-
null
- Configuring DRE Settings
- Configuring HTTP Acceleration
- Configuring MAPI Acceleration
- Configuring Encrypted MAPI Acceleration
- About Encrypted MAPI Acceleration
- Terms Used with Microsoft Active Directory
- Work flow for Configuring Encrypted MAPI
- Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings
- Configuring a Machine Account Identity
- Creating and Configuring a User Account
- Configuring Microsoft Active Directory
- Managing Domain Identities and Encrypted MAPI State
- Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
- Cisco WAAS MAPI over HTTP
- Configuring SMB Acceleration
- Configuring ICA Acceleration
- Configuring SSL Acceleration
- About SSL Acceleration
- Checklist for Configuring SSL Acceleration
- Prerequisites for Configuring SSL Acceleration
- Configuring SSL Global Settings
- Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key
- Working with Cipher Lists
- Working with CA Certificates
- Configuring SSL Management Services
- Configuring SSL Peering Service
- Using SSL Accelerated Services
- Updating a Certificate and Key in an SSL Accelerated Service
- Configuring SSL Acceleration for SaaS Applications
- Determining Server Domains Used by SaaS Applications
- Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
- About SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Checklist for Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Preparing to Use SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate
- Creating Single-Sided SMART-SSL Accelerated Service Certificate
- Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Accelerated Services on a Single-Sided Device Group
- Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
- Modifying the Accelerator Load Indicator and CPU Load-Monitoring Threshold
- Viewing a List of Applications on a Cisco WAE Device or Device Group
- Viewing a Policy Report for a Device or Device Group
- Viewing a Class Map Report for a Device or Device Group
- Restoring Optimization Policies and Class Maps
- Monitoring Applications and Class Maps
- Defining Default DSCP Marking Values
- Modifying the Position of an Optimization Policy
- Modifying the Acceleration TCP Settings
- About Acceleration TCP Settings
- Modifying the Acceleration TCP Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
- Configuring TCP Keepalives Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
- Calculating the TCP Buffers for High BDP Links
- Modifying the TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
- Configuring TCP Adaptive Buffer Settings Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Configuring Application Acceleration
This chapter describes how to configure the optimization policies, which determine the types of application traffic that is accelerated over your WAN on your Cisco WAAS system.

Note![]() Throughout this chapter, the term Cisco WAAS device is used to refer collectively to the Cisco Wide Area Application Services (Cisco WAAS) Central Managers and Cisco Wide Area Application Engines (WAEs) in your network. The term Cisco WAE refers to Cisco WAE and Cisco Wide Area Virtualization Engine (Cisco WAVE) appliances, and Cisco Virtual WAAS (Cisco vWAAS) instances.
Throughout this chapter, the term Cisco WAAS device is used to refer collectively to the Cisco Wide Area Application Services (Cisco WAAS) Central Managers and Cisco Wide Area Application Engines (WAEs) in your network. The term Cisco WAE refers to Cisco WAE and Cisco Wide Area Virtualization Engine (Cisco WAVE) appliances, and Cisco Virtual WAAS (Cisco vWAAS) instances.
About Application Acceleration
The Cisco WAAS software comes with more than 150 predefined optimization policies that determine the type of application traffic your Cisco WAAS system optimizes and accelerates. These predefined policies cover the most common type of application traffic on your network. For a list of the predefined policies, see Appendix A, “Predefined Optimization Policy.”
Each optimization policy contains the elements shown in Table 12-1 .
Table 12-1 Optimization Policy Elements
You can use the Cisco WAAS Central Manager GUI to modify the predefined policies and to create additional policies for other applications. For more information on creating optimization policies, see Creating a New Traffic Optimization Policy. For more information on viewing reports, restoring policies, monitoring applications, and other functions, see Managing Application Acceleration.

Note![]() All application definitions configured in the Cisco WAAS Central Manager are globally applied to all the Cisco WAAS devices that register with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, regardless of the device group membership configuration.
All application definitions configured in the Cisco WAAS Central Manager are globally applied to all the Cisco WAAS devices that register with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, regardless of the device group membership configuration.
Cisco WAAS policies can apply two kinds of optimizations to matched traffic:
- Layer 4 optimizations that include Transport Flow Optimization (TFO), Data Redundancy Elimination (DRE), and Lempel-Ziv (LZ) compression. These features can be applied to all types of TCP traffic.
- Layer 7 optimizations that accelerate application-specific protocols. The application accelerators control these kinds of optimizations.
For a specified optimization policy, for Cisco WAAS Version 4.4.1 and later, the DRE feature can use different caching modes, shown in Table 12-2 .
The predefined optimization policies are configured to use the optimal DRE caching mode, depending on the typical application traffic, although you can change the mode if you want.
Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features
This section contains the following topics:
- About Global Optimization Features
- Procedure for Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features
- Configuring Optimization and Acceleration from the Cisco WAAS CLI
About Global Optimization Features
The global optimization features determine if traffic flow optimization (TFO), data redundancy elimination (DRE), and persistent compression are enabled on a device or device group. By default, all of these features are enabled. If you choose to disable one of these features, the device will be unable to apply the full Cisco WAAS optimization techniques to the traffic that it intercepts.
In addition, the global optimization features include each of the following application accelerators:
- Microsoft End Port Mapper (EPM)
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Independent Computing Architecture (ICA)
- Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI)
- Server Message Block (SMB)
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- SSL Interposer
By default, all of the application accelerators are enabled except SMB, SSL Interposer and Encrypted MAPI.

Note![]() The application accelerators require specific types of licenses to operate: a Transport license for TFO, DRE, and LZ optimization, and an Enterprise license for all other application accelerators. For more information on installing and managing licenses, see Managing Cisco WAAS Software Licenses in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings”.
The application accelerators require specific types of licenses to operate: a Transport license for TFO, DRE, and LZ optimization, and an Enterprise license for all other application accelerators. For more information on installing and managing licenses, see Managing Cisco WAAS Software Licenses in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings”.
Procedure for Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features
- You must enable the accelerator on both of the peer Cisco WAEs at either end of a WAN link for all application accelerators to operate, except for single-sided SMART-SSL acceleration.
- In the case of single-sided SMART-SSL acceleration, you do not need a peer Cisco WAE to exist or for both Cisco WAEs to have the SSL Interposer accelerator enabled.
To enable or disable a global optimization feature, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
The Enabled Features window appears (Figure 12-1).
Figure 12-1 Enabled Features Window
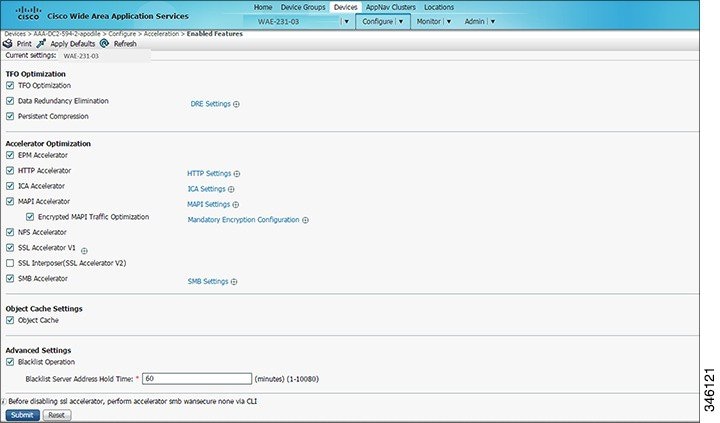
For Cisco WAAS Express Devices
In the Enabled Features window for a device group, two SMB Accelerator options are shown, one for Cisco ISR-WAAS devices and one for all other kinds of Cisco WAEs.
–![]() HTTP accelerator express (see Configuring HTTP Acceleration)
HTTP accelerator express (see Configuring HTTP Acceleration)
–![]() SSL accelerator express (see Configuring SSL Acceleration)
SSL accelerator express (see Configuring SSL Acceleration)
- For a Cisco WAAS device running Cisco WAAS Version 6.x and a Cisco WAAS Express peer device running Cisco IOS Release 15.6(3)M, 15.6(2)T1 or later, TLS1 is supported, but SSL3 is removed. Before upgrading Cisco WAAS Express to one of these Cisco IOS releases, configure TLS1 in the Cisco WAAS Express Device Group:
1. Navigate to Device Groups > DeviceGroupName > Configure > Enabled Features.
2. Select the SSL Accelerator Express Peering Service.
3. From the SSL Version: dropdown list, select TLS1.
5. Upgrade the Cisco WAAS Express.
- For information on upgrading and interoperability, see the Release Note for Cisco Wide Area Application Services.
- If you try to enable DRE on a Cisco WAAS Express device on which it is not supported, a message stating that it is not supported is displayed.
- The Restore Predefined Settings icon for Cisco WAAS Express applies the predefined settings for HTTP/HTTPS, and SSL cipher list and peering service.
Step 3![]() Check the check boxes adjacent to the optimization features that you want to enable, and uncheck the check boxes adjacent to the features that you want to disable.
Check the check boxes adjacent to the optimization features that you want to enable, and uncheck the check boxes adjacent to the features that you want to disable.
For a description of each of the optimization features, see Key Services of Cisco WAAS in the chapter “Introduction to Cisco WAAS” .
Some features have additional settings that you can configure by clicking the link next to the setting name. Hover your cursor over the small target icon next to the link to see a dialog box that shows the current settings.
- If you check the Data Redundancy Elimination check box, you can click the DRE Settings link as a shortcut to the DRE Settings Configuration window. For more information, see Configuring DRE Settings.
- If you check the HTTP Accelerator check box, you can click the HTTP Settings link as a shortcut to the HTTP/HTTPS Settings window. For more information, see Configuring HTTP Acceleration.
- If you check the ICA Accelerator check box, you can click the ICA Settings link as a shortcut to the ICA Acceleration Configuration window. For more information, see Configuring ICA Acceleration.
- If you check the MAPI Accelerator check box, you can click the MAPI Settings link as a shortcut to the MAPI Settings window. For more information, see Configuring MAPI Acceleration.

Note![]() When you check the MAPI Accelerator check box, Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization is enabled by default.
When you check the MAPI Accelerator check box, Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization is enabled by default.
- If you check the Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization check box, you can click the Mandatory Encryption Configuration link as a shortcut to the Encrypted Services Configuration window. For more information, see Configuring Encrypted MAPI Acceleration.

Note![]() You must enable MAPI acceleration first for Encrypted MAPI acceleration to be enabled.
You must enable MAPI acceleration first for Encrypted MAPI acceleration to be enabled.
- If you check the SMB Accelerator check box, you can click the SMB Settings link as a shortcut to the SMB Acceleration Configuration window. For more information, see Configuring SMB Acceleration.
- If you check the SSL Accelerator check box, you must configure additional settings to enable SSL acceleration. For more information, see Configuring SSL Acceleration. For Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.1 and later, you can accelerate Microsoft Office 365 traffic. For more information, see Checklist for Configuring Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS.
- If you check the SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) check box, you must configure additional settings to enable SMART-SSL acceleration.
By default, the SSL Interposer is by default SMART-SSL enabled on a fresh installation: on new Cisco WAAS OVA deployments, Cisco WAAS ENCS 5400-W platforms, and Cisco WAAS Version 5.5.7 to Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.1 upgrades. This is disabled when you upgrade the devices from Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.3 to Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.1. For more information, see Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration.

Note![]() Both SSL accelerator and SMART-SSL can co-exist on a device.
Both SSL accelerator and SMART-SSL can co-exist on a device.
Step 4![]() To enable the object cache, at the Object Cache Settings pane, check the Object Cache check box.
To enable the object cache, at the Object Cache Settings pane, check the Object Cache check box.
Cisco WAAS performs object caching to increase client application performance for SMB file access. Object caching also minimizes bandwidth and latency over the WAN, by avoiding the repeated transfer of data over the WAN.

Note![]() Object Cache is not supported on Cisco vWAAS-200 and Cisco vWAAS-150 platforms.
Object Cache is not supported on Cisco vWAAS-200 and Cisco vWAAS-150 platforms.
- To enable an individual application accelerator object cache: Controls to enable and disable an individual object cache are displayed in that application accelerator’s Advanced Settings screen.
- To ensure that the object cache and individual application accelerator object cache work successfully, consider these guidelines:
–![]() Each application accelerator object cache can be enabled or disabled independent of whether or not the global object cache is enabled or disabled.
Each application accelerator object cache can be enabled or disabled independent of whether or not the global object cache is enabled or disabled.
–![]() Enabling the object cache does not automatically enable individual application accelerator object caches.
Enabling the object cache does not automatically enable individual application accelerator object caches.
–![]() You can enable or disable an individual application accelerator object cache whether or not the associated application accelerator is enabled or disabled.
You can enable or disable an individual application accelerator object cache whether or not the associated application accelerator is enabled or disabled.
–![]() Verify that disk assignments have been made to object cache before you enable object cache.
Verify that disk assignments have been made to object cache before you enable object cache.
–![]() The object cache has a limit of 15 GB. A request of a size larger than this limit will not cache the complete file. For example, for a file size of 25 GB, only 15 GB of this file would be cached.
The object cache has a limit of 15 GB. A request of a size larger than this limit will not cache the complete file. For example, for a file size of 25 GB, only 15 GB of this file would be cached.

Note![]() To ensure that the object cache and SMB application accelerator work successfully, enable the object cache before you enable the SMB application accelerator.
To ensure that the object cache and SMB application accelerator work successfully, enable the object cache before you enable the SMB application accelerator.
Step 5![]() In the Advanced Settings pane, uncheck the Blacklist Operation check box if you want to disable it.
In the Advanced Settings pane, uncheck the Blacklist Operation check box if you want to disable it.
This behavior can result from network devices (such as firewalls) that block TCP setup packets that have options, and from asymmetric routes. The Cisco WAE can keep track of origin servers (such as those behind firewalls) that cannot receive optioned TCP packets, and learns not to send out TCP packets with options to these blacklisted servers.

Note![]() Cisco WAAS is able to accelerate traffic between Cisco branch WAEs and Cisco data center WAEs in situations where optioned TCP packets are dropped. We recommend that you leave the blacklist operation feature enabled.
Cisco WAAS is able to accelerate traffic between Cisco branch WAEs and Cisco data center WAEs in situations where optioned TCP packets are dropped. We recommend that you leave the blacklist operation feature enabled.
Step 6![]() To change the default Blacklist Server Address Hold Time of 60 minutes, enter the new time in minutes in the Blacklist Server Address Hold Time field. The valid range is 1 minute to 10080 minutes (1 week).
To change the default Blacklist Server Address Hold Time of 60 minutes, enter the new time in minutes in the Blacklist Server Address Hold Time field. The valid range is 1 minute to 10080 minutes (1 week).
When a server IP address is added to the blacklist, it remains there for the configured hold time. After that time, subsequent connection attempts will again include TCP options so that the Cisco WAE can redetermine if the server can receive them. It is useful to retry sending TCP options periodically because network packet loss may cause a server to be erroneously blacklisted.
You can shorten or lengthen the blacklist time by changing the Blacklist Server Address Hold Time field.
The changes are saved to the device or device group.
Configuring Optimization and Acceleration from the Cisco WAAS CLI
Global Configuration Commands Used to Configure Optimization and Acceleration
Table 12-3 shows the Cisco WAAS CLI global configuration commands used to configure optimization and acceleration.
Table 12-3 Cisco WAAS CLI Commands Used to Configure Optimization and Acceleration
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
Configure TFO optimization, DRE, and persistent compression. |
||
Optimization and Acceleration Configuration Guidelines
- Considering the following guidelines for configuring optimization and acceleration:
- When object cache is enabled, you are prompted to confirm the repurposing of SMB resources if the disk has not already been partitioned for object cache.
- If this is the first time disk resources are being assigned to object cache, the object-cache enable command will prompt you to reboot the device, since the disk partitioning only takes effect on the next reboot. The configuration is then saved, and the object cache does not have to be re-enabled on the next reboot.
- To ensure success of the object-cache enable command, verify the following two conditions:
–![]() Disk assignments have been made to object cache before you run this command.
Disk assignments have been made to object cache before you run this command.
–![]() Run this command before you run the accelerator smb global configuration command.
Run this command before you run the accelerator smb global configuration command.
- To ensure that each application accelerator object cache and the global object cache function successfully, note these guidelines:
–![]() Each application accelerator object cache can be enabled or disabled independent of whether or not the global object cache is enabled or disabled.
Each application accelerator object cache can be enabled or disabled independent of whether or not the global object cache is enabled or disabled.
–![]() Before you run the no object-cache enable global configuration command to disable the global object cache, you must disable all individual application accelerator object caches.
Before you run the no object-cache enable global configuration command to disable the global object cache, you must disable all individual application accelerator object caches.
–![]() The object-cache enable global configuration command does not automatically enable individual application accelerator object caches.
The object-cache enable global configuration command does not automatically enable individual application accelerator object caches.
–![]() You can enable or disable an individual application accelerator object cache whether or not the associated application accelerator is enabled or disabled.
You can enable or disable an individual application accelerator object cache whether or not the associated application accelerator is enabled or disabled.
Configuring Individual Application Accelerators and Features
This section contains the following topics:
- Configuring DRE Settings
- Configuring HTTP Acceleration
- Configuring MAPI Acceleration
- Configuring Encrypted MAPI AccelerationConfiguring SMB Acceleration
- Configuring ICA Acceleration
- Configuring SSL Acceleration
- Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
Configuring DRE Settings
About DRE
Data Redundancy Elimination (DRE) is one of the critical technologies used to identify redundant data patterns in application traffic, replacing them with signatures that Cisco WAAS devices transfer across the WAN to regenerate the original data. The result is optimal usage of WAN bandwidth and improved end-user response time.
Configuring DRE Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To enable general DRE settings, check the Data Redundancy Elimination check box in the Enabled Features window.
To configure the DRE auto bypass and load monitor settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > DRE Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > DRE Settings.
The DRE Settings window appears.
Step 3![]() Check the Enable DRE auto bypass check box to generate an alarm and automatically DRE bypass application traffic.
Check the Enable DRE auto bypass check box to generate an alarm and automatically DRE bypass application traffic.

Note![]() If you do not enable DRE auto bypass, the Device Status alarm displays yellow and the traffic gets bypassed without forwarding to the Service Node (SN). We recommend that you do not disable DRE through the configuration. Instead, configure individual policies to bypass DRE functionality.
If you do not enable DRE auto bypass, the Device Status alarm displays yellow and the traffic gets bypassed without forwarding to the Service Node (SN). We recommend that you do not disable DRE through the configuration. Instead, configure individual policies to bypass DRE functionality.
Step 4![]() Check the Enable DRE Load Monitor check box to enable load report.
Check the Enable DRE Load Monitor check box to enable load report.
- The disk latency maximum can be set from 1-1000; the default value is 5.
- The DRE load threshold can be set from 50-99; the default value is 95.
The changes are saved to the device or device group.
Configuring DRE Settings Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Consider the following guidelines for configuring DRE settings using the Cisco WAAS CLI:
Configuring HTTP Acceleration
About HTTP Acceleration
The HTTP application accelerator accelerates HTTP traffic. To optimize HTTPS, you must enable both SSL and HTTP and also have protocol chaining enabled.
The default Web Optimization policy is defined to send traffic to the HTTP accelerator. The Web optimization policy uses the HTTP class map, which matches traffic on ports 80, 8080, 8000, 8001, and 3128. If you expect HTTP traffic on other ports, add the other ports to the HTTP class map.
Configuring HTTP Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To configure the HTTP acceleration settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To enable the HTTP accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
To enable the HTTP accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
Step 2![]() The Enabled Features window appears.
The Enabled Features window appears.
a.![]() At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the HTTP Accelerator check box.
At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the HTTP Accelerator check box.
Step 3![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 4![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > HTTP/HTTPS Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > HTTP/HTTPS Settings.
The HTTP/HTTPS Acceleration Settings window appears (Figure 12-2).

Note![]() For Cisco WAAS Express, the HTTP acceleration settings are the same, but the fields are laid out differently in the HTTP/HTTPS Settings window.
For Cisco WAAS Express, the HTTP acceleration settings are the same, but the fields are laid out differently in the HTTP/HTTPS Settings window.
Figure 12-2 HTTP/HTTPS Settings Window
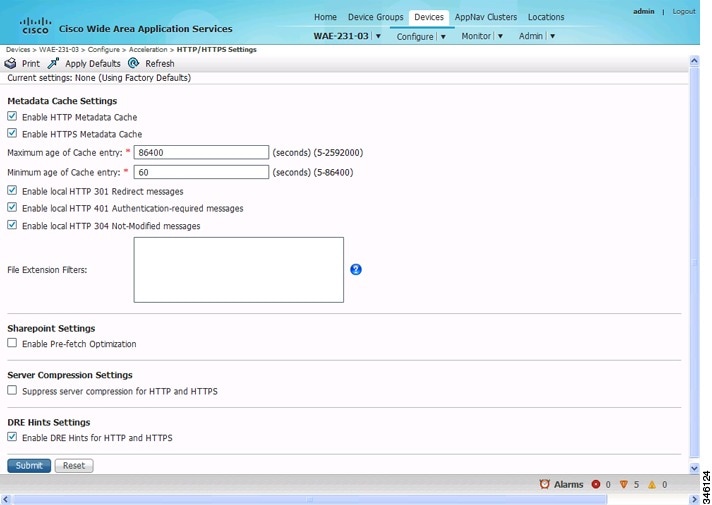
Step 5![]() Configure the metadata cache settings. At the Metadata Cache Settings pane:
Configure the metadata cache settings. At the Metadata Cache Settings pane:
a.![]() To enable the Cisco WAE to cache each HTTP header (metadata) information, check the Enable HTTP metadatacache caching check box. The default setting is checked.
To enable the Cisco WAE to cache each HTTP header (metadata) information, check the Enable HTTP metadatacache caching check box. The default setting is checked.
This check box must be checked to enable any of the other settings in the Metadata Cache Settings area. If this box is not checked, no header caching is done.
For details on HTTP metadata caching, see HTTP Metadata Caching.
b.![]() To enable the Cisco WAE to cache HTTPS header (metadata) information (HTTP as payload in SSL traffic), check the Enable HTTPS metadatacache caching check box. The default setting is checked.
To enable the Cisco WAE to cache HTTPS header (metadata) information (HTTP as payload in SSL traffic), check the Enable HTTPS metadatacache caching check box. The default setting is checked.
For details on HTTP metadata caching, see HTTP Metadata Caching.
c.![]() In the Maximum age of a cache entry field, enter the maximum number of seconds to retain HTTP header information in the cache. The default is 86,400 seconds (24 hours). Valid time periods range from 5–2,592,000 seconds (30 days).
In the Maximum age of a cache entry field, enter the maximum number of seconds to retain HTTP header information in the cache. The default is 86,400 seconds (24 hours). Valid time periods range from 5–2,592,000 seconds (30 days).
d.![]() In the Minimum age of a cache entry field, enter the minimum number of seconds for which to retain HTTP header information in the cache. The default is 60 seconds. Valid time periods range from 5 to 86,400 seconds (24 hours).
In the Minimum age of a cache entry field, enter the minimum number of seconds for which to retain HTTP header information in the cache. The default is 60 seconds. Valid time periods range from 5 to 86,400 seconds (24 hours).
e.![]() To enable the Cisco WAE to cache and to locally serve HTTP 301 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 301 redirect messages check box. The default setting is checked.
To enable the Cisco WAE to cache and to locally serve HTTP 301 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 301 redirect messages check box. The default setting is checked.
f.![]() To enable the Cisco WAE to cache and locally serve HTTP 401 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 401 Authentication-required messages check box. The default setting is checked.
To enable the Cisco WAE to cache and locally serve HTTP 401 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 401 Authentication-required messages check box. The default setting is checked.
g.![]() To enable the Cisco WAE to cache HTTP 200 and HTTP 304 messages and locally serve HTTP 304 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 304 Not-Modified messages check box. The default setting is checked.
To enable the Cisco WAE to cache HTTP 200 and HTTP 304 messages and locally serve HTTP 304 messages, check the Enable local HTTP 304 Not-Modified messages check box. The default setting is checked.
h.![]() To configure specific file extensions to which metadata caching is to be applied, enter the file extensions in the File extension filters field at the far right of the window. Separate multiple extensions with a comma, for example, jpeg, gif, png, and do not include the dot at the beginning of the file extension.
To configure specific file extensions to which metadata caching is to be applied, enter the file extensions in the File extension filters field at the far right of the window. Separate multiple extensions with a comma, for example, jpeg, gif, png, and do not include the dot at the beginning of the file extension.
By default, no file extension filters are defined and therefore, metadata caching applies to all file types.
Step 6![]() To allow the Cisco WAAS Edge WAE to prefetch data, at the Sharepoint Settings pane, check the Enable Pre-fetch Optimization check box. The default for this setting is unchecked.
To allow the Cisco WAAS Edge WAE to prefetch data, at the Sharepoint Settings pane, check the Enable Pre-fetch Optimization check box. The default for this setting is unchecked.
- The prefetch optimization benefits the Web browser-based Microsoft Office applications when they access Microsoft Office Word and Microsoft Office Excel documents that are hosted on a Microsoft SharePoint Server 2010. To view Microsoft Word documents, you must have Microsoft Silverlight installed on your system.
- By checking the Enable Pre-fetch Optimization check box, you are directing the Cisco WAAS Edge WAE to prefetch the subsequent pages of the documents from the SharePoint server before the client actually requests them, and serve them from the cache when the request from the client arrives. You can now seamlessly scroll through the document without having to wait for the content to load.

