Cisco Catalyst Center 2.3.7 Data Sheet
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
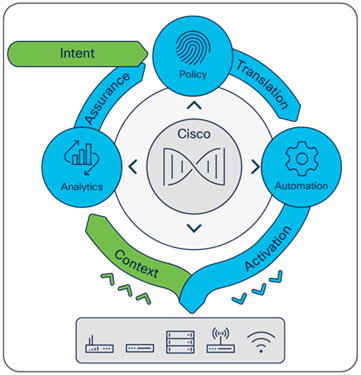
Cisco Catalyst™ Center, formerly Cisco DNA Center, is a powerful network controller and management dashboard that empowers you to take charge of your network, optimize your Cisco investment, and lower your IT spending. Catalyst Center provides a single dashboard for every fundamental management task to simplify running your network. With this platform, IT can respond to changes and challenges faster and more intelligently.
Design: Design your network using intuitive workflows, starting with locations where your network devices will be deployed. Users of Cisco Prime® Infrastructure and the Cisco® Application Policy Infrastructure Controller Enterprise Module (APIC-EM) can simply import existing network designs and device images into Catalyst Center.
● Policy: Define user and device profiles that facilitate highly secure access and network segmentation based on business needs. Application policies enable your business-critical applications to provide a consistent level of performance regardless of network congestion.
● Provision: Use policy-based automation to deliver services to the network based on business priority and to simplify device deployment. Zero-touch device provisioning and software image management features reduce device installation or upgrade time from hours to minutes and bring new remote offices online with plug-and-play ease from an off-the-shelf Cisco device. Additionally, the Cisco Secure Network Analytics (formerly Cisco Stealthwatch) service provisions network elements to send NetFlow and Encrypted Traffic Analytics (ETA) to the analytics service.
● Assurance: Enable every point on the network to become a sensor, sending continuous streaming telemetry on application performance and user connectivity in real time. This, coupled with automatic path-trace visibility and guided remediation, means network issues are resolved in minutes — before they become problems. Automated NetFlow switch configuration for Cisco Secure Network Analytics provides detection and mitigation of threats, even when they are hidden in encrypted traffic.
● Platform: An open and extensible platform allows third-party applications and processes to exchange data and intelligence with Catalyst Center. This improves IT operations by automating workflow processes based on network intelligence coming from Catalyst Center.
Catalyst Center
Catalyst Center is a centralized network management system to bring all this functionality into an integrated controller and present it through a single pane of glass. It can be deployed on a hardware appliance or as a virtual appliance.

How Catalyst Center works
Catalyst Center is a software solution that offers flexible deployment options. It can be deployed either on the Catalyst Center hardware appliance or as a virtual appliance on AWS. The solution receives telemetry data from network devices including switches, routers, access points, and controllers. For a device to be authorized to send data to Catalyst Center, that device must be included in your organization’s Catalyst or Cisco DNA license subscription. Cisco encourages customers to purchase complete Catalyst Center functionality through a Catalyst or Cisco DNA Advantage license subscription. Limited Catalyst Center functionality is also available through a Cisco DNA Essentials license subscription. Wireless, switching, and SD-WAN and routing subscriptions are available for 3- and 5-year terms; wireless and switching are also available in a 7-year term. All Catalyst and Cisco DNA software license subscription options include embedded Cisco software support and downloads.
The links below open matrices detailing the main features included in each respective suite.
In addition to the licenses, the Expansion Pack is a flexible way to purchase Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), Cisco Spaces, Cisco Secure Network Analytics (previously Stealthwatch), Cisco ThousandEyes®, and other licenses, appliances, and services in one convenient bundle. Enhance your Cisco networking solutions such as SD-Access, Cisco zero-trust solutions, Encrypted Traffic Analytics (ETA), location analytics, and assurance. You can add the pack to your Catalyst or Cisco DNA software licenses and choose the license count that fits your needs.
Introduction to Smart Licensing
Cisco Smart Licensing is a flexible licensing model that provides you with an easier, faster, and more consistent way to purchase and manage software across the Cisco portfolio and across your organization. And it’s secure – you control what users can access. With Smart Licensing you get:
● Easy activation: Smart Licensing establishes a pool of software licenses that can be used across the entire organization—no more Product Activation Keys (PAKs).
● Unified management: My Cisco Entitlements (MCE) provides a complete view into all of your Cisco products and services in an easy-to-use portal, so you always know what you have and what you are using.
● License flexibility: Your software is not node-locked to your hardware, so you can easily use and transfer licenses as needed.
To use Smart Licensing, you must first set up a Smart Account on Cisco Software Central (software.cisco.com).
For a more detailed overview of Cisco Licensing, go to cisco.com/go/licensingguide.
Table 1. Catalyst Center Automation features and benefits
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Network discovery |
Automatically discovers and maps network devices to a physical topology with detailed device-level data. The discovery function uses the following protocols and methods to retrieve device information, such as IP addresses, neighboring devices, and hosts connected to the device:
● Cisco Discovery Protocol
● Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) for endpoints
● IP Device Tracking (IPDT) and Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) entries for host discovery
● LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) for discovering IP phones and some servers
● Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) versions 2 and 3
|
| Inventory |
Retrieves and saves details, such as host IP addresses, MAC addresses, and network attachment points, about devices in its database. After the initial discovery, Catalyst Center periodically scans the network to create a “single source of truth” for IT. This inventory includes all network devices, along with an abstraction for the entire enterprise network. It keeps an updated inventory of devices and software images on that device for version control and provides data to applications (such as Software Image Management [SWIM] and Cisco EasyQoS) so that the correct device and image version are used. It allows applications to be device independent, so configuration differences between devices are not a problem.
|
| Network design and profile based management |
Allows you to manage your network in a hierarchical fashion by letting you add areas and buildings on a geospatial map. You can start by defining your sites, then add buildings to sites and add floors with detailed floor plans to the buildings. Catalyst Center lets the user define profiles, which consist of common network settings such as device credentials, DHCP, DNS server, AAA server, IP address pool, etc. Wireless settings such as SSIDs and RF profiles can be created globally and customized at site levels. These profiles form the basis for network automation. Network profiles can be created for Cisco Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS), routing, firewall (including Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance [ASA]), switching, and wireless.
|
| Cisco Network Plus and Play (PnP) |
Allows off-the-shelf Cisco devices to be provisioned simply by connecting them to the network. Cisco Network PnP provides a secure, scalable, seamless, and unified zero-touch-deployment experience for customers across Cisco's entire enterprise network portfolio of wired and wireless devices. Deploy new devices in minutes, without onsite support visits. Eliminate repetitive tasks and eliminate staging. Network PnP reduces the burden on enterprises by greatly simplifying the deployment process for new devices, which can significantly lower Operating Expenditures (OpEx) as well. For more details, refer to the solution guide for the Network Plug and Play application:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Plug-and-Play/solution/guidexml/b_pnp-solution-guide.html.
|
| Software Image Management (SWIM) |
Manages software upgrades and controls the consistency of image versions and configurations across your network. Speeds and simplifies the deployment of new software images and patches. Pre- and post-checks help ensure no adverse effects from an upgrade. This is an easy way to build a central repository of software images and apply them to devices. Administrators can mark software images as golden for a device family, allowing them to upgrade devices to the software image and patch versions that are in compliance with the golden versions defined in the repository. Patches are supported in Catalyst Center from intent to pre- and post-checks in the same way that we manage regular images. It also tracks when software maintenance updates, subpackages, ROM Monitor, AP Service Pack, and AP Device Pack upgrades are applied to the base image.
|
| Network compliance audit and remediation |
Network compliance audit feature allows network operators to quickly assess the devices that don’t adhere to corporate standards. The network compliance remediation feature allows network operators to automatically sync running (production) configurations with startup configurations for all the network elements. Network operators can select one or many devices, view and validate the change, select and sync those devices, and remediate them to maintain compliance. These two features reduce human involvement and error and helps ensure that the network is running the intended configuration standards.
|
| Device tagging |
An administrator can tag network devices in order to associate devices that share a common attribute. For example, you can create a tag and use it to group devices based on a platform ID, Cisco IOS release, or location. Allows for grouping of devices based on specialized needs.
|
| Configuration drift visibility |
Allows network operators to compare any two device configuration versions in a very visual manner. Having different versions of a device configuration available allows for accurate accountability of every configuration change.
|
| Device replacement and RMA workflows |
Workflow templates allow for the replacement (RMA) of switches, routers, and access points. Includes restoration of Cisco IOS Software, configurations, and licenses. Also completes device replacement in operational systems such as Cisco ISE, certificate servers, and Catalyst Center inventory. Saves time and retains existing setup, licenses, and KPI trends.
|
| Branch deployment automation |
Simplified workflows for physical and virtual branch automation; day-0 router, and NFV design. Onboard WAN devices and services through these easy steps:
Configure network settings, service provider, and IP pools.
