- Signalling Overview
- Configuring RSVP
- Control Plane DSCP Support for RSVP
- Configuring RSVP Support for Frame Relay
- RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- RSVP Message Authentication
- RSVP Fast Local Repair
- RSVP Interface-Based Receiver Proxy
- RSVP Aggregation
- MPLS TE-Tunnel-Based Admission Control
- Configuring Subnetwork Bandwidth Manager
- RSVP over UDP
- Index
Contents
- RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- Feature Information for
- Feature Overview
- Benefits
- Restrictions
- Supported Platforms
- Prerequisites
- Configuration Tasks
- Enabling RSVP on an Interface
- Setting the Resource Provider
- Disabling Data Packet Classification
- Configuring Class and Policy Maps
- Attaching a Policy Map to an Interface
- Verifying RSVP Scalability Enhancements Configuration
- Monitoring and Maintaining RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- Configuration Examples
- Example Configuring CBWFQ to Accommodate Reserved Traffic
- Example Configuring the Resource Provider as None with Data Classification Turned Off
- Additional References
- Glossary
RSVP Scalability Enhancements
This document describes the Cisco Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) scalability enhancements. It identifies the supported platforms, provides configuration examples, and lists related IOS command line interface (CLI) commands.
This document includes the following major sections:
- Feature Information for
- Feature Overview
- Supported Platforms
- Prerequisites
- Configuration Tasks
- Monitoring and Maintaining RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- Configuration Examples
- Additional References
- Glossary
Feature Information for
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
Feature Overview
RSVP typically performs admission control, classification, policing, and scheduling of data packets on a per-flow basis and keeps a database of information for each flow. RSVP scalability enhancements let you select a resource provider (formerly called a quality of service (QoS) provider) and disable data packet classification so that RSVP performs admission control only. This facilitates integration with service provider (differentiated services (DiffServ)) networks and enables scalability across enterprise networks.
Class-based weighted fair queueing (CBWFQ) provides the classification, policing, and scheduling functions. CBWFQ puts packets into classes based on the differentiated services code point (DSCP) value in the packet’s Internet Protocol (IP) header, thereby eliminating the need for per-flow state and per-flow processing.
The figure below shows two enterprise networks interconnected through a service provider (SP) network. The SP network has an IP backbone configured as a DiffServ network. Each enterprise network has a voice gateway connected to an SP edge/aggregation device via a wide area network (WAN) link. The enterprise networks are connected to a private branch exchange (PBX).
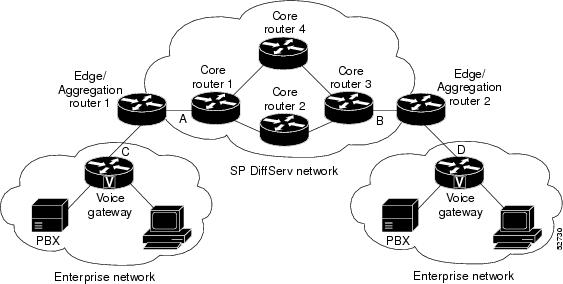
The voice gateways are running classic RSVP, which means RSVP is keeping a state per flow and also classifying, marking, and scheduling packets on a per flow basis. The edge/aggregation devices are running classic RSVP on the interfaces (labeled C and D) connected to the voice gateways and running RSVP for admission control only on the interfaces connected to core routers 1 and 3. The core devices in the DiffServ network are not running RSVP, but are forwarding the RSVP messages to the next hop. The core devices inside the DiffServ network implement a specific per hop behavior (PHB) for a collection of flows that have the same DSCP value.
The voice gateways identify voice data packets and set the appropriate DSCP in their IP headers such that the packets are classified into the priority class in the edge/aggregation devices and in core routers 1, 2, 3 or 1, 4, 3.
The interfaces or the edge/aggregation routers (labeled A and B) connected to core routers 1 and 3 are running RSVP, but are doing admission control only per flow against the RSVP bandwidth pool configured on the DiffServ interfaces of the edge/aggregation devices. CBWFQ is performing the classification, policing, and scheduling functions.
Benefits
Enhanced Scalability
RSVP scalability enhancements handle similar flows on a per-class basis instead of a per-flow basis. Since fewer resources are required to maintain per-class QoS guarantees, faster processing results, thereby enhancing scalability.