Note![]() SharePoint prefetch optimization works with view in browser mode only.
SharePoint prefetch optimization works with view in browser mode only.
Step 7![]() To configure the Cisco WAE to suppress server compression between the client and the server, at the Server Compression Settings pane, check the Suppress server compression for HTTP and HTTPS check box. The default setting is checked.
To configure the Cisco WAE to suppress server compression between the client and the server, at the Server Compression Settings pane, check the Suppress server compression for HTTP and HTTPS check box. The default setting is checked.
- By checking the Suppress server compression for HTTP and HTTPS check box, you are directing the Cisco WAE to remove the Accept-Encoding value from HTTP and HTTPS request headers, which prevents the web server from compressing HTTP and HTTPS data that it sends to the client. This allows the Cisco WAE to apply its own compression to the HTTP and HTTPS data, which typically results in more optimum compression than that of the web server, for most files.
- For some file types that rarely change, such as.css and.js files, this setting is ignored and web server compression is allowed.
Step 8![]() To send DRE hints to the DRE module for improved DRE performance, at the DRE Hints Settings pane, check the Enable DRE Hints for HTTP and HTTPS check box. The DRE hint feature is enabled by default.
To send DRE hints to the DRE module for improved DRE performance, at the DRE Hints Settings pane, check the Enable DRE Hints for HTTP and HTTPS check box. The DRE hint feature is enabled by default.
The changes are saved to the device or device group.
Configuring HTTP Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Consider the following guidelines for configuring HTTP acceleration using the Cisco WAAS CLI:
- To configure HTTP acceleration from the CLI, run the accelerator http global configuration command.
- To show the contents of the metadata cache, run the show cache http-metadatacache EXEC command.
- To clear the metadata cache, run the clear cache http-metadatacache EXEC command.
- To enable or disable specific HTTP accelerator features for specific clients or IP subnets, use the HTTP accelerator subnet feature. For more details, see HTTP Accelerator Subnets.
HTTP Metadata Caching
The metadata caching feature allows the HTTP accelerator in the Cisco Branch WAE to cache particular server responses and respond locally to clients. The following server response messages are cached:
- HTTP 200 OK (Applies to If-None-Match and If-Modified-Since requests)
- HTTP 301 redirect
- HTTP 304 not modified (Applies to If-None-Match and If-Modified-Since requests)
- HTTP 401 authentication required
Metadata caching is not applied in the following cases:
- Requests and responses that are not compliant with RFC standards
- URLs containing over 255 characters
- 301 and 401 responses with cookie headers
- Use of HEAD method
- Pipelined transactions

Note![]() The metadata caching feature is available for Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.1 and later, where the earliest Cisco WAAS version in the Cisco Branch WAE is Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.1. The metadata caching feature can interoperate with an HTTP accelerator on a Cisco Data Center WAE that has an earlier Cisco WAAS version.
The metadata caching feature is available for Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.1 and later, where the earliest Cisco WAAS version in the Cisco Branch WAE is Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.1. The metadata caching feature can interoperate with an HTTP accelerator on a Cisco Data Center WAE that has an earlier Cisco WAAS version.
HTTP Accelerator Subnets
About HTTP Accelerator Subnets
An HTTP accelerator subnet allows you to selectively enable or disable specific HTTP optimization features for specific IP subnets by using an Access Control List (ACL). This feature can be applied to the following HTTP optimizations:
To define IP subnets, run the ip access-list global configuration command. For more information on configuring subnets, refer to the ip access-list global configuration command in the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference. You can use both standard and extended ACLs.
Configuring an HTTP Accelerator Subnet
To configure a subnet for an HTTP accelerator feature, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Enable global configuration for all the HTTP accelerator features that you want to use.
Enable global configuration for all the HTTP accelerator features that you want to use.
Step 2![]() Create an IP access list to use for a subnet of traffic:
Create an IP access list to use for a subnet of traffic:
Step 3![]() Associate the ACL with a specific HTTP accelerator feature. For information about associating an ACL with an HTTP accelerator feature, see the accelerator http global configuration command in the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
Associate the ACL with a specific HTTP accelerator feature. For information about associating an ACL with an HTTP accelerator feature, see the accelerator http global configuration command in the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
In this example, the HTTP metadata cache feature applies to all the connections that match the conditions specified in the extended access list md_acl.
In the following example, the HTTP suppress-server-encoding feature applies to all the connections that match the conditions specified in the standard access list 10:
For the features (in this example, DRE hints and HTTPS metadata cache) that do not have an ACL associated with them, global configuration is used and the features are applicable to all the connections.
Configuring MAPI Acceleration
About MAPI Acceleration
Consider the following MAPI acceleration features and guidelines:
- The MAPI application accelerator accelerates Microsoft Outlook Exchange traffic that uses the Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI) protocol.
–![]() For Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.x and later, Microsoft Outlook 2000 to 2013 clients are supported.
For Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.x and later, Microsoft Outlook 2000 to 2013 clients are supported.
–![]() For Cisco WAAS Version 5.2.x and earlier, Microsoft Outlook 2000 to 2010 clients are supported.
For Cisco WAAS Version 5.2.x and earlier, Microsoft Outlook 2000 to 2010 clients are supported.
- Clients can be configured with Outlook in cached or noncached mode; both modes are accelerated.
- Secure connections that use message authentication (signing) are not accelerated.
- Microsoft Outlook 2007 and 2010 have encryption enabled by default. You must disable encryption to benefit from the MAPI application accelerator.
- MAPI accelerator and the EPM accelerator:
–![]() The EPM application accelerator must be enabled for the MAPI application accelerator to operate. EPM is enabled by default. Additionally, the system must define an optimization policy of type EPM, specify the MAPI UUID, and have an Accelerate setting of MAPI. This policy, MAPI for the Email-and-Messaging application, is defined by default.
The EPM application accelerator must be enabled for the MAPI application accelerator to operate. EPM is enabled by default. Additionally, the system must define an optimization policy of type EPM, specify the MAPI UUID, and have an Accelerate setting of MAPI. This policy, MAPI for the Email-and-Messaging application, is defined by default.
–![]() EPM traffic, such as MAPI, does not normally use a predefined port. If your Microsoft Outlook administrator has configured Microsoft Outlook in a nonstandard way to use a static port, you must create a new basic optimization policy that accelerates MAPI traffic with a class map that matches the static port that was configured for Microsoft Outlook.
EPM traffic, such as MAPI, does not normally use a predefined port. If your Microsoft Outlook administrator has configured Microsoft Outlook in a nonstandard way to use a static port, you must create a new basic optimization policy that accelerates MAPI traffic with a class map that matches the static port that was configured for Microsoft Outlook.
- If the Cisco WAE becomes overloaded with connections, the MAPI application accelerator continues to accelerate MAPI connections by using internally reserved connection resources. If the reserved resources are also exceeded, new MAPI connections are passed through until connection resources become available.
- When you enable MAPI acceleration, Encrypted MAPI acceleration is enabled by default. For more information on Encrypted MAPI acceleration, see Configuring Encrypted MAPI Acceleration.
Configuring MAPI Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To configure MAPI acceleration settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To enable the MAPI accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
To enable the MAPI accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
Step 2![]() The Enabled Features window appears.
The Enabled Features window appears.
a.![]() At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the MAPI Accelerator check box.
At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the MAPI Accelerator check box.
Step 3![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 4![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > MAPI Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > MAPI Settings.
The MAPI Acceleration Settings window appears (Figure 12-3).
Figure 12-3 MAPI Acceleration Settings Window
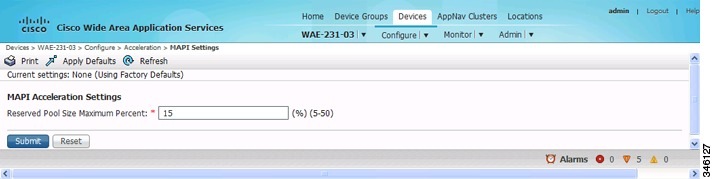
Step 5![]() In the Reserved Pool Size Maximum Percent field, enter the maximum percent of connections in order to restrict the maximum number of connections reserved for MAPI optimization during TFO overload.
In the Reserved Pool Size Maximum Percent field, enter the maximum percent of connections in order to restrict the maximum number of connections reserved for MAPI optimization during TFO overload.
- The maximum percent of connections is specified as a percent of the TFO connection limit of the platform. Valid percent ranges from 5 to 50 percent. The default is 15 percent, which reserves approximately 0.5 connection for each client-server association group optimized by the MAPI accelerator.
- The client maintains at least one association group per server to which it connects, with an average of about three connections per association group. For deployments that see a greater average number of connections per association group, or where TFO overload is a frequent occurrence, a higher value for reserved pool size maximum percent is recommended.
- Reserved connections remain unused when the device is not under TFO overload. Reserved connections are released when the association group is terminated.
The changes are saved to the device or device group.
Configuring Encrypted MAPI Acceleration
This section contains the following topics:
- About Encrypted MAPI Acceleration
- Terms Used with Microsoft Active Directory
- Work flow for Configuring Encrypted MAPI
- Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings
- Configuring a Machine Account Identity
- Creating and Configuring a User Account
- Configuring Microsoft Active Directory
- Managing Domain Identities and Encrypted MAPI State
- Microsoft Outlook and Exchange Versions Supported for Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
- Configuration Prerequisites for Optimizing MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
- MAPI Acceleration Charts for Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
About Encrypted MAPI Acceleration
The Encrypted MAPI (EMAPI) acceleration feature provides WAN optimization for secure MAPI application protocols using Microsoft Kerberos security protocol and Microsoft Windows Active Directory identity for authentication of clients or servers or both in the domain.

Note![]() You must enable MAPI acceleration first for Encrypted MAPI acceleration to be enabled. Encrypted MAPI acceleration is enabled by default.
You must enable MAPI acceleration first for Encrypted MAPI acceleration to be enabled. Encrypted MAPI acceleration is enabled by default.
Terms Used with Microsoft Active Directory
The following terms are used with Microsoft Active Directory and Cisco Encrypted MAPI acceleration:
- Microsoft Active Directory: A set of directory-based and identity-based services developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. The Microsoft Active Directory Domain Services (DS) domain controller stores information about domain users and devices
- User Identity: An Active Directory user account. The Microsoft Active Directory employs the user identity to authenticate the user, and to grant appropriate access to domain resources.
- Machine Account Identity: A computer (machine) account used to authenticate the user's computer access to Microsoft Active Directory Domain Services. Each Windows Active Directory computer has a unique machine (computer) account.
For more information on Microsoft Active Directory, see the “Microsoft Developer Network Active Directory” pages.
Work flow for Configuring Encrypted MAPI
To configure Encrypted MAPI traffic acceleration, complete the tasks listed in Table 12-4 . These tasks must be performed on both Cisco data center WAEs and Cisco branch WAEs unless specified as Not Required or Optional.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Configure DNS Settings. |
To configure DNS settings, see Configuring the DNS Server in the chapter “Configuring Network Settings” . |
Configure NTP Settings. |
To synchronize the time with Microsoft Active Directory, see Configuring NTP Settings in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings” . |
Verify Cisco WAE devices are registered and online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. |
To verify Cisco WAE devices are registered and online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, see Devices Window in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” . |
Configure SSL Peering Service. |
To configure SSL Peering Service, see Configuring SSL Peering Service. |
Verify WAN Secure mode is enabled. |
To verify WAN Secure mode is enabled, run the show accelerator wansecure EXEC command. |
(Optional) Configure windows domain settings and perform domain join. The domain join function automatically creates the machine account in Active Directory. |
To configure Windows Domain Server Authentication settings, see Configuring Microsoft Windows Domain Server Authentication Settings in the chapter “Configuring Administrative Login Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting” . |
Configure domain identities (for machine account and optional user accounts). |
To configure a machine account identity, see Configuring a Machine Account Identity. (Optional) To create a user account and configure a user account identity, see Creating and Configuring a User Account. Note that configuring domain identities is not required on Cisco branch WAE devices. |
Enable Microsoft Windows Domain Encrypted Service. |
To enable the Microsoft Windows Domain Encrypted Service, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services page and check the Enable Encrypted Service check box. |
Enable Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization. |
To enable Encrypted MAPI Traffic, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features. |
Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings
To configure encrypted MAPI settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Configure DNS settings.
Configure DNS settings.
The Cisco WAAS DNS server must be a part of the DNS system of Microsoft Windows Active Directory domains to resolve DNS queries for traffic encryption.
For more information about configuring DNS settings, see Configuring the DNS Server in the chapter “Configuring Network Settings” .
Step 2![]() Configure NTP settings to synchronize the time with the Active Directory.
Configure NTP settings to synchronize the time with the Active Directory.
The Cisco WAAS device has to be in synchronization with the Active Directory for Encrypted MAPI acceleration. The Cisco WAAS NTP server must share time synchronization with the Active Directory Domain Controllers’ domains for which traffic encryption is required. Out-of-sync time causes Encrypted MAPI acceleration to fail.
For more information about synchronizing time with the Active Directory, see Configuring NTP Settings in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings” .
Step 3![]() Verify if Cisco WAE devices are registered and are online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Verify if Cisco WAE devices are registered and are online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
For more information about verifying that Cisco WAE devices are registered and are online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, see Devices Window in Chapter 15, “Monitoring Your WAAS Network.”
Step 4![]() Configure the SSL Peering Service.
Configure the SSL Peering Service.

Note![]() The SSL accelerator must be enabled and in running state.
The SSL accelerator must be enabled and in running state.
For more information about configuring the SSL Peering Service, see Configuring SSL Peering Service.
Step 5![]() Verify if WAN Secure mode is enabled.
Verify if WAN Secure mode is enabled.
accelerator mapi wansecure-mode {always | auto | none}
Step 6![]() (Optional on Cisco data center WAEs if user accounts only are used for domain identity configuration in Step 7.)
(Optional on Cisco data center WAEs if user accounts only are used for domain identity configuration in Step 7.)
Configure Microsoft Windows domain settings and perform a domain join. (A domain join automatically creates the machine account in Active Directory.)

Note![]() Performing a domain join of the Cisco WAE is not required on Cisco branch WAE devices.
Performing a domain join of the Cisco WAE is not required on Cisco branch WAE devices.
To configure Microsoft Windows Domain Server Authentication settings, see Configuring Microsoft Windows Domain Server Authentication Settings in the chapter “Configuring Administrative Login Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting” .

Note![]() Kerberos and Microsoft Windows NT LAN Manager (Microsoft Windows NTLM) authentication are used for Encrypted MAPI acceleration. For Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.1 and later, encrypted NTLM traffic is supported for EMAPI, and the Cisco WAE device optimizes NTLM traffic for domains configured with NTLM authentication.
Kerberos and Microsoft Windows NT LAN Manager (Microsoft Windows NTLM) authentication are used for Encrypted MAPI acceleration. For Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.1 and later, encrypted NTLM traffic is supported for EMAPI, and the Cisco WAE device optimizes NTLM traffic for domains configured with NTLM authentication.
Step 7![]() Configure domain identities. This is not required for Cisco branch WAEs.
Configure domain identities. This is not required for Cisco branch WAEs.
- As highlighted in Step 6, you must have at least one account, either user or machine, that is configured with a domain identity. Each device can support up to five domain identities, one machine account identity and four user account identities. This allows a Cisco WAAS device to accelerate up to five domain trees.
- You must configure a domain identity for each domain with an exchange server that has clients to be accelerated.
a.![]() Configure the machine account identity (for more information, see Configuring a Machine Account Identity).
Configure the machine account identity (for more information, see Configuring a Machine Account Identity).
- A machine account for the core device is automatically created during the join process described in the Microsoft Windows Domain Server authentication procedure in Step 6. If you are using a machine account, a machine account identity must be configured for this account.
- Each device supports only one machine account identity.
b.![]() Create and configure optional user accounts (for more information, see Creating and Configuring a User Account).
Create and configure optional user accounts (for more information, see Creating and Configuring a User Account).
- For additional security, you can utilize up to four optional user accounts for additional security. Multiple user accounts provide greater security than having all of the core devices using a single user account. You must configure a user account identity for each user account, whether you are utilizing an existing user account or creating a new one.
Step 8![]() Enable the Windows Domain Encrypted Service. (This is enabled by default.)
Enable the Windows Domain Encrypted Service. (This is enabled by default.)
a.![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
b.![]() From the menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears.
c.![]() Check the Enable Encrypted Service check box.
Check the Enable Encrypted Service check box.
d.![]() To save the changes, click Submit.
To save the changes, click Submit.
Step 9![]() Enable Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization.
Enable Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization.
a.![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
The Enabled Features window appears (Figure 12-1).
b.![]() In the Enabled Features window, check the Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization check box.
In the Enabled Features window, check the Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization check box.
c.![]() In the Enabled Features window, check the MAPI Accelerator check box.
In the Enabled Features window, check the MAPI Accelerator check box.

Note![]() To enable Encypted MAPI, you must also check the MAPI Accelerator check box. (Encrypted MAPI traffic optimization is enabled by default.)
To enable Encypted MAPI, you must also check the MAPI Accelerator check box. (Encrypted MAPI traffic optimization is enabled by default.)
For more information on the Enabled Features window, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features.
Configuring a Machine Account Identity
For definitions of machine account identity and other Microsoft Active Directory terms, see Terms Used with Microsoft Active Directory.
To configure an identity for a machine account, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears.
Step 3![]() Click the Add Domain Identity button.
Click the Add Domain Identity button.
The Domain Identity dialog box appears (Figure 12-4).

Note![]() Each Cisco WAAS device to be accelerated must have a domain identity.
Each Cisco WAAS device to be accelerated must have a domain identity.
Figure 12-4 Domain Identity Dialog Box
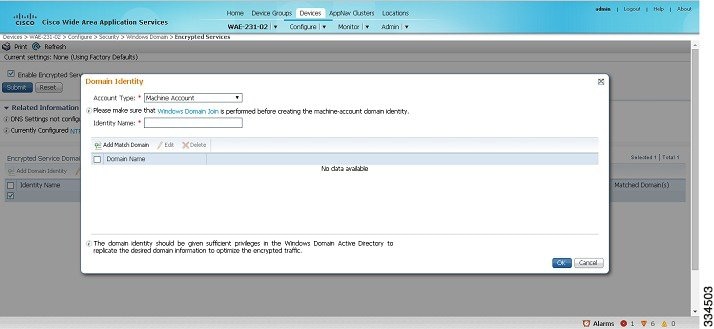
a.![]() From the Account Type drop-down list, choose Machine Account.
From the Account Type drop-down list, choose Machine Account.

Note![]() You must complete the Microsoft Windows domain join before you create the machine account domain identity. For more information, see Configuring Microsoft Windows Domain Server Settings on a Cisco WAAS Device in the chapter “Configuring Administrative Login Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting”.
You must complete the Microsoft Windows domain join before you create the machine account domain identity. For more information, see Configuring Microsoft Windows Domain Server Settings on a Cisco WAAS Device in the chapter “Configuring Administrative Login Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting”.
b.![]() In the Identity Name field, enter the Identity Name. Use only alphanumeric characters, up to a maximum of 32 characters.
In the Identity Name field, enter the Identity Name. Use only alphanumeric characters, up to a maximum of 32 characters.

Note![]() The domain identity must have sufficient privileges in the Windows Domain Active Directory to replicate the desired domain information to optimize encrypted traffic. To configure privileges, see Configuring Microsoft Active Directory.
The domain identity must have sufficient privileges in the Windows Domain Active Directory to replicate the desired domain information to optimize encrypted traffic. To configure privileges, see Configuring Microsoft Active Directory.
Step 4![]() To add the child domains of the domain (with which the device is registered) for which the Domain Identity should optimize the encrypted traffic, click the Add Match Domain button.
To add the child domains of the domain (with which the device is registered) for which the Domain Identity should optimize the encrypted traffic, click the Add Match Domain button.
You can add up to 32 child domains. If you do not want the Domain Identity to optimize the traffic for any of the child domains, you can delete the selected match domain items.

Note![]() The child domains feature is available on devices running Cisco WAAS Version 5.4 and later.
The child domains feature is available on devices running Cisco WAAS Version 5.4 and later.
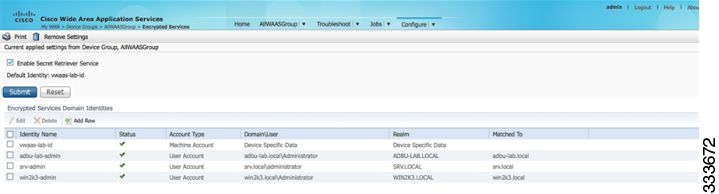
The domain identity appears in the Encrypted Services Domain Identities list (Figure 12-5).
Figure 12-5 Encrypted Services—Domain Identity
Creating and Configuring a User Account
For definitions of user account, user account identity and other Microsoft Active Directory terms, see Terms Used with Microsoft Active Directory.
To create a user account and configure a user account identity, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears (Figure 12-6).
Figure 12-6 Encrypted Services
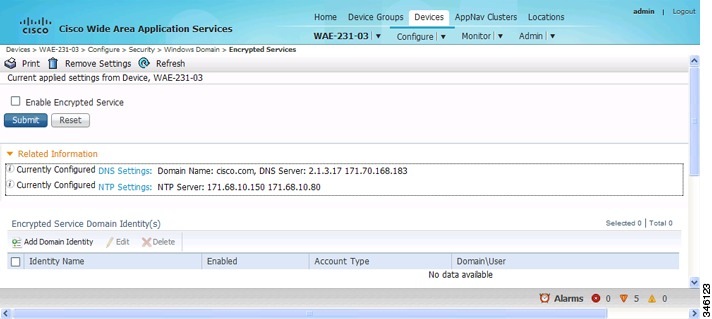
Step 3![]() To add a user account domain identity, in the Encrypted Service Domain Identity(s) table listing area, click Add Domain Identity.
To add a user account domain identity, in the Encrypted Service Domain Identity(s) table listing area, click Add Domain Identity.
The Domain Identity window appears (Figure 12-7).
Figure 12-7 Add Domain Identity—User Account
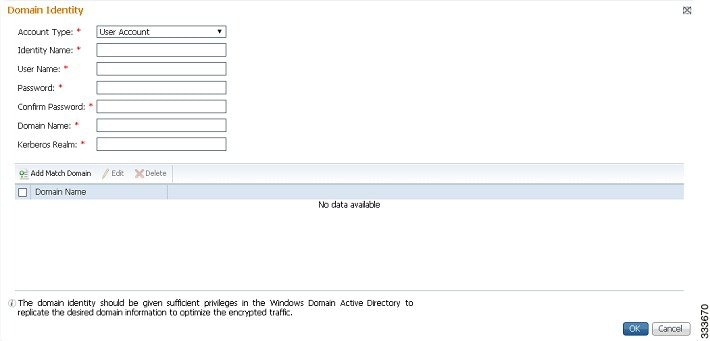
a.![]() From the Account Type drop-down list, choose User Account.
From the Account Type drop-down list, choose User Account.
b.![]() In the Identity Name field, enter the identity name. Use only alphanumeric characters, up to a maximum of 32 characters.
In the Identity Name field, enter the identity name. Use only alphanumeric characters, up to a maximum of 32 characters.
c.![]() Enter a username and password.
Enter a username and password.
f.![]() To add the child domains of the domain (with which the device is registered) for which the Domain Identity should optimize the encrypted traffic, click the Add Match Domain button.
To add the child domains of the domain (with which the device is registered) for which the Domain Identity should optimize the encrypted traffic, click the Add Match Domain button.
You can add up to 32 child domains. If you do not want the Domain Identity to optimize the traffic for any of the child domains, you can delete the selected match domain items.

Note![]() The domain identity must have sufficient privileges in the Windows Domain Active Directory to replicate the desired domain information to optimize encrypted traffic. For information about configuring privileges, see Configuring Microsoft Active Directory.
The domain identity must have sufficient privileges in the Windows Domain Active Directory to replicate the desired domain information to optimize encrypted traffic. For information about configuring privileges, see Configuring Microsoft Active Directory.
The domain identity appears in the Encrypted Services Domain Identities list.

Note![]() Secure Store encryption is used for the user account domain identity password. If Secure Store cannot be opened, an alarm is raised indicating that the configuration updates could not be stored on the device. After Secure Store can be opened and the configuration updates are successfully stored on the device, the alarm is cleared.
Secure Store encryption is used for the user account domain identity password. If Secure Store cannot be opened, an alarm is raised indicating that the configuration updates could not be stored on the device. After Secure Store can be opened and the configuration updates are successfully stored on the device, the alarm is cleared.
Configuring Microsoft Active Directory
To grant Cisco WAAS permission to accelerate Microsoft Exchange-encrypted email sessions, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Using an account with Domain Administrator privileges, launch the Active Directory Users and Computers application.
Using an account with Domain Administrator privileges, launch the Active Directory Users and Computers application.

