Enable Secure Boot for Cisco Catalyst Center
Secure boot
Secure boot helps you to ensure that Cisco hardware platforms run authentic and unmodified code. Secure boot establishes a root of trust to prevent your network devices from running unauthorized or malicious software.
The root of trust starts with the firmware as it can't be modified. The Cisco Integrated Management Controller (Cisco IMC) and BIOS firmware include the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) secure boot certificates. These certificates are organized in a hierarchy as defined by the UEFI specification. This hierarchy can't be modified after it's loaded on the system.
Hierarchy
PK → KEK → DB
The root of trust is in the firmware that hosts the platform key (PK), key exchange key (KEK), and key database (DB). The PK validates the certificates in the KEK, and the KEK validates the certificates in the DB. The DB contains the end entity certificate that is used to verify the signatures of all boot programs. In UEFI secure boot terms, the PK, KEK, and DB are referred to as auth variables.
Boot order
During the Catalyst Center UCS system boot, the firmware validates itself and then activates the UEFI key hierarchy for the Catalyst Center platform based on the product ID (PID).
After secure boot is activated, the system can boot only the software that is signed by the UEFI secure boot Catalyst Center certificate. To successfully boot from a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or hard disk, ensure that you have the correct Catalyst Center signature. After secure boot is enabled, it can't be disabled in the Cisco IMC and BIOS.
Requirements
This table lists the secure boot requirements.
| Secure boot requirement | Description |
|---|---|
|
Hardware |
|
|
Appliance |
DN2-HW-APL DN2-HW-APL-L DN2-HW-APL-XL |
|
Firmware |
|
|
UCS firmware |
4.0(4h) |
|
