- Signalling Overview
- Configuring RSVP
- Control Plane DSCP Support for RSVP
- Configuring RSVP Support for Frame Relay
- RSVP Scalability Enhancements
- RSVP Refresh Reduction and Reliable Messaging
- RSVP Message Authentication
- RSVP Fast Local Repair
- RSVP Interface-Based Receiver Proxy
- RSVP Aggregation
- MPLS TE-Tunnel-Based Admission Control
- Configuring Subnetwork Bandwidth Manager
- RSVP over UDP
- Index
Contents
- RSVP Message Authentication
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for RSVP Message Authentication
- Restrictions for RSVP Message Authentication
- Information About RSVP Message Authentication
- Feature Design of RSVP Message Authentication
- Global Authentication and Parameter Inheritance
- Per-Neighbor Keys
- Key Chains
- Benefits of RSVP Message Authentication
- How to Configure RSVP Message Authentication
- Enabling RSVP on an Interface
- Configuring an RSVP Authentication Type
- Configuring an RSVP Authentication Key
- Enabling RSVP Key Encryption
- Enabling RSVP Authentication Challenge
- Configuring RSVP Authentication Lifetime
- Configuring RSVP Authentication Window Size
- Activating RSVP Authentication
- Verifying RSVP Message Authentication
- Configuring a Key Chain
- Binding a Key Chain to an RSVP Neighbor
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Configuration Examples for RSVP Message Authentication
- Example RSVP Message Authentication Per-Interface
- Example RSVP Message Authentication Per-Neighbor
- Additional References
- Feature Information for RSVP Message Authentication
- Glossary
RSVP Message Authentication
The Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) Message Authentication feature provides a secure method to control quality of service (QoS) access to a network.
History for the RSVP Message Authentication Feature
|
Release |
Modification |
|---|---|
|
12.2(15)T |
This feature was introduced. |
|
12.0(26)S |
Restrictions were added for interfaces that use Fast Reroute (FRR) node or link protection and for RSVP hellos for FRR for packet over SONET (POS) interfaces. |
|
12.0(29)S |
Support was added for per-neighbor keys. |
|
12.2(33)SRA |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SRA. |
|
12.2(33)SXH |
This feature was integrated into Cisco IOS Release 12.2(33)SXH. |
- Finding Feature Information
- Prerequisites for RSVP Message Authentication
- Restrictions for RSVP Message Authentication
- Information About RSVP Message Authentication
- How to Configure RSVP Message Authentication
- Configuration Examples for RSVP Message Authentication
- Additional References
- Feature Information for RSVP Message Authentication
- Glossary
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table at the end of this module.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Prerequisites for RSVP Message Authentication
Ensure that RSVP is configured on one or more interfaces on at least two neighboring devices that share a link within the network.
Restrictions for RSVP Message Authentication
- The RSVP Message Authentication feature is only for authenticating RSVP neighbors.
- The RSVP Message Authentication feature cannot discriminate between various QoS applications or users, of which many may exist on an authenticated RSVP neighbor.
- Different send and accept lifetimes for the same key in a specific key chain are not supported; all RSVP key types are bidirectional.
- Authentication for graceful restart hello messages is supported for per-neighbor and per-access control list (ACL) keys, but not for per-interface keys.
- You cannot use the ip rsvp authentication key and the ip rsvp authentication key-chain commands on the same device interface.
- For a Multiprotocol Label Switching/Traffic Engineering (MPLS/TE) configuration, use per-neighbor keys with physical addresses and device IDs.
Information About RSVP Message Authentication
- Feature Design of RSVP Message Authentication
- Global Authentication and Parameter Inheritance
- Per-Neighbor Keys
- Key Chains
- Benefits of RSVP Message Authentication
Feature Design of RSVP Message Authentication
Network administrators need the ability to establish a security domain to control the set of systems that initiate RSVP requests.