Design a router or virtual profile.
Assign to sites and provision network devices.
|
| Wireless automation |
Intent-based workflows for simplified wireless deployment and automation:
● Network profiles: a profile is a container of wireless properties that can represent single or multiple sites
● Simplified SSID creation
● Advanced RF support for wireless networks
● A single workflow to enable Cisco FlexConnect® or centralized wireless deployment.
● PnP provisioning for APs
● IP Access Control List (ACL) support
● Access and access control policy for SD-Access Wireless only
● For more details, please refer to the
Wireless Automation white paper.
|
| Cisco StackWise Virtual support |
Base automation (inventory, discovery, SWIM, topology, and template programmer) and assurance support for Cisco Catalyst® 9500 and 9400 Series StackWise Virtual switches. StackWise Virtual technology on the Cisco Catalyst 9000 platform allows the clustering of two physical switches together into a single logical entity, resulting in enhancements in all areas of network design, including high availability, scalability, management, and maintenance. Customers can now use Catalyst Center to manage the StackWise Virtual device, along with monitoring the health and status of StackWise Virtual ports and links.
|
| Policy creation |
Allows the creation of policies based on business intent for a particular part of the network. Users can be assigned policies for the services they consume, and these policies follow them throughout the network. Policies are translated by Catalyst Center into network-specific and device-specific configurations that can be adjusted dynamically based on network conditions. Of foundational importance for intent-based networking, policies define the business intent that is desired and allow the network to guarantee services.
|
| Application policy creation |
Allows policies to be assigned to applications based on business relevance. These applications can then be attached to sites (locations) where the policy should be applied. This feature allows business-critical applications to have greater QoS priority in the sites where their use is relevant. It is important for mission-critical applications such as machine-to-machine control in manufacturing or life-saving devices in healthcare, as well as for business-critical applications such as video in customer experience centers or voice in support sites.
|
| Rogue management and aWIPS |
Supports the detection of rogue and Cisco Adaptive Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (aWIPS) threats on your network from within Catalyst Center. The Rogue and aWIPS Dashboard provides detailed threat analysis and a global view of all rogue access points detected in the network, with insight into the highest priority threats so that they can be quickly identified. The Threat 360 view on this dashboard provides further details on any specific threat. This includes a map view for quick location, and all affected clients.
|
| Meraki discovery and integration |
Provides for the discovery of all Cisco Meraki® devices in the network and integrates them into the Catalyst Center dashboard. It provides for a single pane of glass for both Cisco and Meraki devices.
|
| Meraki wireless provisioning |
Provision SSIDs in Meraki access points through Catalyst Center. Meraki access points can be assigned SSIDs through Catalyst Center without having to open the Meraki dashboard.
|
Table 2. Catalyst Center Assurance features and benefits
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Network and Cltent Health dashboards |
Assurance dashboards that give a high-level overview of the health of every network device and client on the network, wired and wireless. They provide the top 10 global issues and allow the administrator to expand views by geographical site, device list, client list, or topology. Any poorly connected devices or communication issues are highlighted, with suggested remediation. Users can customize how the health score is computed.
|
| Application Health dashboard |
Provides a general overview of the health of all applications on the network. Includes a special section on applications that have been tagged as business relevant. Business-relevant application issues are highlighted, with suggested remediation for any anomalies.
|
| ThousandEyes integration |
Cisco ThousandEyes agents can be installed on all supported switches through a GUI-based installation process in Catalyst Center. The application resides on the switch’s flash storage, providing significant time and cost savings to deploy ThousandEyes. Data from the ThousandEyes agents is used by Catalyst Center to provide visibility into application performance and help the administrator pinpoint problem domains.
|
| Webex and Micosoft Teams integration |
Provides a consolidated view of quality metrics for audio, video, and shared components and enables administrators to troubleshoot Webex and Microsoft Teams performance. Network operators can quickly identify and resolve issues in Catalyst Center without having to switch between multiple interfaces.
|
| Cisco AI Network Analytics |
Using AI and machine learning, Cisco AI Network Analytics drives intelligence in the network, empowering administrators to improve performance and issue resolution accurately and effectively. We are taking network analytics to a new level where noise and false positives are significantly reduced and enabling customers to very accurately identify issues, trends, anomalies, and root causes.
●
Intelligent issue detection and analysis
● AI-driven personalized baselining: No two networks are the same. AI-driven technologies can learn the user trends, services, and application metrics that are specific to your network. Catalyst Center Assurance can then create a customized performance curve for analytical decisions. The AI-driven baseline for the performance parameters that are unique to your network is constantly adapted as your network grows and changes. From there, the AI-driven analytics engine (both on premises and in the Cisco cloud) can make accurate decisions for what is normal and what is not, based on this personalized baseline.
● AI-driven anomaly detection: The system can accurately detect performance issues and ignore unusual but harmless network anomalies. This reduces noise while accurately identifying anomalies that have the greatest impact on your network. AI-driven predictive analytics and proactive insights allow users to anticipate and prevent failures. The machine learning engine can predict increases in Wi-Fi interference, onboarding delays, office traffic load, etc. This is because, in IP networks, a problematic event is often preceded by a benign event or series of events. By learning how series of events are correlated to one another, predictive analytics can help network administrators anticipate the unexpected.
● AI-driven accelerated remediation: Cisco AI Network Analytics provides accelerated remediation through machine learning, which identifies the most critical variables related to the root cause of a given problem. This helps users detect issues and vulnerabilities, perform complex root cause analysis (using a Machine Reasoning Engine; see below), and execute corrective actions faster than ever. In coming releases, we will enable machine reasoning to execute the logical troubleshooting steps that an engineer would perform in order to resolve a problem. Both of these capabilities accelerate remediation, making your team more precise in problem solving and more productive overall.
● AI-driven Site Analytics: Site Analytics helps IT teams proactively identify underlying issues that can have a sitewide impact on user experience. It gives the network administrator a single view of customizable KPIs to help them understand the health of devices, users, and applications.
|
| Machine Reasoning Engine (MRE) |
Defines the next intelligence evolution and helps in complex workflows where the result of one action determines the next. It closely resembles how human beings themselves reason things out and accomplish multistep tasks. An example where Catalyst Center uses MRE is to find and fix potentially crippling routing loops that require a careful analysis spanning multiple devices. This allows your new IT team members to accomplish complex tasks instead of escalating them and saves time for your more seasoned IT team members by automating tedious workflows.
