- Feature Information for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Prerequisites for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Restrictions for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Information About Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuring Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication
- Verifying Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuration Examples for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Additional References
Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
The Certificate-based MACsec Encryption feature uses 802.1X port-based authentication with Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) to carry Certificates for router ports where MACsec encryption is required. EAP-TLS mechanism is used to do the mutual authentication and to get the Master Session Key (MSK) from which the Connectivity Association Key (CAK) is derived for the MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) protocol.
- Feature Information for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Prerequisites for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Restrictions for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Information About Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuring Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication
- Verifying Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Configuration Examples for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
- Additional References
Feature Information for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Certificate-based MACsec Encryption |
Cisco IOS XE Everest Release 16.6.1 |
The Certificate-based MACsec Encryption feature uses 802.1X port-based authentication with Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) to carry Certificates for router ports where MACsec encryption is required. EAP-TLS mechanism is used to do the mutual authentication and to get the Master Session Key (MSK) from which the Connectivity Association Key (CAK) is derived for the MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) protocol. |
Prerequisites for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
-
Ensure that you have a Certificate Authority (CA) server configured for your network.
-
Generate a CA certificate.
-
Ensure that you have configured Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) Release 2.0. Refer to the Cisco Identity Services Engine Administrator Guide, Release 2.3.
-
Ensure that both the participating devices, the CA server, and Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) are synchronized using Network Time Protocol (NTP). If time is not synchronized on all your devices, certificates will not be validated.
-
Ensure that 802.1x authentication and AAA are configured on your device.
Restrictions for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Information About Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
MKA MACsec is supported on router-to-router links. Using IEEE 802.1X Port-based Authentication with Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP-TLS), you can configure MKA MACsec between device ports. EAP-TLS allows mutual authentication and obtains an MSK (master session key) from which the connectivity association key (CAK) is derived for MKA protocol. Device certificates are carried, using EAP-TLS, for authentication to the AAA server.
Call Flow for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Suppllicants are unauthorized devices that try to gain access to the network. Authenticators are devices that control the physical access to the network based on the authentication status of the supplicant.
As shown in the following diagram, the devices are connected directly. The router acts as both EAP Supplicant and Authenticator on the port.
The figure below depicts two EAP call flows (with separate EAP-Session ID) on the router. The red flow depicts Router 1 as supplicant and Router 2 as authenticator and the blue flow is vice-versa.
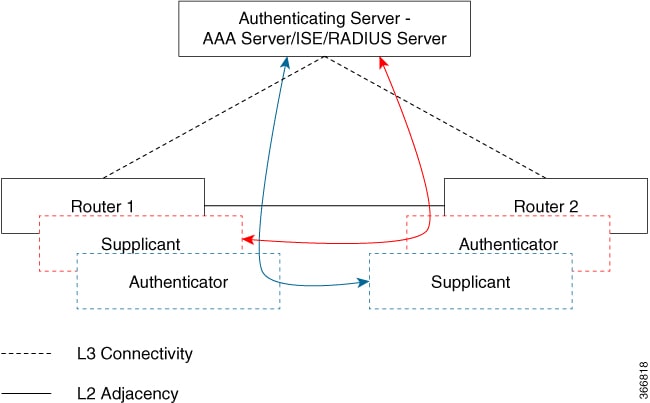
When the interface is configured for 802.1x role as both, The authentication manager creates a session with supplicant/authenticator role and both trigger EAP with both a supplicant as well as an authenticator role (separate EAP flow with separate EAP session ID).
Based on the MAC address of the peer, if the local MAC of the interface is less than the peer MAC, the authenticator role's MSK used for MKA session; if the MAC is higher then the supplicant role’s MSK is used for MKA session (to derive the CAK).
In the example above, if Router 1 MAC address is less than Router 2, then the MSK obtained from the Blue EAP session is used as EAP-MSK for the MKA (Router 1 acts as authenticator and Router 2 as supplicant). This ensures that Router 1 acts as MKA Key Server and Router 2 will be the Non-Key Server.
If the Router 2 MAC Address is less than Router 1 then MSK obtained from the Red EAP flow is used ( by both routers) as EAP-MSK for the MKA session.
Configuring Certificate-based MACsec Encryption using Remote Authentication
To configure MACsec with MKA on point-to-point links, perform these tasks:
- Configuring Certificate Enrollment
- Enabling 802.1x Authentication and Configuring AAA
- Configuring EAP-TLS Profile and 802.1x Credentials
- Applying the 802.1x MKA MACsec Configuration on Interfaces
Configuring Certificate Enrollment
Generating Key Pairs
Configuring Enrollment using SCEP
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) is a Cisco-developed enrollment protocol that uses HTTP to communicate with the certificate authority (CA) or registration authority (RA). SCEP is the most commonly used method for sending and receiving requests and certificates.
