocked-disabled, unassigned (ETSI) service state.
If the PPM was preprovisioned using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot this task is unnecessary, unless the PPM has an Out-of-Service and Autonomous Management, Unassigned (OOS-AUMA,UAS) (ANSI) or unlocked-disabled, unassigned (ETSI) service state.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card where you want to provision PPM settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card where you want to provision PPM settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
Step 5![]() Click OK. The newly created port appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Click OK. The newly created port appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Step 6![]() If you want to provision a PPM on another port, repeat Steps 3 through 5 . If not, continue with Step 7
If you want to provision a PPM on another port, repeat Steps 3 through 5 . If not, continue with Step 7![]() .
.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G274 Verify Topologies for ETR_CLO and ISC Services
This task verifies that the DWDM network topology can support the IBM ETR_CLO and ISC services. |
|
Step 1![]() Display your site plan in Cisco TransportPlanner.
Display your site plan in Cisco TransportPlanner.
Step 2![]() Verify that the topology where you plan to run the ETR_CLO or ISC service can support the service. The following topologies support ETR_CLO or ISC:
Verify that the topology where you plan to run the ETR_CLO or ISC service can support the service. The following topologies support ETR_CLO or ISC:
–![]() 40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
–![]() 40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
Figure 6-1 shows a single-span topology as displayed in Cisco TransportPlanner.
Figure 6-1 Single-Span Topology

–![]() 40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
–![]() 40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
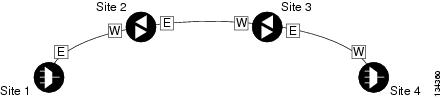
Line amplifiers can be installed between the terminal sites, but intermediate (traffic terminating) sites cannot be installed. Figure 6-2 shows a point-to-point topology as shown in Cisco TransportPlanner.
Figure 6-2 Point-to-Point Topology
–![]() 40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-MUX-C and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
–![]() 40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
40-WSS-C/40-WSS-CE and 40-DMX-C/40-DMX-CE cards
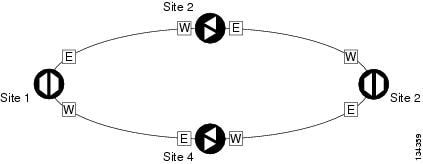
Line amplifiers can be installed between the hubs. Figure 6-3 shows two hub nodes with no line amplifier nodes installed. Figure 6-4 shows two hub nodes with line amplifier nodes installed.
Figure 6-3 Hubs with No Line Amplifiers
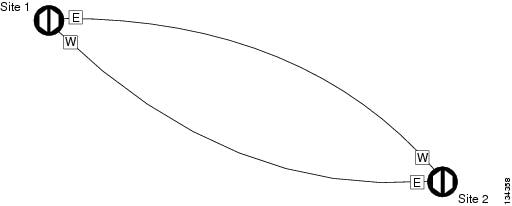
Figure 6-4 Hubs with Line Amplifiers
Step 3![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate
This task provisions the line rate for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP cards. |
|
| G277 Provision a Multirate PPM G274 Verify Topologies for ETR_CLO and ISC Services, if you are provisioning an ETR_CLO service. |
|

Note![]() The optical line rate for cards with single-rate PPMs is provisioned automatically when you complete the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM if the trunk port is out of service. If the optical line rate was provisioned automatically, you do not need to complete this task for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card. If the trunk port was in-service when you provisioned the PPM, complete this task to provision the optical line rate manually for those cards.
The optical line rate for cards with single-rate PPMs is provisioned automatically when you complete the G277 Provision a Multirate PPM if the trunk port is out of service. If the optical line rate was provisioned automatically, you do not need to complete this task for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card. If the trunk port was in-service when you provisioned the PPM, complete this task to provision the optical line rate manually for those cards.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card where you want to provision PPM ports. If the data rate that you are provisioning is DV-6000, HDTV, ESCON, SDI/D1 Video, ISC1, ISC3 (for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards), or ETR_CLO, complete the following steps. Otherwise, continue with Step 4.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card where you want to provision PPM ports. If the data rate that you are provisioning is DV-6000, HDTV, ESCON, SDI/D1 Video, ISC1, ISC3 (for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards), or ETR_CLO, complete the following steps. Otherwise, continue with Step 4.
a.![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs.
Click the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs.
b.![]() In the ITU-T G.709 OTN field for the respective PPM, choose Disable.
In the ITU-T G.709 OTN field for the respective PPM, choose Disable.
c.![]() In the FEC field for the respective PPM, choose Disable.
In the FEC field for the respective PPM, choose Disable.
Step 2![]() For the TXP_MR-10G card, click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs. For all other cards, go to Step
For the TXP_MR-10G card, click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs. For all other cards, go to Step ![]() 4 .
4 .
Step 3![]() In the Data Rate Selection area, click Create and choose the type of port from the drop-down list. The supported port types are SONET (including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy) and 10G Ethernet LAN Phy.
In the Data Rate Selection area, click Create and choose the type of port from the drop-down list. The supported port types are SONET (including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy) and 10G Ethernet LAN Phy.
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Step 5![]() In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Port dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Port dialog box appears.
Step 6![]() In the Create Port dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create Port dialog box, complete the following:
- Port—Choose the port and port number from the drop-down list. The first number indicates the PPM in the Pluggable Port Modules area, and the second number indicates the port number on the PPM. For example, the first PPM with one port appears as 1-1 and the second PPM with one port appears as 2-1. The PPM number can be 1 to 4, but the port number is always 1.
- Port Type—Choose the type of port from the drop-down list. The port type list displays the supported port rates on your PPM. See Table 6-3 for definitions of the supported rates on the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card.
Step 7![]() Click OK. The row in the Pluggable Ports area turns white if the physical SFP is installed and light blue if the SFP is not installed.
Click OK. The row in the Pluggable Ports area turns white if the physical SFP is installed and light blue if the SFP is not installed.
If the optical parameter values differ from the NE Default settings, change the port state to In-Service (for ANSI) or Unlocked (for ETSI) to synchronize the values with the NE Default settings.
Step 8![]() Repeat Steps 5 through 7 to configure the rest of the port rates as needed.
Repeat Steps 5 through 7 to configure the rest of the port rates as needed.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
TXP_MR_10G3 |
|
|
|
If the port mode is FC_GE_ISC:
|
|
Note If you have an OTU2 signal in which the OPU2 has been generated by multiplexing four ODU1 signals, choose SONET as the port rate. This allows the OTU2 signal to be transported transparently in standard or E-FEC regenerator configuration. |
|
2.Automatically provisioned when the PPM is created if the trunk port is out of service. |
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
This task deletes PPM provisioning for SFPs or XFPs installed on TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card. |
|

Note![]() Before deleting a PPM, delete the PPM from the provisioning pane.
Before deleting a PPM, delete the PPM from the provisioning pane.

Note![]() This task does not apply to the TXP_MR_10G card. To change the TXP_MR_10G data rate, complete the G365 Provision the TXP_MR_10G Data Rate.
This task does not apply to the TXP_MR_10G card. To change the TXP_MR_10G data rate, complete the G365 Provision the TXP_MR_10G Data Rate.

Note![]() You cannot delete a PPM if the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card is part of a regenerator group. For OTU2_XP card, you cannot delete a PPM if the card configuration is in Standard Regen or Enhanced FEC mode.
You cannot delete a PPM if the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card is part of a regenerator group. For OTU2_XP card, you cannot delete a PPM if the card configuration is in Standard Regen or Enhanced FEC mode.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card where you want to delete PPM settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card where you want to delete PPM settings.
Step 2![]() Verify that the PPM port Service State is OOS,DSBLD. If the PPM port is OOS,DSBLD, go to Step
Verify that the PPM port Service State is OOS,DSBLD. If the PPM port is OOS,DSBLD, go to Step ![]() 3 . If it is not OOS,DSBLD, follow the tasks in G128 Manage Pluggable Port Modules, to change the Service State of the PPM port to OOS,DSBLD.
3 . If it is not OOS,DSBLD, follow the tasks in G128 Manage Pluggable Port Modules, to change the Service State of the PPM port to OOS,DSBLD.
Step 3![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Step 4![]() To delete a PPM and the associated ports:
To delete a PPM and the associated ports:
a.![]() In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click the PPM that you want to delete. The highlight changes to dark blue.
In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click the PPM that you want to delete. The highlight changes to dark blue.
b.![]() Click Delete. The Delete PPM dialog box appears.
Click Delete. The Delete PPM dialog box appears.
c.![]() Click Yes. The PPM provisioning is removed from the Pluggable Port Modules area and the Pluggable Ports area.
Click Yes. The PPM provisioning is removed from the Pluggable Port Modules area and the Pluggable Ports area.

Note![]() You cannot delete a PPM until its port is in the OOS,DSBLD state. You cannot delete a client port if the client is in the In Service and Normal (IS-NR) (ANSI) or Unlocked-enabled (ETSI) service state, is in a protection group, has a generic communications channel (GCC) or data communications channel (DCC), is a timing source, has circuits or overhead circuits, or transports Link Management Protocol channels or links. You can delete a client port (except the last port) if the trunk port is in service and the client port is in the OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state. You can delete the last client port only if the trunk port is in a OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state for all cards except the MXP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards. For more information about port states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
You cannot delete a PPM until its port is in the OOS,DSBLD state. You cannot delete a client port if the client is in the In Service and Normal (IS-NR) (ANSI) or Unlocked-enabled (ETSI) service state, is in a protection group, has a generic communications channel (GCC) or data communications channel (DCC), is a timing source, has circuits or overhead circuits, or transports Link Management Protocol channels or links. You can delete a client port (except the last port) if the trunk port is in service and the client port is in the OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state. You can delete the last client port only if the trunk port is in a OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI) service state for all cards except the MXP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards. For more information about port states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 5![]() Verify that the PPM provisioning is deleted:
Verify that the PPM provisioning is deleted:
- In the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, or OTU2_XP card view, CTC shows an empty port after the PPM is deleted.
- If the SFP or XFP is physically present when you delete the PPM provisioning, CTC transitions to the deleted state, the ports (if any) are deleted, and the PPM is represented as a gray graphic in CTC. The SFP or XFP can be provisioned again in CTC, or the equipment can be removed. If the equipment is removed, the graphic disappears.
Step 6![]() If you need to remove the PPM hardware (the SFP or XFP), complete the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
If you need to remove the PPM hardware (the SFP or XFP), complete the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G33 Create a Y-Cable Protection Group

Note![]() Y-cable protection is available for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards when they are provisioned in 10GE MXP, 20GE MXP, or 10GE TXP mode. Y-cable protection cannot be provisioned for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards when they are provisioned in L2-over-DWDM mode. Y-cable protection is available for the OTU2_XP card when it is provisioned in the TXP card mode. Y-cable protection is not supported on IB_5G.
Y-cable protection is available for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards when they are provisioned in 10GE MXP, 20GE MXP, or 10GE TXP mode. Y-cable protection cannot be provisioned for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards when they are provisioned in L2-over-DWDM mode. Y-cable protection is available for the OTU2_XP card when it is provisioned in the TXP card mode. Y-cable protection is not supported on IB_5G.

Note![]() If you are provisioning Y-cable protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards, the Ethernet mode must be set to 1000 and 10000 Mbps respectively. To provision the Ethernet mode, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
If you are provisioning Y-cable protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards, the Ethernet mode must be set to 1000 and 10000 Mbps respectively. To provision the Ethernet mode, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.

Note![]() There is a traffic hit of upto a couple hundred milliseconds on the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXP_MR_10DME cards in Y-cable configuration when a fiber cut or SFP failure occurs on one of the client ports.
There is a traffic hit of upto a couple hundred milliseconds on the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXP_MR_10DME cards in Y-cable configuration when a fiber cut or SFP failure occurs on one of the client ports.

Note![]() For SONET or SDH payloads, Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a Y-cable protection group.
For SONET or SDH payloads, Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a Y-cable protection group.
Step 1![]() View the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix (see Table 4-1) for your site. Verify the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards that need Y-cable protection groups. (Cards requiring Y-cable protection are indicated with “Y-Cable” in the Traffic Matrix table Protection Type column. Refer to the Cisco TransportPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for more information.)
View the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix (see Table 4-1) for your site. Verify the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards that need Y-cable protection groups. (Cards requiring Y-cable protection are indicated with “Y-Cable” in the Traffic Matrix table Protection Type column. Refer to the Cisco TransportPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for more information.)
Step 2![]() Verify that the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards are installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7. Table 6-4 lists the protection types available in the ONS 15454 for DWDM client cards.
Verify that the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards are installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7. Table 6-4 lists the protection types available in the ONS 15454 for DWDM client cards.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| GE_XP4 10GE_XP5 |
Pairs a working transponder or muxponder card or port with a protect transponder or muxponder card or port. The protect port must be on a different card than the working port and it must be the same card type as the working port. The working and protect port numbers must be the same, that is, Port 1 can only protect Port 1, Port 2 can only protect Port 2, and so on. Note The working and protect card must be in the same shelf for a multishelf node. |
|
A splitter protection group is automatically created when a TXPP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card is installed. You can edit the splitter protection group name. |
||
A splitter protection group is configurable for the OTU2_XP card. You can create a splitter protection group on Ports 3 and 4 of the OTU2_XP card using the G199 Create a Splitter Protection Group for the OTU2_XP Card. |
||
In the Layer 2 (L2) card mode 1+1 protection is provided to protect the card against client port and card failure. |
|
|
Step 3![]() Verify that pluggable ports are provisioned for the same payload and payload rate on the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards where you will create the Y-cable protection group:
Verify that pluggable ports are provisioned for the same payload and payload rate on the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP cards where you will create the Y-cable protection group:
a.![]() Display the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card in card view.
Display the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card in card view.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tab.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tab.
c.![]() Verify that a pluggable port is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and the payload type and rate is provisioned for it in the Pluggable Ports area. If they are not the same, for example, if the pluggable port and rate are not the same, you must either delete the provisioned rate and create a new rate to match using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot or replace the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) using the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
Verify that a pluggable port is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and the payload type and rate is provisioned for it in the Pluggable Ports area. If they are not the same, for example, if the pluggable port and rate are not the same, you must either delete the provisioned rate and create a new rate to match using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot or replace the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) using the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
Step 4![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Step 5![]() In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
Step 6![]() In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
- Name—Type a name for the protection group. The name can have up to 32 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. Special characters are permitted. For TL1 compatibility, do not use question mark (?), backslash (\), or double quote (“) characters.
- Type—Choose Y Cable from the drop-down list.
- Protect Port—From the drop-down list, choose the port that will be the standby or protection port to the active port. The list displays the available transponder or muxponder ports. If transponder or muxponder cards are not installed, no ports appear in the drop-down list.
After you choose the protect port, a list of available working ports appear in the Available Ports list. If no cards are available, no ports appear. If this occurs, you can not complete this task until you install the physical cards or preprovision the ONS 15454 slots using the G353 Preprovision a Slot.
Step 7![]() From the Available Ports list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Ports. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Ports list.
From the Available Ports list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Ports. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Ports list.
Step 8![]() Complete the remaining fields:
Complete the remaining fields:
- Revertive—Check this check box if you want traffic to revert to the working port after failure conditions remain corrected for the amount of time entered in the Reversion Time field.
- Reversion time—If Revertive is checked, select a reversion time from the drop-down list. The range is 0.5 to 12.0 minutes. The default is 5.0 minutes. Reversion time is the amount of time that will elapse before the traffic reverts to the working card. The reversion timer starts after conditions causing the switch are cleared.

Note The Bidirectional switching option is available for Y-cable protection groups only in the following cases:
- On the MXP_MR_10DME card when ISC3_PEER_1G/ISC3_PEER_2G is the client payload.
- On the MXP_MR_10DME and MXP_MR_2.5G cards when Fibre Channel is the client payload. In this case Bidirectional switching is:
–![]() Automatically enabled when Distance Extension is enabled.
Automatically enabled when Distance Extension is enabled.
–![]() Automatically disabled when Distance Extension is disabled.
Automatically disabled when Distance Extension is disabled.
The Bidirectional switching option is available for all SONET and SDH 1+1 protection groups.
Step 10![]() Repeat this procedure for every Y-cable protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Repeat this procedure for every Y-cable protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G199 Create a Splitter Protection Group for the OTU2_XP Card

Note![]() A splitter protection group is automatically created when a TXPP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, or PSM card is installed. You can edit the splitter protection group name for these cards. The splitter protection group is deleted when you delete the TXPP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, or PSM card.
A splitter protection group is automatically created when a TXPP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, or PSM card is installed. You can edit the splitter protection group name for these cards. The splitter protection group is deleted when you delete the TXPP_MR_2.5G, MXPP_MR_2.5G, or PSM card.

Note![]() Splitter protection is available for the OTU2_XP card when it is provisioned in Transponder configuration only. In a splitter-protected Transponder configuration, Port 1 is the client port, Port 3 is the working trunk port, and Port 4 is the standby trunk port.
Splitter protection is available for the OTU2_XP card when it is provisioned in Transponder configuration only. In a splitter-protected Transponder configuration, Port 1 is the client port, Port 3 is the working trunk port, and Port 4 is the standby trunk port.

Note![]() For SONET or SDH payloads, Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a splitter protection group.
For SONET or SDH payloads, Loss of Pointer Path (LOP-P) alarms can occur on a split signal if the ports are not in a splitter protection group.
Step 1![]() View the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix (see Table 4-1) for your site. Verify which OTU2_XP card needs a splitter protection group. (Cards requiring splitter protection are indicated with “Splitter” in the Traffic Matrix table Protection Type column. Refer to the Cisco TransportPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for more information.)
View the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix (see Table 4-1) for your site. Verify which OTU2_XP card needs a splitter protection group. (Cards requiring splitter protection are indicated with “Splitter” in the Traffic Matrix table Protection Type column. Refer to the Cisco TransportPlanner DWDM Operations Guide for more information.)
Step 2![]() Verify that the OTU2_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Verify that the OTU2_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Step 3![]() Verify that the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is provisioned for the same payload rate as the pluggable port on the OTU2_XP card where you will create the splitter protection group:
Verify that the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is provisioned for the same payload rate as the pluggable port on the OTU2_XP card where you will create the splitter protection group:
a.![]() Display the OTU2_XP card in card view.
Display the OTU2_XP card in card view.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Module tabs.
c.![]() Verify that a pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and that the payload rate of the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is same as the payload rate of the pluggable port on the OTU2_XP card provisioned in the Pluggable Ports area. If they are not the same, you must either delete the provisioned rate and create a new rate to match using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot or replace the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) using the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
Verify that a pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is provisioned in the Pluggable Port Module area, and that the payload rate of the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) slot is same as the payload rate of the pluggable port on the OTU2_XP card provisioned in the Pluggable Ports area. If they are not the same, you must either delete the provisioned rate and create a new rate to match using the G273 Preprovision an SFP or XFP Slot or replace the pluggable port (SFP or XFP) using the G64 Remove an SFP or XFP.
Step 4![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Step 5![]() In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
Step 6![]() In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
- Name—Type a name for the protection group. The name can have up to 32 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. Special characters are permitted. For TL1 compatibility, do not use question mark (?), backslash (\), or double quote (“) characters.
- Type—Choose Splitter from the drop-down list.
- Protect Card—From the drop-down list, choose the port that will be the standby or protection port to the active port. The list displays the available OTU2_XP ports. If transponder or muxponder cards are not installed or if the trunk ports of the card are part of a regenerator group, no ports appear in the drop-down list.
After you choose the protect port, a list of available working ports appear in the Available Cards list. If no cards are available, no ports appear. If this occurs, you cannot complete this task until you install the physical cards or preprovision the ONS 15454 slots using the G353 Preprovision a Slot.
Step 7![]() From the Available Cards list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Cards. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Cards list.
From the Available Cards list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in Protect Cards. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Cards list.
Step 8![]() Complete the remaining fields:
Complete the remaining fields:
- Revertive—Check this check box if you want traffic to revert to the working port after failure conditions remain corrected for the amount of time entered in the Reversion Time field.
- Reversion time—If Revertive is checked, select a reversion time from the drop-down list. The range is 0.5 to 12.0 minutes. The default is 5.0 minutes. Reversion time is the amount of time that will elapse before the traffic reverts to the working card. The reversion timer starts after conditions causing the switch are cleared.

Note![]() The Bidirectional Switching option is not applicable for splitter protection groups.
The Bidirectional Switching option is not applicable for splitter protection groups.
Step 10![]() Repeat this procedure for every splitter protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Repeat this procedure for every splitter protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G198 Create 1+1 Protection for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to protect the card against client port and card failure. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to protect the card against client port and card failure. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Step 3![]() Complete the G242 Create an Internal Patchcord Manually by selecting the Trunk to Trunk (L2) option, at the trunk port where you want to create 1+1 protection.
Complete the G242 Create an Internal Patchcord Manually by selecting the Trunk to Trunk (L2) option, at the trunk port where you want to create 1+1 protection.
Step 4![]() Complete the G461 Create a 1+1 Protection Group for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards to create a protection group.
Complete the G461 Create a 1+1 Protection Group for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards to create a protection group.
Step 5![]() Configure the standby port behavior, by setting the Protection Action to None or Squelch. For detailed information on how to configure the standby port behavior, see the, G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Configure the standby port behavior, by setting the Protection Action to None or Squelch. For detailed information on how to configure the standby port behavior, see the, G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.

Note![]() Do not enable squelch in a 1 + 1 protection group, if the 100FX, 100LX, and ONS-SE-ZE-EL SFP are used in the protection group and is connected to the peer via the parallel cable (not Y-cable).
Do not enable squelch in a 1 + 1 protection group, if the 100FX, 100LX, and ONS-SE-ZE-EL SFP are used in the protection group and is connected to the peer via the parallel cable (not Y-cable).

