- Cisco TrustSec SGT Exchange Protocol IPv4
- TrustSec SGT Handling: L2 SGT Imposition and Forwarding
- Cisco TrustSec with SXPv4
- Enabling Bidirectional SXP Support
- Cisco TrustSec Interface-to-SGT Mapping
- Cisco TrustSec Subnet to SGT Mapping
- Flexible NetFlow Export of Cisco TrustSec Fields
- Cisco TrustSec SGT Caching
- CTS SGACL Support
- Accessing TrustSec Operational Data Externally
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Information About Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- How to Configure Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Translation Tables Refresh
Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
The ACI TrustSec Integration provides a solution interconnecting the administrative domains of Cisco TrustSec and Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) to provide a consistent end-to-end policy segmentation.
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Information About Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- How to Configure Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Additional References for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- Feature Information for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
Restrictions for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
- There is no high availability support for the SG-EPG (Security Group-End Point Group) control plane and data-plane tables.
-
This feature is applicable for a single ACI tenant with multiple VRFs.
-
While High Availability (HA) cannot be configured on an Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router, an HA network can be designed by introducing a second Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router, where normal routing will provide the redundant path.
-
VRF names with hyphens are not supported.
Information About Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
How Cisco TrustSec and ACI Works?
Cisco TrustSec is a system that provides security for Cisco TrustSec-enabled network devices at each routing hop. In this system, each network device works to authenticate and authorize its neighbor devices, and then apply some level of security (group tagging, role-based access control lists (ACLs), encryption, and so on) to traffic between the devices. The Cisco TrustSec-enabled device acts as a border router. Cisco Identity Service Engine (ISE) is the designated domain manager for the Cisco TrustSec device. Cisco ISE is the primary source of group namespace and role-based policy information for Cisco TrustSec devices. Cisco ISE authenticates and authorizes end points into Security Groups (SGs).
Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) automates IT tasks and accelerates data center application deployments. It accomplishes this using a business-relevant software defined networking (SDN) policy model across networks, servers, storage, security, and services.
Cisco TrustSec and Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) networks are similar in semantics of group-based policy framework. Users and resources in both networks are categorized into groups and access is provided across groups. However, Cisco TrustSec and ACI differ in syntax and representation of group identity, and its propagation across the network. For instance, Cisco TrustSec networks use security group tagging, while ACI networks use end-point group (EPG).
Earlier to release Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1 and Cisco ISE 2.2, the interaction between TrustSec and ACI was limited to:
-
The creation and exchange of Security Groups from the TrustSec Domain into the ACI Domain.
-
The creation and exchange of Endpoint Groups (EPGs) from the ACI Domain into the TrustSec Domain.
In this system, Cisco ISE 2.1 exchanged information with API through REST calls to the Application Policy Infrastructure Controller-Data Center (APIC-DC) API.
Effective with Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1 and Cisco ISE 2.2, the mapping of security group tag with an ACI VNID that is used to represent an EPG is done dynamically. The same is true for traffic sourced from the ACI domain, wherein the VNID is translated into SGT for enforcement in the TrustSec domain. Hence, the TrustSec and ACI integration feature leverages the initial group information exchange to provide a data plane integration, where traffic source from either domain is dynamically translated into the destination domain's policy group structure - that is, source security group tag (SGT) is translated to ACI EPG and vice versa. This exchange allowed these new Security Groups or Endpoint Groups to be used in policies within the respective domains.
