Preparation for Appliance Configuration Overview
Before you can successfully configure your Cisco DNA Center appliance, first complete the following tasks:
-
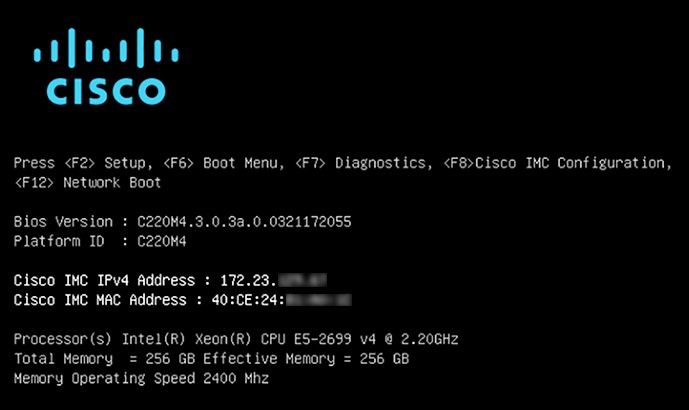
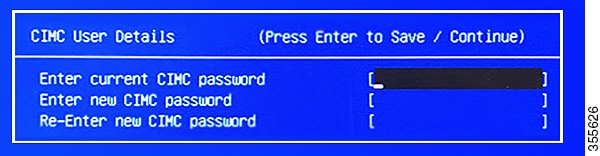
Enable browser access to the appliance's Cisco IMC (see Enable Browser Access to Cisco Integrated Management Controller).
