Troubleshoot EIGRP on FTD Devices Managed by FMC
Available Languages
Download Options
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
Introduction
This document describes how to verify and troubleshoot EIGRP configuration on FTD managed by FMC.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
- Cisco Secure Firewall Management Center (FMC)
- Cisco Secure Firewall Threat Defense (FTD)
Components Used
- FTDv in version 7.4.2.
- FMCv in version 7.4.2.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
EIGRP is an advanced distance vector routing protocol that combines features of both distance vector and link-state protocols. It offers fast convergence by maintaining routing information from neighbors, allowing quick adaptation to alternate routes. EIGRP is efficient, utilizing partial, triggered updates for route or metric changes instead of periodic full updates.
For communication, EIGRP operates directly on the IP layer (Protocol 88) and uses the Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) for guaranteed, ordered packet delivery. It supports both multicast and unicast, with hello messages specifically using multicast addresses 224.0.0.10 or FF02::A.
EIGRP operation is fundamentally based on the information stored in three tables:
- Neighbor table: This table maintains a record of directly connected EIGRP devices with which an adjacency has been successfully established.
- Topology table: This table stores all learned routes advertised by neighbors, including all feasible paths to a specific destination and their associated metrics, allowing for an evaluation of their quality and the number of available paths.
- Routing table: This table contains the best path for each destination, known as the 'Successor.' This Successor route is the one actively used for forwarding traffic and is subsequently advertised to other EIGRP neighbors.