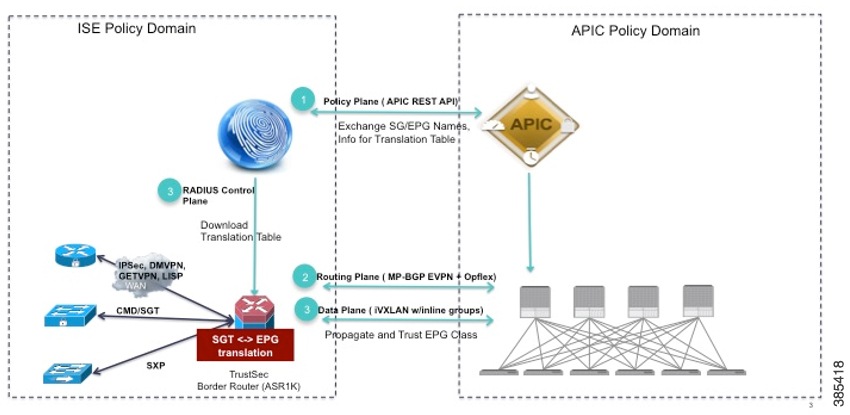
Cisco ISE interfaces with ACI Controller, which is also called APIC-DC, to learn EPG names, share SG names and corresponding EPG value, SGT value and VRF Name. This allows Cisco ISE to create and populate SG-EPG translation tables, which are obtained by the border device to translate TrustSec-ACI identifiers as traffic passes across the domains.
Cisco TrustSec device communicates with Cisco ISE through a RADIUS server using PAC Provisioning and Environment Data download. Refer to the sections titled "Protected Access Credential (PAC)" and "PAC Provisioning" in this chapter for more information about PAC.
For more information on TrustSec–ACI Policy Plane Integration, refer TrustSec – ACI Policy Plane Integration
Cisco TrustSec-ACI Workflow
TrustSec and ACI domain intersect at the control plane and data plane levels. With Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1, the earlier policy plane integration (available in ISE 2.1) has been further extended and enhanced to include the data plane integration and ISE 2.2.
The ACI TrustSec Integration feature enables interaction between Cisco TrustSec and ACI in the following ways:
- Enable SG-EPG Translations-Enables control plane interactions by acquiring the operational data from the authentication server that maps security groups to endpoint groups and vice versa.Use the cts sg-epg translation command to do this.
- Enable EPG Propagation-Enables the data plane interactions to propagate the translated SG to EPG information from Cisco TrustSec to ACI domain and vice versa. Use the group-based policy command on ACI device to translate the SG to EPG.
A high-level workflow of the interaction is as follows:
- When the cts
sg-epg
translation command is configured, Cisco TrustSec device sends an announcement to ISE about its intent of functioning as a border router to ISE through the sg-epg-translation string in the RADIUS Cisco AV pair cts-device-capability. sg-epg-translation is a new string added to the Cisco AV pair. The RADIUS Cisco AV pair is included in each Environment Data Download RADIUS request to ISE.

Note
If the environment data is downloaded and the command is configured later, an environment data refresh is triggered. - ISE responds with the table names to Cisco TrustSec device.
- Cisco TrustSec device sends a request to download the translation tables.

Note
The translation tables are not pushed to the data-path unless the SG-EPG translation is enabled on an interface. - If SG-EPG translation is enabled on an interface, Cisco TrustSec control plane receives a notification pushing the tables to datapath.
- The control plane sends a notification to the data-path notifying that the tables are being pushed to data-plane for programming.
- The data-path initializes and sends an acknowledgment to the control plane to program the tables.
- If the data-path responds with an affirmative acknowledgment, the control plane pushes the translation tables to data-path. If a negative acknowledgment is received, the control plane updates the local state that programming in data-path has failed.
In addition to the above workflow, the following steps may be required:
- When SG-EPG translation is disabled on an interface in which the SG-EPG translation was configured earlier, the control plane notifies the data-path to delete the tables. However, the table will be retained in the control plane as long as the global command cts sg-epg translation is configured.
- In case SG-EPG translation is enabled on an interface but the global command is not configured, the table is not downloaded from ISE. When the global command is configured, the control plane verifies that the command is enabled on one interface and the datapath is programmed accordingly.
Cisco TrustSec and ACI Interaction Scenarios
This section explains the interactions between the Cisco TrustSec device and ISE in different scenarios.
