Release Notes for Ultra Cloud Core: Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
This Release Notes identifies changes and issues related to the software release of 5G Converged Core Session Management Function (SMF).
The key highlights of this release include:
· Enhanced roaming QoS control: Visited network operators gain comprehensive control over QoS for inbound roamers, effectively safeguarding the quality of experience for local users.
· vSMF selection control for Roaming: Network operators achieve granular control over roaming subscriber management, enabling optimized resource allocation and ensuring high-quality user experience.
· N10 registration enhancement: Modifies the N10 registration timing in the session creation call flow to align with later 3GPP releases, ensuring the SMF obtains subscribed slices from the UDM before registration for accurate slice determination.
· Low footprint deployments for SMF: Introduces AIO models designed to support resource-optimized, high-capacity SMF deployments.
For more information about Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, see the Related resources section.
Release lifecycle milestones
The following table provides EoL milestones for Cisco UCC SMF software:
Table 1. EoL milestone information for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Milestone |
Date |
| First Customer Ship (FCS) |
31-Oct-2025 |
| End of Life (EoL) |
31-Oct-2025 |
| End of Software Maintenance (EoSM) |
01-May-2027 |
| End of Vulnerability and Security Support (EoVSS) |
01-May-2027 |
| Last Date of Support (LDoS) |
30-Apr-2028 |
These milestones and the intervals between them are defined in the Cisco Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) Software Release Lifecycle Product Bulletin available on cisco.com.
This section provides a brief description of the new software features introduced in this release.
Table 2. New software features for Ultra Cloud Core – Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Product impact |
Feature |
Description |
| Software Reliability |
The Roaming Quality of Service (QoS) Control feature gives operators in a visited network full control to manage and enforce QoS for inbound roamers, protecting local user experience from being degraded by visiting users. Command introduced: profile qos vplmn_qos { ambr ul ambr_ul | ambr dl ambr_dl | qi5 qci_value | arp priority-level priority_value | arp preempt-cap { not_preempt | may_preempt } | arp preempt-vuln { not_preemptable | preemptable} } — Used to configure a QoS profile with specific AMBR, QCI, and ARP parameters.
Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable the feature |
|
| Software Reliability |
The N10 Registration Enhancement modifies the timing of N10 registration within the session creation call flow. This enhancement addresses changes introduced in later 3GPP releases, moving the N10 registration from an initial step to the final step in the call flow. The N10 Registration Enhancement addresses a specific problem in 5G networks where the SMF needs to determine the correct slice for N10 registration. The enhancement ensures that the SMF first obtains the subscribed slices from the UDM via an N10 subscription and then uses this information to perform N10 registration as the last step in the call flow. This is particularly relevant for 5G UEs connecting via 5G/Wi-Fi RAT. Command Introduced: profile dnn dnn-profile-name n10 delay-registration rat-type [ NR | WIFI | NR-REDCAP | all ] Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable the feature |
|
| Software Reliability |
This feature enables the SMF to explicitly indicate to the NRF when it should not be selected as a visited SMF (vSMF) for roaming scenarios by setting the vsmfSupportInd flag to false in NFRegister and NFUpdate messages. This behavior is configurable and can be enabled at runtime, allowing precise control over SMF selection as vSMF without impacting system performance, ensuring seamless network operation and compatibility. Command introduced: supported-features [ suppress-vsmf ] - Enable this configuration to include vsmfSupportInd IE in smfInfo in NfProfile Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration required to enable the feature |
|
| Upgrade |
AIO models are designed to support low footprint deployments for SMF. Deploying the AIO models allows the network operators to deploy high-capacity deployments in a resource-optimized manner. |
|
| Software Reliability |
Real-time location reporting for 5G SA and 4G voice call setup |
The SMF now supports fetching real-time user location and notifying the PCF before a 5G SA or 4G voice call is established. This feature allows the SMF to retrieve the latest user location from the AMF using the Namf_EventExposure service. It installs a new rule on the default bearer/flow for location fetching and then moves this rule to the voice bearer/flow for subsequent voice call setup, ensuring accurate location reporting and seamless voice call establishment.
|
| Software Reliability |
IPv6 support for SMF |
This release supports the deployment and configuration of SMF on IPv6 network through SMI. |
| Hardware Reliability |
Supermicro server validation |
SMF has been tested and validated for deployment on the Supermicro server. |
This section provides a brief description of the behavior changes introduced in this release.