For more information, read the blog:
https://blogs.cisco.com/networking/machine-reasoning-is-the-new-ai-ml-technology-that-will-save-you-time-and-facilitate-offsite-netops. |
| Wireless 3D Analyzer |
The Wireless 3D Analyzer provides granular analysis of millions of spatial RF data points and the ability to visualize wireless coverage. Network operators can identify the areas most affected by RF strengths, view client locations, simulate different RF environments, and conduct spatial planning and prediction of the interior environment. After loading basic architectural structural information, network operators can enter a virtual office space and move an access point or create an imaginary wall and see the resulting impact on Wi-Fi signal propagation. The Wireless 3D Analyzer helps network operators maximize WLAN performance and identify trouble spots and WLAN design issues faster.
|
| Wireless Network Services Analytics |
View Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services for wireless devices across Cisco and all third-party servers in a global comprehensive view. This capability includes the overall health of these critical services all in one place, highlighting the worst-performing service server, site-level impact, and scope of end-user impact. This helps network operators reduce overall issue-ticket resolution time and leads to lower ticket volume.
|
| Global assurance event viewer |
The global assurance event viewer gives the network administrator a consolidated view of events from all devices, where they can search and filter on the events that are most important to address. The event view allows the user to identify, correlate, and troubleshoot network issues and quickly get to the root cause.
|
| Power over Ethernet analytics |
Provides visibility into the power loads that a switch is experiencing. Endpoint devices that are pulling too much power, as well as switches that are approaching overload, are flagged. Granular visibility shows the available power on any switch for quick installation of IoT endpoint devices.
|
| Path Trace |
Allows the operator to visualize the path of an application or service from the client through all devices and to the server. A common, and critical, troubleshooting task that normally requires 6 to 10 minutes is displayed instantly upon clicking a client or application. Troubleshoots issues along the network path.
● Run a path trace from source to destination to quickly get key performance statistics for each device along the network path.
● Identify ACLs that may be blocking or affecting the traffic flow.
|
| True Trace |
Captures live traffic on devices for path analysis. Catalyst Center’s True Trace extends the current path trace capability and provides KPIs for each hop, granular reasons for path degradation, and downloadable packet capture files. These deep insights enable faster troubleshooting in enterprise deployments and lead to operational savings.
|
| Application QoS (Quality of Service) support for industrial switches |
Authors and pushes QoS policies to Cisco Catalyst IE3300 and IE3400 Rugged Series Switches from Catalyst Center’s Application QoS. Applies default QoS trust settings as well as queuing settings based on Cisco Validated Designs, or writes a custom QoS policy for these devices. This removes the complexity of pushing a QoS policy and helps organizations ensure a good experience for end users in industrial environments.
|
| Wi-Fi 6 and 6e Readiness dashboard |
Prepares your network for the new Wi-Fi standard, verifying your hardware and configuration compatibility and checking your capacity readiness. This visibility will speed your upgrade and help ensure that you are upgrading the neediest locations first. After upgrading, advanced wireless analytics will indicate performance and capacity gains as a result of the Wi-Fi 6 deployment.
It categorizes wireless clients by Wi-Fi version (protocol) and indicates areas where upgrade is most urgent. Shows wireless system performance following upgrade.
The Wi-Fi 6 Readiness dashboard allows customers to visualize two main aspects. First, it shows the readiness of their network with respect to Wi-Fi 6 across several different sites and locations. Key aspects of the readiness assessment include how many Wi Fi 6-capable clients are seen in the network, whether the user has the right AP model to support Wi-Fi 6, whether the APs and Wireless LAN controllers (WLCs) are running the right OS version, whether the Wi-Fi 6 configuration is enabled, etc. Second, the dashboard allows the user to visualize the benefits of the Wi-Fi 6 network in terms of higher capacity, superior connectivity, and lower latencies on Catalyst Center Analytics and Assurance. After upgrading, advanced wireless analytics indicate performance and capacity gains as a result of the Wi-Fi 6 deployment.
For more information, see
https://blogs.cisco.com/networking/cisco-dna-your-fastest-route-to-wi-fi-6. |
| Device 360 and Client 360 |
Provide assurance and overall health of devices, including parameters such as memory or CPU utilization, uplink availability, and other KPIs to help operators be more proactive and enable them to predict future issues. Device 360 and Client 360 help you understand what problems have happened, when and why they happened, and how much of an impact they have. They also provide suggested remediation, resolved issue lists, and historical data to help troubleshoot issues.
|
| Application Experience |
Tracks performance of predefined “critical business applications.” Shows user experience and performance metrics. Provides specialized rapid troubleshooting per application and per client. Enables unparalleled visibility and performance control over the applications that are critical to your core business, on a per-user basis. Multimedia monitoring uses Performance processing for Real-Time Protocol (RTP) streams, allowing teams to verify the quality of critical real-time applications such as multimedia. URL monitoring provides visibility into cloud-based (URL-based) applications so that their performance is optimized. Application Experience provides users the performance they need on the applications that are key to their company role.
|
| Reporting |
Derive insights into your network and its operations by creating reports. Catalyst Center offers a set of pre-canned reports that can be generated in several formats and have flexible scheduling and configuration options to customize for your operational needs. Supported use cases include:
● Capacity planning: Understand how devices in your network are being utilized.
● Change of pattern: Track how usage pattern trends change on the network. Usage pattern trends may include clients, devices, bands, or applications.
● Operational reporting: Review reports about network operations, such as upgrade completions or provisioning failures.
|
| Wireless Sensor dashboard |
Shows overall tests, connectivity statistics, and top wireless issues discovered by Cisco Aironet Active Sensors. Includes test results for DHCP, DNS, host reachability, RADIUS, email, Microsoft Exchange Server, web, FTP, and a complete IP SLA for data throughput speed, latency, jitter, and packet loss. Provides guided remediation for any test failures.
|
| Streaming telemetry |
Enables network devices to send near-real-time telemetry information to Catalyst Center. The data can be used to optimize networks, locate where problems occur, and investigate issues in a collaborative manner. Telemetry data (events, KPIs) can be exported and surfaced through event-driven notifications.
|
| Traffic Telemetry Appliance |
This hardware solution collects networking data, processes it, and provides streaming telemetry to Catalyst Center. This can be useful in areas of your network where you do not have devices that support the types of telemetry that you need to collect from the local network, including NetFlow, Application Visibility and Control (AVC), Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR), NBAR2, etc. This appliance can also perform Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) on network traffic in order to support Cisco AI Endpoint Analytics. This is a strong solution for areas with only Layer-2 network devices or for branch offices with third-party switches that do not support transmission of real-time telemetry.
For more information, see the data sheet:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/cloud-systems-management/dna-traffic-telemetry-appliances/datasheet-c78-744352.html. |
| Network time travel |
Allows the operator to see device or client performance in a timeline view to understand the network state when an issue occurred. Allows an operator to go back in time up to 14 days and see the cause of a network issue, instead of trying to re-create the issue in a lab.
● Rewind time to when the issue occurred
● See a history of critical events
● View all the information on the user or network device changes to the selected time
|
| On-device analytics |
Assurance and analytics are performed on the Cisco switch, router, or wireless controller where the anomaly was discovered. Critical metrics can be identified and immediately acted on before an incident occurs. KPIs that are core to business operations can be maintained in real time, and close to the users that rely on them.
|
| Connectivity analytics for Apple iOS, Samsung and Intel devices |
Detailed analytics and insights from the device’s point of view, without the need for installing an agent on the device.
|
| Intelligent Capture |
Provides support for a direct communication link between Catalyst Center and APs, so that each of the APs can communicate with Catalyst Center directly. Using this channel, Catalyst Center can receive packet capture data, AP and client statistics, and spectrum data. With the direct communication link between Catalyst Center and APs, Cisco Intelligent Capture allows you access to data from APs that is not available from the wireless controllers.
|
| AI-Enhanced Radio Resource Management (RRM) |
Uses AI to boost wireless network performance and user experience by proactively learning the network's trends and patterns to enhance how wireless endpoints operate over time.
|
| AP Power Save |
Improves sustainability by enabling the wireless network to use 20 percent less power during off-peak times by shutting off radios, lowering spatial streams, lowering port speeds, and disabling USB ports when there are no users.
|
| Multivendor device visibility |
Provides visibility into third-party devices, including reachability and topology.
|
Table 3. SD-Access features and benefits
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Enhanced visibility into endpoints and traffic patterns |
The Endpoint Analytics application in Catalyst Center identifies and classifies endpoint devices on a campus network with the use of AI/ML. Through the use of various profiling methods, including Deep Packet Inspection (DPI), it establishes visibility into what is on the network so that new endpoints can be authenticated and assigned an appropriate policy for network usage, security, and segmentation.