The RSVP Message Authentication feature permits neighbors in an RSVP network to use a secure hash to sign all RSVP signaling messages digitally, thus allowing the receiver of an RSVP message to verify the sender of the message without relying solely on the sender’s IP address as is done by issuing the ip rsvp neighbor command with an ACL.
The signature is accomplished on a per-RSVP-hop basis with an RSVP integrity object in the RSVP message as defined in RFC 2747. This method provides protection against forgery or message modification. However, the receiver must know the security key used by the sender in order to validate the digital signature in the received RSVP message.
Network administrators manually configure a common key for each RSVP neighbor interface on the shared network. A sample configuration is shown in the figure below.
RSVP Message Authentication Configuration
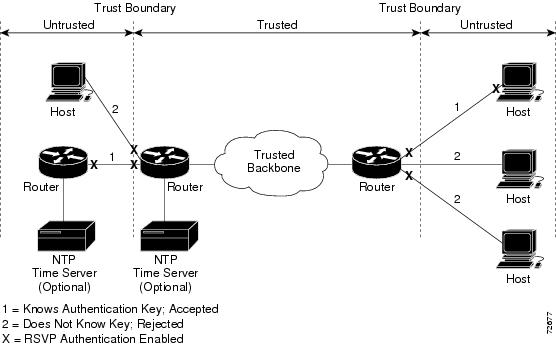
Global Authentication and Parameter Inheritance
You can configure global defaults for all authentication parameters including key, type, window size, lifetime, and challenge. These defaults are inherited when you enable authentication for each neighbor or interface. However, you can also configure these parameters individually on a per-neighbor or per-interface basis in which case the inherited global defaults are ignored.
Using global authentication and parameter inheritance can simplify configuration because you can enable or disable authentication without having to change each per-neighbor or per-interface attribute. You can activate authentication for all neighbors by using two commands, one to define a global default key and one to enable authentication globally. However, using the same key for all neighbors does not provide the best network security.
 Note | RSVP uses the following rules when choosing which authentication parameter to use when that parameter is configured at multiple levels (per-interface, per-neighbor, or global). RSVP goes from the most specific to the least specific; that is, per-neighbor, per-interface, and then global. The rules are slightly different when searching the configuration for the right key to authenticate an RSVP message-- per-neighbor, per-ACL, per-interface, and then global. |
Per-Neighbor Keys
In the figure below, to enable authentication between Internet service provider (ISP) Routers A and B, A and C, and A and D, the ISPs must share a common key. However, sharing a common key also enables authentication between ISP Routers B and C, C and D, and B and D. You may not want authentication among all the ISPs because they might be different companies with unique security domains.
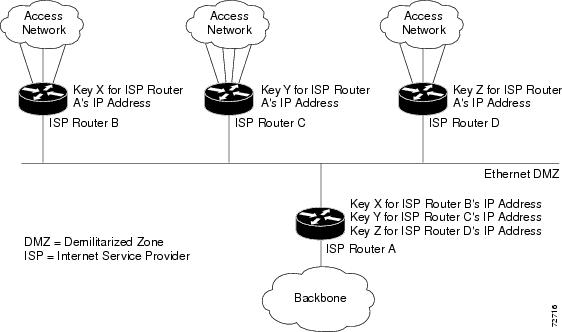
On ISP Router A, you create a different key for ISP Routers B, C, and D and assign them to their respective IP addresses using RSVP commands. On the other devices, create a key to communicate with ISP Router A’s IP address.
Key Chains
For each RSVP neighbor, you can configure a list of keys with specific IDs that are unique and have different lifetimes so that keys can be changed at predetermined intervals automatically without any disruption of service. Automatic key rotation enhances network security by minimizing the problems that could result if an untrusted source obtained, deduced, or guessed the current key.
 Note | If you use overlapping time windows for your key lifetimes, RSVP asks the Cisco software key manager component for the next live key starting at time T. The key manager walks the keys in the chain until it finds the first one with start time S and end time E such that S <= T <= E. Therefore, the key with the smallest value (E-T) may not be used next. |
Benefits of RSVP Message Authentication
Improved Security
The RSVP Message Authentication feature greatly reduces the chance of an RSVP-based spoofing attack and provides a secure method to control QoS access to a network.
