Table Of Contents
Configuring the Existing and New Storage
Preparing for Data Migration
This chapter describes how to prepare for a data migration job. It includes the following sections:
•
Planning a Data Migration Job
Planning a Data Migration Job
Traditional data migration is a complex procedure, which requires coordination of activities that may be performed by vendor representatives and multiple IT groups. Activities may need to occur at specific times to minimize service disruption.
Cisco MDS DMM is designed to minimize the dependency on multiple organizations, and is designed to minimize service disruption. However, even with Cisco MDS DMM, data migration is a fairly complex activity. We recommend that you create a plan to ensure a smooth data migration.
To create your data migration plan, use the following steps:
1.
Document the SAN topology for the data migration. Identify and obtain any additional equipment and software licenses.
2.
Design the mapping of source LUNs to destination LUNs.
Identify the LUNs that need to be migrated and the impacted servers. The Server Lunmap Discovery (SLD) tool provides assistance in identifying this information. (See Checking Storage ASL Status for additional information about the SLD tool).
Calculate the storage requirements of the new LUNs. Identify the LUNs on the new storage subsystem. The new storage LUNs need to be the same size or larger than the matching existing storage LUN.
3.
Develop a schedule for the migration job.
Identify any required equipment and resources. Availability of external resources (such as a vendor service representative) may impact your schedule.
Identify periods of low user activity and I/O activity, to minimize disruption during the migration. Cisco MDS DMM provides features to minimize user impact. For example, you can schedule the migration to run during nonpeak hours or configure a slow migration rate.
Identify any required pre-migration configuration changes. (These changes are described in the following sections.)
Plan for one short window in which service is not be available during server reconfiguration. (This enables you to access the new storage after the data migration is completed).
4.
As a precaution, ensure that any critical data on the existing storage has a recent back up.
Pre-Migration Configuration
Prior to performing a data migration job, ensure that the existing storage, the new storage, and the fabric switches are configured as required. The following sections describe the tasks to be completed:
•
Configuring Switches and SSMs
•
Configuring the Existing and New Storage
Configuring Switches and SSMs
The Cisco MDS DMM feature executes on the SSM. The DMM feature supports data migration for storage LUNs exposed anywhere on the SAN fabric (that is, the storage port can be connected to the switch hosting the SSM or to another switch).
If necessary, provision an SSM on an MDS switch in each fabric. We recommend that you install the SSMs on the switches that are connected to the existing storage ports.
If the existing or new storage port is on a different switch than the SSM, ISL network traffic will increase during the migration, as all traffic between the existing and new storage is directed through the SSM. Also, if the server port is on a different switch than the SSM, ISL network traffic will increase during the migration, as all traffic between the server and the storage is directed through the SSM.
Ensure that Cisco MDS DMM is the only active intelligent application on the SSMs being used for the data migration job.
Configuring the Existing and New Storage
Complete the following configuration tasks for the storage devices:
•
New Storage—Connect the new storage to the SAN. Create LUN maps and LUN masks. Configure access lists for the new storage.
•
Existing Storage—Check that the LUNs are mapped.
•
VSANs—Ensure that the existing storage and new storage port pair in each fabric is configured in the same VSAN. Also ensure that for each existing storage port VSAN, there is atleast one new storage port and the server port has to be configured in the same VSAN.
•
Zones—Optionally, you can reconfigure zoning to add new storage. Cisco MDS DMM does not enforce zoning for the new storage. If you do not configure the zoning before migration, you must complete this action before server accesses the new storage.
Checking Storage ASL Status
The DMM feature contains the Array-Specific Library (ASL), which is a database of information about specific storage array products. DMM uses the ASL to correlate the LUN maps between multi-path port pairs.
Use the SLD tool to check the ASL status of LUNs on a storage array port. If the LUNs are all ASL=Yes, the Cisco MDS DMM feature automatically correlates the LUN maps.
If some or all of the LUNs result in ASL=No, contact Cisco support.
