Seamless Migration of VPLS Network to EVPN Network
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Feature Description |
|
Seamless Migration of VPLS Network to EVPN Network |
Release 7.11.1 |
You can now provision EVPN service on existing VPLS-enabled PEs individually, thus ensuring a seamless VPLS-to-EVPN migration without traffic disruption. This feature is supported only on Q200-based line cards. |
Although VPLS is a widely deployed Layer 2 VPN technology, customers prefer to migrate their VPLS network to EVPN to leverage the scaling benefits and ease of deployment. Recognizing the significance of preserving investments in VPLS, certain service providers seek ways to seamlessly connect their existing VPLS networks with the new networks running EVPN.
You can now migrate the PE nodes from legacy VPLS to EVPN gradually and incrementally without any service disruption.
Instead of performing a network-wide software upgrade at the same time on all PEs, this feature provides the flexibility to migrate one PE at a time. Thus allows the coexistence of legacy VPLS and EVPN-VPLS dual-stack in the core for a given L2 attachment circuit (AC) over the same MPLS network.
In the EVPN network, VPN instances are grouped by EVPN instance ID (EVI-ID). Similar to other L2VPN technologies, EVPN instances are also associated with route-targets and route-distinguisher. EVPN uses a control plane for learning and propagating MAC unlike traditional VPLS, where MAC is learned in the data plane using flood and learn technique. In EVPN, MAC routes are carried by the MP-BGP protocol. In EVPN enabled PEs, PEs import the MAC route along with the label to their respective EVPN forwarding table only if their route targets (RTs) match. An EVPN PE router is capable of performing VPLS and EVPN L2 bridging in the same VPN instance. When both EVPN and BGP-AD PW are configured in a VPN instance, the EVPN PEs advertise the BGP VPLS autodiscovery (AD) route and the BGP EVPN Inclusive Multicast route (type-3) for a given VPN Instance. Route type-3 referred to as ingress replication multicast route, is used to send broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic. Other remote PEs import type-3 routes for the same VPN instance only if the sending PE RTs match with their configured RT. Thus, at the end of these route-exchanges, EVPN capable PEs discover all other PEs in the VPN instance and their associated capabilities. The type-3 routes used by PE to send its BUM traffic to other PEs ensure that PEs with the same RTs receive the BUM traffic. EVPN advertises the customer MAC address using type-2 route.
Seamless migration allows you to upgrade the VPLS PE routers to EVPN one by one without any network service disruption. Consider the following topology where PE1, PE2, PE3, and PE4 are interconnected in a full-meshed network using VPLS PW.
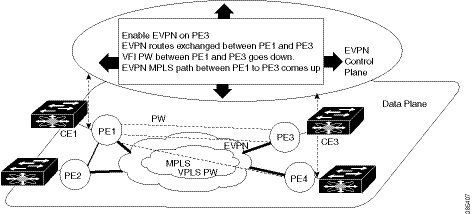
You can introduce the EVPN service to all the selected VPLS provider edge (PE) nodes simultaneously. However, to avoid traffic disruption, provision EVPN service on existing VPLS-enabled PEs one by one.
-
To migrate from VPLS to EVPN, enable EVPN in a VPN instance of VPLS service on PE1, which starts advertising the EVPN inclusive multicast route to other PE nodes.
Since no inclusive multicast routes are received from other PE nodes, VPLS pseudowires between PE1 and other PE nodes remain active.
-
PE1 forwards traffic using VPLS pseudowires and advertises all MAC addresses learned from CE1 using EVPN route type-2.
-
Next, enable EVPN on PE3, and it starts advertising an inclusive multicast route to other PE nodes.
-
PE1 and PE3 discover each other through EVPN routes and shut down pseudowires between them.
EVPN service replaces VPLS service between PE1 and PE3.
-
PE1 keeps running VPLS service with PE2 and PE4 and starts EVPN service with PE3 in the same VPN instance called EVPN seamless integration with VPLS.
-
Migrate the remaining PE nodes until all four PE nodes are enabled with the EVPN service.
-
Eventually, the VPLS service is completely replaced with the EVPN service in the network, and all VPLS pseudowires are shut down.
 Feedback
Feedback