Group-based policy analytics simplify the delivery of segmentation policies. It uses analytical models to visualize the activity between endpoint profiles, scalable groups, and host groups in order to verify that the network policies are optimizing performance and security. The feature provides a way for users and endpoints to be identified and categorized, and for granular access privileges to be provided to the resources that each endpoint requires, while segmenting them from everything else.
|
| Granular multilevel segmentation |
SD-Access, through Catalyst Center, creates virtual overlays over the underlying physical infrastructure and segments the network without regard to its topology. SD-Access also segments at a micro level by enforcing group-based policies through the network infrastructure. The resulting granular segmentation controls traffic flows without using complex firewalls and Access Control Lists (ACLs), which can be difficult and costly to maintain.
Benefits of fabric infrastructure optimizations:
● Automates VRF configurations (lines of business, departments, etc.) and create overlay virtual networks
● Onboards users with 802.1X, MAB, Active Directory, and static authentication. With an option to move users in a critical VLAN during the unavailability of ISE.
● Includes a resilient control-plane architecture using LISP pub/sub that allows for dynamic path optimization toward available internet services. It simplifies fabric site design, routing convergence, and troubleshooting tasks.
● Simplifies network operations with a standard, error-free underlay network using LAN automation
● Uses Encrypted Traffic Analytics (ETA) to further enhance analysis of traffic through AVC and NetFlow
Ease of migration to SD-Access fabric:
● Layer-2 handoff at border is a key capability, allowing hosts in an SD-Access fabric to communicate with the traditional network at Layer 2.
● Fabric provides support for end hosts that require Layer-2 flooding; for example, building management systems, audio-visual equipment, etc.
● SD-Access introduces the support of existing access VLANs, allowing users to retain their existing access VLAN IDs when creating macro segments in the fabric. Customers can retain existing access VLAN IDs when connecting directly to the SD-Access fabric edge to simplify and speed up their SD-Access segmentation journey.
● Macrosegmentation without ISE capability is suited for deployments that have fabric at the distribution layer connecting downstream to an external Layer-2 switching domain. Customers can deploy an automated network fabric and use macrosegmentation with virtual networks without ISE.
Deployment flexibility with SD-Access fabric:
● SD-Access offers a distributed campus design with automated intersite connectivity with end-to-end policy and segmentation.
● Fabric in a Box allows the border node, control plane node, and edge node to run on the same fabric node, simplifying fabric deployment for a small site or a branch.
● SD-Access extended nodes extend the enterprise network by providing connectivity to non-carpeted spaces of an enterprise. This allows network connectivity and management of IoT devices and the deployment of traditional enterprise end devices in outdoor and non-carpeted environments, such as distribution centers, warehouses, or campus parking lots.
● SD-Access fabric offers two options for integrating wireless access:
● SD-Access Wireless using a VXLAN distributed data plane and a centralized control plane provides a consistent fabric experience and policy simplification for wired and wireless access.
● Over the top involves running a traditional Cisco Unified Wireless Network architecture with Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAPs) on top of a fabric wired network. This is a possible migration step to full SD-Access wireless implementation.
● Multisite remote border feature allows users to segregate untrusted traffic from various fabric sites to a firewall at the DMZ.
● Fabric zone features allow administrators to control the provisioning of IP subnets on select fabric edge nodes for better site scalability and security.
● SD-Access supports IPv4 as well as IPv6 endpoints.
● Cisco SD-Access offers support for the Cisco Wide Area Bonjour application, allowing users to discover and use shared services with minimal intervention and configuration.
● Secure network device onboarding of Catalyst 9000 extended nodes using 802.1X-based authentication and authorization.
Simplified fabric operations:
SD-Access Assurance allows users to detect, diagnose, and troubleshoot fabric issues in real time with minimized downtime and a better experience. The newly introduced SD-Access Assurance landing page contains overall fabric health for each fabric site deployed. KPIs configured on the fabric nodes provide insights for faster issue identification and suggested actions to remediate issues. KPIs are organized into categories to quickly triage control plane, infrastructure, and connectivity issues.
● Fabric control plane provides reachability checks between the fabric edge/border and the fabric control plane node.
● Fabric infrastructure validates the AAA server status from the fabric edge and policy extended nodes to the Identity Services Engine (ISE).
● Fabric connectivity provides reachability checks from the edge to the fabric border, and control-plane and port- channel connectivity checks between the fabric edge and the extended nodes.
● Support for ThousandEyes Agent on Catalyst 9000 switches operating in an SD-Access Fabric role. This provides the ability to run tests that provide performance metrics and end-to-end visibility.
Fabric UX2.0 provides administrators with an enhanced experience in the user interface that integrates simplicity, flexibility, and a rich, intuitive context.
|
| Continuous verification of trust |
Trust Analytics is an aggregation of various inputs and sources into a single, comprehensive, flexible trust score. Trust Analytics detects traffic from endpoints that are exhibiting unusual behavior. When anomalies in the network are detected, Trust Analytics lowers the trust score for the endpoint to limit or completely deny access to the network through integration with ISE. The feature expedites the detection and containment of untrustworthy endpoints that could lead to a security breach.
|
Table 4. SD-Access features and benefits
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) |
Allows users to be mapped to one of the four predefined roles. The role determines what types of operations a user can perform within the system.
|
| Backup and restore |
Supports complete backup and restore of the entire database for added protection.
|
| ISE integration |
Integrates with ISE through pxGrid or API for fabric overlay support.
|
| Workflows |
Catalyst Center workflows are step-by-step guides through particular tasks; for example, “Create a role,” “Refresh AP,” etc. Workflows can be paused and revisited through the “in-progress” library on the workflow homepage. The workflow homepage can be found by clicking the menu icon on the GUI and clicking on “Workflows.” The home page will have a library of workflows along with in-progress workflows.
|
| Activity center |
The activity center is a centralized space to find audit logs and scheduled tasks. Audit logs record system events that occurred, when and where they occurred, and which users initiated them. With audit logging, configuration changes to the system are logged in separate log files for auditing. The Scheduled Tasks tab allows you to view upcoming, in-progress, completed, and failed administrative tasks, such as OS updates or device replacements.
|
| FIPS 140-2 support |
Catalyst Center includes support for FIPS-140-2-compliant cryptography modules, ensuring that only strong NIST-approved ciphers are used, and enabling deployment in security-conscious verticals such as public sector, finance, and healthcare. During installation, the administrator can choose to enable FIPS, which will ensure only NIST-approved ciphers are used for data encryption.
|
Table 5. Catalyst Center platform capabilities
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Northbound REST APIs |
The Catalyst Center platform supports Representational State Transfer (REST) APIs at the northbound layer for programmability. The Catalyst Center API provides support for the following features:
● Discovery, device inventory, and network topology
● SWIM, Plug and Play (PnP), wireless, SD-Access, and application policy
● Template programmer and command runner
● Assurance: site, device, and client health-monitoring and path tracing
● NFV provisioning
● Configuring event management notifications through APIs
|
| IT Service Management (ITSM) integration |
Minimizes the need for handoffs, deduplicates issues, and optimizes processes for proactive insights and faster remediation. Out-of-the-box integration exists with ServiceNow. The generic APIs exposed by the Catalyst Center platform enable partners and developers to integrate with any ITSM system.