The SLD tool is launched from the supervisor module CLI. To check the status of a storage port, perform this task:
The following example shows how to display ASL status for a storage port:
router# show sld module 4 vsan 100 server-pwwn 21:00:00:e0:8b:08:5e:3e target-pwwn 50:06:0e:80:04:2c:5c:70=================================================================================Id LUN Id Device Type Size Vendor Product Id Serial Number ASL Status=================================================================================1 0x0 DASD 1.95GB VendorA ModelB5 11356 Yes Active2 0x1 DASD 1.95GB VendorA ModelB5 11356 Yes Active3 0x2 DASD 1.95GB VendorA ModelB5 11356 Yes Active4 0x3 DASD 1.95GB VendorA ModelB5 11356 Yes Active=================================================================================The SLD tool can also be launched from DMM GUI. To perform Server LUN Discovery, complete the following steps:
1.
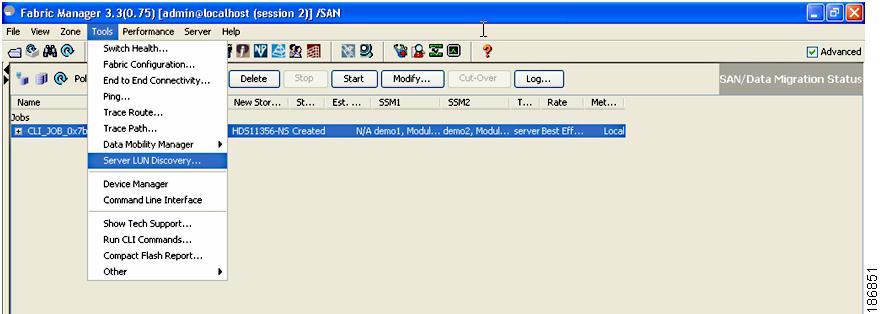
Choose Tools > Server LUN Discovery.
Figure 3-1 Server LUN Discovery
2.
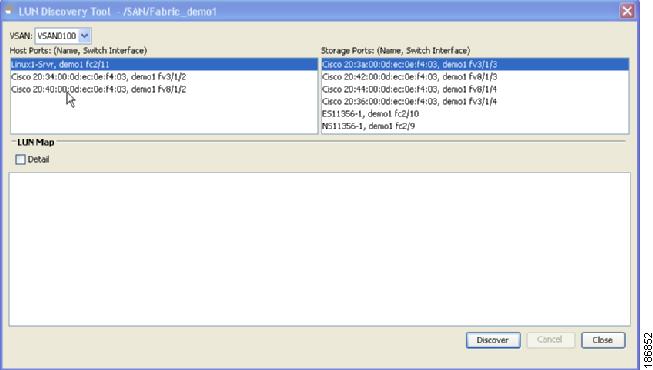
Select the VSAN and then select the Host Port for which you want to do the discovery and choose the Storage Port on which you have to do the discovery.
Figure 3-2 Server LUN discovery tool (SAN, host and storage port)
3.
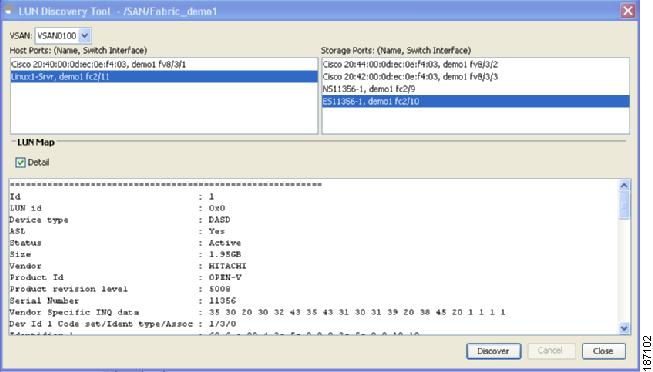
Click Discover.
The following example shows how to display the ASL status:
Figure 3-3 Example
Note
We recommend not to run the SLD tool on a server storage port pair that is already configured in a DMM job.
Configuring Enclosures
Before creating a migration job, you need to ensure that the server and storage ports are included in enclosures.
If the server ports are not already included in existing enclosures, you need to create enclosures for the server ports. If the server has multiple single-port HBAs, all of these ports need to be included in one enclosure. Enclosures for existing and new storage ports are created automatically.
For information on how to configure enclosures, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Configuring the SAN Fabric
If the SAN is a heterogeneous SAN, you may need to install new MDS switches or adjust the SAN topology to meet DMM requirements. For additional information about SAN topologies, refer to Chapter 6, "Understanding DMM Topologies."

 Feedback
Feedback