The following table explains the interactions between the Cisco TrustSec device and ISE on the control plane, based on the configuration status of the cts sg-epg translation command, when ISE is connected to an Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) device.
|
cts sg-epg translation Command |
ACI Settings Checkbox is Selected on ISE |
ACI Settings Checkbox is not Selected on ISE |
|---|---|---|
|
Command is not configured |
ISE does not include SG-EPG tables in Environment Data download as the device does not advertise SG-EPG translation capability. ISE downloads SG-Name table, which is a combination of group names defined on ISE and group names in APIC. |
No SG-EPG tables in Environment Data download. SG-Name table includes groups defined in ISE. |
|
Command is configured on the device |
sg-epg-translation is specified in the cts-device-capability attribute of the Environment Data download request to ISE from the Cisco TrustSec device configured for SG-EPG translation. A value of 1 is sent in the Environment Data download for sg-epg-translation-return-code, indicating that the checkbox is selected. ISE includes SG-EPG tables in Environment Data download because the device advertised the SG-EPG translation capability in the download request. ISE downloads SG-Name table, which is a combination of group names defined on ISE and group names in APIC. |
A value of 0 is sent in the Environment Data download for sg-epg-translation-return-code, indicating that the checkbox is not selected. ISE does not include any SG-EPG tables in Environment Data download. SG-Name table specifies groups defined in ISE. |
|
Command is configured on the device but there is no SG-EPG table on the ISE |
This could be due to an error on ISE, such as, ACI connectivity failure, incorrect APIC URL or security credentials. Although the ACI Settings checkbox is enabled, ISE fails to obtain EPG or VRF names from APIC because of an internal error. So, there is no SG-EPG translation table available to download. A value of 1 is sent in the Environment Data download for sg-epg-translation-return-code, indicating that the checkbox is selected. |
— |
|
No form of the command is configured |
Device purges SG-EPG translation tables from its control plane and data plane. Subsequent Environment Data Download refresh does not advertise SG-EPG translation capability on the device. |
No change in the behavior of the device. |
The following table explains the interactions between the Cisco TrustSec device and ISE on the control plane, based on configuration status of the cts sg-epg translation command, when ISE is not connected to an APIC device.
|
cts sg-epg translation Command |
ACI Settings is not enabled on ISE |
|---|---|
|
Command is not configured |
No SG-EPG tables in Environment Data download. SG-Name table includes groups defined in ISE. |
|
Command is configured on the device |
sg-epg-translation is specified in the cts-device-capability attribute of the Environment Data download request to ISE from the Cisco TrustSec device configured for SG-EPG translation. Environment Data Download from ISE does not contain the cts:sg-epg-translation-return-code attribute indicating that ISE does not support the ACI TrustSec integration functionality. Normal TrustSec Environment Data download behavior. SG-Name table specifies groups defined in ISE. Environment Data Download is refreshed to include sg-epg-translation to upgrade ISE to an ACI-aware version. |
|
No form of the command is configured |
SG-EPG translation feature is turned off on the device. Subsequent Environment Data Download refresh requests does not advertise SG-EPG translation capability on the router. |
Protected Access Credential (PAC)
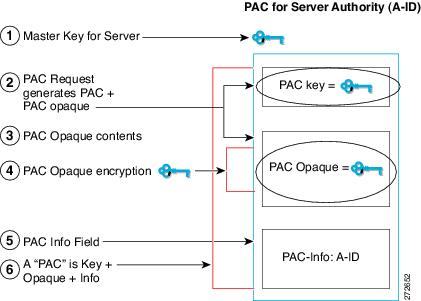
The PAC is a unique shared credential used to mutually authenticate client and server. It is associated with a specific client username and a server authority identifier (A-ID). A PAC removes the need for Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and digital certificates.
Creating a PAC consists of the following steps:
Server A-ID maintains a local key (master key) that is only known by the server.
When a client, which is referred to in this context as an initiator identity (I-ID), requests a PAC from the server, the server generates a randomly unique PAC key and PAC-Opaque field for this client.