Table 3. Behavior changes for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Description |
Behavior changes |
| N26 IDFT False prevents R15 DFT enablement [CSCwq54957] |
Previous Behavior: Direct data forwarding was not supported in prior releases because specific changes were introduced to enable Release 16's data forwarding behavior during 4G to 5G handovers. Due to which SMF incorrectly processed handover requests where both DFT and IDFT flags were false, treating them as if DFT was true. New Behavior: Direct data forwarding is supported in all releases, aligning with the 3GPP specification for 4G to 5G handovers. |
| BGP server operation on IPv6-only interfaces [CSCwq86050] |
Previous Behavior: To run a BGP server on an interface with IPv6, both IPv6 and IPv4 addresses were required. The IPv4 address on that interface served as both the GRPC endpoint IP and the Router ID. New Behavior: BGP servers can now operate on interfaces configured with only IPv6 addresses. In this setup, the IPv6 address will be used for the GRPC endpoint. For the Router ID, a new IPv4 address must be added to the loopback (lo) interface, and this loopback IP will then function as the Router ID. |
| New CLI parameters for route update failure handling [CSCwr07151] |
Previous Behavior: The failure handling of route update (chunk information) was enabled or disabled through a single configuration command "failure-handling route-updates deactivate”. New Behavior: SMF provides these additional configuration options to monitor the failure handling of route updates: · timeout: Sets the maximum wait time (in seconds) for a route update confirmation. If exceeded, the route chunk transitions from Init to Failed state and enters quarantine. · timeout-monitor-frequency: Defines how often (in seconds) the system checks for route chunks stuck in the Init state. · chunk-quarantine-timer: Specifies the duration (in seconds) a failed route chunk remains in quarantine before being released and re-attempted. · chunk-quarantine-limit: Limits the maximum number of failed IP chunks per UPF that can be in quarantine, preventing indefinite looping of failed updates. Customer Impact: The customer will have better control over route update failure handling, enhancing network stability and resource management. |
| BGP neighbor reset behavior for dynamic policy changes [CSCwq91862] |
Previous Behavior: Whenever a new dynamic policy is added or an existing one is updated, the system performed a BGP hard reset. This caused BGP sessions to restart, cleared all learned routes, and required the system to relearn them after re-establishing connections. In some cases, this reset happened twice during policy or interface updates. New Behavior: All dynamic policy additions, updates, or deletions now trigger only a BGP soft reset, eliminating hard resets for these operations. Customer Impact: Network stability is improved as disruptive hard resets are no longer triggered during dynamic policy operations. Policy changes are applied more quickly through BGP soft resets, with minimal impact on routing. Downtime is reduced by eliminating session flaps and avoiding unnecessary route withdrawal or additional cycles. |
| Standardized error cause values for VSMF rejections during 4G to 5G handover [CSCwr59317] |
Previous Behavior: When the VSMF rejected a create request during a 4G home-routed to 5G roamer Handover (HO), it returned a non-standard cause value in the error response. The cause field contained a specific but non-standardized string detailing the rejection reason, rather than a 3GPP-compliant cause code. This behavior was prevalent across all vSMF/hSMF procedures, where non-standard cause values were consistently returned in failure responses. New Behavior: The VSMF now returns standardized 3GPP-compliant cause values in its failure responses, aligning SMF failure handling with 3GPP standards. Specifically, for rejections due to insufficient resources during a 4G to 5G roamer HO, the cause field will now explicitly reflect "INSUFFICIENT_RESOURCES". The detailed, specific reason for the rejection will be provided in the detail field. This change ensures adherence to 3GPP specifications and improves interoperability, clarity for troubleshooting, and overall system compliance. |
| 5QI rejection during VSMF modification not working as expected [CSCwr67543] |
Previous Behavior: During VSMF modification, if 5QI rejection occurred, the UE still created QoS flows before receiving the rejection. These rejected flows were visible in N1 messages, causing confusion and delayed rejection handling. The system effectively performed post-creation rejection, which was not ideal. New Behavior: With the recent feature enhancement, rejected 5QI flows are now rejected upfront during the modification process. No QoS flows are created at the UE when rejection occurs. Rejected flows are no longer included in N1 messages, ensuring clean signaling and proper synchronization between network and UE. This behavior aligns with the updated VSMF design and 3GPP-compliant modification flow handling. |
| Improved handling of QoS override procedures in VSMF [CSCwq95221] |
Previous Behavior: When the VSMF overrides the default QoS for a session, it triggered an unexpected VSMF modify procedure, even if the change did not require notifying the HSMF. As a result, the system generated additional modify messages that did not include any relevant Information Element (IE) reflecting what was overridden. This led to increased signaling traffic and potential confusion during message analysis, as the specific change was not clear. New Behavior: If the VSMF overrides the default QoS, it no longer initiates a new modify procedure towards the HSMF unless it is necessary. This change ensures that only meaningful modifications result in signaling updates, reducing unnecessary message exchanges. Consequently, signaling becomes more efficient, and operators can more easily interpret the purpose of modifying messages, leading to streamlined operations and improved system performance. |
This table lists the resolved issues in this specific software release.
