Introduction to Service meshes and Istio
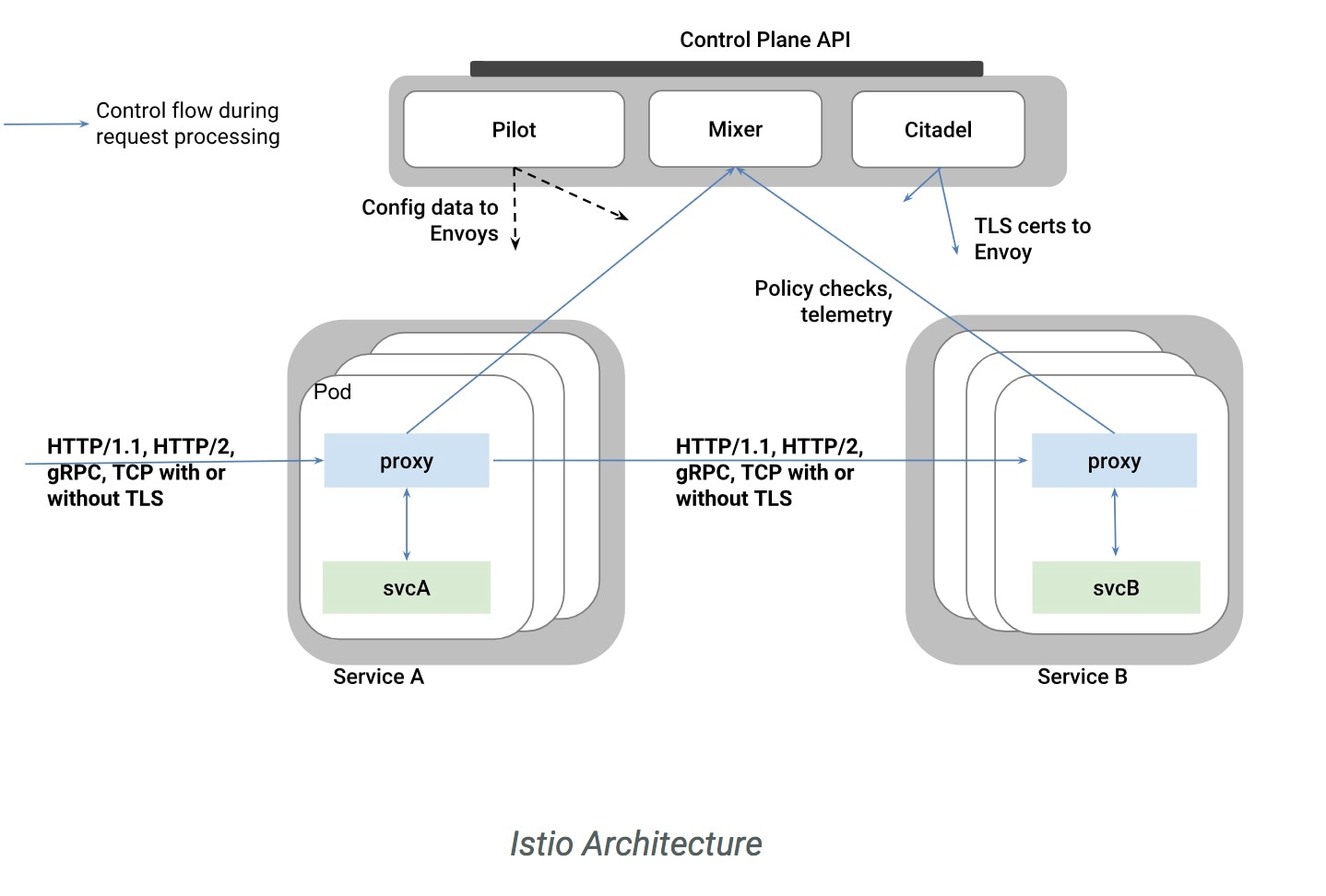
Cisco Container Platform includes support for Istio service meshes. An Istio service mesh is logically split into a data plane and a control plane. The data plane is composed of a set of intelligent proxies (Envoy) and the control plane provides a reliable Istio framework. The term Istio is sometimes also used as a synonym to refer to the entire service mesh stack that includes the Control Plane and the Data Plane components (although strictly istio is the control plane and a proxy like envoy is the data plane).
The Service mesh technology allows you to construct North-South and East-West L4 and L7 application traffic meshes. It provides containerized applications a language-independent framework that removes several common tasks related to L4 and L7 application networking from the actual application code while enhancing operational capabilities including monitoring, security, load balancing and troubleshooting for these applications. These tasks include L4 and L7 service routing and load balancing, support for polyglot environments in a language-independent manner and advanced telemetry. You can deploy a service mesh in a multi-cloud topology allowing these functions to operate with applications that run across multiple separate cloud deployments.