Note![]() When you configure L2 1 + 1 protection on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, set the Protection Action to None on the client ports. Setting the Protection Action as Squelch results in unexpected switching behavior.
When you configure L2 1 + 1 protection on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, set the Protection Action to None on the client ports. Setting the Protection Action as Squelch results in unexpected switching behavior.
Step 6![]() Configure the standby and active port speed, by setting the mode parameter to Auto or 1000 or any other values. For detailed information on how to configure the standby port behavior, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Configure the standby and active port speed, by setting the mode parameter to Auto or 1000 or any other values. For detailed information on how to configure the standby port behavior, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G461 Create a 1+1 Protection Group for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This procedure creates a 1+1 protection group for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE slots where internal patchcords were created. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Step 2![]() In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
In the Protection Groups area, click Create.
Step 3![]() In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
In the Create Protection Group dialog box, enter the following:
- Name—Type a name for the protection group. The name can have up to 32 alphanumeric (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) characters. Special characters are permitted. For TL1 compatibility, do not use question mark (?), backslash (\), or double quote (“) characters.
- Type—Choose L2 1+1 (port) from the drop-down list.
- Protect Port—From the drop-down list, choose the port that will be the standby or protection port for the active port. The list displays the available transponder or muxponder ports. If transponder or muxponder cards are not installed, no ports appear in the drop-down list.
After you choose the protect port, a list of available working ports appear in the Available Ports list. If no cards are available, no ports appear. If this occurs, you cannot complete this task until you install the physical cards or preprovision the ONS 15454 slots using the G353 Preprovision a Slot.
Step 4![]() From the Available Ports list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in the Protected Port drop-down list. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Ports list.
From the Available Ports list, select the port that will be protected by the port you selected in the Protected Port drop-down list. Click the top arrow button to move the port to the Working Ports list.
Step 5![]() Complete the remaining fields:
Complete the remaining fields:
- Revertive—Check this check box if you want traffic to revert to the working port after failure conditions remain corrected for the amount of time entered in the Reversion Time field.
- Reversion time—If Revertive is checked, select a reversion time from the drop-down list. The range is 0.5 to 12.0 minutes. The default is 5.0 minutes. Reversion time is the amount of time that will elapse before the traffic reverts to the working card. The reversion timer starts after conditions causing the switch are cleared.
The bidirectional switching option is available for SONET and SDH 1+1 protection groups.
Step 7![]() Repeat this procedure for every 1+1 protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Repeat this procedure for every 1+1 protection group indicated in the Cisco TransportPlanner Traffic Matrix.
Step 8![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G98 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and threshold settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G277 Provision a Multirate PPM (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G229 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
- G230 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
- G231 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
- G232 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder SONET or SDH Line Threshold Settings
- G320 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line RMON Thresholds for 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON Payloads
- G305 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G306 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G234 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
- G367 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G229 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
This task changes the card settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-5 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-5 .

Note![]() The Card subtab Framing Type and Tunable Wavelengths fields are display-only. Framing Type shows the card framing type, either SONET or SDH, depending on whether the card is installed in an ANSI or ETSI chassis. The Tunable Wavelengths field shows the tunable wavelengths for the physical TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G that is installed.
The Card subtab Framing Type and Tunable Wavelengths fields are display-only. Framing Type shows the card framing type, either SONET or SDH, depending on whether the card is installed in an ANSI or ETSI chassis. The Tunable Wavelengths field shows the tunable wavelengths for the physical TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G that is installed.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G230 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
This task changes the line settings for the client port of the TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-6 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-6 .

Note![]() The 2.5G multirate transponder trunk settings are provisioned in the G305 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds.
The 2.5G multirate transponder trunk settings are provisioned in the G305 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
The user can assign a logical name for each of the ports shown by filling in this field. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(OC-N and STM-N payloads only) Sets the signal fail bit error rate. |
||
(OC-N and STM-N payloads only) Sets the signal degrade bit error rate. |
||
|
||
(OC-N and STM-N payloads only) Sets the automatic in-service soak period. |
||
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G231 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
This task changes the section trace settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards. |
|

Note![]() This task only applies to SONET services.
This task only applies to SONET services.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-7 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-7 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G367 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
This task changes the trunk wavelength settings for the TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-8 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-8 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G232 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder SONET or SDH Line Threshold Settings
This task changes the line threshold settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards carrying OC-3/STM-1, OC-12/STM-4, and OC-48/STM-16 payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings in Table 6-9 .
Modify any of the settings in Table 6-9 .

Note![]() Some parameters and options in Table 6-9 do not apply to all TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G cards. If a parameter or option does not apply, that parameter or option does not appear in CTC.
Some parameters and options in Table 6-9 do not apply to all TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G cards. If a parameter or option does not apply, that parameter or option does not appear in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G320 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Line RMON Thresholds for 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON Payloads
This task changes the line remote monitoring (RMON) threshold settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards carrying the 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In card view, display the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In card view, display the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-10 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-10 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Enter the appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Enter the appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G305 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G trunk port alarm and threshold crossing alert (TCA) thresholds. |
|

Note![]() In this task, trunk port refers to Port 2 for TXP_MR_2.5G cards, and to Ports 2 and 3 for TXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
In this task, trunk port refers to Port 2 for TXP_MR_2.5G cards, and to Ports 2 and 3 for TXPP_MR_2.5G cards.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Pluggable Port Modules tab. Under Pluggable Ports, record the Rate that is provisioned.
Click the Pluggable Port Modules tab. Under Pluggable Ports, record the Rate that is provisioned.
Step 3![]() Look up the rate in Table 6-11 and note whether it is 2R or 3R.
Look up the rate in Table 6-11 and note whether it is 2R or 3R.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
3R6 |
|||
|
|
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 5![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it and click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it and click Refresh.
Step 6![]() Referring to Table 6-12 , verify the trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High and RX Power Low depending on whether the rate is 2R or 3R. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-12 , verify the trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High and RX Power Low depending on whether the rate is 2R or 3R. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Step 8![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 9![]() Verify the trunk port Alarm thresholds for RX Power High is –7 dBm, and for RX Power Low is –26 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the trunk port Alarm thresholds for RX Power High is –7 dBm, and for RX Power Low is –26 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G306 Provision the 2.5G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Referring to Table 6-13 , verify the Port 1 (client) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-13 , verify the Port 1 (client) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
|
(by CTC) |
(SFP) |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 6![]() Referring to Table 6-14 , verify the Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-14 , verify the Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 8![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G234 Change the 2.5G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
This task changes the OTN settings for TXP_MR_2.5G and TXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_2.5G or TXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-15 through 6-18 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-15 through 6-18 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM settings independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM settings independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-15 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-16 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > G.709 Thresholds tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Port7 |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
Table 6-17 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Threshold tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-18 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G96 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and threshold settings for 10G multirate transponder cards including the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G277 Provision a Multirate PPM (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|

Note![]() The TXP_MR_10G card does not support PPMs.
The TXP_MR_10G card does not support PPMs.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() If you are provisioning a TXP_MR_10G card, complete the G365 Provision the TXP_MR_10G Data Rate, and if you are provisioning a TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C card, complete the G712 Provision the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C Data Rate. If not, continue with Step 4.
If you are provisioning a TXP_MR_10G card, complete the G365 Provision the TXP_MR_10G Data Rate, and if you are provisioning a TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C card, complete the G712 Provision the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C Data Rate. If not, continue with Step 4.
Step 4![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G216 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
- G217 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
- G218 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
- G219 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads Including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy
- G319 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line RMON Thresholds for 10G Ethernet LAN Phy Payloads
- G301 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G302 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G221 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
- G368 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G365 Provision the TXP_MR_10G Data Rate
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs.
Step 4![]() In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure.
Return to your originating procedure.
DLP-G712 Provision the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C Data Rate
This task changes the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C card data rate. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10E or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Pluggable Port Modules tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Port Modules area, click Create. The Create PPM dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
In the Create PPM dialog box, complete the following:
Step 5![]() Click OK. The newly created PPM appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable
Click OK. The newly created PPM appears in the Pluggable Port Modules area. The row in the Pluggable
Step 6![]() Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Port Modules area turns white and the Actual Equipment Type column lists the equipment name.
Step 7![]() In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Ports dialog box appears.
In the Pluggable Ports area, click Create. The Create Ports dialog box appears.
Step 8![]() In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
- SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) (including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy)
- 10G Ethernet LAN Phy
- 10G FIBER Channel
- (TXP-MR-10EX_C card only) IB_5G
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure.
Return to your originating procedure.
DLP-G216 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
This task changes the card settings for the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, or TXP_MR_10E_L card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, or TXP_MR_10E_L card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-19 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-19 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G217 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
This task changes the line settings for TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET/SDH/Ethernet tabs. SONET is the option for ANSI shelves when 10G Ethernet WAN phy is the Pluggable Port Rate, SDH is the option for ETSI shelves when 10G Ethernet WAN phy is the Pluggable Port Rate, and Ethernet is the option for ANSI or ETSI shelves when 10GE LAN Phy is the Pluggable Port Rate.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET/SDH/Ethernet tabs. SONET is the option for ANSI shelves when 10G Ethernet WAN phy is the Pluggable Port Rate, SDH is the option for ETSI shelves when 10G Ethernet WAN phy is the Pluggable Port Rate, and Ethernet is the option for ANSI or ETSI shelves when 10GE LAN Phy is the Pluggable Port Rate.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-20 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-20 .

Note![]() In Table 6-20, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all 10G multirate transponder cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-20, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all 10G multirate transponder cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy only) Sets the signal fail bit error rate. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy only) Sets the signal degrade bit error rate. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy only) The optical transport type. |
|||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled, or it can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
|
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy only) Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
|||
(TXP_MR_10E, OC192 only) Sets the ProvidesSync card parameter. If checked, the card is provisioned as a network element (NE) timing reference. |
|||
(TXP_MR_10E, OC192 only) Sets the EnableSync card parameter. Enables synchronization status messages (S1 byte), which allow the node to choose the best timing source. |
|||
(TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10G LAN Phy only) Sets the maximum Ethernet packet size. |
|||
(TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10G LAN Phy only) Sets the incoming MAC address. |
|||
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G218 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
This task changes the line section trace settings for the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C transponder cards. |
|

Note![]() The Section Trace tab is available for the 10G Multirate Transponder cards only if no PPMs are provisioned, or the OC192 PPM is provisioned. The tab is not available if a 10G Ethernet LAN Phy or 10G Fibre Channel PPM is provisioned.
The Section Trace tab is available for the 10G Multirate Transponder cards only if no PPMs are provisioned, or the OC192 PPM is provisioned. The tab is not available if a 10G Ethernet LAN Phy or 10G Fibre Channel PPM is provisioned.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-21 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-21 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G368 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
This task changes the trunk wavelength settings for the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards. |
|

Note![]() Before modifying the wavelength settings, change the port state to OOS,DSBLD (for ANSI) or Locked,disabled (for ETSI) and delete the circuit and patchcord provisioning present on the port. Payload or communication channel provisioning can be retained.
Before modifying the wavelength settings, change the port state to OOS,DSBLD (for ANSI) or Locked,disabled (for ETSI) and delete the circuit and patchcord provisioning present on the port. Payload or communication channel provisioning can be retained.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-22 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-22 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G219 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads Including 10G Ethernet WAN Phy
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-23 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-23 .

Note![]() Parameters shown in Table 6-23 do not apply to all 10G multirate transponder cards. If the parameter or option does not apply, it is not shown in CTC.
Parameters shown in Table 6-23 do not apply to all 10G multirate transponder cards. If the parameter or option does not apply, it is not shown in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G319 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder Line RMON Thresholds for 10G Ethernet LAN Phy Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C transponder cards carrying the physical 10G Ethernet LAN payload. |
|
Step 1![]() Display the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
Display the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-24 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-24 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).

Note![]() To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G301 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C trunk port alarm and threshold cross alert (TCA) thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-25 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-25 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-26 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-26 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G302 Provision the 10G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-27 , verify the Port 1 (Client) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-27 , verify the Port 1 (Client) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Hit Enter, then click Apply.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
|
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IB_5G8 |
|
|
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-28 , provision the Port 1 (Client) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned.
Referring to Table 6-28 , provision the Port 1 (Client) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
|
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IB_5G9 |
|
|
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G221 Change the 10G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
This task changes the line OTN settings for the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, and TXP_MR_10EX_C transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10G, TXP_MR_10E, TXP_MR_10E_C, TXP_MR_10E_L, or TXP_MR_10EX_C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-29 through 6-32 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-29 through 6-32 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-29 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
Table 6-30 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-31 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Thresholds tab.
Table 6-32 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G292 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds
This procedure changes the line settings, PM parameters, and threshold settings for 40G multirate transponder cards (40E-TXP-C, 40ME-TXP-C). |
|

Note![]() The 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards does not support PPMs.
The 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards does not support PPMs.

Note![]() The maximum ambient operating temperature for 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C cards is 500 Celsius.
The maximum ambient operating temperature for 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C cards is 500 Celsius.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the transponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() If you are provisioning a 40E-TXP-C or 40ME-TXP-C card, complete the G656 Provision the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C Data Rate. If not, continue with Step 4.
If you are provisioning a 40E-TXP-C or 40ME-TXP-C card, complete the G656 Provision the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C Data Rate. If not, continue with Step 4.
Step 4![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G657 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
- G658 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
- G659 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder SONET, SDH, or Ethernet Line Settings
- G660 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
- G661 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads
- G663 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G664 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G665 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G656 Provision the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C Data Rate
This task changes the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C card data rate. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the card data rate settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Data Rate Selection tabs.
Step 4![]() In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
In the Create Port dialog box, choose one of the following data rates:
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure.
Return to your originating procedure.
DLP-G657 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Card Settings
This task changes the card settings of the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-33 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-33 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G658 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Settings
This task changes the line settings of the 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-34 .
Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-34 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Assigns a logical name for each of the ports shown by filling in this field. |
User-defined. The port name can be up to 32 alphanumeric or special characters, or both. The port name is blank by default. For information on assigning a port name, see the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, see the Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, see Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
|
||
Automatic in-service soak time. The duration of time that must pass with an uninterrupted signal before the traffic/termination transitions to the IS-NR (ANSI) or unlocked-enabled (ETSI) service state. |
||
(Display only) Displays the optical reach distance of the port. |
||
Applicable only to client port 1. When the termination mode is set to transparent, squelch or AIS (OC-768, or STM-256, or OTU3 payloads only) is enabled. For section/line termination mode, AIS (OC-768, or STM-256 only) is enabled. |
||
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G659 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder SONET, SDH, or Ethernet Line Settings
This task changes the SONET, SDH, or Ethernet line settings for 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the SONET, SDH, or Ethernet line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the SONET, SDH, or Ethernet line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET/SDH/Ethernet tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET/SDH/Ethernet tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-35 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-35 .

Note![]() In Table 6-35, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all 40G multirate transponder cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-35, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all 40G multirate transponder cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Note Port 17 and Port 18 are trunk ports that support STM64 payload in a single-card configuration. These ports are interlink ports in a double-card configuration (ADM-10G peer group). |
|||
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled, or it can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
|
Displays the optical reach distance of the client and trunk port. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G660 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Section Trace Settings
This task changes the line section trace settings of the 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-37 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-37 .
Step 5![]() Click Default to restore default values.
Click Default to restore default values.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G661 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings of 40E-TXP-C and 40ME-TXP-C transponder cards carrying SONET or SDH payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-38 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-38 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G663 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C trunk port alarm and threshold cross alert (TCA) thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Under Types area, verify that the TCA radio button is selected. If not, click it, then click Refresh.
Under Types area, verify that the TCA radio button is selected. If not, click it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-39 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) TCA thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-39 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) TCA thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Step 5![]() Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 7![]() Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 8![]() Referring to Table 6-39 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) alarm thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-39 , verify the trunk port (Port 2) alarm thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Step 9![]() Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 11![]() Click Default to restore default values.
Click Default to restore default values.
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G664 Provision the 40G Multirate Transponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Under Types area, verify that the TCA radio button is selected. If not, click it, then click Refresh.
Under Types area, verify that the TCA radio button is selected. If not, click it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-41 , verify the client port (Port 1) TCA thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Referring to Table 6-41 , verify the client port (Port 1) TCA thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting the existing value, and entering the new value. Press Enter, then click Apply.
Step 5![]() Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
|
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 7![]() Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 8![]() Referring to Table 6-42 , provision the client port (Port 1) alarm thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned.
Referring to Table 6-42 , provision the client port (Port 1) alarm thresholds for Laser Bias High, RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned.
Step 9![]() Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
Under Intervals area, select 15 Min or 1 Day, then click Refresh.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G665 Change the 40G Multirate Transponder OTN Settings
This task changes the line OTN settings of the 40E-TXP-C, and 40ME-TXP-C transponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40E-TXP-C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-43 through 6-46 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-43 through 6-46 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End, 15 Min and 1 Day, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End, 15 Min and 1 Day, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-43 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
Table 6-44 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-45 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Thresholds tab.
Table 6-46 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Click Default to restore default settings.
Click Default to restore default settings.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G170 Provision the ADM-10G Card Peer Group, Ethernet Settings, Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds
This procedure creates an ADM-10G peer group and changes line settings, PM parameters, and threshold settings for ADM-10G cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G411 Provision an ADM-10G PPM and Port (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the ADM-10G card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the ADM-10G card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() To provision a peer group, complete the G403 Create the ADM-10G Peer Group.
To provision a peer group, complete the G403 Create the ADM-10G Peer Group.
Step 4![]() To provision Ethernet settings, complete the G469 Provision the ADM-10G Card Ethernet Settings.
To provision Ethernet settings, complete the G469 Provision the ADM-10G Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 5![]() To change line settings, complete the following tasks as needed:
To change line settings, complete the following tasks as needed:
Step 6![]() To change thresholds, complete the following tasks as needed:
To change thresholds, complete the following tasks as needed:
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G403 Create the ADM-10G Peer Group
This task creates peer group protection for two ADM-10G cards within the same node, located on the same shelf. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards, for two ADM-10G cards (located on the same shelf) for which a peer group is desired. |
|

Note![]() You cannot perform this task on a single ADM-10G card; it is only available if a second ADM-10G card can be accessed through the interlink ports (Port 17 and Port 18).
You cannot perform this task on a single ADM-10G card; it is only available if a second ADM-10G card can be accessed through the interlink ports (Port 17 and Port 18).

Note![]() Due to a hardware limitation, you cannot provision the SDCC/LDCC on Port 17.
Due to a hardware limitation, you cannot provision the SDCC/LDCC on Port 17.

Note![]() Perform this task on only one of the two peer cards.
Perform this task on only one of the two peer cards.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() In the ADM Group Peer drop-down list, choose the slot number (for example, 14) where the companion ADM-10G card is located.
In the ADM Group Peer drop-down list, choose the slot number (for example, 14) where the companion ADM-10G card is located.
Step 4![]() In the ADM Peer Group field, enter a group name.
In the ADM Peer Group field, enter a group name.

Note![]() The Card Parameters Tunable Wavelengths area is read-only and does not contain any wavelengths until circuits are separately provisioned for the card.
The Card Parameters Tunable Wavelengths area is read-only and does not contain any wavelengths until circuits are separately provisioned for the card.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G469 Provision the ADM-10G Card Ethernet Settings
This task changes the Ethernet settings for the ADM-10G card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Ethernet tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Ethernet tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Ethernet tab as described in Table 6-47 . The parameters that appear depend on the card mode.
Modify any of the settings for the Ethernet tab as described in Table 6-47 . The parameters that appear depend on the card mode.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G397 Change the ADM-10G Line Settings
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-48 as needed.
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-48 as needed.

Note![]() In Table 6-48, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all ADM-10G cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-48, some parameter tabs do not always apply to all ADM-10G cards. If a tab does not apply, it will not appear in CTC.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Note Port 17 and Port 18 are trunk ports that support OC192 payload in a single-card configuration. These ports are interlink ports in a double-card configuration (ADM-10G peer group). |
Note Port 17 and Port 18 are trunk ports that support STM64 payload in a single-card configuration. These ports are interlink ports in a double-card configuration (ADM-10G peer group). |
||
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled, or it can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
|
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
||
Shows the supported wavelengths of the trunk port after the card is installed in the format: first wavelength-last wavelength-frequency spacing-number of supported wavelengths. For example, 1529.55nm-1561.83nm-50gHz-8 are supported wavelengths. |
Shows the supported wavelengths of the trunk port after the card is installed in the format: first wavelength-last wavelength-frequency spacing-number of supported wavelengths. For example, 1529.55nm-1561.83nm-50gHz-8 are supported wavelengths. |
Step 5![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET or SDH tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET or SDH tabs.
Step 6![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-49 as needed.
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-49 as needed.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G398 Change the ADM-10G Line Section Trace Settings
This task changes the line section trace settings for the ADM-10G cards. |
|

Note![]() The Section Trace tab is available for ports configured as OC-N (Ports 1 through 16, Ports 17 and 18 [only in a single-card configuration] and Port 19). Section trace is not available on interlink ports.
The Section Trace tab is available for ports configured as OC-N (Ports 1 through 16, Ports 17 and 18 [only in a single-card configuration] and Port 19). Section trace is not available on interlink ports.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the section trace settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the section trace settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-50 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-50 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G399 Change the ADM-10G Line Thresholds for SONET and SDH Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for ADM-10G cards carrying SONET payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line threshold settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line threshold settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET or SDH Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET or SDH Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-51 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-51 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G412 Change the ADM-10G Line RMON Thresholds for the 1G Ethernet Payload
This task changes the line RMON threshold settings for an ADM-10G card carrying the 1G Ethernet payload. |
|

Note![]() This task can only be performed if the ADM-10G card has at least one PPM port provisioned for Gigabit Ethernet.
This task can only be performed if the ADM-10G card has at least one PPM port provisioned for Gigabit Ethernet.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line RMON thresholds. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the line RMON thresholds. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose the applicable Ethernet variable. See Table 6-52 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose the applicable Ethernet variable. See Table 6-52 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Type an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Type the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G400 Provision the ADM-10G Interlink or Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the ADM-10G interlink or trunk port alarm and threshold crossing alert (TCA) thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the interlink or trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the interlink or trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-53 , verify the interlink or trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.
Referring to Table 6-53 , verify the interlink or trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-54 , verify the interlink or trunk port alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.
Referring to Table 6-54 , verify the interlink or trunk port alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G401 Provision the ADM-10G Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the ADM-10G card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, check it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-13 and Table 6-14, verify the Port 1 to 16 (Client) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.
Referring to Table 6-13 and Table 6-14, verify the Port 1 to 16 (Client) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-13 and Table 6-14, verify the interlink ports 17-1 and 18-1 for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low settings. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.
Referring to Table 6-13 and Table 6-14, verify the interlink ports 17-1 and 18-1 for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low settings. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and pressing Enter.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G402 Change the ADM-10G OTN Settings
This task changes the line OTN settings for the ADM-10G cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the ADM-10G card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-55 through 6-58 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-55 through 6-58 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio buttons and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio buttons and click Refresh.
Table 6-55 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
Table 6-56 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > ITU-T G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-57 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Thresholds tab.
Table 6-58 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G333 Add an ADM-10G card to an Existing Topology
This procedure adds an ADM-10G card to an existing topology. Perform the steps in this procedure when OCHNC and DCC are present in the network. In case of OCH trails, delete all the circuits in Step 3 that traverses the port before deleting the OCH-trail. |
|
|
|
Step 1![]() If path protected circuits exist between Node A and Node B, complete the DLP-A197 Initiate a Path Protection Force Switch task. This task applies a force switch on the path between Node A and Node B.
If path protected circuits exist between Node A and Node B, complete the DLP-A197 Initiate a Path Protection Force Switch task. This task applies a force switch on the path between Node A and Node B.
Step 2![]() Complete the G129 Add a DWDM Node task to add Node C.
Complete the G129 Add a DWDM Node task to add Node C.
Step 3![]() Complete the G106 Delete Optical Channel Network Connections task to delete OCHNC circuit between Node A and Node B.
Complete the G106 Delete Optical Channel Network Connections task to delete OCHNC circuit between Node A and Node B.
Step 4![]() Complete the G59 Create, Delete, and Manage Optical Channel Network Connections, task to create OCHNC circuit between Node A-->Node C and Node C-->Node B for wavelength connectivity.
Complete the G59 Create, Delete, and Manage Optical Channel Network Connections, task to create OCHNC circuit between Node A-->Node C and Node C-->Node B for wavelength connectivity.