|
| IP Address Management (IPAM) integration |
Allows for a seamless import of IP pools for Catalyst Center workflows from external IPAM systems and the synchronization of IP pool and subpool usage information between the two systems. Out-of-the-box integration exists with Infoblox and
BlueCat. The Catalyst Center platform provides generic APIs to integrate with any IPAM system.
|
| Events and notifications |
The Catalyst Center platform webhooks allow third-party applications to receive notifications and listen to any events detected by Catalyst Center Assurance, automation, and other task-based operational workflows.
|
Table 6. Correlated insights
| Feature |
Description and benefits |
| Wireless insights |
Client onboarding
● Association failures
● Authentication failures
● IP address failures
● Client exclusion
● Excessive onboarding time
● Excessive authentication time
● Excessive IP addressing time
● AAA, DHCP reachability
Client experience
● Throughput analysis
● Roaming pattern analysis
● Sticky client
● Slow roaming
● Excessive roaming
● RF, roaming pattern
● Dual-band clients prefer 2.4 GHz
● Excessive interference
● Apple iOS client disconnect
Network coverage and capacity
● Coverage hole
● AP license utilization
● Client capacity
● Radio utilization
Network device monitoring
● Availability
● Crash, AP join failure
● High availability
● CPU, memory
● Flapping AP, hung radio
● Power supply failures
|
| Sensor issues |
Sensor onboarding
● Association failures
● Authentication failures
● IP address failures
● Sensor exclusion
● Excessive onboarding time
● Excessive authentication time
● Excessive IP addressing time
● AAA, DHCP reachability
Sensor experience
● Throughput analysis
● Outlook web response time
● Web server response time
● SSH server response time
● Mail server response time
● FTP server response time
● Excessive radio interference
|
| Routing issues |
Router health
● High CPU
● High memory
Routing technologies
● BGP AS mismatch, flap
● OSPF adjacency failure
● Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) adjacency failure
Connectivity
● Interface high utilization
● LAN connectivity down/flap
● IP SLA to SP gateway connectivity
|
| Switching issues (nonfabric) |
Client onboarding
● Client or device DHCP
● Client or device DNS
● Client authentication or authorization
Switch
● CPU, memory, temperature
● Modules
● Power over Ethernet (PoE) power
● Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) table
|
| SD-Access issues |
Border and edge reachability
● Control plane reachability
● Edge reachability
● Border reachability
● Routing protocol
● MAP server
Data plane
● Border and edge connectivity
● Border node health
● Access node health
● Network services DHCP, DNS, AAA
Policy plane
● ISE or pxGrid connectivity
● Border node policy
● Edge node policy
Client onboarding
● Client or device DHCP
● Client or device DNS
● Client authentication or authorization
Switch
● CPU, memory, temperature
● Modules
● PoE power
● TCAM table
|
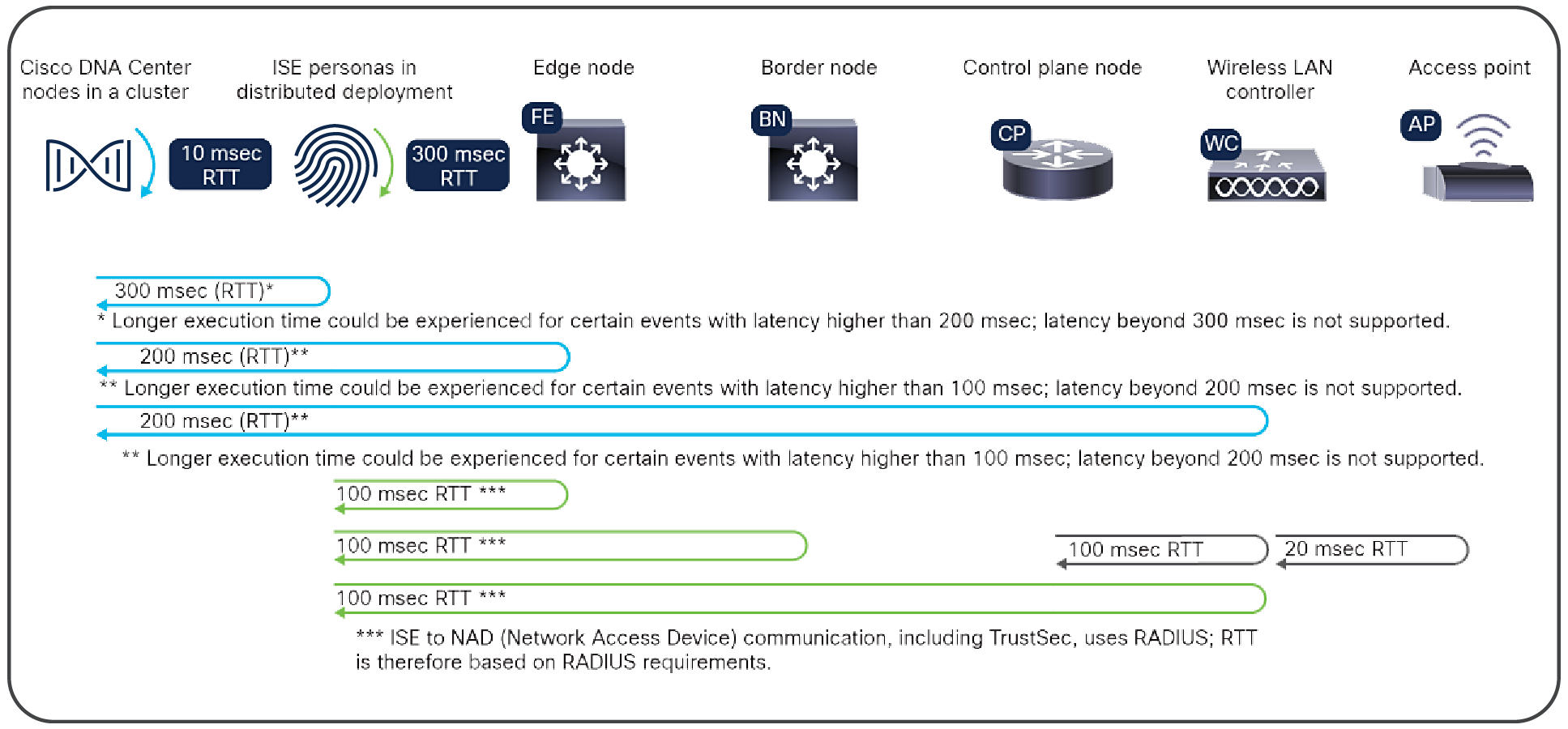
Maximum latency supported, roundtrip time
The following tables outline the Cisco SD-Access platform scale. The limits in this section are not necessarily dependent on Catalyst Center, but rather depend on the model of device and its capacity design.
Table 7. Cisco SD-Access control plane node scale
| Cisco SD-Access control plane node scale |
|
||||||||||||
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
ASR 1000, 4000 Series ISR |
ASR 1000 4000 Series ISR |
CSR |
|
||||||||
| Device |
9300/L |
9300X |
9400 |
9400X |
9500 |
9500X |
9500H |
9600 |
9600X |
8 GB RAM |
16 GB RAM |
1000v |
|
| End-points |
16,000 |
32,000 |
80,000 |
112,000 |
80,000 |
1,000,000 |
150,000 |
150,000 |
1,000,000 |
100,000 |
200,000 |
200,000 |
|
Table 8. Cisco SD-Access border node scale
| Cisco SD-Access border node scale |
|||||||||||
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
ASR 1000, 4000 Series ISR |
ASR 1000, 4000 Series ISR |
||||||||
| Device |
9300/L |
9300X |
9400 Sup-XL/Y SD-Access sdm template |
9400X |
9500 |
9500H |
9500X |
9600 |
9600X |
8 GB RAM |
16 GB RAM |
| Virtual networks1 |
256 |
256 |
256 |
1000 |
256 |
256 |
1000 |
256 |
1000 |
128 |
128 |
| IPv4 routes |
8000 |
32,000 |
64,000 |
96,000 |
64,000 |
48,000 |
512,000 |
48,000 |
512,000 |
1,000,000 |
4,000,000 |
| Fabric host entries2 (host /32 or /128) |
16,000 |
32,000 |
70,000 |
96,000 |
70,000 |
150,000 |
512,000 |
150,000 |
512,000 |
1,000,000 |
4,000,000 |
| IPv4: SGT bindings |
10,000 |
32,000 |
40,000 |
109,000 |
40,000 |
200,000 |
200,000 |
200,000 |
200,000 |
750,000 |
750,000 |
| SGT/DGT policies |
8000 |
7400 |
8000 |
32,000 |
8000 |
16,000 |
32,000 |
32,000 |
32,000 |
64,000 |
64,000 |
| SG-ACEs (contract actions) |
5000 |
4800 |
18,000 |
16,000 |
18,000 |
13,000 |
4000 |
27,000 |
4000 |
64,000 |
64,000 |
Fabric host entries include access points and classic and policy-extended nodes.