Note![]() This group is for accounts that Cisco WAAS will use to optimize Microsoft Exchange traffic. Regular users and computers should not be added to this group.
This group is for accounts that Cisco WAAS will use to optimize Microsoft Exchange traffic. Regular users and computers should not be added to this group.
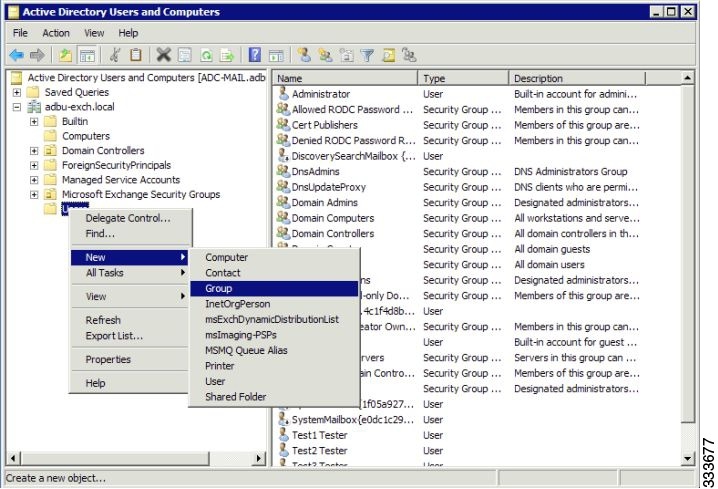
a.![]() Right-click the Unit to contain the new group and choose New > Group (Figure 12-8).
Right-click the Unit to contain the new group and choose New > Group (Figure 12-8).
Figure 12-8 Active Directory—Add Group
b.![]() In the Group field, enter a name and select the following attributes:
In the Group field, enter a name and select the following attributes:
Step 3![]() Configure the permissions required by Cisco WAAS.
Configure the permissions required by Cisco WAAS.
a.![]() From the menu bar in the Active Directory Users and Computers application window, choose View > Advanced Features.
From the menu bar in the Active Directory Users and Computers application window, choose View > Advanced Features.
b.![]() Right-click the root of the domain and choose Properties.
Right-click the root of the domain and choose Properties.
c.![]() Click the Security tab (Figure 12-9).
Click the Security tab (Figure 12-9).
Figure 12-9 Active Directory—Security Tab
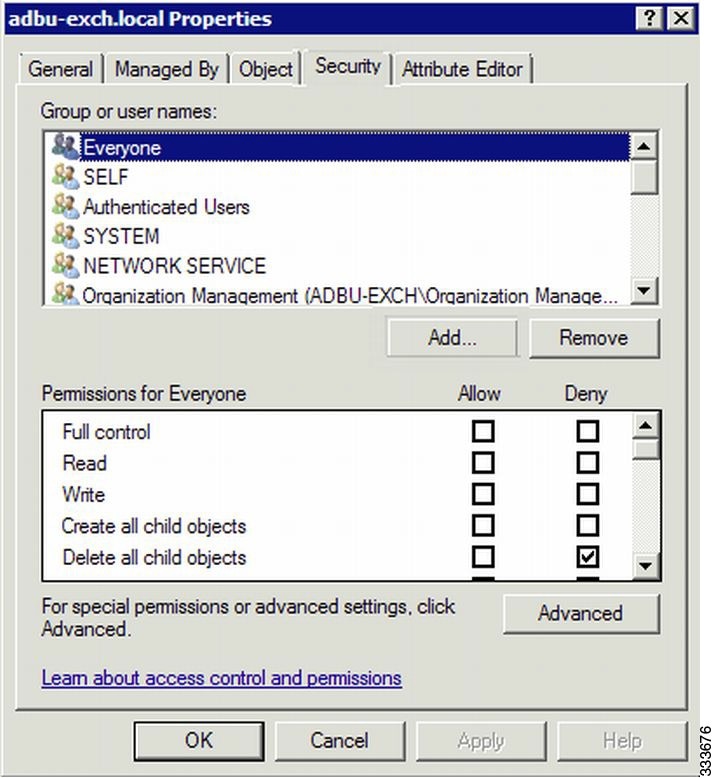
d.![]() In the Group or User Names section, click Add.
In the Group or User Names section, click Add.
e.![]() In the Enter the object names to select field, enter the name of the new group.
In the Enter the object names to select field, enter the name of the new group.
f.![]() To add the new group to the list, click OK.
To add the new group to the list, click OK.
g.![]() Check the check box adjacent to the new group in the Group or user names list and set the following permissions to Allow:
Check the check box adjacent to the new group in the Group or user names list and set the following permissions to Allow:
–![]() Replicating Directory Changes
Replicating Directory Changes
–![]() Replicating Directory Changes All
Replicating Directory Changes All
Step 4![]() Add an account to the group.
Add an account to the group.
User or workstation (computer) accounts must be added to the new group for WAAS Exchange Encrypted email optimization.
a.![]() Right-click on the account you want to add and select the Member Of tab.
Right-click on the account you want to add and select the Member Of tab.
c.![]() Choose the new group you created and click OK.
Choose the new group you created and click OK.
The configuration of Active Directory permissions is complete.
Managing Domain Identities and Encrypted MAPI State
Editing an Existing Domain Identity

Note![]() If the password for a user account has been changed in the Active Directory, you must edit the user account domain identity on the Cisco WAAS device to match the new Active Directory password.
If the password for a user account has been changed in the Active Directory, you must edit the user account domain identity on the Cisco WAAS device to match the new Active Directory password.
–![]() For a machine account identity, only the state of the domain identity (enabled or disabled) can be modified from a Cisco WAAS device.
For a machine account identity, only the state of the domain identity (enabled or disabled) can be modified from a Cisco WAAS device.
–![]() For a user account identity, only the state of the domain identity (enabled or disabled) and the password can be modified from a Cisco WAAS device.
For a user account identity, only the state of the domain identity (enabled or disabled) and the password can be modified from a Cisco WAAS device.
To change the password for a user account domain identity on a Cisco WAAS device if the password for the account in the Active Directory has changed, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears.
Step 3![]() Select the user account domain identity to modify and click the Edit icon.
Select the user account domain identity to modify and click the Edit icon.
The Domain Identity window appears.
Step 4![]() In the Password field, change the password. The password should be the same as the password for the account in Active Directory.
In the Password field, change the password. The password should be the same as the password for the account in Active Directory.
Deleting an Existing Domain Identity
To delete a domain identity on a WAAS device, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears.
Step 3![]() Select one or more domain identities to delete, and then click the Delete icon to remove the domain identity configured on the Cisco WAAS device.
Select one or more domain identities to delete, and then click the Delete icon to remove the domain identity configured on the Cisco WAAS device.
If the domain identity is being used for optimizing encrypted traffic, a warning message appears.
Step 4![]() To accept the procedure, click OK.
To accept the procedure, click OK.
To cancel the procedure, click Cancel.
Disabling Encrypted MAPI
To disable Encrypted MAPI, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Disable Encrypted Service.
Disable Encrypted Service.
a.![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Security > Windows Domain > Encrypted Services.
The Encrypted Services window appears.
b.![]() Uncheck the Enable Encrypted Service check box.
Uncheck the Enable Encrypted Service check box.
c.![]() To save the changes, click Submit.
To save the changes, click Submit.
Step 3![]() Disable Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization.
Disable Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization.
a.![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
The Enabled Features window appears.
b.![]() Uncheck the Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization check box.
Uncheck the Encrypted MAPI Traffic Optimization check box.
c.![]() To save the changes, click Submit.
To save the changes, click Submit.
Viewing Encrypted MAPI Acceleration Statistics
To view the statistics for Encrypted MAPI connections, see the Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI) Acceleration Charts in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
Remote Procedure Call over HTTP (RPC over HTTP) allows Microsoft Outlook clients to access Microsoft Exchange servers from outside the enterprise network using HTTP or HTTPS as a transport for the RPC protocol. It allows a client on the Internet to connect securely to a Microsoft Exchange Server without having to log into a virtual private network (VPN) first.
An RPC-HTTP (RPC-H) module in Cisco WAAS, integrated into the existing Cisco WAAS MAPI optimizer, will provide Cisco WAAS the ability to optimize MAPI over RPC-HTTP(S) traffic.
Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.x and later supports L7 optimization for RPC-HTTP(S) traffic.
Microsoft Outlook and Exchange Versions Supported for Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
Table 12-5 shows the clients and servers that support Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S).
Table 12-5 Clients and Servers Supporting Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
Microsoft Exchange 2013 and Microsoft Exchange 2016 can be configured for MAPI over HTTP support. MAPI over HTTP traffic will not be optimized by MAPI accelerator. However, MAPI over HTTP traffic will get L4 optimization benefits from Cisco WAAS.
Configuration Prerequisites for Optimizing MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
To complete prerequisites for configuring optimization of MAPI RPC over HTTP(S), follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Ensure that the SSL, HTTP and MAPI accelerators are enabled. If you have enabled SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) on both branch and data center devices, MAPI over RPC HTTPS will use Smart-SSL and not SSL Accelerator V1.
Ensure that the SSL, HTTP and MAPI accelerators are enabled. If you have enabled SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) on both branch and data center devices, MAPI over RPC HTTPS will use Smart-SSL and not SSL Accelerator V1.
Step 2![]() Configure SSL acceleration. For more information on configuring SSL acceleration, see Configuring SSL Acceleration. If you enable SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) on both Cisco branch and Cisco data center devices, MAPI over RPC HTTPS will use Smart-SSL and not SSL Accelerator V1.
Configure SSL acceleration. For more information on configuring SSL acceleration, see Configuring SSL Acceleration. If you enable SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) on both Cisco branch and Cisco data center devices, MAPI over RPC HTTPS will use Smart-SSL and not SSL Accelerator V1.
Step 3![]() When you configure SSL acceleration, be sure to enable protocol chaining, by checking the Enable protocol chaining check box in the SSL Accelerated Services window.
When you configure SSL acceleration, be sure to enable protocol chaining, by checking the Enable protocol chaining check box in the SSL Accelerated Services window.

Note![]() If protocol chaining is not enabled, the Cisco WAAS device will only optimize SSL traffic on the specified IP address and port.
If protocol chaining is not enabled, the Cisco WAAS device will only optimize SSL traffic on the specified IP address and port.
Step 4![]() Configure a Microsoft Windows domain identity on the core device, for Encrypted MAPI connections.
Configure a Microsoft Windows domain identity on the core device, for Encrypted MAPI connections.
Step 5![]() Verify that encryption is enabled in the MAPI accelerator. For more information on Encrypted MAPI settings, refer to Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings
Verify that encryption is enabled in the MAPI accelerator. For more information on Encrypted MAPI settings, refer to Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings
MAPI Acceleration Charts for Cisco WAAS MAPI RPC over HTTP(S)
The MAPI Acceleration report displays MAPI acceleration statistics. For Cisco WAAS Version 5.5.3 and later, the following MAPI acceleration charts are added or modified:
- MAPI: Handled Traffic Pattern: A new pie diagram that shows the three different types of traffic handled by the MAPI AO. For more information, see MAPI: Handled Traffic Pattern in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
- MAPI: Connection Details—An existing chart for MAPI session connection statistics, MAPI: Connection Details now includes a new classification for optimized TCP and RPC-HTTP(S) MAPI connections. For more information, see MAPI: Connection Details in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
Cisco WAAS MAPI over HTTP
MAPI over HTTP provides the ability for Messaging API (MAPI) clients and servers to communicate across HTTP connection that no longer use RPC technology. This provides faster re-connects and improved reliability.
Release 6.4.3 provides optimization support for MAPI over HTTP traffic. This is enabled by default and uses SMART-SSL acceleration and protocol chaining to intercept and accelerate the MAPI over HTTP traffic. To ensure this optimization, you need to enable the SMART-SSL (SSL Accelerator v2) accelerator.
For more information on how to set up the exchange service, see, Using SSL Accelerated Services.
The MAPI Acceleration report displays MAPI acceleration statistics. For more information, see MAPI: Handled Traffic Pattern and MAPI: Connection Details in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
Microsoft Outlook and Exchange Versions Supported for Cisco WAAS MAPI over HTTP
Table 12-6 shows the clients and servers supporting Cisco WAAS MAPI over HTTP:
Table 12-6 Clients and Servers Supported for Cisco WAAS MAPI over HTTP
Configuring SMB Acceleration
About SMB Acceleration
The Service Message Block (SMB) application accelerator handles optimizations of file server operations. These optimizations apply to SMBv1, SMBv2 and SMBv3. You can configure the SMB application accelerator to perform the file server optimizations shown in Table 12-7 .
Table 12-7 SMB Application Accelerator File Server Optimizations
Configuring SMB Accelerator Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To configure the SMB Accelerator settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
The Enabled Features window appears (Figure 12-1).
a.![]() At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the SMB Accelerator check box.
At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the SMB Accelerator check box.
Step 3![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name (or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name (or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 4![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > SMB Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > SMB Settings.
The SMB Settings window appears (Figure 12-10).
Figure 12-10 SMB Accelerator Configuration Window
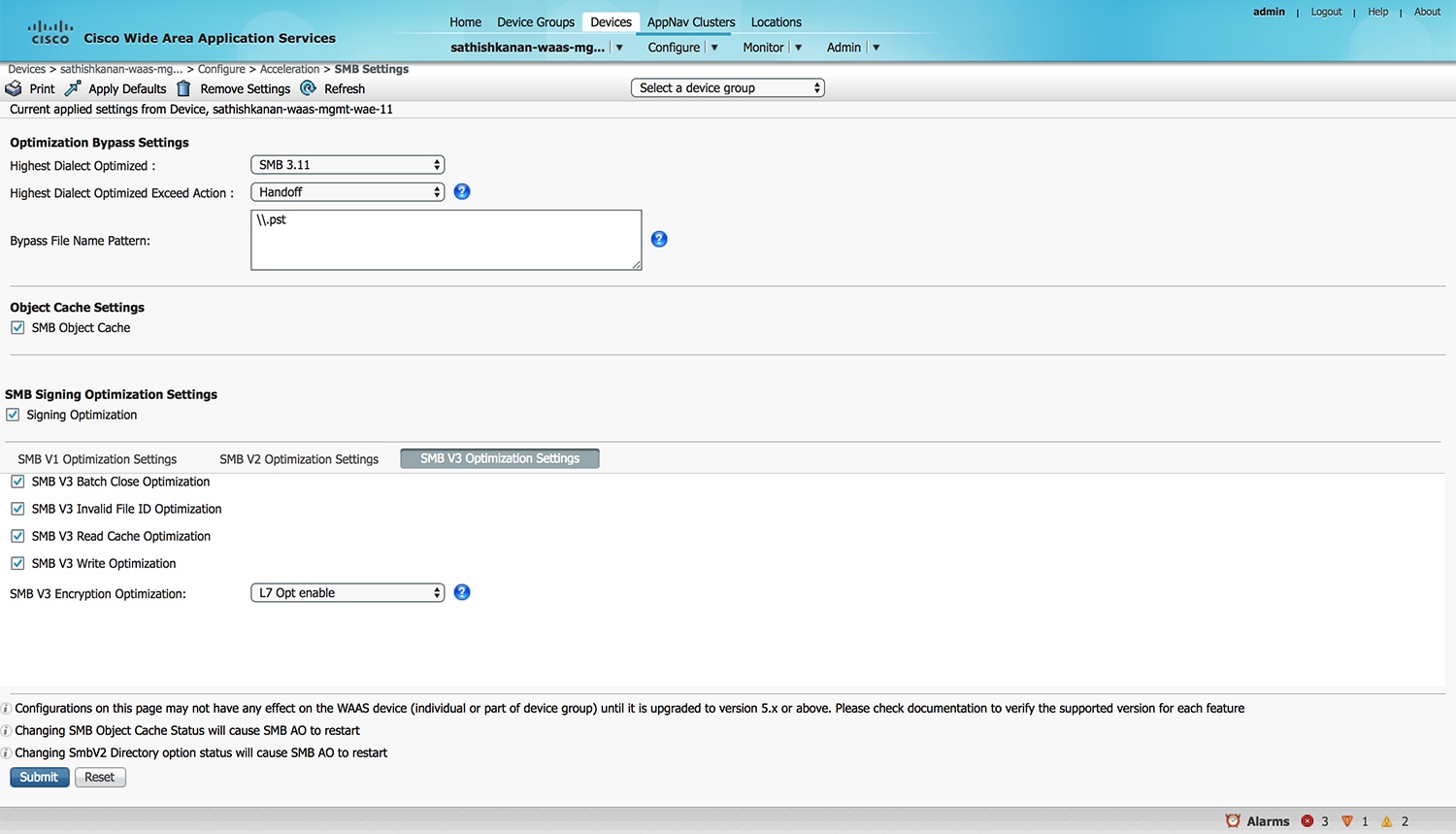
Step 5![]() From the Highest Dialect Optimized drop-down list, choose the highest dialect to optimize. The available options are:
From the Highest Dialect Optimized drop-down list, choose the highest dialect to optimize. The available options are:
Step 6![]() From the Highest Dialect Optimized Exceed Action drop-down list, choose the action for the dialects that are higher than the one chosen as the highest dialect to optimize:
From the Highest Dialect Optimized Exceed Action drop-down list, choose the action for the dialects that are higher than the one chosen as the highest dialect to optimize:
- Mute: The dialects higher than the one chosen as the highest dialect to optimize are removed from the negotiation list. This is the default selection.

Note![]() The Mute option of SMB AO is deprecated in dialects 3.x and 2.0 of SMB; muting within these versions has been found to be unsuccessful in terms of optimization.
The Mute option of SMB AO is deprecated in dialects 3.x and 2.0 of SMB; muting within these versions has been found to be unsuccessful in terms of optimization.
- Handoff: If the negotiated dialect is higher than the chosen highest dialect to optimize, the connection is handed off to the generic accelerator.

Note![]() For SMB 2.1 only, you must use the Cisco WAAS CLI to configure the Handoff parameter, using the accelerator smb smb2-1 exceed-action handoff global configuration command. If you use the Cisco WAAS Central Manager to select the Handoff parameter for SMB 2.1, the Highest Dialect Optimized Exceed Action will not take effect, and Handoff will not be displayed in commands like the show running-configuration command or the show accelerator smb command.
For SMB 2.1 only, you must use the Cisco WAAS CLI to configure the Handoff parameter, using the accelerator smb smb2-1 exceed-action handoff global configuration command. If you use the Cisco WAAS Central Manager to select the Handoff parameter for SMB 2.1, the Highest Dialect Optimized Exceed Action will not take effect, and Handoff will not be displayed in commands like the show running-configuration command or the show accelerator smb command.
Step 7![]() In the Bypass File Name Pattern field, enter the patterns for the file names that you want the SMB accelerator to bypass optimization for. The files whose names match the specified expressions are not optimized.
In the Bypass File Name Pattern field, enter the patterns for the file names that you want the SMB accelerator to bypass optimization for. The files whose names match the specified expressions are not optimized.
Step 8![]() To enable disk caching for SMB traffic, check the SMB Object Cache check box.
To enable disk caching for SMB traffic, check the SMB Object Cache check box.
Step 9![]() To enable optimization of signed SMB v2 and v3 traffic, check the Signing Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
To enable optimization of signed SMB v2 and v3 traffic, check the Signing Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
An SMB connection request can originate from the Branch office to the Data Center or vice-versa. For every connection, the Cisco WAE near the requester take the Cisco Edge WAE’s role, and the Cisco WAE near the SMB server takes the Cisco Core WAE’s role.
The following prerequisites, at the Cisco Core WAE and Cisco Edge WAE, are necessary to ensure that a signed connection is optimized:
- If an SMB connection is either a signed SMBv2 or an encrypted SMBv3, or has originated from an SMBv3 enabled client such as Windows 8 and above, then you must configure an identity as a pre-requisite to receive SMB optimization at Layer 7. Otherwise, you will only get Layer 4 (TDL) optimization benefits on these connections.
- It is sufficient to configure either a user identity or a machine identity; the administrator can decide based on ease of configuration. Both configurations are equal and serve the purpose of key retrieval. Domain-join is required only for machine identity.
a.![]() On the Cisco Core WAE, configure a valid user-identity with administrator privileges to enable secret-retrieval to fetch and cache the longterm service key of the SMB server by running the following global configuration command.
On the Cisco Core WAE, configure a valid user-identity with administrator privileges to enable secret-retrieval to fetch and cache the longterm service key of the SMB server by running the following global configuration command.
windows-domain encryption-service identity [identity] user-account name
[admin-username] domain [your.domain] realm [your.domain] password
To verify the identity configuration, run the following EXEC Command.
show windows-domain encryption-service identity detail
(Optional) To configure a machine identity, instead of using user identity, you can also follow the steps in the procedure Configuring a Machine Account Identity.
b.![]() For Kerberos Authentication to work correctly, ensure time synchronization between Client, Server, Cisco Core WAE and the Domain Controller.
For Kerberos Authentication to work correctly, ensure time synchronization between Client, Server, Cisco Core WAE and the Domain Controller.
- To verify whether a connection is signed or not, look into the SMBv2 Negotiate packet. The Signing Required field should be set to True in either the Negotiate Request or the Negotiate Response exchange.
- To verify if a connection has originated from a SMB3 capable client, look into the SMBv2 Negotiate Request packet. Under the dialects list, you should see some or all of the following dialects: SMB3.0, SMB3.02, or SMB3.11.
These configurations are similar to the EMAPI configuration. For more information, see Step 6 of the procedure Configuring Encrypted MAPI Settings.
c.![]() Verify that the WAN Secure mode is enabled. WAN Secure’s secure connection enables the key to be transported to the Edge WAE.
Verify that the WAN Secure mode is enabled. WAN Secure’s secure connection enables the key to be transported to the Edge WAE.
The default recommended mode is Auto. To verify the state of WAN Secure mode, run the following EXEC command:
To change the state of WAN Secure, run the following global configuration command:
accelerator smb wansecure-mode {always | auto | none}
d.![]() Verify that the Cisco WAE devices are registered and are online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Verify that the Cisco WAE devices are registered and are online with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Step 10![]() To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV1 Optimization Settings tab.
To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV1 Optimization Settings tab.
The SMB accelerator does not perform read-ahead, write, and lock-ahead optimizations for Microsoft Office if this optimization is disabled. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable named pipe optimization by caching named pipe sessions and positive RPS responses, check the Named Pipe Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable caching pathnames of files not found, check the ‘Not Found’ Cache Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable SMB to configure a centralized print deployment, check the Print Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable SMB to optimize the quantity of read-ahead data from the file, check the Read Ahead Optimization check box. SMB performs a read-ahead optimization only when the file is opened using the OpLock feature. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable the Write optimization by speeding up the write responses to the client, check the Write Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default
Step 11![]() To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV2 Optimization Settings tab.
To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV2 Optimization Settings tab.
- To enable asynchronous files to close optimizations, check the Batch Close Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable optimization of files with invalid file handle values, check the Invalid FID Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable read response caching, check the SMBV2 Read Cache Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- Check the SMBV2 Write Optimization check box to enable asynchronous write operations. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable optimization of directory browsing performance for SMB v2 traffic, check the Directory Service Optimization check box. The check box is checked by default. Directory service optimization is available on devices or device groups running Cisco WAAS Version 6.1.1 or later.
Step 12![]() To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV3 Optimization Settings tab.
To perform the following tasks, click the SMBV3 Optimization Settings tab.
- To enable asynchronous files to close optimizations, check the SMB v3 Batch Close Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable optimization of files with invalid file handle values, check the SMB v3 Invalid FID Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable read response caching, check the SMB v3 Read Cache Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- To enable asynchronous write operations, check the SMB v3 Write Optimization check box. This check box is checked by default.
- From the SMB v3 Encryption Optimization drop down box, choose the type of optimization you want: L7 Optimization, L4-only optimization, or Disable SMB v3 encrypted optimization. L7 optimization is selected by default.
Step 13![]() To save the changes, click Submit.
To save the changes, click Submit.
Configuring SMB Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
To configure SMB acceleration using the Cisco WAAS CLI, run the accelerator smb global configuration command.
Use the following operating guidelines for the accelerator smb global configuration command.
- The enterprise license is required to start the SMB accelerator.
- The show running-config EXEC mode command displays non-default settings only. Therefore, the command no accelerator smb enable does not show up in the running configuration if the SMB accelerator is disabled, while the accelerator smb enable command does display if the SMB accelerator is enabled.
- Use the accelerator smb signing unwrap enable command to verify signature of the signed request packets at the Cisco Edge WAE. This checks whether the packet is modified/tampered while coming over the LAN. However, since the packet usually travels in the LAN from the Client to the Cisco Edge WAE, chances of man-in-middle attacks are less likely and you may choose to disable Edge side signature verification for request packets.
- Use the accelerator smb wansecure-mode always command to enable WAN Secure mode for optimizing signed SMBv2 traffic. The default is always. The WAN Secure mode configuration for both the Cisco Edge WAE and Cisco Core WAE must match (be set at always) for the SMB accelerator to optimize signed SMBv2 connections. Even if one side has none set, then the signed connections would be handed over for generic optimization.
- Use the accelerator smb wansecure-mode none to disable the wansecure -mode.
- WAN Secure mode requires that the SSL application accelerator is enabled. Use the accelerator ssl enable global configuration command to enable the SSL accelerator.
- For more information on the accelerator smb global configuration command, see the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
Configuring ICA Acceleration
About ICA Acceleration
The Independent Computing Architecture (ICA) application accelerator provides WAN optimization on a Cisco WAAS device for ICA traffic that is used to access a virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). This is done through a process that is both automatic and transparent to the client and server.
ICA acceleration is enabled on a Cisco WAAS device by default.
Configuring ICA Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To configure ICA acceleration, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To enable the ICA accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
To enable the ICA accelerator, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features window.
Step 2![]() The Enabled Features window appears (Figure 12-1).
The Enabled Features window appears (Figure 12-1).
a.![]() At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the ICA Accelerator check box.
At the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the ICA Accelerator check box.
Step 3![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 4![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > ICA Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > ICA Settings.
The ICA Acceleration Configuration window appears.
Figure 12-11 ICA Acceleration Configuration Window
Step 5![]() Check the Enable Multi Stream ICA check box to allow the client and server up to three additional TCP connections that optimize multistream ICA traffic.
Check the Enable Multi Stream ICA check box to allow the client and server up to three additional TCP connections that optimize multistream ICA traffic.
Step 6![]() From the WAN Secure Mode drop-down list, choose the mode. The options are:
From the WAN Secure Mode drop-down list, choose the mode. The options are:

Note![]() The state of WAN Secure mode in both Cisco Branch WAE and Cisco Data Center WAE must match for connections to get optimized with the ICA accelerator.
The state of WAN Secure mode in both Cisco Branch WAE and Cisco Data Center WAE must match for connections to get optimized with the ICA accelerator.
Step 7![]() To configure DSCP values for MSI priority levels: In the DSCP Settings (QoS) under ICA Streams section, check the Enable DSCP Tagging check box. These values override the defaults.
To configure DSCP values for MSI priority levels: In the DSCP Settings (QoS) under ICA Streams section, check the Enable DSCP Tagging check box. These values override the defaults.
Consider the following ranges and guidelines:
–![]() Very High-Priority MSI (default of 41): Typically real-time traffic, such as audio.
Very High-Priority MSI (default of 41): Typically real-time traffic, such as audio.
–![]() High-Priority MSI (default of 41): Typically interactive traffic.
High-Priority MSI (default of 41): Typically interactive traffic.
–![]() Medium-Priority MSI (default of 21): Typically bulk data.
Medium-Priority MSI (default of 21): Typically bulk data.
–![]() Low-Priority MSI (default of 0, best effort): Typically background traffic, such as printing.
Low-Priority MSI (default of 0, best effort): Typically background traffic, such as printing.
The changes are saved to the device or device group.
Configuring ICA Acceleration Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Consider the following guidelines for configuring ICA acceleration using the Cisco WAAS CLI:
Configuring ICA over SOCKS
About ICA over SOCKS
Consider the following operating guidelines for configuring ICA over Socket Secure (SOCKS):
- In a typical deployment where NetScaler is deployed as a Socket Secure (SOCKS) proxy, the connections from the client go to the SOCKS server instead of the XenApp server.
- Because the ICA application accelerator accepts and intercepts only ICA and CGP packets, the packets with SOCKS headers are not recognized and the connection is handed off. The ICA traffic does not get optimized in such scenarios.
- The Cisco WAAS software supports optimizing ICA traffic redirected over SOCKS proxy servers for Cisco WAAS Version 6.3.1 and later.
Configuring ICA over SOCKS Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
- Make the necessary changes on the NetScaler Gateway to enable the SOCKS proxy (Cache redirection server).
- Make the equivalent and required changes on the StoreFront server along with updates to the default.ica file.
- Consider the following NetScaler gateway limitations for ICA over SOCKS:
–![]() Non-default ports configured with Multi-Port Policy on XenApp for Multi-Stream ICA (MSI) are not supported.
Non-default ports configured with Multi-Port Policy on XenApp for Multi-Stream ICA (MSI) are not supported.
–![]() SOCKS with ICA over SSL is not supported.
SOCKS with ICA over SSL is not supported.
–![]() SOCKS Version 4 is not supported. ICA over SOCKS Version 5 is supported for the NetScaler gateway.
SOCKS Version 4 is not supported. ICA over SOCKS Version 5 is supported for the NetScaler gateway.
To configure ICA over SOCKS, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name (or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name (or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Class-Map.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Class-Map.
Step 3![]() Edit the class-map named Citrix and add the required port number using the Add Match Condition option.
Edit the class-map named Citrix and add the required port number using the Add Match Condition option.
The port number added in the class-map should be the same as the one configured for the SOCKS proxy, on the NetScaler gateway.

Note![]() If the SOCKS proxy port is running on ICA or CGP ports, 1494 or 2498, then you do not need to modify the existing configuration.
If the SOCKS proxy port is running on ICA or CGP ports, 1494 or 2498, then you do not need to modify the existing configuration.
Step 4![]() Select the branch device and make the necessary changes for the port number.
Select the branch device and make the necessary changes for the port number.
Alternately, run the class-map type match-any citrix global configuration command to make these changes.
Configuring ICA over SSL
The Cisco WAAS software supports optimizing ICA over SSL. This allows the client and server to use the ICA protocol over an encrypted connection. To support optimizing ICA over SSL, perform the following steps:
- Configure ICA acceleration. See Configuring ICA Acceleration.
- Configure SSL acceleration. See Configuring SSL Acceleration.

Note![]() When you are configuring SSL acceleration, be sure to enable protocol chaining. If protocol chaining is not enabled, the Cisco WAAS device will only optimize SSL traffic on the specified IP address and port.
When you are configuring SSL acceleration, be sure to enable protocol chaining. If protocol chaining is not enabled, the Cisco WAAS device will only optimize SSL traffic on the specified IP address and port.
Configuring SSL Acceleration
This section contains the following topics:
- About SSL Acceleration
- Checklist for Configuring SSL Acceleration
- Prerequisites for Configuring SSL Acceleration
- Configuring SSL Global Settings
- Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key
- Working with Cipher Lists
- Working with CA Certificates
- Configuring SSL Management Services
- Configuring SSL Peering Service
- Using SSL Accelerated Services
- Updating a Certificate and Key in an SSL Accelerated Service
- Configuring SSL Acceleration for SaaS Applications
- Determining Server Domains Used by SaaS Applications
About SSL Acceleration
The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) application accelerator optimizes traffic on SSL encrypted connections. If SSL acceleration is not enabled, the Cisco WAAS software DRE optimizations are not very effective on SSL-encrypted traffic. The SSL application acceleration enables Cisco WAAS to decrypt and apply optimizations while maintaining the security of the connection.
Consider the following operating guidelines for SSL acceleration:
- On a Cisco WAAS Express device, only SSL cipher list, SSL certificate authorities, and SSL peering service configuration are supported.
- The SSL accelerator does not optimize protocols that do not start their SSL and Transport Layer Security (TLS) handshake from the very first byte. The only exception is HTTPS that goes through a proxy (where the HTTP accelerator detects the start of SSL and TLS). In this case, both HTTP and SSL accelerators optimize the connection.
The SSL application accelerator supports SSL Version 3 (SSLv3) and Transport Layer Security Version 1 (TLSv1) protocols. If a TLSv1.1 or TLSV1.2 client request is received, negotiation will not occur. Manual bypass of TLSv1.1 or TLSv1.2 packets is required in order to make these client and server connections.
Checklist for Configuring SSL Acceleration
Table 12-8 provides an overview of the steps you must complete to set up and enable SSL acceleration.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Prepare for configuring SSL acceleration. |
Identify the information that you need to gather before configuring SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS devices. For more information, see Prerequisites for Configuring SSL Acceleration. |
Enable secure store, the Enterprise License, and SSL acceleration. |
Enable Secure Store on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, which is required for secure handling of the SSL encryption certificates and keys. For more information, see Enabling Secure Store Encryption on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager Enable the Enterprise License. For more information, see Enabling Enterprise Licenses on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAEs Enable SSL acceleration. For more information, see Using SSL Accelerated Services. |
Enable SSL application optimization. |
For more information, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features. |
Configure SSL acceleration settings. |
(Optional) Configure the basic setup of SSL acceleration. For more information, see Configuring SSL Global Settings. |
Create and manage cipher lists. |
(Optional) Select and set up the cryptographic algorithms used on your Cisco WAAS devices. For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists. |
Set up Certificate Authority certificates. |
(Optional) Select, import, and manage certificate authority (CA) certificates. For more information, see Working with CA Certificates. |
Configure SSL management services. |
(Optional) Configure the SSL connections used between the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAE devices. For more information, see Configuring SSL Management Services. |
Configure SSL peering service. |
(Optional) Configure the SSL connections used between peer Cisco WAE devices for carrying optimized SSL traffic. For more information, see the Configuring SSL Peering Service. |
Configure and enable SSL-accelerated services. |
Add, configure, and enable services to be accelerated by the SSL application optimization feature. For more information, see Using SSL Accelerated Services. |
Prerequisites for Configuring SSL Acceleration
Confirming Your Network Information
Before you configure SSL acceleration, verify the following information about your network:
- The services that you want to be accelerated on the SSL traffic
- The server IP address and port information
- The public key infrastructure (PKI) certificate and private key information, including the certificate common name and Certificate Authority (CA) signing information
- The cipher suites supported
- The SSL versions supported
Figure 12-12 shows how the Cisco WAAS software handles SSL application optimization.
Figure 12-12 SSL Acceleration Block Diagram
When you configure SSL acceleration, you must configure SSL-accelerated service on the Cisco server-side (Data Center) WAE devices. The Cisco client-side (Branch) WAE should have its Secure Store initialized and unlocked or opened, but does not need to have the SSL-accelerated service configured. However, for SSL acceleration services to work, the SSL accelerator must be enabled on both Cisco Data Center WAEs and Cisco Branch WAEs. The Cisco WAAS Central Manager provides SSL management services and maintains the encryption certificates and keys.
Enabling Secure Store Encryption on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
Before you can use SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS system, you must enable Secure Store encryption on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. For more information on this procedure, see Configuring Secure Store Encryption Settings in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings” .
Enabling Enterprise Licenses on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAEs
Before you can use SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS system, you must enable the Enterprise license. For more information on this procedure, see Managing Cisco WAAS Software Licenses in the chapter “Configuring Other System Settings” .
Enabling SSL Acceleration on Cisco WAAS Devices
Before you can use SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS system, you must enable SSL acceleration on Cisco WAAS devices. For more information on this procedure, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features.

Note![]() If the SSL accelerator is already running, you must wait for two datafeed poll cycles to be completed when registering a new Cisco WAE with a Cisco WAAS Central Manager before making any configuration changes. Otherwise, the changes may not take effect.
If the SSL accelerator is already running, you must wait for two datafeed poll cycles to be completed when registering a new Cisco WAE with a Cisco WAAS Central Manager before making any configuration changes. Otherwise, the changes may not take effect.
Configuring SSL Global Settings
To configure the SSL acceleration global settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
The SSL Global Settings window appears (Figure 12-13).
Figure 12-13 SSL Global Settings Window
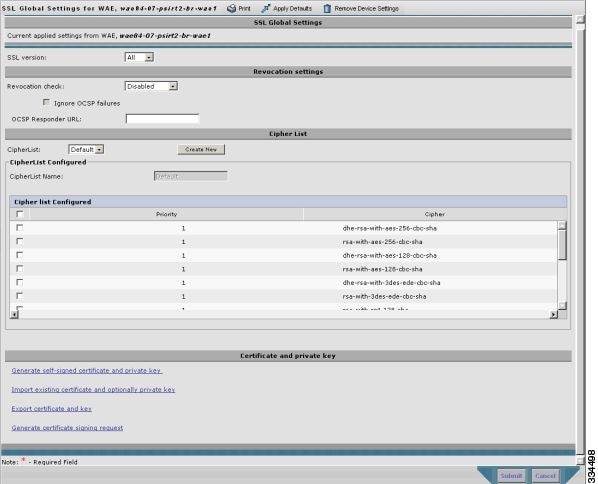
Step 3![]() To configure a device to use SSL settings from a particular device group: From the Select a Device Group drop-down list in the SSL global settings toolbar, choose a device group.
To configure a device to use SSL settings from a particular device group: From the Select a Device Group drop-down list in the SSL global settings toolbar, choose a device group.
- A device can use its own SSL settings, or the SSL settings from a device group. However, you cannot configure a device to use SSL settings from multiple device groups.
- If you have configured a device with specific SSL Accelerated Services and assigned it to a device group, these configurations are lost when you click the Override Group Settings in the Device Group > Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings window.
Step 4![]() From the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
From the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
Step 5![]() (Optional) Set the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) parameters for certificate revocation:
(Optional) Set the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) parameters for certificate revocation:
–![]() To use the OCSP responder specified in the OCSP Responder URL field, choose the ocsp-url.
To use the OCSP responder specified in the OCSP Responder URL field, choose the ocsp-url.
–![]() To use the OCSP responder URL specified in the Certificate Authority, choose ocsp-cert-url.
To use the OCSP responder URL specified in the Certificate Authority, choose ocsp-cert-url.
If the Ignore OCSP failures check box is checked, the SSL accelerator will treat the OCSP revocation check as successful if it does not get a definite response from the OCSP responder.
Step 6![]() From the Cipher List drop-down list, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration. For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
From the Cipher List drop-down list, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration. For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
Step 7![]() Choose a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-14).
Choose a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-14).
Figure 12-14 Configuring Service Certificate and Private Key
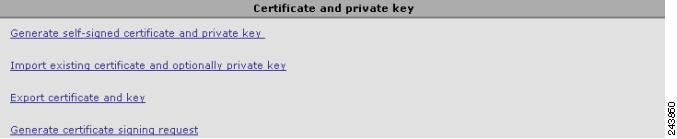
- To direct Cisco WAAS devices to use a self-signed certificate and key pair for SSL, click Generate Self-signed Certificate Key.
- To upload or paste an existing certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
- To export the current certificate and key pair, click Export Certificate Key.
- To renew or replace the existing certificate and key pair, click Generate Certificate Signing Request. The certificate signing request is used by the Certificate Authority to generate a new certificate.

Note![]() The file that you import or export must be in either a PKCS12 format or a Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
The file that you import or export must be in either a PKCS12 format or a Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
- To use the client-configured certificate, click Import existing client certificate and optionally private key.
For information about service certificate and private key configuration, see Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key.
Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key
Generating a Service Certificate and Private Key
To generate a service certificate and private key, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
The SSL Global Settings window appears (Figure 12-13).
Step 3![]() To generate a self-signed certificate and private key, at the Certificate and private key pane, click Generate self-signed certificate and private key. The Generate self-signed certificate and private key window appears (Figure 12-15).
To generate a self-signed certificate and private key, at the Certificate and private key pane, click Generate self-signed certificate and private key. The Generate self-signed certificate and private key window appears (Figure 12-15).
Figure 12-15 Self-Signed Certificate and Private Key
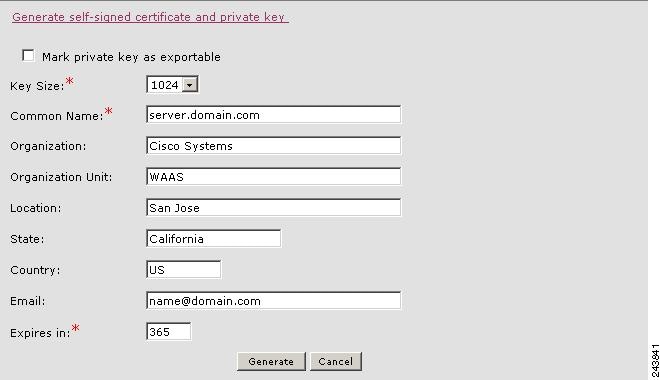
a.![]() To export this certificate and key in the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and the Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box.
To export this certificate and key in the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and the Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box.
b.![]() Fill in the certificate and private key fields.
Fill in the certificate and private key fields.
Consider the following operating guidelines for the Key Size field shown in Table 12-9 :
Table 12-9 Key Size Field Guidelines
Importing an Existing Certificate and Private Key
To import an existing service certificate and private key, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
The SSL Global Settings window appears (Figure 12-13).
Step 3![]() At the Certificate and private key pane, click Import existing certificate and optionally private key.
At the Certificate and private key pane, click Import existing certificate and optionally private key.
The Import existing certificate and optionally private key window appears (Figure 12-16):

Note![]() The Cisco WAAS SSL feature only supports RSA signing/encryption algorithm and keys.
The Cisco WAAS SSL feature only supports RSA signing/encryption algorithm and keys.
Figure 12-16 Importing Existing Certificate or Certificate Chain
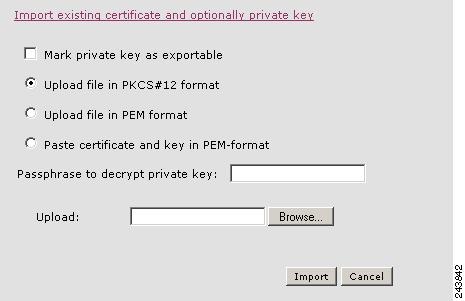
Step 4![]() To export this certificate and key into the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box.
To export this certificate and key into the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box.
Step 5![]() Choose an import format for the certificate and private key to be imported:
Choose an import format for the certificate and private key to be imported:
Consider the following operating guidelines for importing an existing certificate or certificate chain and private key:
- If the certificate and private key are already configured, you can update only the certificate. In this case, the Cisco WAAS Central Manager constructs the certificate and private key pair using the imported certificate and current private key. This functionality can be used to update an existing self-signed certificate to one signed by the CA, or to update an expiring certificate.
- The Cisco WAAS Central Manager allows importing a certificate chain consisting of an end certificate that must be specified first, a chain of intermediate CA certificates that sign the end certificate or intermediate CA certificate, and end with a root CA.
- The Cisco WAAS Central Manager validates the chain and rejects it if the validity date of the CA certificate is expired, or the signing order of certificates in the chain is not consequent.
Step 6![]() At the Upload field, use the Browse button to browse to the file and then select it.
At the Upload field, use the Browse button to browse to the file and then select it.
Step 7![]() In the Passphrase to decrypt private key field, enter a passphrase to decrypt the private key. If the private key is not encrypted, leave this field blank.
In the Passphrase to decrypt private key field, enter a passphrase to decrypt the private key. If the private key is not encrypted, leave this field blank.
Exporting an Existing Certificate and Private Key
To export an existing certificate and private key, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
The SSL Global Settings window appears (Figure 12-13).
Step 3![]() At the Certificate and private key pane, click Export certificate and key.
At the Certificate and private key pane, click Export certificate and key.
The Export certificate and key window appears (Figure 12-17).
Figure 12-17 Export Certificate and Key Window
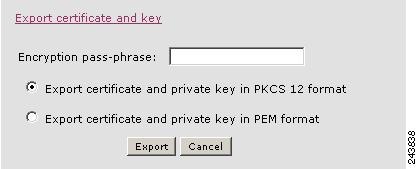
Step 4![]() In the Encryption pass-phrase field, enter the encryption passphrase.
In the Encryption pass-phrase field, enter the encryption passphrase.
Step 5![]() Choose an export format for the certificate:
Choose an export format for the certificate:
For PEM format, both the certificate and private key are included in a single PEM file.

Note![]() The Cisco WAAS Central Manager does not allow the export of certificate and private key if the certificate and key were marked as nonexportable when they were generated or imported.
The Cisco WAAS Central Manager does not allow the export of certificate and private key if the certificate and key were marked as nonexportable when they were generated or imported.
Generating a Certificate Signing Request
To generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Global Settings.
The SSL Global Settings window appears (Figure 12-13).
Step 3![]() At the Certificate and private key pane, click Generate certificate signing request.
At the Certificate and private key pane, click Generate certificate signing request.
The Certificate signing request window appears (Figure 12-18).
Figure 12-18 Generate Certificate Signing Request Window
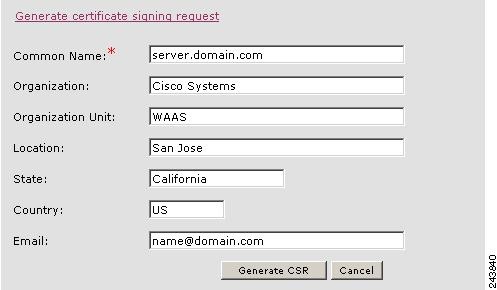
Step 4![]() Configure the CSR settings:
Configure the CSR settings:
Step 5![]() To generate the CSR, click Generate CSR.
To generate the CSR, click Generate CSR.
Step 6![]() To update the current certificate with one signed by the Certificate Authority:
To update the current certificate with one signed by the Certificate Authority:
a.![]() Generate PKCS#10 certificate signing request.
Generate PKCS#10 certificate signing request.
b.![]() Send the generated certificate signing request to the Certificate Authority to generate and sign certificate.
Send the generated certificate signing request to the Certificate Authority to generate and sign certificate.
c.![]() To import the certificate received from the Certificate Authority, click Importing existing certificate and optionally private key.
To import the certificate received from the Certificate Authority, click Importing existing certificate and optionally private key.
The Import existing client certificate and optionally private key window is displayed (Figure 12-19).

Note![]() The size of the key for a generated certificate request is the same as the size of the key in the current certificate.
The size of the key for a generated certificate request is the same as the size of the key in the current certificate.
Figure 12-19 Import Existing Client Certificate and Optionally Private Key Window
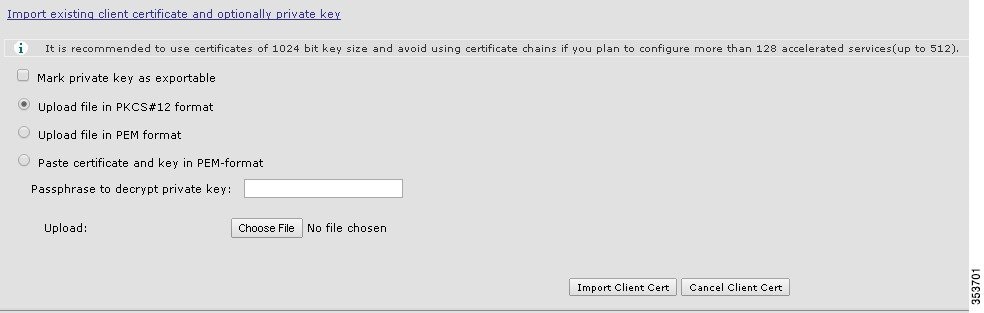
a.![]() To export this certificate and key into the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box
To export this certificate and key into the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device CLI later, check the Mark private key as exportable check box
b.![]() To import an existing client certificate and private key, choose one of the following:
To import an existing client certificate and private key, choose one of the following:
- Upload file in PKCS#12 format (also as Microsoft PFX format)
- Upload file in PEM format
- Paste certificate and private key in PEM content
Consider the following guidelines for importing an existing client certificate and private key:
- If the certificate and private key are already configured, you can update the certificate only. In this case, the Cisco WAAS Central Manager constructs the certificate and private key pair using the imported client certificate and current private key. This functionality can be used to update an existing self-signed certificate to one signed by the Certificate Authority, or to update an expiring certificate.
- The Cisco WAAS Central Manager allows importing a certificate chain consisting of an end certificate that must be specified first, a chain of intermediate CA certificates that sign the end certificate or intermediate CA certificate, and end with a root CA.
c.![]() Enter a pass-phrase to decrypt the private key, or leave this field empty if the private key is not encrypted.
Enter a pass-phrase to decrypt the private key, or leave this field empty if the private key is not encrypted.
d.![]() To navigate to the client-configured certificate and to successfully import the above specified certificate, choose Click Choose File > Import Client Cert.
To navigate to the client-configured certificate and to successfully import the above specified certificate, choose Click Choose File > Import Client Cert.
Working with Cipher Lists
Cipher lists are sets of cipher suites that you can assign to your SSL acceleration configuration. A cipher suite is an SSL encryption method that includes the key exchange algorithm, the encryption algorithm, and the secure hash algorithm.
For dual-sided deployments that use SMART-SSL acceleration, only rsa-with-aes-256-cbc-sha is supported.
To configure a cipher list, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Cipher Lists.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Cipher Lists.
The SSL Cipher Lists window appears (Figure 12-20).