Note![]() The ports on the card in Node C must be tuned to the same wavelength as Node A and Node B.
The ports on the card in Node C must be tuned to the same wavelength as Node A and Node B.
Step 5![]() Create DCC terminations on Node C. See the DLP-A377 Provision Section DCC Terminations task.
Create DCC terminations on Node C. See the DLP-A377 Provision Section DCC Terminations task.
Alternatively, if additional bandwidth is needed for CTC management, complete the DLP-A378 Provision Line DCC Terminations task.
Step 6![]() Ensure that the DCCs are functional between Node A-->Node C and Node C-->Node B. See the G76 Provision DCC/GCC Terminations task.
Ensure that the DCCs are functional between Node A-->Node C and Node C-->Node B. See the G76 Provision DCC/GCC Terminations task.
Step 7![]() Complete the G200 Create, Delete, and Manage STS or VC Circuits for the ADM-10G Card to create pass-through STS or VC circuits in Node C.
Complete the G200 Create, Delete, and Manage STS or VC Circuits for the ADM-10G Card to create pass-through STS or VC circuits in Node C.
Step 8![]() Complete the NTP-A301 Merge Circuits task for each circuit created.
Complete the NTP-A301 Merge Circuits task for each circuit created.
Step 9![]() If path protected circuits exist between Node A and Node B, complete the DLP-A198 Clear a Path Protection Force Switch task. This task clears a force switch on the path between Node A and Node B.
If path protected circuits exist between Node A and Node B, complete the DLP-A198 Clear a Path Protection Force Switch task. This task clears a force switch on the path between Node A and Node B.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G97 Modify the 4x2.5G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and threshold settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards. G277 Provision a Multirate PPM (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G222 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Card Settings
- G223 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Line Settings
- G224 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Section Trace Settings
- G225 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Settings
- G226 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder SONET/SDH Line Thresholds Settings
- G303 Provision the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G304 Provision the 4x2.5G Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G228 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Line OTN Settings
- G369 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
Step 4![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G222 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Card Settings
This task changes the card settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards, including payload type, termination mode, and wavelength. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-59 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-59 .

Note![]() Parameters shown in Table 6-59 do not apply to all 4x2.5G muxponder cards. If the parameter or option does not apply, it is not shown in CTC.
Parameters shown in Table 6-59 do not apply to all 4x2.5G muxponder cards. If the parameter or option does not apply, it is not shown in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G223 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Line Settings
This task changes the line settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) tabs.

Note![]() The SONET tab appears only if you have created a PPM for a given port.
The SONET tab appears only if you have created a PPM for a given port.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-60 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-60 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Display only) Port number. Ports 1 to 4 are client ports (OC-48/STM-16). Port 5 is the DWDM trunk (OC-192/STM-64) that provides wavelength services. Client ports will not appear of the pluggable port module is not provisioned for it. |
||
Provides the ability to assign the specified port a logical name. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled or can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
||
Enables synchronization status messages (S1 byte), which allow the node to choose the best timing source. (This parameter does not appear for the MXP_2.5G_10E trunk port.) |
||
Sets the ProvidesSync card parameter. If checked, the card is provisioned as an NE timing reference. (This parameter does not appear for the MXP_2.5G_10E trunk port.) |
||
|
||
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G224 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Section Trace Settings
This task changes the section trace settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|

Note![]() The Section Trace tab appears only if you have created a PPM for the card.
The Section Trace tab appears only if you have created a PPM for the card.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-61 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-61 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G225 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Settings
This task provisions the trunk settings for the MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|

Note![]() This task does not apply to the MXP_2.5G_10G card.
This task does not apply to the MXP_2.5G_10G card.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Trunk tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Trunk tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-62 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-62 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
(Display only) Displays the port number. Port 5 is the DWDM trunk (OC-192/STM-64) that provides wavelength services. |
||
Provides the ability to assign the specified port a logical name. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled or can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
(OC-N and STM-N payloads only) Sets the automatic in-service soak period. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G369 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
This task changes the trunk wavelength settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-63 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-63 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G226 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder SONET/SDH Line Thresholds Settings
This task changes the SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) line threshold settings for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-64 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-64 .

Note![]() In Table 6-64, some parameter tabs or selections do not always apply to all 4x2.5G muxponder cards. If the tabs or selections do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-64, some parameter tabs or selections do not always apply to all 4x2.5G muxponder cards. If the tabs or selections do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G303 Provision the 4x2.5G Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C trunk port alarm and TCA thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Select TCA (if not already selected), a 15 Min or 1 Day PM interval radio button and then click Refresh.
Select TCA (if not already selected), a 15 Min or 1 Day PM interval radio button and then click Refresh.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-65 , verify the trunk port (Port 5) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-65 , verify the trunk port (Port 5) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-66 , verify the trunk port (Port 5) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-66 , verify the trunk port (Port 5) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G304 Provision the 4x2.5G Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Referring to Table 6-67 , verify the client Port N (where N = 1 through 4) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-67 , verify the client Port N (where N = 1 through 4) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 4![]() Repeat Step 3 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Step 3 to provision each additional client port.
Step 5![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 6![]() Referring to Table 6-68 , verify the client Port N (where N = 1 through 4) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-68 , verify the client Port N (where N = 1 through 4) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 8![]() Repeat Steps 6 and 7 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Steps 6 and 7 to provision each additional client port.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G228 Change the 4x2.5G Muxponder Line OTN Settings
This task changes the line OTN settings for MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, and MXP_2.5G_10EX_C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, MXP_2.5G_10E_L, or MXP_2.5G_10EX_C card where you want to change the line OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, OTN G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, OTN G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-69 through 6-72 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-69 through 6-72 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-69 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.

Note![]() In Table 6-69, some parameter tabs or values do not always apply to all MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, or MXP_2.5G_10E_L cards. If the tabs or values do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-69, some parameter tabs or values do not always apply to all MXP_2.5G_10G, MXP_2.5G_10E, MXP_2.5G_10E_C, or MXP_2.5G_10E_L cards. If the tabs or values do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
Table 6-70 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-71 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Thresholds tab.
Table 6-72 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G99 Modify the 2.5G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and threshold settings for the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G277 Provision a Multirate PPM (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G236 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Client Line Settings
- G237 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Distance Extension Settings
- G238 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder SONET (OC-48)/SDH (STM-16) Settings
- G239 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Section Trace Settings
- G240 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
- G321 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Line Thresholds for 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON Payloads
- G307 Provision the 2.5G Data Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G308 Provision the 2.5G Data Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G370 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings

Note![]() To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G236 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Client Line Settings
This task changes the client line settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-73 .
Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-73 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
The user can assign a logical name for each of the ports shown by filling in this field. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. Note You can provision a string (port name) for each fiber channel/FICON interface on the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G cards, which allows the MDS Fabric Manager to create a link association between that SAN port and a SAN port on a Cisco MDS 9000 switch. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
|
||
The reach distances that appear in the drop-down list depend on the card:
|
||
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G237 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Distance Extension Settings
This task changes the distance extension settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|

Note![]() Distance extension settings can be changed only if the facilities are out of service (OOS,DSBLD).
Distance extension settings can be changed only if the facilities are out of service (OOS,DSBLD).

Note![]() The distance extension parameters only apply to client ports (Ports 1 to 8) and not to the trunk ports (Port 9 for MXP_MR_2.5G card or Ports 9 and 10 for the MXPP_MR_2.5G card).
The distance extension parameters only apply to client ports (Ports 1 to 8) and not to the trunk ports (Port 9 for MXP_MR_2.5G card or Ports 9 and 10 for the MXPP_MR_2.5G card).
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the distance extension settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the distance extension settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. A client port must be provisioned for the tab to be present.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. A client port must be provisioned for the tab to be present.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual
Step 3![]() Locate the Client port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If yes, continue with Step 4. If not, complete the following substeps:
Locate the Client port table row and verify that the Service State column value is OOS-MA,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked-enabled,disabled (ETSI). If yes, continue with Step 4. If not, complete the following substeps:
a.![]() Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Maintenance (ETSI).
Step 4![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Distance Extension tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Distance Extension tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Step 5![]() Modify any of the settings for the Distance Extension tab as described in Table 6-74 .
Modify any of the settings for the Distance Extension tab as described in Table 6-74 .
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G238 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder SONET (OC-48)/SDH (STM-16) Settings
This task changes the SONET (OC-48) or SDH (STM-16) settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|

Note![]() SONET (OC-48)/SDH (STM-16) settings apply only to the trunk ports (Port 9 for the MXP_MR_2.5G card and Ports 9 and 10 for the MXPP_MR_2.5G card.)
SONET (OC-48)/SDH (STM-16) settings apply only to the trunk ports (Port 9 for the MXP_MR_2.5G card and Ports 9 and 10 for the MXPP_MR_2.5G card.)
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the OC-48/STM-64 settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the OC-48/STM-64 settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI). Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI). Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the SONET or SDH tab as described in Table 6-75 .
Modify any of the settings for the SONET or SDH tab as described in Table 6-75 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
9 (trunk for MXP_MR_2.5G) or 9 and 10 (trunks for MXPP_MR_2.5G) |
||
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
SF BER10 |
||
SD BER 1 |
||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled or can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
||
Sets the EnableSync card parameter. Enables synchronization status messages (S1 byte), which allow the node to choose the best timing source. |
||
Sets the Send DoNotUse card state. When checked, sends a DUS message on the S1 byte. |
||
Sets the ProvidesSync card parameter. If checked, the card is provisioned as an NE timing reference. |
|
10.SF BER and SD BER thresholds apply only to trunk ports (Port 9 for MXP_MR_2.5G and Ports 9 and 10 for MXPP_MR_2.5G). |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G239 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Section Trace Settings
This task changes the section trace settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings in the Section Trace tab as described in Table 6-76 .
Modify any of the settings in the Section Trace tab as described in Table 6-76 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G370 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
This task changes the trunk wavelength settings for the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-77 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-77 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G240 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
This task changes the SONET or SDH line threshold settings for MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as shown in Table 6-78 .
Modify any of the settings as shown in Table 6-78 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() In Table 6-78, some parameters or options do not apply to all MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G cards. If the parameters or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-78, some parameters or options do not apply to all MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G cards. If the parameters or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G321 Change the 2.5G Data Muxponder Line Thresholds for 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for MXP_MR_10G and MXPP_MR_2.5G transponder cards carrying the 1G Ethernet or 1G FC/FICON payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() Display the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
Display the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-79 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-79 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G307 Provision the 2.5G Data Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G trunk port alarm and TCA thresholds. |
|

Note![]() Throughout this task, trunk port refers to Port 9 (MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G) and Port 10 (MXPP_MR_2.5G only).
Throughout this task, trunk port refers to Port 9 (MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G) and Port 10 (MXPP_MR_2.5G only).
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 3![]() Verify the trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High is –9 dBm and for RX Power Low is –23 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the trunk port TCA thresholds for RX Power High is –9 dBm and for RX Power Low is –23 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 4![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 5![]() Verify the trunk port Alarm thresholds for RX Power High is –7 dBm and for RX Power Low is –26 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the trunk port Alarm thresholds for RX Power High is –7 dBm and for RX Power Low is –26 dBm. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G308 Provision the 2.5G Data Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the MXP_MR_2.5G and MXPP_MR_2.5G cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_2.5G or MXPP_MR_2.5G card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Referring to Table 6-80 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-80 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
|
(by CTC) |
|
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision each additional client port.
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-81 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-81 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 9![]() Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision each additional client port. When you have finished provisioning client ports, continue with Step 10
Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision each additional client port. When you have finished provisioning client ports, continue with Step 10![]() .
.
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G148 Modify the 10G Data Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and threshold settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C muxponder cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G277 Provision a Multirate PPM (if necessary) G278 Provision the Optical Line Rate (if necessary) |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G333 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Client Line Settings
- G334 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Distance Extension Settings
- G340 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
- G335 Change the 10G Data Muxponder SONET (OC-192)/SDH (STM-64) Settings
- G336 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Section Trace Settings
- G341 Change the 10G Data Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
- G337 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Line RMON Thresholds for Ethernet, 1G FC/FICON, or ISC/ISC3 Payloads
- G338 Provision the 10G Data Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G339 Provision the 10G Data Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G366 Change the 10G Data Muxponder OTN Settings

Note![]() To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G333 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Client Line Settings
This task changes the line settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Client tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-82 .
Modify any of the settings for the Client tab as described in Table 6-82 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
The user can assign a logical name for each of the ports shown by filling in this field. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. Note You can provision a string (port name) for each fiber channel/FICON interface on the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C cards, which allows the MDS Fabric Manager to create a link association between that SAN port and a SAN port on a Cisco MDS 9000 switch. |
|
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
|
||
The reach distances that appear in the drop-down list depend on the card:
|
||
Shuts down the far-end laser in response to certain defects. (Squelch does not apply to ISC COMPACT payloads.) |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G334 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Distance Extension Settings
This task changes the distance extension settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, and MXP_MR_10DMEX_C muxponder card ports provisioned for Fibre Channel or FICON payloads. |
|

Note![]() The distance extension parameters only apply to client ports (Ports 1 to 8) and not to the trunk port (Port 9).
The distance extension parameters only apply to client ports (Ports 1 to 8) and not to the trunk port (Port 9).

Note![]() The client port must be in the OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI) state in order to change the distance extension settings. If a Y-cable is provisioned on the client port, both the working and protect client ports must be in OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI) state before you change the distance extension settings.
The client port must be in the OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI) state in order to change the distance extension settings. If a Y-cable is provisioned on the client port, both the working and protect client ports must be in OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,disabled (ETSI) state before you change the distance extension settings.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the distance extension settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C, MXP_MR_10DME_L, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to change the distance extension settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Distance Extension tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Distance Extension tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-83 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-83 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G340 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Trunk Wavelength Settings
This task changes the trunk wavelength settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the trunk wavelength settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Wavelength Trunk Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Wavelength Trunk Settings tab as described in Table 6-84 .
Modify any of the settings for the Wavelength Trunk Settings tab as described in Table 6-84 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G335 Change the 10G Data Muxponder SONET (OC-192)/SDH (STM-64) Settings
This task changes the OC-192 (ANSI)/STM-64 (ETSI) settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the SONET (OC-192)/SDH (STM-64) settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the SONET (OC-192)/SDH (STM-64) settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI). Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI). Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-85 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-85 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/ special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
SF BER11 |
||
SD BER 1 |
||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled or can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
||
Sets the ProvidesSync card parameter. If checked, the card is provisioned as a NE timing reference. |
||
Sets the EnableSync card parameter. Enables synchronization status messages (S1 byte), which allow the node to choose the best timing source. |
||
Sets the Send DoNotUse card state. When checked, sends a DUS (do not use) message on the S1 byte. |
|
11.SF BER and SD BER thresholds apply only to trunk ports (Port 9 for MXP_MR_2.5G and Ports 9 and 10 for MXPP_MR_2.5G). |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G336 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Section Trace Settings
This task changes the section trace settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings in the Section Trace tab as described in Table 6-86 .
Modify any of the settings in the Section Trace tab as described in Table 6-86 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G341 Change the 10G Data Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
This task changes the SONET or SDH line threshold settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as shown in Table 6-87 .
Modify any of the settings as shown in Table 6-87 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently; 15 Min and 1 Day independently; and Line and Section independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() In Table 6-87, some parameters and options do not apply to all MXP_MR_10DME cards. If the parameter or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-87, some parameters and options do not apply to all MXP_MR_10DME cards. If the parameter or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G337 Change the 10G Data Muxponder Line RMON Thresholds for Ethernet, 1G FC/FICON, or ISC/ISC3 Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L cards carrying Ethernet, FC/FICON, or ISC/ISC3 payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the line threshold settings in card view.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port, either the payload port, for example “1-1 (ONE_GE)”, or the equivalent ITU-T G.7041 GFP (Generic Frame Procedure) port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port, either the payload port, for example “1-1 (ONE_GE)”, or the equivalent ITU-T G.7041 GFP (Generic Frame Procedure) port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet, FC, FICON, or ISC variable. See Table 6-88 for a list of available Ethernet variables, Table 6-89 for a list of FC and FICON variables, Table 6-90 for a list of ISC and ISC3 variables, and Table 6-91 for a list of GFP variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet, FC, FICON, or ISC variable. See Table 6-88 for a list of available Ethernet variables, Table 6-89 for a list of FC and FICON variables, Table 6-90 for a list of ISC and ISC3 variables, and Table 6-91 for a list of GFP variables.
|
|
|
The total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters. |
|
Total number of frames received that are less than 5 bytes. This value is a part of HDLC and GFP port statistics. |
|
Number of received frames that exceed the MTU12. This value is part of HDLC and GFP port statistics. |
|
Number of receive data frames with payload CRC errors when HDLC framing is used. |
|
Number of transmitted data frames with payload CRC errors when HDLC framing is used. |
|
Number of code violations/running disparity errors in the 8b/10b encoded characters received. |
|
12.Frames larger than the MTU, including Jumbo frames, pass through. The MTU, however, is not specified by the user. |
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).

Note![]() To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G338 Provision the 10G Data Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L trunk port alarm and TCA thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 3![]() If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4
If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4![]() .
.
Step 4![]() Verify the trunk port (Port 9) TCA thresholds are set at the values shown as follows. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and press Enter.
Verify the trunk port (Port 9) TCA thresholds are set at the values shown as follows. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and press Enter.
Step 5![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Verify the trunk port (Port 9) Alarm thresholds are set at the values shown as follows. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and press Enter.
Verify the trunk port (Port 9) Alarm thresholds are set at the values shown as follows. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and press Enter.
Step 8![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G339 Provision the 10G Data Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() Referring to Table 6-92 , verify the client ports (Ports 1 through 8) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-92 , verify the client ports (Ports 1 through 8) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
|
|
(XFP) |
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision each additional client port.
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Referring to Table 6-93 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Referring to Table 6-93 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Step 9![]() Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision each additional client port.
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G366 Change the 10G Data Muxponder OTN Settings
This task changes the OTN settings for the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-94 through 6-97 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-94 through 6-97 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-94 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Sets how the ODUk (client payload) is mapped to the optical channel (OTUk). |
Table 6-95 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > G.709 Thresholds tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Port13 |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
||
Numeric. Can be set for Near End or Far End, for 15-minute or one-day intervals, or for SM (OTUk) or PM (ODUk). Select a bullet and click Refresh. |
Table 6-96 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Threshold tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-97 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G293 Modify the 40G Muxponder Card Line Settings and PM Parameter Thresholds
This procedure changes the line and parameter threshold settings of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the muxponder card settings. If you are already logged in, proceed to Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the G103 Back Up the Database to save the existing settings before modifying.
Complete the G103 Back Up the Database to save the existing settings before modifying.
Step 3![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G662 Change the 40G Multirate Muxponder Card Settings
- G666 Change the 40G Muxponder Line Settings
- G667 Change the 40G Muxponder Line SONET (OC-192) or SDH (STM-64), or Ethernet Line Settings
- G668 Change the 40G Muxponder Section Trace Settings
- G669 Change the 40G Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
- G670 Change the 40G Muxponder Line RMON Thresholds for Ethernet, or 10G FC Payloads
- G671 Provision the 40G Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G672 Provision the 40G Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G673 Change the 40G Muxponder OTN Settings

Note![]() To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G662 Change the 40G Multirate Muxponder Card Settings
This task changes the card settings of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify either of the settings described in Table 6-98 .
Modify either of the settings described in Table 6-98 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G666 Change the 40G Muxponder Line Settings
This task changes the line settings of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs. Tabs and parameters vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports tabs. Tabs and parameters vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-99 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-99 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
User-defined. This can be up to 32 alphanumeric or special characters, or both. The port name is blank by default. For information on assigning a port name, see the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. Note You can assign a port name for each fiber channel/FICON interface on the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C card, enabling the MDS Fabric Manager to associate the SAN port and a SAN port on the Cisco MDS 9000 switch. |
||
Sets the port service state unless network conditions prevent the change. For more information, see Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
(Display only) Shows the general condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, see Appendix B, “Administrative and Service States” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
||
|
||
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to the change settings. |
||
Shuts down the far-end laser in response to certain defects. |
||
(Trunk port only) Enables or disables overclock mode on the trunk port. |
||
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G667 Change the 40G Muxponder Line SONET (OC-192) or SDH (STM-64), or Ethernet Line Settings
This task changes the line SONET OC-192 or SDH STM-64, or ethernet line settings for the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the SONET (OC-192) or SDH (STM-64) line, or ethernet line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the SONET (OC-192) or SDH (STM-64) line, or ethernet line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) or Ethernet. Tabs and parameters vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > SONET (ANSI) or SDH (ETSI) or Ethernet. Tabs and parameters vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() To modify the line SONET or SDH settings, see Table 6-100 . To modify the ethernet line settings see Table 6-101 .
To modify the line SONET or SDH settings, see Table 6-100 . To modify the ethernet line settings see Table 6-101 .
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Assigns a logical name assigned to a port. This field is blank by default. |
User-defined. This can be up to 32 alphanumeric or special characters, or both. The port name is blank by default. For information on assigning a port name, see the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
|
(Display only) Displays the ProvidesSync card parameter state. |
||
Sets the EnableSync card parameter. Enables synchronization status messages (S1 byte), which allow the node to choose the best timing source. |
||
Sets the Send DoNotUse card state. When checked, sends a DUS (do not use) message on the S1 byte. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled, or it can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
Note The AINS service state is not supported on interlink ports. |
|
Displays the maximum size of the Ethernet frames accepted by the port. |
|||
Displays the mapping mechanism. Choose GFP framing (the default) or WIS framing. The framing type needs to match the framing type at the far end. |
|||
Enables/disables flow control messaging with its peer port. When enabled, the port can send and receive PAUSE frames when buffer congestion occurs. When disabled, no PAUSE frames are transmitted and the PAUSE frames received are discarded. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G668 Change the 40G Muxponder Section Trace Settings
This task changes the section trace settings of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs. Tabs and parameter selections vary according to the PPM provisioning.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-102 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-102 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G669 Change the 40G Muxponder SONET or SDH Line Thresholds
This task changes the SONET or SDH line threshold settings of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C muxponder cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings shown in Table 6-103 .
Modify any of the settings shown in Table 6-103 .