Firmware for C220 (DN2-HW-APL, DN2-HW-APL-L) |
https://software.cisco.com/download/home/286318809/type/283850974/release/4.0(4h) |
|
Firmware for C480 (DN2-HW-APL-XL) |
https://software.cisco.com/download/home/286318818/type/283850974/release/4.0(4h) |
|
BIOS |
|
|
BIOS for C220 (DN2-HW-APL, DN2-HW-APL-L) |
|
|
BIOS for C480 (DN2-HW-APL-XL) |
|
Install the Cisco IMC firmware
Step 1 | Extract the firmware installation files: |
Step 2 | Log in to the Cisco IMC GUI with admin privileges. |
Step 3 | Click the Navigation pane and choose Admin. |
Step 4 | From the Admin drop-down list, choose Firmware Management. |
Step 5 | In the Firmware Management dialog box, check the BMC check box, and click Update. |
Step 6 | In the Update Firmware dialog box, click Install BMC Firmware through Browser Client. |
Step 7 | Choose the file that you want to install:
|
Step 8 | In the Update Firmware dialog box, click Install Firmware. |
Activate the Cisco IMC firmware
Step 1 | In the Cisco IMC GUI, click the Navigation pane and choose Admin. |
Step 2 | From the Admin drop-down list, choose Firmware Management. |
Step 3 | In the Firmware Management dialog box, check the BMC check box and click Activate. |
Step 4 | In the Activate Firmware dialog box, select the firmware image that you want to activate, and then click Activate Firmware. After you click Activate Firmware, the Cisco IMC shuts down and reboots. The reboot process can take up to 15 minutes. |
Install the Cisco IMC BIOS
Step 1 | |
Step 2 | Log in to the Cisco IMC GUI with admin privileges. |
Step 3 | Click the Navigation pane and choose Admin. |
Step 4 | From the Admin drop-down list, choose Firmware Management. |
Step 5 | In the Firmware Management dialog box, check the BIOS check box and click Update. |
Step 6 | In the Update Firmware dialog box, click Install BIOS Firmware through Browser Client. |