Configuring Enrollment Manually
If your CA does not support SCEP or if a network connection between the router and CA is not possible. Perform the following task to set up manual certificate enrollment:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
| ||
| Step 2 | configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 | crypto pki trustpoint
server name
|
Declares the trustpoint and a given name and enters ca-trustpoint configuration mode. | ||
| Step 4 | enrollment url
url name pem
|
Specifies the URL of the CA on which your device should send certificate requests. An IPv6 address can be added in the URL enclosed in brackets. For example: http:// [2001:DB8:1:1::1]:80. The pem keyword adds privacy-enhanced mail (PEM) boundaries to the certificate request. | ||
| Step 5 | rsakeypair
label
|
Specifies which key pair to associate with the certificate. | ||
| Step 6 | serial-number none
|
The none keyword specifies that a serial number will not be included in the certificate request. | ||
| Step 7 | ip-address none
|
The none keyword specifies that no IP address should be included in the certificate request. | ||
| Step 8 | revocation-check crl
|
Specifies CRL as the method to ensure that the certificate of a peer has not been revoked. | ||
| Step 9 | exit
|
Exits Global Configuration mode. | ||
| Step 10 | crypto pki authenticate
name
|
Retrieves the CA certificate and authenticates it. | ||
| Step 11 | crypto pki enroll
name
|
Generates certificate request and displays the request for copying and pasting into the certificate server. Enter enrollment information when you are prompted. For example, specify whether to include the device FQDN and IP address in the certificate request. You are also given the choice about displaying the certificate request to the console terminal. The base-64 encoded certificate with or without PEM headers as requested is displayed. | ||
| Step 12 | crypto pki import
name
certificate
|
Imports a certificate via TFTP at the console terminal, which retrieves the granted certificate. The device attempts to retrieve the granted certificate via TFTP using the same filename used to send the request, except the extension is changed from “.req” to “.crt”. For usage key certificates, the extensions “-sign.crt” and “-encr.crt” are used. The device parses the received files, verifies the certificates, and inserts the certificates into the internal certificate database on the switch.
| ||
| Step 13 | exit
|
Exits Global Configuration mode. | ||
| Step 14 | show crypto pki certificate
trustpoint name
|
Displays information about the certificate for the trust point. | ||
| Step 15 | copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file. |
Enabling 802.1x Authentication and Configuring AAA
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | aaa new-model
|
Enables AAA. |
| Step 4 | dot1x system-auth-control
|
Enables 802.1X on your device. |
| Step 5 | radius server name
|
Specifies the name of the RADIUS server configuration for Protected Access Credential (PAC) provisioning and enters RADIUS server configuration mode. |
| Step 6 | address ip-address auth-port port-number acct-port port-number
|
Configures the IPv4 address for the RADIUS server accounting and authentication parameters.
|
| Step 7 | automate-tester username username
|
Enables the automated testing feature for the RADIUS server. With this practice, the device sends periodic test authentication messages to the RADIUS server. It looks for a RADIUS response from the server. A success message is not necessary - a failed authentication suffices, because it shows that the server is alive. |
| Step 8 | key string
|
Configures the authentication and encryption key for all RADIUS communications between the device and the RADIUS server. |
| Step 9 | radius-server deadtime minutes
|
Improves RADIUS response time when some servers might be unavailable and skips unavailable servers immediately. |
| Step 10 | exit
|
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 11 | aaa group server radius group-name
|
Groups different RADIUS server hosts into distinct lists and distinct methods, and enters server group configuration mode. |
| Step 12 | server
name
|
Assigns the RADIUS server name. |
| Step 13 | exit
|
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 14 | aaa authentication dot1x default group group-name
|
Sets the default authentication server group for IEEE 802.1x. |
| Step 15 | aaa authorization network default group group-name
|
Sets the network authorization default group. |
Configuring EAP-TLS Profile and 802.1x Credentials
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | eap profile profile-name
|
Configures EAP profile and enters EAP profile configuration mode. |
| Step 4 | method tls
|
Enables EAP-TLS method on the device. |
| Step 5 | pki-trustpoint name
|
Sets the default PKI trustpoint. |
| Step 6 | exit
|
Returns to global configuration mode. |
| Step 7 | dot1x credentials profile-name
|
Configures 802.1x credentials profile and enters dot1x credentials configuration mode.