EIGRP uses metric weights, known as K values, in routing and metric computations to determine the optimal path to a destination. This metric value is derived from a formula that utilizes parameters:
- Bandwidth
- Delay Time
- Reliability
- Loading
- MTU

Note: In the event of a metric tie between multiple paths, the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is used as a tie-breaker, with a higher MTU value being preferred.
-
Successor Route: This is defined as the best path to a specific destination. It is the route that is ultimately installed into the routing table.
-
Feasible Distance (FD): This represents the best calculated metric to reach a particular subnet from the local router perspective.
-
Reported Distance (RD) / Advertised Distance (AD): This is the distance (metric) to a specific subnet as reported by a neighbor. For a path to be considered a feasible successor, the Reported Distance from the neighbor must be less than the local router Feasible Distance to that same destination.
-
Feasible Successor (FS): This is a backup path to a destination, providing an alternate route in case the primary Successor Route fails. A path qualifies as a Feasible Successor if its Reported Distance (from the advertising neighbor) is strictly less than the Feasible Distance of the current Successor Route to the same destination.
Network Diagram
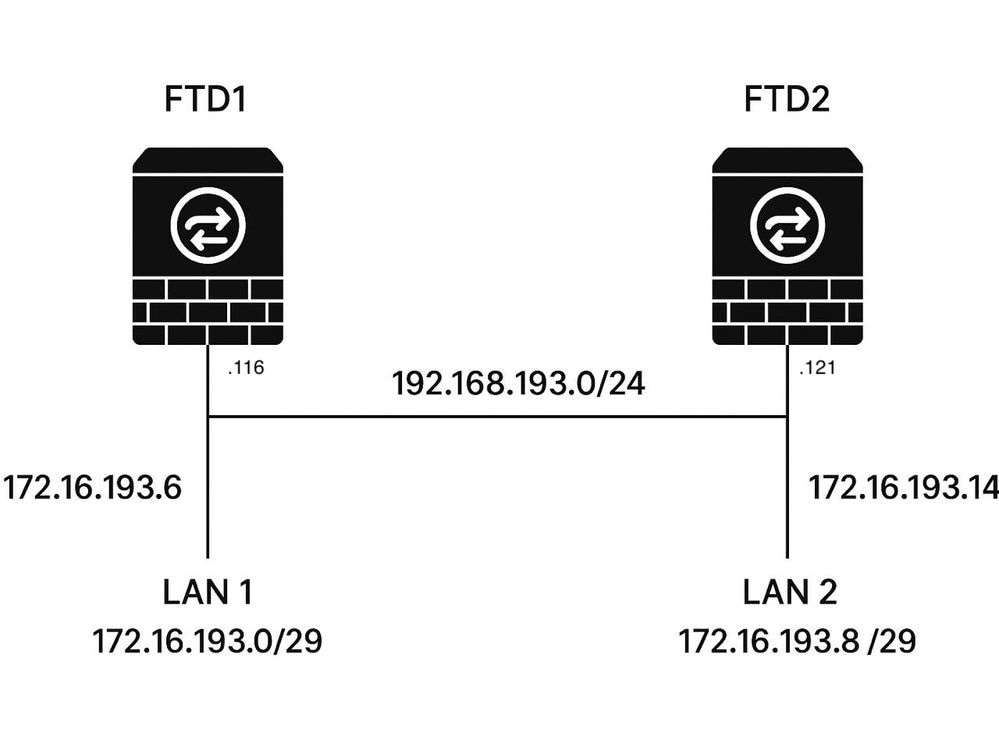 Network Diagram
Network Diagram
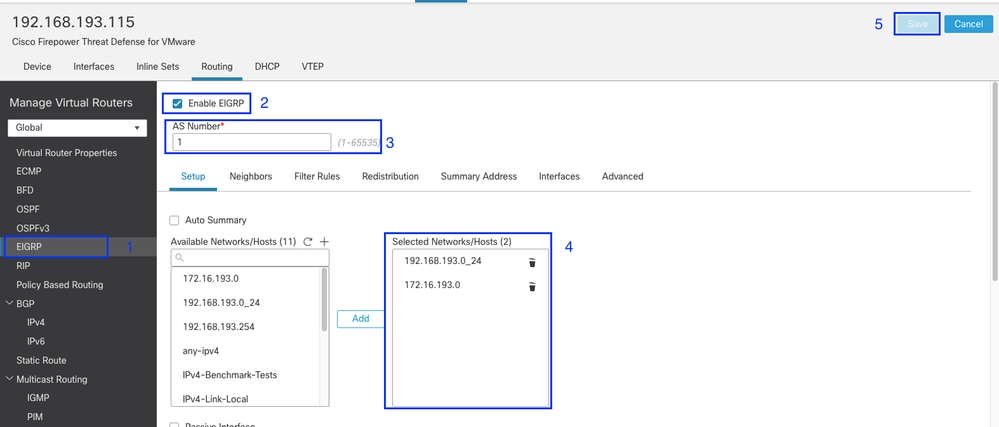
Basic Configuration
Navigate to Devices > Device Management:
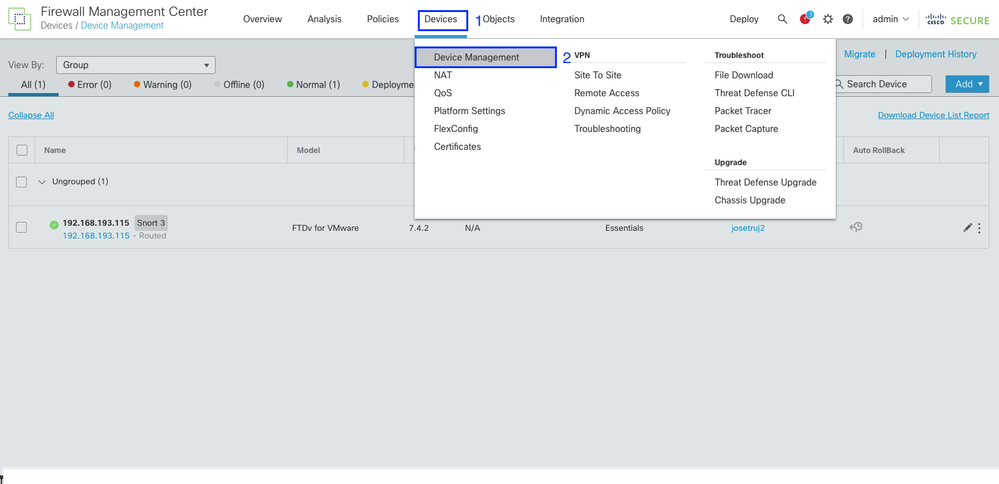
Select device:
Click the Routing tab.
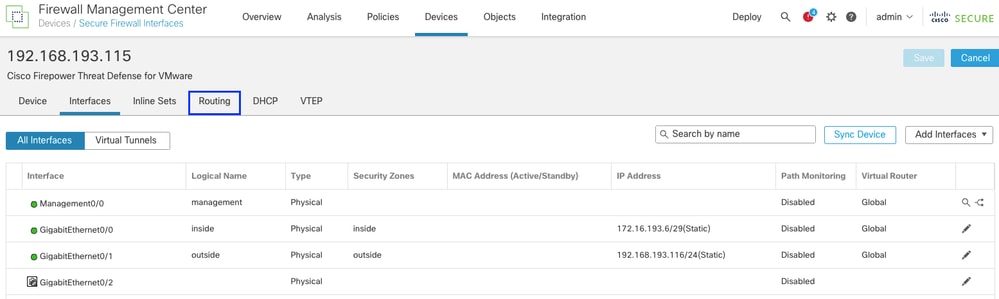
Click EIGRP in the left menu.
