Table Of Contents
Cisco MDS DMM Features and Capabilities
Product Overview
Data migration is the process of copying data from an existing storage device to a new storage device. Data migration is required for storage array upgrades and for consolidation or replacement of existing storage arrays. Traditional methods of migrating data can be complex and can cause service disruptions.
Cisco MDS Data Mobility Manager (DMM) for the Cisco MDS 9000 family of switches provides capabilities and features that simplify data migration and minimize service disruptions.
This chapter includes the following sections:
•
Cisco MDS DMM Features and Capabilities
About Cisco MDS DMM
Traditional data migration methods can be complex and disruptive, often requiring extensive rewiring and reconfiguration of the SAN infrastructure. Configuration changes to servers and storage subsystems require coordination among different IT groups and storage vendor service representatives. Server downtime requires advanced scheduling with potentially long lead times.
Cisco MDS DMM is an intelligent software application that runs on the Storage Services Module (SSM) of an MDS switch. With Cisco MDS DMM, no rewiring or reconfiguration is required for the server, the existing storage, or the SAN fabric. The SSM can be located anywhere in the fabric, as Cisco MDS DMM operates across the SAN. Data migrations are enabled and disabled by software control from the Cisco Fabric Manager.
Cisco MDS DMM provides a graphical user interface (GUI) (integrated into Fabric Manager) for configuring and executing data migrations. There is also a command-line interface (CLI), which is suitable for creating scripts.
Cisco MDS DMM can be used in SANs that have only Cisco MDS 9000 switches as well as those containing a heterogeneous mixture of Cisco and other vendor switches.
Application downtime is a critical factor in data migration, as prolonged periods of downtime are difficult to schedule. Cisco MDS DMM minimizes application downtime. Existing data is available to the applications while the migration is performed. Cisco MDS DMM uses hardware and software resources on the SSM to move data to the new storage. This approach ensures that data migration adds no processing overhead to the servers.
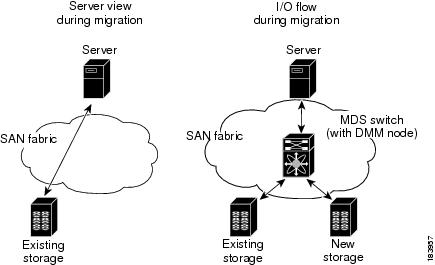
Cisco MDS DMM supports online migration, allowing applications to continue to access the existing storage devices. During data migration, all traffic between the server and storage flows through the SSM, as shown in Figure 1-1 (right side). The SSM coordinates all server access to the storage and performs the data migration. The migration activity is transparent to the server, which continues to have full access to the data. Figure 1-1 (left side) shows the server's view of the network during data migration. The server is unaware of the SSM, the new storage, and the migration activity.
Figure 1-1 Data Migration Using Cisco MDS DMM
Cisco MDS DMM performs data migration without any additional layer of virtualization. Cisco MDS DMM requires only SSM configuration to enable the feature and SAN configuration to access the new storage array. Cisco MDS DMM can be enabled (when data needs to be migrated) and disabled (after the migration is completed) without any major SAN or host reconfiguration.
Concepts and Terminology
Cisco MDS DMM uses the following concepts and terminology:
Existing Storage
The storage that is currently used by the application server. The data contained in the existing storage will be migrated to the new storage.
New Storage
The storage to which the data will be migrated.
Logical Unit Number (LUN)
A Logical Unit Number (LUN) is a reference to a unit of storage that you can specify for migration. The LUN is only a unique number in the context of a storage port.
Data Migration Session
A data migration session migrates the data from one LUN in the existing storage to a LUN in the new storage.
Data Migration Job
A data migration job defines a set of LUNs to be migrated together. A data migration session is created for each LUN that is to be migrated. The data migration job is the main unit of configuration and management. For example, the migration rate and other attributes are configured for the data migration job. The data migration job (and not individual sessions) can be started or stopped.
Method 1 Data Migration
For the section of existing storage LUN whose data is already migrated to new storage LUN, any new SCSI Write I/Os from the server is written to both the existing and new storage LUN before sending a response back to the server. Method 1 is typically used in local data migration.
Method 2 Data Migration
SCSI Write I/Os from the server to any section of existing storage LUN are written only to the existing storage LUN. The Write I/O changes to the existing storage LUN are marked in the Modified Region Log [MRL] before sending a response back to the server. These changes are then migrated to the new storage LUN in subsequent iterations. Method 2 is typically used in remote data centre migration.
SSM
An SSM is an MDS switch module that provides intelligent services. The Cisco MDS DMM feature executes on the SSM.
Peer SSM
In a dual-fabric topology, a data migration job runs on an SSM in each fabric. The two SSMs are peers. SSMs communicate with their peer SSMs to coordinate the data migration jobs.
Fibre Channel Redirect
Fibre Channel redirect (FC-Redirect) allows on-demand insertion and removal of SSM intelligent services with minimal disruption to existing traffic. No configuration changes are required on the server or storage devices. Cisco MDS DMM uses the FC Redirect capability to redirect traffic to the SSM. This redirection is transparent to the host and storage devices.
