- Locator ID Separation Protocol (LISP) Overview
- Configuring LISP (Locator ID Separation Protocol)
- LISP Multicast
- LISP Shared Model Virtualization
- LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- LISP Host Mobility Across Subnet
- LISP Delegate Database Tree (DDT)
- LISP ESM Multihop Mobility
- LISP Support for Disjoint RLOC Domains
- Redistribution of RIB Routes into LISP
- Export Map Server Site Database in Map Server
- LISP Data Plane Security
- LISP Reliable Registration
- Overlapping Prefix
- LISP Generalized SMR
- TTL Propagate Disable and Site-ID Qualification
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Finding Feature Information
- Information About LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- How to Configure LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Configuration Examples for LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Additional References
- Feature Information for LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest caveats and feature information, see Bug Search Tool and the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the feature information table.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Information About LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Overview of LISP Virtualization
- LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- LISP Parallel Model Virtualization Architecture
- LISP Parallel Model Virtualization Implementation Considerations and Caveats
Overview of LISP Virtualization
Deploying physical network infrastructure requires both capital investments for hardware, as well as manpower investments for installation and operational management support. When distinct user groups within an organization desire to control their own networks, it rarely makes economic sense for these user groups to deploy and manage separate physical networks. Physical plants are rarely utilized to their fullest, resulting in stranded capacity (bandwidth, processor, memory, etc.). In addition, the power, rack space, and cooling needs to physical plants do not satisfy modern “green” requirements. Network virtualization offers the opportunity to satisfy organizational needs, while efficiently utilizing physical assets.
The purpose of network virtualization, as shown in the figure below, is to create multiple, logically separated topologies across one common physical infrastructure.
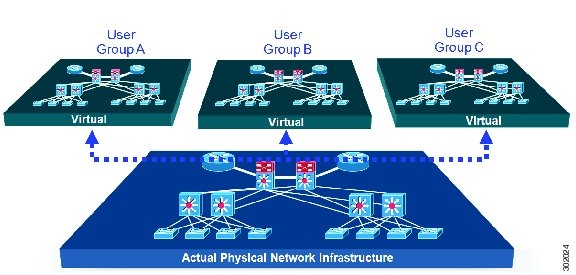
When considering the deployment of a virtualized network environment, take into account both the device and the path level.
Device Level Virtualization
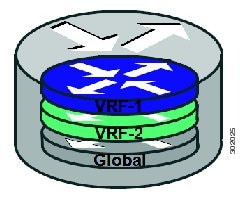
Virtualization at the device level entails the use of the virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) to create multiple instances of Layer 3 routing tables, as illustrated in the figure below. VRFs provide segmentation across IP addresses, allowing for overlapped address space and traffic separation. Separate routing, QoS, security, and management policies can be applied to each VRF instance. An IGP or EGP routing process is typically enabled within a VFR, just as it would be in the global (default) routing table. As described in detail below, LISP binds VRFs to instance IDs for similar purposes.
Path Level Virtualization
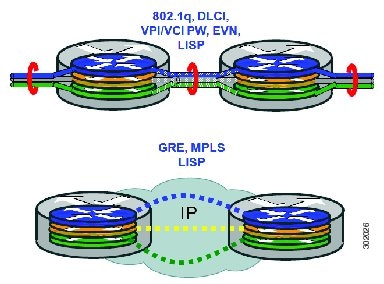
VRF table separation is maintained across network paths using any number of traditional mechanisms, as illustrated in the figure below. Single-hop path segmentation (hop-by-hop) is typically accomplished by techniques such as 802.1q VLANs, VPI/VCI PW, or EVN. LISP can also be used. Traditional multi-hop mechanisms include MPLS and GRE tunnels. As described in detail below, LISP binds VRFs to instance IDs (IIDs), and then these IIDs are included in the LISP header to provide data plane (traffic flow) separation for single or multihop needs.
LISP Virtualization at the Device Level
Recalling that LISP implements Locator ID separation and, in so doing, creates two namespaces (EIDs and RLOCs), it is easy to see that LISP virtualization can consider both EID and RLOC namespaces for virtualization. That is, either or both can be virtualized.
EID virtualization—Enabled by binding a LISP instance ID to an EID VRF. Instance IDs are numerical tags defined in the LISP canonical address format (LCAF) draft, and are used to maintain address space segmentation in both the control plane and data plane.