Multiple Environments
The RSVP Message Authentication feature can be used in traffic engineering (TE) and non-TE environments as well as with the subnetwork bandwidth manager (SBM).
Multiple Platforms and Interfaces
The RSVP Message Authentication feature can be used on any supported RSVP platform or interface.
How to Configure RSVP Message Authentication
The following configuration parameters instruct RSVP on how to generate and verify integrity objects in various RSVP messages.
 Note | There are two configuration procedures: full and minimal. There are also two types of authentication procedures: interface and neighbor. |
Per-Interface Authentication--Full Configuration
Perform the following procedures for a full configuration for per-interface authentication:
Per-Interface Authentication--Minimal Configuration
Perform the following tasks for a minimal configuration for per-interface authentication:
Per-Neighbor Authentication--Full Configuration
Perform the following procedures for a full configuration for per-neighbor authentication:
Per-Neighbor Authentication--Minimal Configuration
Perform the following tasks for a minimal configuration for per-neighbor authentication:
- Enabling RSVP on an Interface
- Configuring an RSVP Authentication Type
- Configuring an RSVP Authentication Key
- Enabling RSVP Key Encryption
- Enabling RSVP Authentication Challenge
- Configuring RSVP Authentication Lifetime
- Configuring RSVP Authentication Window Size
- Activating RSVP Authentication
- Verifying RSVP Message Authentication
- Configuring a Key Chain
- Binding a Key Chain to an RSVP Neighbor
- Troubleshooting Tips
Enabling RSVP on an Interface
Perform this task to enable RSVP on an interface.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4. ip rsvp bandwidth [interface-kbps [single-flow-kbps]]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Configuring an RSVP Authentication Type
Perform this task to configure an RSVP authentication type.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: For interface authentication: Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication type sha-1
Example: Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1 type sha-1
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 type sha-1
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication type sha-1
|
Specifies the algorithm used to generate cryptographic signatures in RSVP messages on an interface or globally.
| ||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring an RSVP Authentication Key
Perform this task to configure an RSVP authentication key.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
4.
ip
rsvp
authentication
key
passphrase
5.
exit
7.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode.
| ||||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||||
| Step 4 |
ip
rsvp
authentication
key
passphrase
Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication key 11223344
Example: |
Specifies the data string (key) for the authentication algorithm.
| ||||
| Step 5 |
exit
Example: Device(config-if)# exit |
Exits to global configuration mode. | ||||
| Step 6 | Do one of the following:
Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1 key-chain xzy
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 key-chain xzy
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication key-chain xzy
|
Specifies the data string (key chain) for the authentication algorithm.
| ||||
| Step 7 |
end
Example:
Device(config)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Enabling RSVP Key Encryption
Perform this task to enable RSVP key encryption when the key is stored in the configuration. (This prevents anyone from seeing the clear text key in the configuration file.)
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
key
config-key
1
string
4.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
key
config-key
1
string
Example: Device(config)# key config-key 1 11223344 |
Enables key encryption in the configuration file.
| ||
| Step 4 |
end
Example:
Device(config)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Enabling RSVP Authentication Challenge
Perform this task to enable RSVP authentication challenge.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: For interface authentication: Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication challenge
Example: Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1 challenge
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 challenge
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication challenge
|
Makes RSVP perform a challenge-response handshake on an interface or globally when RSVP learns about any new challenge-capable neighbors on a network.
| ||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring RSVP Authentication Lifetime
Perform this task to configure the lifetimes of security associations between RSVP neighbors.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: For interface authentication: Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication lifetime 00:05:00
Example: Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1 lifetime 00:05:00
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 lifetime 00:05:00
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication 00:05:00
|
Controls how long RSVP maintains security associations with RSVP neighbors on an interface or globally.