Additional border node scale considerations:
/32 (IPv4) or /128 (IPv6) entries are used when the border node forwards traffic from outside the fabric to a host in the fabric.
For all switches except Cisco Catalyst 9500 Series High Performance Switches and Cisco Catalyst 9600 Series Switches:
● IPv4 uses one TCAM entry (fabric host entries) for every IPv4 IP address.
● IPv6 uses two TCAM entry (fabric host entries) for every IPv6 IP address.
For the Cisco Catalyst 9500 Series High Performance Switches and Cisco Catalyst 9600 Series Switches:
● IPv4 uses one TCAM entry (fabric host entries) for every IPv4 IP address.
● IPv6 uses one TCAM entry (fabric host entries) for every IPv6 IP address.
● Cisco SD-Access Layer-2 handoff border node scale considerations
Table 9. Cisco SD-Access Layer-2 handoff border node scale considerations
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
ASR 1000, 4000 Series ISR |
ASR 1000, 4000 Series ISR |
||||||
| Device |
9300/L |
9300X |
9400 |
9400X |
9500 |
9500H |
9600 |
8 GB RAM |
16 GB RAM |
| Endpoints |
8,000 |
32,000 |
16,000 |
100,000 |
16,000 |
32,000 |
32,000 |
NOT supported |
NOT supported |
These numbers are the sum of the total numbers of endpoints both inside and outside the fabric site when the site has a border node with a Layer-2 handoff.
A maximum of 6000 hosts can be connected outside the fabric for all platforms that support Layer-2 border handoff.
The border node with a Layer-2 handoff contains a combination of local and remote LISP entries.
Local entries = LISP database
Remote entries = LISP map-cache
Example:
The Cisco Catalyst 9300 Series Switches support 8000 total entries.
If the fabric site has 6000 endpoints (map-cache), then only 2000 endpoints (database) can be in the traditional network beyond the Layer-2 handoff.
Table 10. Cisco-SD Access edge node scale
| Cisco SD-Access edge node scale |
|||||||||
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
Cisco Catalyst |
|||||||
| Device |
9200CX |
9200-L |
9200 |
9200 Enhanced VNs |
9300/L |
9300X |
9400 |
9400X |
9500/H |
| Virtual networks |
16 |
11 |
42 |
323 |
256 |
256 |
256 |
1000 |
256 |
| Endpoints |
4000 |
2000 |
4000 |
4000 |
6000 |
18,000 |
6000 |
70,000 |
6000 |
| IPv4: SGT bindings |
10,000 |
8000 |
10,000 |
10,000 |
10,000 |
32,000 |
40,000 |
109,000 |
40,000 |
| SGT/DGT policies |
2000 |
2000 |
2000 |
2000 |
8000 |
7400 |
8000 |
32,000 |
8000 |
| SG-ACEs |
1200 |
1,000 |
1000 |
1000 |
5000 |
4800 |
18,000 |
16,000 |
18,000 |
INFRA_VN is not a VRF definition. It is associated with the global routing table.
DEFAULT_VN is not user-defined; it is automatically created in Catalyst Center. It is present for historical (backward-compatibility) reasons; its use is neither necessary nor recommended.2
DEFAULT_VN, if used in host onboarding, is provisioned as a VRF definition and counts as a “user-defined VN.”
Table 11. Cisco-SD Access WLC scale
| Cisco SD-Access WLC scale |
||
| Device |
Number of access points |
Number of clients |
| Catalyst 9800-L |
250/500 (Perf. License) |
5000/10000 (Perf. License) |
| Catalyst 9800-40 |
2000 |
32,000 |
| Catalyst 9800-80 |
6000 |
64,000 |
| Catalyst CW9800H1 |
6000 |
64,000 |
| Catalyst CW9800H2 |
6000 |
64,000 |
| Catalyst CW9800M |
3000 |
32,000 |
| Catalyst 9800-CL (4 CPU/8 GB RAM) |
1000 |
10,000 |
| Catalyst 9800-CL (6 CPU/16 GB RAM) |
3000 |
32,000 |
| Catalyst 9800-CL (10 CPU/32 GB RAM) |
6000 |
64,000 |
Table 12. Cisco-SD Access WLC scale
| Cisco SD-Access edge node scale for access points and wireless endpoints |
||||||
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
|||||
| Device |
9200-L |
92001 |
9300-L1 |
9300/X |
9400/X |
9500/H |
| Access points |
Not supported |
25 |
50 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| Wireless endpoints |
Not supported |
500 |
1000 |
4000 |
4000 |
4000 |
The switches above have limits on access tunnels. An access tunnel is created between the fabric edge node and a fabric-mode AP that is either directly attached or attached through a directly-connect extended node.
Table 13. Cisco-SD Access embedded wireless controller scale
| Cisco SD-Access embedded wireless controller scale |
|||||
| Family |
Cisco Catalyst |
||||
| Device |
9200/L |
9300-L |
9300 |
9400 |
9500/H |
| Access points |
Not supported |
50 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| Wireless endpoints |
Not supported |
1000 |
4000 |
4000 |
4000 |
The embedded wireless scale is the same irrespective of the role of the device (edge, Fabric in a Box, border, or control plane).
For existing Meraki branch customers who want to explore using Catalyst Center and Cisco Catalyst 9000 switches, or for customers with mixed environments, Catalyst Center now offers a single management pane of glass. This is an API-driven dashboard integration that supports all existing Meraki hardware and software at no additional license cost.
Meraki integration provides:
● Single dashboard inventory across all platforms (Meraki, Cisco Catalyst, Cisco Integrated Services Routers [ISRs], and Aironet)
● Up-or-down status of all devices in a single platform
● Use existing Meraki API keys; no additional license required
● Ability to assign SSIDs to Meraki access points from within Catalyst Center
Catalyst Center offers flexible deployment options. It can be deployed on a hardware appliance or as a virtual appliance, on either VMware ESXi or AWS.
The third generation of the Catalyst Center appliance is available in three form factors and comes with the Catalyst Center image preloaded on it and ready for installation.
Tables 14 and 15 capture the scale information for Catalyst Center when deployed on physical appliances.