Step 7 | Choose the file that you want to install:
|
Step 8 | In the Update Firmware dialog box, click Install Firmware. |
Activate the Cisco IMC BIOS
Step 1 | In the Cisco IMC GUI, click the Navigation pane and choose Admin. |
Step 2 | From the Admin drop-down list, choose Firmware Management. |
Step 3 | In the Firmware Management dialog box, check the BIOS check box and click Activate. |
Step 4 | In the Activate Firmware dialog box, select the firmware image to activate and click Activate Firmware. |
Enable the UEFI secure boot mode
Step 1 | Log in to the Cisco IMC GUI with admin privileges. |
Step 2 | Click the Navigation pane and choose . |
Step 3 | In the BIOS tab, click the Configure Boot Order tab. |
Step 4 | Check the UEFI Secure Boot check box and click Save Changes. 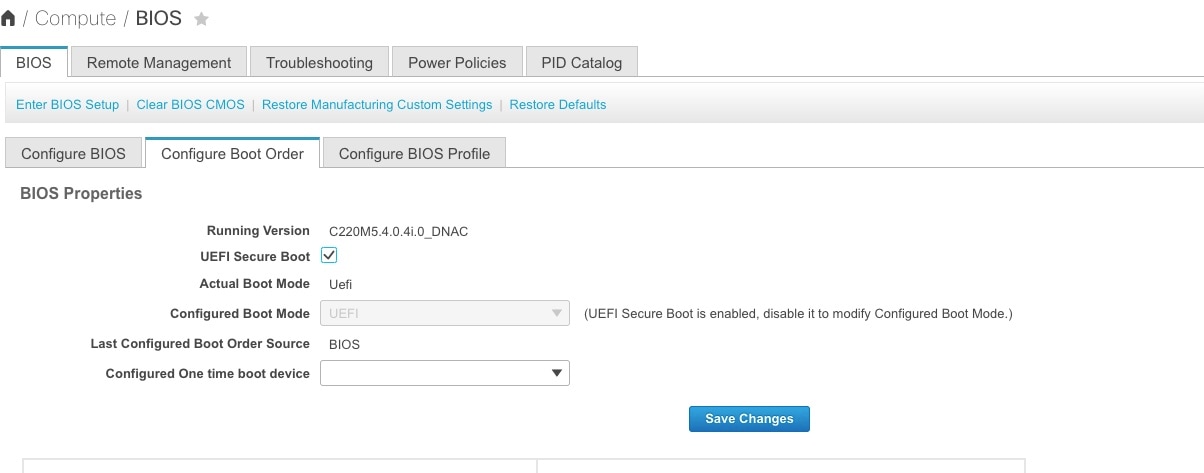
The machine reboots. |
Configure the boot order
Configure the first EFI boot order option to the Hard Disk Drive (HDD). Based on the mode of installation, the second boot order option can be:
- Cisco IMC-mapped DVD,
- KVM-mapped DVD, or
- USB flash drive.
Step 1 | Restart the machine and while BIOS is loading, press F2 to enter the BIOS setup. 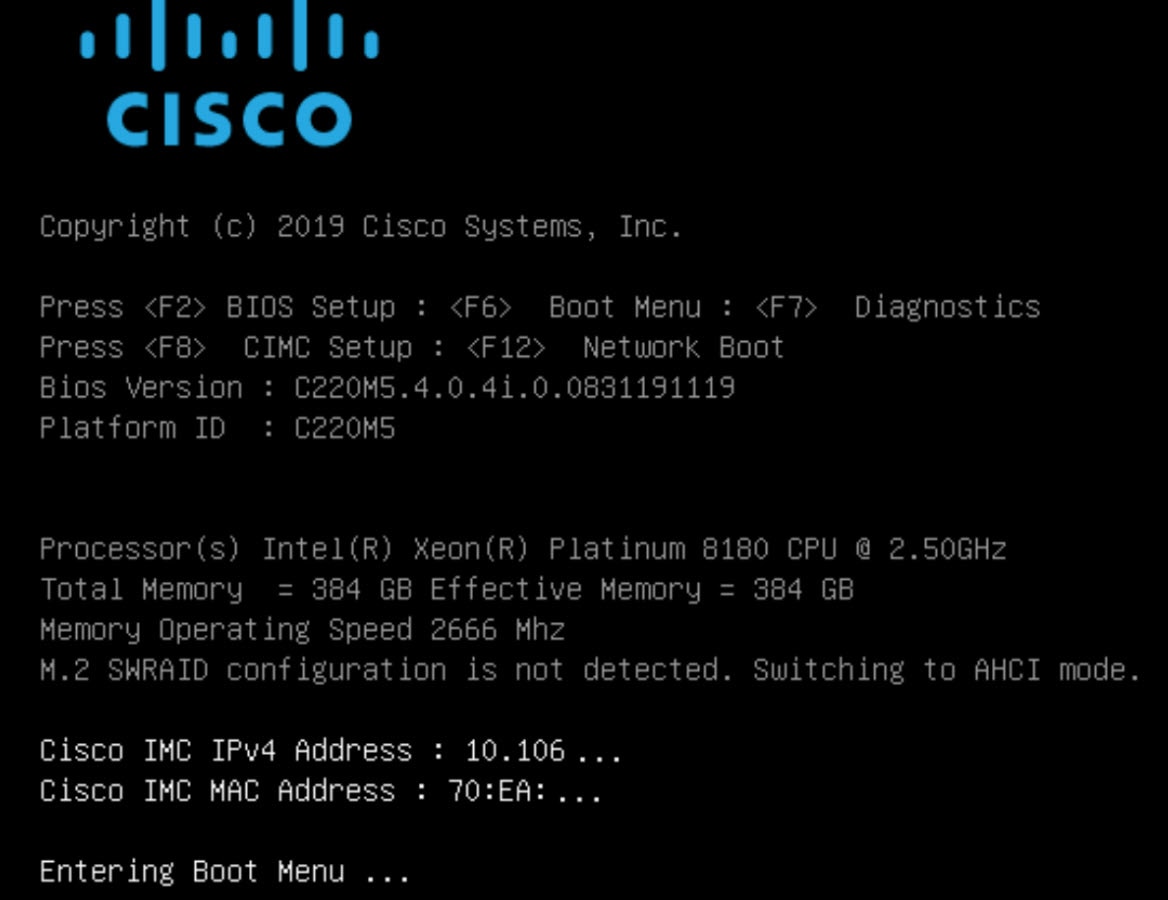
|
Step 2 | In the Navigation pane, click the Boot Options tab. |
Step 3 | From the Boot Options tab, scroll down to the Boot Option Priorities area. |
Step 4 | In the Boot Option Priorities area, set the Boot Option #1 field to UEFI OS (the HDD). |
Step 5 | Set the Boot Option #2 field to one of these options:
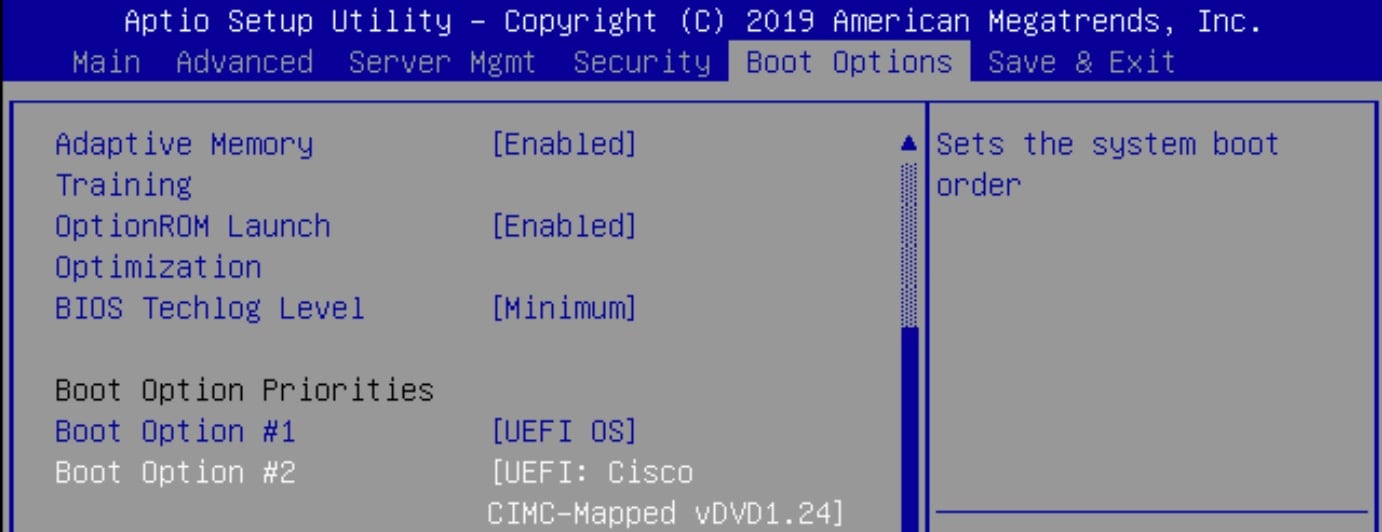
In this example figure, Boot Option #2 is set to Cisco IMC Mapped DVD. Before you set the boot order, map the secure boot-enabled ISO. Without mapping, these options are unavailable. This mapping is also needed for USB flash drive to view it as an option. |
Step 6 | Press F10 and save the configuration. 