| ||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Configuring RSVP Authentication Window Size
Perform this task to configure the RSVP authentication window size.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: For interface authentication: Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication window-size 2
Example: Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1 window-size 2
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 window-size
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication window-size 2
|
Specifies the maximum number of authenticated messages that can be received out of order on an interface or globally.
| ||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Activating RSVP Authentication
Perform this task to activate RSVP authentication.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
type
number
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
interface
type
number
Example: Device(config)# interface Ethernet0/0 |
Enters interface configuration mode.
| ||
| Step 4 | Do one of the following:
Example: For interface authentication: Example:
Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication
Example: Example: For neighbor authentication: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor address 10.1.1.1
Example:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1
Example: Example: For a global default: Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication
|
Activates RSVP cryptographic authentication on an interface or globally.
| ||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-if)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Verifying RSVP Message Authentication
Perform this task to verify that the RSVP Message Authentication feature is functioning.
1.
enable
2.
show
ip
rsvp
interface
[detail]
[interface-type
interface-number]
3.
show
ip
rsvp
authentication
[detail] [from{ip-address |
hostname}] [to {ip-address |
hostname}]
4.
show
ip
rsvp
counters
[authentication |
interface
interface-unit |
neighbor |
summary]
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
show
ip
rsvp
interface
[detail]
[interface-type
interface-number]
Example: Device# show ip rsvp interface detail |
Displays information about interfaces on which RSVP is enabled, including the current allocation budget and maximum available bandwidth. | ||
| Step 3 |
show
ip
rsvp
authentication
[detail] [from{ip-address |
hostname}] [to {ip-address |
hostname}]
Example: Device# show ip rsvp authentication detail |
Displays the security associations that RSVP has established with other RSVP neighbors. | ||
| Step 4 |
show
ip
rsvp
counters
[authentication |
interface
interface-unit |
neighbor |
summary]
Example: Device# show ip rsvp counters summary Example: Example: Device# show ip rsvp counters authentication |
Displays all RSVP counters.
|
Configuring a Key Chain
Perform this task to configure a key chain for neighbor authentication.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
key
chain
name-of-chain
4. {key [key-ID] | key-string [text] | accept-lifetime [start-time {infinite | end-time | duration seconds}] | send-lifetime [start-time {infinite | end-time | duration seconds}]
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||||
| Step 3 |
key
chain
name-of-chain
Example: Device(config)# key chain neighbor_V |
Enters key-chain mode. | ||||
| Step 4 | {key [key-ID] |
key-string [text] |
accept-lifetime [start-time {infinite |
end-time |
duration
seconds}] |
send-lifetime [start-time {infinite |
end-time |
duration
seconds}]
Example: Device(config-keychain)# key 1 Example: Example: Device(config-keychain)# key-string ABcXyz |
Selects the parameters for the key chain. (These are submodes.)
| ||||
| Step 5 |
end
Example:
Device(config-keychain)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Binding a Key Chain to an RSVP Neighbor
Perform this task to bind a key chain to an RSVP neighbor for neighbor authentication.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
4.
end
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Device> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Device# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | Do one of the following:
Example:
Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list 1 key-chain neighbor_V
|
Binds a key chain to an IP address or to an ACL and enters key-chain mode.
| ||
| Step 4 |
end
Example:
Device(config-keychain)# end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Troubleshooting Tips
After you enable RSVP authentication, RSVP logs system error events whenever an authentication check fails. These events are logged instead of just being displayed when debugging is enabled because they may indicate potential security attacks. The events are generated when:
- RSVP receives a message that does not contain the correct cryptographic signature. This could be due to misconfiguration of the authentication key or algorithm on one or more RSVP neighbors, but it may also indicate an (unsuccessful) attack.
- RSVP receives a message with the correct cryptographic signature, but with a duplicate authentication sequence number. This may indicate an (unsuccessful) message replay attack.
- RSVP receives a message with the correct cryptographic signature, but with an authentication sequence number that is outside the receive window. This could be due to a reordered burst of valid RSVP messages, but it may also indicate an (unsuccessful) message replay attack.
- Failed challenges result from timeouts or bad challenge responses.