Improved Device Performance
RSVP scalability enhancements improve device performance by reducing the cost for data packet classification and scheduling, which decrease central processing unit (CPU) resource consumption. The saved resources can then be used for other network management functions.
Restrictions
- Sources should not send marked packets without an installed reservation.
- Sources should not send marked packets that exceed the reserved bandwidth.
- Sources should not send marked packets to a destination other than the reserved path.
Supported Platforms
- Cisco 2600 series
- Cisco 3600 series (Cisco 3620, 3640, and 3660)
- Cisco 3810 multiservice access concentrator
- Cisco 7200 series
- Cisco 7500 route/switch processor (RSP) only
Prerequisites
The network must support the following Cisco IOS features before the RSVP scalability enhancements are enabled:
- Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP)
- Class-based weighted fair queueing (CBWFQ)
Configuration Tasks
Enabling RSVP on an Interface
To enable RSVP on an interface, use the following command, beginning in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp bandwidth [interface-kbps] [single-flow-kbps] |
Enables RSVP on an interface. |
 Note | The bandwidth that you configure on the interface must match the bandwidth that you configure for the CBWFQ priority queue. See the section on Configuration Examples. |
Setting the Resource Provider
 Note | Resource provider was formerly called QoS provider. |
To set the resource provider, use the following command, beginning in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp resource-provider none
|
Sets the resource provider to none. |
 Note | Setting the resource provider to none instructs RSVP to not associate any resources, such as WFQ queues or bandwidth, with a reservation. |
Disabling Data Packet Classification
To turn off (disable) data packet classification, use the following command, beginning in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp data-packet classification none
|
Disables data packet classification. |
 Note | Disabling data packet classification instructs RSVP not to process every packet, but to perform admission control only. |
Configuring Class and Policy Maps
To configure class and policy maps, use the following commands, beginning in global configuration mode:
1. Device(config)# class-map class-map-name
2. Device(config)# policy-map policy-map-name
DETAILED STEPS
Attaching a Policy Map to an Interface
To attach a policy map to an interface, use the following command, beginning in interface configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device(config-if)# service-policy {input | output} policy-map-name |
Attaches a single policy map to one or more interfaces to specify the service policy for those interfaces. |
 Note | If at the time you configure the RSVP scalability enhancements, there are existing reservations that use classic RSVP, no additional marking, classification, or scheduling is provided for these flows. You can also delete these reservations after you configure the RSVP scalability enhancements. |
Verifying RSVP Scalability Enhancements Configuration
1. Enter the show ip rsvp interface detailcommand to display information about interfaces, subinterfaces, resource providers, and data packet classification. The output in the following example shows that the ATM 6/0 interface has resource provider none configured and data packet classification is turned off:
2. Enter the show ip rsvp installed detailcommand to display information about interfaces, subinterfaces, their admitted reservations, bandwidth, resource providers, and data packet classification.
3. Wait for a while, then enter the show ip rsvp installed detailcommand again. In the following output, notice there is no increment in the number of packets classified:
DETAILED STEPS
Monitoring and Maintaining RSVP Scalability Enhancements
To monitor and maintain RSVP scalability enhancements, use the following commands in EXEC mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device# show ip rsvp installed
|
Displays information about interfaces and their admitted reservations. |
Device# show ip rsvp installed detail
|
Displays additional information about interfaces and their admitted reservations. |
Device# show ip rsvp interface
|
Displays RSVP-related interface information. |
Device# show ip rsvp interface detail
|
Displays additional RSVP-related interface information. |
Device# show queueing [custom | fair | priority | random-detect [interface serial-number]] |
Displays all or selected configured queueing strategies and available bandwidth for RSVP reservations. |
Configuration Examples
- Example Configuring CBWFQ to Accommodate Reserved Traffic
- Example Configuring the Resource Provider as None with Data Classification Turned Off
Example Configuring CBWFQ to Accommodate Reserved Traffic
The following output shows a class map and a policy map being configured for voice:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# class-map match-all voice Device(config-cmap)# match access-group 100 Device(config-cmap)# exit Device(config)# policy-map wfq-voip Device(config-pmap)# class voice Device(config-pmap-c)# priority 24 Device(config-pmap-c)# end Device#
 Note | The bandwidth that you configured for the CBWFQ priority queue (24 kbps) must match the bandwidth that you configured for the interface. See the section Enabling RSVP on an Interface. |
The following output shows an access list being configured:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# access-list 100 permit udp any any range 16384 32500
The following output shows a class being applied to the outgoing interface:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# int atm6/0 Device(config-if)# service-policy output wfq-voip
The following output shows bandwidth being configured on an interface:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# int atm6/0 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp bandwidth 24
 Note | The bandwidth that you configure for the interface (24 kbps) must match the bandwidth that you configured for the CBWFQ priority queue. |
Example Configuring the Resource Provider as None with Data Classification Turned Off
The showrun command displays the current configuration in the device:
Device# show run
int atm6/0
class-map match-all voice
match access-group 100
!