Virtual Target
A virtual target (VT) is a proxy target address for a storage port. During data migration, the FC-Redirect feature redirects traffic from the server to a VT on the SSM.
Virtual Initiator
A virtual initiator (VI) is a proxy initiator address for a server host bus access (HBA) port. During data migration, the SSM uses a VI to forward redirected traffic to the existing storage port. The SSM also uses the VI to forward data migration traffic to the new storage.
Control Plane Processor
The control plane processor (CPP) is the main processor in the SSM. DMM runs on the CPP.
Data Path Processors
The data path processors (DPPs) are a set of resource processors in the SSM. The DPP transfers blocks of data across the switch without impacting the CPP. DMM uses a VI on the DPP for migrating data.
Cisco MDS DMM Features and Capabilities
Cisco MDS DMM supports the following features and capabilities:
Server-Based Migration
In server-based migration, the focus is data migration for the storage used by a particular server (or server HBA port). All LUNs accessed by the selected server are available for migration to new storage.
Storage-Based Migration
In storage-based migration, the focus is data migration for storage exposed by a particular storage array (or storage array port). All LUNs in the specified storage array are available for migration to new storage.
Online Data Migration
Cisco MDS DMM is designed to provide online data migration. The existing storage is available to server applications while the SSM performs the data migration. During migration, data reads from the server are directed to the existing storage. DMM ensures that data writes are processed correctly. For example, if the write is to a storage segment already migrated, the write is mirrored to the existing and new storage.
Offline Data Migration
During offline data migration, servers must not initiate reads or writes to the existing storage. Any server application using the existing storage must be quiesced. Offline data migration is faster than online data migration and can be used for non critical data applications.
Method 1 Data Migration
For the section of existing storage LUN whose data is already migrated to new storage LUN, any new SCSI Write I/Os from the Server is written to both the existing and new storage LUN before sending a response back to the server. Method 1 is typically used in local data migration.
Method 2 Data Migration
SCSI Write I/Os from the server to any section of existing storage LUN are written only to the existing storage LUN. The Write I/O changes to the existing storage LUN are marked in the Modified Region Log [MRL] before sending a response back to the server. These changes are then migrated to the New Storage LUN in subsequent iterations. Method 2 is typically used in remote data centre migration.
Configuration Using Cisco Fabric Manager GUI
The Cisco MDS DMM GUI is integrated into Fabric Manager. The DMM GUI provides a wizard to guide you through the steps required to configure a data migration job. To minimize customer impact, you can schedule the start time for a data migration and you can configure the rate of data migration. The wizard also prompts you to perform tasks on external entities such as the fabric switch and the storage devices.
The DMM GUI also provides a job status screen, for monitoring and managing data migration jobs and sessions.
Configuration Using CLI
Cisco MDS DMM provides a set of CLI commands, which are suitable for creating scripts. These commands are accessed from the MDS switch command console or telnet session.
Migration to Larger LUN
To increase the amount of data that an existing server can access, Cisco MDS DMM facilitates migration to a larger LUN. After the migration, expand the file system on the LUN to take advantage of the increased storage space.
Heterogeneous Storage Migration
Cisco MDS DMM can migrate data between storage devices from different vendors. The supported devices are listed in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Interoperability document, which is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/storage/san_switches/mds9000/interoperability/matrix/Matrix.pdf
Heterogeneous SAN Environments
Cisco MDS DMM supports data migration on SANs that contain third party vendor switches (such as Brocade). The existing and new storage devices must be attached to an MDS switch.
Offline Verification
Cisco MDS DMM supports verification of the new storage. The existing storage is offline during the verification.
Simultaneous Migration of Multiple LUNs
Cisco MDS DMM supports multiple simultaneous data migration jobs and simultaneous data migration sessions within a job.
Dual Fabric Support
Cisco MDS DMM supports data migration for dual fabric topology. In this topology, servers are connected to storage devices across two independent SAN fabrics and the servers are configured for multipathing.
Cisco MDS DMM also supports data migration for single fabric SANs with single-path or multipath configurations.
Delayed Server Reconfiguration
After the data is copied from the existing storage to the new storage, you can delay the reconfiguration of the server to access the new storage. During this period, all writes are mirrored to the existing storage and the new storage. This description assumes Method 1.
Data Migration Overview
A data migration job typically comprises three major stages (see Figure 1-2).
In the pre-migration stage, create a plan for data migration, configure the new storage, and create the DMM job. In the migration stage, start the data migration job and monitor its progress. In the post-migration phase, prepare the server to use the new storage, delete the data migration job, and remove the old storage.
Figure 1-2 Data Migration Stages
The following sections provide an overview of the typical data migration stages (additional details are covered in subsequent chapters):
Pre-Migration
In the pre-migration stage, create a plan for the migration, configure the new storage, and create the data migration job. Full details about pre-migration activities are covered in Chapter 3, "Preparing for Data Migration."
Plan
Create a plan for data migration, identifying external dependencies and activities that need to be scheduled.
Configure
Configure the new storage device and any other configuration.