To troubleshoot the RSVP Message Authentication feature, use the following commands in privileged EXEC mode.
|
Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Device# debug ip rsvp authentication |
Displays output related to RSVP authentication. |
Device# debug ip rsvp dump signalling
|
Displays brief information about signaling (Path and Resv) messages. |
Device# debug ip rsvp errors
|
Displays error events including authentication errors. |
Configuration Examples for RSVP Message Authentication
Example RSVP Message Authentication Per-Interface
In the following example, the cryptographic authentication parameters, including type, key, challenge, lifetime, and window size are configured; and authentication is activated:
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# interface e0/0 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication type sha-1 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication key 11223344 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication challenge Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication lifetime 00:30:05 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication window-size 2 Device(config-if)# ip rsvp authentication
In the following output from the show ip rsvp interface detail command, notice the cryptographic authentication parameters that you configured for the Ethernet0/0 interface:
Device# show ip rsvp interface detail
Et0/0:
Bandwidth:
Curr allocated: 0 bits/sec
Max. allowed (total): 7500K bits/sec
Max. allowed (per flow): 7500K bits/sec
Max. allowed for LSP tunnels using sub-pools: 0 bits/sec
Set aside by policy (total): 0 bits/sec
Neighbors:
Using IP encap: 0. Using UDP encap: 0
Signalling:
Refresh reduction: disabled
Authentication: enabled
Key: 11223344
Type: sha-1
Window size: 2
Challenge: enabled
In the preceding example, the authentication key appears in clear text. If you enter the key-config-key 1 string command, the key appears encrypted, as in the following example:
Device# show ip rsvp interface detail
Et0/0:
Bandwidth:
Curr allocated: 0 bits/sec
Max. allowed (total): 7500K bits/sec
Max. allowed (per flow): 7500K bits/sec
Max. allowed for LSP tunnels using sub-pools: 0 bits/sec
Set aside by policy (total): 0 bits/sec
Neighbors:
Using IP encap: 0. Using UDP encap: 0
Signalling:
Refresh reduction: disabled
Authentication: enabled
Key: <encrypted>
Type: sha-1
Window size: 2
Challenge: enabled
In the following output, notice that the authentication key changes from encrypted to clear text after the no key config-key 1 command is issued:
Device# show running-config interface e0/0 Building configuration... Current configuration :247 bytes ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.101.2 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip pim dense-mode no ip mroute-cache no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500 ip rsvp authentication key 7>70>9:7<872>?74 ip rsvp authentication end Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# no key config-key 1 Device(config)# end
Device# show running-config *Jan 30 08:02:09.559:%SYS-5-CONFIG_I:Configured from console by console int e0/0 Building configuration... Current configuration :239 bytes ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 192.168.101.2 255.255.255.0 no ip directed-broadcast ip pim dense-mode no ip mroute-cache no cdp enable ip rsvp bandwidth 7500 7500 ip rsvp authentication key 11223344 ip rsvp authentication end
Example RSVP Message Authentication Per-Neighbor
In the following example, a key chain with two keys for each neighbor is defined, then an access list and a key chain are created for neighbors V, Y, and Z and authentication is explicitly enabled for each neighbor and globally. However, only the neighbors specified will have their messages accepted; messages from other sources will be rejected. This enhances network security.
For security reasons, you should change keys on a regular basis. When the first key expires, the second key automatically takes over. At that point, you should change the first key’s key-string to a new value and then set the send lifetimes to take over after the second key expires. The device will log an event when a key expires to remind you to update it.
The lifetimes of the first and second keys for each neighbor overlap. This allows for any clock synchronization problems that might cause the neighbors not to switch keys at the right time. You can avoid these overlaps by configuring the neighbors to use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize their clocks to a time server.
For an MPLS/TE configuration, physical addresses and device IDs are given.