Note![]() In Table 6-103, some parameters and options do not apply to all 40-G-MXP-C cards. If the parameter or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
In Table 6-103, some parameters and options do not apply to all 40-G-MXP-C cards. If the parameter or options do not apply, they do not appear in CTC.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G670 Change the 40G Muxponder Line RMON Thresholds for Ethernet, or 10G FC Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings of 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card carrying Ethernet, or 10G FC payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings in the card view.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the line threshold settings in the card view.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the payload port— for example “1-1 (TEN_GE)”, or the equivalent ITU-T G.7041 GFP (Generic Frame Procedure) port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the payload port— for example “1-1 (TEN_GE)”, or the equivalent ITU-T G.7041 GFP (Generic Frame Procedure) port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet or FC variable. See Table 6-104 for a list of available Ethernet variables, Table 6-105 for a list of FC, and Table 6-105 for a list of GFP variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet or FC variable. See Table 6-104 for a list of available Ethernet variables, Table 6-105 for a list of FC, and Table 6-105 for a list of GFP variables.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, choose an alarm type. The alarm type indicates whether or not an event is triggered by the type of threshold.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, choose an alarm type. The alarm type indicates whether or not an event is triggered by the type of threshold.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Enter the number of Sample Period occurrences.
Enter the number of Sample Period occurrences.
Step 9![]() Enter the number of Rising Threshold occurrences.
Enter the number of Rising Threshold occurrences.
To trigger the alarm, the measured value of a threshold must always move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network moves from below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds to 1001 collisions.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences for the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences for the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the exact opposite of a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded.
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G671 Provision the 40G Muxponder Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the trunk port alarm and TCA thresholds of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 3![]() If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4
If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4![]() .
.
Step 4![]() Verify the trunk port (Port 5) TCA thresholds are set at the values shown as follows:
Verify the trunk port (Port 5) TCA thresholds are set at the values shown as follows:
Provision new thresholds as needed by replacing the old values with new ones.
Step 5![]() Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Verify the trunk port (Port 5) alarm thresholds are set at the values shown as follows:
Verify the trunk port (Port 5) alarm thresholds are set at the values shown as follows:
Provision new thresholds as needed replacing the old values with new ones.
Step 8![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G672 Provision the 40G Muxponder Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds of the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4
If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. If it is selected, continue with Step 4![]() .
.
Step 4![]() Referring to Table 6-107 , verify the client ports (Ports 1 through 4) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by replacing the old values with new ones.
Referring to Table 6-107 , verify the client ports (Ports 1 through 4) TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface at the other end. Provision new thresholds as needed by replacing the old values with new ones.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
|
|
(XFP) |
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ONS-XC-10G-1470 through ONS-XC-10G-1610 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
Step 6![]() Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision the additional client ports.
Repeat Steps 3 and 4 to provision the additional client ports.
Step 7![]() Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types area, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 8![]() Referring to Table 6-108 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed replacing the old values with new ones.
Referring to Table 6-108 , verify the client port (Ports 1 through 8) Alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low based on the client interface that is provisioned. Provision new thresholds as needed replacing the old values with new ones.
|
|
(XFP) |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
|||||
ONS-XC-10G-30.3 through ONS-XC-10G-61.4 |
Step 10![]() Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision additional client ports.
Repeat Steps 7 and 8 to provision additional client ports.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G673 Change the 40G Muxponder OTN Settings
This task changes the OTN settings for the 40G-MXP-C, 40E-MXP-C, and 40ME-MXP-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the 40G-MXP-C, or 40E-MXP-C card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-109 through 6-112 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-109 through 6-112 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End, 15 Min and 1 Day, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End, 15 Min and 1 Day, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-109 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-110 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-111 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Threshold tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-112 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G281 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Channel Group Settings
This procedure changes the channel group settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the channel group settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the channel group settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G611 Create a Channel Group Using CTC
- G612 Modify the Parameters of the Channel Group Using CTC
- G613 Add or Remove Ports to or from an Existing Channel Group Using CTC
- G614 Delete a Channel Group Using CTC
- G615 Retrieve Information on Channel Group, REP, CFM, and EFM Using CTC
- G616 View Channel Group PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
- G617 View Channel Group Utilization PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
- G618 View Channel Group History PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
- G619 Create a Channel Group on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Step 3![]() Stop. You have completed this procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G611 Create a Channel Group Using CTC
This task creates a channel group on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() You can create up to 11 channel groups on the GE_XP and GE_XPE cards and up to 2 channel groups on the 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards. You can create a channel group with ports only when the ports do not have any UNI QinQ settings or NNI SVLAN settings. Otherwise, the channel group will be created with empty ports.
You can create up to 11 channel groups on the GE_XP and GE_XPE cards and up to 2 channel groups on the 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards. You can create a channel group with ports only when the ports do not have any UNI QinQ settings or NNI SVLAN settings. Otherwise, the channel group will be created with empty ports.
For information on interaction of LACP with other protocols, see the Protocol Compatibility list in the Transponder and Muxponder Cards chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Step 3![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 4![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
Step 5![]() Click Create. The Channel Group Creation dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Channel Group Creation dialog box appears.
Step 6![]() Enter the name of the channel group in the Name field.
Enter the name of the channel group in the Name field.
Step 7![]() From the Stand Alone list, choose the ports that will belong to this channel group and click the right arrow button to move the selected ports to the Bundled list.
From the Stand Alone list, choose the ports that will belong to this channel group and click the right arrow button to move the selected ports to the Bundled list.
Step 8![]() From the LACP Mode drop-down list, choose the LACP mode as needed:
From the LACP Mode drop-down list, choose the LACP mode as needed:
- On—Default mode. In this mode, the ports will not exchange LACP packets with the partner ports.
- Active—In this mode, the ports will send LACP packets at regular intervals to the partner ports.
- Passive—In this mode, the ports will not send LACP packets until the partner ports send LACP packets. After receiving the LACP packets from the partner ports, the ports will send LACP packets.
Step 9![]() From the LACP Hashing drop-down list, select the LACP hashing algorithm that the protocol uses to perform the load balancing task between the bundled ports.
From the LACP Hashing drop-down list, select the LACP hashing algorithm that the protocol uses to perform the load balancing task between the bundled ports.
The following hashing algorithms are supported:
- Ucast SA VLAN Incoming Port
- Ucast DA VLAN Incoming Port
- Ucast SA DA VLAN Incoming port
- Ucast Src IP TCP UDP
- Ucast Dst IP TCP UDP
- Ucast Src Dst IP TCP UDP
A new row is added in the LACP table and all the other parameters in the channel group are set to default values. The default values of these parameters are taken from the first port that is attached to the channel group.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G612 Modify the Parameters of the Channel Group Using CTC

Note![]() Ports cannot be added or removed using this procedure. For adding or removing the ports, see G613 Add or Remove Ports to or from an Existing Channel Group Using CTC.
Ports cannot be added or removed using this procedure. For adding or removing the ports, see G613 Add or Remove Ports to or from an Existing Channel Group Using CTC.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to modify the parameters of the channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to modify the parameters of the channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to modify the parameters of the channel group.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to modify the parameters of the channel group.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
Step 4![]() Choose a channel group from the existing channel groups.
Choose a channel group from the existing channel groups.
Step 5![]() Modify the channel group settings as described in Table 6-113 .
Modify the channel group settings as described in Table 6-113 .

Note![]() When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G613 Add or Remove Ports to or from an Existing Channel Group Using CTC
This task adds or removes ports to or from an existing channel group. |
|
Before You Begin
- You can assign up to eight ports to a channel group on GE_XP and GE_XPE cards and up to three ports on the 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards.
- You can assign the ports to a channel group only if the ports are in OOS-DSBLD admin state. The ports must not have any UNI QinQ rule or NNI SVLAN configuration.
- If the channel group is configured in UNI mode, only the UNI ports can be added to the channel group. If the channel group is configured in NNI mode, only the NNI ports can be added to the channel group.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want add ports to an existing channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want add ports to an existing channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to add ports to an existing channel group.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to add ports to an existing channel group.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
Step 4![]() Choose a channel group from the existing channel groups.
Choose a channel group from the existing channel groups.
Step 5![]() Click Add/Remove Ports. The Add/Remove Ports dialog box appears.
Click Add/Remove Ports. The Add/Remove Ports dialog box appears.
Step 6![]() To add ports to an existing channel group, complete the following:
To add ports to an existing channel group, complete the following:
From the Stand Alone list, choose the required ports and click the right arrow button to move the selected ports to the Bundled list.
Step 7![]() To remove ports from an existing channel group, complete the following:
To remove ports from an existing channel group, complete the following:
From the Bundled list, choose the required ports and click the left arrow button to move the selected ports to the Stand Alone list.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G614 Delete a Channel Group Using CTC
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete the channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete the channel group. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XP card where you want to delete the channel group.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XP card where you want to delete the channel group.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Channel Groups tabs.
Step 4![]() Choose a channel group that you want to delete.
Choose a channel group that you want to delete.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G615 Retrieve Information on Channel Group, REP, CFM, and EFM Using CTC
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view and retrieve information on the channel group, REP, CFM, and EFM. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view and retrieve information on the channel group, REP, CFM, and EFM. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Maintenance > Show Commands tabs.
In card view, click the Maintenance > Show Commands tabs.
Step 4![]() From the Command drop-down list, choose a command.
From the Command drop-down list, choose a command.
The following commands are supported:
- ETH LACP—Displays detailed LACP information from the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards.
- REP TOPO—Displays the topology information for a specific REP segment.
- REP TOPO ARCHIVE—Displays the previous topology information for a specific REP segment.
- REP INTERFACE—Displays information on the REP interface status and configuration. You can retrieve detailed information for each segment by selecting Detailed from the Level drop-down list and providing the segment ID.
- OAM DISCOVERY—Displays discovery information for all the EFM interfaces or for a specific EFM interface.
- OAM SUMMARY—Displays the active EFM sessions on a device.
- OAM STATISTICS—Displays detailed information about the EFM packets.
- OAM STATUS—Displays information about the EFM configurations for all the EFM interfaces or for a specific interface.
For more information, see the Pseudo Command Line Interface Reference chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 5![]() From the Level drop-down list, choose Normal or Detailed.
From the Level drop-down list, choose Normal or Detailed.
Step 6![]() Click Show. Depending on the command, the appropriate output appears in the text area.
Click Show. Depending on the command, the appropriate output appears in the text area.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G616 View Channel Group PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This task enables you to view current statistical performance monitoring (PM) counts on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards and channel groups to detect possible performance problems. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group PM counts on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group PM counts on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 2![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group statistics. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group statistics. The card view appears.
Step 3![]() Click the Performance > Channel Groups > Statistics tabs.
Click the Performance > Channel Groups > Statistics tabs.
Step 4![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each channel group on the card appear in the Statistics tab.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each channel group on the card appear in the Statistics tab.
View the PM parameter names in the Param column. The current PM parameter values appear in the Port # (CHGRP) column. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the “Performance Monitoring” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.

Note![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G617 View Channel Group Utilization PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This task enables you to view line utilization PM counts on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards and channel groups to detect possible performance problems. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group utilization PM parameters on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group utilization PM parameters on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 2![]() In node view, double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group utilization. The card view appears.
In node view, double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group utilization. The card view appears.
Step 3![]() Click the Performance > Channel Groups > Utilization tabs.
Click the Performance > Channel Groups > Utilization tabs.
Step 4![]() Click Refresh. The utilization percentages for each channel group on the card appear in the Utilization tab.
Click Refresh. The utilization percentages for each channel group on the card appear in the Utilization tab.
View the Port # column to find the channel group you want to monitor.
The transmit (Tx) and receive (Rx) bandwidth utilization values, for the previous time intervals, appear in the Prev- n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the “Performance Monitoring” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.

Note![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G618 View Channel Group History PM Parameters for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This task enables you to view historical PM counts at selected time intervals on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards and channel groups to detect possible performance problems. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group history PM parameters on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the channel group history PM parameters on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 2![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group history PM data. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card where you want to view the channel group history PM data. The card view appears.
Step 3![]() Click the Performance > Channel Groups > History tabs.
Click the Performance > Channel Groups > History tabs.
Step 4![]() From the Port field, choose a channel group.
From the Port field, choose a channel group.
Step 5![]() Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each channel group on the card appear in the History tab.
Click Refresh. Performance monitoring statistics for each channel group on the card appear in the History tab.
View the PM parameter names that appear in the Param column. The PM parameter values appear in the Prev- n columns. For PM parameter definitions, refer to the “Performance Monitoring” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.

Note![]() To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
To refresh, reset, or clear PM counts, see the G73 Change the PM Display.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G283 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card CFM Settings
This procedure changes the CFM settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the CFM settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the CFM settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G621 Enable or Disable CFM on the Card Using CTC
- G622 Enable or Disable CFM for Each Port Using CTC
- G623 Create a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
- G624 Delete a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
- G625 Create a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
- G626 Modify a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
- G627 Delete a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
- G628 Map a Maintenance Association Profile to a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
- G629 Create a MEP Using CTC
- G630 Delete a MEP Using CTC
- G631 Create a MIP Using CTC
- G632 Delete a MIP Using CTC
- G633 Ping MEP Using CTC
- G634 Traceroute MEP Using CTC
- G615 Retrieve Information on Channel Group, REP, CFM, and EFM Using CTC
- G635 Enable CFM on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Step 3![]() Stop. You have completed this procedure.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G621 Enable or Disable CFM on the Card Using CTC
This task allows you to enable or disable CFM on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() CFM is disabled on the card by default. CFM must be enabled at both card and port levels for the CFM service to work.
CFM is disabled on the card by default. CFM must be enabled at both card and port levels for the CFM service to work.
For information on interaction of CFM with other protocols, see the Protocol Compatibility list in the Transponder and Muxponder Cards chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable CFM on the card. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable CFM on the card. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > Security tab.
In card view, click the Provisioning > Security tab.
Step 4![]() Uncheck the MAC security check box to disable MAC security.
Uncheck the MAC security check box to disable MAC security.
Step 5![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Global Settings tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Global Settings tabs.
Step 6![]() Check the Enable CFM check box that is present at the bottom of the screen.
Check the Enable CFM check box that is present at the bottom of the screen.
Step 7![]() Choose the value for CC Timer field. The value can be 1 second, 10 seconds, or 1 minute.
Choose the value for CC Timer field. The value can be 1 second, 10 seconds, or 1 minute.

Note![]() Continuity Check (CC) messages are periodically exchanged between maintenance end points (MEPs). The CC Timer field is used to set the time frequency for transmission of CC messages.
Continuity Check (CC) messages are periodically exchanged between maintenance end points (MEPs). The CC Timer field is used to set the time frequency for transmission of CC messages.
Step 8![]() Click Apply to enable CFM on the card.
Click Apply to enable CFM on the card.

Note![]() Uncheck the Enable CFM check box to disable CFM on the card.
Uncheck the Enable CFM check box to disable CFM on the card.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G622 Enable or Disable CFM for Each Port Using CTC
This task allows you to enable or disable CFM for each port on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() CFM must be enabled at both card and port levels for the CFM service to work. However, CFM is enabled on all the ports by default.
CFM must be enabled at both card and port levels for the CFM service to work. However, CFM is enabled on all the ports by default.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable CFM for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable CFM for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Global Settings tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Global Settings tabs.
Step 4![]() If you want to enable CFM on a specific port, check the Enable CFM check box against that port.
If you want to enable CFM on a specific port, check the Enable CFM check box against that port.
Step 5![]() Choose the value for CC Timer field. The value can be 1 second, 10 seconds, or 1 minute.
Choose the value for CC Timer field. The value can be 1 second, 10 seconds, or 1 minute.

Note![]() Continuity Check (CC) messages are periodically exchanged between MEPs. The CC Timer field is used to set the time frequency for transmission of CC messages.
Continuity Check (CC) messages are periodically exchanged between MEPs. The CC Timer field is used to set the time frequency for transmission of CC messages.
Step 6![]() Click Apply to enable CFM on the port.
Click Apply to enable CFM on the port.

Note![]() Uncheck the Enable CFM check box against the port to disable CFM on the port.
Uncheck the Enable CFM check box against the port to disable CFM on the port.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G623 Create a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to create a maintenance domain profile on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Before You Begin
- You can create up to eight maintenance domain profiles on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards.
- The maximum number of characters for the maintenance domain profile and the maintenance association profile must not exceed 43 characters.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Domain Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > Domain Profiles tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Domain Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > Domain Profiles tabs.

Note![]() Use the network view to store the domain profile on multiple nodes.
Use the network view to store the domain profile on multiple nodes.
Step 5![]() Enter the name of the domain in the Domain Name field.
Enter the name of the domain in the Domain Name field.
Step 6![]() Enter the level of the domain profile in the Level field. The range of the domain profile level is from 0 to 7.
Enter the level of the domain profile in the Level field. The range of the domain profile level is from 0 to 7.
Step 8![]() Choose the card slot where you want to store this domain profile and click OK.
Choose the card slot where you want to store this domain profile and click OK.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G624 Delete a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to delete a maintenance domain profile on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Domain Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > Domain Profiles tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > Domain Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > Domain Profiles tabs.
Step 4![]() Select the domain profiles that you want to delete.
Select the domain profiles that you want to delete.
Step 5![]() Check the on Node check box.
Check the on Node check box.
Step 6![]() Click Delete Sel. row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears.
Click Delete Sel. row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears.
Step 7![]() Choose the card slot where you want to delete this profile and click OK. The Deleting Profile dialog box appears.
Choose the card slot where you want to delete this profile and click OK. The Deleting Profile dialog box appears.
Step 8![]() In the Deleting Profile dialog box, click Yes.
In the Deleting Profile dialog box, click Yes.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G625 Create a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to create a maintenance association profile on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() You can create up to 1500 maintenance association profiles on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards.
You can create up to 1500 maintenance association profiles on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.

Note![]() Use the network view to store the maintenance association profile on multiple nodes.
Use the network view to store the maintenance association profile on multiple nodes.
Step 5![]() Enter the name of the maintenance association in the Maintenance Profile Name field.
Enter the name of the maintenance association in the Maintenance Profile Name field.
Step 6![]() Enter the VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the VLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Enter the VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the VLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Step 7![]() Check the CC Enable check box to receive Continuity Check messages.
Check the CC Enable check box to receive Continuity Check messages.
Step 9![]() Choose the card slot where you want to store this maintenance association profile and click OK.
Choose the card slot where you want to store this maintenance association profile and click OK.
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G626 Modify a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to modify a maintenance association profile on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() Ensure that the maintenance association profile you want to modify is not associated with a maintenance domain profile.
Ensure that the maintenance association profile you want to modify is not associated with a maintenance domain profile.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to modify a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to modify a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.
Step 4![]() Select the maintenance association profiles that you want to modify.
Select the maintenance association profiles that you want to modify.
Step 5![]() Click Modify Selected Profile(s). The Modify MA Profile dialog box appears.
Click Modify Selected Profile(s). The Modify MA Profile dialog box appears.
Step 6![]() Modify the values as required and click OK.
Modify the values as required and click OK.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G627 Delete a Maintenance Association Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to delete a maintenance association profile on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() Ensure that the maintenance association profile you want to delete is not associated with a maintenance domain profile.
Ensure that the maintenance association profile you want to delete is not associated with a maintenance domain profile.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a maintenance association profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA Profiles tabs or in node/network view, click the Provisioning > CFM Profiles > MA Profiles tabs.
Step 4![]() Select the maintenance association profiles that you want to delete.
Select the maintenance association profiles that you want to delete.
Step 5![]() Check the on Node check box.
Check the on Node check box.
Step 6![]() Click Delete Sel. row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears.
Click Delete Sel. row(s). The CFM Profile Deleting dialog box appears.
Step 7![]() Choose the card slot where you want to delete this profile and click OK. The Deleting Profile dialog box appears.
Choose the card slot where you want to delete this profile and click OK. The Deleting Profile dialog box appears.
Step 8![]() In the Deleting Profile dialog box, click Yes.
In the Deleting Profile dialog box, click Yes.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G628 Map a Maintenance Association Profile to a Maintenance Domain Profile Using CTC
This task allows you to map a maintenance association profile to a maintenance domain profile on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() Ensure that you have already created maintenance domain profiles and maintenance association profiles.
Ensure that you have already created maintenance domain profiles and maintenance association profiles.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to map a maintenance association profile to a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to map a maintenance association profile to a maintenance domain profile. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA-Domain Mapping tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MA-Domain Mapping tabs.
Step 4![]() From the main drop-down list, choose a maintenance domain profile.
From the main drop-down list, choose a maintenance domain profile.
Step 5![]() Click Link MA Profiles. The Link MA Profiles dialog box appears.
Click Link MA Profiles. The Link MA Profiles dialog box appears.
Step 6![]() From the Available Profiles list, choose the required MA profiles and click the right arrow button to move the MA profiles to the Linked Profiles list and click OK.
From the Available Profiles list, choose the required MA profiles and click the right arrow button to move the MA profiles to the Linked Profiles list and click OK.

Note![]() The maintenance association profiles that are mapped with a specific maintenance domain profile must have a unique SVLAN ID.
The maintenance association profiles that are mapped with a specific maintenance domain profile must have a unique SVLAN ID.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G629 Create a MEP Using CTC
This task allows you to create a Maintenance End Point (MEP) for a given VLAN range on a specific maintenance domain. |
|

Note![]() You can create up to 255 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XP and 10GE_XP cards. You can create up to 500 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards.
You can create up to 255 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XP and 10GE_XP cards. You can create up to 500 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MEP tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MEP tabs.
Step 4![]() Click Create. The Create MEP dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create MEP dialog box appears.
Step 5![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose a port where you want to create the MEP.
From the Port drop-down list, choose a port where you want to create the MEP.

Note![]() CFM must be enabled on the port to create a MEP. The port must not belong to a channel group.
CFM must be enabled on the port to create a MEP. The port must not belong to a channel group.
Step 6![]() From the Domain drop-down list, choose a maintenance domain.
From the Domain drop-down list, choose a maintenance domain.
Step 7![]() Enter the SVLAN ID in the Vlan Id field.
Enter the SVLAN ID in the Vlan Id field.

