Recording of Packet Flows in NetFlow
The packet in NetFlow is recorded as follows:
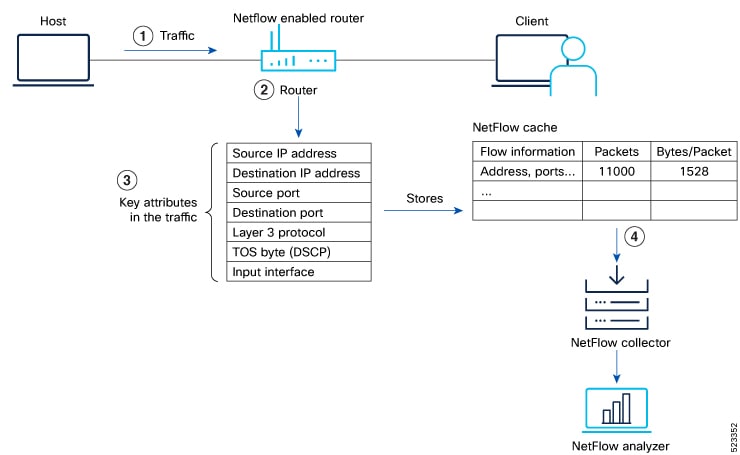
In NetFlow, the focus is on recording and collecting full packet flows in the network traffic data. When NetFlow is configured on the router, the router collects flow data by extracting key field attributes from the packet streams, and generates a flow record. This record, along with accounting information, is stored in the database or NetFlow Cache. The extracted records, once sampled, are exported to one or more NetFlow collectors via the UDP transport layer protocol. This exported data has several purpose: enterprise accounting and ISP billing, and so on.
Here's how NetFlow handles the recording of packet flows:
-
Flow Creation: NetFlow creates flow records by monitoring network traffic passing through the router. As a packet stream traverses a router interface, the packets are collected and an internal header is appended. These packets are dispatched to the line card's CPU, which generate a flow record. The router extracts pertinent header details from the packets and creates cache entries. The packets are subject to a policer, which helps protect the internal control plane. With each subsequent arrival of a packet from the same flow, the cache entry is updated. Flow records persist within the line card's cache until they age out due to timer expiration.
When the expiry of the set timer occurs, the NetFlow is generated. There are timers (two of them) running for flow aging.
-
The active timer signifies the maximum allowable duration for a particular cache entry's existence, even if matched by received sampled packets.
-
The inactive timer represents the duration without receipt of a sampled packet corresponding to a specific cache entry.
-
-
Datagram Generation: The NetFlow agent generates NetFlow datagrams that contain information about the packets. These datagrams include details such as source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, protocol information, and various flow statistics.
-
Data Export: The NetFlow datagrams are periodically exported from the NetFlow agent to a designated NetFlow collector or analyzer. The export can be done using protocols like UDP or TCP, and the datagrams are typically sent in a structured format like IPFIX or JSON.
A flow record is sent to the NetFlow collector in the following scenarios:
-
The flow has been inactive or active for an extended period.
-
The user triggers the export of the flow.
-
The flow concludes, which is particularly relevant when TCP connections are terminated.
-
-
Analysis and Reporting: Upon receiving the NetFlow data, the NetFlow collector or analyzer processes and analyzes the information. It aggregates the sampled data to provide statistical insights into network traffic, including top talkers, protocol distribution, traffic patterns, and other metrics.


 Feedback
Feedback