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# key chain neighbor_V Device(config-keychain)# key 1 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string R72*UiAXy Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 02:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# key 2 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string Pl349&DaQ Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 01:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# exit Device(config)# key chain neighbor_Y Device(config-keychain)# key 3 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string *ZXFwR!03 Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 02:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# key 4 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string UnGR8f&lOmY Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 01:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# exit Device(config)# key chain neighbor_Z Device(config-keychain)# key 5 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string P+T=77&/M Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 02:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# key 6 Device(config-keychain-key)# key-string payattention2me Device(config-keychain-key)# send-life 01:00:00 1 jun 2003 02:00:00 1 aug 2003 Device(config-keychain-key)# exit Device(config-keychain)# exit Device(config)# end
 Note | You can use the key-config-key 1 string command to encrypt key chains for an interface, a neighbor, or globally. |
Device# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Device(config)# ip access-list standard neighbor_V Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.1 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.2 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.3 <------- router ID Device(config-std-nacl)# exit Device(config)# ip access-list standard neighbor_Y Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.4 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.5 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.6 <------- router ID Device(config-std-nacl)# exit Device(config)# ip access-list standard neighbor_Z Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.7 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.8 <------- physical address Device(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.9 <------- router ID Device(config-std-nacl)# exit Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list neighbor_V key-chain neighbor_V Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list neighbor_Y key-chain neighbor_Y Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication neighbor access-list neighbor_Z key-chain neighbor_Z Device(config)# ip rsvp authentication Device(config)# end
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the RSVP Message Authentication feature.
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
RSVP commands: complete command syntax, command mode, defaults, usage guidelines, and examples |
Cisco IOS Quality of Service Solutions Command Reference |
|
QoS features including signaling, classification, and congestion management |
"Quality of Service Overview" module |
|
Inter-AS features including local policy support and per-neighbor keys authentication |
"MPLS Traffic Engineering--Inter-AS-TE" module |
Standards
|
Standards |
Title |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
|
MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
RFCs |
Title |
|---|---|
|
RFC 1321 |
The MD5 Message Digest Algorithm |
|
RFC 2104 |
HMAC: Keyed-Hashing for Messaging Authentication |
|
RFC 2205 |
Resource Reservation Protocol |
|
RFC 2209 |
RSVP--Version 1 Message Processing Rules |
|
RFC 2401 |
Security Architecture for the Internet Protocol |
|
RFC 2747 |
RSVP Cryptographic Authentication |
|
RFC 3097 |
RSVP Crytographic Authentication--Updated Message Type Value |
|
RFC 3174 |
US Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA1) |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for RSVP Message Authentication
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
RSVP Message Authentication |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S |
In Cisco IOS XE Release 3.8S, support was added for the Cisco ASR 903 Router. |
Glossary
bandwidth --The difference between the highest and lowest frequencies available for network signals. The term also is used to describe the rated throughput capacity of a given network medium or protocol.
DMZ--demilitarized zone. The neutral zone between public and corporate networks.
flow --A stream of data traveling between two endpoints across a network (for example, from one LAN station to another). Multiple flows can be transmitted on a single circuit.
key --A data string that is combined with source data according to an algorithm to produce output that is unreadable until decrypted.
QoS --quality of service. A measure of performance for a transmission system that reflects its transmission quality and service availability.
router --A network layer device that uses one or more metrics to determine the optimal path along which network traffic should be forwarded. Routers forward packets from one network to another based on network layer information.
RSVP --Resource Reservation Protocol. A protocol that supports the reservation of resources across an IP network. Applications running on IP end systems can use RSVP to indicate to other nodes the nature (bandwidth, jitter, maximum burst, and so on) of the packet streams they want to receive.
security association --A block of memory used to hold all the information RSVP needs to authenticate RSVP signaling messages from a specific RSVP neighbor.
spoofing --The act of a packet illegally claiming to be from an address from which it was not actually sent. Spoofing is designed to foil network security mechanisms, such as filters and access lists.
TE --traffic engineering. The techniques and processes used to cause routed traffic to travel through the network on a path other than the one that would have been chosen if standard routing methods had been used.
trusted neighbor --A device with authorized access to information.