Note![]() The specified VLAN must be configured on the selected port. The specified VLAN must also appear in the MA-Domain Mapping table.
The specified VLAN must be configured on the selected port. The specified VLAN must also appear in the MA-Domain Mapping table.
Step 8![]() Enter the MP ID (identifier of the maintenance end point) in the MPID field and click OK. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.
Enter the MP ID (identifier of the maintenance end point) in the MPID field and click OK. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.
The MP ID must not be the same between the maintenance end points.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G630 Delete a MEP Using CTC
This task allows you to delete a MEP on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MEP tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MEP tabs.
Step 4![]() Select the MEPs that you want to delete.
Select the MEPs that you want to delete.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G631 Create a MIP Using CTC
This task allows you to create a Maintenance Intermediate Point (MIP) for a given VLAN range with a specific maintenance level. |
|

Note![]() You can create up to 255 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XP and 10GE_XP cards. You can create up to 500 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards.
You can create up to 255 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XP and 10GE_XP cards. You can create up to 500 MEPs and MIPs on the GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a MIP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a MIP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MIP tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MIP tabs.
Step 4![]() Click Create. The Create MIP dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create MIP dialog box appears.
Step 5![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose a port where you want to create the MIP.
From the Port drop-down list, choose a port where you want to create the MIP.

Note![]() The port must not belong to a channel group.
The port must not belong to a channel group.
Step 6![]() From the Level drop-down list, choose a maintenance level. The range of the maintenance level is from 0 to 7.
From the Level drop-down list, choose a maintenance level. The range of the maintenance level is from 0 to 7.
Step 7![]() Enter the SVLAN range in the Vlan range field. The range of the SVLAN is from 1 to 4093.
Enter the SVLAN range in the Vlan range field. The range of the SVLAN is from 1 to 4093.

Note![]() The specified SVLAN must be configured on the selected port.
The specified SVLAN must be configured on the selected port.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G632 Delete a MIP Using CTC
This task allows you to delete a MIP on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a MIP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to delete a MIP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MIP tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Configuration > MIP tabs.
Step 4![]() Select the MIPs that you want to delete.
Select the MIPs that you want to delete.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
This task allows you to display the output of the ping command on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to ping MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to ping MEP. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Ping tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Ping tabs.
Step 4![]() Enter the MP ID value in the MPID field. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.
Enter the MP ID value in the MPID field. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.

Note![]() Remote MP ID user cannot ping local MP ID.
Remote MP ID user cannot ping local MP ID.
Step 5![]() (Optional) Enter the MAC address of the remote maintenance point in the Mac Addr field. The format of MAC address is abcd.abcd.abcd.
(Optional) Enter the MAC address of the remote maintenance point in the Mac Addr field. The format of MAC address is abcd.abcd.abcd.
Step 6![]() Enter the SVLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the SVLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Enter the SVLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the SVLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Step 7![]() Enter the domain name in the Domain Name field.
Enter the domain name in the Domain Name field.
Step 8![]() Enter the size of the ping packet in the DataGram Size field. The default value is 100.
Enter the size of the ping packet in the DataGram Size field. The default value is 100.
Step 9![]() Enter the number of ping packets in the No of Requests field. The default value is 5.
Enter the number of ping packets in the No of Requests field. The default value is 5.
Step 10![]() Click Ping. The output of the ping command appears in the Ping Response area.
Click Ping. The output of the ping command appears in the Ping Response area.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G634 Traceroute MEP Using CTC
This task allows you to display the output of the traceroute command on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the output of the traceroute command. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to view the output of the traceroute command. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Traceroute tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > CFM > Traceroute tabs.
Step 4![]() Enter the remote MP ID value in the MPID field. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.
Enter the remote MP ID value in the MPID field. The range of the MP ID is from 1 to 8191.
Step 5![]() (Optional) Enter the MAC address of the remote maintenance point in the Mac Addr field. The format of MAC address is abcd.abcd.abcd.
(Optional) Enter the MAC address of the remote maintenance point in the Mac Addr field. The format of MAC address is abcd.abcd.abcd.
Step 6![]() Enter the SVLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the SVLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Enter the SVLAN ID in the VLAN ID field. The range of the SVLAN ID is from 1 to 4093.
Step 7![]() Enter the domain name in the Domain Name field.
Enter the domain name in the Domain Name field.
Step 8![]() Click TraceRoute Response.
Click TraceRoute Response.
The output of the traceroute command appears in the TraceRoute Response area.
- Verify the RlyHit message is shown in the traceroute display and LTM reaches a maintenance point whose MAC address matches the target MAC address.
- Verify the RlyFDB message is shown in the traceroute display when the next hop address is found in the forwarding database.
- Verify the RlyMPDB message is shown in the traceroute display when the next hop address is found in the CCDN.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G285 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card EFM Settings
This procedure changes the EFM settings of the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the EFM settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the EFM settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G639 Enable or Disable EFM for Each Port Using CTC
- G640 Configure EFM Parameters Using CTC
- G641 Configure EFM Link Monitoring Parameters Using CTC
- G642 Enable Remote Loopback for Each Port Using CTC
- G615 Retrieve Information on Channel Group, REP, CFM, and EFM Using CTC
- G643 Enable EFM on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G639 Enable or Disable EFM for Each Port Using CTC
This task allows you to enable or disable EFM for each port on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Before You Begin
- You can enable EFM on both UNI and NNI ports.
- You cannot enable or disable EFM for ports that belong to a channel group.
- For information on interaction of EFM with other protocols, see the Protocol Compatibility list in the Transponder and Muxponder Cards chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable EFM for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable or disable EFM for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs. The EFM details appear for each port.
In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs. The EFM details appear for each port.
Step 4![]() From the EFM State drop-down list, choose Enabled.
From the EFM State drop-down list, choose Enabled.
Step 5![]() Click Apply to enable EFM for that port.
Click Apply to enable EFM for that port.

Note![]() From the EFM State drop-down list, choose Disabled to disable EFM for that port.
From the EFM State drop-down list, choose Disabled to disable EFM for that port.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G640 Configure EFM Parameters Using CTC
This task allows you to configure EFM parameters on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to configure EFM parameters. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to configure EFM parameters. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Configuration tabs.
Step 4![]() Modify the EFM parameter settings as described in Table 6-114 .
Modify the EFM parameter settings as described in Table 6-114 .
Step 5![]() Click Apply to save the changes.
Click Apply to save the changes.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G641 Configure EFM Link Monitoring Parameters Using CTC
This task allows you to configure EFM link monitoring parameters for each port on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to configure EFM link monitoring parameters. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to configure EFM link monitoring parameters. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Link Monitoring tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Link Monitoring tabs.
Step 4![]() Modify the EFM link monitoring parameter settings as described in Table 6-115 .
Modify the EFM link monitoring parameter settings as described in Table 6-115 .
Step 5![]() Click Apply to save the changes.
Click Apply to save the changes.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G642 Enable Remote Loopback for Each Port Using CTC
This task allows you to enable remote loopback for each port on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable the remote loopback for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable the remote loopback for each port. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Loopback tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > EFM > Loopback tabs.
The remote loopback type details appear for each port.
Step 4![]() From the Remote Loopback Type drop-down list, choose Remote Loopback.
From the Remote Loopback Type drop-down list, choose Remote Loopback.
Step 5![]() Click Apply to save the changes.
Click Apply to save the changes.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G287 Manage the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card REP Settings
This procedure changes the REP settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the REP settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the REP settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G713 Provision Administrative VLAN for Ports in a REP Segment Using CTC
- G645 Create a Segment Using CTC
- G646 Edit a Segment Using CTC
- G647 Activate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
- G648 Deactivate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
- G615 Retrieve Information on Channel Group, REP, CFM, and EFM Using CTC
- G649 Create a Segment on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
- G650 Configure STCN on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
- G651 Configure Preemption Delay on the Primary Edge Port Using PCLI
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G713 Provision Administrative VLAN for Ports in a REP Segment Using CTC
This task allows you to provision administrative VLAN for NNI and UNI ports in a REP segment on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() One administrative CVLAN and one administrative SVLAN can be provisioned for each card. The REP segments using NNI ports send Hardware Flood Layer (HFL) messages using the administrative SVLAN. The REP segments using UNI ports send HFL messages using the administrative CVLAN. The two VLANs need not be the same.
One administrative CVLAN and one administrative SVLAN can be provisioned for each card. The REP segments using NNI ports send Hardware Flood Layer (HFL) messages using the administrative SVLAN. The REP segments using UNI ports send HFL messages using the administrative CVLAN. The two VLANs need not be the same.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to provision administrative VLAN. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to provision administrative VLAN. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Admin VLAN Configuration tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Admin VLAN Configuration tabs.
Step 4![]() To provision administrative VLAN for NNI ports in a REP segment, perform the following steps:
To provision administrative VLAN for NNI ports in a REP segment, perform the following steps:
a.![]() From the SVLAN drop-down list, choose a SVLAN. The following table describes the REP convergence time for SVLANs.
From the SVLAN drop-down list, choose a SVLAN. The following table describes the REP convergence time for SVLANs.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
c.![]() To associate the chosen SVLAN with the NNI ports, see G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports.
To associate the chosen SVLAN with the NNI ports, see G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports.
Step 5![]() To provision administrative VLAN for UNI ports in a REP segment, perform the following steps:
To provision administrative VLAN for UNI ports in a REP segment, perform the following steps:
a.![]() Enter the CVLAN in the CVLAN field.
Enter the CVLAN in the CVLAN field.
c.![]() To associate the CVLAN with the UNI ports, see G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings.
To associate the CVLAN with the UNI ports, see G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G645 Create a Segment Using CTC
This task allows you to create a segment on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Before You Begin
- You can create up to three segments on a card. Each segment can have up to two ports on the same switch.
- You must configure the REP administrative VLAN to activate the HFL.
- Before creating REP segments, you must configure the administrative VLAN or use the default VLAN 1 and add the ports to the segment. Only one SVLAN can be configured per card for all the three segments. REP uses the administrative VLAN to flood its own control traffic.
- The administrative CVLAN is required if a REP port is configured as a UNI port. However, the REP ports are configured as NNI ports in many configurations, and hence the administrative CVLAN is not required in these configurations. The option to configure the administrative CVLAN is present in CTC.
- You must configure two edge ports in the segment. A segment has only one primary edge port. If you configure two ports in a segment as the primary edge port, for example, ports on different switches, REP selects one of the ports to serve as the primary edge port based on port priority.
- If REP is enabled on two ports on a switch, both the ports must be either regular ports or edge ports. However, if the No-neighbor port is configured, one port can be an edge port and another port can be a regular port.
- You can also optionally configure where to send segment topology change notifications (STCNs) and VLAN load balancing (VLB). STCNs are enabled only for primary edge ports. VLB configurations are enabled on any edge ports.
- For information on interaction of REP with other protocols, see the Protocol Compatibility list in the Transponder and Muxponder Cards chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a segment. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to create a segment. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs.
In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs.
Step 4![]() Click Create. The Create Segment wizard appears.
Click Create. The Create Segment wizard appears.
Step 5![]() Enter the segment ID in the Segment field. The range of the segment ID is from 1 to 1024.
Enter the segment ID in the Segment field. The range of the segment ID is from 1 to 1024.
Step 6![]() From the Port drop-drown list, choose a REP port that must belong to this segment.
From the Port drop-drown list, choose a REP port that must belong to this segment.

Note![]() A REP port can belong to only one segment.
A REP port can belong to only one segment.
Step 7![]() From the Port Role area, choose whether you want to configure the port as an edge port or a regular port. The options are:
From the Port Role area, choose whether you want to configure the port as an edge port or a regular port. The options are:
a.![]() Edge—The port is configured as an edge port.
Edge—The port is configured as an edge port.
- Check the Primary check box to configure the edge port as a primary edge port. A segment can have only one primary edge port.

Note![]() If an edge port is configured as primary edge port, the other edge port in the ring automatically becomes secondary edge port. If neither edge port is configured as primary edge port, one edge port is automatically selected as primary edge port, and the other edge port is secondary edge port. Configuring an edge port as a primary edge port is not mandatory. However, it is recommended since VLAN load balancing must be configured on the node with the primary edge port.
If an edge port is configured as primary edge port, the other edge port in the ring automatically becomes secondary edge port. If neither edge port is configured as primary edge port, one edge port is automatically selected as primary edge port, and the other edge port is secondary edge port. Configuring an edge port as a primary edge port is not mandatory. However, it is recommended since VLAN load balancing must be configured on the node with the primary edge port.
- Uncheck the Primary check box to configure the edge port as a secondary edge port.
- (Optional) Check the Preferred check box to configure the regular or edge port as a preferred alternate port (alternate to primary edge port). This port blocks a range of SVLANs for VLAN load balancing. There is no limit on the number of preferred ports in a REP ring. The preferred port, if configured, is relevant even without VLAN load balancing, as it takes priority over non-preferred ports for alternate port election.

Note![]() Configuring a port as preferred does not ensure that it becomes the alternate port; it only gets preference over the other ports that are not configured as preferred when an alternate port is elected.
Configuring a port as preferred does not ensure that it becomes the alternate port; it only gets preference over the other ports that are not configured as preferred when an alternate port is elected.
- Check the NoNeighbor check box if the edge port must not have a neighbor port. REP does not check for neighbor adjacency.

Note![]() When the NoNeighbor check box is checked, ensure that only one segment is created.
When the NoNeighbor check box is checked, ensure that only one segment is created.
b.![]() None—The port is configured as a regular port. If you choose this option, Segment Topology Change Notifications (STCN) and VLAN Load Balancing (VLB) configurations are disabled.
None—The port is configured as a regular port. If you choose this option, Segment Topology Change Notifications (STCN) and VLAN Load Balancing (VLB) configurations are disabled.
Check the Preferred check box to configure the regular port as a preferred alternate port.
Step 8![]() From the STCN area, configure the destination of STCN messages:
From the STCN area, configure the destination of STCN messages:
a.![]() Check the Enable check box to enable sending STCN messages.
Check the Enable check box to enable sending STCN messages.
b.![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the STCN port to send STCN messages or enter the segment ID in the Segment field to send STCN messages. The STCN port and REP port must be unique.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the STCN port to send STCN messages or enter the segment ID in the Segment field to send STCN messages. The STCN port and REP port must be unique.
Step 9![]() From the VLAN Load Balancing area, configure VLAN Load Balancing on the primary edge port:
From the VLAN Load Balancing area, configure VLAN Load Balancing on the primary edge port:
a.![]() Check the Enable check box to enable VLB.
Check the Enable check box to enable VLB.
b.![]() Enter a single SVLAN or range of SVLANs in the SVLAN field. These SVLANs are blocked at the alternate ports. The primary edge port blocks the remaining VLANs.
Enter a single SVLAN or range of SVLANs in the SVLAN field. These SVLANs are blocked at the alternate ports. The primary edge port blocks the remaining VLANs.
c.![]() Enter the Rep PortId in the Rep PortId field to identify the VLAN blocking alternate port. This unique port ID is automatically generated when REP is enabled.
Enter the Rep PortId in the Rep PortId field to identify the VLAN blocking alternate port. This unique port ID is automatically generated when REP is enabled.
d.![]() Check the Preferred check box to select the segment port previously identified as the preferred alternate port for VLAN load balancing.
Check the Preferred check box to select the segment port previously identified as the preferred alternate port for VLAN load balancing.
When you check Preferred under VLAN Load Balancing area, you configure VLAN load balancing to use one of the previously configured preferred ports (under the Port Role area) to be the load balancing port. This restricts the load balancing port to be one among the preferred ports, but you cannot select a specific preferred port.
Step 10![]() From the VLB Preempt Delay area, enter the trigger delay for automatic VLB activation. The range is 15 to 300 seconds.
From the VLB Preempt Delay area, enter the trigger delay for automatic VLB activation. The range is 15 to 300 seconds.
Step 12![]() Enter the details of the second port to add it to the segment.
Enter the details of the second port to add it to the segment.
Repeat Step 6 to 10 when the first port is configured as a regular port and the second port is configured as a primary edge port. Repeat Step 6 to 7 when the first port is configured as a primary edge port and the second port is configured as a regular port.
Step 14![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G646 Edit a Segment Using CTC
This task allows you to edit a segment on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() You can edit only the STCN and VLB entries for a segment.
You can edit only the STCN and VLB entries for a segment.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to edit a segment. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to edit a segment. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
Step 4![]() Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Step 6![]() Modify the values as required and click Finish.
Modify the values as required and click Finish.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G647 Activate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
This task allows you to activate VLAN load balancing on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() When VLAN load balancing is activated, the default configuration is manual preemption with the delay timer disabled.
When VLAN load balancing is activated, the default configuration is manual preemption with the delay timer disabled.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to activate VLAN load balancing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to activate VLAN load balancing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
Step 4![]() Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G648 Deactivate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
This task allows you to deactivate VLAN load balancing on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to deactivate VLAN load balancing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to deactivate VLAN load balancing. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Verify that the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card is installed in L2-over-DWDM mode. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 3![]() In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
In card view, click the Provisioning > REP > Segment tabs. The list of segments appear.
Step 4![]() Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Choose a segment from the list of segments.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G165 Modify the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE Cards Ethernet Parameters, Line Settings, and PM Thresholds
This procedure changes Ethernet, line, and PM threshold settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
a.![]() Display the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card in card view.
Display the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card in card view.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
c.![]() Verify that the card mode is set to the mode designated by your site plan:
Verify that the card mode is set to the mode designated by your site plan:
–![]() L2-over-DWDM (GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE)
L2-over-DWDM (GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE)
–![]() 10GE TXP (10GE_XP or 10 GE_XPE)
10GE TXP (10GE_XP or 10 GE_XPE)
If the card mode is set correctly, continue with Step 4. If not, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 4![]() Complete the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Complete the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 5![]() If the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted in the GE_XPE card, complete the following tasks, as needed.
If the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted in the GE_XPE card, complete the following tasks, as needed.
Step 6![]() If the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card mode is L2-over-DWDM, complete the following tasks, as needed. If the card mode is not L2-over-DWDM, continue with Step 7.
If the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card mode is L2-over-DWDM, complete the following tasks, as needed. If the card mode is not L2-over-DWDM, continue with Step 7.
- G381 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 Protection Settings
- G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database
- G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports
- G383 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Quality of Service Settings
- G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings
- G205 Enable Link Integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards.
- G385 Provision the MAC Filter Settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card
- G204 Enable IGMP Snooping on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards or G220 Enable IGMP Snooping on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
- G206 Enable MVR on a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card or G224 Enable MVR on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
- G460 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC or G226 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
Step 7![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:

Note![]() To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
To use the Alarm Profiles tab, including creating alarm profiles and suppressing alarms, see Chapter10, “Manage Alarms”
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings
This task changes the Ethernet settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > Ethernet tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > Ethernet tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Ethernet tab as described in Table 6-117 . The parameters that appear depend on the card mode.
Modify any of the settings for the Ethernet tab as described in Table 6-117 . The parameters that appear depend on the card mode.
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
(Display only) The Port number ( n - n) and rate (GE or TEN_GE). |
|||
The maximum size of the Ethernet frames accepted by the port. The port must be in OOS/locked state. |
|||
Sets the Ethernet mode. The port must be in OOS/locked state before setting the card mode. Note For GE_XP and GE_XPE cards that are in Y-cable protection groups, Mode must be set to 1000 Mbps for those client ports that are configured in Y-cable. |
Note If Mode is set to Auto on the GE_XP or GE_XPE port, autonegotiation gets enabled on the peer port. 
Note |
||
Enables/disables flow control messaging with its peer port. When enabled, the port can send and receive PAUSE frames when buffer congestion occurs. When disabled, no PAUSE frames are transmitted and the PAUSE frames received are discarded. Note Flow control messaging is symmetric and not negotiated. When flow control is enabled on one port, the other end of the link (peer port) is not considered. That is, even if flow control is disabled on the peer port, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card will send PAUSE frames. |
|||
(GE_XPE card only) Sets the Media Type. Note PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised if the Media Type is not set to Ethernet Over DS1 (ANSI) or Ethernet Over E1 (ETSI) for ONS-SC-EOP1,Ethernet Over DS3 (ANSI) or Ethernet Over E3 (ETSI) for ONS-SC-EOP3, or DS1 Over Ethernet (ANSI) or E1 Over Ethernet (ETSI) for ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or DS3 Over Ethernet (ANSI) or E3 Over Ethernet (ETSI) ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW. Set the correct Media Type to clear the PROV-MISMATCH alarm. |
|
||
Sets the guaranteed information rate as provided by the service provider service-level agreement. The port must be in OOS/locked state. |
|||
Sets the maximum number of bits that will be transferred per second. The port must be in OOS/locked state before the Committed Burst Size is provisioned. |
|||
The maximum number of bits that are credited for later transfer in the event the committed burst rate cannot be transmitted. The port must be in OOS/locked state before the Excess Burst Size is provisioned. |
|||
Sets the port network interface mode (NIM). This parameter classifies port types designed for the Metro Ethernet market to simplify deployment, management, and troubleshooting. The port must be in OOS/locked state before the NIM is provisioned. |
|||
Enables Quality of Service (QoS) on the port’s egress or output queues. The port must be in OOS/locked state before the Egress QoS is provisioned. |
|||
Enables or disables MAC learning for the port on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. MAC learning is used by Layer 2 switches to learn the MAC addresses of network nodes so the Layer 2 switches send traffic to the right location. Layer 2 switches, including the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards in L2-over-DWDM mode with MAC Learning configured, maintain a MAC learning table that associates the MAC addresses and VLANs with a given port. Note MAC addresses on SVLANs attached to the port must also be enabled to provision MAC address learning on GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards. Note MAC address table aging is 300 seconds. It cannot be changed. |
|||
Provisions the IEEE 802.1p ingress Class of Service (CoS). The CoS.1p bits set the Ethernet frame priority. The port must be in OOS/locked state before the Ingress CoS is provisioned. Ingress CoS is used to set the priority of the Ethernet frame in the service provider network, This parameter is used to set the CoS.1p bits in the SVLAN tag. Ingress CoS applies only to ports provisioned as UNI mode. It does not apply to ports provisioned as NNI mode. |
If CVLAN CoS is configured on a GE_XP or a 10GE_XP card, a PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised. Until this alarm is cleared, provisioning on the card is not possible. The CVLAN CoS configuration takes effect only after QinQ is configured. |
||
Defines the inner Ethertype field. The Ethertype field indicates which protocol is being transported in an Ethernet frame. The inner Ethertype applies to ports provisioned in UNI mode only. It does not apply to ports provisioned as NNI mode. The ports must be OOS/locked before the inner Ethertype is provisioned. |
|||
Defines the outer Ethertype field. The Ethertype field identifies which protocol is being transported in an Ethernet frame. The ports must be OOS/locked before the Outer Ethertype is provisioned. Note The PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised on GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards if more than four different Outer Ethertype options are configured per card. |
|||
Adds multicast-capable ports to the forwarding table for every IP multicast. |
|||
Configures the standby port behavior. Set Protection Action to None if Media Type is set to Ethernet Over DS1 (ANSI) or Ethernet Over E1 (ETSI) for ONS-SC-EOP1, Ethernet Over DS3 (ANSI) or Ethernet Over E3 (ETSI) for ONS-SC-EOP3, or DS1 Over Ethernet (ANSI) or E1 Over Ethernet (ETSI) for ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or DS3 Over Ethernet (ANSI) or E3 Over Ethernet (ETSI) for ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW. |
Table 6-118 shows the inner and outer Ethertype behavior based on the NIM setting (either NNI mode or UNI mode). When the NIM is set to UNI, and the QinQ mode is set to Selective, the Ethertype behavior depends on the SVLAN/CVLAN operation that is provisioned, either Add or Translate. (QinQ parameters are provisioned in the G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings.)

