- Cisco BGP Overview
- Configuring a Basic BGP Network
- Configuring Multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP) Support for CLNS
- Connecting to a Service Provider Using External BGP
- Configuring BGP Neighbor Session Options
- Configuring Internal BGP Features
- Configuring Advanced BGP Features
- BGP Link Bandwidth
- iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
- BGP Multipath Load Sharing for Both eBGP and iBGP in an MPLS-VPN
- Loadsharing IP Packets over More Than Six Parallel Paths
- BGP Policy Accounting Output Interface Accounting
- BGP Cost Community
- BGP Support for IP Prefix Import from Global Table into a VRF Table
- BGP per Neighbor SoO Configuration
- Per-VRF Assignment of BGP Router ID
- BGP Next Hop Unchanged
- BGP Support for the L2VPN Address Family
- BGP 4 MIB Support for Per-Peer Received Routes
- BGP Event-Based VPN Import
- BGP Best External
- BGP PIC Edge for IP and MPLS-VPN
iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
This feature module describes the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature. This feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple iBGP paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed in the IP routing table of the router.
Finding Feature Information
Your software release may not support all the features documented in this module. For the latest feature information and caveats, see the release notes for your platform and software release. To find information about the features documented in this module, and to see a list of the releases in which each feature is supported, see the Feature Information Table at the end of this document.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
iBGP Multipath Load Sharing Overview
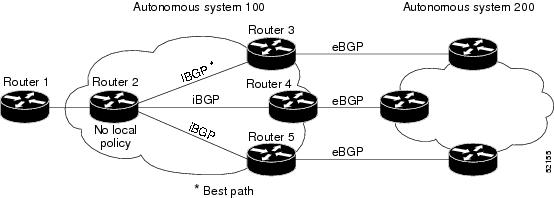
When a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) speaking router with no local policy configured receives multiple network layer reachability information (NLRI) from the internal BGP (iBGP) for the same destination, the router will choose one iBGP path as the best path. The best path is then installed in the IP routing table of the router. For example, in the figure below, although there are three paths to autonomous system 200, Router 2 determines that one of the paths to autonomous system 200 is the best path and uses this path only to reach autonomous system 200.
| Figure 1 | Non-MPLS Topology with One Best Path |
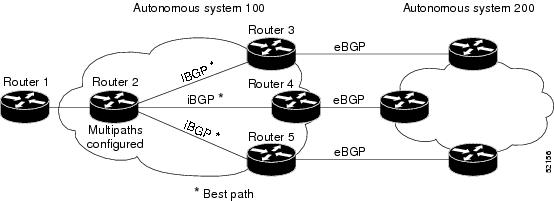
The iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature enables the BGP speaking router to select multiple iBGP paths as the best paths to a destination. The best paths or multipaths are then installed in the IP routing table of the router. For example, on router 2 in the figure below, the paths to routers 3, 4, and 5 are configured as multipaths and can be used to reach autonomous system 200, thereby equally sharing the load to autonomous system 200.
| Figure 2 | Non-MPLS Topology with Three Multipaths |
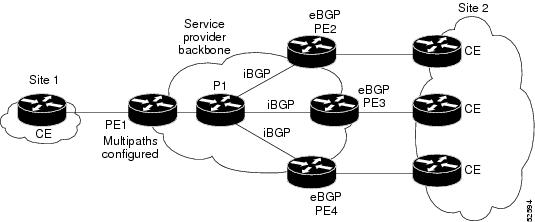
The iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature functions similarly in a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN) with a service provider backbone. For example, on router PE1 in the figure below, the paths to routers PE2, PE3, and PE4 can be selected as multipaths and can be used to equally share the load to site 2.
| Figure 3 | MPLS VPN with Three Multipaths |
For multiple paths to the same destination to be considered as multipaths, the following criteria must be met:
- All attributes must be the same. The attributes include weight, local preference, autonomous system path (entire attribute and not just length), origin code, Multi Exit Discriminator (MED), and Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) distance.
- The next hop router for each multipath must be different.
Even if the criteria are met and multiple paths are considered multipaths, the BGP speaking router will still designate one of the multipaths as the best path and advertise this best path to its neighbors.
Benefits of iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
Configuring multiple iBGP best paths enables a router to evenly share the traffic destined for a particular site.