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, the SSL Cipher Lists window shows the same name and cipher fields, but in a slightly different format.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, the SSL Cipher Lists window shows the same name and cipher fields, but in a slightly different format.
Figure 12-20 SSL Cipher Lists Window
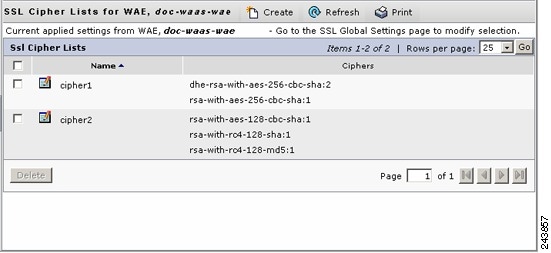
Step 3![]() To add a new cipher list, click Create.
To add a new cipher list, click Create.
The Creating New SSL Cipher List window appears (Figure 12-21).

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, click Add Cipher List to add a new cipher list.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, click Add Cipher List to add a new cipher list.
Figure 12-21 Creating New SSL Cipher List Window
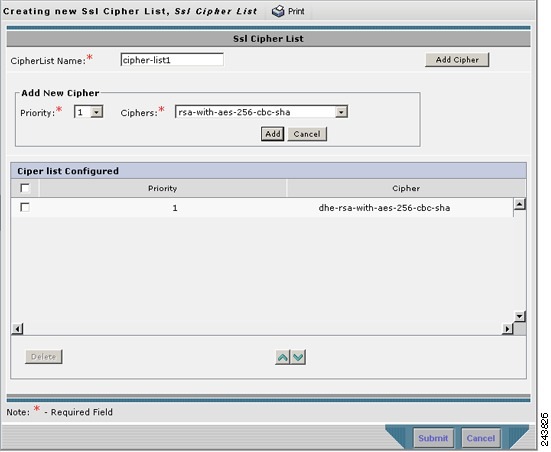
Step 4![]() In the Cipher List Name field, enter a name for your cipher list.
In the Cipher List Name field, enter a name for your cipher list.
Step 5![]() To add cipher suites to your cipher list, click Add Cipher.
To add cipher suites to your cipher list, click Add Cipher.

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, select the ciphers you wish to add, and go to Step 12.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, select the ciphers you wish to add, and go to Step 12.
Step 6![]() From the Ciphers drop-down list, choose the cipher suite to add.
From the Ciphers drop-down list, choose the cipher suite to add.

Note![]() If you are establishing an SSL connection to a Microsoft IIS server, do not select a DHE-based cipher suite.
If you are establishing an SSL connection to a Microsoft IIS server, do not select a DHE-based cipher suite.
Step 7![]() From the Priority drop-down list, choose the priority number for the selected cipher suite.
From the Priority drop-down list, choose the priority number for the selected cipher suite.

Note![]() When SSL peering service is configured, the priority associated with a cipher list on a core device takes precedence over the priority associated with a cipher list on an edge device.
When SSL peering service is configured, the priority associated with a cipher list on a core device takes precedence over the priority associated with a cipher list on an edge device.
Step 8![]() To include the selected cipher suite on your cipher list, click Add. To leave the list as it is, click Cancel.
To include the selected cipher suite on your cipher list, click Add. To leave the list as it is, click Cancel.
Step 9![]() To add more cipher suites to your list, repeat Step 5 through Step 8.
To add more cipher suites to your list, repeat Step 5 through Step 8.
Step 10![]() (Optional) To change the priority of a cipher suite, check the Cipher Suite check box, and then use the up or down arrow buttons located below the cipher list to change priority.
(Optional) To change the priority of a cipher suite, check the Cipher Suite check box, and then use the up or down arrow buttons located below the cipher list to change priority.

Note![]() The client-specified order for ciphers overrides the cipher list priority assigned here if the cipher list is applied to an accelerated service. The priorities assigned in this cipher list are only applicable if the cipher list is applied to SSL peering and management services.
The client-specified order for ciphers overrides the cipher list priority assigned here if the cipher list is applied to an accelerated service. The priorities assigned in this cipher list are only applicable if the cipher list is applied to SSL peering and management services.
Step 11![]() (Optional) To remove a cipher suite from the list, check the cipher suite’s box and then click Delete.
(Optional) To remove a cipher suite from the list, check the cipher suite’s box and then click Delete.
Step 12![]() After you have completed configuring the cipher list, click Submit.
After you have completed configuring the cipher list, click Submit.

Note![]() To save the cipher list configuration for a Cisco WAAS Express device, click OK. SSL configuration changes are not applied on the device until the security license has been enabled on the device.
To save the cipher list configuration for a Cisco WAAS Express device, click OK. SSL configuration changes are not applied on the device until the security license has been enabled on the device.
Working with CA Certificates
About CA Certificates
Use the Cisco WAAS SSL acceleration feature to configure the Certificate Authority (CA) certificates used by your system. You can use one of the many CA certificates included with Cisco WAAS, or import your own CA certificate.
Configuring and Managing CA Certificates
To configure and manage your CA certificates, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Certificate Authorities.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Certificate Authorities.
The SSL CA Certificate List window appears (Figure 12-22).
There is also an Aggregate Settings field configurable as Yes or No. To complete the procedure for Cisco WAAS Express, move to Step 4.
Figure 12-22 SSL CA Certificate List Window
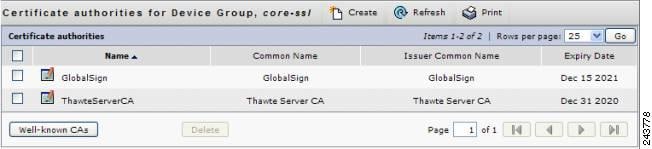
Step 3![]() To add one of the preloaded CA certificates that is included with Cisco WAAS:
To add one of the preloaded CA certificates that is included with Cisco WAAS:
b.![]() Choose the pre-existing CA certificate you want to add and click Import.
Choose the pre-existing CA certificate you want to add and click Import.
The selected CA certificate is added to the list in the SSL CA Certificate List area.
Step 4![]() To add your own CA certificate:
To add your own CA certificate:
The Creating New CA Certificate window appears (Figure 12-23).

Note![]() To add your own CA certificate to a Cisco WAAS Express device, click Add CA. Enter the name and the URL, and then click Get CA Certificate. After this, move to Step 6.
To add your own CA certificate to a Cisco WAAS Express device, click Add CA. Enter the name and the URL, and then click Get CA Certificate. After this, move to Step 6.
Figure 12-23 Creating New CA Certificate Window
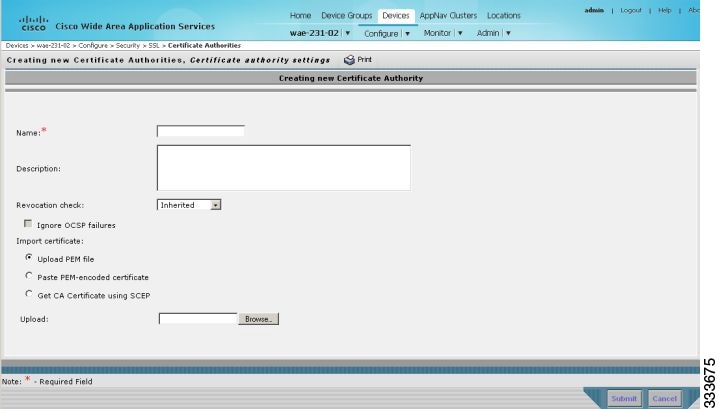
b.![]() In the Certificate Name field, type a name for the certificate.
In the Certificate Name field, type a name for the certificate.
c.![]() (Optional) In the Description field, type a description of the CA certificate.
(Optional) In the Description field, type a description of the CA certificate.
d.![]() From the Revocation check drop-down list, choose Disable to disable OCSP revocation of certificates signed by this CA.
From the Revocation check drop-down list, choose Disable to disable OCSP revocation of certificates signed by this CA.
- To mark the revocation check successful if the OCSP revocation check failed, check the Ignore OCSP failures check box.
e.![]() To add the certificate information, choose one of the following:
To add the certificate information, choose one of the following:
If you are uploading a file, it must be in a PEM format. Browse to the file that you want to use and click Upload.
If you are pasting the CA certificate information, paste the text of the PEM format certificate into the Paste PEM-encoded certificate field.
This option automatically configures the certificate authority using Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). If you are using the automated certificate enrollment procedure, enter the CA URL and click Get Certificate. The contents of the certificate are displayed in text and PEM formats.
To complete the automated certificate enrollment procedure, configure the SSL auto enrollment settings in Configuring SSL Auto Enrollment.
f.![]() To save the changes, click Submit.
To save the changes, click Submit.
Step 5![]() (Optional) To remove a CA from the list, select it and then click the Delete icon located in the toolbar.
(Optional) To remove a CA from the list, select it and then click the Delete icon located in the toolbar.
Step 6![]() After you have completed configuring the CA certificate list, click Submit.
After you have completed configuring the CA certificate list, click Submit.

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, click OK to save the CA certificate configuration.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, click OK to save the CA certificate configuration.
Configuring SSL Auto Enrollment
The Cisco WAAS SSL acceleration feature allows you to enroll certificates automatically for a device (or device group) using Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP). After the CA certificate is obtained, configure the SSL auto enrollment settings.
You must configure the CA authority before configuring auto enrollment settings.
To configure SSL auto enrollment settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Auto Enrollment.
Choose Configure > Security > SSL > Auto Enrollment.
The SSL Auto Enrollment Settings window appears (Figure 12-24).
Figure 12-24 SSL Auto Enrollment Settings Window
Step 3![]() At the CA Settings pane, configure the CA settings:
At the CA Settings pane, configure the CA settings:

Note![]() The CA, CA URL, and Challenge Password are required to enable SSL auto enrollment.
The CA, CA URL, and Challenge Password are required to enable SSL auto enrollment.
Step 4![]() At the Certificate Signing Request pane, configure the Certificate Signing Request settings:
At the Certificate Signing Request pane, configure the Certificate Signing Request settings:
Step 5![]() From the Key Size drop-down list, choose the key size. Valid values are 512, 768, 1024, 1536, or 2048.
From the Key Size drop-down list, choose the key size. Valid values are 512, 768, 1024, 1536, or 2048.
Step 6![]() Check the Enable Enroll box.
Check the Enable Enroll box.
After you have submitted the settings, you can check the enrollment status in the Machine Certificate section in the SSL Global Settings window and in the Alerts window.
Configuring SSL Management Services
SSL management services are the SSL configuration parameters that affect secure communications between the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and the Cisco WAE devices (Figure 12-12). The certificate and key pairs used are unique for each Cisco WAAS device. Therefore, SSL management services can only be configured for individual devices, not device groups.
To configure SSL management services, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name.
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > Management Service.
Choose Configure > Security > Management Service.
The Management Services window appears (Figure 12-25).
Figure 12-25 SSL Management Services Window
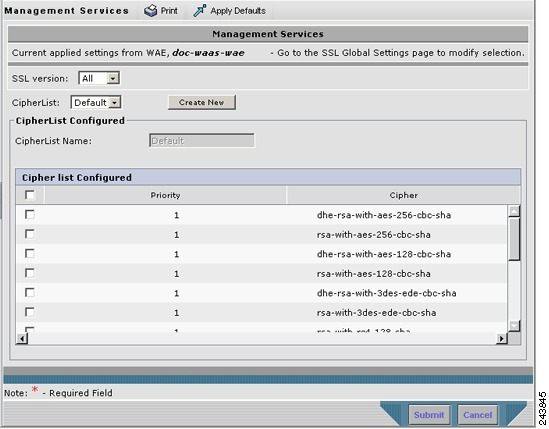
Step 3![]() From the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
From the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
Consider the following configuration guidelines for SSL connections:
- Management-service SSL version and cipher settings configured for the Cisco WAAS Central Manager are also applied to SSL connections between the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and the browser of the user.
- Primary and standby Cisco WAAS Central Managers must share a common management service version or cipher list. Changing the management service version and cipher list settings may result in a loss of connectivity between the primary Cisco WAAS Central Manager and the standby Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAE devices.
The following cipher lists are supported in SSL Acceleration (Legacy SSL Acceleration).
- dhe-rsa-with-aes-256-cbc-sha
- rsa-with-aes-256-cbc-sha
- dhe-rsa-with-aes-128-cbc-sha
- rsa-with-aes-128-cbc-sha
- dhe-rsa-with-3des-ede-cbc-sha
- rsa-with-3des-ede-cbc-sha
- rsa-with-rc4-128-sha
- rsa-with-rc4-128-md5
- dhe-rsa-with-des-cbc-sha
- rsa-export1024-with-rc4-56-sha
- rsa-export1024-with-des-cbc-sha
- dhe-rsa-export-with-des40-cbc-sha
- rsa-export-with-des40-cbc-sha
- rsa-export-with-rc4-40-md5
- rsa-with-des-cbc-sha
Consider the following configuration guidelines for ciphers:
- All browsers support SSLv3 and TLSv1 protocols, but TLSv1 may not be enabled by default on certain browsers. Therefore, you must enable it in your browser.
- Configuring ciphers or protocols that are not supported in your browser will result in connection loss between the browser and the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. If this occurs, to restore the connection: configure the Cisco WAAS Central Manager management service SSL settings to the default in the Cisco WAAS CLI to restore the connection.
Some browsers, such as Internet Explorer, do not correctly handle a change of SSL version and cipher settings on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, which can result in the browser showing an error page after you submit the changes. If this occurs, reload the page.
- To configure additional ciphers, see the supported ciphers in Preparing to Use SMART-SSL Acceleration/ SSL Accelerator v2.
Step 4![]() In the Cipher List pane, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration.
In the Cipher List pane, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration.
For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
Configuring SSL CA Signed Certificate
To enable trusted SSL communication between the Cisco WAAS Central Manager the web browser, export the SSL CA signed certificate. The default certificate for enabling SSL communication is the Cisco WAAS Central Manager self signed certificate. To use a different certificate, you must configure it.
To configure the SSL certificate, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > CM > Configure > Security > SSL Admin Service.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > CM > Configure > Security > SSL Admin Service.
The default certificate is displayed.
Step 2![]() Select the PKI operation:
Select the PKI operation:
a.![]() To upload or paste an existing certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
To upload or paste an existing certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
b.![]() To export the current certificate and key pair, click Export Certificate Key.
To export the current certificate and key pair, click Export Certificate Key.
c.![]() The file that you import or export must be in either a PKCS12 format or a Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
The file that you import or export must be in either a PKCS12 format or a Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) format.
d.![]() To configure the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device to use a self-signed certificate and key pair for SSL, click Generate Self-signed Certificate Key.
To configure the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAAS device to use a self-signed certificate and key pair for SSL, click Generate Self-signed Certificate Key.
Consider the following operating guidelines for the Key Size field, shown in Table 12-10 :
Table 12-10 Key Size Field Guidelines
Step 3![]() To register the certificate, click Submit.
To register the certificate, click Submit.
The Cisco WAAS Central Manager now uses the specified certificate for SSL communication.
Configuring SSL Peering Service
SSL peering service configuration parameters control the secure communications established by the SSL accelerator between Cisco WAE devices while optimizing SSL connections (Figure 12-12). The peering service certificate and private key is unique for each Cisco WAAS device and can be configured for individual devices only, not device groups.
To configure SSL peering service, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name.
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Security > Peering Service.
Choose Configure > Security > Peering Service.
The Peering Service window appears (Figure 12-26).
Figure 12-26 SSL Peering Service Window
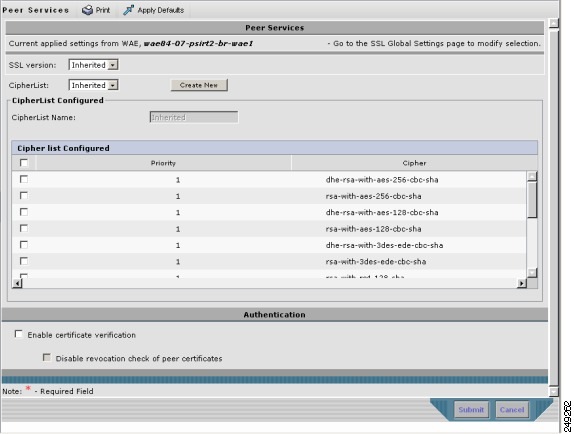
Step 3![]() From the SSL Version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
From the SSL Version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
Consider the following SSL guidelines:
Step 4![]() To enable verification of peer certificates, check the Enable Certificate Verification check box.
To enable verification of peer certificates, check the Enable Certificate Verification check box.
- If certificate verification is enabled, Cisco WAAS devices that use self-signed certificates will not be able to establish peering connections to each other and, therefore, will not be able to accelerate SSL traffic.
- For dual-sided deployments that use SMART-SSL acceleration, you can use your certificate or use the peer certificate.
Step 5![]() To disable OCSP certificate revocation checking, check the Disable revocation check for this service check box.
To disable OCSP certificate revocation checking, check the Disable revocation check for this service check box.
This option is not available for Cisco WAAS Express devices.
Step 6![]() At the Cipher List pane, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration between the WAE device peers.
At the Cipher List pane, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration between the WAE device peers.
- To use the cipher list configured in SSL Global Settings, choose Inherited.
- For dual-sided deployments that use SMART-SSL acceleration, only rsa-with-aes-256-cbc-sha is supported.
- In a Cisco WAAS Express device, the list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration is displayed in the Cipher List pane.
- For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, SSL configuration changes will not be applied on the device until the security license has been enabled on the device.
Using SSL Accelerated Services
After you have enabled and configured SSL acceleration on your WAAS system, you must define at least one service to be accelerated on the SSL path.
For Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 and later, the SMART- SSL feature is enhanced to allow you more control of SSL traffic:
- Use the DSCP marking feature for optimized traffic, which allows better QoS management for the overall network.
- Configure more than one service with the same port and Any server IP address. However, the secondary flag should be marked to differentiate services with multiple Any/Port which have already been added by other service.
After configuration is complete, it is reflected in Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name) > Configure > Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
–![]() You must mark a service as Secondary to proceed with IP Any and same port. After a service is marked as secondary, no other IP Any is allowed, but you can add different IP with ports, server, name and domain name to the secondary service.
You must mark a service as Secondary to proceed with IP Any and same port. After a service is marked as secondary, no other IP Any is allowed, but you can add different IP with ports, server, name and domain name to the secondary service.
–![]() You cannot mark a service as Secondary without Any address configuration.
You cannot mark a service as Secondary without Any address configuration.
–![]() You cannot remove the Secondary settings if the SSL accelerated service is enabled.
You cannot remove the Secondary settings if the SSL accelerated service is enabled.
- The above features are visible on the Cisco WAAS Central Manager only when the devices are running Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 and later.
To configure SSL-accelerated services, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
Step 3![]() To delete an accelerated service, select the service and click Delete.
To delete an accelerated service, select the service and click Delete.
Step 4![]() To define a new accelerated service, click Create. A maximum of 512 accelerated services are allowed.
To define a new accelerated service, click Create. A maximum of 512 accelerated services are allowed.
The Basic SSL Accelerated Services Configuration window appears (Figure 12-27).
Figure 12-27 SSL-Accelerated Services - Basic Window
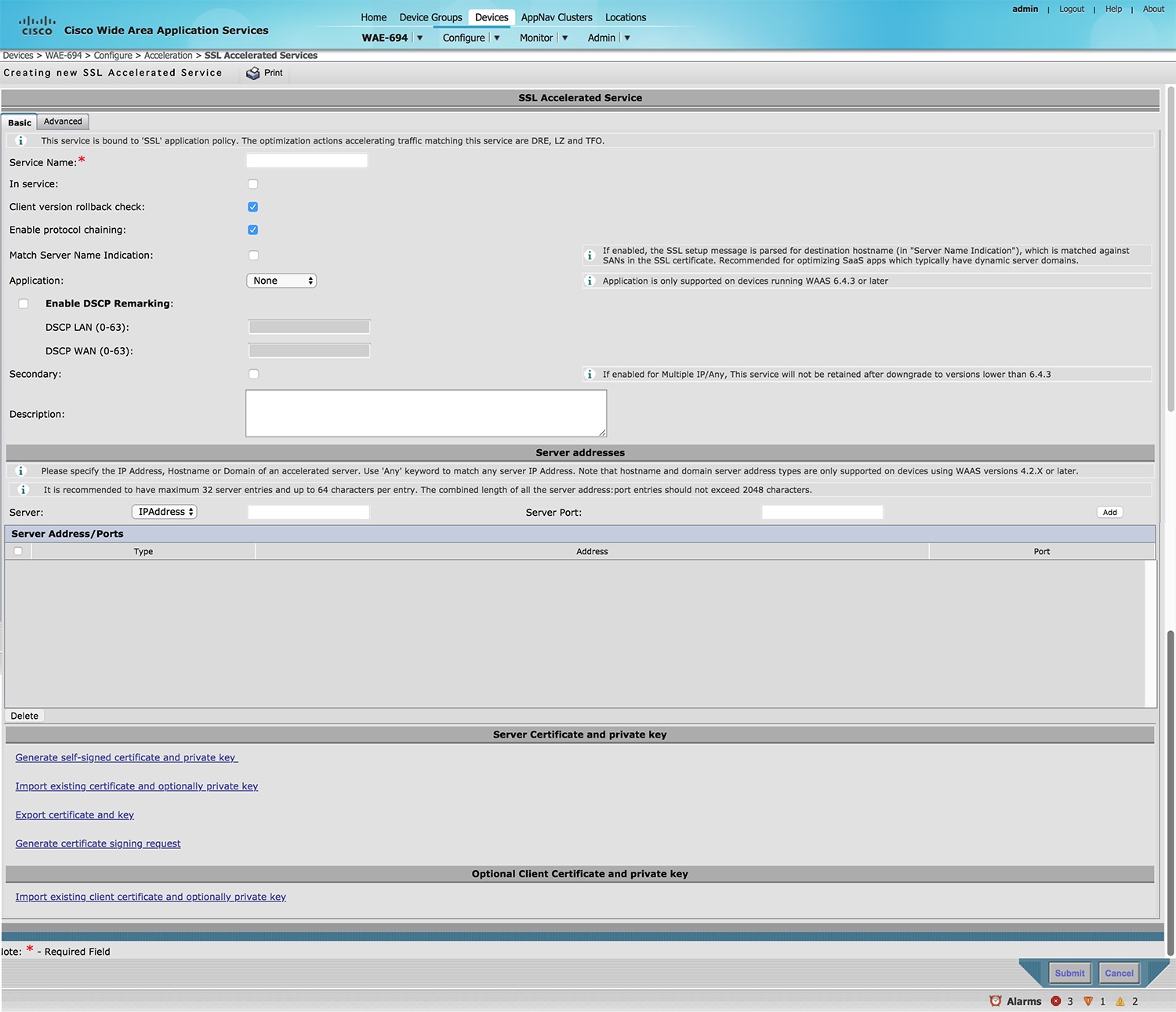
Step 5![]() At the SSL Accelerated Service pane:
At the SSL Accelerated Service pane:
a.![]() In the Service Name field, enter a name for the service.
In the Service Name field, enter a name for the service.
b.![]() To enable this accelerated service, check the In service check box.
To enable this accelerated service, check the In service check box.
c.![]() To enable client version rollback check, check the Client version rollback check check box.
To enable client version rollback check, check the Client version rollback check check box.
Enabling the client version rollback check does not allow connections with an incorrect client version to be optimized.
d.![]() To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box.
To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box.
For more information, see Configuring SSL Acceleration for SaaS Applications.
e.![]() To enable protocol chaining, check the Enable protocol chaining check box.
To enable protocol chaining, check the Enable protocol chaining check box.
Enabling protocol chaining allows other protocols to be optimized over SSL.
f.![]() From the Application drop-down list, choose the SAAS application that needs to be optimized.
From the Application drop-down list, choose the SAAS application that needs to be optimized.
This field is displayed only on the devices running Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 or later.
g.![]() Check the Enable DSCP Remarking and enter values in the DSCP LAN and DSCP WAN fields. The available values are 0 to 63.
Check the Enable DSCP Remarking and enter values in the DSCP LAN and DSCP WAN fields. The available values are 0 to 63.
- The Enable DSCP Remarking check box is unchecked (disabled) by default.
- For this configuration to be applicable to all devices that are part of a device group, all devices in the device group must be running Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 or later. If any of the devices has a version earlier than Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3, the configurations will not apply to that device.
h.![]() To configure the accelerated service to use multiple IP addresses, check the Secondary checkbox.
To configure the accelerated service to use multiple IP addresses, check the Secondary checkbox.
This is applicable only for Cisco WAAS devices running Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 or later.
Checking the Secondary check box ensures the following actions for this accelerated service:
- This accelerated service is distinguished from the primary accelerated service using multiple IP addresses.
- This accelerated service is not pushed down to other devices that are part of the device group that are running a Cisco WAAS version that is earlier than Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3.
- This accelerated service is removed during a downgrade.
Step 6![]() At the Server addresses pane:
At the Server addresses pane:
a.![]() From the Server drop-down list, choose IP Address, Hostname, or Domain as the SSL service endpoint type.
From the Server drop-down list, choose IP Address, Hostname, or Domain as the SSL service endpoint type.
b.![]() In the associated Server field, enter one of the following:
In the associated Server field, enter one of the following:
- Server IP address (or proxy IP address) of the accelerated server, up to a maximum of 32 IP addresses.To specify any server IP address, use the keyword Any. Server IP address keyword Any is supported for Cisco WAAS Software Version 4.2.x and later.
- Hostname of the accelerated server, up to a maximum of 32 hostnames. Hostname server address type is supported for Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.x and later.
- Domain of the accelerated server, up to a maximum of 32 domains. Domain server address type is supported for Cisco WAAS Version 4.2.x or later.
c.![]() At the Server Port field, enter the port associated with the service to be accelerated.
At the Server Port field, enter the port associated with the service to be accelerated.
Step 7![]() Click Add to add each address. If you specify a server hostname, the Cisco WAAS Central Manager resolves the hostname to the IP address and adds it to the Server IP/Ports table.
Click Add to add each address. If you specify a server hostname, the Cisco WAAS Central Manager resolves the hostname to the IP address and adds it to the Server IP/Ports table.
Step 8![]() To remove an IP address from the list, click Delete.
To remove an IP address from the list, click Delete.
Step 9![]() Configure a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-28).
Configure a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-28).
Figure 12-28 Configuring Service Certificate and Private Key