|
Install Catalyst Center
Step 1 | Ensure that the:
|
Step 2 | Restart the appliance and while the BIOS is loading, press F6 to enter the Boot Selection. 
|
Step 3 | Choose the ISO boot drive from the Cisco IMC Mapped DVD (tested), USB flash drive (not tested), or KVM Mapped DVD (not tested). 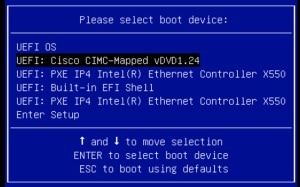
In this example image, the chosen ISO boot drive is Cisco IMC Mapped DVD (tested). |
Step 4 | Choose the Maglev Installer mode, which is the default in the System Boot menu, to proceed with the installation. 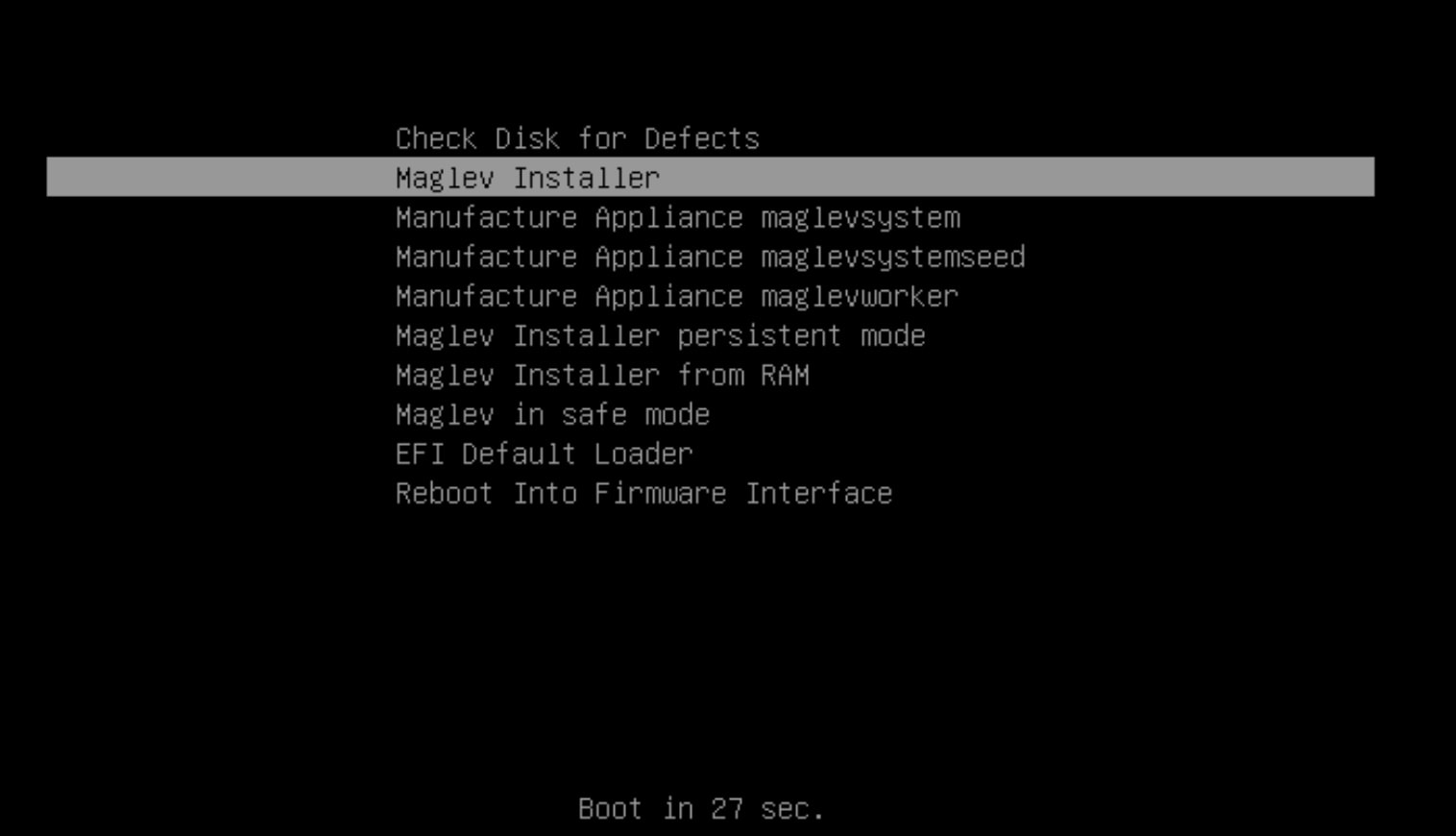