policy-map wfq-voip
class voice
priority 24
class class-default
fair-queue
!
interface ATM6/0
ip address 20.20.22.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
no ip route-cache cef
atm uni-version 4.0
atm pvc 1 0 5 qsaal
atm pvc 2 0 16 ilmi
atm esi-address 111111111181.00
no atm auto-configuration
no atm ilmi-keepalive
pvc blue 200/100
abr 700 600
inarp 1
broadcast
encapsulation aal5snap
service-policy output wfq-voip
!
ip rsvp bandwidth 24 24
ip rsvp signalling dscp 48
access-list 100 permit udp any any range 16384 32500
Here is output from the showiprsvpinterfacedetail command before resource provider none is configured and data-packet classification is turned off:
Device# show ip rsvp interface detail
AT6/0:
Bandwidth:
Curr allocated: 190K bits/sec
Max. allowed (total): 112320K bits/sec
Max. allowed (per flow): 112320K bits/sec
Neighbors:
Using IP encap: 1. Using UDP encaps: 0
DSCP value used in Path/Resv msgs: 0x30
Here is output from the showqueueingcommand before resource provider none is configured and data packet classification is turned off:
Device# s
how queueing int atm6/0
Interface ATM6/0 VC 200/100
Queueing strategy: weighted fair
Output queue: 63/512/64/3950945 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 2/5/64 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 450 kilobits/sec
 Note | New reservations do not reduce the available bandwidth (450 kilobits/sec shown above). Instead RSVP performs admission control only using the bandwidth limit configured in the iprsvpbandwidth command. The bandwidth configured in this command should match the bandwidth configured in the CBWFQ class that you set up to handle the reserved traffic. |
The following output shows resource provider none being configured:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# int atm6/0 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp resource-provider none Device(config-if)# end Device#
The following output shows data packet classification being turned off:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# int atm6/0 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp data-packet classification none Device(config-if)# end Device#
Here is output from the showiprsvpinterfacedetail command after resource provider none has been configured and data packet classification has been turned off:
Device# show ip rsvp interface detail
AT6/0:
Bandwidth:
Curr allocated: 190K bits/sec
Max. allowed (total): 112320K bits/sec
Max. allowed (per flow): 112320K bits/sec
Neighbors:
Using IP encap: 1. Using UDP encaps: 0
DSCP value used in Path/Resv msgs: 0x30
RSVP Data Packet Classification is OFF
RSVP resource provider is: none
The following output from the showiprsvpinstalleddetail command verifies that resource provider none is configured and data packet classification is turned off:
Device# show ip rsvp installed detail RSVP: ATM6/0 has the following installed reservations RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 14, Source port is 14 Reserved bandwidth: 50K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 50K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 3192 packets (1557696 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 42 packets (20496 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 271 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 45880 reserved, 603 best-effort RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 10, Source port is 10 Reserved bandwidth: 20K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 20K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 1348 packets (657824 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 0 packets (0 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 296 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 17755 reserved, 0M best-effort
The following output shows no increments in packet counts after the source sends data packets that match the reservation:
Device# show ip rsvp installed detail RSVP: Ethernet3/3 has no installed reservations RSVP: ATM6/0 has the following installed reservations RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 14, Source port is 14 Reserved bandwidth: 50K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 50K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 3192 packets (1557696 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 42 packets (20496 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 282 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 44051 reserved, 579 best-effort RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 10, Source port is 10 Reserved bandwidth: 20K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 20K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 1348 packets (657824 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 0 packets (0 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 307 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 17121 reserved, 0M best-effort
The following output shows that data packet classification is enabled again:
Device# configure terminal Device(config)# int atm6/0 Device(config-if) no ip rsvp data-packet classification Device(config-if)# end
The following output verifies that data packet classification is occurring:
Device# show ip rsvp installed detail Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. RSVP: ATM6/0 has the following installed reservations RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 14, Source port is 14 Reserved bandwidth: 50K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 50K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 3683 packets (1797304 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 47 packets (22936 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 340 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 42201 reserved, 538 best-effort RSVP Reservation. Destination is 145.20.20.212, Source is 145.10.10.211, Protocol is UDP, Destination port is 10, Source port is 10 Reserved bandwidth: 20K bits/sec, Maximum burst: 1K bytes, Peak rate: 20K bits/sec Min Policed Unit: 0 bytes, Max Pkt Size: 1514 bytes Resource provider for this flow: None Conversation supports 1 reservations Data given reserved service: 1556 packets (759328 bytes) Data given best-effort service: 0 packets (0 bytes) Reserved traffic classified for 364 seconds Long-term average bitrate (bits/sec): 16643 reserved, 0M best-effort
Here is output from the showrun command after you have performed all the previous configuration tasks:
Device# show run int atm6/0
class-map match-all voice
match access-group 100
!