Note![]() A packet can exit out of any UNI/NNI port if the outermost tag in the packet matches with the SVLAN provisioned on that port. In other words, in the egress path, the inner tags (even if present) of the packet are not matched with the inner SVLAN or CVLAN provisioned on the port.
A packet can exit out of any UNI/NNI port if the outermost tag in the packet matches with the SVLAN provisioned on that port. In other words, in the egress path, the inner tags (even if present) of the packet are not matched with the inner SVLAN or CVLAN provisioned on the port.

Note![]() The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be configured based on the expected packet size to ensure that no packets are dropped when Flow Control is enabled. For example, if the CIR is 40% and packet size is 1 KB, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size should be set to 1 MB.
The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be configured based on the expected packet size to ensure that no packets are dropped when Flow Control is enabled. For example, if the CIR is 40% and packet size is 1 KB, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size should be set to 1 MB.

Note![]() When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G684 Provision the GE_XPE Card PDH Ethernet Settings
This task changes the PDH Ethernet settings for the GE_XPE card. |
|
|
|

Note![]() The Provisioning > Ether Ports > PDH Ethernet Parameters tab is available in GE_XPE card view only, provided the PPM for GE_XPE port is created in FE mode.
The Provisioning > Ether Ports > PDH Ethernet Parameters tab is available in GE_XPE card view only, provided the PPM for GE_XPE port is created in FE mode.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE card where you want to change the PDH Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE card where you want to change the PDH Ethernet settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > PDH Ethernet Parameters tabs. The PDH Ethernet Parameters tab appear only when the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted.
Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > PDH Ethernet Parameters tabs. The PDH Ethernet Parameters tab appear only when the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the PDH Ethernet Parameters tab as described in Table 6-119 .
Modify any of the settings for the PDH Ethernet Parameters tab as described in Table 6-119 .
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Table 6-120 provides jitter buffer values for different payloads. Note The traffic is down if the jitter buffer is set to >=192000 when Media Type is set to DS1 over Ethernet (ANSI) (for ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW) and E1 Over Ethernet (ETSI) (for ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW). |
|||
Enter the source IP address. Only Unicast IP addresses are accepted. |
|||
Enter the peer IP address. Only Unicast IP addresses are accepted. |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G685 Provision the GE_XPE Card Electrical Lines Settings
This task changes the Electrical Lines settings for the GE_XPE card. |
|
|
|

Note![]() The Provisioning > Ether Ports > Electrical Lines tab is available in GE_XPE card view only, provided the PPM for GE_XPE port is created in FE mode.
The Provisioning > Ether Ports > Electrical Lines tab is available in GE_XPE card view only, provided the PPM for GE_XPE port is created in FE mode.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE card where you want to change the Electrical Lines settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE card where you want to change the Electrical Lines settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > Electrical Lines tabs. The Electrical Lines tab appear only when the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted.
Click the Provisioning > Ether Ports > Electrical Lines tabs. The Electrical Lines tab appear only when the ONS-SC-E1-T1-PW or ONS-SC-E3-T3-PW SFP is inserted.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings for the Electrical Lines > DS1 or Electrical Lines > DS3 tab as described in Table 6-121 .
Modify any of the settings for the Electrical Lines > DS1 or Electrical Lines > DS3 tab as described in Table 6-121 .
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G381 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 Protection Settings
This task provisions the Layer 2 protection settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards when the cards are provisioned in L2-over-DWDM mode. |
|

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.

Note![]() GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 protection settings must be planned for the entire VLAN ring. One card in the ring is provisioned as the master card and one of its port is set to Blocking. The master card coordinates the protection switching for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE in a VLAN ring.
GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 protection settings must be planned for the entire VLAN ring. One card in the ring is provisioned as the master card and one of its port is set to Blocking. The master card coordinates the protection switching for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE in a VLAN ring.

Note![]() You can choose to enable another card in the ring to be the master card. However, only one card in the ring can be provisioned as master card. Make sure that the provisioning settings on the card that was previously configured as the master are disabled as soon as another card is enabled as the master card. To perform this task complete the G507 Enable a Different GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card as the Master Card
You can choose to enable another card in the ring to be the master card. However, only one card in the ring can be provisioned as master card. Make sure that the provisioning settings on the card that was previously configured as the master are disabled as soon as another card is enabled as the master card. To perform this task complete the G507 Enable a Different GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card as the Master Card
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the protection settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the protection settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Status column, modify the port protection status by clicking the appropriate table cell and choosing one of the following from the drop-down list:
In the Status column, modify the port protection status by clicking the appropriate table cell and choosing one of the following from the drop-down list:

Note![]() One port of the master card within a VLAN ring must be set to Blocking. All other ports must be set to Forwarding.
One port of the master card within a VLAN ring must be set to Blocking. All other ports must be set to Forwarding.
Step 4![]() Check the Master
Check the Master![]() check box if you want the card to serve as the protection coordinator for the VLAN ring. If not, continue with Step 5
check box if you want the card to serve as the protection coordinator for the VLAN ring. If not, continue with Step 5![]() .
.
Step 5![]() From the Protection drop-down list, choose one of the following:
From the Protection drop-down list, choose one of the following:
- Enabled—Enables protection.
- Disabled—Disables protection.
- Forced—Converts all the SVLANs to protected SVLANs irrespective of the SVLAN protection configuration in the SVLAN database. This is applicable to a point-to-point linear topology. The SVLAN protection must be forced to move all SVLANs, including protected and unprotected SVLANs, to the protect path irrespective of provisioned SVLAN attributes.
Step 6![]() From the Hold Off Time drop-down list, choose one of the following:
From the Hold Off Time drop-down list, choose one of the following:

Note![]() To get consistent results ensure Hold Off Time values are the same throughout the ring.
To get consistent results ensure Hold Off Time values are the same throughout the ring.

Note![]() FAPS is an Layer 2 protection enabled on a VLAN. When a fiber fault occurs, Layer 1 protection is triggered immediately to restore the traffic. Setting the Hold Off Time option prevents Layer 2 FAPS protection from triggering at the same time as Layer 1 protection thereby avoiding traffic hits.
FAPS is an Layer 2 protection enabled on a VLAN. When a fiber fault occurs, Layer 1 protection is triggered immediately to restore the traffic. Setting the Hold Off Time option prevents Layer 2 FAPS protection from triggering at the same time as Layer 1 protection thereby avoiding traffic hits.
Step 7![]() Set the following parameters for FAPS switching with CRC errors:
Set the following parameters for FAPS switching with CRC errors:
a.![]() Switch with CRC Alarm—Check this check box to enable FAPS switching with CRC errors.
Switch with CRC Alarm—Check this check box to enable FAPS switching with CRC errors.
b.![]() CRC Threshold—Threshold for CRC error count. The default CRC threshold value is 10(-e)2. The available options are 10(-e)2, 10(-e)3, and 10(-e)4.
CRC Threshold—Threshold for CRC error count. The default CRC threshold value is 10(-e)2. The available options are 10(-e)2, 10(-e)3, and 10(-e)4.
c.![]() CRC Soak Count—Number of times the CRC error rate exceeds the CRC threshold value before raising the DATA-CRC alarm. The default CRC Soak Count is 10. The valid range is from 3 to 10.
CRC Soak Count—Number of times the CRC error rate exceeds the CRC threshold value before raising the DATA-CRC alarm. The default CRC Soak Count is 10. The valid range is from 3 to 10.
d.![]() CRC Poll Interval—Time interval (in seconds) between the successive polls. The default CRC Poll Interval is 60 seconds.
CRC Poll Interval—Time interval (in seconds) between the successive polls. The default CRC Poll Interval is 60 seconds.
For example, if the CRC Threshold value = 10(-e)2, CRC Soak Count = 10, and CRC Poll Interval = 60 seconds, then FAPS occurs when the incoming CRC error rate is more than 10(-e)2 continuously across 10 poll intervals (10*60 = 600 seconds).
e.![]() Clear/Supress CRC Alarm—Uncheck the Clear/Supress CRC Alarm check box for FAPS to occur. If you check this check box, the DATA-CRC alarm gets cleared and FAPS does not occur.
Clear/Supress CRC Alarm—Uncheck the Clear/Supress CRC Alarm check box for FAPS to occur. If you check this check box, the DATA-CRC alarm gets cleared and FAPS does not occur.

Note![]() As along as the Clear/Supress CRC Alarm checkbox is checked, the DATA-CRC alarm is not raised on that port and FAPS does not occur.
As along as the Clear/Supress CRC Alarm checkbox is checked, the DATA-CRC alarm is not raised on that port and FAPS does not occur.

Note![]() For consistent result, ensure that all the values that are set in Step 7 are same throughout the ring.
For consistent result, ensure that all the values that are set in Step 7 are same throughout the ring.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G507 Enable a Different GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card as the Master Card
This task provisions another GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card on a stable VLAN ring, to be the master card when the cards are provisioned in L2-over-DWDM mode. |
|
| G381 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 Protection Settings |
|

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.

Note![]() Do not attempt to change the master card when there is a failure in the FAPS ring.
Do not attempt to change the master card when there is a failure in the FAPS ring.

Note![]() GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 protection must be enabled for the entire VLAN ring. One card in the ring is provisioned as the master card and one of its port is set to Blocking. The master card coordinates the protection switching for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards in a VLAN ring.
GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 protection must be enabled for the entire VLAN ring. One card in the ring is provisioned as the master card and one of its port is set to Blocking. The master card coordinates the protection switching for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards in a VLAN ring.

Note![]() You can choose to enable another card in the ring to be the master card. However, only one card in the ring can be provisioned as master card. Make sure that the provisioning settings on the card that was previously configured as the master are disabled as soon as another card is enabled as the master card.
You can choose to enable another card in the ring to be the master card. However, only one card in the ring can be provisioned as master card. Make sure that the provisioning settings on the card that was previously configured as the master are disabled as soon as another card is enabled as the master card.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card in a VLAN ring where you want to enable master card provisioning. The card view appears. Perform the following steps:
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card in a VLAN ring where you want to enable master card provisioning. The card view appears. Perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
b.![]() From the Status drop-down list, choose Blocking for a trunk port.
From the Status drop-down list, choose Blocking for a trunk port.

Note![]() One port of the master card within a VLAN ring must be set to Blocking. All other ports must be set to Forwarding.
One port of the master card within a VLAN ring must be set to Blocking. All other ports must be set to Forwarding.
c.![]() Check the Master check box for the card that serves as the protection coordinator for the VLAN ring.
Check the Master check box for the card that serves as the protection coordinator for the VLAN ring.
d.![]() From the Protection drop-down list, choose Enabled.
From the Protection drop-down list, choose Enabled.
Step 2![]() The master card provisioning on the other card must be disabled. Perform the following steps:
The master card provisioning on the other card must be disabled. Perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
b.![]() Uncheck the Master check box for the card where Master node provisioning must be disabled.
Uncheck the Master check box for the card where Master node provisioning must be disabled.
d.![]() From the Protection drop-down list, choose Disabled.
From the Protection drop-down list, choose Disabled.
Step 3![]() The protection on the card that was disabled in Step 2 must be enabled again. Perform the following steps:
The protection on the card that was disabled in Step 2 must be enabled again. Perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Protection tabs.
b.![]() From the Protection drop-down list, choose Enabled.
From the Protection drop-down list, choose Enabled.
d.![]() From the Status drop-down list, choose Forwarding on both ports.
From the Status drop-down list, choose Forwarding on both ports.
Step 4![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.

Note![]() This task can only be performed on ports provisioned as NNI. See the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
This task can only be performed on ports provisioned as NNI. See the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the SVLAN port settings. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the SVLAN port settings. The card view appears.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > SVLAN tabs.
Click the Provisioning > SVLAN tabs.
Step 3![]() For each SVLAN shown in the table, click the check box under the Port [ port name ] table cell to include the SVLAN in that port. If you do not want the SVLAN included, uncheck the check box.
For each SVLAN shown in the table, click the check box under the Port [ port name ] table cell to include the SVLAN in that port. If you do not want the SVLAN included, uncheck the check box.

Note![]() If no SVLANs appear in the SVLAN tab, complete the G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
If no SVLANs appear in the SVLAN tab, complete the G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G383 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Quality of Service Settings
This task provisions the Weighted Round Robin (WRR) value and bandwidth for QoS Class of Service (CoS) egress queues on a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card port. |
|

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode and the port must have QoS enabled. Refer to the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode and the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings, if needed.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode and the port must have QoS enabled. Refer to the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode and the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings, if needed.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the QoS settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the QoS settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > QoS tabs.
Click the Provisioning > QoS tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Port field at the bottom of the window, choose the port where you want to provision the QoS settings.
In the Port field at the bottom of the window, choose the port where you want to provision the QoS settings.
Step 4![]() For each CoS egress queue, 0 through 7, define the following:
For each CoS egress queue, 0 through 7, define the following:

Note![]() The GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE define a set of eight queues, one queue for each CoS. Only one of the queues can be assigned the 0 WRR weight (Strict Priority).
The GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE define a set of eight queues, one queue for each CoS. Only one of the queues can be assigned the 0 WRR weight (Strict Priority).
Step 5![]() Click Apply. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Click Apply. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G470 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Class of Service (CoS) Settings
This task provisions Class of Service (CoS) settings on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card. |
|

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode and the port must be in OOS state.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode and the port must be in OOS state.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the CoS settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the CoS settings.
Step 2![]() Complete the following task:
Complete the following task:
- Refer to the Ingress CoS section in the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 3![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.

Note![]() This task can only be performed on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards UNI ports. (To provision the port Ethernet parameters, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.)
This task can only be performed on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards UNI ports. (To provision the port Ethernet parameters, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.)
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the QinQ settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the QinQ settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > QinQ tabs.
Click the Provisioning > QinQ tabs.
Step 3![]() Click the Port field and choose the port where you want to provision QinQ.
Click the Port field and choose the port where you want to provision QinQ.
Channel groups configured in UNI mode appear in the Port field along with the physical ports.
Step 4![]() Click the Mode field and choose one of the following modes from the drop-down list:
Click the Mode field and choose one of the following modes from the drop-down list:
- Selective—The incoming Ethernet packet is checked against the CVLAN and SVLAN table. If the CVLAN is not found, the packet is dropped. If you choose Selective, add an entry in the QinQ tab to map the administrative CVLAN to the SVLAN (if it is not same as the one used for data).
- Transparent—All incoming packets are transported with the additional VLAN chosen in the SVLAN field. If you choose transparent, the traffic on administrative CVLAN will pass through.
Step 5![]() Click the BPDU field and choose one of the following bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) modes from the drop-down list:
Click the BPDU field and choose one of the following bridge protocol data unit (BPDU) modes from the drop-down list:
–![]() 01-80-c2-00-00-00—IEEE 802.1D
01-80-c2-00-00-00—IEEE 802.1D
–![]() 01-80-c2-00-00-02—Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
01-80-c2-00-00-02—Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
–![]() 01-80-0c-cc-cc-cc—VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+)
01-80-0c-cc-cc-cc—VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+)
–![]() 01-00-c-cc-cc-cc—Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) type 0x2000, VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) type 0x2003, Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP), type 0x0104, Uni-Directional Link Detection (UDLD) type 0x111, Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) type 0x2004
01-00-c-cc-cc-cc—Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) type 0x2000, VLAN Trunk Protocol (VTP) type 0x2003, Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP), type 0x0104, Uni-Directional Link Detection (UDLD) type 0x111, Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) type 0x2004
Step 6![]() If the Mode was set to Selective, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 7.
If the Mode was set to Selective, complete the following steps. If not, continue with Step 7.
b.![]() Click the CVLAN table and type in the CVLAN range. You can enter a single value or a range using “–” between the two ends of the range.
Click the CVLAN table and type in the CVLAN range. You can enter a single value or a range using “–” between the two ends of the range.

Note![]() If you are using Software Release 8.5 or earlier, it is recommended that you do not specify a CVLAN range due to certain limitations in the feature.
If you are using Software Release 8.5 or earlier, it is recommended that you do not specify a CVLAN range due to certain limitations in the feature.
c.![]() Click the SVLAN table cell and choose an SVLAN from the drop-down list.
Click the SVLAN table cell and choose an SVLAN from the drop-down list.
d.![]() Click the Operation table cell and choose an operation:
Click the Operation table cell and choose an operation:
–![]() Add (default)—Adds the SVLAN on top of the CVLAN. The operation default can be applied for any UNI port.
Add (default)—Adds the SVLAN on top of the CVLAN. The operation default can be applied for any UNI port.
–![]() Translate—CVLAN is translated with the SVLAN value.
Translate—CVLAN is translated with the SVLAN value.
–![]() Double Add—(GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) Adds an inner and an outer SVLAN to double tagged packets only. CVLAN settings are not required. If this double tagged selective operation is present on a port, no other selective operation can be present.
Double Add—(GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) Adds an inner and an outer SVLAN to double tagged packets only. CVLAN settings are not required. If this double tagged selective operation is present on a port, no other selective operation can be present.
–![]() Translate Add—(GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) CVLAN gets translated to inner SVLAN and the SVLAN is added.
Translate Add—(GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) CVLAN gets translated to inner SVLAN and the SVLAN is added.

Note![]() If Double Add and Translate Add are configured on a GE_XP or a 10GE_XP card, a PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised. Until this alarm is cleared, provisioning on the card is not possible.
If Double Add and Translate Add are configured on a GE_XP or a 10GE_XP card, a PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised. Until this alarm is cleared, provisioning on the card is not possible.

Note![]() A CVLAN with a value of 0 means “untagged packet”.
A CVLAN with a value of 0 means “untagged packet”.

Note![]() Two or more CVLANs cannot be translated over the same SVLAN.
Two or more CVLANs cannot be translated over the same SVLAN.
e.![]() (GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) Click the COS table cell and choose a value from the drop down list.
(GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards only) Click the COS table cell and choose a value from the drop down list.
g.![]() Continue with Step 10.
Continue with Step 10.
Step 7![]() If the Mode was set to Transparent, in the SVLAN field, choose the SVLAN to be added to incoming packets.
If the Mode was set to Transparent, in the SVLAN field, choose the SVLAN to be added to incoming packets.
Step 8![]() Click DSCP-Cos mapping Table to provision CoS based on DSCP for each port.
Click DSCP-Cos mapping Table to provision CoS based on DSCP for each port.
Step 9![]() For each DSCP, choose a CoS value from 0 to 7 and click OK.
For each DSCP, choose a CoS value from 0 to 7 and click OK.
Step 10![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G221 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This task enables MAC address learning on SVLANS for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable MAC Address Learning. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable MAC Address Learning. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:
- G460 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
- G226 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G460 Enable MAC Address Learning on SVLANs for GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This task enables MAC address learning on SVLANs attached to the port of a GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE card. |
|
| G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode |
|

Note![]() MAC address learning is applicable only for GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards. If MAC address learning is configured on a GE_XP or a 10GE_XP card, a PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised. Until this alarm is cleared, provisioning on the card is not possible.
MAC address learning is applicable only for GE_XPE and 10GE_XPE cards. If MAC address learning is configured on a GE_XP or a 10GE_XP card, a PROV-MISMATCH alarm is raised. Until this alarm is cleared, provisioning on the card is not possible.

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. Refer to the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode if needed.
To perform this task, the GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. Refer to the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode if needed.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE card where you want to enable MAC address learning.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XPE or 10GE_XPE card where you want to enable MAC address learning.
Step 2![]() Enable MAC address learning on the port. Perform the following steps:
Enable MAC address learning on the port. Perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click Provisioning > Ethernet.
Click Provisioning > Ethernet.
b.![]() Check the MAC Learning check box.
Check the MAC Learning check box.