The PAC-Opaque field contains the randomly generated PAC key along with other information such as an I-ID and key lifetime.
PAC Key, I-ID, and Lifetime in the PAC-Opaque field are encrypted with the master key.
A PAC-Info field that contains the A-ID is created.
The PAC is distributed or imported to the client automatically.
 Note | The server does not maintain the PAC or the PAC key, enabling the EAP-FAST server to be stateless. |
The figure below describes the PAC's construction. A PAC consists of the PAC-Opaque, PAC Key, and PAC-Info fields. The PAC-Info field contains the A-ID.
PAC Provisioning
In Secure RADIUS, the PAC key is provisioned into each device during authentication to derive the shared secret. Since the RADIUS ACS does not store the PAC key for each device, the clients must also send an additional RADIUS attribute containing the PAC-Opaque field, which is a variable length field that can only be interpreted by the server to recover the required information and validate the peer’s identity and authentication. For example, the PAC-Opaque field may include the PAC key and the PAC’s peer identity.
The PAC-Opaque field format and contents are specific to the PAC server on which it is issued. The RADIUS server obtains the PAC Key from the PAC-Opaque field and derives the shared secret the same way clients do. Secure RADIUS only modifies the way shared secret is derived and not its usage.
EAP-FAST Phase 0 is used to automatically provision a client with a PAC.
Deploying Devices in High Availability Setup
Perform the following steps when deploying devices in an HA setup:
Clear the credentials from all the devices which are part of the HA setup.
Boot the stack setup and establish the device roles (active, standby, and members).
Configure the credentials on the active device. Use the cts credentials id id password password command to configure the credentials.
 Note | While adding a new device to an existing stack, ensure that you clear the credentials on the fresh device and then add it to the existing stack setup. |
How to Configure Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
-
ISE configuration: The Identity Services Engine needs to be configured to interconnect with ACI and generate the SG-EPG mapping tables.
-
TrustSec device configuration: This step involves the configuration of the control plane and the data-path.
-