|
| Step 8 | username username
|
Sets the authentication user ID. |
| Step 9 | pki-trustpoint name
|
Sets the default PKI trustpoint. |
| Step 10 | end
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Applying the 802.1x MKA MACsec Configuration on Interfaces
To apply MKA MACsec using EAP-TLS to interfaces, perform the following task:
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable
|
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal
|
Enters global configuration mode. |
| Step 3 | interface
interface-id
|
Identifies the MACsec interface, and enter interface configuration mode. The interface must be a physical interface. |
| Step 4 | macsec
|
Enables MACsec on the interface. |
| Step 5 | authentication periodic
|
Enables reauthentication for this port. |
| Step 6 | authentication timer reauthenticate interval
|
Sets the reauthentication interval. |
| Step 7 | access-session host-mode multi-domain
|
Allows hosts to gain access to the interface. |
| Step 8 | access-session closed
|
Prevents preauthentication access on the interface. |
| Step 9 | access-session port-control auto
|
Sets the authorization state of a port. |
| Step 10 | dot1x pae both
|
Configures the port as an 802.1X port access entity (PAE) supplicant and authenticator. |
| Step 11 | dot1x credentials profile
|
Assigns a 802.1x credentials profile to the interface. |
| Step 12 | dot1x supplicant eap profile
name
|
Assigns the EAP-TLS profile to the interface. |
| Step 13 | service-policy type control subscriber
control-policy name
|
Applies a subscriber control policy to the interface. |
| Step 14 | exit
|
Returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
| Step 15 | show macsec interface
|
Displays MACsec details for the interface. |
| Step 16 | copy running-config startup-config
|
(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file. |
Verifying Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
The show mka sessions command displays a summary of active MACsec Key Agreement (MKA) Protocol sessions.
Device# show mka sessions
Total MKA Sessions....... 1
Secured Sessions... 1
Pending Sessions... 0
====================================================================================================
Interface Local-TxSCI Policy-Name Inherited Key-Server
Port-ID Peer-RxSCI MACsec-Peers Status CKN
====================================================================================================
Te0/1/3 74a2.e625.4413/0013 *DEFAULT POLICY* NO YES
19 74a2.e625.4c22/0012 1 Secured 1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Device# show macsec status interface te0/1/2 Capabilities: Ciphers Supported: GCM-AES-128 GCM-AES-256 Cipher: GCM-AES-128 Confidentiality Offset: 0 Replay Window: 64 Delay Protect Enable: FALSE Access Control: must-secure Transmit SC: SCI: 74A2E6254C220012 Transmitting: TRUE Transmit SA: Next PN: 412 Delay Protect AN/nextPN: 99/0 Receive SC: SCI: 74A2E62544130013 Receiving: TRUE Receive SA: Next PN: 64 AN: 0 Delay Protect AN/LPN: 0/0
Device# show access-session interface te1/0/1 details
Interface: TenGigabitEthernet1/0/1
IIF-ID: 0x17298FCD
MAC Address: f8a5.c592.13e4
IPv6 Address: Unknown
IPv4 Address: Unknown
User-Name: DOT1XCRED
Status: Authorized
Domain: DATA
Oper host mode: multi-host
Oper control dir: both
Session timeout: N/A
Common Session ID: 000000000000000BB72E8AFA
Acct Session ID: Unknown
Handle: 0xc3000001
Current Policy: MUSTS_1
Local Policies:
Security Policy: Must Secure
Security Status: Link Secured
Server Policies:
Method status list:
Method State
dot1xSup Authc Success
dot1x Authc Success
Configuration Examples for Certificate-based MACsec Encryption
Example: Enrolling the Certificate
Configure Crypto PKI Trustpoint: crypto pki trustpoint POLESTAR-IOS-CA enrollment terminal subject-name CN=ASR1000x1@polestar.com, C=IN, ST=KA, OU=ENG,O=Polestar revocation-check none rsakeypair mkaioscarsa storage nvram: ! Manual Installation of Root CA certificate: crypto pki authenticate POLESTAR-IOS-CA
Example: Enabling 802.1x Authentication and AAA Configuration
aaa new-model dot1x system-auth-control radius server ISE address ipv4 <ISE ipv4 address> auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 automate-tester username dummy key dummy123 radius-server deadtime 2 ! aaa group server radius ISEGRP server name ISE ! aaa authentication dot1x default group ISEGRP aaa authorization network default group ISEGRP
Example: Configuring EAP-TLS Profile and 802.1X Credentials
eap profile EAPTLS-PROF-IOSCA method tls pki-trustpoint POLESTAR-IOS-CA ! dot1x credentials EAPTLSCRED-IOSCA username asr1000@polestar.company.com pki-trustpoint POLESTAR-IOS-CA !
Example: Applying 802.1X, PKI, and MACsec Configuration on the Interface
interface TenGigabitEthernet0/1 macsec network-link authentication periodic authentication timer reauthenticate <reauthentication interval> access-session host-mode multi-host access-session closed access-session port-control auto dot1x pae both dot1x credentials EAPTLSCRED-IOSCA dot1x supplicant eap profile EAPTLS-PROF-IOSCA service-policy type control subscriber DOT1X_POLICY_RADIUS
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Security commands |
|
Standards and RFCs
|
Standard/RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
IEEE 802.1AE |
Media Access Control (MAC) Security |
|
IEEE 802.1X-2010 |
Port-Based Network Access Control |
|
RFC 4493 |
The AES-CMAC Algorithm |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
 Feedback
Feedback