Note![]() If the per port MAC address learning is configured on a GE_XP or 10 GE_XP cards, before upgrading to a GE_XPE or 10 GE_XPE card, enable MAC address learning per SVLAN. Not doing so disables MAC address learning.
If the per port MAC address learning is configured on a GE_XP or 10 GE_XP cards, before upgrading to a GE_XPE or 10 GE_XPE card, enable MAC address learning per SVLAN. Not doing so disables MAC address learning.
Step 3![]() Enable MAC address learning on the SVLAN attached to the port. Perform the following steps:
Enable MAC address learning on the SVLAN attached to the port. Perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click SVLAN > SVLAN DB tabs.
Click SVLAN > SVLAN DB tabs.
b.![]() Click Load. This loads an SVLAN database from a network node or local file and replaces any SVLANs that are in the network view VLAN DB table.
Click Load. This loads an SVLAN database from a network node or local file and replaces any SVLANs that are in the network view VLAN DB table.
c.![]() Check the MAC Learning check box related to the SVLAN (one or more than one SVLAN) to be configured with MAC address learning.
Check the MAC Learning check box related to the SVLAN (one or more than one SVLAN) to be configured with MAC address learning.
d.![]() Click Store. This records and enables the new configuration.
Click Store. This records and enables the new configuration.
Step 4![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G385 Provision the MAC Filter Settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the MAC filter settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the MAC filter settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Security > MAC Filter tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Security > MAC Filter tabs.
Step 3![]() Click the port for which you want to create a MAC filter.
Click the port for which you want to create a MAC filter.
Step 5![]() In the Edit MAC Address dialog box, click Add. A new table entry appears with the MAC address 00-00-00-00-00-00.
In the Edit MAC Address dialog box, click Add. A new table entry appears with the MAC address 00-00-00-00-00-00.
Step 6![]() In the MAC Address Port field, type in the MAC address you want to filter over the default 00-00-00-00-00-00 address.
In the MAC Address Port field, type in the MAC address you want to filter over the default 00-00-00-00-00-00 address.
Step 7![]() If you want to add more MAC addresses, repeat Steps 5 and 6 . (Up to eight MAC addresses can be added for each port.) If not, click OK.
If you want to add more MAC addresses, repeat Steps 5 and 6 . (Up to eight MAC addresses can be added for each port.) If not, click OK.
Step 8![]() On the MAC Filter table, provision the Allowed check box:
On the MAC Filter table, provision the Allowed check box:
Step 10![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 9 for each port of the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card that you want to set up.
Repeat Steps 3 through 9 for each port of the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card that you want to set up.
Step 11![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G237 Retrieve and Clear MAC Addresses on SVLANs for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This procedure retrieves and clears MAC addresses learned on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|


Note![]() It is not possible to simultaneously retrieve learned MAC addresses from both CTC and TL1 interfaces.
It is not possible to simultaneously retrieve learned MAC addresses from both CTC and TL1 interfaces.
Step 1![]() In the node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to retrieve the MAC addresses.
In the node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to retrieve the MAC addresses.
Step 2![]() To retrieve the MAC addresses learned, perform the following steps:
To retrieve the MAC addresses learned, perform the following steps:
a.![]() Click Maintenance > MAC Addresses > Learned.
Click Maintenance > MAC Addresses > Learned.
b.![]() In the SVLAN field, type a valid SVLAN range. The SVLAN range is from 1 to 4093.
In the SVLAN field, type a valid SVLAN range. The SVLAN range is from 1 to 4093.
The table displays the following fields:
–![]() MAC Address—Displays the MAC address for the port.
MAC Address—Displays the MAC address for the port.
–![]() VLAN—Displays the VLAN identifier for the port.
VLAN—Displays the VLAN identifier for the port.
–![]() Port—Displays the port number.
Port—Displays the port number.
Right-click the column heading to display the following options:
–![]() Row Count—Displays the number of learned MAC addresses retrieved.
Row Count—Displays the number of learned MAC addresses retrieved.
–![]() Sort Column—Sorts the table by the column’s values.
Sort Column—Sorts the table by the column’s values.
–![]() Hide Column—Hides the column from view.
Hide Column—Hides the column from view.
–![]() Reorder Columns Visibility—Displays all hidden columns.
Reorder Columns Visibility—Displays all hidden columns.
Step 3![]() Click Refresh to refresh the list of MAC addresses learned.
Click Refresh to refresh the list of MAC addresses learned.
Step 4![]() Click Clear to clear the MAC addresses learned on all the SVLANS of the card.
Click Clear to clear the MAC addresses learned on all the SVLANS of the card.

Note![]() It is not possible to delete the MAC addresses learned on a per SVLAN basis.
It is not possible to delete the MAC addresses learned on a per SVLAN basis.
Step 5![]() To view card MAC addresses, complete the G546 View Card MAC Addresses on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards.
To view card MAC addresses, complete the G546 View Card MAC Addresses on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G546 View Card MAC Addresses on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This task allows you to view the MAC addresses for each client and trunk port and the CPU port of the card. |
|
Step 1![]() To view the card MAC addresses, click Maintenance > MAC Addresses > Card. The MAC addresses for each client and trunk port and the CPU port are displayed.
To view the card MAC addresses, click Maintenance > MAC Addresses > Card. The MAC addresses for each client and trunk port and the CPU port are displayed.
The table displays the following fields:
Step 2![]() Return to your originating procedure.
Return to your originating procedure.
NTP-G311 Provision the Storm Control Settings for GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This task provisions the storm control settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards when the cards are provisioned in L2-over-DWDM mode. |
|

Note![]() To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
To perform this task, the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card must be in L2-over-DWDM mode. To change the card mode, complete the G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the storm control settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the storm control settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Security > Storm Control tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Security > Storm Control tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-122 .
Modify any of the settings as described in Table 6-122 .
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G205 Enable Link Integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This task enables link integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable link integrity. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable link integrity. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:
- G509 Enable Link Integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
- G216 Enable Link Integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G509 Enable Link Integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This task enables link integrity on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2![]() Create or load an SVLAN profile. To create a SVLAN profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.
Create or load an SVLAN profile. To create a SVLAN profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.

Note![]() Make sure the Link Integrity check box is selected to enable link integrity for a profile and save it to the node.
Make sure the Link Integrity check box is selected to enable link integrity for a profile and save it to the node.
Step 3![]() Associate the SVLAN profile (with Link Integrity enabled) to a SVLAN on a port. To do this perform the following steps:
Associate the SVLAN profile (with Link Integrity enabled) to a SVLAN on a port. To do this perform the following steps:
a.![]() In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > SVLAN tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > SVLAN tabs.
c.![]() Enter the SVLANs or SVLAN range in the SVLAN to View text box.
Enter the SVLANs or SVLAN range in the SVLAN to View text box.
A table appears that displays SVLANs and available ports. The SVLAN profiles that was created must be applied to a SVLAN and a port. However, make sure the SVLAN has already been associated with the port via the QinQ tab (For information on how to associate a SVLAN to a port, see the G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings).
d.![]() Select the SVLAN for a port and choose the available SVLAN profile from the drop-box.
Select the SVLAN for a port and choose the available SVLAN profile from the drop-box.
Step 4![]() AIS action must be set on a per-UNI port basis. Select None or Squelch from the AIS action drop-down list. For detailed instructions, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
AIS action must be set on a per-UNI port basis. Select None or Squelch from the AIS action drop-down list. For detailed instructions, see the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G289 Provision CVLAN Rate Limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card
This task provisions CVLAN rate limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() You cannot provision CVLAN rate limiting on channel groups.
You cannot provision CVLAN rate limiting on channel groups.
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to provision CVLAN rate limiting. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to provision CVLAN rate limiting. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 3![]() Create or load a CVLAN profile by setting Committed Info Rate, Committed Burst, Excess Info, Excess Burst. To create a CVLAN Profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.
Create or load a CVLAN profile by setting Committed Info Rate, Committed Burst, Excess Info, Excess Burst. To create a CVLAN Profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.
Step 4![]() Associate the CVLAN profile to a CVLAN on a UNI port. To do this perform the following steps:
Associate the CVLAN profile to a CVLAN on a UNI port. To do this perform the following steps:
a.![]() In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > CVLAN tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > CVLAN tabs.
c.![]() Enter the CVLANs or CVLAN range in the CVLANS to View text box.
Enter the CVLANs or CVLAN range in the CVLANS to View text box.
A table appears that displays CVLANs and available ports. The CVLAN profiles that were created must be applied to a CVLAN and port. However, make sure the CVLAN has already been associated with the port via the QinQ tab (For information on how to associate a CVLAN profile to a UNI port, see G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings).
d.![]() Select the CVLAN for a given port and choose the available CVLAN profile from the drop-down list.
Select the CVLAN for a given port and choose the available CVLAN profile from the drop-down list.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G208 Provision SVLAN Rate Limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card
This task provisions SVLAN rate limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable SVLAN rate limiting. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable SVLAN rate limiting. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:
- G515 Provision SVLAN Rate Limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card Using CTC
- G225 Provision SVLAN Rate Limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card Using PCLI
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G515 Provision SVLAN Rate Limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card Using CTC
This task provisions SVLAN rate limiting on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2![]() Create or load a SVLAN profile by setting Committed Info Rate, Committed Burst, Excess Info, Excess Burst. To create a SVLAN Profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.
Create or load a SVLAN profile by setting Committed Info Rate, Committed Burst, Excess Info, Excess Burst. To create a SVLAN Profile see G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile.
Step 3![]() Associate the SVLAN profile to a SVLAN on a port. To do this, perform the following steps:
Associate the SVLAN profile to a SVLAN on a port. To do this, perform the following steps:
a.![]() In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE card. The card view appears.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > SVLAN tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Profiles Mapping > SVLAN tabs.
c.![]() Enter the SVLANs or SVLAN range in the SVLAN to View text box.
Enter the SVLANs or SVLAN range in the SVLAN to View text box.
A table appears that displays SVLANs and available ports. The SVLAN profiles that were created must be applied to a SVLAN and port. However, make sure the SVLAN has already been associated with the port via the QinQ tab (For information on how to associate a SVLAN profile to a UNI port, see G384 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE QinQ Settings and to a NNI port see G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports).
d.![]() Select the SVLAN for a given port and choose the available SVLAN profile from the drop-down list.
Select the SVLAN for a given port and choose the available SVLAN profile from the drop-down list.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G471 Create a SVLAN or CVLAN Profile

Note![]() You cannot associate SVLAN or CVLAN profiles to channel groups. You can associate a CVLAN profile only to a UNI port.
You cannot associate SVLAN or CVLAN profiles to channel groups. You can associate a CVLAN profile only to a UNI port.
Step 1![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > SVLAN > Profiles tabs.
Click the Provisioning > SVLAN > Profiles tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Add and a profile is added to the Profiles tab. Modify any of the settings as follows:
Click Add and a profile is added to the Profiles tab. Modify any of the settings as follows:
- Name—The profile name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters.
- Committed Info Rate—Sets the guaranteed information rate as provided by the service provider service-level agreement. The default value is 100 and the range is 0 to 100 percent.
- Committed Burst—Sets the maximum number of bits that will be transferred per second.
- Peak Info Rate—Sets the maximum information rate as provided by the service provider service-level agreement. The default value is 100 and the range is 0 to 100 percent. However, the value must be greater or equal to than the Committed Info Rate.
- Peak Burst Size—The maximum number of bits that are credited for later transfer in the event the committed burst rate cannot be transmitted.
- Link Integrity—Enables link integrity for the SVLAN profile. Do not check this check box if you are creating a CVLAN profile.

Note![]() When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
When you set the Committed Info Rate above 40% on 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE cards, the Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size must be set to at least 32K. The Committed Burst Size and Excess Burst Size can be increased based on the packet size and Committed Info Rate value.
Step 5![]() In the Store Profile(s) dialog box, choose one of the following:
In the Store Profile(s) dialog box, choose one of the following:
- To Node(s)—Stores the SVLAN profile at one or more network nodes. Choose the network nodes where you want to store the SVLAN profile. To choose more than one node, press the Shift key, or click Select All.
- To File—Stores the SVLAN profile in a file. Enter a file name, then click Browse to navigate to a local or network drive where you want to store the file.
Step 7![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G204 Enable IGMP Snooping on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards
This procedure enables Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping on a per-SVLAN basis on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable IGMP snooping. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable IGMP snooping. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:
- G511 Enable IGMP Snooping, IGMP Fast Leave and IGMP Report Suppression on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC.
- G220 Enable IGMP Snooping on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
- G217 Enable IGMP Fast-Leave Processing on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
- G219 Enable IGMP Report Suppression on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G511 Enable IGMP Snooping, IGMP Fast Leave and IGMP Report Suppression on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using CTC
This procedure explains how to enable IGMP snooping, IGMP fast leave and IGMP report suppression on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards using CTC. |
|
Step 1![]() From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
From the View menu, choose Go to Network View.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > SVLAN > SVLAN DB tabs. Click Load to load the SVLANs on the card where IGMP must be enabled.
Click the Provisioning > SVLAN > SVLAN DB tabs. Click Load to load the SVLANs on the card where IGMP must be enabled.
Step 3![]() For each SVLAN shown in the table, select the following:
For each SVLAN shown in the table, select the following:
- IGMP—Check the IGMP check box to enable IGMP for the selected SVLAN.
- IGMP Fast Leave—Checking the IGMP Fast Leave causes the switch to immediately remove a port from the IP multicast group when it detects an IGMP, version 2 (IGMPv2) leave message on that port.
- IGMP Suppression—Check the IGMP Suppression check box to enable a single IGMP report to be sent to each multicast group in response to a single query.
Step 5![]() In the Store SVLAN DB dialog box, choose one of the following:
In the Store SVLAN DB dialog box, choose one of the following:
- To Node/Shelf/Card—Select the node and shelf. All the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards in L2 over DWDM mode are displayed. Select the card where you want to store the SVLAN DB.
- Stores the SVLAN database at one or more network nodes. Choose the network nodes where you want to store the SVLAN database. To choose more than one node, press the Shift key, or click Select All.
- To File—Stores the SVLAN database in a file. Enter a file name, then click Browse to navigate to a local or network drive where you want to store the file.
- Select the card on which you want to save the changes made in step 3.

Note![]() If you want to add the multicast-capable ports to the forwarding table for every IP multicast, select the IGMP Static Router Port check box as described in the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
If you want to add the multicast-capable ports to the forwarding table for every IP multicast, select the IGMP Static Router Port check box as described in the G380 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Ethernet Settings.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G206 Enable MVR on a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card
This procedure enables Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable IGMP snooping. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to enable IGMP snooping. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Complete the following tasks, as needed:
Complete the following tasks, as needed:
- G513 Enable MVR on a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card Using CTC.
- G224 Enable MVR on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Cards Using PCLI.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G513 Enable MVR on a GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card Using CTC
This procedure enables Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) on GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE cards using CTC. |
|
G382 Add and Remove SVLANS to/from GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE NNI Ports |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to enable MVR. The card view appears.
In node view (single-shelf mode), or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to enable MVR. The card view appears.

Note![]() At least one SVLAN must be configured on the card.
At least one SVLAN must be configured on the card.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > MVR tabs. The MVR Settings tab appears.
Click the Provisioning > MVR tabs. The MVR Settings tab appears.
Step 3![]() Check the Enabled check box and enter the following information:
Check the Enabled check box and enter the following information:
- IGMP CVLAN—Check box to enable IGMP snooping on CVLAN. This check box is enabled only when MVR is enabled through the Enabled check box.
- Multicast SVLAN—Select the MVR SVLAN ID. The default value is the SVLAN with the lowest ID configured on the card. The drop box lists all the SVLANs on the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card.

Note![]() SVLAN selected here can not be used for UNI port, make sure that the corresponding SVLAN on the NNI port is checked.
SVLAN selected here can not be used for UNI port, make sure that the corresponding SVLAN on the NNI port is checked.
- Multicast Address—Sets the specified multicast group address as the MVR multicast group. The default address is 239.255.255.255 and the range is 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. Except the subrange [224-239].[0/128].0.x.
- Count—Sets the range of any additional multicast group addresses. The default is 1, and range is 1 to 256.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G386 Provision the Gigabit Ethernet Trunk Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task changes the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card trunk port alarm and TCA thresholds. |
|

Note![]() The GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards have two trunk ports. The GE_XP and GE_XPE trunk ports are 21-1 and 22-1 on the card graphic and 21 (Trunk) and 22 (Trunk) on the Optics Thresholds table. The 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE card trunk ports are 3-1 and 4-1 on the card graphic and 3 (Trunk) and 4 (Trunk) on the Optics Thresholds table.
The GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards have two trunk ports. The GE_XP and GE_XPE trunk ports are 21-1 and 22-1 on the card graphic and 21 (Trunk) and 22 (Trunk) on the Optics Thresholds table. The 10GE_XP and 10GE_XPE card trunk ports are 3-1 and 4-1 on the card graphic and 3 (Trunk) and 4 (Trunk) on the Optics Thresholds table.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 3![]() If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. When TCA is selected, continue with Step 4
If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. When TCA is selected, continue with Step 4![]() .
.
Step 4![]() Verify the trunk port TCA thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-123 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the trunk port TCA thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-123 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 5![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Verify the trunk port alarm thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-124 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the trunk port alarm thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-124 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 8![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 7 to provision the second trunk port.
Repeat Steps 3 through 7 to provision the second trunk port.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G387 Provision the Gigabit Ethernet Client Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the client port alarm and TCA thresholds for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|

Note![]() The GE_XP card has 20 client ports. The ports are 1-1 through 20-1 on the card graphic and 1 (Client) through 20 (Client) on the Optics Thresholds table. The 10GE_XP card has 2 client ports. The ports are 1-1 and 2-1 on the card graphic and 1 (Client) and 2 (Client) on the Optics Thresholds table.
The GE_XP card has 20 client ports. The ports are 1-1 through 20-1 on the card graphic and 1 (Client) through 20 (Client) on the Optics Thresholds table. The 10GE_XP card has 2 client ports. The ports are 1-1 and 2-1 on the card graphic and 1 (Client) and 2 (Client) on the Optics Thresholds table.

Note![]() The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
The hardware device that plugs into a TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or ADM-10G card faceplate to provide a fiber interface to the card is called a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP or XFP). In CTC, SFPs and XFPs are called pluggable port modules (PPMs). SFPs/XFPs are hot-swappable input/output devices that plug into a port to link the port with the fiber-optic network. Multirate PPMs have provisionable port rates and payloads. For more information about SFPs and XFPs, refer to the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the client port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs. The TCA thresholds are shown by default.
Step 3![]() If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. When TCA is selected, continue with Step 4
If TCA is not selected, click TCA and then click Refresh. When TCA is selected, continue with Step 4![]() .
.
Step 4![]() Verify the client port TCA thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-125 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the client port TCA thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-125 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1000Base-SX (1Gbps)16 |
||||
|
|

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 5![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Verify the client port Alarm thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-126 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
Verify the client port Alarm thresholds are provisioned as shown in Table 6-126 . Provision new thresholds as needed by double-clicking the threshold value you want to change, deleting it, entering a new value, and hitting Enter.
|
|
Power High |
Power Low |
Power High |
Power Low |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1000Base-SX (1Gbps)17 |
||||
|
|
Step 8![]() Repeat Steps 3 through 7 to provision each additional client port.
Repeat Steps 3 through 7 to provision each additional client port.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G388 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE Card RMON Thresholds
This task changes the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card RMON threshold settings. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the RMON thresholds.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), display the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the RMON thresholds.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose an individual port, or choose All to provision RMON thresholds for all ports.
From the Port drop-down list, choose an individual port, or choose All to provision RMON thresholds for all ports.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-127 for a list of available Ethernet RMON variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-127 for a list of available Ethernet RMON variables.

Note![]() Variable descriptions were obtained from the following Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Requests for Comment (RFCs): RFC 3635, RFC 2233, and RFC 1757. Refer to the RFCs for additional information.
Variable descriptions were obtained from the following Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Requests for Comment (RFCs): RFC 3635, RFC 2233, and RFC 1757. Refer to the RFCs for additional information.
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, indicate whether the event will be triggered by the rising threshold, the falling threshold, or both the rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Type in an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Type in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).
Step 12![]() To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds. If not, continue with Step 12
To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds. If not, continue with Step 12![]()
Step 13![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G389 Change the Gigabit Ethernet Optical Transport Network Settings
This task changes the optical transport network (OTN) settings for the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, or 10GE_XPE card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs, then choose one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, or Trail Trace Identifier.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-128 through 6-131 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-128 through 6-131 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End; 15 Min and 1 Day; and SM and PM independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-128 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-129 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > ITU-T G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-130 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Threshold tab.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Table 6-131 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G314 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card on a FAPS Ring
| “NTP-G15 Install the Common Control Cards” in the Cisco ONS 15454 Hardware Installation Guide G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
Perform any of the following tasks as needed:
- G687 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card Facing Master Card on a FAPS Ring
- G688 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card Between the Slave Cards on a FAPS Ring
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G687 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card Facing Master Card on a FAPS Ring
This procedure adds a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card that faces the master card on a FAPS ring. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP or 10GE_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Verify that the GE_XP or 10GE_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Step 3![]() Insert the new GE-XP card with XFP on the slot.
Insert the new GE-XP card with XFP on the slot.
Step 4![]() Change the GE_XP card mode to L2-over-DWDM. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Change the GE_XP card mode to L2-over-DWDM. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 5![]() Create and store an SVLAN database on the new GE_XP card. See G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
Create and store an SVLAN database on the new GE_XP card. See G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
Step 6![]() Enable FAPS protection on the new card.
Enable FAPS protection on the new card.
Step 7![]() Attach SVLAN to the trunk ports of the new card.
Attach SVLAN to the trunk ports of the new card.
Step 8![]() Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 22 on the master card that is facing toward the new card. This action places port 22 in the blocking state and port 21 in the forwarding state.
Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 22 on the master card that is facing toward the new card. This action places port 22 in the blocking state and port 21 in the forwarding state.
FAPS configuration mismatch alarm is raised on the master card.
Step 9![]() Switch the traffic to the protect path.
Switch the traffic to the protect path.
Step 10![]() Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card that is facing toward the new card.
Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card that is facing toward the new card.
Step 11![]() Connect the fiber from the slave card (that is facing toward the new card) to the new card in segment B.
Connect the fiber from the slave card (that is facing toward the new card) to the new card in segment B.
Step 12![]() Connect the fiber from the master card to the new card in segment A.
Connect the fiber from the master card to the new card in segment A.
Step 13![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card that is facing toward the new card.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card that is facing toward the new card.
Step 14![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the new card to bring up segment B.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the new card to bring up segment B.
Step 15![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the new card.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the new card.

Note![]() The FAPS state of the new card will be in the forwarding state for both the ports and port 21 of the slave card will be in the blocking state.
The FAPS state of the new card will be in the forwarding state for both the ports and port 21 of the slave card will be in the blocking state.
Step 16![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the master card to bring up segment A.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the master card to bring up segment A.

Note![]() The FAPS state of port 21 on the master card will be in the blocking state and port 22 will be in the forwarding state. The trunk ports of the remaining GE_XP cards will be in the forwarding state. The port 21 of the slave card (that is facing toward the new card) will change to the forwarding state.
The FAPS state of port 21 on the master card will be in the blocking state and port 22 will be in the forwarding state. The trunk ports of the remaining GE_XP cards will be in the forwarding state. The port 21 of the slave card (that is facing toward the new card) will change to the forwarding state.
Step 17![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G688 Add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP Card Between the Slave Cards on a FAPS Ring
This procedure adds a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card between the two slave cards on a FAPS ring. |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to add a GE_XP or 10GE_XP card on a FAPS ring.
Step 2![]() Verify that the GE_XP or 10GE_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Verify that the GE_XP or 10GE_XP card is installed according to the requirements specified in Table 4-7.
Step 3![]() Insert the new GE-XP card with XFP on the slot.
Insert the new GE-XP card with XFP on the slot.
Step 4![]() Change the GE_XP card mode to L2-over-DWDM. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Change the GE_XP card mode to L2-over-DWDM. See G379 Change the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Card Mode.
Step 5![]() Create and store an SVLAN database on the new GE_XP card. See G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
Create and store an SVLAN database on the new GE_XP card. See G421 Create and Store an SVLAN Database.
Step 6![]() Attach SVLAN to the trunk ports of the new card.
Attach SVLAN to the trunk ports of the new card.
Step 7![]() Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 22 on both the slave cards that are facing toward the new card.
Choose OOS,DSBLD from the Admin State column for port 22 on both the slave cards that are facing toward the new card.
Step 8![]() Connect the fiber from the slave card to the new card in segment B.
Connect the fiber from the slave card to the new card in segment B.
Step 9![]() Connect the fiber from the master card to the new card in segment A.
Connect the fiber from the master card to the new card in segment A.
Step 10![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the slave card.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the slave card.
Step 11![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the new card to bring up segment B.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 22 on the new card to bring up segment B.
Step 12![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the new card.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the new card.
Step 13![]() Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card to bring up segment A.
Choose IS from the Admin State column for port 21 on the slave card to bring up segment A.
Step 14![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G197 Provision the OTU2_XP Card Line Settings, PM Parameters, and Thresholds
This procedure changes line settings, PM parameters, and threshold setting for the OTU2_XP card. |
|
G179 Install the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, ADM-10G, and OTU2_XP Cards |
|
Step 1![]() Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Complete the G46 Log into CTC at the node where you want to change the card settings. If you are already logged in, continue with Step 2.
Step 2![]() As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
As needed, complete the G103 Back Up the Database to preserve the existing transmission settings.
Step 3![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card.
a.![]() Display the OTU2_XP card in card view.
Display the OTU2_XP card in card view.
b.![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
c.![]() Verify that the card mode is set to the mode designated by your site plan:
Verify that the card mode is set to the mode designated by your site plan:
–![]() 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy
10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy
If the card mode is set correctly, continue with Step 6. If not, complete the G452 Change the OTU2_XP Card Mode.
Step 5![]() Refer to the “OTU2_XP Card Configuration Rules” section in chapter “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual before performing any task listed
Refer to the “OTU2_XP Card Configuration Rules” section in chapter “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual before performing any task listed![]() in Step 6
in Step 6![]() .
.
Step 6![]() Perform any of the following tasks as needed.
Perform any of the following tasks as needed.