Restrictions on iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
Route Reflector Limitation
With multiple iBGP paths installed in a routing table, a route reflector will advertise only one of the paths (one next hop).
Memory Consumption Restriction
Each IP routing table entry for a BGP prefix that has multiple iBGP paths uses approximately 350 bytes of additional memory. We recommend not using this feature on a router with a low amount of available memory and especially when the router is carrying a full Internet routing table.
How To Configure iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
- Configuring iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
- Verifying iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
- Monitoring and Maintaining iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
Configuring iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
To configure the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature, use the following command in router configuration mode:
| Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router(config-router)# maximum-paths ibgp maximum-number |
Controls the maximum number of parallel iBGP routes that can be installed in a routing table. |
Verifying iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
To verify that the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature is configured correctly, perform the following steps:
DETAILED STEPS
Monitoring and Maintaining iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
To display iBGP Multipath Load Sharing information, use the following commands in EXEC mode, as needed:
| Command |
Purpose |
|---|---|
Router# show ip bgp ip-prefix |
Displays attributes and multipaths for a network in a non-MPLS topology. |
Router# show ip bgp vpnv4 all ip-prefix |
Displays attributes and multipaths for a network in an MPLS VPN. |
Router# show ip route ip-prefix |
Displays routing information for a network in a non-MPLS topology. |
Router# show ip route vrf vrf-name ip-prefix |
Displays routing information for a network in an MPLS VPN. |
Configuration Examples
Both examples assume that the appropriate attributes for each path are equal and that the next hop router for each multipath is different.
- Example iBGP Multipath Load Sharing in a Non-MPLS Topology
- Example iBGP Multipath Load Sharing in an MPLS VPN Topology
Example iBGP Multipath Load Sharing in a Non-MPLS Topology
The following example shows how to set up the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature in a non-MPLS topology (see the figure below).
| Figure 4 | Non-MPLS Topology Example |

Router 2 Configuration
router bgp 100 maximum-paths ibgp 3
Example iBGP Multipath Load Sharing in an MPLS VPN Topology
The following example shows how to set up the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature in an MPLS VPN topology (see the figure below).
| Figure 5 | MPLS VPN Topology Example |

Router PE1 Configuration
router bgp 100 address-family ipv4 unicast vrf site2 maximum-paths ibgp 3
Additional References
The following sections provide references related to the iBGP Multipath Load Sharing feature.
Related Documents
| Related Topic |
Document Title |
|---|---|
| BGP multipath load sharing for both eBGP and iBGP in an MPLS-VPN |
"BGP Multipath Load Sharing for Both eBGP and iBGP in an MPLS-VPN" |
| Advertising the bandwidth of an autonomous system exit link as an extended community |
" BGP Link Bandwidth" |
| BGP commands |
Cisco IOS IP Routing: BGP Command Reference |
| Cisco IOS master command list, all releases |
Standards
| Standard |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified standards are supported by this feature, and support for existing standards has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
MIBs
| MIBs |
MIBs Link |
|---|---|
| No new or modified MIBs are supported by this feature, and support for existing MIBs has not been modified by this feature. |
To locate and download MIBs for selected platforms, Cisco IOS XE software releases, and feature sets, use Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL: |
RFCs
| RFC |
Title |
|---|---|
| No new or modified RFCs are supported by this feature, and support for existing RFCs has not been modified by this feature. |
-- |
Technical Assistance
| Description |
Link |
|---|---|
| The Cisco Support website provides extensive online resources, including documentation and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. To receive security and technical information about your products, you can subscribe to various services, such as the Product Alert Tool (accessed from Field Notices), the Cisco Technical Services Newsletter, and Really Simple Syndication (RSS) Feeds. Access to most tools on the Cisco Support website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. |
Feature Information for iBGP Multipath Load Sharing
The following table provides release information about the feature or features described in this module. This table lists only the software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that software release train also support that feature.
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to www.cisco.com/go/cfn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
| Table 1 | Feature Information for iBGP Multipath Load Sharing |
| Feature Name |
Releases |
Feature Information |
|---|---|---|
| iBGP multipath load sharing |
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1 |
This feature was introduced on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. The following commands were modified by this feature: maximum paths ibgp, show ip bgp, show ip bgp vpnv4, show ip route, show ip route vrf. |
Cisco and the Cisco Logo are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. A listing of Cisco's trademarks can be found at www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1005R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
 Feedback
Feedback