RLOC virtualization—Tying locator addresses and associated mapping services to the specific VRF within which they are reachable enables RLOC virtualization.
Because LISP considers virtualization of both EID and RLOC namespaces, two models of operation are defined: shared model and parallel model. For completeness, the discussions below begin first with a review of the default (non-virtualized) model of LISP, and then cover the details of shared and parallel models.
Default (Non-Virtualized) LISP Model
By default, LISP is not virtualized in either EID space or RLOC space. That is, unless otherwise configured, both EID and RLOC addresses are resolved in the default (global) routing table. This concept is illustrated in the figure below.
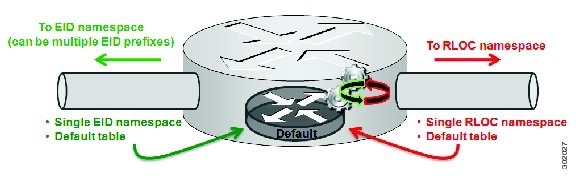
As shown in the figure above, both EID and RLOC addresses are resolved in the default table. The mapping system must also be reachable via the default table. This default model can be thought of as a single instantiation of the parallel model of LISP virtualization where EID and RLOC addresses are within the same namespace such as is the case in this default table.
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
LISP parallel model virtualization ties virtualized EID space associated with VRFs to RLOCs associated with the same or different VRFs. This concept is illustrated in the figure below.
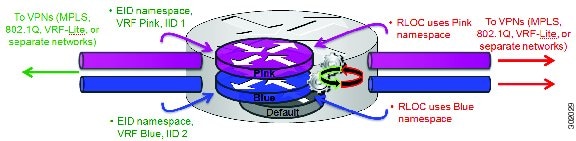
As shown in the figure above, EID space is virtualized through its association with VRFs, and these VRFs are tied to LISP Instance IDs to segment the control plane and data plane in LISP. A common, “shared” locator space, the default (global) table as shown in the figure above, is used to resolve RLOC addresses for all virtualized EIDs. The mapping system must also be reachable via the common locator space as well.
The example illustrated in the figure above shows virtualized EID space associated with a VRF (and bound to an Instance ID) being tied to locator space associated with the same VRF, in this case - Pink/Pink and Blue/Blue. However, this is not required; the EID VRF does not need to match the RLOC VRF. In any case, a mapping system must be reachable via the associated locator space. Multiple parallel instantiations can be defined.
In the most general case, shared model and parallel model may be combined such that multiple EID VRFs share a common RLOC VRF, and multiple instantiations of this architecture are implemented on the same platform, as shown in the figure below.
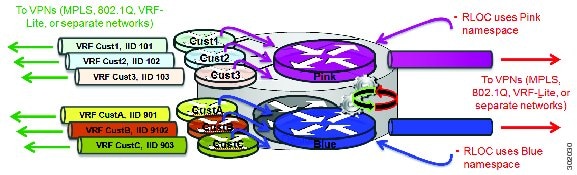
As shown in the figure above, shared and parallel models are combined to associate several EID instances to one shared RLOC VRF, and then several other EID instances to another shared RLOC VRF.
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization Architecture
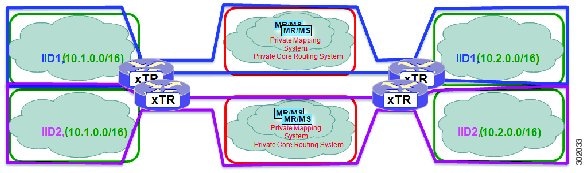
Architecturally, LISP parallel model virtualization can be deployed in single or multitenancy configurations. In the parallel model multitenancy case, a set of xTRs is shared (virtualized) among multiple customers, and each customer uses their own private (segmented) core infrastructure and mapping system. All sites associated with the customer use the same instance ID and are part of a VPN using their own EID namespace as shown in the figure below.