policy-map wfq-voip
class voice
priority 24
class class-default
fair-queue
!
interface ATM6/0
ip address 20.20.22.1 255.255.255.0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
no ip route-cache cef
atm uni-version 4.0
atm pvc 1 0 5 qsaal
atm pvc 2 0 16 ilmi
atm esi-address 111111111181.00
no atm auto-configuration
no atm ilmi-keepalive
pvc blue 200/100
abr 700 600
inarp 1
broadcast
encapsulation aal5snap
service-policy output wfq-voip
!
ip rsvp bandwidth 24 24
ip rsvp signalling dscp 48
ip rsvp data-packet classification none
ip rsvp resource-provider none
access-list 100 permit udp any any range 16384 32500
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the RSVP Scalability Enhancements feature.
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
QoS commands: complete command syntax, command modes, command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference |
|
QoS configuration tasks related to RSVP |
"Configuring RSVP" module |
Standards
|
Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
RFC 2206 (RSVP Management Information Base using SMIv2) |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 2205 |
Resource Reservation Protocol |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Glossary
admission control --The process in which an RSVP reservation is accepted or rejected based on end-to-end available network resources.
aggregate --A collection of packets with the same DSCP.
bandwidth --The difference between the highest and lowest frequencies available for network signals. This term also describes the rated throughput capacity of a given network medium or protocol.
CBWFQ -- Class-based weighted fair queueing. A queueing mechanism that extends the standard WFQ functionality to provide support for user-defined traffic classes.
Class-based weighted fair queueing -- See CBWFQ .
differentiated services --See DiffServ.
differentiated services code point --See DSCP.
DiffServ --An architecture based on a simple model where traffic entering a network is classified and possibly conditioned at the boundaries of the network. The class of traffic is then identified with a DS code point or bit marking in the IP header. Within the core of the network, packets are forwarded according to the per-hop behavior associated with the DS code point.
DSCP --Differentiated services code point. The six most significant bits of the 1-byte IP type of service (ToS) field. The per-hop behavior represented by a particular DSCP value is configurable. DSCP values range between 0 and 63.
enterprise network --A large and diverse network connecting most major points in a company or other organization.
flow --A stream of data traveling between two endpoints across a network (for example, from one LAN station to another). Multiple flows can be transmitted on a single circuit.
packet --A logical grouping of information that includes a header containing control information and (usually) user data. Packets most often refer to network layer units of data.
PBX --Private branch exchange. A digital or analog telephone switchboard located on the subscriber premises and used to connect private and public telephone networks.
PHB --Per hop behavior. A DiffServ concept that specifies how specifically marked packets are to be treated by each DiffServ device.
QoS --Quality of service. A measure of performance for a transmission system that reflects its transmission quality and service availability.
quality of service --See QoS.
Resource Reservation Protocol --See RSVP.
RSVP --Resource Reservation Protocol. A protocol for reserving network resources to provide quality of service guarantees to application flows.
Voice over IP --See VoIP.
VoIP --Voice over IP. The ability to carry normal telephony-style voice over an IP-based internet maintaining telephone-like functionality, reliability, and voice quality.
Weighted Fair Queueing --See WFQ.
WFQ --Weighted fair queueing. A queue management algorithm that provides a certain fraction of link bandwidth to each of several queues, based on relative bandwidth applied to each of the queues.