–![]() To configure the Cisco WAAS devices to use a self-signed certificate and key pair for SSL, click Generate self-signed certificate key.
To configure the Cisco WAAS devices to use a self-signed certificate and key pair for SSL, click Generate self-signed certificate key.
–![]() To upload or paste an existing certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
To upload or paste an existing certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
For SaaS applications, the certificate must have the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) information.
–![]() To export the current certificate and key pair, click Export Certificate Key.
To export the current certificate and key pair, click Export Certificate Key.
–![]() To renew or replace the existing certificate and key pair, click Generate Certificate Signing Request. The certificate signing request is used by the CA to generate a new certificate.
To renew or replace the existing certificate and key pair, click Generate Certificate Signing Request. The certificate signing request is used by the CA to generate a new certificate.
The file to be imported or exported must be in either PKCS12 format or PEM format.
–![]() To use the client configured certificate, click Import existing client certificate and optionally private key.
To use the client configured certificate, click Import existing client certificate and optionally private key.
Step 10![]() (Optional) To change the service certificate or private key for an existing SSL-accelerated service, follow these guidelines:
(Optional) To change the service certificate or private key for an existing SSL-accelerated service, follow these guidelines:
a.![]() At the SSL Accelerated Service pane, uncheck the In service check box.
At the SSL Accelerated Service pane, uncheck the In service check box.
b.![]() To disable the service, click Submit, and then wait five minutes.
To disable the service, click Submit, and then wait five minutes.
c.![]() Check the In service check box.
Check the In service check box.
d.![]() To re-enable the service, click Submit.
To re-enable the service, click Submit.
e.![]() Alternatively, in the Cisco WAE CLI:
Alternatively, in the Cisco WAE CLI:
–![]() Run the no inservice SSL-accelerated service configuration command.
Run the no inservice SSL-accelerated service configuration command.
–![]() Run the inservice SSL-accelerated service configuration command.
Run the inservice SSL-accelerated service configuration command.
To change the service certificate or private key for multiple SSL-accelerated services, restart all the accelerated services by disabling and then re-enabling the SSL accelerator.
- For service certificate and private key configuration steps, see Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key.
Step 11![]() To configure SSL parameters for the service, click Advanced Settings tab.
To configure SSL parameters for the service, click Advanced Settings tab.
The Advanced SSL Accelerated Services Configuration window appears (Figure 12-29).
Figure 12-29 SSL Accelerated Services—Advanced Window
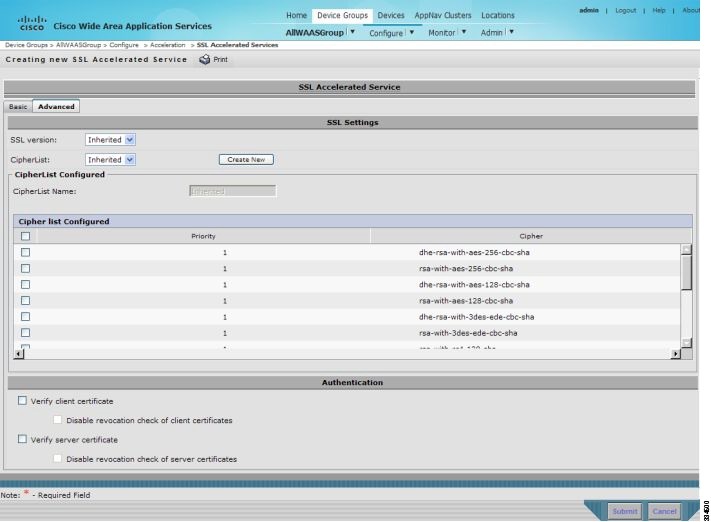
a.![]() (Optional) At the SSL Settings pane, from the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
(Optional) At the SSL Settings pane, from the SSL version drop-down list, choose the type of SSL protocol to use:
- To use the SSL protocol configured in Global SSL Settings window, choose Inherited. For more information on configuring global SSL settings, see Configuring SSL Global Settings.
- To use the SSL Version 3 protocol, choose SSL3.
- To use the Transport Layer Security Version 1 protocol (TLS Version 1), choose TLS1.
- To use both the SSL Version 3 and TLS 1 protocols, choose All.
b.![]() (Optional) At the SSL Settings pane, from the Cipher List drop-down list, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration between the Cisco WAE device peers, or choose Inherited to use the cipher list configured in SSL global settings. For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
(Optional) At the SSL Settings pane, from the Cipher List drop-down list, choose a list of cipher suites to be used for SSL acceleration between the Cisco WAE device peers, or choose Inherited to use the cipher list configured in SSL global settings. For more information, see Working with Cipher Lists.
c.![]() (Optional) To set the OCSP parameters for certificate revocation, follow these steps:
(Optional) To set the OCSP parameters for certificate revocation, follow these steps:
- To enable the verification of client certificate check, check the Verify client certificate check box.
- To disable OCSP client certificate revocation checking, check the Disable revocation check for this service check box.
- To enable verification of server certificate check, check the Verify server certificate check box.
- To disable OCSP server certificate revocation checking, check the Disable revocation check for this service check box.

Note![]() If the server and client devices are using self-signed certificates and certificate verification is enabled, Cisco WAAS devices will not be able to accelerate SSL traffic.
If the server and client devices are using self-signed certificates and certificate verification is enabled, Cisco WAAS devices will not be able to accelerate SSL traffic.
d.![]() After you have completed the configuration of the SSL accelerated service, click Submit.
After you have completed the configuration of the SSL accelerated service, click Submit.
Updating a Certificate and Key in an SSL Accelerated Service
To update a service certificate or private key in an SSL Accelerated Service, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
Step 3![]() In the in the Name column for the specified service, click Edit SSL Accelerated Service.
In the in the Name column for the specified service, click Edit SSL Accelerated Service.
Step 4![]() Choose a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-28) to either re-generate a self-signed certificate and private key, or to import an updated certificate and/or key.
Choose a certificate and key pair method (Figure 12-28) to either re-generate a self-signed certificate and private key, or to import an updated certificate and/or key.
a.![]() Enter the required details.
Enter the required details.
b.![]() Depending on the chosen method, click Generate or Import.
Depending on the chosen method, click Generate or Import.
- When you update a certificate for an SSL Accelerated Service and want it to be used by it, you must stop and start the configured SSL Accelerated Service.
This step is required because the existing certificate and key are stored in memory on the accelerators. Updating the certificate and key via the steps described above is insufficient because it does not update the certificate and key in memory.
- To ensure the updated certificate for the SSL Accelerated Service is used, follow the steps below as well.
Step 5![]() In the in the Name column for the specified service, click Edit SSL Accelerated Service button.
In the in the Name column for the specified service, click Edit SSL Accelerated Service button.
Step 6![]() Remove the check mark for In service, then click Submit.
Remove the check mark for In service, then click Submit.
Step 7![]() Click the Edit SSL Accelerated Service button in the Name column for the service in question for one last time.
Click the Edit SSL Accelerated Service button in the Name column for the service in question for one last time.
Step 8![]() Enable the check mark for In service.
Enable the check mark for In service.
Configuring SSL Acceleration for SaaS Applications
SaaS applications are typically served from multiple SSL server farms, with multiple hosts spanning several data centers.
- For SSL services hosted in the enterprise data center, the IT administrator knows and controls the SSL server IP and can provide it to the Cisco data center WAAS. But for an SSL service that is hosted at a third-party SaaS provider in the cloud, the SSL server IP address is not controlled by the IT administrator because the cloud provider uses multiple Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and data centers. Even for a single SaaS service, there might be multiple server IP addresses that can change dynamically. This leads to inadvertent errors due to namespace and certificate mismatch for SaaS applications.
- Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.3 and later support acceleration of two additional SaaS applications: ServiceNow and SalesForce over the SSL protocol. These are in addition to the existing applications: Microsoft Office 365 and YouTube.
- The configuration of SSL-accelerated services for SaaS applications solves the issue of namespace and certificate mismatch for SaaS applications, and ensures that these applications are optimized.
To configure the SSL-accelerated services for SaaS applications, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To create an SSL-accelerated service for a SaaS application, follow Step 1 through Step 8 in Using SSL Accelerated Services.
To create an SSL-accelerated service for a SaaS application, follow Step 1 through Step 8 in Using SSL Accelerated Services.
Step 2![]() To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box, or run the match sni command on the core WAAS device.
To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box, or run the match sni command on the core WAAS device.
Step 3![]() Consider the following guidelines to match subject alternative names:
Consider the following guidelines to match subject alternative names:
We recommend this setting for optimizing cloud-based SaaS applications to avoid namespace/certificate mismatch errors that are caused due to the changing nature of the SaaS server domains and IP addresses.
Step 4![]() To specify the server IP address of the accelerated server, use the keyword Any.
To specify the server IP address of the accelerated server, use the keyword Any.
Step 5![]() Direct all SSL traffic for SaaS applications to port 443.
Direct all SSL traffic for SaaS applications to port 443.
Step 6![]() Consider the following guidelines for directing all SSL traffic for SaaS applications to port 443:
Consider the following guidelines for directing all SSL traffic for SaaS applications to port 443:
Step 7![]() To to upload or paste a certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
To to upload or paste a certificate and key pair, click Import Existing Certificate Key.
To identify the server domains that need to be added for optimizing SaaS applications, follow the steps described in Determining Server Domains Used by SaaS Applications.
Step 8![]() To complete the configuration of the SSL-accelerated service for the SaaS application, click Submit.
To complete the configuration of the SSL-accelerated service for the SaaS application, click Submit.
Determining Server Domains Used by SaaS Applications
This section describes how determine server domains used by SaaS applications, and (optionally) how to optimize these server domains.
To view the list of server domain names that do not match the existing SSL certificate, and therefore are not optimized:
1.![]() Check the Match Server Name Indication check box.
Check the Match Server Name Indication check box.
2.![]() Log in to the core Cisco WAAS device
Log in to the core Cisco WAAS device
3.![]() Run the sh crypto ssl services accelerated-service service-name command.
Run the sh crypto ssl services accelerated-service service-name command.
4.![]() If you want to optimize any of these server domain names, select and add them to your certificate by performing the following steps below.
If you want to optimize any of these server domain names, select and add them to your certificate by performing the following steps below.
The server domain names list contains a maximum of 128 server names.
To select and add server domain names to your certificate for optimization, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Identify the relevant servers to be added.
Identify the relevant servers to be added.
Step 2![]() Run the sh crypto ssl services accelerated-service service-name command to see additional details regarding the count and last seen information of the server name.
Run the sh crypto ssl services accelerated-service service-name command to see additional details regarding the count and last seen information of the server name.
Step 3![]() To enable SNI debugs, to view additional information regarding IP address and hostnames, run the debug accelerator ssl sni command.
To enable SNI debugs, to view additional information regarding IP address and hostnames, run the debug accelerator ssl sni command.
Step 4![]() To create a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with the relevant server domain names of the SaaS applications in the subject alternative names extension of the certificate, log in to the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), or OpenSSL, or other available customer tool.
To create a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with the relevant server domain names of the SaaS applications in the subject alternative names extension of the certificate, log in to the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), or OpenSSL, or other available customer tool.
- When you add the SAN to the certificate: use commas to separate domain names.
- A list of hostnames on a domain can be secured with a single certificate. For example, you can add a.b.c.com and c.b.com as *.b.c.com.
- For a new hostname on another domain, you must make a new entry. For example, you must add b.c.com as b.c.com or *.c.com.
- You can also secure hostnames on different base domains in the same certificate. For example, you can add a.b.com and a.b.net.
- Refer to the highlighted area in the example certificate below.
Step 5![]() Submit the certificate to the Enterpise CA.
Submit the certificate to the Enterpise CA.
Step 6![]() Import the signed certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.
Import the signed certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.
The Enterprise root CA must be present in the browser as trusted root CA.
Step 7![]() To disable the accelerated service, uncheck the In service checkbox and click Submit.
To disable the accelerated service, uncheck the In service checkbox and click Submit.
Step 8![]() Upload the new certificate and re-enable the service.
Upload the new certificate and re-enable the service.

Note![]() The server names vary as per the accelerated service that you have configured. Refer to the names below that need to be included in the certificate for the respective accelerated service.
The server names vary as per the accelerated service that you have configured. Refer to the names below that need to be included in the certificate for the respective accelerated service.
Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
This section contains the following topics:
- About SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Checklist for Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Preparing to Use SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate
- Creating Single-Sided SMART-SSL Accelerated Service Certificate
- Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Accelerated Services on a Single-Sided Device Group
About SMART-SSL Acceleration
SMART-SSL is an encryption service that enables Layer 7 application network services, such as FTP, HTTP, DNS, to optimize traffic on SSL and TLS encrypted applications. SMART-SSL enables content caching for SSL and TLS applications (HTTP object cache for HTTPS traffic) in both single-sided and dual-sided deployment.
With the evolution of cloud services, there is a critical need to provide application optimization. For Cisco WAAS Version 6.4.1 and later, SMART-SSL optimization is enabled using both single-sided and dual-sided mode.
- In a single-sided deployment, the interposing device does not require a peer device to process the SMART-SSL traffic flow. SMART-SSL traffic flows directly to the edge device without having to go through the core device.
- The dual-sided deployment uses the same configuration procedure as in SSL Accelerator V1. Therefore, the SSL accelerator service configuration is done at the core device in the data center.
Dual-sided deployments for SMART-SSL (or SSL Accelerator V2), use TLS1.2 as the SSL version and rsa-with-aes-256-cbc-sha as the cipher suit.
- To configure SMART-SSL acceleration, you can use your own certificate or use the peering device’s certificate. For more information, see Configuring SSL Peering Service.
- To ensure this optimization, you must to enable the SMART-SSL (SSL Accelerator v2) accelerator.
Checklist for Configuring SMART-SSL Acceleration
- Table 12-11 provides a checklist for setting up and enabling SMART-SSL acceleration.
Table 12-11 Checklist for Configuring SSLv2 Acceleration
|
|
|
|---|---|
Prepare to configure SMART-SSL acceleration. |
Identify the information you need to gather before configuring SMART-SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS devices. For more information, see Preparing to Use SMART-SSL Acceleration. |
Set up to use existing Enterprise Root CA certificates |
(Optional) Create, import, and manage existing Enterprise Root certificate authority (CA) certificates. For more information, see Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate. |
Enable SMART-SSL application optimization. |
Activate the SMART-SSL acceleration feature. For more information, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features. |
Set up accelerated service certificates. |
Create, import, and use certificates for SMART-SSL acceleration. For more information, see Creating Single-Sided SMART-SSL Accelerated Service Certificate. |
Configure and enable SSL-accelerated services. |
Add, configure, and enable services to be accelerated by the SMART-SSL application optimization feature. For more information, see Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Accelerated Services on a Single-Sided Device Group. |
Preparing to Use SMART-SSL Acceleration
Before configuring SMART-SSL acceleration, consider these specifications:
- Services to be accelerated on the SMART-SSL traffic: You must create a certificate to optimize these services using their URLs or domain names, such as www.google.com, or *.google.com.
- Server IP address and port information: Optionally, if the URL or domain name cannot be used, you can specify a server IP address. If you have specified a URL, you can still specify a port.
- Public key infrastructure (PKI) certificate and private key information, including the certificate common name and CA-signing information.
- SSL versions supported: SSLv3, TLS1.0, TLS1.1, TLS1.2.
- Supported ciphers: The following is a list of the 27 supported ciphers.
TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, /* 0x000A */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA,/* 0x0016 */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, /* 0x002F */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0033 */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, /* 0x002F */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0039 */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, /* 0x003C */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256, /* 0x003D */ TLS_RSA_WITH_CAMELLIA_128_CBC_SHA,/* 0x0041 */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_CAMELLIA_128_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0045 */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, /* 0x0067 */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256, /* 0x006B */ TLS_RSA_WITH_CAMELLIA_256_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0084 */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_CAMELLIA_256_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0088 */ TLS_RSA_WITH_SEED_CBC_SHA, /* 0x0096 */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_SEED_CBC_SHA, /* 0x009A */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, /* 0x009C */ TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, /* 0x009D */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, /* 0x009E */ TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, /* 0x009F */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA, /* 0xC012 */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA, /* 0xC013 */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA, /* 0xC014 */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256, /* 0xC027 */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384, /* 0xC028 */ TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256, /* 0xC02F TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 /* 0xC030 */

Note![]() For SMART-SSL to work, the default SSL policy must be in place. If the policy is modified, for example, if accelerate http policy is applied for an SSL class map, the SSL accelerator starts optimizing, but the SMART-SSL accelerator does not optimize.
For SMART-SSL to work, the default SSL policy must be in place. If the policy is modified, for example, if accelerate http policy is applied for an SSL class map, the SSL accelerator starts optimizing, but the SMART-SSL accelerator does not optimize.
Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate
About Root CA Certificates
A root Certificate Authority (CA) certificate is a certificate issued by a trusted certificate authority and is in turn trusted by domain clients. A root CA certificate is used to sign all the certificates that will be used by the Cisco WAAS for SSL interposing during client and server SSL handshake for optimizing the applications or the URLs.
The root CA certificate must be able to accept Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs) that include subject alternative names and generate certificates that include subject alternative names.
- The subject alternative name is an extension to the X.509 protocol that allows various values to be associated with a security certificate (SSL certificate).
- Subject alternative names can include IP addresses, email addresses, universal resource identifiers (URIs), alternative common Domain Name System (DNS) names, alternatives to the distinguished name, and other information.
- You can install this on all machines that will be communicating with services using SSL certificates generated by this root certificate.
Using an Existing Root CA Certificate
If your organization already has a well-known root CA certificate, you can use it. You can also import a new CA certificate using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager GUI.
For more information, see Working with CA Certificates.
Creating a Root CA Certificate
To create a new root CA certificate, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To create a new root CA certificate, use a Linux machine with an OpenSSL version of 1.0.1e or later.
To create a new root CA certificate, use a Linux machine with an OpenSSL version of 1.0.1e or later.
Step 2![]() Create the root CA certificate key. This signs all issued certificates.
Create the root CA certificate key. This signs all issued certificates.
Step 3![]() Create the self-signed root CA certificate, with the key generated in Step 2.
Create the self-signed root CA certificate, with the key generated in Step 2.
Step 4![]() Verify the root CA certificate.
Verify the root CA certificate.
Step 5![]() Import the certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store in the client browser.
Import the certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store in the client browser.
Step 6![]() Install the root CA certificate and intermediate CA certificate.
Install the root CA certificate and intermediate CA certificate.
Creating Single-Sided SMART-SSL Accelerated Service Certificate
To create the certificate to be used with the single-sided SMART-SSL accelerated service certificate, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To create a new encryption key pair, use OpenSSL as shown below:
To create a new encryption key pair, use OpenSSL as shown below:
Step 2![]() For the application to be optimized, create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), key pair, and other needed attributes, such as Common Name, Company and SubjAltName.
For the application to be optimized, create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), key pair, and other needed attributes, such as Common Name, Company and SubjAltName.
For example, for YouTube, ensure that the subjectAltNames have all URLs that YouTube servers include in their certificate, which you want to optimize.
Alternately, to create a CSR from the Cisco WAAS Central Manager GUI, follow the steps described in Generating and Managing a Service Certificate and Private Key.
Step 3![]() To create a new proxy server certificate, sign the above generated CSR with your existing Enterprise Root CA, or the one created above.
To create a new proxy server certificate, sign the above generated CSR with your existing Enterprise Root CA, or the one created above.
This will generate a.crt or.pem certifcate file.
To ensure that the created accelerated service proxy certificate will be authenticated and accepted by the client browser, the CA certificate used to sign this accelerated service certificate must be present in the client browser root CA certificate store.
a.![]() Refer to your browser’s Settings or Options menu for that browser’s Certificates and Import locations.
Refer to your browser’s Settings or Options menu for that browser’s Certificates and Import locations.
d.![]() Reload the browser for the cloud application.
Reload the browser for the cloud application.
The browser will pick up the new certificate.
Step 4![]() Cisco WAAS allows importing certificates with PKCS12 format. To generate the PKCS12 format from the certificate file and your private key, run the open ssl command.
Cisco WAAS allows importing certificates with PKCS12 format. To generate the PKCS12 format from the certificate file and your private key, run the open ssl command.
Step 5![]() To import this certificate into the Cisco WAAS device group, run the crypto import EXEC command and thereafter be used in the accelerated server configuration as server-cert-key.
To import this certificate into the Cisco WAAS device group, run the crypto import EXEC command and thereafter be used in the accelerated server configuration as server-cert-key.
Follow these guidelines for importing the certificate:
- The CA certificate used to sign this Accelerated SSL Service (ASVC) certificate must exist in the browser root CA certificate store in order for the accelerated service proxy certificate creation to be authenticated and accepted by the browser.
- The Cisco WAAS Central Manager CA certificate repository does not include the CN=GTE CyberTrust Global Root certificate. You must manually import the CN=GTE CyberTrust Global Root certificate and then configure it from the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, or the device that will use it, to validate Microsoft Office 365 certificates.
Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Accelerated Services on a Single-Sided Device Group
Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Acceleration on a Single-Sided Device Group Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
- Ensure that the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAEs are running Cisco WAAS Software Version 6.2.x or later.
- Ensure that the new device group supports single-sided acceleration. To create a device group, see Creating a Device Group in the chapter “Using Device Groups and Device Locations” .
- Create an accelerated service certificate for Cisco WAN optimization.
To enable the SMART-SSL settings on the specified device group, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Device Groups > device-group-name.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Device Groups > device-group-name.
Step 2![]() Select the device group to enable for SMART-SSL settings.
Select the device group to enable for SMART-SSL settings.