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization Implementation Considerations and Caveats
When the LISP Parallel Model Virtualization is implemented, several important considerations and caveats are important. Each router lisp value instantiation is considered by software to be a separate process. Instance IDs must be unique only within a router lisp instantiation. Review the example below:
xTR-1(config)# vrf definition alpha xTR-1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4 xTR-1(config-vrf-af)# exit xTR-1(config)# vrf definition beta xTR-1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4 xTR-1(config-vrf-af)# exit xTR-1(config-vrf)# vrf definition gamma xTR-1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4 xTR-1(config-vrf-af)# exit xTR-1(config-vrf)# vrf definition delta xTR-1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4 xTR-1(config-vrf-af)# exit xTR-1(config-vrf)# exit xTR-1(config)# router lisp 1 xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# locator-table vrf alpha xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# eid-table vrf beta instance-id 101 xTR-1(config-router-lisp-eid-table)# exit xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# exit xTR-1(config)# router lisp 2 xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# locator-table vrf gamma xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# eid-table vrf delta instance-id 101 xTR-1(config-router-lisp-eid-table)# exit xTR-1(config-router-lisp)# eid-table vrf beta instance-id 201 The vrf beta table is not available for use as an EID table (in use by router lisp 1 EID instance 101 VRF)
In the above example, four VRFs are created; alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. The router lisp instantiation router lisp 1 is created and associated with the locator-table VRF named alpha. Next, the EID table VRF named beta is specified and associated with instance ID 101. Next, a new router lisp instantiation, router lisp 2, is created and associated with the locator-table VRF named gamma. Next, EID table VRF named delta is specified and also associated with instance ID 101. These two instance IDs are unrelated to each other; one is relevant only within router lisp 1 and the other is only relevant within router lisp 2.
In the above example, also observe that while under router lisp 2, an attempt is made to configure an EID table VRF named beta. Note that the router is unable to use this EID table VRF since it (beta) is already associated with an eid-table command within the router lisp 1 instantiation.
You can re-use an instance ID, and which EID VRF it is decapsulated into depends on the router lisp instantiation and locator-table VRF that it is associated with. You cannot connect the same EID VRF to more than one locator-table VRF, however.
How to Configure LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Configure Simple LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
- Verifying and Troubleshooting LISP Virtualization
Configure Simple LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
Perform these tasks to enable and configure LISP ITR/ETR (xTR) functionality and LISP map resolver and map server for LISP parallel model virtualization.
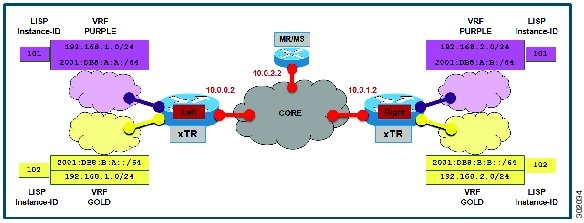
The configuration implemented in this task and illustrated in the figure below is for two LISP sites that are connected in parallel mode. Each LISP site uses a single edge router configured as both an ITR and ETR (xTR), with a single connection to its upstream provider. However, the upstream connection is VLAN-segmented to maintain RLOC space separation within the core. Two VRFs are defined here: BLUE and GREEN. IPv4 RLOC space is used in each of these parallel networks. Both IPv4 and IPv6 EID address space is used. The LISP site registers to one map server/map resolver (MS/MR), which is segmented to maintain the parallel model architecture of the core network.
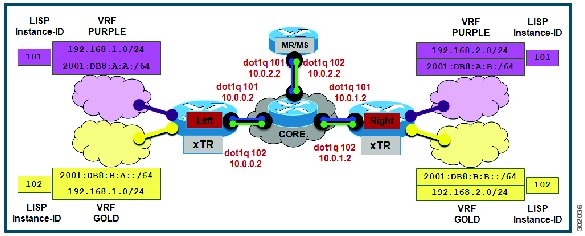
The components illustrated in the topology shown in the figure above are described below:
-
LISP site: -
The CPE functions as a LISP ITR and ETR (xTR).
-
Both LISP xTRs have two VRFs: GOLD and PURPLE, with each VRF containing both IPv4 and IPv6 EID-prefixes, as shown in the figure above. Note the overlapping prefixes, used for illustration purposes. A LISP instance-id is used to maintain separation between two VRFs. Note that in this example, the share key is configured “per-VPN.�?
-
Each LISP xTR has a single RLOC connection to a parallel IPv4 core network.
-
Perform the steps in this task (once through for each xTR in the LISP site) to enable and configure LISP ITR and ETR (xTR) functionality when using a LISP map-server and map-resolver for mapping services. The example configurations at the end of this task show the full configuration for two xTRs (Left-xTR and Right-xTR).
The configuration below assumes that the referenced VRFs were created using the vrf definition command.