The following figure shows a high-level architecture summary of an Istio based service mesh architecture. In Cisco Container Platform, the components of Istio and Envoy are supported in the upstream Istio community. The Control and Data Plane components of the solution, including Pilot, Mixer, Citadel and the data plane Envoy proxy for both North-South and East-West load balancing, are supported on Cisco Container Platform.
For more information on these technologies, refer to the upstream community documentation pages for istio and envoy.
 Note |
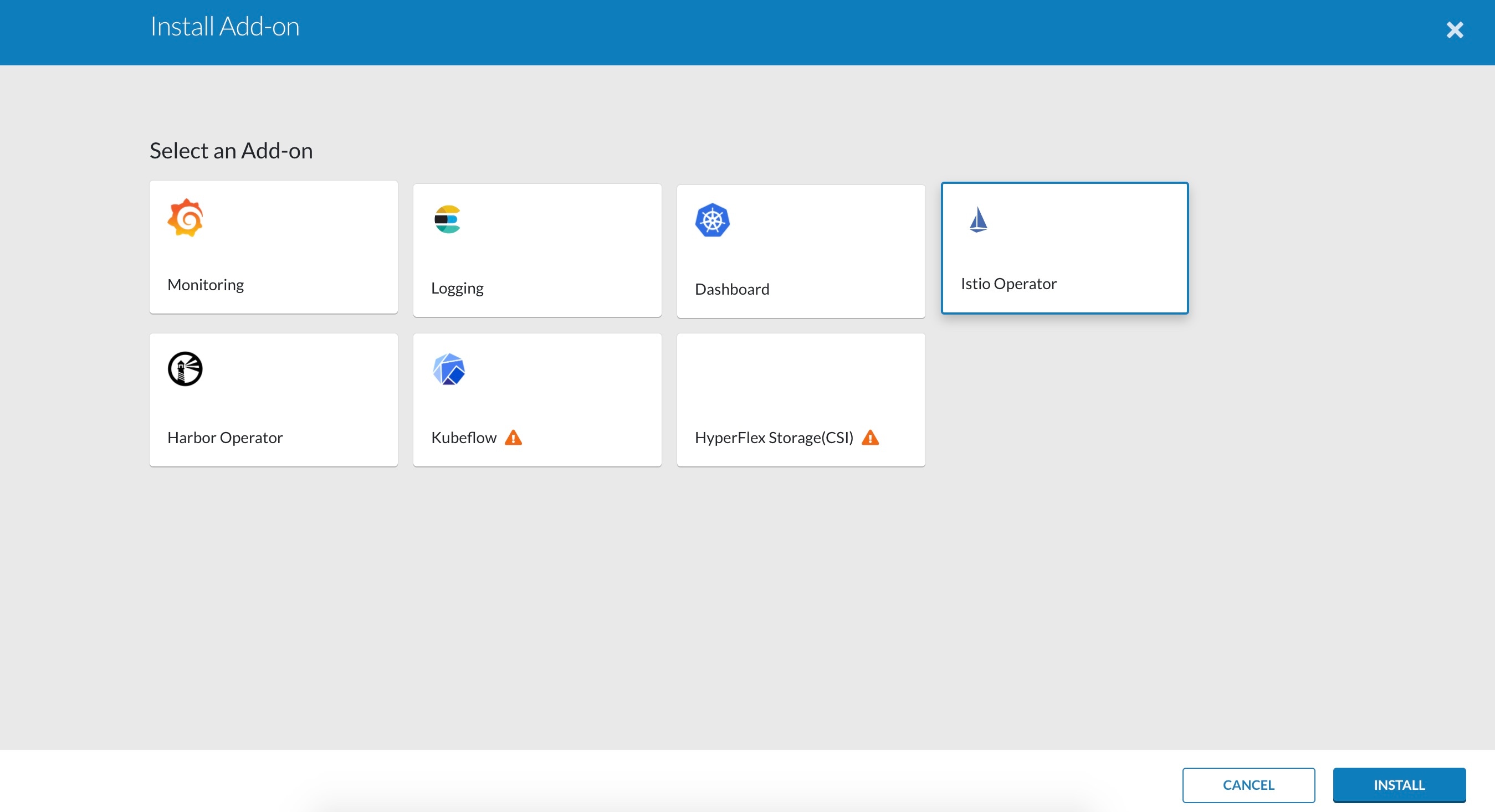
Currently, this feature is marked as a Technology Preview feature and uses the Istio community version v0.8.0. You need to contact your service representative for support details for the version of Cisco Container Platform that you happen to be running. |
 Feedback
Feedback