Click Enable EIGRP.
Assign the AS number (1-65535).
Select one network/host. You can either select a previously created object from the 'Available Network/Host' list, or you can create a new object by clicking the plus (+) button.
Click Save.
Validation
Here are the minimum requirements for EIGRP neighbor adjacency:
- AS number must match.
- The interface must be active and reachable.
- As a best practice, Hello and Hold timers must match.
- K-values must match.
- No Access Lists must be blocking EIGRP traffic.
Validation Using CLI
- show run router eigrp
- show eigrp neighbors
- show eigrp topology
- show eigrp interfaces
- show route eigrp
- show eigrp traffic
- debug ip eigrp neighbor
- debug eigrp packets
firepower# show run router eigrp
router eigrp 1
no default-information in
no default-information out
no eigrp log-neighbor-warnings
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
network 192.168.193.0 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.193.8 255.255.255.248
firepower#
firepower# show eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1)
H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq
(sec) (ms) Cnt Num
0 192.168.193.121 outside 14 21:45:04 40 240 0 30
firepower# show eigrp topology
EIGRP-IPv4 Topology Table for AS(1)/ID(192.168.193.121)
Codes: P - Passive, A - Active, U - Update, Q - Query, R - Reply,
r - reply Status, s - sia Status
P 192.168.193.0 255.255.255.0, 1 successors, FD is 512
via Connected, outside
P 172.16.193.0 255.255.255.248, 1 successors, FD is 768
via 192.168.193.116 (768/512), outside
P 172.16.193.8 255.255.255.248, 1 successors, FD is 512
via Connected, inside
firepower# show eigrp interfaces
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
outside 1 0 / 0 10 0 / 1 50 0
inside 0 0 / 0 0 0 / 1 0 0
firepower#
firepower# show route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, V - VPN
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, + - replicated route
SI - Static InterVRF, BI - BGP InterVRF
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.193.254 to network 0.0.0.0
D 172.16.193.0 255.255.255.248
[90/768] via 192.168.193.116, 02:32:58, outside
firepower# show route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, V - VPN
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, + - replicated route
SI - Static InterVRF, BI - BGP InterVRF
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.193.254 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 [1/0] via 192.168.193.254, outside
D 172.16.193.0 255.255.255.248
[90/768] via 192.168.193.116, 02:33:41, outside
C 172.16.193.8 255.255.255.248 is directly connected, inside
L 172.16.193.14 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, inside
C 192.168.193.0 255.255.255.0 is directly connected, outside
L 192.168.193.121 255.255.255.255 is directly connected, outside
firepower#
firepower# show eigrp traffic
EIGRP-IPv4 Traffic Statistics for AS(1)
Hellos sent/received: 4006/4001
Updates sent/received: 4/4
Queries sent/received: 0/0
Replies sent/received: 0/0
Acks sent/received: 3/2
SIA-Queries sent/received: 0/0
SIA-Replies sent/received: 0/0
Hello Process ID: 2503149568
PDM Process ID: 2503150496
Socket Queue:
Input Queue: 0/2000/2/0 (current/max/highest/drops)
firepower#
Troubleshoot
Scenario 1 - Debug IP EIGRP Neighbor
Debug commands can be utilized to observe any changes in neighbor states.
firepower# debug ip eigrp neighbor
firepower#
EIGRP: Holdtime expired
Going down: Peer 192.168.193.121 total=0 stub 0, iidb-stub=0 iid-all=0
EIGRP: Handle deallocation failure [0]
EIGRP: Neighbor 192.168.193.121 went down on outside
Run the show eigrp neighbors command to validate the neighbor status between the FTDs.
firepower# show eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1)
Verify the status of the interfaces using the show interface ip brief command. You can observe that the GigabitEthernet0/1 interface is administratively down.
firepower# show interface ip brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0 172.16.193.14 YES CONFIG up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.193.121 YES CONFIG administratively down up
GigabitEthernet0/2 192.168.194.24 YES manual up up
Internal-Control0/0 127.0.1.1 YES unset up up
Internal-Control0/1 unassigned YES unset up up
Internal-Data0/0 unassigned YES unset down up
Internal-Data0/0 unassigned YES unset up up
Internal-Data0/1 169.254.1.1 YES unset up up
Internal-Data0/2 unassigned YES unset up up
Management0/0 203.0.113.130 YES unset up up
Scenario 2 - Authentication
The FTD supports the MD5 hash Algorithm to authenticate EIGRP packets. By default, this authentication is disabled.