1.
configure
terminal
2.
router
lisp
lisp-instantiation-number
3.
locator-table
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
4.
eid-table
vrfEID-vrf-name
instance-id
instance-id
5.
database-mapping
EID-prefix/prefix-length
locator
priority
priority
weight
weight
6. Repeat Step 4 until all EID-to-RLOC mappings within this eid-table vrf and instance ID for this LISP site are configured.
7.
exit
8.
ipv4
itr
map-resolver
map-resolver-address
9.
ipv4
etr
map-server
map-server-address
key
key-type
authentication-key
10.
ipv4
itr
11.
ipv4
etr
12.
ipv6
itr
map-resolver
map-resolver-address
13.
ipv6
etr
map-server
map-server-address
key
key-type
authentication-key
14.
ipv6
itr
15.
ipv6
etr
16.
exit
17.
ip
route
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
ipv4-prefix
next-hop
18.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
Example:
The examples below show the complete configuration for the LISP topology illustrated in the figure above and in this task. On the xTRs, the VRFs and EID prefixes are assumed to be attached to VLANs configured on the devices.
Example configuration for the Left xTR:
hostname Left-xTR ! ipv6 unicast-routing ! vrf definition PURPLE address-family ipv4 exit address-family ipv6 exit ! vrf definition GOLD address-family ipv4 exit address-family ipv6 exit ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet1/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 101 vrf forwarding PURPLE ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:A:A::1/64 ! interface Ethernet1/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 102 vrf forwarding GOLD ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:B:A::1/64 ! router lisp eid-table vrf PURPLE instance-id 101 database-mapping 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:A:A::/64 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 eid-table vrf GOLD instance-id 102 database-mapping 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:B:A::/64 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 exit ! ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv4 itr ipv4 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Left-key ipv4 etr ipv6 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv6 itr ipv6 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Left-key ipv6 etr exit ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.1 !
Example configuration for Right xTR:
hostname Right-xTR ! ipv6 unicast-routing ! vrf definition PURPLE address-family ipv4 exit address-family ipv6 exit ! vrf definition GOLD address-family ipv4 exit address-family ipv6 exit ! interface Ethernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet1/0.1 encapsulation dot1q 101 vrf forwarding PURPLE ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:A:B::1/64 ! interface Ethernet1/0.2 encapsulation dot1q 102 vrf forwarding GOLD ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:B:B::1/64 ! router lisp eid-table vrf PURPLE instance-id 101 database-mapping 192.168.2.0/24 10.0.1.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:A:B::/64 10.0.1.2 priority 1 weight 1 eid-table vrf GOLD instance-id 102 database-mapping 192.168.2.0/24 10.0.1.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:B:B::/64 10.0.1.2 priority 1 weight 1 exit ! ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv4 itr ipv4 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Right-key ipv4 etr ipv6 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv6 itr ipv6 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Right-key ipv6 etr exit ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.1.1 !
Configuring a Private LISP Mapping System for LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
Perform this task to configure and enable standalone LISP map server/map resolver functionality for LISP parallel model virtualization. In this task, a Cisco router is configured as a standalone map resolver/map server (MR/MS) for a private LISP mapping system. Because the MR/MS is configured as a stand-alone device, it has no need for LISP alternate logical topology (ALT) connectivity. All relevant LISP sites must be configured to register with this map server so that this map server has full knowledge of all registered EID prefixes within the (assumed) private LISP system.
Mapping system: Figure 9. Simple LISP Site with One IPv4 RLOC and One IPv4 EID 
-
One map resolver/map server (MS/MR) system is shown in the figure above and assumed available for the LISP xTR to register to within the proper parallel RLOC space. The MS/MR has an IPv4 RLOC address of 10.0.2.2, within each VLAN/VRF (Green and Blue) providing parallel model RLOX separation in the IPv4 core.
-
The map server site configurations are virtualized using LISP instance IDs to maintain separation between the two VRFs, PURPLE and GOLD.
-
Repeat this task for all router lisp instantiations and RLOC VRFs.