Currently, only the Maglev Installer mode is supported. Pressing any key other than Enter in this menu, causes the menu to freeze. Either press Enter or wait until it times out and proceed with the default option. As a workaround, restart the appliance and begin again from Step 1. |
Step 5 | Use the same procedure in the Maglev Configuration wizard as in a regular Catalyst Center installation. For more information about the Maglev Configuration wizard, see the Cisco Catalyst Center Installation Guide. 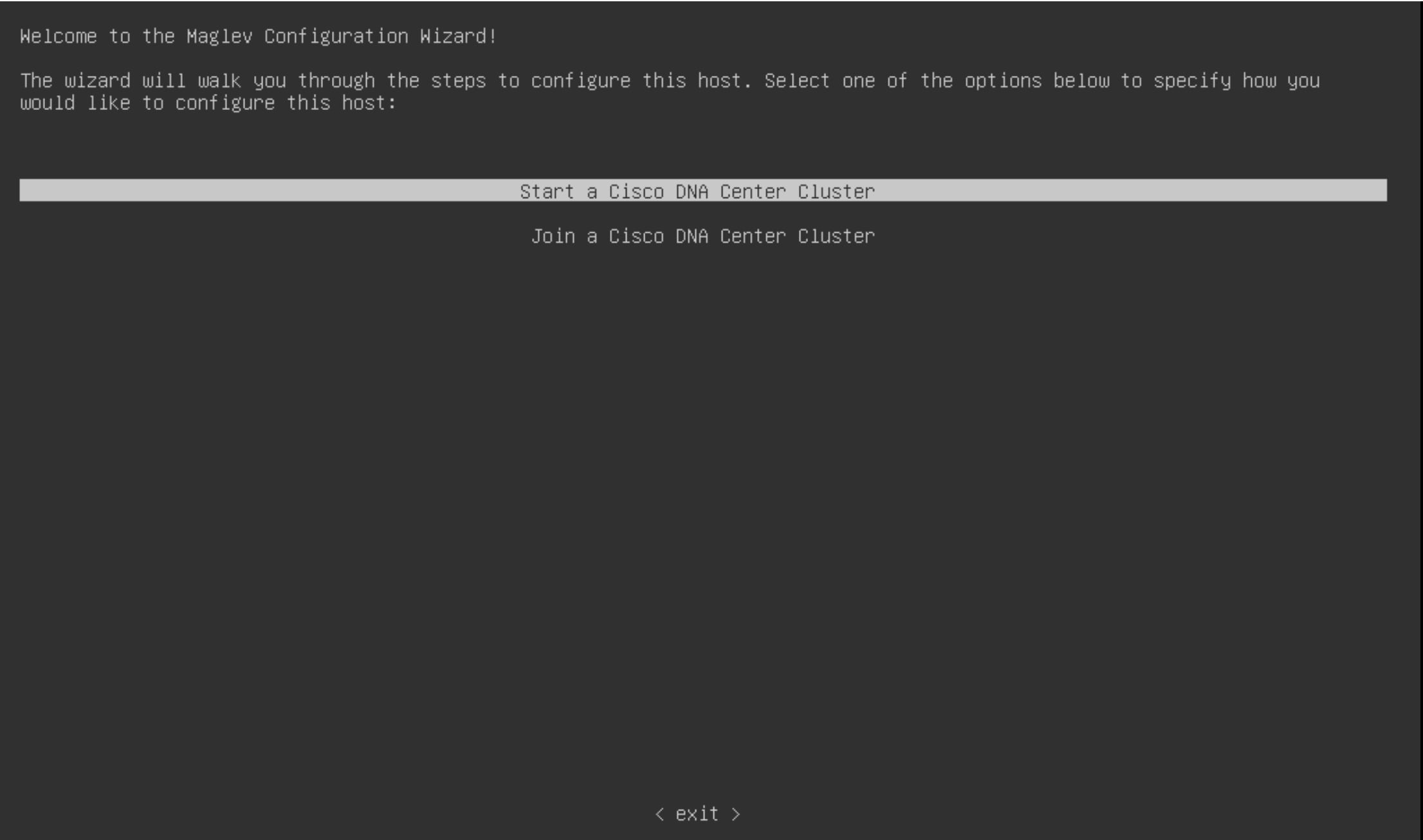
|
Verify secure boot
This section explains how to:
- verify that the ISO image supports EFI boot,
- verify the disk UEFI secure boot, and
- verify the extensible firmware interface image signature.
Verify that the ISO image supports EFI boot
Step 1 | Use these commands to verify that the ISO image that you use to install Catalyst Center supports EFI boot: |
Step 2 | In the output for the parted command, locate the EFI boot partition. For example: |
Considerations when burning an ISO to a USB flash drive
Secure boot recognizes only VFAT/FAT16 partitions. Therefore, you must format the USB flash drive as VFAT. Use an ISO writing tool, such as Etcher (https://www.balena.io/etcher/), to flash the ISO to the USB flash drive. Confirm that the ISO is secure UEFI bootable; see Verify that the ISO image supports EFI boot.