Note![]() Add only branch devices to this group.These devices will optimize the SSL traffic as it passes through them.
Add only branch devices to this group.These devices will optimize the SSL traffic as it passes through them.
Step 3![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Enabled Features.
Step 4![]() To enable SMART SSL acceleration, at the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) check box.
To enable SMART SSL acceleration, at the Accelerator Optimization pane, check the SSL Interposer (SSL Accelerator V2) check box.
Step 5![]() To create an SSL accelerated service for the device group, choose Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
To create an SSL accelerated service for the device group, choose Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
The Creating new SSL Accelerated Service window appears.
Step 7![]() At the SSL Accelerated Service pane, enter the name of your service, and check the In service box.
At the SSL Accelerated Service pane, enter the name of your service, and check the In service box.
(Optional) Enter a short description for the SSL accelerated service.
Step 8![]() At the Server Addresses pane:
At the Server Addresses pane:
a.![]() In the IP Address field, enter Any.
In the IP Address field, enter Any.
b.![]() In the Server Port field, enter 443.
In the Server Port field, enter 443.
Step 9![]() At the Certificate and Private Key pane:
At the Certificate and Private Key pane:
a.![]() Click Import Existing Certificate and Optionally Private Key.
Click Import Existing Certificate and Optionally Private Key.
b.![]() Click Upload File in PKCS#12 Format.
Click Upload File in PKCS#12 Format.
c.![]() In the Password field, enter the password to be used to export the certificate.
In the Password field, enter the password to be used to export the certificate.
d.![]() Use the Browse button to locate the certificate to be imported.
Use the Browse button to locate the certificate to be imported.
e.![]() Click Import to import the certificate.
Click Import to import the certificate.
A confirmation screen appears, with the certificate information.
Step 10![]() To complete the configuration of the SSL-accelerated service to use single sided optimization, click Submit.
To complete the configuration of the SSL-accelerated service to use single sided optimization, click Submit.
(Optional) Alternatively, to automate the entire process using a script, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC). For further information on contacting TAC, see the Cisco Support and Downloads page, Contacts/Support Cases section.
Step 11![]() To monitor the SMART-SSL accelerated service optimization statistics:
To monitor the SMART-SSL accelerated service optimization statistics:
- To use the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, see the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
- To use the Cisco WAAS CLI, run the show statistics encryption-services exec command.
Configuring and Managing SMART-SSL Acceleration on a Single-Sided Device Group Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
- Ensure that the Cisco WAAS Central Manager and Cisco WAEs are running Cisco WAAS Software Version 6.2.x or later.
- Ensure that the new device group supports single-sided acceleration. To create a device group, see Creating a Device Group in the chapter “Using Device Groups and Device Locations” .
- Create an accelerated service certificate for Cisco WAN optimization.
To configure and manage SMART-SSL accelerated services on a single-sided device group using the Cisco WAAS CLI, use these command guidelines:
- To enable SMART-SSL acceleration from the Cisco WAAS CLI, run the crypto encryption-service enable global configuration command.
- The SSL accelerator and the SMART-SSL accelerator use the same configuration commands. However, for the SMART-SSL configuration, only a limited set of keywords are supported. Table 12-12 shows the Cisco WAAS CLI command keywords that are supported for SMART-SSL acceleration.
Table 12-12 Cisco WAAS CLI Command Keywords Supported for SMART-SSL Acceleration
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
About Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
Microsoft Office365 supports business-critical applications such as Outlook, SharePoint, Excel and PowerPoint, and use of Microsoft Office 365 as SaaS has also increased. As enterprises move toward SaaS applications such as Microsoft Office 365, performance and user experience of these applications has also become more important.
Cisco WAAS support for Microsoft Office 365 traffic acceleration and optimization was introduced in Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.5 (for optimization between the on-premise data center and the customer branch, only). For Cisco WAAS Version 6.2.1 and later, traffic to Microsoft Office 365 is optimized until it reaches the cloud, by implementing a solution that includes:
- Enabling Cisco WAAS as SaaS over Microsoft Azure.
- Positioning Cisco WAAS as SaaS near to Microsoft Office 365 service by configuration.
- Routing and DNAT using CSR in Microsoft Azure.
- Using Cisco Intelligent WAN (Cisco IWAN) as transport.
- Detecting Microsoft Office 365 traffic using the Cisco SSL accelerator.
Checklist for Configuring Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
Table 12-13 shows the steps needed to set up and enable Microsoft Office 365 using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Table 12-13 Checklist for Configuring Microsoft Office 365 Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
|
|
|
|---|---|
Prepare to configure SSL acceleration. |
Identify the information that you need to gather before configuring SSL acceleration on your Cisco WAAS devices For more information, see Prerequisites for Configuring SSL Acceleration. |
Set up root CA certificates |
(Optional) Create, import, and manage certificate authority (CA) certificates. For more information, see Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate. |
Enable SSL application optimization. |
Enable the SSL acceleration feature. For more information, see Enabling and Disabling Global Optimization Features and Configuring SSL Acceleration. |
Set up accelerated service certificates. |
Create, import, and use certificates for Microsoft Office 365 acceleration. For more information, see Creating a Microsoft 365 Accelerated Service Certificate. |
Configure and enable Microsoft 365 acceleration. |
Add, configure, and enable Microsoft 365 acceleration using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. For more information, see Configuring Microsoft 365 Acceleration for Cisco WAAS. |
Prerequisites for Configuring Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
Before you create a Microsoft Office 365 accelerated service using the Cisco WAAS Central Manger, you must have completed the following:
- Deployed Virtual Network in Azure
- Deployed CSR 1000v for secure network extension and Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT)
- Deployed Microsoft Azure on Cisco vWAAS
- Configured Microsoft Azure route tables
- Configured Microsoft Azure CSR
- Registered the Microsoft Azure Cisco vWAAS device with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
Creating a Microsoft 365 Accelerated Service Certificate
You must create a root CA certificate before you create a Microsoft 365 accelerated service certificate. For more information, see:
- Using a Root CA Certificate to Sign Cisco WAAS Accelerated Service Exported Certificate
- Checklist for Configuring Microsoft Office 365 for Cisco WAAS
To create the certificate to be used with Microsoft 365 acceleration, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() To create a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with the relevant server domain names of the Microsoft Office 365 application in the subject alternative names extension of the certificate, log in to the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), OpenSSL, or other available customer tool
To create a new Certificate Signing Request (CSR) with the relevant server domain names of the Microsoft Office 365 application in the subject alternative names extension of the certificate, log in to the Microsoft Management Console (MMC), OpenSSL, or other available customer tool
Step 2![]() In the following example certificate, refer to the highlighted area.
In the following example certificate, refer to the highlighted area.
Step 3![]() Submit the certificate to the Enterprise CA.
Submit the certificate to the Enterprise CA.
Step 4![]() Import the signed certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.\
Import the signed certificate from the Enterprise CA to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.\

Note![]() The Enterprise root CA must be present in browser as trusted root CA.
The Enterprise root CA must be present in browser as trusted root CA.
Step 5![]() To ensure that the created accelerated service proxy certificate will be authenticated and accepted by the client browser, the CA certificate used to sign this accelerated service certificate must be present in the client browser root CA certificate store.
To ensure that the created accelerated service proxy certificate will be authenticated and accepted by the client browser, the CA certificate used to sign this accelerated service certificate must be present in the client browser root CA certificate store.
a.![]() Refer to your browser’s Settings or Options menu for that browser’s Certificates and Import locations.
Refer to your browser’s Settings or Options menu for that browser’s Certificates and Import locations.
d.![]() Reload the browser for the cloud application.
Reload the browser for the cloud application.
The browser will pick up the new certificate.
Configuring Microsoft 365 Acceleration for Cisco WAAS
Configuring Microsoft Office 365 Acceleration for Cisco WAAS Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To configure Microsoft Office 365 acceleration for Cisco WAAS using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Register your Microsoft Azure Cisco vWAAS device with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. If the Cisco WAAS Central Manager is in a different network add routes for reachability.
Register your Microsoft Azure Cisco vWAAS device with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager. If the Cisco WAAS Central Manager is in a different network add routes for reachability.
Step 2![]() Create a Microsoft Office 365 accelerated service for the device group:
Create a Microsoft Office 365 accelerated service for the device group:
a.![]() Choose Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
Choose Acceleration > SSL Accelerated Services.
The Creating New SSL Accelerated Service window appears.
Step 3![]() At the SSL Accelerated Service pane:
At the SSL Accelerated Service pane:
a.![]() In the Service Name field, enter the name of the service o365,
In the Service Name field, enter the name of the service o365,
b.![]() To enable this service, check the In Service check box.
To enable this service, check the In Service check box.
c.![]() To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box or run the match sni command on the core WAAS device.
To match subject alternative names, check the Match Server Name Indication check box or run the match sni command on the core WAAS device.
Consider the following guidelines to match subject alternative names:
- If enabled, the SSL accelerator parses the initial SSL connection setup message for the destination hostname (in the SSL protocol extension called Server Name Indication) and uses that to match it with the Subject Alternate Names list in the SSL certificate on the WAAS device.
- We recommend this setting for optimizing cloud-based SaaS applications to avoid namespace/certificate mismatch errors that are caused due to the changing nature of the SaaS server domains and IP addresses.
- Most current browsers provide Server Name Indication (SNI) support. Ensure that you use a browser that supports SNI.
- The Match Server Name Indication option is available on devices running Cisco WAAS Version 5.3.5 and later.
d.![]() (Optional) Provide a short description.
(Optional) Provide a short description.
Step 4![]() At the Server addresses pane:
At the Server addresses pane:
a.![]() To specify the server IP address of the accelerated server, in the Server Port field, enter the keyword Any.
To specify the server IP address of the accelerated server, in the Server Port field, enter the keyword Any.
b.![]() To direct traffic to port 443, in the Server Port field enter 443.
To direct traffic to port 443, in the Server Port field enter 443.
Step 5![]() At the Certificate and Private Key pane:
At the Certificate and Private Key pane:
a.![]() Click Import Existing Certificate and Optionally Private Key.
Click Import Existing Certificate and Optionally Private Key.
b.![]() Click Upload File in PKCS#12 Format.
Click Upload File in PKCS#12 Format.
c.![]() In the Password field, enter the password to be used to export the certificate.
In the Password field, enter the password to be used to export the certificate.
d.![]() Use the Browse button to locate the certificate to be imported.
Use the Browse button to locate the certificate to be imported.
e.![]() Click Import to import the certificate.
Click Import to import the certificate.
A confirmation screen appears, with the certificate information.
Step 6![]() To complete the configuration of the Microsoft Office 365, click Submit.
To complete the configuration of the Microsoft Office 365, click Submit.
Step 7![]() To monitor accelerated service optimization statistics, see the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Acceleration Charts in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
To monitor accelerated service optimization statistics, see the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Acceleration Charts in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
Configuring Microsoft Office 365 Acceleration for Cisco WAAS Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Consider the following guidelines for configuring Microsoft Office 365 acceleration for Cisco WAAS using the Cisco WAAS CLI:
- To copy the Microsoft Office 365 certificate (o365.pfx) to the Cisco data center WAE and to import the certificate, run the following EXEC command:
crypto import pkcs12 Azure_o365.p12 pkcs12 disk office365.pfx
Instead of importing multi-domain certificates from the device, you can use remote methods to import the certificate from servers, including the methods FTP and HTTP.
- To configure the application accelerated service in the Cisco WAE with the imported certificate, run the following SSL Accelerated Service Configuration Mode command:
Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update
Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update enables caching of objects used in Microsoft Windows operating system (OS) and application updates. Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update is enabled by default, and enabled only for specific sites.
This section contains the following topics:
- Benefits of Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update
- Viewing Statistics for Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update
- Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update and Akamai Cache Engine
Benefits of Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update
The Microsoft Windows OS and application updates are managed by update clients such as Microsoft Windows Update. Microsoft Windows Update downloads the updates via HTTP, often in combination with Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) to help facilitate the downloads. Clients use HTTP range request to fetch updates.
The objects that comprise the updates, such as.cab files, are typically cacheable, so that HTTP object cache is a significant benefit for this process.
For example, for Microsoft Windows 7 and Microsoft Windows 8 OS updates, via direct Internet or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Version 2012 and 2012 R2, more than 98% of the update files, such as.cab,.exe, and.psf files, are served from cache on subsequent updates. Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update reduces the volume of WAN offload bytes and reduces response time for subsequent Windows updates.
Viewing Statistics for Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update
There are two ways to view data generated by Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update.
- To use the Cisco WAAS Central manager to view data generated by Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update, see Top Sites, in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” . The Top Sites report provides information such as WAN response time and WAN offload bytes.
- For Cisco WAAS Version 6.1.1x and later, the cache engine access log file has two additional fields, which provide Microsoft Windows Update statistics:
–![]() rm-w (range miss, wait): The main transaction, a cache miss, which waited for the sub-transaction to fetch the needed bytes.
rm-w (range miss, wait): The main transaction, a cache miss, which waited for the sub-transaction to fetch the needed bytes.
–![]() rm-f (range miss, full): The sub-transaction, a cache write of the entire document.
rm-f (range miss, full): The sub-transaction, a cache write of the entire document.
In this example, there are two log lines: the main transaction and the sub-transaction, when a range is requested on an object that is not in cache:
This example shows a cache hit when a range is requested on an object that is either completely in cache, or in the process of being downloaded. If the object is in the process of being downloaded, then the main transaction has latched onto a sub-transaction like the one shown in Example 1.
Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update and Akamai Cache Engine
Cisco support for Microsoft Windows Update enables Akamai Cache Engine to support Microsoft Windows Update caching in two ways:
- Download and cache full objects even when ranges within objects that not in cache are requested.
- Future range requests on the objects can be served out of cache.
There is a limit, set by OTT metadata during the Akamai Connect registration process, from the start of the object (the number of bytes or the percent of file length) where the download functionality is triggered. A request of a size above the set limit does not initiate a full object download, and the request is forwarded to the origin as is.

To disable Cisco Support for Microsoft Windows Update, you must disable OTT caching. To do this, uncheck the Over the Top Cache check box. However, unchecking the Over the Top Cache check box disables all OTT functionality, both global and custom OTT configurations.
For more information on the Akamai Connect registration process, see Activating the Akamai Connect License in the chapter “Configuring Cisco WAAS with Akamai Connect” .
Creating a New Traffic Optimization Policy
Table 12-14 provides an overview of the steps you must complete to create a new traffic optimization policy.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Prepare to create an optimization policy. |
Complete prerequisite tasks before creating a new optimization policy on your Cisco WAAS devices. For more information, see Preparing to Create an Optimization Policy. |
Create an application definition. |
Identify general information about the application to be optimized, such as the application name and whether or not the Cisco WAAS Central Manager will collect statistics about this application. For more information, see Creating an Application Definition. |
Create an optimization policy. |
Determine the type of action your Cisco WAAS device or device group performs on specific application traffic. This step includes the following required tasks:
For more information, see Creating an Optimization Policy. |
Preparing to Create an Optimization Policy
Before you create a new optimization policy, complete the following tasks:
- Review the list of optimization policies on your Cisco WAAS system and verify that none of these policies already cover the type of traffic you want to define. To view a list of the predefined policies that come bundled with the Cisco WAAS system, see Appendix A, “Predefined Optimization Policy.”
- Identify a match condition for the new application traffic. For example, if the application uses a specific destination or source port, you can use that port number to create a match condition. You can also use a source or destination IP address for a match condition.
- Identify the device or device group that requires the new optimization policy. We recommend that you create optimization policies on device groups so that the policy is consistent across multiple Cisco WAAS devices.
Creating an Application Definition
The first step in creating an optimization policy is to set up an application definition that identifies general information about the application, such as the application name, and whether or not you want the Cisco WAAS Central Manager to collect statistics about the application. You can create up to 255 application definitions on your Cisco WAAS system.
To create an application definition, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Applications.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Applications.
The Applications window appears, which displays a list of all the applications on the Cisco WAAS system, and the device or device group from which each gets the settings.
Step 2![]() At the Applications window, perform the following tasks:
At the Applications window, perform the following tasks:
If the statistics are being collected for the application, the Enable Statistics column displays Yes.
Step 3![]() Create a new application:
Create a new application:
a.![]() Click the Add Application icon in the taskbar.
Click the Add Application icon in the taskbar.
The Applications window appears.
b.![]() In the Name field, enter a name for this application. Use only alphanumeric characters; the application name cannot contain spaces and special characters.
In the Name field, enter a name for this application. Use only alphanumeric characters; the application name cannot contain spaces and special characters.
c.![]() (Optional) In the Comments field, enter a comment.
(Optional) In the Comments field, enter a comment.
The entered comment appears in the Applications window.
d.![]() To allow the Cisco WAAS Central Manager to collect data for this application, check the Enable Statistics check box. To disable data collection for this application, uncheck the Enable Statistics check box.
To allow the Cisco WAAS Central Manager to collect data for this application, check the Enable Statistics check box. To disable data collection for this application, uncheck the Enable Statistics check box.
- The Cisco WAAS Central Manager GUI can display statistics for up to 25 applications and 25 class maps. An error message is displayed if you try to enable more than 25 statistics for either applications or class maps.
- However, you can use the Cisco WAAS CLI to view statistics for all the applications that have policies on a specific Cisco WAAS device. For more information, refer to the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
- Historical data for an application that has statistics collection enabled, and then disabled, and then re-enabled:
The historical data is retained from when the statistics collection was first enabled, and when it was re-enabled, but a gap in data will exist for the period when statistics collection was disabled.
An application cannot be deleted if there is an optimization policy using it. However, if you delete an application for which statistics were collected, and then later recreate the application, the historical data for the application is lost. Only data collected since the re-creation of the application is displayed.

Note The WAAS Central Manager does not start collecting data for this application until you finish creating the entire optimization policy.
The application definition is saved and is displayed in the application list.
Creating an Optimization Policy
After you create an application definition, create an optimization policy that determines the action a Cisco WAAS device takes on the specified traffic.
- You create an optimization policy that directs a Cisco WAAS device to apply TCP optimization and compression to all application traffic that travels over a specific port or to a specific IP address.
You can create up to 512 optimization policies on your Cisco WAAS system.
- The traffic-matching rules are present in the application class map. These rules, known as match conditions, use Layer 2 and Layer 4 information in the TCP header to identify traffic.
To create an optimization policy, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
The Optimization Policies window appears (Figure 12-30).
Consider the following guidelines for optimization policies for Cisco WAAS Express:
The Enable Service Policy option, the DSCP option, and the Protocol column in the list of policy rules are not applicable to Cisco WAAS Express.
To ensure that FTP data is optimized when Cisco WAAS Express is used with the Cisco ISR G2, use the ISR G2's IOS crypto map software.
Figure 12-30 Optimization Policies Window
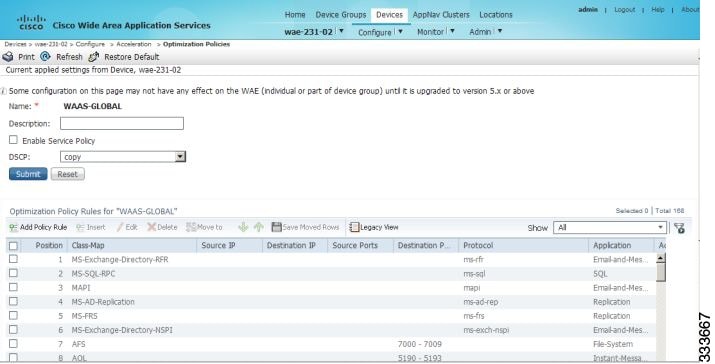
The Optimization Policies window displays information about all the optimization policies that reside on the selected device or device group, as well as the position of each policy.
Consider the following guidelines for configuring optimization policies:
- The position of each policy determines the order in which Cisco WAAS refers to that policy when determining how to handle application traffic.
- To change the position of a policy, see Modifying the Position of an Optimization Policy.
- The Optimization Policies window also displays the class map, source and destination IP addresses, source and destination ports, protocol, application, action, and accelerates assigned to each policy.
- If there are Cisco WAAS Version 4.x devices, click the Legacy View taskbar icon to view the policies as they appear in a Cisco WAAS Version 4.x device.
- All new devices, or devices that been configured with restore factory default settings, have their own polices and class maps. These devices that are not assigned to any device group within two data feeds continue to have their own policies, even after being registered with the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
–![]() After these devices are assigned to device groups, the Force Device Group Settings icon appears in the Optimization Policies window in device group level. To correct this, use the Force Group Settings to ensure that all devices in the specified group have the same configuration.
After these devices are assigned to device groups, the Force Device Group Settings icon appears in the Optimization Policies window in device group level. To correct this, use the Force Group Settings to ensure that all devices in the specified group have the same configuration.
–![]() For more information on Force Group Settings, see Procedure for Forcing Device Group Settings in the chapter “Using Device Groups and Device Locations” .
For more information on Force Group Settings, see Procedure for Forcing Device Group Settings in the chapter “Using Device Groups and Device Locations” .
At the Optimization Policies window, you can perform the following tasks:
- Configure a description.
- Configure the Enable Service Policy setting.
- Configure the DSCP setting. This DSCP setting field configures DSCP settings at the device or device group level.

Note![]() The device uses this policy setting to determine what optimizations are performed only if the Enable Service Policy is set.
The device uses this policy setting to determine what optimizations are performed only if the Enable Service Policy is set.
- To delete one or more optimization policies, select the policies to be deleted, and click the Delete icon.
- To modify a policy, check the policy and click the Edit icon.
- To restore predefined policies and class maps, see Restoring Optimization Policies and Class Maps.
- Create an optimization policy, as described in the following steps.
Step 3![]() To create a new optimization policy, click the Add Policy Rule icon in the taskbar.
To create a new optimization policy, click the Add Policy Rule icon in the taskbar.
The Optimization Policy Rule pop-up window appears (Figure 12-31).
Figure 12-31 Add Optimization Policy Rule Window
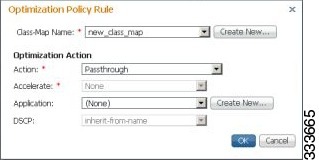
Step 4![]() From the Class-Map Name drop-down list, do one of the following:
From the Class-Map Name drop-down list, do one of the following:
For information on creating a new class map, see Creating an Optimization Class Map for an Optimization Policy.
Step 5![]() From the Action drop-down list, choose the action that the specified Cisco WAAS device should take on the defined traffic. For a description of each action, see Table 12-15 .
From the Action drop-down list, choose the action that the specified Cisco WAAS device should take on the defined traffic. For a description of each action, see Table 12-15 .
Step 6![]() Consider the following guidelines for class map actions:
Consider the following guidelines for class map actions:
- For a Cisco WAAS Express device, the following subset of actions is available: Passthrough, TFO Only, TFO with LZ, TFO with DRE, and TFO with DRE and LZ.
- When ICA acceleration is enabled, all the connections are processed with the DRE mode as Unidirectional, and acceleration type is shown as TIDL (TCP optimization, ICA acceleration, DRE, and LZ).
- When configuring optimization policies on a device group:
–![]() If the device group contains devices running a Cisco WAAS version earlier than 4.4.1 and you are configuring an action that includes Unidirectional or Adaptive caching, the caching mode is converted to Bidirectional.
If the device group contains devices running a Cisco WAAS version earlier than 4.4.1 and you are configuring an action that includes Unidirectional or Adaptive caching, the caching mode is converted to Bidirectional.
–![]() When devices running a Cisco WAAS version earlier than 4.4.1 join a device group that is configured with optimization policies that use Unidirectional or Adaptive caching, the caching mode is converted to Bidirectional.
When devices running a Cisco WAAS version earlier than 4.4.1 join a device group that is configured with optimization policies that use Unidirectional or Adaptive caching, the caching mode is converted to Bidirectional.
In both of these cases, we recommend that you upgrade all the devices to the same software version or create different device groups for devices with incompatible versions.
Table 12-15 Class Map Action Descriptions
|
|
|
|---|---|
Prevents the Cisco WAAS device from optimizing the application traffic defined in this policy by using TFO, DRE, or compression. Traffic that matches this policy can still be accelerated if an accelerator is chosen from the Accelerate drop-down list. |
|
Applies a different TFO techniques to matching traffic. TFO techniques include BIC-TCP, window size maximization and scaling, and selective acknowledgment. For more information on the TFO feature, see Transport Flow Optimization in the chapter “Introduction to Cisco WAAS” . |
|
Applies both TFO and DRE with adaptive caching to matching traffic. |
|
Applies both TFO and DRE with unidirectional caching to matching traffic. |
|
Applies both TFO and DRE with bidirectional caching to matching traffic. |
|
Applies both TFO and the LZ compression algorithm to matching traffic. LZ compression functions similarly to DRE, but uses a different compression algorithm to compress smaller data streams and maintains a limited compression history. |
|
Applies TFO, DRE with adaptive caching, and LZ compression to matching traffic. |
|
Applies TFO, DRE with unidirectional caching, and LZ compression to matching traffic. |
|
Applies TFO, DRE with bidirectional caching, and LZ compression to matching traffic. |
Step 7![]() From the Accelerate drop-down list, choose one of the following additional acceleration actions that your WAAS device should take on the defined traffic:
From the Accelerate drop-down list, choose one of the following additional acceleration actions that your WAAS device should take on the defined traffic:
- None : No additional acceleration is done.
- MS PortMapper : Accelerate using the Microsoft Endpoint Port Mapper (EPM).
- SMB Adaptor : Accelerate using the SMB Accelerators.
- HTTP Adaptor : Accelerate using the HTTP Accelerator.
- MAPI Adaptor : Accelerate using the MAPI Accelerator.
- ICA Adaptor : Accelerate using the ICA Accelerator.
- For a Cisco WAAS Express devices, HTTP Express is available as an accelerator.
Step 8![]() Specify the application that you want to associate with this policy by performing either of the following:
Specify the application that you want to associate with this policy by performing either of the following:
- From the Application drop-down list, choose an existing application such as the one that you created, as described in Creating an Application Definition. This list displays all the predefined and new applications on your Cisco WAAS system.
- To create an application, click New Application.
a.![]() Specify the application name.
Specify the application name.
b.![]() Enable statistics collection.
Enable statistics collection.
c.![]() To save the new application and return to the Optimization Policy window, click OK.
To save the new application and return to the Optimization Policy window, click OK.
The new application is automatically assigned to this device or device group.
Step 9![]() (Optional) From the DSCP Marking drop-down list, choose one of the following:
(Optional) From the DSCP Marking drop-down list, choose one of the following:
–![]() DSCP is the combination of IP Precedence and Type of Service (ToS) fields. DSCP is a field in an IP packet that enables different levels of service to be assigned to network traffic. Levels of service are assigned by marking each packet on the network with a DSCP code and associating a corresponding level of service. For more information, see RFC 2474.
DSCP is the combination of IP Precedence and Type of Service (ToS) fields. DSCP is a field in an IP packet that enables different levels of service to be assigned to network traffic. Levels of service are assigned by marking each packet on the network with a DSCP code and associating a corresponding level of service. For more information, see RFC 2474.
–![]() DSCP marking does not apply to pass-through traffic.
DSCP marking does not apply to pass-through traffic.
–![]() In a Cisco WAAS Express device, the DSCP Marking drop-down list is not shown.
In a Cisco WAAS Express device, the DSCP Marking drop-down list is not shown.
–![]() For the DSCP marking value, you can choose to use the global default values (see Defining Default DSCP Marking Values) or select one of the other defined values. Or, you can use copy, as described above.
For the DSCP marking value, you can choose to use the global default values (see Defining Default DSCP Marking Values) or select one of the other defined values. Or, you can use copy, as described above.
The new policy appears in the Optimization Policies window (Figure 12-30).
Creating an Optimization Class Map for an Optimization Policy
You can create an optimization class map for an optimization policy in two ways:
- In the device context, choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Class-Map, and then click the Add Class-Map taskbar icon. The Optimization Class-Map pane is displayed.
- While adding or editing a policy rule, as described in Creating an Optimization Policy, click Create New next to the Class-Map Name drop-down list. The Optimization Class-Map pane is displayed.
To create an optimization class map for an optimization policy, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() Enter a name for this application class map. The name cannot contain spaces or special characters.
Enter a name for this application class map. The name cannot contain spaces or special characters.