1.
enable
2.
configure
terminal
3.
router
lisp
lisp-instantiation-number
4.
locator-table
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
5.
site
site-name
6.
authentication-key [key-type]
authentication-key
7.
eid-prefix
instance-id
instance-id
EID-prefix
8.
eid-prefix
instance-id
instance-id
EID-prefix
9.
exit
10.
ipv4
map-resolver
11.
ipv4
map-server
12.
ipv6
map-resolver
13.
ipv6
map-server
14.
exit
15.
ip
route
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
ipv4-prefix
next-hop
16.
exit
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 |
enable
Example: Router> enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. | ||
| Step 2 |
configure
terminal
Example: Router# configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 3 |
router
lisp
lisp-instantiation-number
Example: Router(config)# router lisp |
Creates the specified LISP instantiation number and enters LISP configuration mode ( software only). All subsequent LISP commands apply to that router LISP instantiation. | ||
| Step 4 |
locator-table
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
Example: Router(config)# locator-table vrf BLUE |
Configures a router lisp instantiation to use the specified VRF as RLOC space when encapsulating EIDs and sending control plane packets. | ||
| Step 5 |
site
site-name
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# site Purple |
Specifies a LISP site named Purple and enters LISP site configuration mode. | ||
| Step 6 |
authentication-key [key-type]
authentication-key
Example: Router(config-router-lisp-site)# authentication-key 0 Purple-key |
Configures the password used to create the SHA-2 HMAC hash for authenticating the map register messages sent by an ETR when registering to the map server.
| ||
| Step 7 |
eid-prefix
instance-id
instance-id
EID-prefix
Example: Router(config-router-lisp-site)# eid-prefix instance-id 101 192.168.1.0/24 |
| ||
| Step 8 |
eid-prefix
instance-id
instance-id
EID-prefix
Example: Router(config-router-lisp-site)# eid-prefix instance-id 101 2001:db8:a:a::/64 |
| ||
| Step 9 |
exit
Example: Router(config-router-lisp-site)# exit |
Exits LISP site configuration mode and returns to LISP configuration mode. | ||
| Step 10 |
ipv4
map-resolver
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# ipv4 map-resolver |
Enables LISP map resolver functionality for EIDs in the IPv4 address family within this router lisp instantiation. | ||
| Step 11 |
ipv4
map-server
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# ipv4 map-server |
Enables LISP map server functionality for EIDs in the IPv4 address family within this router lisp instantiation. | ||
| Step 12 |
ipv6
map-resolver
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# ipv6 map-resolver |
Enables LISP map resolver functionality for EIDs in the IPv6 address family within this router lisp instantiation. | ||
| Step 13 |
ipv6
map-server
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# ipv6 map-server |
Enables LISP map server functionality for EIDs in the IPv6 address family within this router lisp instantiation. | ||
| Step 14 |
exit
Example: Router(config-router-lisp)# exit |
Exits LISP configuration mode and returns to global configuration mode. | ||
| Step 15 |
ip
route
vrf
rloc-vrf-name
ipv4-prefix
next-hop
Example: Router(config)# ip route vrf BLUE 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.1 |
Configures a default route to the upstream next hop for all IPv4 destinations, reachable within the specified RLOC VRF. | ||
| Step 16 |
exit
Example: Router(config)# exit |
Exits global configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
Example:
Example configuration for the map server/map resolver.
hostname MSMR ! vrf definition BLUE address-family ipv4 exit ! vrf definition GREEN address-family ipv4 exit ! ipv6 unicast-routing ! interface Ethernet0/0.101 encapsulation dot1Q 101 vrf forwarding BLUE ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface Ethernet0/0.102 encapsulation dot1Q 102 vrf forwarding GREEN ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.0 ! router lisp 1 locator-table vrf BLUE site Purple authentication-key PURPLE-key eid-prefix instance-id 101 192.168.1.0/24 eid-prefix instance-id 101 192.168.2.0/24 eid-prefix instance-id 101 2001:DB8:A:A::/64 eid-prefix instance-id 101 2001:DB8:A:B::/64 ! ipv4 map-server ipv4 map-resolver ipv6 map-server ipv6 map-resolver ! router lisp 2 locator-table vrf GREEN site Gold authentication-key GOLD-key eid-prefix instance-id 102 192.168.1.0/24 eid-prefix instance-id 102 192.168.2.0/24 eid-prefix instance-id 102 2001:DB8:B:A::/64 eid-prefix instance-id 102 2001:DB8:B:B::/64 ! ipv4 map-server ipv4 map-resolver ipv6 map-server ipv6 map-resolver ! ip route vrf GREEN 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.1 ip route vrf BLUE 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.1
Verifying and Troubleshooting LISP Virtualization
After configuring LISP, verifying and troubleshooting LISP configuration and operations may be performed by following the optional steps described below. Note that certain verification and troubleshooting steps may only apply to certain types of LISP devices.