Create the Data Migration Job
Create and configure the data migration job using the DMM GUI. You can create a job without a schedule or you can specify the day and time for the job to start.
Migration
In the migration stage, jobs with a configured schedule jobs start automatically. Manually start unscheduled data migration jobs.
Start the Migration
A data migration job comprises one or more data migration sessions. A data migration session performs the migration of one LUN from the existing storage to the new storage.
During migration, the DMM feature ensures the integrity of the storage data by intercepting all traffic from the server and storage ports involved in the migration job.
Cisco MDS DMM directs all server-initiated reads and writes to the existing storage. If the server initiates a write to a region that has already been migrated, the write is mirrored to the new storage for Method 1. For Method 2, if the server initiates a write to a region that is already migrated, the MRL gets updated for that region while the data gets migrated in the background subsequently.
Monitor
During migration, you can monitor progress of the DMM job by using the job status display for Method1in the DMM GUI. For Method 2 jobs, the Est. TOC field determines when to issue the Finish command.
Post-Migration
In the post-migration stage, reconfigure the server to use the new storage. The exact post-migration configuration steps vary depending on the operating system of the server.
Method 1
To configure the post-migration steps for Method 1, follow these steps.
Schedule
Schedule a time (and the personnel) to reconfigure the server to use the new storage and remove references to the existing storage.
Verify
Optionally, verify the data integrity between the existing and new storage after the migration has completed. The existing storage must be offline during the verification.
Delete
To delete a data migration job,follow these steps:
· Shut down the server applications to stop accessing the existing storage.
· Use the DMM GUI to delete the completed data migration job.
· Reconfigure the server to access the new storage.
Method 2
To configure the post-migration steps for Method 2, follow these steps.
Schedule
Schedule a time (and the personnel) to reconfigure the server to use the new storage and remove references to the existing storage.
Finish
The finish process for a data migration job involves a series of activities which must be completed in sequence:
To complete Method 2 data migration, follow these steps.
•
Click Finish to stop access to the existing storage.
The existing storage LUNs are offline for the servers. Cisco DMM migrates the changed blocks from the existing storage LUNs to the new storage LUNs for the last time. See Finishing Jobs, page 4-27 for more details.
Verify Job
Optionally, you can verify the data integrity between existing and new storage after the Finish operation is completed. The existing storage LUNs will be offline during the verification. This optional operation can be peformed just before deleting a job.
Delete
To delete a data migration job [in Method 2], follow these steps:
–
Use the DMM GUI to delete the completed data migration job.
–
Reconfigure the server to access the new storage.
Note
Restarting stopped or failed state for Method 1, restarts the job from the beginning. Restarting stopped or failed state for Method 2, restarts the job from the point where the job failed or stopped.
Software Requirements
Cisco MDS DMM has the following software requirements:
•
MDS switches hosting the storage or the SSM must be running SAN-OS release 3.2(1) or later for Method 1. SAN-OS Release 3.3(1a) is required for Method 2.
•
The Fabric Manager server must be running software release 3.2(1) or later.
Hardware Requirements
Cisco MDS DMM software application executes in the SSM of an MDS switch.
SSM-Capable Switches
The following switches support the SSM:
•
All MDS 9200 family switches
•
All MDS 9500 family switches
Storage Ports
The storage ports must connect to Cisco MDS switches that support FC-Redirect. All Cisco MDS switches support FC-Redirect, with the following exceptions:
•
MDS 9124
•
MDS 9134
•
MDS 9020
Server HBA Ports
The server HBA ports can be connected to any switch (Cisco or third-party vendor).
SAN Fabric
Note the following hardware-related requirements:
•
Cisco MDS DMM supports single-fabric and dual-fabric topologies. The DMM feature requires at least one SSM in each fabric.
•
The Cisco MDS DMM feature is supported in homogeneous and heterogeneous SAN fabrics. SSMs can be located on any SSM-capable MDS switch in the fabric. However, the SSM and the storage ports must either be located on the same switch or connected through a Cisco SAN.
Deployment Guidelines
When planning and configuring data migration using Cisco MDS DMM, follow these deployment guidelines:
•
We recommend that you install the SSM in the same MDS switch as the existing storage and connect the new storage to the same switch. Data migration causes increased inter-switch link (ISL) traffic if the existing storage or new storage devices are connected to different switches than the SSM.
•
MDS DMM supports 16 simultaneous jobs on each SSM.
•
Do not add the same initiator/target port pair into more than one migration job simultaneously.
•
When using multipath ports, the server must not send simultaneous I/O write requests to the same LUN from both multipath ports. The first I/O request must be acknowledged as completed before initiating the second I/O request.
•
DMM is not compatible with LUN zoning.
•
DMM is not compatible with inter-VSAN routing (IVR). The server and storage ports must be included in the same VSAN.
•
DMM is not compatible with SAN device virtualization (SDV). The server and storage ports cannot be virtual devices, or physical devices associated with a virtual device.
•
For assistance on DMM and FC/IP write acceleration, contact cisco support.
•
DMM does not support migration to a smaller destination LUN.

 Feedback
Feedback