To burn an ISO to a new USB flash drive, complete these steps:
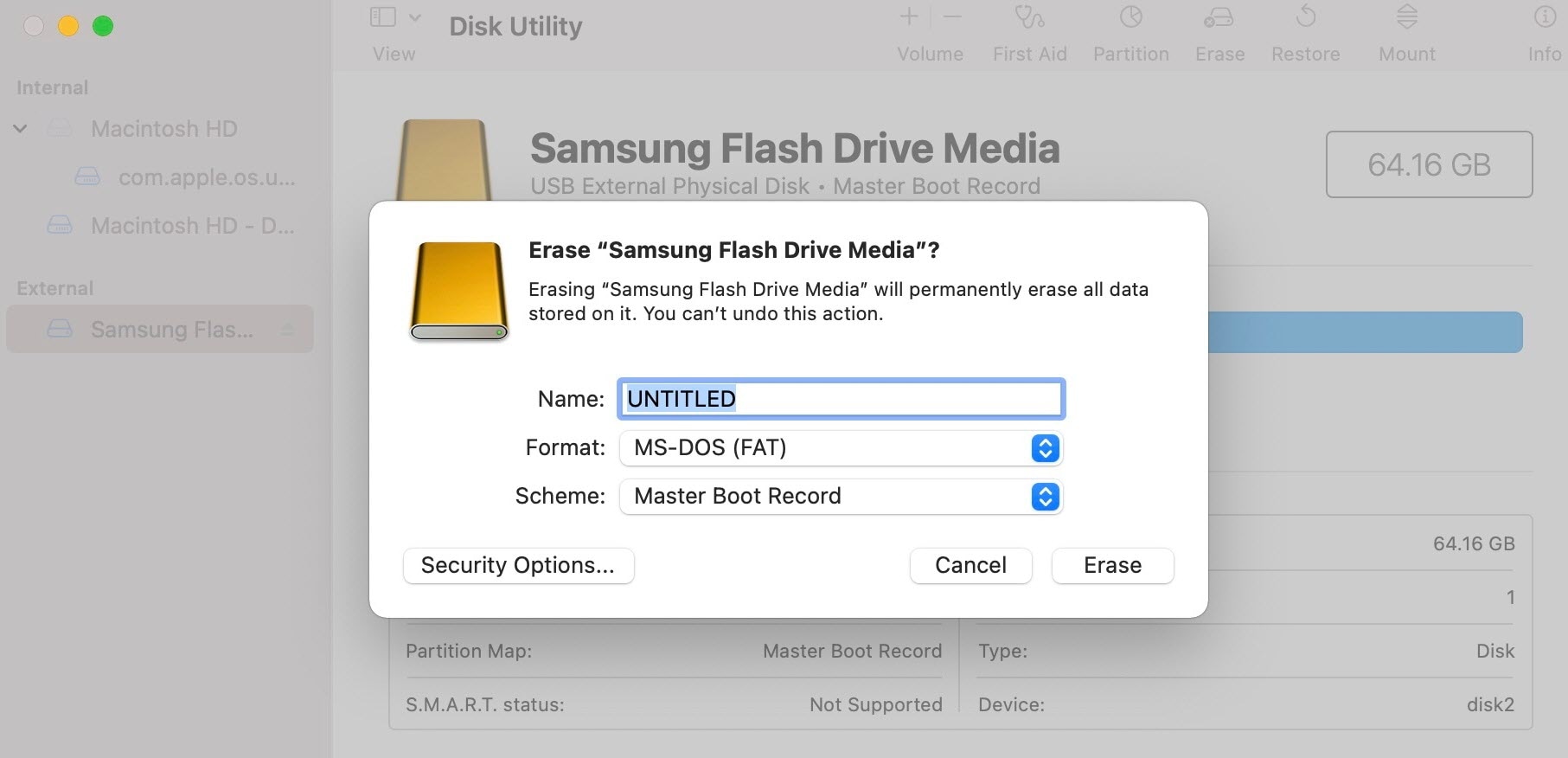
- Download the secure boot-compatible ISO from cisco.com. Use a USB flash drive with at least 64 GB, as the ISO requires at least 33 GB.
- Format the USB flash drive as "MS-DOS (FAT)" using the Mac "Disk Utility".
- Use Etcher to burn the secure boot-compatible ISO to the USB flash drive. For more information, see "Prepare the Appliance for Configuration" in the Cisco Catalyst Center Installation Guide. The Catalyst Center appliance, which has secure boot enabled in its Cisco IMC, detects the ISO on the USB flash drive.
Verify the disk UEFI secure boot
After installation, the fat16 partition contains the esp flag.
$ sudo parted /dev/sda print
Disk /dev/sda: 215GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
1 1049kB 2097kB 1049kB primary bios_grub
2 2097kB 51.2GB 51.2GB ext4 primary
3 51.2GB 51.5GB 251MB fat16 primary boot, esp
4 51.5GB 215GB 163GB ext4 primary
The output of mount | grep efivars shows the efivarfs mounted.