-
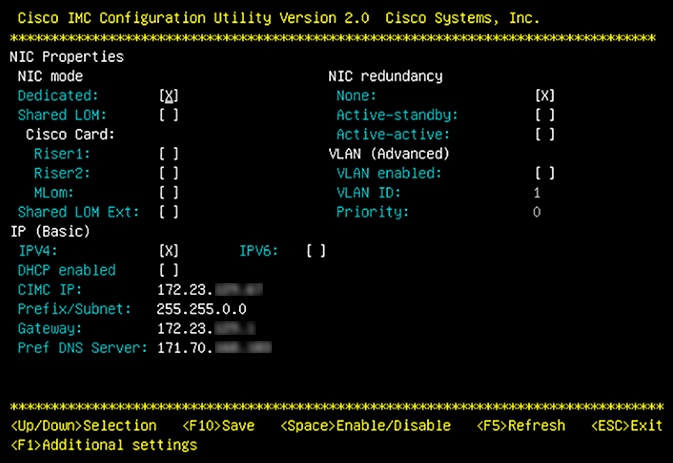
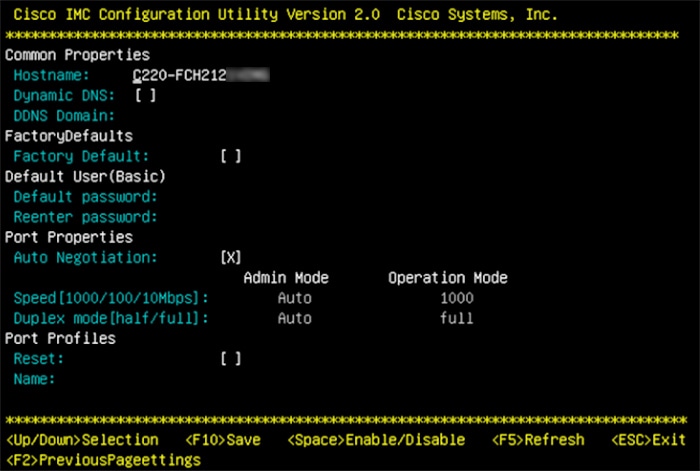
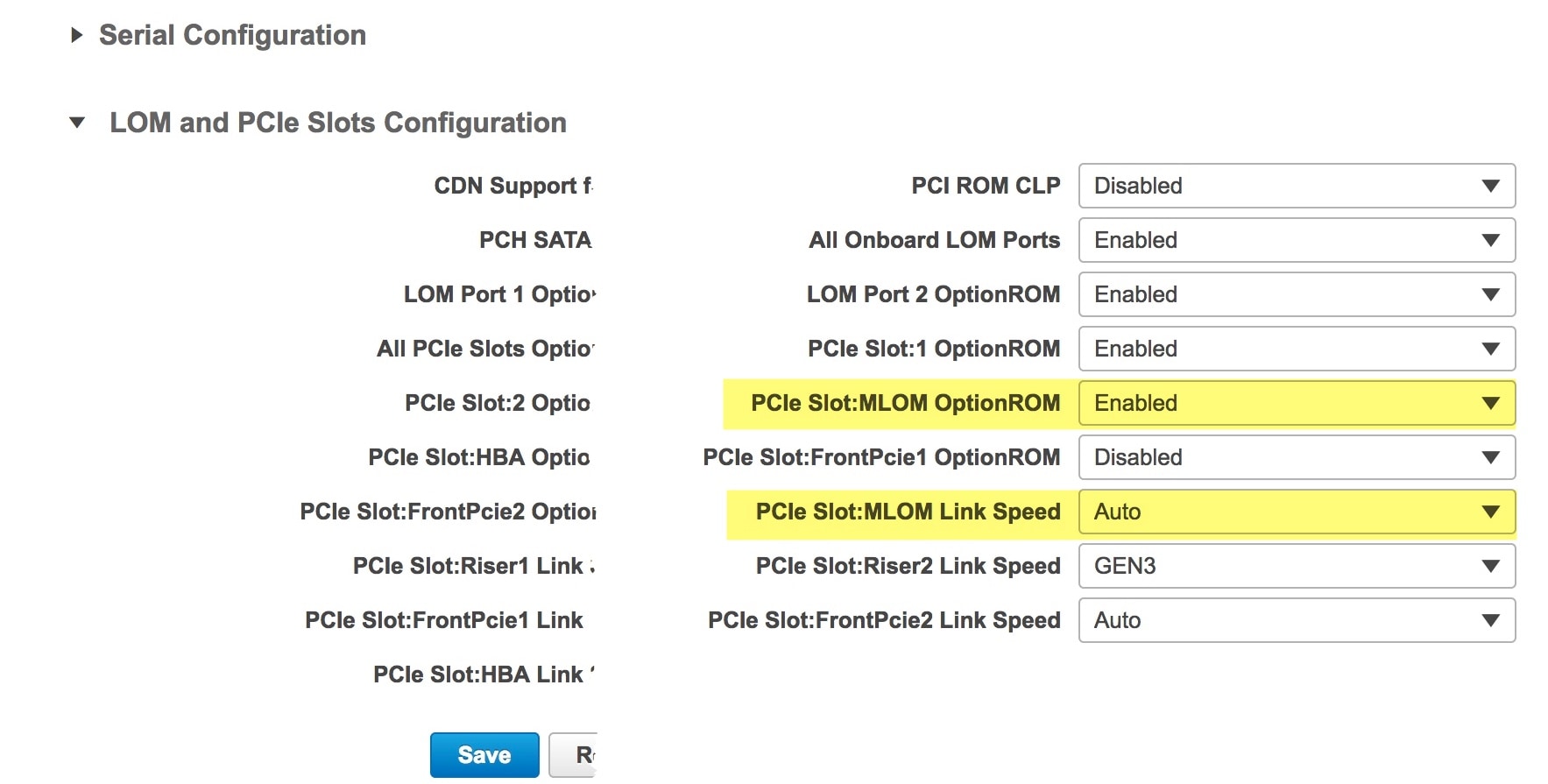
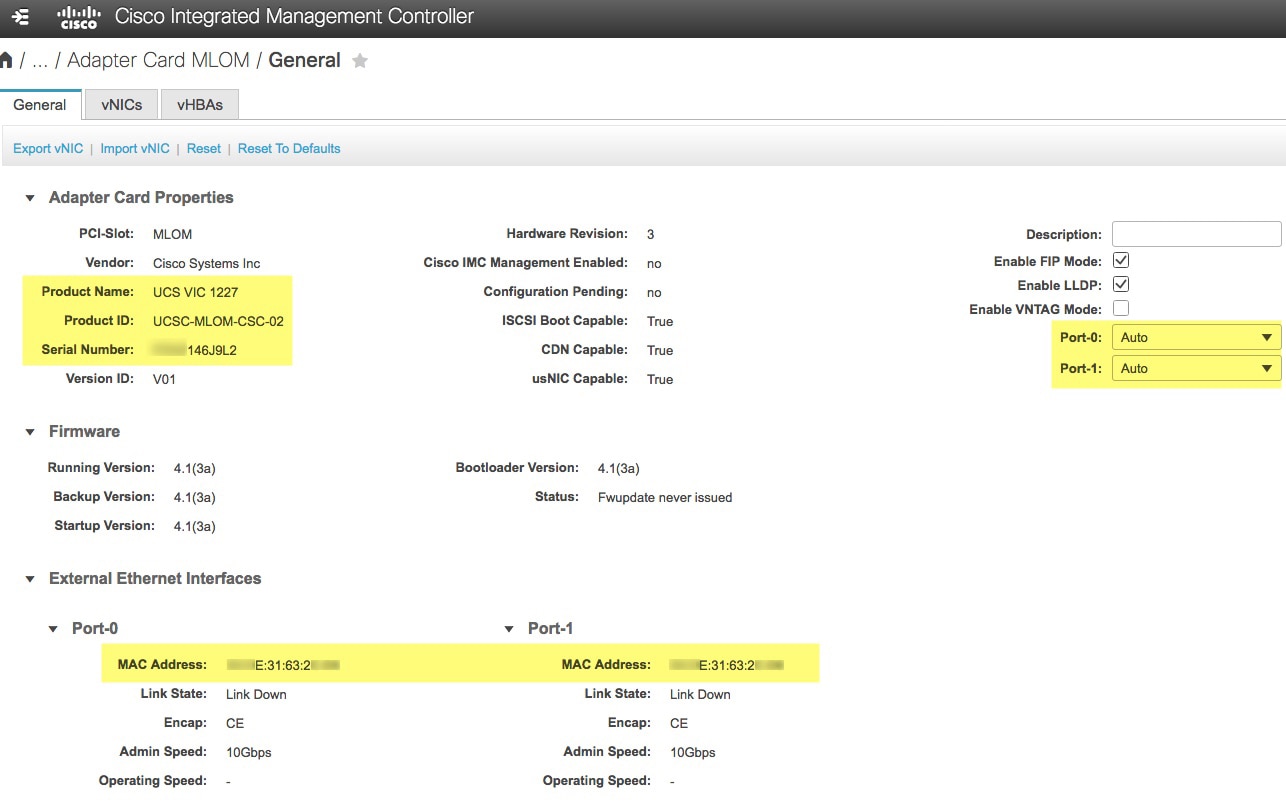
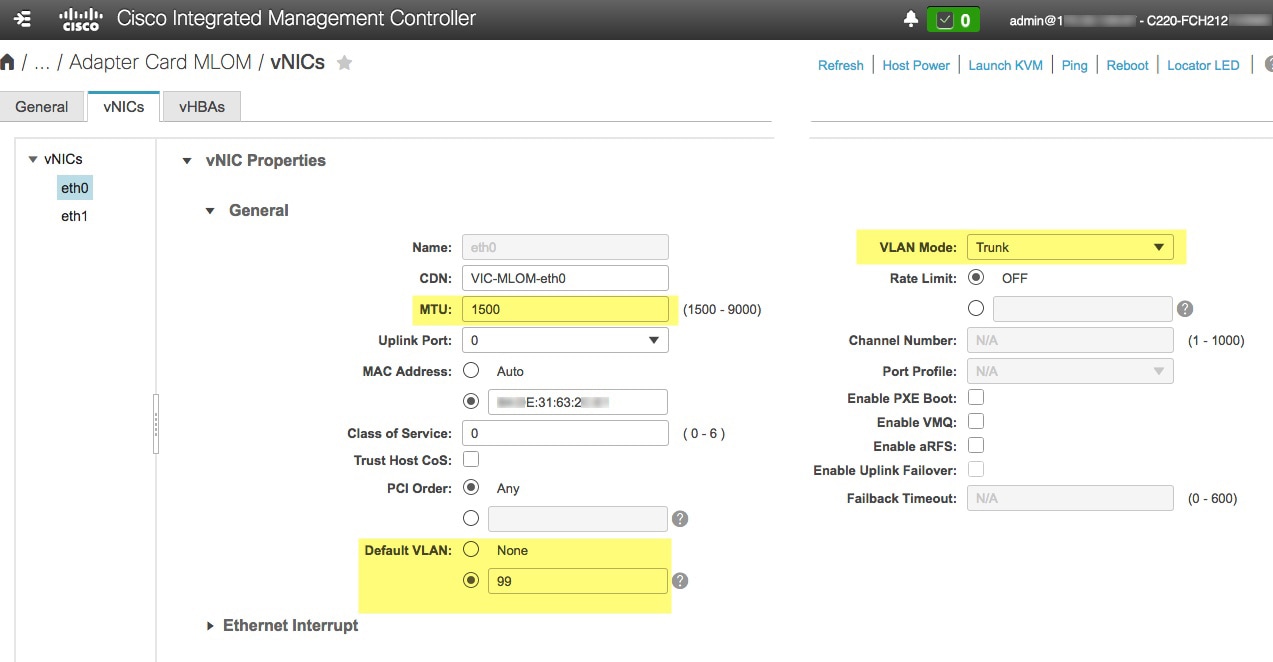
Use Cisco IMC to check and adjust important hardware and switch settings (see Execute Preconfiguration Checks).
-
Cisco DNA Center software is preinstalled on your appliance, but you may need to reinstall the software in certain situations (such as before you change the current cluster link configuration). If this is the case, you must also complete the tasks described in Reimage the Appliance.

Note
If you do not need to reimage your appliance, proceed to Appliance Configuration Overview.


 Feedback
Feedback