In this task, the topology is shown in the figure below and the configuration is from the “Configure Simple LISP Shared Model Virtualization” task, but the commands are applicable to both LISP shared and parallel model virtualization.
 Note | The following examples do not show every available command and every available output display. Refer to the Cisco IOS LISP Command Reference for detailed explanations of each command. |
1.
enable
2.
show running-config | section router lisp
3.
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
4.
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
map-cache
5.
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
database [eid-table
vrf
vrf-name]
6.
show
lisp
site [name
site-name]
7.
lig {[self {ipv4 |
ipv6}] | {hostname |
destination-EID}
8.
ping {hostname |
destination-EID}
9.
clear [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
map-cache
DETAILED STEPS
| Step 1 |
enable
Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted. Example: Router> enable |
| Step 2 |
show running-config | section router lisp
The show running-config | section router lisp command is useful for quickly verifying the LISP configuration on the device. This command applies to any LISP device. The following is sample output from the show running-config | section router lisp command when a simple LISP site is configured with virtualized IPv4 and IPv6 EID prefixes and a shared IPv4 core: Example: Router# show running-config | section router lisp router lisp eid-table vrf PURPLE instance-id 101 database-mapping 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:A:A::/64 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 eid-table vrf GOLD instance-id 102 database-mapping 192.168.1.0/24 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 database-mapping 2001:DB8:B:A::/64 10.0.0.2 priority 1 weight 1 exit ! ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv4 itr ipv4 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Left-key ipv4 etr ipv6 itr map-resolver 10.0.2.2 ipv6 itr ipv6 etr map-server 10.0.2.2 key Left-key ipv6 etr exit |
| Step 3 |
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
The show ip lisp and show ipv6 lisp commands are useful for quickly verifying the operational status of LISP as configured on the device, as applicable to the IPv4 and IPv6 address families respectively. This command applies to any LISP device. Example: The first example shows a summary of LISP operational status and IPv6 address family information by EID table:
Router# show ipv6 lisp eid-table summary
Instance count: 2
Key: DB - Local EID Database entry count (@ - RLOC check pending
* - RLOC consistency problem),
DB no route - Local EID DB entries with no matching RIB route,
Cache - Remote EID mapping cache size, IID - Instance ID,
Role - Configured Role
Interface DB DB no Cache Incom Cache
EID VRF name (.IID) size route size plete Idle Role
PURPLE LISP0.101 1 0 1 0.0% 0.0% ITR-ETR
GOLD LISP0.102 1 0 1 0.0% 0.0% ITR-ETR
Example: The second example shows LISP operational status and IPv6 address family information for the VRF named PURPLE: Router# show ipv6 lisp eid-table vrf PURPLE Instance ID: 101 Router-lisp ID: 0 Locator table: default EID table: PURPLE Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR): enabled Egress Tunnel Router (ETR): enabled Proxy-ITR Router (PITR): disabled Proxy-ETR Router (PETR): disabled Map Server (MS): disabled Map Resolver (MR): disabled Map-Request source: 2001:DB8:A:A::1 ITR Map-Resolver(s): 10.0.2.2 ETR Map-Server(s): 10.0.2.2 (00:00:24) ITR use proxy ETR RLOC(s): none Example: The third example shows LISP operational status and IPv6 address family information for the instance ID of 101:
Router# show ipv6 lisp instance-id 101
Instance ID: 101
Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR): enabled
Egress Tunnel Router (ETR): enabled
Proxy-ITR Router (PITR): disabled
Proxy-ETR Router (PETR): disabled
Map Server (MS): disabled
Map Resolver (MR): disabled
Map-Request source: 2001:DB8:A:A::1
ITR Map-Resolver(s): 10.0.2.2
ETR Map-Server(s): 10.0.2.2 (00:00:11)
ITR Solicit Map Request (SMR): accept and process
Max SMRs per map-cache entry: 8 more specifics
Multiple SMR suppression time: 60 secs
ETR accept mapping data: disabled, verify disabled
ETR map-cache TTL: 1d00h
|
| Step 4 |
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
map-cache
