- Configuring ERSPAN
- Configuring Routing Between VLANs with IEEE 802.1Q Encapsulation
- IEEE 802.1Q-in-Q VLAN Tag Termination
- VLAN Mapping to Gigabit EtherChannel Member Links
- Configuring Routing Between VLANs
- EtherChannel Flow-Based Limited 1 1 Redundancy
- Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- VLANs over IP Unnumbered SubInterfaces
- Resilient Ethernet Protocol (REP)
- REP Access Gateway
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Information About Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- How to Enable Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Configuration Examples for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Information About Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
The Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing feature allows different flows of traffic over a Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) interface to be identified based on the packet header and then mapped to the different member links of the port channel. This feature enables you to apply flow-based load balancing and VLAN-manual load balancing to specific port channels.
- Finding Feature Information
- Restrictions for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Information About Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- How to Enable Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Configuration Examples for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Information About Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
- Additional References
- Feature Information for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Restrictions for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
Information About Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
Flow-Based Load Balancing
Flow-based load balancing identifies different flows of traffic based on the key fields in the data packet. For example, IPv4 source and destination IP addressees can be used to identify a flow. The various data traffic flows are then mapped to the different member links of a port channel. After the mapping is done, the data traffic for a flow is transmitted through the assigned member link. The flow mapping is dynamic and changes when there is any change in the state of a member link to which a flow is assigned. The flow mappings can also change if member links are added to or removed from the GEC interface. Multiple flows can be mapped to each member link.
Buckets for Flow-Based Load Balancing
Load balancing dynamically maps traffic flows to the member links of a GEC interface through the concept of buckets. The various defined traffic flows are mapped to the buckets and the buckets are evenly distributed among the member links. Each port channel maintains 16 buckets, with one active member link associated with each bucket. All traffic flows mapped to a bucket use the member link to which the bucket is assigned.
The router creates the buckets-to-member links mappings when you apply flow-based load balancing to a port channel and the port channel has at least one active member link. The mappings are also created when the first member link is added, or comes up, and the load-balancing method is set to flow-based.
When a member link goes down or is removed from a port channel, the buckets associated with that member link are redistributed among the other active member links in a round-robin fashion. When a member link comes up or is added to a port channel, some of the buckets associated with other links are assigned to this link.
The figure below illustrates an example of 16 buckets distributed among three member links. The numbers shown in the buckets are the bucket IDs. Note that the first member link has an extra bucket.
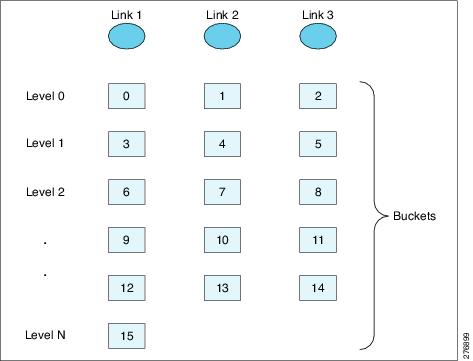
If you change the load-balancing method, the bucket-to-member link mappings for flow-based load balancing are deleted. The mappings are also deleted if the port channel is deleted or the last member link in the port channel is deleted or goes down.
Load Balancing on Port Channels
GEC interfaces can use either dynamic flow-based load balancing or VLAN-manual load balancing. You can configure the load-balancing method globally for all port channels or directly on specific port channels. The global configuration applies only to those port channels for which you have not explicitly configured load balancing. The port-channel configuration overrides the global configuration.
Flow-based load balancing is enabled by default at the global level. You must explicitly configure VLAN load balancing or the load-balancing method is flow-based.
For more information about configuring VLAN load balancing, see the module VLAN Mapping to Gigabit EtherChannel (GEC) Member Links.
The table below lists the load-balancing method that is applied to port channels based on the configuration:
|
Global Configuration |
Port-Channel Configuration |
Load Balancing Applied |
|---|---|---|
|
Not configured |
Not configured |
Flow-based |
|
|
Flow-based |
Flow-based |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
VLAN-manual |
|
VLAN-manual |
Not configured |
VLAN-manual |
|
Flow-based |
Flow-based |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
VLAN-manual |
The table below lists the configuration that results if you change the global load-balancing method.
|
Port-Channel Configuration |
Global Configuration |
Action Taken at Port Channel |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
– |
From |
To |
– |
|
Not configured |
Not configured |
VLAN-manual |
Changed from flow-based to VLAN-manual |
|
VLAN-manual |
Not configured |
Changed from VLAN-manual to flow-based |
|
|
Configured |
Any |
Any |
No change |
The table below lists the configuration that results if you change the port-channel load-balancing method.
|
Global Configuration |
Port-Channel Configuration |
Action Taken at Port Channel |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
– |
From |
To |
– |
|
Not configured |
Not configured |
VLAN-manual |
Changed from flow-based to VLAN-manual |
|
Not configured |
Flow-based |
No action taken |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
Flow-based |
Changed from VLAN-manual to flow-based |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
Not configured |
Changed from VLAN-manual to flow-based |
|
|
Flow-based |
VLAN-manual |
Changed from flow-based to VLAN-manual |
|
|
Flow-based |
Not configured |
No action taken |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
Not configured |
VLAN-manual |
No action taken |
|
Not configured |
Flow-based |
Changed from VLAN-manual to flow-based |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
Flow-based |
Changed from VLAN-manual to flow-based |
|
|
VLAN-manual |
Not configured |
No action taken |
|
|
Flow-based |
VLAN-manual |
Changed from flow-based to VLAN-manual |
|
|
Flow-based |
Not configured |
Changed from flow-based to VLAN-manual |
How to Enable Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
- Configuring Load Balancing on a Port Channel
- Verifying Load-Balancing Configuration on a GEC Interface
Configuring Load Balancing on a Port Channel
To configure load balancing on a port channel, perform the following steps. Repeat these steps for each GEC interface.