Control plane configuration: The control plane needs to be configured to connect to the ISE and download the SG-EPG translation tables.
-
Data-path or data plane configuration: The data-path connects to the servers in the APIC policy domain by performing the translations using the SG-EPG mapping tables. Configure the data-path to download the tables from the control plane and enable programming of these tables.
-
Once the above configuration is done, the TrustSec ACI interaction can be verified using a list of show commands.
Configuring ISE
Interconnection between Identity Service Engine (ISE) and ACI is required to exchange SG and EPG mappings and policy elements. To enable this interconnection, the TrustSec-ACI Policy Element Exchange option must be enabled in the Settings tab (Work Centers >> TrustSec >> Settings) in ISE. If this option is not enabled, communication between ISE and ACI will not be possible.
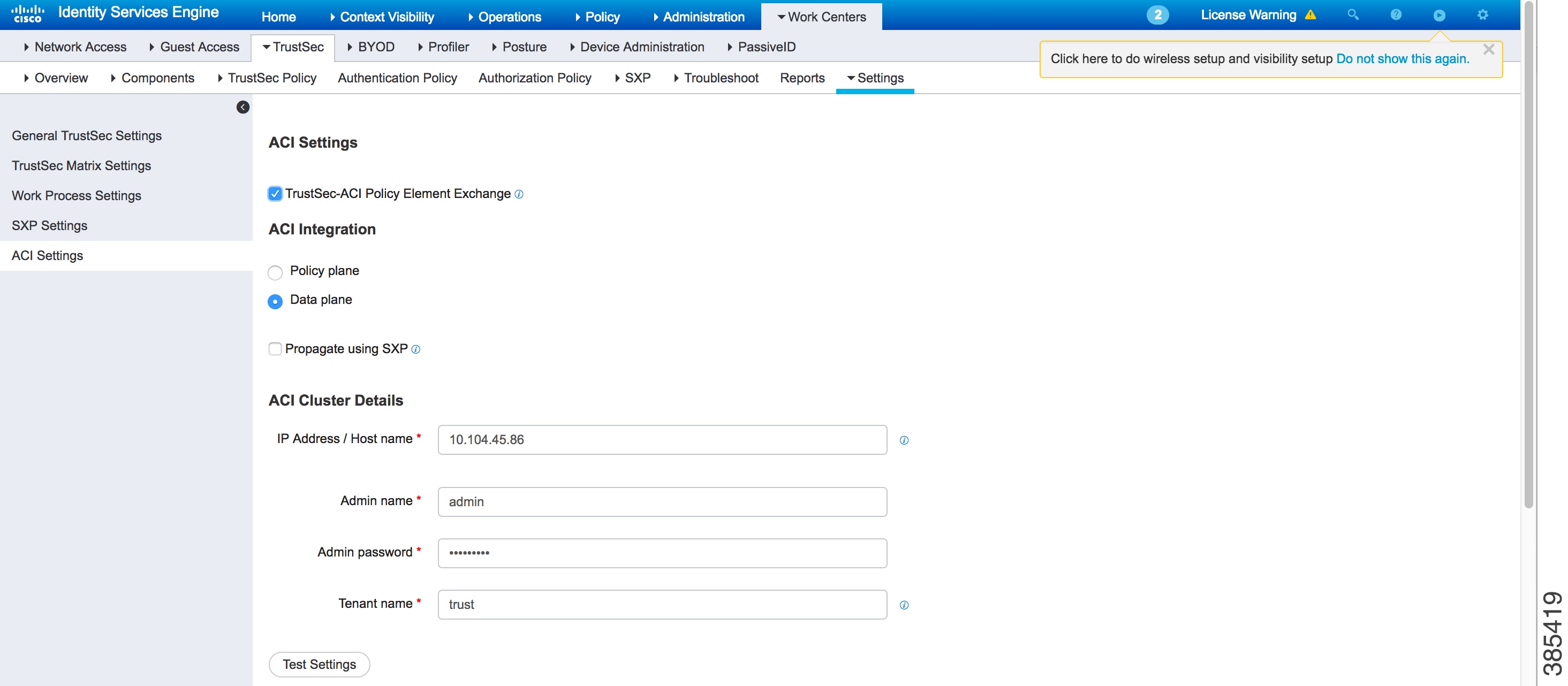
For more information, click the following link:
Configuring the TrustSec Device
To configure a TrustSec device, first configure the control plane and then configure the data-path.
- Configuring the Control Plane
- Configuring the Data Plane or Data-Path
- Verifying Cisco TrustSec ACI Interaction
Configuring the Control Plane
Device> enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# cts sg-epg translation
Configuring the Data Plane or Data-Path
For the control plane to connect to the data-path and send the SG-EPG mapping table, configure the data-path. The command group-based policy is used to perform this configuration.
 Note | Any communication between the data-path and the data center in the APIC Policy Domain, happens through the NVE interface. Hence, use the group-based policy command from the NVE interface. |
Device# enable Device# configure terminal Device(config)# vrf definition evpn2 Device(config-vrf)# exit Device(config)# interface nve3 Device(config-if)# no ip address Device(config-if)# source-interface Loopback3 Device(config-if)# host-reachability protocol bgp Device(config-if)# group-based policy Device(config-if)# member vni 10000 vrf evpn2 Device(config-if)# no mop enabled Device(config-if)# no mop sysid Device(config-if)# end
Verifying Cisco TrustSec ACI Interaction
show cts sg-epg translations Command
Use the show cts sg-epg translations command to list the entries in the control plane.