The show ip lisp map-cache and show ipv6 lisp map-cache commands are useful for quickly verifying the operational status of the map cache on a device configured as an ITR or PITR, as applicable to the IPv4 and IPv6 address families respectively. Example: The following example shows IPv6 mapping cache information based on a configuration when a simple LISP site is configured with virtualized IPv4 and IPv6 EID prefixes and a shared IPv4 core. This example output assumes that a map-cache entry has been received for another site with the IPv6 EID prefix 2001:db8:b:b::/64. Router# show ip lisp map-cache eid-table vrf GOLD LISP IPv6 Mapping Cache for EID-table vrf GOLD (IID 102), 2 entries ::/0, uptime: 01:09:52, expires: never, via static send map-request Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request 2001:DB8:B:B::/64, uptime: 00:00:10, expires: 23:59:42, via map-reply, complete Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt 10.0.1.2 00:00:10 up 1/1 |
| Step 5 |
show [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
database [eid-table
vrf
vrf-name]
The show ip lisp database and show ipv6 lisp database commands are useful for quickly verifying the operational status of the database mapping on a device configured as an ETR, as applicable to the IPv4 and IPv6 address families respectively. Example: The following example shows IPv6 mapping database information for the VRF named GOLD. Router# show ipv6 lisp database eid-table vrf GOLD LISP ETR IPv6 Mapping Database for EID-table vrf GOLD (IID 102), LSBs: 0x1, 1 entries EID-prefix: 2001:DB8:B:A::/64 10.0.0.2, priority: 1, weight: 1, state: site-self, reachable |
| Step 6 |
show
lisp
site [name
site-name]
The show lisp site command is useful for quickly verifying the operational status of LISP sites, as configured on a map server. This command only applies to a device configured as a map server. The following example output is based on a configuration when a simple LISP site is configured with virtualized IPv4 and IPv6 EID prefixes and shows the information for the instance ID of 101. Example:
Router# show lisp site instance-id 101
LISP Site Registration Information
Site Name Last Up Who Last Inst EID Prefix
Register Registered ID
Left 00:00:36 yes 10.0.0.2 101 192.168.1.0/24
00:00:43 yes 10.0.0.2 101 2001:DB8:A:A::/64
Right 00:00:31 yes 10.0.1.2 101 192.168.2.0/24
00:00:02 yes 10.0.1.2 101 2001:DB8:A:B::/64
Example: This second example shows LISP site information for the IPv6 EID prefix of 2001:db8:a:a:/64 and instance ID of 101.
Router# show lisp site 2001:db8:a:a:/64 instance-id 101
LISP Site Registration Information
Site name: Left
Allowed configured locators: any
Requested EID-prefix:
EID-prefix: 2001:DB8:A:A::/64 instance-id 101
First registered: 02:41:55
Routing table tag: 0
Origin: Configuration
Registration errors:
Authentication failures: 4
Allowed locators mismatch: 0
ETR 10.0.0.2, last registered 00:00:22, no proxy-reply, no map-notify
TTL 1d00h
Locator Local State Pri/Wgt
10.0.0.2 yes up 1/1
|
| Step 7 |
lig {[self {ipv4 |
ipv6}] | {hostname |
destination-EID}
The LISP Internet Groper (lig) command is useful for testing the LISP control plane. The lig command can be used to query for the indicated destination hostname or EID, or the routers local EID-prefix. This command provides a simple means of testing whether a destination EID exists in the LISP mapping database system, or your site is registered with the mapping database system. This command is applicable for both the IPv4 and IPv6 address families and applies to any LISP device that maintains a map cache (for example, if configured as an ITR or PITR). The following example output is based on a configuration when a simple LISP site is configured with virtualized IPv4 and IPv6 EID prefixes and shows the information for the instance ID of 101 and the IPv4 EID prefix of 192.168.2.1. Example: Router# lig instance-id 101 192.168.2.1 Mapping information for EID 192.168.2.1 from 10.0.1.2 with RTT 12 msecs 192.168.2.0/24, uptime: 00:00:00, expires: 23:59:52, via map-reply, complete Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt 10.0.1.2 00:00:00 up 1/1 Example: This second example output shows information about the VRF named PURPLE: Router# lig eid-table vrf PURPLE self Mapping information for EID 192.168.1.0 from 10.0.0.1 with RTT 20 msecs 192.168.1.0/24, uptime: 00:00:00, expires: 23:59:52, via map-reply, self Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt 10.0.0.1 00:00:00 up, self 1/1 |
| Step 8 |
ping {hostname |
destination-EID}