Note![]() For information about the OTU2_XP card configuration rules, refer to the “OTU2_XP Card Configuration Rules” section of the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
For information about the OTU2_XP card configuration rules, refer to the “OTU2_XP Card Configuration Rules” section of the “Transponder and Muxponder Cards” chapter in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual.
- G453 Change the OTU2_XP Card Settings
- G454 Change the OTU2_XP Line Settings
- G455 Change the OTU2_XP Line Section Trace Settings
- G456 Change the OTU2_XP Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads
- G457 Provision the OTU2_XP Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
- G462 Change the OTU2_XP Line RMON Thresholds for the 10G Ethernet and 10G FC Payloads
- G458 Change the OTU2_XP OTN Settings
- G523 Change the OTU2_XP Path Trace Settings
- G524 Provision the OTU2_XP Path Settings for 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy Configuration
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
DLP-G453 Change the OTU2_XP Card Settings
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the card settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the card settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tab.
Click the Provisioning > Card tab.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-132 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-132 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G454 Change the OTU2_XP Line Settings
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports/SONET/Ethernet tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Ports/SONET/Ethernet tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-133 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-133 .
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
User-defined. Name can be up to 32 alphanumeric/special characters. Blank by default. See the G104 Assign a Name to a Port. |
||
Sets the port service state. For more information about administrative states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
(Display only) Identifies the autonomously generated state that gives the overall condition of the port. Service states appear in the format: Primary State-Primary State Qualifier, Secondary State. For more information about service states, refer to the “Administrative and Service States” appendix in the Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual. |
|||
Sets the ALS function mode. The DWDM transmitter supports ALS according to ITU-T G.644 (06/99). ALS can be disabled, or it can be set for one of three mode options. |
|
|
|
Displays the optical reach distance of the client/trunk ports. |
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
The Reach options depend on the traffic type that has been selected. |
|
Sets the automatic in-service soak period. Double-click the time and use the up and down arrows to change settings. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] only) Sets the signal fail bit error rate. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] only) Sets the signal degrade bit error rate. |
|||
(SONET [ANSI] or SDH [ETSI] only) The optical transport type. |
Note When Type is set to SDH in a SONET (ANSI) provisioning, SDCC or LDCC on OTU2_XP cards cannot be provisioned. |
||
The maximum size of the Ethernet frames accepted by the port. The port must be in OOS/locked state. |
|||
Flow Control (Only when the card is in 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode) |
Enables/disables flow control messaging with its peer port. When enabled, the port can send and receive PAUSE frames when buffer congestion occurs. When disabled, no PAUSE frames are transmitted and the PAUSE frames received are discarded. |
||
Client Distance (Only when the card is in 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode) |
Sets the fiber distance between the client of OTU2_XP card and the LAN port that is connected to the OTU2_XP client port. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G455 Change the OTU2_XP Line Section Trace Settings
This task changes the line section trace settings for the OTU2_XP card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the section trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the section trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line > Section Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-134 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-134 .
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
If a TIM on Section overhead alarm arises because of a J0 overhead string mismatch, no alarm indication signal is sent to downstream nodes if this box is checked. This is a display-only parameter under the following conditions:
|
|||
Displays the current transmit string; sets a new transmit string. You can click the button on the right to change the display. Its title changes, based on the current display mode. Click Hex to change the display to hexadecimal (button changes to ASCII); click ASCII to change the display to ASCII (button changes to Hex). |
|||
Displays the current expected string; sets a new expected string. You can click the button on the right to change the display. Its title changes, based on the current display mode. Click Hex to change the display to hexadecimal (button changes to ASCII); click ASCII to change the display to ASCII (button changes to Hex). |
|||
(Display only) Displays the current received string. You can click Refresh to manually refresh this display, or check the Auto-refresh check box to automatically refresh the display every 5 seconds. |
|||
If checked, automatically refreshes the display every 5 seconds. |
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G456 Change the OTU2_XP Line Thresholds for SONET or SDH Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for the OTU2_XP card carrying SONET or SDH payload. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line threshold settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > SONET Thresholds (ANSI) or SDH Thresholds (ETSI) tabs.

Note![]() If you have enabled 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy on the OTU2_XP card, the STS option is automatically enabled.
If you have enabled 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy on the OTU2_XP card, the STS option is automatically enabled.
Only near end STS thresholds are supported. No STS thresholds are support for Far End.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the OTU2_XP card path threshold settings on a LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode, as seen in Table 6-135 .
Modify any of the OTU2_XP card path threshold settings on a LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode, as seen in Table 6-135 .
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Step 4![]() Modify any of the OTU2_XP Card Line Threshold settings described in Table 6-136
Modify any of the OTU2_XP Card Line Threshold settings described in Table 6-136
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Step 6![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G457 Provision the OTU2_XP Port Alarm and TCA Thresholds
This task provisions the OTU2_XP port alarm and threshold crossing alert (TCA) thresholds. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the trunk port alarm and TCA settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Optics Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, select it, then click Refresh.
Under Types, verify that the TCA radio button is checked. If not, select it, then click Refresh.
Step 4![]() Refer to Table 6-137 to provision the port TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low.
Refer to Table 6-137 to provision the port TCA thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.

Note![]() Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Do not modify the Laser Bias parameters.
Step 6![]() Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Under Types, click the Alarm radio button and click Refresh.
Step 7![]() Refer to Table 6-138 to provision the port alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low.
Refer to Table 6-138 to provision the port alarm thresholds for RX Power High, RX Power Low, TX Power High, and TX Power Low.

Note![]() You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify 15 Min and 1 Day independently. To do so, choose the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Step 9![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G462 Change the OTU2_XP Line RMON Thresholds for the 10G Ethernet and 10G FC Payloads
This task changes the line threshold settings for OTU2_XP card carrying the 10G Ethernet or 10G FC payloads. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line threshold in the card view.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the line threshold in the card view.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line Thresholds > RMON Thresholds tabs.
Step 3![]() Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Click Create. The Create Threshold dialog box appears.
Step 4![]() From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
From the Port drop-down list, choose the applicable port.
Step 5![]() From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-139 and Table 6-140 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
From the Variable drop-down list, choose an Ethernet variable. See Table 6-139 and Table 6-140 for a list of available Ethernet variables.
|
|
|
Total number of octets received on the interface, including framing characters. |
|
Total number of fiber channel frames received that are less than the minimum 36-byte frame. This is inclusive of header, SOF, EOF, and CRC with no data bytes. |
|
Total number of fiber channel frames received that exceed the maximum 2148-byte frame. This is inclusive of header, SOF, EOF, CRC, and data bytes. |
|
Total number of fiber channel frames received with CRC errors. |
|
The number of inbound packets, which were chosen to be discarded even though no errors had been detected to prevent their being delivered to a higher-layer protocol. One possible reason for discarding such a packet could be to free up buffer space.18 |
|
Total number of octets transmitted out of the interface, including framing characters.1 |
|
Number of transmitted data frames with payload CRC errors when HDLC framing is used.1 |
|
|
18.This variable is supported when the 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy mode is enabled on the OTU2_XP card. |
Step 6![]() From the Alarm Type drop-down list, choose the event triggers. The available options are rising threshold, falling threshold, or rising and falling thresholds.
From the Alarm Type drop-down list, choose the event triggers. The available options are rising threshold, falling threshold, or rising and falling thresholds.
Step 7![]() From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
From the Sample Type drop-down list, choose either Relative or Absolute. Relative restricts the threshold to use the number of occurrences in the user-set sample period. Absolute sets the threshold to use the total number of occurrences, regardless of time period.
Step 8![]() Enter an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Enter an appropriate number of seconds for the Sample Period.
Step 9![]() Enter in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
Enter in the appropriate number of occurrences for the Rising Threshold.
For a rising type of alarm, the measured value must move from below the falling threshold to above the rising threshold. For example, if a network is running below a rising threshold of 1000 collisions every 15 seconds and a problem causes 1001 collisions in 15 seconds, the excess occurrences trigger an alarm.
Step 10![]() Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
Enter the appropriate number of occurrences in the Falling Threshold field. In most cases a falling threshold is set lower than the rising threshold.
A falling threshold is the counterpart to a rising threshold. When the number of occurrences is above the rising threshold and then drops below a falling threshold, it resets the rising threshold. For example, when the network problem that caused 1001 collisions in 15 seconds subsides and creates only 799 collisions in 15 seconds, occurrences fall below a falling threshold of 800 collisions. This resets the rising threshold so that if network collisions again spike over a 1000 per 15-second period, an event again triggers when the rising threshold is crossed. An event is triggered only the first time a rising threshold is exceeded (otherwise, a single network problem might cause a rising threshold to be exceeded multiple times and cause a flood of events).

Note![]() To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
To view all RMON thresholds, click Show All RMON thresholds.
Step 12![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G458 Change the OTU2_XP OTN Settings
This task changes the OTN line settings for the OTU2_XP card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the OTN settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the OTN settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs. Then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, Trail Trace Identifier, or Proactive Protection Regen.
Click the Provisioning > OTN tabs. Then click one of the following subtabs: OTN Lines, ITU-T G.709 Thresholds, FEC Thresholds, Trail Trace Identifier, or Proactive Protection Regen.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-29 through 6-32 .
Modify any of the settings described in Tables 6-29 through 6-32 .

Note![]() You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
You must modify Near End and Far End independently, 15 Min and 1 Day independently, and SM and PM independently. To do so, select the appropriate radio button and click Refresh.
Table 6-141 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > OTN Lines tabs.
Table 6-142 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > ITU-T G.709 Thresholds tab.
Table 6-143 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > FEC Thresholds tab.
Table 6-144 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Trail Trace Identifier tab.

Note![]() You cannot change the Path Trail Trace Identifier settings when the OTU2_XP card is in the Standard Regen mode, and if the ODU transparency is set to “Transparent Standard Use”.
You cannot change the Path Trail Trace Identifier settings when the OTU2_XP card is in the Standard Regen mode, and if the ODU transparency is set to “Transparent Standard Use”.
You can change the Path Trail Trace Identifier settings when the OTU2_XP card is in the Standard Regen mode, and if the ODU transparency is set to “Cisco Extended Use”.
Table 6-145 describes the values on the Provisioning > OTN > Proactive Protection Regen tabs.

Note![]() Proactive protection regen is supported on ports of OTU2_XP only in Standard Regen and Enhanced FEC mode.
Proactive protection regen is supported on ports of OTU2_XP only in Standard Regen and Enhanced FEC mode.
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G523 Change the OTU2_XP Path Trace Settings
This task changes the path trace settings for the OTU2_XP card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the path trace settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the path trace settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Path> J1 Path Trace tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Path> J1 Path Trace tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-146 .
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-146 .
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
DLP-G524 Provision the OTU2_XP Path Settings for 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy Configuration
This task changes the path settings of the OTU2_XP card for 10G Ethernet LAN Phy to WAN Phy configuration. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the path settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the OTU2_XP card where you want to change the path settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Path > SONET/SDH tab. You can now provision the SF BER and SD BER values.
Click the Provisioning > Path > SONET/SDH tab. You can now provision the SF BER and SD BER values.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the OTU2_XP path settings described in Table 6-147 .
Modify any of the OTU2_XP path settings described in Table 6-147 .
Step 5![]() Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
Return to your originating procedure (NTP).
NTP-G162 Change the ALS Maintenance Settings
This procedure changes the ALS maintenance settings for the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, and OTU2_XP cards. |
|

Note![]() The automatic laser shutdown (ALS) function is normally disabled for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, and OTU2_XP cards. Enable ALS only when the cards are directly connected to each other.
The automatic laser shutdown (ALS) function is normally disabled for TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, and OTU2_XP cards. Enable ALS only when the cards are directly connected to each other.
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card where you want to change the ALS maintenance settings.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the TXP, MXP, GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, 10GE_XPE, or OTU2_XP card where you want to change the ALS maintenance settings.
Step 2![]() Click the Maintenance > ALS tabs.
Click the Maintenance > ALS tabs.
Step 3![]() Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-148 . The provisionable parameters are listed
Modify any of the settings described in Table 6-148 . The provisionable parameters are listed![]() in the Options column in the table.
in the Options column in the table.
Step 4![]() Click Apply. If the change affects traffic, a warning message displays. Click Yes to complete the change.
Click Apply. If the change affects traffic, a warning message displays. Click Yes to complete the change.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
This procedure forces an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L cards. |
|

Note![]() Perform Step 1 through Step 4 if you are updating the node software. Otherwise continue with Step 5 to force FPGA image upgrade on MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Perform Step 1 through Step 4 if you are updating the node software. Otherwise continue with Step 5 to force FPGA image upgrade on MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Step 1![]() Close the CTC window, if open.
Close the CTC window, if open.
Step 2![]() Delete the CTC Cache from the CTC Launcher browser window.
Delete the CTC Cache from the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 3![]() Close the CTC Launcher browser window.
Close the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 4![]() Relaunch the CTC Launcher browser window.
Relaunch the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 5![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card to be upgraded.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf mode), double-click the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card to be upgraded.
Step 6![]() For all ports being provisioned on the card, click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
For all ports being provisioned on the card, click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
a.![]() Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Disabled (ETSI).
Click the Admin State table cell and choose OOS,DSBLD (ANSI) or Locked,Disabled (ETSI).
Step 7![]() Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Card tabs.
Step 8![]() Change the Card Mode as needed:
Change the Card Mode as needed:
- FC-GE_ISC—Choose this option if you will provision any of the following PPM port rates: FC1G (Ports 1-1 through 4-1), FC2G (Ports 1-1 and 3-1 only), FICON1G (Ports 1-1 through 4-1), FICON2G (Ports 1-1 and 3-1 only), ONE_GE (Ports 1-1 through 4-1), ISC3 COMPAT (Ports 1-1 through 4-1), ISC3 PEER 1G (Ports 1-1 through 4-1), and ISC3 PEER 2G (Ports 1-1 and 3-1 only).
- FC4G—Choose this option if you will provision an FC4G or FICON4G PPM (Port 1-1 only).
Step 9![]() Click the Force FPGA Update button. This upgrades the FPGA image in the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card, as appropriate. The MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card reboots and the FPGA now contains the updated image.
Click the Force FPGA Update button. This upgrades the FPGA image in the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card, as appropriate. The MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card reboots and the FPGA now contains the updated image.
Step 10![]() For all ports being provisioned on the card, click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
For all ports being provisioned on the card, click the Provisioning > Line tabs.
a.![]() Click the Admin State table cell and choose IS (ANSI) or Unlocked (ETSI).
Click the Admin State table cell and choose IS (ANSI) or Unlocked (ETSI).
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G196 Force FPGA Update When the Card is Part of a Protection Group
This procedure forces an upgrade of the FPGA image on the MXP_MR_10DME_C and MXP_MR_10DME_L cards when the card is part of a protection group. |
|

Note![]() This procedure applies to a near-end node that has two MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L cards, one card acting as the working card and the other as the protect card. The far-end node has a similar configuration. The near-end working card trunk port is connected to the far-end working card trunk port. The near-end protect card trunk port is connected to the far-end protect card trunk port.
This procedure applies to a near-end node that has two MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L cards, one card acting as the working card and the other as the protect card. The far-end node has a similar configuration. The near-end working card trunk port is connected to the far-end working card trunk port. The near-end protect card trunk port is connected to the far-end protect card trunk port.

Note![]() Perform Step 1 through Step 4 if you are updating the node software. Otherwise, continue with Step 5 to force FPGA image upgrade on MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Perform Step 1 through Step 4 if you are updating the node software. Otherwise, continue with Step 5 to force FPGA image upgrade on MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Step 1![]() Close the CTC window, if open.
Close the CTC window, if open.
Step 2![]() Delete the CTC Cache from the CTC Launcher browser window.
Delete the CTC Cache from the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 3![]() Close the CTC Launcher browser window.
Close the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 4![]() Relaunch the CTC Launcher browser window.
Relaunch the CTC Launcher browser window.
Step 5![]() Ensure traffic is running on the near-end and far-end working cards for each protection group on the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Ensure traffic is running on the near-end and far-end working cards for each protection group on the MXP_MR_10DME_C or MXP_MR_10DME_L card.
Step 6![]() In node view (single-node mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tab.
In node view (single-node mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Protection tab.
Step 7![]() For each protection group, verify that the working card client port is reported as working/active and the protect card client port is reported as protect/standby.
For each protection group, verify that the working card client port is reported as working/active and the protect card client port is reported as protect/standby.
Step 8![]() Repeat Steps 6 and 7 for the far-end node.
Repeat Steps 6 and 7 for the far-end node.
Step 9![]() For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G182 Apply a Lockout to prevent traffic from switching to the protect card.
For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G182 Apply a Lockout to prevent traffic from switching to the protect card.
Step 10![]() At the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G192 Force FPGA Update to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the protect card.
At the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G192 Force FPGA Update to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the protect card.
Step 11![]() For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G183 Clear a Lock-On or Lockout to remove a lockout and return a protection group to its usual switching method.
For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G183 Clear a Lock-On or Lockout to remove a lockout and return a protection group to its usual switching method.
Step 12![]() For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete theG179 Apply a Force Y-Cable or Splitter Protection Switch to move traffic from the working to the protect card.
For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete theG179 Apply a Force Y-Cable or Splitter Protection Switch to move traffic from the working to the protect card.
Step 13![]() At the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G192 Force FPGA Update to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the working card.
At the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G192 Force FPGA Update to force an upgrade of the FPGA image on the working card.
Step 14![]() For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G180 Clear a Manual or Force Y-Cable or Splitter Protection Switch to clear a Force protection switch on the working card. If the protection group is revertive, this operation causes the traffic to revert to the working card. If the protection group is non-revertive, this operation causes the traffic to remain on the protect card.
For each protection group on the near-end and far-end nodes, complete the G180 Clear a Manual or Force Y-Cable or Splitter Protection Switch to clear a Force protection switch on the working card. If the protection group is revertive, this operation causes the traffic to revert to the working card. If the protection group is non-revertive, this operation causes the traffic to remain on the protect card.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G232 Enabling Error Decorrelator
This task enables error decorrelator on a TXP_MR_10EX_C, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card. |
|
Step 1![]() In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10EX_C, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to enable error decorrelator.
In node view (single-shelf mode) or shelf view (multishelf view), double-click the TXP_MR_10EX_C, MXP_2.5G_10EX_C, or MXP_MR_10DMEX_C card where you want to enable error decorrelator.
Step 2![]() Click the Provisioning > Line> Error Decorrelator Settings tabs.
Click the Provisioning > Line> Error Decorrelator Settings tabs.
Step 3![]() In the Error Decorrelator Settings area, Select Enable.
In the Error Decorrelator Settings area, Select Enable.

Note![]() To inter-operate with other cards, disable the error decorrelator.
To inter-operate with other cards, disable the error decorrelator.
Click the Provisioning > Line> Error Decorrelator Settings tabs and then select Disable.
NTP-G315 Enable or Disable the Wavelength Drifted Channel Automatic Shutdown Feature
This procedure allows you to enable or disable the wavelength drifted channel automatic shutdown feature for 40-SMR1-C, 40-SMR2-C, 80-WXC-C, 40-WXC-C, and 40-WSS-C cards. |
|
Step 1![]() In the node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Defaults tabs. The Node Defaults page opens.
In the node view (single-shelf mode) or multishelf view (multishelf mode), click the Provisioning > Defaults tabs. The Node Defaults page opens.
Step 2![]() Select the card from the Defaults Selector pane where you want to enable or disable the wavelength drifted channel automatic shutdown feature.
Select the card from the Defaults Selector pane where you want to enable or disable the wavelength drifted channel automatic shutdown feature.
Step 3![]() Select the <card name>.config.card.WavelengthDrift from the Default Name column. Choose Disable or Enable from the Default Value drop-down list for the selected card.
Select the <card name>.config.card.WavelengthDrift from the Default Name column. Choose Disable or Enable from the Default Value drop-down list for the selected card.
For example, if you select 40-SMR2-C card from the Defaults Selector folder, the Default Name column reads “40-SMR2-C.config.card.WavelengthDrift”.
Step 4![]() Click Apply to save changes.
Click Apply to save changes.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
NTP-G316 Enable REP and FAPS on the same port
This task allows you enable REP and FAPS on the same port for the GE_XP and 10GE_XP cards. |
|

Note![]() The FAPS master node on the edge ring should never be the node that has a common FAPS and REP port.
The FAPS master node on the edge ring should never be the node that has a common FAPS and REP port.
You can configure REP and FAPS on port 22 and 21 for GE_XP cards, and port 4 and 3 for 10GE_XP cards.
Step 1![]() To enable REP, complete the following procedures:
To enable REP, complete the following procedures:
a.![]() G645 Create a Segment Using CTC
G645 Create a Segment Using CTC
b.![]() G647 Activate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
G647 Activate VLAN Load Balancing Using CTC
Step 2![]() To enable FAPS, complete the G381 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 Protection Settings.
To enable FAPS, complete the G381 Provision the GE_XP, 10GE_XP, GE_XPE, and 10GE_XPE Layer 2 Protection Settings.
Stop. You have completed this procedure.
 Feedback
Feedback