Table 14. Scale and hardware specifications
| SKU |
DN-SW-APL |
DN3-HW-APL |
DN3-HW-APL-L |
DN3-HW-APL-XL |
| Description |
Catalyst Center Virtual Appliance |
Cisco UCS® C220 M6 |
Cisco UCS C220 M6 |
Cisco UCS C240 M6 Rack Server 80 cores |
| Catalyst Center system scale |
||||
| Total Network Devices |
5000 |
5000 |
8,000 |
18,000 |
| M Scale Profile 1 |
1000 (Switch, Router, WLC) + 4000 APs |
Intentionally Left Blank |
Intentionally Left Blank |
|
| M Scale Profile 2 |
2000 (Switch, Router, WLC) + 3000 APs |
Intentionally Left Blank |
Intentionally Left Blank |
|
| L and XL Scale Non-fabric |
Intentionally Left Blank |
Intentionally Left Blank |
2000 (Switch, Router, WLC) + 6000 APs |
5000 (Switch, Router, WLC) + 13000 APs |
| L and XL Scale Fabric |
Intentionally Left Blank |
Intentionally Left Blank |
4000 (SW, Router, WLC) + 4000 APs |
8000 (SW, Router, WLC) + 10000 APs |
| Wireless sensors |
600 |
600 |
800 |
1600 |
| Concurrent endpoints |
25,000 |
25,000 |
40,000 |
100,000 |
| Transient endpoints |
75,000 |
75,000 |
120,000 |
750,000 |
| Ratio of endpoints to wired wireless |
Any Any |
Any Any |
Any Any |
Any Any |
| Site elements |
2500 |
2500 |
5000 |
10,000 |
| Wireless controllers |
500 |
500 |
1000 |
2000 |
| Physical ports2 |
48,000 |
48,000 |
192,000 |
480,000 |
| Combined physical2 and logical ports |
120,000 |
120,000 |
480,000 |
1,500,000 |
| API rate limit |
Rate Limit is managed at a specific API level |
Rate Limit is managed at a specific API level |
Rate Limit is managed at a specific API level |
|
| NetFlow flows/sec |
30,000 |
30,000 |
48,000 |
120,000 |
| Concurrent software image updates |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| Catalyst Center SD-Access scale |
||||
| Fabric sites3 |
500 |
500 |
1000 |
2000 |
| Catalyst Center scale per fabric site |
||||
| Layer 3 Virtual Networks |
64/site |
64/site |
128/site |
256/site |
| Fabric devices |
500/site |
500/site |
600/site |
1200/site |
| Scalable groups |
4000 |
4000 |
4000 |
4000 |
| Access contracts |
500 |
500 |
500 |
500 |
| Group-based policies |
25,000 |
25,000 |
25,000 |
25,000 |
| IP pools4 |
1005 |
1005 |
3006 |
10007 |
| Layer 2 Virtual Networks4 |
2005 |
2005 |
6006 |
10007 |
Table 15. Scale for 3 node DN3-HW-APL-XL cluster
| Description |
Supported scale |
| Devices1 |
10,000 |
| Wireless access points |
25,000 |
| Concurrent endpoints |
300,000 |
| Transient endpoints |
750,000 |
| Physical ports2 |
768,000 |
| Combined physical2 and logical ports |
2,000,000 |
| NetFlow |
250,000 flows/sec |
Note
Hardware appliance specifications
The Catalyst Center appliance is available in three form factors and comes with the Catalyst Center image preloaded on it and ready for installation. For more detailed information on these Cisco UCS appliances, click on the data sheet link beside each hardware series in Table 16.
Table 16. Physical specification
| Physical specifications |
DN3-HW-APL and DN3-HW-APL-L |
DN3-HW-APL-XL |
| Part number for ordering |
DN3-HW-APL and DN3-HW-APL-L |
DN3-HW-APL-XL |
| Hardware series |
UCS C220 M6 (data sheet) |
UCS C240 M6 (data sheet) |
| 2 hot-pluggable, redundant 2300W Titanium certified AC |
2 hot-pluggable, redundant 2300W Titanium certified AC |
|
| Physical dimensions |
Height: 1.70 in. (4.3 cm) Width: 16.9 in. (42.9 cm) Depth: 18.9 in. (48.0 cm) |
Height: 3.42 in. (8.7 cm) Width: 16.9 in. (42.9 cm) Depth: 18.9 in. (48.0 cm) |
| Temperature: operating |
Dry bulb temperature of 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F) |
Dry bulb temperature of 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F) |
| Temperature: nonoperating |
Dry bulb temperature of -40°C to 65°C (- 40°F to 149°F) |
Dry bulb temperature of -40°C to 65°C (- 40°F to 149°F) |
| Humidity: operating |
10% to 90% and 28°C (82.4°F) maximum dew-point temperature, non-condensing environment |
10% to 90% and 28°C (82.4°F) maximum dew-point temperature, non-condensing environment |
| Humidity: nonoperating |
5% to 93% relative humidity, noncondensing, with a maximum wet bulb temperature of 28°C across the 20°C to 40°C dry bulb range. |
5% to 93% relative humidity, noncondensing, with a maximum wet bulb temperature of 28°C across the 20°C to 40°C dry bulb range. |
| Altitude: operating |
A maximum elevation of 3050 meters |
A maximum elevation of 3050 meters |
| Altitude: nonoperating |
An elevation of 0 to 12,000 meters (39,370 ft) |
An elevation of 0 to 12,000 meters (39,370 ft) |
| Network and management I/O |
Supported connectors: One 1 Gigabit Ethernet dedicated management port Two 1/10 Gigabit BASE-T Ethernet LAN ports One RS-232 serial port (RJ-45 connector) One 15-pin VGA2 connector Two USB 3.0 connectors One front-panel KVM connector that is used with a KVM cable, which provides two USB 2.0s, one VGA, and one serial (DB-9) connector |
Supported connectors: One 1 Gigabit Ethernet dedicated management port Two 1/10 Gigabit BASE-T Ethernet LAN ports One RS-232 serial port (RJ-45 connector) One 15-pin VGA2 connector Two USB 3.0 connectors One front-panel KVM connector that is used with a KVM cable, which provides two USB 2.0s, one VGA, and one serial (DB-9) connector |
| Regulatory standards compliance: Safety and EMC |
||
| Regulatory compliance |
Products should comply with CE Markings per directives 2014/30/EU and 2014/35/EU |
|
| Safety |
UL 60950-1 Second Edition CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1 Second Edition EN 60950-1 Second Edition IEC 60950-1 Second Edition AS/NZS 60950-1 GB4943 2001 |
|
| EMC: Emissions |
47CFR Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A AS/NZS CISPR32 Class A CISPR32 Class A EN55032 Class A ICES003 Class A VCCI Class A EN61000-3-2 EN61000-3-3 KN32 Class A CNS13438 Class A |
|
| EMC: Immunity |
EN55024 CISPR24 EN300386 KN35 |
|
Virtual appliance requirements
Catalyst Center can be deployed as a virtual appliance on AWS or VMware ESXi. For the system requirements, see Tables 17 and 18.
Table 17. Virtual appliance requirements for VMware ESXi
| Specification |
Requirement |
| Processors |
32 vCPUs with 64 GHz dedicated to the VM |
| Memory |
256-GB Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) dedicated to the VM |
| Storage |
3 TB |
| ESXi |
VMware vSphere (which includes ESXi and vCenter Server) 7.0.x or later, including all patches |
| I/O bandwidth |
180 MB/sec |
| Input/output operations per second (IOPS) |
2000 to 2500 |
| Network interface card (NIC) |
1 Gbps network per network port |
Table 18. Virtual appliance requirements for AWS
| Specification |
Requirement |
| Instance type |
r5a.8xlarge |
| Cores |
32 vCPU, either Intel® or AMD-based host |
| RAM |
256 GB |
| Storage |
4 TB |
| Storage type |
GP3 EBS |
Table 19 captures the fabric VN limits for devices in the fabric when deploying Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.
