Understanding External Storage Management
A Cisco HyperFlex System provides consolidated access to both SAN storage and Network Attached Storage (NAS) over the unified fabric. By unifying storage access, a Cisco Unified Computing System can access storage over Ethernet, Fibre Channel, Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), and iSCSI.
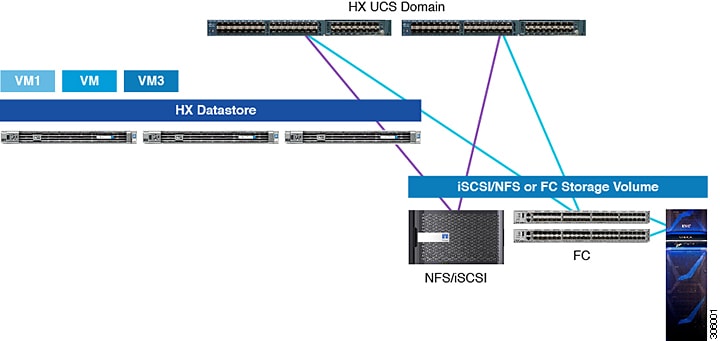
The following image depicts a Cisco HyperFlex System integrated with external storage.

 Feedback
Feedback