The following example output from the ping command is based on a configuration when a simple LISP site is configured with virtualized IPv4 and IPv6 EID prefixes. (Note that ping is not a LISP command and does not know about an EID table or an instance ID. When virtualization is included, output limiters can only be specified by VRF.) Example: Router# ping vrf PURPLE 2001:DB8:a:b::1 source 2001:DB8:a:a::1 rep 100 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 100, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:A:B::1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 2001:DB8:A:A::1%PURPLE !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (100/100), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/1 ms Example: Router# ping vrf GOLD Protocol [ip]: ipv6 Target IPv6 address: 2001:db8:b:b::1 Repeat count [5]: Datagram size [100]: Timeout in seconds [2]: Extended commands? [no]: y Source address or interface: 2001:db8:b:a::1 . . . Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2001:DB8:B:B::1, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 2001:DB8:B:A::1%GOLD !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/0/0 ms |
| Step 9 |
clear [ip |
ipv6]
lisp
map-cache
The clear ip lisp map-cache and clear ipv6 lisp map-cache commands remove all IPv4 or IPv6 dynamic LISP map-cache entries stored by the router. This can be useful trying to quickly verify the operational status of the LISP control plane. This command applies to a LISP device that maintains a map cache (for example, if configured as an ITR or PITR). Example: The following example displays IPv4 mapping cache information for instance ID 101, shows the command used to clear the mapping cache for instance ID 101, and displays the show information after clearing the cache. Router# show ip lisp map-cache instance-id 101 LISP IPv4 Mapping Cache for EID-table vrf PURPLE (IID 101), 2 entries 0.0.0.0/0, uptime: 00:25:17, expires: never, via static send map-request Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request 192.168.2.0/24, uptime: 00:20:13, expires: 23:39:39, via map-reply, complete Locator Uptime State Pri/Wgt 10.0.1.2 00:20:13 up 1/1 Router# clear ip lisp map-cache instance-id 101 Router# show ip lisp map-cache instance-id 101 LISP IPv4 Mapping Cache, 1 entries 0.0.0.0/0, uptime: 00:00:02, expires: never, via static send map-request Negative cache entry, action: send-map-request |
Configuration Examples for LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
Complete configuration examples are available within each task under the “How to Configure LISP Parallel Model Virtualization” section.
Additional References
Related Documents
|
Document Title |
Location |
|---|---|
|
Cisco IOS IP Routing: LISP Command Reference |
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_lisp/command/ip-lisp-cr-book.html |
|
Enterprise IPv6 Transitions Strategy Using the Locator/ID Separation Protocol |
|
|
Cisco IOS LISP0 Virtual Interface, Application Note, Version 1.0 |
|
|
Cross-Platform Release Notes for Cisco IOS Release 15.2M&T |
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/15_2m_and_t/release/notes/15_2m_and_t.html |
Standards
|
Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
|
IANA Address Family Numbers |
http://www.iana.org/assignments/address-family-numbers/address-family-numbers.xml |
MIBs
|
MIB |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
|
None |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/go/mibs |
RFCs
|
RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
|
draft-ietf-lisp-22 |
Locator/ID Separation Protocol (LISP) http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-lisp-22 |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-ms-16 |
LISP Map Server http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-lisp-ms-16 |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-alt-10 |
LISP Alternative Topology (LISP+ALT) http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-lisp-alt-10 |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-LCAF-06 |
LISP Canonical Address Format (LCAF) http://tools.ietf.org/wg/lisp/ |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-interworking-06 |
Interworking LISP with IPv4 and IPv6 http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-lisp-interworking-06 |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-lig-06 |
LISP Internet Groper (LIG) http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-lisp-lig-06 |
|
draft-ietf-lisp-mib-03 |
LISP MIB http://tools.ietf.org/wg/lisp/draft-ietf-lisp-mib/ |
Technical Assistance
|
Description |
Link |
|---|---|
|
The Cisco Support and Documentation website provides online resources to download documentation, software, and tools. Use these resources to install and configure the software and to troubleshoot and resolve technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support and Documentation website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for LISP Parallel Model Virtualization
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
|
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization |
15.2(3)T |
LISP Parallel Model Virtualization ties virtualized EID space associated with VRFs to RLOCs associated with the same or different VRFs. |
 Feedback
Feedback