To enable the MD5 hash algorithm, mark the 'MD5 Authentication' checkbox. It is crucial that authentication settings match on both devices; if enabled on one device but not the other, neighbor adjacency can not form between them.
Verify this configuration using debug eigrp packets.
firepower# debug eigrp packets
(UPDATE, REQUEST, QUERY, REPLY, HELLO, IPXSAP, PROBE, ACK, STUB, SIAQUERY, SIAREPLY)EIGRP Packet debugging is on
firepower#
EIGRP: outside: ignored packet from 192.168.193.121, opcode = 5 (authentication off or key-chain missing)
EIGRP: Received HELLO on outside nbr 172.16.193.14
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on outside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on inside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: outside: ignored packet from 192.168.193.121, opcode = 5 (authentication off or key-chain missing)
EIGRP: Received HELLO on outside nbr 172.16.193.14
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on inside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on outside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: outside: ignored packet from 192.168.193.121, opcode = 5 (authentication off or key-chain missing).
You can observe a message indicating that authentication is off or that the key chain is missing. In this scenario, this typically occurs when authentication is enabled on one peer but not on the other.
EIGRP: outside: ignored packet from 192.168.193.121, opcode = 5 (authentication off or key-chain missing).
Verify with show run interface <EIGRP interface>.
Firepower1# show run interface GigabitEthernet0/1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 192.168.193.121 255.255.255.0
authentication key eigrp 1 ***** key-id 10
authentication mode eigrp 1 md5
Firepower2# show run interface GigabitEthernet0/1
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif outside
security-level 0
ip address 192.168.193.116 255.255.255.0
Scenario 3 - Passive Interfaces
When EIGRP is configured, EIGRP hello packets are typically sent and received on interfaces where the network is enabled.
However, if an interface is configured as passive, EIGRP suppresses the exchange of hello packets between two routers on that interface, which results in the loss of neighbor adjacency. Consequently, this action not only prevents the router from advertising routing updates out of that interface but also stops it from receiving routing updates from that interface.
Run the show eigrp neighbors command to validate the neighbor status between the FTDs.
firepower# show eigrp neighbors
EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(1)
You can verify the EIGRP packets being sent and the interfaces they are sent through using the debug eigrp packets command.
FTD 1
Firepower1#
(UPDATE, REQUEST, QUERY, REPLY, HELLO, IPXSAP, PROBE, ACK, STUB, SIAQUERY, SIAREPLY)EIGRP Packet debugging is on
firepower#
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on outside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on inside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on outside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on inside
AS 1, Flags 0x0:(NULL), Seq 0/0 interfaceQ 0/0 iidbQ un/rely 0/0
EIGRP: Sending HELLO on outside
FTD 2
Firepower2# debug eigrp packets
(UPDATE, REQUEST, QUERY, REPLY, HELLO, IPXSAP, PROBE, ACK, STUB, SIAQUERY, SIAREPLY)EIGRP Packet debugging is on
Firepower2#
In this scenario, FTD 2 is not sending EIGRP hello messages because its inside and outside interfaces are configured as passive. Verify this with the show run router eigrp command.
Firepower2# show run router eigrp
router eigrp 1
no default-information in
no default-information out
no eigrp log-neighbor-warnings
no eigrp log-neighbor-changes
network 192.168.193.0 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.193.8 255.255.255.248
passive-interface outside
passive-interface inside

Note: In order to stop all configured debug processes, please use the undebug all command.
Related Information
Revision History
| Revision | Publish Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
1.0 |
23-Sep-2025
|
Initial Release |
Contributed by Cisco Engineers
- Jose Luis Trujillo EspindolaTechnical Consulting Engineer
Contact Cisco
- Open a Support Case

- (Requires a Cisco Service Contract)
 Feedback
Feedback