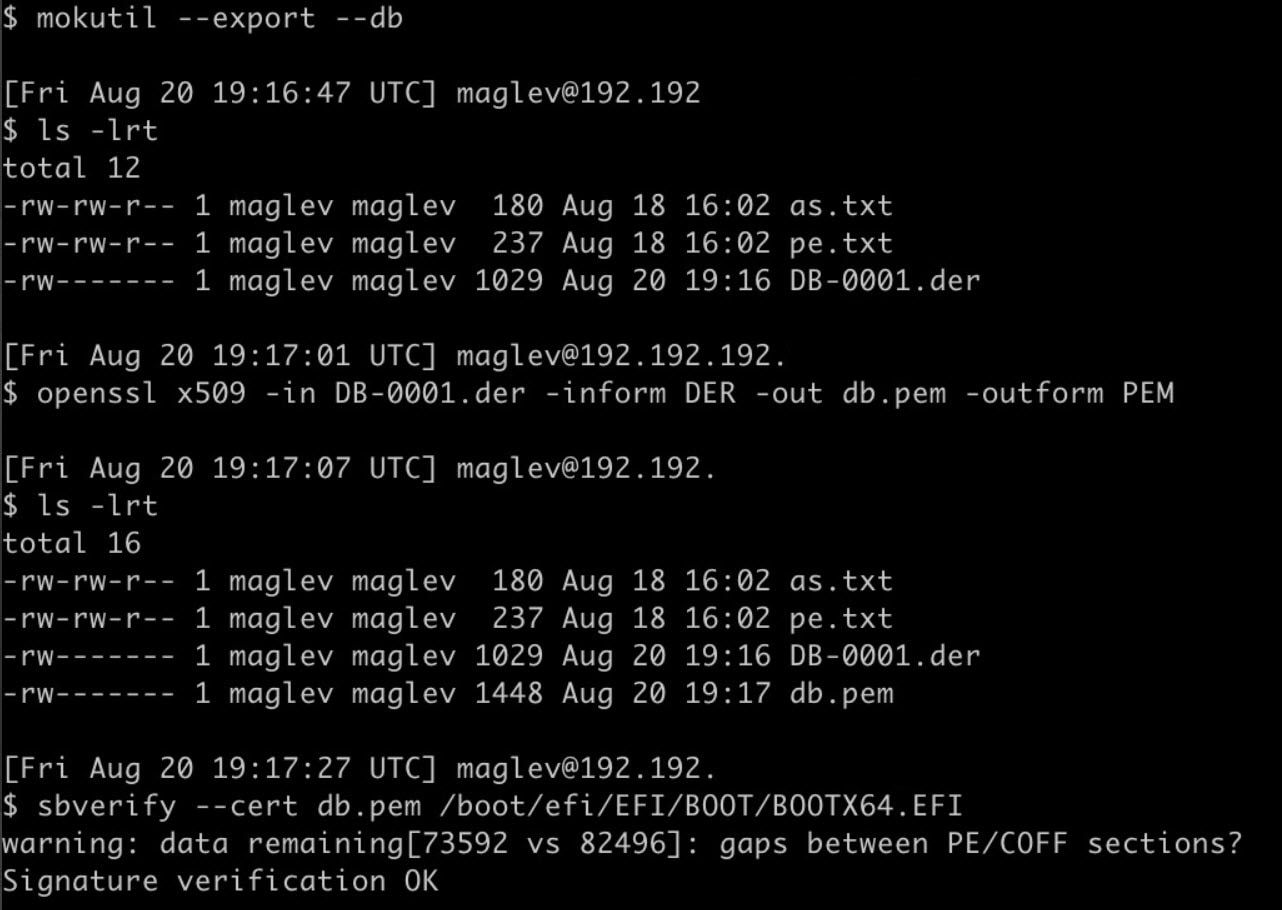
Verify the extensible firmware interface image signature
Catalyst Center images are signed using the SHA-256 hash algorithm. The signature uses the PKCS7 scheme with the RSA-2048 key.
Step 1 | After the system boots in secure boot, enter these commands:
A disk that is booted by secure boot contains these sample EFI boot images: |
Step 2 | To verify the EFI image signature, enter these commands:
|