Note![]() You must create a unique class map name across all types. For example, you cannot use the same name for an optimization class map and an AppNav class map.
You must create a unique class map name across all types. For example, you cannot use the same name for an optimization class map and an AppNav class map.

Note![]() For Cisco WAAS Express, the class map name cannot contain the following prefixes, which are case sensitive: class, optimize, passthrough, application, accelerate, tfo, dre, lz, or sequence-interval. You must manually change existing class map names containing any of these prefixes.
For Cisco WAAS Express, the class map name cannot contain the following prefixes, which are case sensitive: class, optimize, passthrough, application, accelerate, tfo, dre, lz, or sequence-interval. You must manually change existing class map names containing any of these prefixes.
Step 2![]() (Optional) Enter a description.
(Optional) Enter a description.
Step 3![]() From the Type drop-down list, choose the class map type.
From the Type drop-down list, choose the class map type.
Step 4![]() After you have chosen the class map type, enter the match conditions. Click the Add Match Condition icon.
After you have chosen the class map type, enter the match conditions. Click the Add Match Condition icon.
Step 5![]() The Adding a New Match Condition window appears (Figure 12-32).
The Adding a New Match Condition window appears (Figure 12-32).
Figure 12-32 Adding a New Match Condition Window
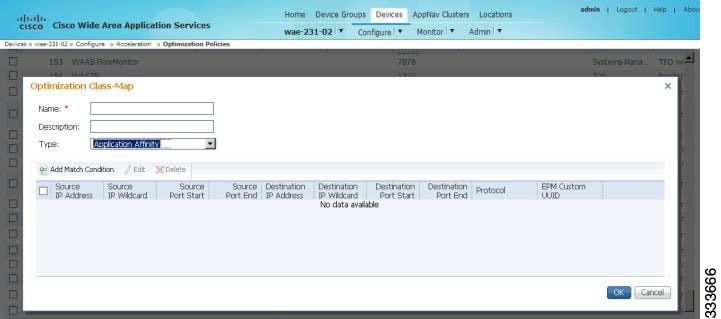

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, Protocol and EPM Custom UUID settings are not applicable.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, Protocol and EPM Custom UUID settings are not applicable.
Step 6![]() To create a condition for a specific type of traffic, enter a value in a Destination or Source field.
To create a condition for a specific type of traffic, enter a value in a Destination or Source field.
For example, to match all the traffic going to IP address 10.10.10.2, enter that IP address in the Destination IP Address field.
Consider the following guidelines for creating conditions:
- To specify a range of IP addresses, enter a wildcard subnet mask in either the Destination IP Wildcard field or Source IP Wildcard field in dotted decimal notation, such as 0.0.0.255 for /24.
- To match traffic that uses dynamic port allocation, from the Protocol drop-down list, choose the corresponding application identifier.
For example, to match Microsoft Exchange Server traffic that uses the MAPI protocol, choose mapi. To enter a custom EPM UUID, choose epm-uuid and enter the UUID in the EPM Custom UUID field.
Step 7![]() Add additional match conditions, as needed. If any one of the conditions is matched, the class is considered as matched.
Add additional match conditions, as needed. If any one of the conditions is matched, the class is considered as matched.
Step 8![]() To save the class map, click OK.
To save the class map, click OK.
Managing Application Acceleration
This section contains the following topics:
- Modifying the Accelerator Load Indicator and CPU Load-Monitoring Threshold
- Viewing a List of Applications on a Cisco WAE Device or Device Group
- Viewing a Policy Report for a Device or Device Group
- Viewing a Class Map Report for a Device or Device Group
- Restoring Optimization Policies and Class Maps
- Monitoring Applications and Class Maps
- Defining Default DSCP Marking Values
- Modifying the Position of an Optimization Policy
- Modifying the Acceleration TCP Settings
Modifying the Accelerator Load Indicator and CPU Load-Monitoring Threshold
High CPU utilization can adversely affect current optimized connections. To avoid CPU overload, you can enable CPU load monitoring and set the load monitoring threshold.
- When the average CPU utilization on the device exceeds the set threshold for 2 minutes, the device stops accepting new connections and passes new connections, if any, through.
- When the average CPU utilization falls below the threshold for 2 minutes, the device resumes accepting optimized connections.
- When a CPU overload condition occurs, the polling interval is reduced to an interval of 2 seconds. Although the average CPU utilization may fall below the threshold during this time and the overload condition cleared, the CPU alarm may still be present. The CPU alarm is cleared only when the overload condition does not reappear in the next 2-minute-interval poll.
To modify the accelerator load indicator threshold and CPU load monitoring for a Cisco WAE device, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Accelerator Threshold.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Accelerator Threshold.
The Accelerator Threshold window appears.
Step 3![]() To enable CPU Load Monitoring, check the Enable check box. (The default is enabled.)
To enable CPU Load Monitoring, check the Enable check box. (The default is enabled.)
Step 4![]() In the Accelerator Load Indicator Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
In the Accelerator Load Indicator Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
Step 5![]() In the CPU Load Higher Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 98.
In the CPU Load Higher Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 98.
Step 6![]() In the In the CPU Load Lower Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 90.
In the In the CPU Load Lower Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 90.
Step 7![]() In the Window Size field, enter a value between 1 to 16. The default value is 4.
In the Window Size field, enter a value between 1 to 16. The default value is 4.
Step 8![]() In the Sampling Intervals Avg Time field, enter a value between 1 and 120. The default is 10.
In the Sampling Intervals Avg Time field, enter a value between 1 and 120. The default is 10.
Step 9![]() In the Overloaded State Time field, enter a value between 1 to 120. The default value is 10.
In the Overloaded State Time field, enter a value between 1 to 120. The default value is 10.
If the device group is running Cisco WAAS Version 6.x or later, you can configure additional settings to monitor the CPU load for the device group.
Step 11![]() To enable CPU Load Monitoring, check the Enable check box. (The default is enabled.)
To enable CPU Load Monitoring, check the Enable check box. (The default is enabled.)
Step 12![]() To enable Linux softirq monitoring, check the Enable softirq Monitoring checkbox.
To enable Linux softirq monitoring, check the Enable softirq Monitoring checkbox.
Step 13![]() In the Accelerator Load Indicator Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
In the Accelerator Load Indicator Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
Step 14![]() In the CPU Load Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
In the CPU Load Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 80 and 100. The default is 95.
Step 15![]() In the CPU Load Higher Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 98.
In the CPU Load Higher Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 98.
Step 16![]() In the In the CPU Load Lower Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 90.
In the In the CPU Load Lower Monitoring Threshold field, enter a percent value between 1 and 100. The default is 90.
Step 17![]() In the Window Size field enter a value between 1 to 16. The default value is 4.
In the Window Size field enter a value between 1 to 16. The default value is 4.
Step 18![]() In the Sampling Intervals Avg Time field enter a value between 1 and 120. The default is 10.
In the Sampling Intervals Avg Time field enter a value between 1 and 120. The default is 10.
Step 19![]() In the Overloaded State Time field, enter a value between 1 to 120. The default value is 10.
In the Overloaded State Time field, enter a value between 1 to 120. The default value is 10.
Viewing a List of Applications on a Cisco WAE Device or Device Group
To view a list of applications that reside on a Cisco WAE device or device group, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
The Optimization Policies window appears.
Step 3![]() To sort the column by application name so that you can locate a specific application more easily, click the Application column header.
To sort the column by application name so that you can locate a specific application more easily, click the Application column header.
Step 4![]() Consider the following guidelines for viewing a list of applications on a Cisco WAE device or device group:
Consider the following guidelines for viewing a list of applications on a Cisco WAE device or device group:
- If there are Cisco WAAS devices running Cisco WAAS Version 4.x devices, click the Legacy View taskbar icon to view the policies as they appear in a Cisco WAAS Version 4.x device.
- To edit an optimization policy, check the box next to the application and click the Edit taskbar icon.
- If you determine that one or more policies are not needed, check the check box next to each of these applications and click the Delete taskbar icon.
- If you determine that a new policy is needed, click the Add Policy Rule taskbar icon (for more information, see Creating an Optimization Policy).
Viewing a Policy Report for a Device or Device Group
To view a report of a policy residing on each WAE device or device group, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policy Report (Figure 12-33).
From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policy Report (Figure 12-33).
The Optimization Policy Report window appears, with the Policy Report for Devices tab displayed.
Consider the following guidelines for viewing a policy report.
- The policy report lists each device (or device group) and the overall policy count on the device (or device group) referencing this application.
- The policy report includes both active policies (those in use by the device or device group), and backup policies (those not in use by the device when the device gets its configuration from a device group).
- When the device is deassigned from the device group, the backup policies are applied back to the device and become active again.
- An application cannot be deleted unless the No. of Policies field is 0.
Figure 12-33 Optimization Policy Report
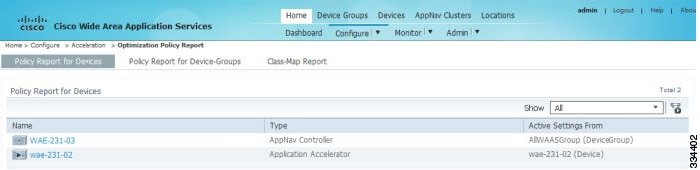
Step 2![]() To view the number of devices per device group and the number of active policies in the device group, click the Policy Report for Device-Groups tab.
To view the number of devices per device group and the number of active policies in the device group, click the Policy Report for Device-Groups tab.
Step 3![]() To see the optimization policies that are defined on a particular device or group, click the corresponding device or device group. The policies are displayed in the Optimization Policies window.
To see the optimization policies that are defined on a particular device or group, click the corresponding device or device group. The policies are displayed in the Optimization Policies window.
Step 4![]() For information about viewing a class map report, see Viewing a Class Map Report for a Device or Device Group.
For information about viewing a class map report, see Viewing a Class Map Report for a Device or Device Group.
Viewing a Class Map Report for a Device or Device Group
To view a report of the class maps that reside on each Cisco WAE device or device group, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policy Report.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policy Report.
The Policy Report for Devices tab appears.
Step 2![]() To view a report of the devices and device groups on which the class map is configured, click the Class-Map Report tab.
To view a report of the devices and device groups on which the class map is configured, click the Class-Map Report tab.
Step 3![]() To see the devices or device groups on which the class maps reside, select the class map and then click the View icon.
To see the devices or device groups on which the class maps reside, select the class map and then click the View icon.
Restoring Optimization Policies and Class Maps
The Cisco WAAS system allows you to restore the predefined policies and class maps that shipped with the Cisco WAAS system. For a list of the predefined policies, see Appendix A, “Predefined Optimization Policy.”
If you made changes to the predefined policies that have negatively impacted how a Cisco WAAS device handles application traffic, you can override your changes by restoring the predefined policy settings.
To restore predefined policies and class maps, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
The Optimization Policies window appears.
Step 3![]() To restore more than 150 policies and class maps that shipped with the Cisoc WAAS software, and to remove new policies that were created on the system, click the Restore Default taskbar icon.
To restore more than 150 policies and class maps that shipped with the Cisoc WAAS software, and to remove new policies that were created on the system, click the Restore Default taskbar icon.
If a predefined policy has been changed, these changes are lost and the original settings are restored.
Monitoring Applications and Class Maps
After you create an optimization policy, monitor the associated application to verify that your Cisco WAAS system is handling the application traffic as expected.
Before you monitor an application, you must have enabled statistics collection for that application. For more information, see Creating an Application Definition.
To monitor an application, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Monitor Classmaps.
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Configure > Acceleration > Monitor Classmaps.
Step 2![]() Select the class map on which to enable statistics and then click Enable.
Select the class map on which to enable statistics and then click Enable.
Consider the following guidelines for monitoring applications and class maps:
–![]() To monitor a specific application, run the TCP Summary report. For more information, see the TCP Summary Report in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
To monitor a specific application, run the TCP Summary report. For more information, see the TCP Summary Report in the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network” .
–![]() If you try to display more than 25 statistics for either applications or class maps, an error message is displayed.
If you try to display more than 25 statistics for either applications or class maps, an error message is displayed.
- To view statistics for all applications that have policies on a specific Cisco WAAS device, use the Cisco WAAS CLI. For more information, see the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
Step 3![]() To configure Cisco WAAS charts to display Class Map data:
To configure Cisco WAAS charts to display Class Map data:
b.![]() Choose the Classifier series.
Choose the Classifier series.
This configuration option applies to most Cisco WAAS charts.
Defining Default DSCP Marking Values
About Default DSCP Marking Values
According to policies that you define in an application definition and an optimization policy, the Cisco WAAS software allows you to set a DSCP value on packets that it processes.
- A DSCP value is a field in an IP packet that enables different levels of service to be assigned to the network traffic.
- The levels of service are assigned by marking each packet on the network with a DSCP code and associating a corresponding level of service.
- The DSCP marking determines how packets for a connection are processed externally to Cisco WAAS. DSCP is the combination of IP Precedence and Type of Service (ToS) fields.
- For more information, see RFC 2474.
- Thisattribute can be defined at the following levels:
- Global: Define global defaults for the DSCP value for each device (or device group) in the Optimization Policies page for that device (or device group). This value applies to the traffic if a lower level value is not defined.
- Policy: Define the DSCP value in an optimization policy. This value applies only to traffic that matches the class maps defined in the policy and overrides the application or global DSCP value.
Defining the Default DSCP Marking Value
To define the default DSCP marking value, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
The Optimization Policies window appears.
Step 3![]() Choose a value from the DSCP drop-down list. The default setting is copy, which copies the DSCP value from the incoming packet and uses it for the outgoing packet.
Choose a value from the DSCP drop-down list. The default setting is copy, which copies the DSCP value from the incoming packet and uses it for the outgoing packet.
Step 4![]() Click OK to save the settings.
Click OK to save the settings.
Modifying the Position of an Optimization Policy
About Optimization Policy Positions
Considering the following configuration guidelines for optimization policy positions:
- Each optimization policy has an assigned position that determines the order in which a Cisco WAAS device refers to the policy in an attempt to classify traffic.
For example, when a Cisco WAAS device intercepts traffic, it refers to the first policy in the list to try to match the traffic to an application. If the first policy does not provide a match, the Cisco WAAS device moves on to the next policy in the list.
- Consider the position of policies that pass through traffic as unoptimized, because placing these policies at the top of the list can cancel out optimization policies that appear farther down the list.
For example, If you have two optimization policies that match traffic going to IP address 10.10.10.2, and one policy optimizes this traffic and a second policy in a higher position passes through this traffic, then all traffic going to 10.10.10.2 will go through the Cisco WAAS system unoptimized.
For this reason, ensure that your policies do not have overlapping matching conditions, and monitor the applications you create to make sure that WAAS is handling the traffic as expected.
- For more information on monitoring applications, see the chapter “Monitoring Your Cisco WAAS Network”
Modifying the Position of an Optimization Policy
To modify the position of an optimization policy, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > Optimization Policies.
The Optimization Policies window appears (Figure 12-34).

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, all policies are grouped under the waas_global category.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, all policies are grouped under the waas_global category.
For a list of predefined policies, see Appendix A, “Predefined Optimization Policy.”
Figure 12-34 Optimization Policies Window

Step 3![]() To modify the position of an optimization policy, use one of the following methods:
To modify the position of an optimization policy, use one of the following methods:
- Select the policy you want to move, and then use the up and down arrow icons in the taskbar to move that policy higher or lower in the list.
- Select the policy you want to move, and then, to specify the new position, click Move To.
- Select the policy, and then drag and drop it into the new position.
Step 4![]() To save the new policy position(s), click Save Moved Rows.
To save the new policy position(s), click Save Moved Rows.
Step 5![]() (Optional) To create a new optimization policy at a particular position:
(Optional) To create a new optimization policy at a particular position:
a.![]() Select the policy above the location.
Select the policy above the location.
Step 6![]() If a device goes through all the policies in the list without making a match, the Cisco WAAS device passes the traffic through unoptimized.
If a device goes through all the policies in the list without making a match, the Cisco WAAS device passes the traffic through unoptimized.

Note![]() For a Cisco WAAS Express device, the class default policy must be last. This policy cannot be modified or deleted.
For a Cisco WAAS Express device, the class default policy must be last. This policy cannot be modified or deleted.
Step 7![]() To save changes, click the Save Moved Rows.
To save changes, click the Save Moved Rows.
Step 8![]() If you determine that a policy is not needed, follow these steps to delete the policy:
If you determine that a policy is not needed, follow these steps to delete the policy:
a.![]() Select the policy you want to delete.
Select the policy you want to delete.
b.![]() Click the Delete icon in the taskbar.
Click the Delete icon in the taskbar.
A default policy that maps to a default class map matching any traffic cannot be deleted.
Step 9![]() If you determine that a new policy is needed, click the Add Policy taskbar icon to create the policy.
If you determine that a new policy is needed, click the Add Policy taskbar icon to create the policy.
For more information, see Creating an Optimization Policy.
Modifying the Acceleration TCP Settings
About Acceleration TCP Settings
In most cases, you do not need to modify the acceleration TCP settings, because your Cisco WAAS system automatically configures the acceleration TCP settings based on the hardware platform of the Cisco WAE device.
–![]() When you first install the Cisco WAE device in your network.
When you first install the Cisco WAE device in your network.
–![]() When you enter the restore factory-default command on the Cisco WAAS device.
When you enter the restore factory-default command on the Cisco WAAS device.
For more information about this command, see the Cisco Wide Area Application Services Command Reference.
- The Cisco WAAS system automatically adjusts the maximum segment size (MSS) to match the advertised MSS of the client or server for each connection. The Cisco WAAS system uses the lower of 1432 or the MSS value advertised by the client or server.
- If your Cisco WAAS network has high BDP links, you may need to adjust the default buffer settings automatically configured for your WAE device. For more information, see Calculating the TCP Buffers for High BDP Links.
- If you want to adjust the default TCP adaptive buffering settings for your WAE device, see Modifying the TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Modifying the Acceleration TCP Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
To modify the acceleration TCP settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > TCP Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > TCP Settings.
The Acceleration TCP Settings window appears.
Step 3![]() Check the Send TCP Keepalive check box. (By default, this check box is checked.)
Check the Send TCP Keepalive check box. (By default, this check box is checked.)
Step 4![]() Checking the Send TCP Keepalive check box allows this Cisco WAE device or group to disconnect the TCP connection from its peer device if no response is received from the TCP keepalive exchange.
Checking the Send TCP Keepalive check box allows this Cisco WAE device or group to disconnect the TCP connection from its peer device if no response is received from the TCP keepalive exchange.
–![]() In this case, the two peer WAE devices will exchange TCP keepalives on a TCP connection, and if no response is received for the keepalives for a specific period, the TCP connection will be torn down.
In this case, the two peer WAE devices will exchange TCP keepalives on a TCP connection, and if no response is received for the keepalives for a specific period, the TCP connection will be torn down.
–![]() When the keepalive option is enabled, any short network disruption in the WAN will cause the TCP connection between peer WAE devices to be disconnected.
When the keepalive option is enabled, any short network disruption in the WAN will cause the TCP connection between peer WAE devices to be disconnected.
Step 5![]() Modify the TCP acceleration settings as needed.
Modify the TCP acceleration settings as needed.
- For a description of TCP acceleration settings, see Table 12-16 .
- For information on how to calculate these settings for high Bandwidth-Delay-Product (BDP) links, see Calculating the TCP Buffers for High BDP Links.
Step 6![]() If you are deploying the Cisco WAE across a high BDP link, you can set recommended values for the send and receive buffer sizes by clicking Set High BDP recommended values.
If you are deploying the Cisco WAE across a high BDP link, you can set recommended values for the send and receive buffer sizes by clicking Set High BDP recommended values.
For more information about calculating TCP buffers for high BDP links, see Calculating the TCP Buffers for High BDP Links.
Step 7![]() Considering the following guidelines for segment sizes and configuring jumbo MTU settings:
Considering the following guidelines for segment sizes and configuring jumbo MTU settings:
- If the original and optimized maximum segment sizes are set to their default values and you configure a jumbo MTU setting, the segment sizes are changed to the jumbo MTU setting minus 68 bytes.
- If you have configured custom maximum segment sizes, their values are not changed if you configure a jumbo MTU.
- For more information on jumbo MTU, see Configuring a Jumbo MTU in the chapter “Configuring Network Settings” .
Configuring TCP Keepalives Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Use the following commands to configure TCP keepalives:
- To configure TCP keepalives, run the tfo tcp keepalive global configuration command.
- To configure TCP acceleration settings, run the following global configuration commands:
–![]() tfo tcp optimized-receive-buffer
tfo tcp optimized-receive-buffer
–![]() tfo tcp optimized-send-buffer
tfo tcp optimized-send-buffer
Calculating the TCP Buffers for High BDP Links
You can deploy Cisco WAAS software in different network environments, involving multiple link characteristics such as bandwidth, latency, and packet loss. All Cisco WAAS devices are configured to accommodate networks with maximum Bandwidth-Delay-Product (BDP), up to the values listed below:
- Cisco WAE-512: Default BDP is 32 KB
- Cisco WAE-612: Default BDP is 512 KB
- Cisco WAE-674: Default BDP is 2048 KB
- WAE-7341: Default BDP is 2048 KB
- Cisco WAE-7371: Default BDP is 2048 KB
- All Cisco WAVE platforms: Default BDP is 2048 KB
Consider the following operating guidelines for BDP:
- If your Cisco WAAS network provides higher bandwidth, or if higher latencies are involved, use the following formula to calculate the actual link BDP:
BDP [Kbytes] = (link BW [Kbytes/sec] * Round-trip latency [Sec])
- When multiple links 1..N are the links for which the Cisco WAE is optimizing traffic, the maximum BDP should be calculated as follows:
MaxBDP = Max (BDP(link 1),..,BDP(link N))
- If the calculated MaxBDP is greater than the DefaultBDP for your Cisco WAE model, modify the Acceleration TCP to accommodate that calculated BDP.
- After you calculate the size of the MaxBDP, enter a value that is equal to or greater than twice the MaxBDP in the Send Buffer Size and Receive Buffer Size fields for the optimized connection in the Acceleration TCP Settings window.

Note![]() These manually configured buffer sizes are applicable only if TCP adaptive buffering is disabled. TCP adaptive buffering is normally enabled, and allows the Cisco WAAS system to dynamically vary the buffer sizes. For more information on TCP adaptive buffering, see Modifying the TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
These manually configured buffer sizes are applicable only if TCP adaptive buffering is disabled. TCP adaptive buffering is normally enabled, and allows the Cisco WAAS system to dynamically vary the buffer sizes. For more information on TCP adaptive buffering, see Modifying the TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager.
Modifying the TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings Using the Cisco WAAS Central Manager
In most cases you do not need to modify the adaptive TCP adaptive buffering settings, because your Cisco WAAS system automatically configures the TCP adaptive buffering settings based on the network bandwidth and delay experienced by each connection. Adaptive buffering allows the Cisco WAAS software to dynamically vary the size of the send and receive buffers to increase performance and more efficiently use the available network bandwidth.
To modify the acceleration TCP adaptive buffering settings, follow these steps:
Step 1![]() From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
From the Cisco WAAS Central Manager menu, choose Devices > device-name ( or Device Groups > device-group-name).
Step 2![]() Choose Configure > Acceleration > TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings.
Choose Configure > Acceleration > TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings.
The TCP Adaptive Buffering Settings window appears.
Step 3![]() To enable TCP adaptive buffering, check the Enable check box. (By default, this is enabled.)
To enable TCP adaptive buffering, check the Enable check box. (By default, this is enabled.)
Step 4![]() In the Send Buffer Size and Receive Buffer Size fields, enter the maximum size, in kilobytes, of the send and receive buffers.
In the Send Buffer Size and Receive Buffer Size fields, enter the maximum size, in kilobytes, of the send and receive buffers.
Configuring TCP Adaptive Buffer Settings Using the Cisco WAAS CLI
Use the following commands to configure the TCP adaptive buffer settings:
- To configure TCP adaptive buffer settings, run the tfo tcp adaptive-buffer-sizing global configuration command:
 Feedback
Feedback