Device# show cts sg-epg translations Total Entries: 7 Last update time: 13:10:12 IST Thu Aug 14 2016 Next refresh time: 14:10:12 IST Thu Aug 14 2016 * Represents truncated names Status Codes: A – Active -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Security-Group Endpoint-Group VRF Status -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2:TrustSec_Device 16397 WAN-Blue (2) A 4:Network_Services 49160 Management-VRF-nam* (100) A 14:PCI_Servers 32784 Management-VRF-nam* (100) A 15:BYOD 32780 Management-VRF-nam* (100) A 255:Quarantined_System* 49163 WAN-Blue (2) A 10001:store_webEPG 49154 WAN-Blue (2) A 10002:store_dbEPG 32771 WAN-Blue (2) A
The command lists the mappings with key fields:
- Number of entries in the table
- Last Update Time and Next Update Time
- Security/Endpoint Group Name and Number
- VRF with both Name and Number
- Status Code
The explanation for the Status column is as follows:
- A—Active, indicates the translation entry is downloaded in the control plane, active and functional in the data plane. The security group to endpoint groups translations (and vice versa) are functional only for entries in A state.
show cts sg-epg translations default-epg Command
Use the show cts sg-epg translations default-epg command to find an endpoint groups value for a given VRF when the corresponding endpoint groups value is not present in the primary SG-EPG translation table.
Device# show cts sg-epg translations default-epg Total Entries : 2 Last update time: 13:10:12 IST Thu Aug 14 2016 Next refresh time: 14:10:12 IST Thu Aug 14 2016 * Represents truncated names Status Codes: A – Active -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Default EPG VRF Status -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16391 corp (2) A 32772 default (65535) A
show cts-sg-epg translations default-sg Command
Use the show cts-sg-epg translations default-sg command to translate an endpoint groups value to SGT, when the corresponding endpoint groups value is not present in the primary SG-EPG translation table.
Device# show cts sg-epg translations default-sg
Total Entries: 1
Last update time: 13:10:12 IST Thu Aug 04 2016
Next refresh time: 14:10:12 IST Thu Aug 04 2016
* Represents truncated names
A – Active
Default SGT: 22 | Status: A
show platform hardware qfp active feature cts datapath commands
Use the show platform hardware qfp active feature cts datapath commands to show the entries in the data-path.
Device# show platform hardware qfp active feature cts datapath sg-epg-stats
Total number of SGT to EPG Mappings = 6
Total number of failed SGT to EPG translations = 0
==============================================================================
VRF-ID SGT Value EPG Value Translation Time since last
count translation
(sec)
==============================================================================
2 7 16391 0 -
2 10018 49169 0 -
2 10011 49167 0 -
3 255 49157 0 -
2 10004 16416 0 -
Device#show platform hardware qfp active feature cts datapath sg-epg-stats
Total number of SGT to EPG Mappings = 6
Total number of failed SGT to EPG translations = 0
==============================================================================
VRF-ID SGT Value EPG Value Translation Time since last
count translation
(sec)
==============================================================================
2 7 16391 0 -
2 10018 49169 0 -
2 10011 49167 0 -
3 255 49157 0 -
2 10004 16416 0 -
Translation Tables Refresh
Translation tables are refreshed along the following scenarios:
-
The download of SG-EPG tables is tied to Environment Data download. So, the Environment Data refresh timer triggers the refresh of SG-EPG tables too.
-
A force refresh of the SG-EPG tables can be done by issuing the Environment Data refresh command cts refresh environment-data.
-
A CoA (Change of Authorization) from ISE can also be issued if there are updates to the tables on ISE.
Additional References for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Security commands |
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference: Commands A to C Cisco IOS Security Command Reference: Commands D to L |
|
Cisco TrustSec Policies Configuration |
|
|
TrustSec–ACI Policy Plane Integration |
|
|
BGP-EVPN or VxLAN configuration |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Cisco TrustSec and ACI Integration
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
ACI TrustSec Integration |
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.5.1. |
The ACI TrustSec Integration feature provides a solution interconnecting the administrative domains of Cisco TrustSec and Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) to provide a consistent end-to-end policy enforcement experience. The following commands were introduced or modified: cts refresh environment-data, cts sg-epg translation, show cts sg-epg translations, show cts sg-epg translations default-epg, show cts-sg-epg translations default-sg. |
 Feedback
Feedback