Table 19. Fabric VN limits (The current maximum VRF validation is based on lower limit of 1 and upper limit of 128, even if the device can support more than 128).
| Device series |
Max VRFs |
| Cisco Catalyst 6800 Series Switches |
1000 (128) |
| Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches |
1000 (128) |
| Data center switches (Cisco Nexus 7000 Series Switches) |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco Cloud Services Router 1000V Series |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco 4000 Series Integrated Services Routers |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco 4400 Series Integrated Services Routers |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco 4200 Series Integrated Services Routers |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco 4300 Series Integrated Services Routers |
4000 (128) |
| Cisco Catalyst 9300/9300X Series Switches |
256 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9300 L Series Switches |
256 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9500 Series Switches |
256 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9500H Series Switches |
256 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9400 Series Switches |
256 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9200-L Switch Stack |
1 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9200 Switch Stack |
4 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9200-24PB Switch |
32 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9200-48PB Switch |
32 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9200CX Switch |
16 |
| Cisco Catalyst 9600 Series Switches |
256 |
Table 20. Role-based access control
| Role |
Privilege |
| Network-Admin-Role |
Users with this role have full access to all of the network-related Catalyst Center functions. They do not have access to system-related functions, such as application management, users (except for changing their own passwords), and backup and restore. |
| Observer-Role |
Users with this role have view-only access to all Catalyst Center functions. |
| Telemetry-Admin-Role |
Users with this role have the ability to perform system-level functions within Catalyst Center. |
| Super-Admin-Role |
Users with this role have full access to all of the Catalyst Center functions. They can create other user profiles with various roles, including those with the Super-Admin-Role. |
Catalyst Center provides coverage for Cisco enterprise switching, routing, and mobility products. For a complete list of Cisco products supported, please see our compatibility matrix, which is updated regularly.
Catalyst Center compatibility matrix:
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/Website/enterprise/catalyst_center_compatibility_matrix/index.html.
Cisco SD-Access compatibility matrix:
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/Website/enterprise/sda_compatibility_matrix/index.html.
Cisco environmental sustainability
Information about Cisco’s environmental sustainability policies and initiatives for our products, solutions, operations, and extended operations or supply chain is provided in the “Environment Sustainability” section of Cisco’s Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Report.
Reference links to information about key environmental sustainability topics (mentioned in the “Environment Sustainability” section of the CSR Report) are provided in the following table.
Table 21. Link to information about key environment sustainability topics
| Sustainability topic |
Reference |
| Information on product material content laws and regulations |
|
| Information on electronic waste laws and regulations, including products, batteries, and packaging |
Reference links to product-specific environmental sustainability information that is mentioned in relevant sections of this data sheet are provided in Table 22.
Table 22. Link to product-specific environmental sustainability information
| Sustainability topic |
Reference |
| General |
|
| Product compliance |
|
| Power |
|
| Power supply |
|
| Material |
|
| Dimensions |
|
Cisco makes the packaging data available for informational purposes only. It may not reflect the most current legal developments, and Cisco does not represent, warrant, or guarantee that it is complete, accurate, or up to date. This information is subject to change without notice.
Product usage telemetry provides valuable information about the status and capabilities of the Catalyst Center appliance. Catalyst Center is configured to automatically connect and transmit product usage data to Cisco. Product usage telemetry is used by Cisco to improve appliance lifecycle management for IT teams who have deployed Catalyst Center. Collecting this data helps the product teams serve customers better. This data and related insights enable Cisco to proactively identify potential issues, improve services and support, facilitate discussions to gather additional value from new and existing features, and assist IT teams with inventory report of license entitlement and upcoming renewals.
All product usage telemetry data is transmitted to Cisco through an encrypted channel. The categories of data collected in the product usage telemetry are the Cisco.com ID, system telemetry, feature usage telemetry and network device (for example, switch or router) inventory, and license entitlement. The collection of product usage telemetry will be enabled by default and cannot be disabled from the product. Customers may contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for changes in collection settings.
For detailed product usage telemetry information collected, please see Table 23.
Table 23. Catalyst Center product usage telemetry usage and benefits
| Category |
Data elements |
Purpose of collection |
| Cisco.com |
Cisco.com user ID |
Identify customer account |
| System |
Deployment information (Catalyst Center appliance serial number, Catalyst Center appliance platform, Catalyst Center appliance machine ID) Connectivity with Catalyst Center Operational metrics (CPU, memory, file system, uptime) for pods Signed End-User License Agreement (EULA) flag Application stack and packages deployed |
Identify potential issues in customers’ environments to prevent problems and improve the product |
| Feature usage |
Customer dwell time in application UI pages Site_member_details: Name of site, instance UUID of device, support level of device, device family, and host name Assurance usage: number of sites, area, building, floor, wireless LAN controller (WLC), switch, Access Point (AP), number of clients (wired and wireless) and health score, sensor counts, sensor tests count, AI network analytics configuration flag, AP count with RF stats enabled, number of anomaly captures enabled, number of data packet captures enabled, and network telemetry max input rate (NetFlow, syslogs, traps) SD-Access usage: number of fabrics created, number of fabric domains per domain type, number of devices per fabric role by site, number of edge nodes and of border nodes and of control-plane nodes by device type, number of clients on fabric, number of access contracts, number of scalable group tags, number of virtual networks by site, number of IP pools, number of SSIDs, Cisco ISE version and status, number of group-based policies, number of access policy contracts, number of Cisco ACI scalable groups, number of APs and WLCs in fabric, number of each transit type, number of rogue AP/client messages, number of fabric sites by authentication mode, and number of ports by static port assignment Automation usage: number of devices provisioned using PnP, number of PnP devices by source, number of golden images and image repository details, number of successful/failed image activations and/or distributions, number of SMU images by type, number of application policies created and/or deployed, number of favorite applications, number of custom applications (sets), number of consumer applications, number of queueing profiles, number of excluded devices, number of devices in each policy, number of draft policies, number of policies using nondefault queueing profiles, device controllability check, site area/building/floor counts, number of SSA enablement/disablement tasks by status, number of SSA precheck failures by type and successes/failures per device family, Cisco Secure Network Analytics registration status, number of devices by SSA-enabled status, number of devices with security advisory match, number of security advisory scans, vManage integration status, MRE root cause analysis count and duration, number of MRE user feedbacks, number of devices with CVSS scores, number of devices by replacement status, WAB SDG node count, number of onboarding templates created and provisioned successfully on devices, number of devices with templates applied, and number of network profiles by site and namespace Catalyst Center as a Platform usage: number of event subscriptions by state, DaaS-runtime usage |
Facilitate customer adoption and customer value |
| Network device inventory and license entitlement |
Network device inventory (serial number, software version, platform ID, and reachability errors). Number of devices per device support level, number of devices per device role, number of port types per device type, IDP instances enabled, number of devices by Ethernet channel control method, number of devices by acltype associated site information, uptime in days by device type, host count by device type, and number of devices by configuration type License entitlement information (network device type, Cisco Smart Software Manager registration status, Catalyst Center subscription level, hardware support contract coverage, and number of days until license expires) |
Assist customers in tracking and maintaining license entitlement and renewals |
For information on Catalyst Center privacy, please refer to Cisco’s Personal Data Privacy.
Flexible payment solutions to help you achieve your objectives
Cisco Capital® makes it easier to get the right technology to achieve your objectives, enable business transformation, and help you stay competitive. We can help you reduce the total cost of ownership, conserve capital, and accelerate growth. In more than 100 countries, our flexible payment solutions can help you acquire hardware, software, services, and complementary third-party equipment in easy, predictable payments. Learn more.
See how Catalyst Center helps you move faster, lower costs, and reduce risk: https://cisco.com/go/catalystcenter.
| New or revised topic |
Described in |
Date |
| Updated for release 2.3.7 |
Entire document |
September 2024 |
| Updated product name |
Entire document |
September 2024 |
| Added DN3s |
September 2024 |
|
| Consolidated scale for fabric and non-fabric deployments |
September 2024 |
|
| Updated Appliance Scale for fabric and non-fabric deployments |
April 2025 |
|
| Modified the IPv4: SGT bindings of the 9500H |
Table 8 |
October 2025 |
| Modified the API Rate Limit |
October 2025 |
|
| Transient Endpoints |
October 2025 |
|
| Removed reference to non-supported software |
October 2025 |