If you have already configured your desired load-balancing method globally and want to use that method for all port channels, you need not perform this task. To configure load balancing globally, use the port-channel load-balancing vlan-manual command. If you do not configure the global command, flow-based load balancing is applied to all port channels.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
interface
port-channel
channel-number
4.
load-balancing
{flow | vlan}
5.
end
DETAILED STEPS
Verifying Load-Balancing Configuration on a GEC Interface
Use these show commands to verify the load-balancing configuration and to display information about the bucket distribution on the port channel. You can use these commands in any order.
1.
show
running-config
interface
port-channel
channel-number
2.
show
etherchannel
load-balancing
3.
show
interfaces
port-channel
channel-number
etherchannel
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
show
running-config
interface
port-channel
channel-number
Use this command to verify the configuration of the port channel. Example: Router# show running-config interface port-channel 1 Building configuration... Current configuration : 88 bytes ! interface Port-channel1 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 no negotiation auto load-balancing flow end |
| Step 2 |
show
etherchannel
load-balancing
Use this command to display the load-balancing method applied to each port channel. The following example shows output for a configuration with load balancing set globally to VLAN-manual and set to flow-based on port channel 1: Example:
Router# show etherchannel load-balancing
EtherChannel Load-Balancing Method:
Global LB Method: vlan-manual
Port-Channel: LB Method
Port-channel1 : flow-based
|
| Step 3 |
show
interfaces
port-channel
channel-number
etherchannel
Use this command to display the bucket distribution currently in use. The following example shows output for an interface with load balancing set to flow-based: Example:
Router(config)# show interface port-channel 2 etherchannel
All IDBs List contains 3 configured interfaces
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/6 (index: 0)
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/7 (index: 1)
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/0 (index: 2)
Active Member List contains 1 interfaces
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/0
Passive Member List contains 2 interfaces
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/6
Port: GigabitEthernet2/1/7
Load-Balancing method applied: flow-based
Bucket Information for Flow-Based LB:
Interface: Buckets
GigabitEthernet2/1/0:
Bucket 0 , Bucket 1 , Bucket 2 , Bucket 3
Bucket 4 , Bucket 5 , Bucket 6 , Bucket 7
Bucket 8 , Bucket 9 , Bucket 10, Bucket 11
Bucket 12, Bucket 13, Bucket 14, Bucket 15
|
Configuration Examples for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
Flow-Based Load Balancing Example
The following example shows a configuration where flow-based load balancing is configured on port-channel 2 while the VLAN-manual method is configured globally:
! no aaa new-model port-channel load-balancing vlan-manual ip source-route . . . interface Port-channel2 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 no negotiation auto load-balancing flow ! interface Port-channel2.10 ip rsvp authentication key 11223344 ip rsvp authentication ! interface Port-channel2.50 encapsulation dot1Q 50 ! interface GigabitEthernet2/1/0 no ip address negotiation auto cdp enable channel-group 2 !
Information About Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
The five-tuple hash support for gigabit etherchannel (GEC) flow-based load balancing feature decides which member link to use for routing traffic based on the following five parameters:
-
Destination IP address
-
Source Port
-
Destination Port
-
Protocol ID (type of protocol: TCP/UDP)
Earlier, the GEC flow-based load balancing feature was applicable only for layer 3 (network layer). With the five-tuple hash support, it’s applicable for layer 4 (TCP/IP layer) also. But it is supported only for the TCP and UDP, layer 4 protocols.
- Restrictions for Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
- Configuring Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
Restrictions for Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
The five-tuple hash support for GEC flow-based load balancing feature is not supported for MPLS traffic.
Configuring Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing
Use the port-channel load-balance-hash-algo command to enable the five-tuple hash support for GEC flow-based load balancing feature.
The following example shows how to configure a five-tuple hash support for GEC flow-based load balancing feature:
Device (config)# port-channel load-balance-hash-algo ? src-dst-ip Source XOR Destination IP Addr src-dst-mixed-ip-port Source XOR Destination Port, IP addr
The src-dst-mixed-ip-port option specifies load distribution based on the hash value obtained from the calculation of five parameters: source ip address, destination ip address, source port, destination port, and L4 protocol.
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing feature.
Related Documents
|
Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS commands |
|
|
Cisco IOS LAN switching commands |
Cisco IOS LAN Switching Command Reference |
Standards
|
Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS XE software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
|
RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.|
Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Flow-Based per Port-Channel Load Balancing |
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.5 |
This feature allows different flows of traffic over a GEC interface to be identified and mapped to the different member links. It also enables you to apply load balancing to specific port channels. The following commands were introduced or modified: load-balancing, port-channel load-balancing vlan-manual, show etherchannel load-balancing, show interfaces port-channel etherchannel. |
|
IPv6 Loadbalancing on GEC |
Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S |
The IPv6 Loadbalancing on GEC feature provides load balancing for IPv6 traffic on Gigabit EtherChannel. |
|
Five-Tuple Hash Support for GEC Flow-based Load Balancing |
Cisco IOS XE Everest 16.4.1 |
The five-tuple hash support for gigabit etherchannel (GEC) flow-based load balancing feature decides which member link to use for routing traffic based on the hash value obtained from the calculation of 5 parameters: source ip address, destination ip address, source port, destination port, and L4 protocol. |
 Feedback
Feedback