Note: This software release may contain bug fixes first introduced in other releases. To see additional information, click the bug ID to access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. To search for a documented Cisco product issue, type in the browser: <bug_number> site:cisco.com
Table 4. Resolved issues for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Bug ID |
Description |
| SMF |
|
| With cilium we see high response times for S11/S5 request and high message processing time for host n/w pods |
|
| N26 IDFT false - R15 DFT not getting enabled |
|
| PCSCF restoration in between Idle exit not handled |
|
| For half attach scenarios for 2g/3g over 5g, SmContextCreateReq is treated as HO request |
|
| Collision - wifi-lteHO with Rule deletion not successful |
|
| Collision - LTE-NR with IMexit and UE_init modify - - Rule delete not successful |
|
| VONR multi-party call failure after chf disabled |
|
| SMF not sending Query URR after AMBR change after updating version spec under profile compliance |
|
| Multiple network element pcf - expedite response not working |
|
| Multiple disconnect reasons pegged for the same session when PDU session is denied due to PDU type mismatch. |
|
| AMF-SET - SMF sending request to deregistered AMF |
|
| N4 Wrong ULI format error logs - when the session/bearer is without ULI |
|
| SMF is sending ratType as empty in lower compliance for the NR_redcap towards CHF and PCF |
|
| XnHO triggered while 5G to 4G HO after retrieve complete |
|
| Incorrect NotificationURI format for N7 and N40 |
|
| VSMF sending EBI 0, resulting in Handover failure |
|
| VSMF not sending mapped slice information to UE |
|
| VSMF is not sending hoPreparationIndication during 4G to 5G Handover |
|
| SMF-restart seen with AMF sending complete in s11create |
|
| SMF-REDCAP - Lower-compliance - RATTYPE sent empty in 4G to 5G for REDCAP |
|
| EPSFB - DLDR collision - invalid_rat_type for DLDR getting pegged |
|
| SMF sending 404 - Retrieve and N1N2failurenotification collision |
|
| SMF fails to process the addition of pccrule belonging to default flow with packetFilterUsage true post N2 failure |
|
| SMF-Service restart when 5qI is missing in policy create response |
|
| IoT |
|
| SMF Missing IEs in N40 Update/Terminate Messages after MBR when using CHF 15.3.0.std version |
|
There are no open bugs in this specific software release.
This section lists compatibility information of the Cisco UCC software products that are verified to work with this version of the UCC SMF software.
Table 5. Compatibility information for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Product |
Supported Release |
| Ultra Cloud Core SMI |
2025.04.1.15 |
| Ultra Cloud CDL |
1.12.3 |
| Ultra Cloud Core UPF |
2025.04.0.i5 |
| Ultra Cloud cnSGWc |
2025.04.0 |
This section provides information about the release packages associated with UCC SMF software.
Table 6. Software packages for Ultra Cloud Core - Session Management Function, Release 2025.04.0
| Software Package |
Description |
Release |
| ccg-2025.04.0.SPA.tgz |
The SMF offline release signature package. This package contains the SMF deployment software, NED package, as well as the release signature, certificate, and verification information. |
2025.04.0 |
| ncs-6.4.8-ccg-nc-2025.04.0.tar.gz |
The NETCONF NED package. This package includes all the yang files that are used for NF configuration. Note that NSO is used for the NED file creation. |
6.4.8.1 |
| ncs-6.1.14-ccg-nc-2025.04.0.tar.gz |
6.1.14 |
Cloud native product version numbering system
The show helm list command displays detailed information about the version of the cloud native product currently deployed.
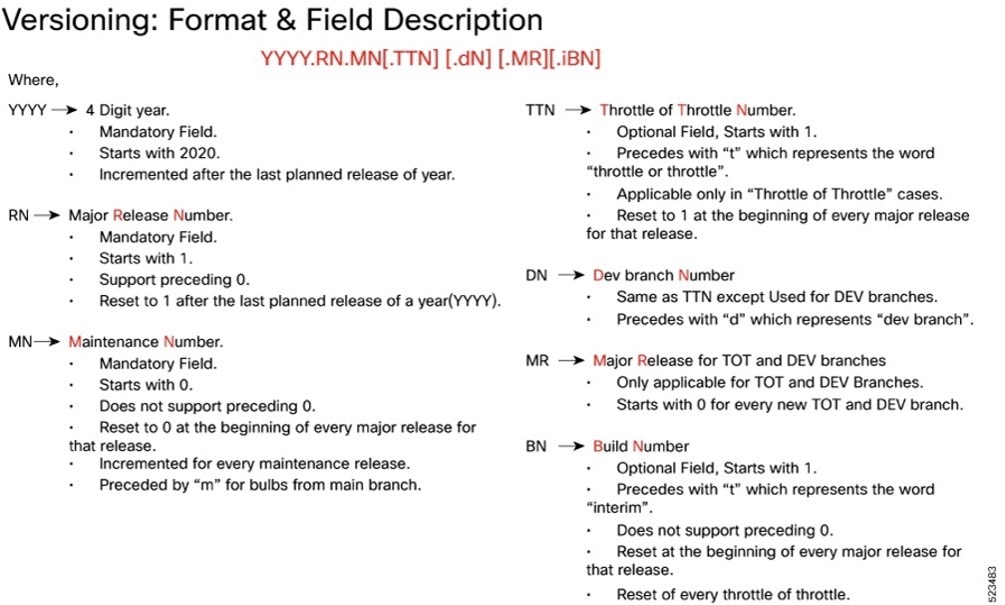
Image checksum information is available through Cisco.com Software Download Details. To find the checksum, hover the mouse pointer over the software image you have downloaded.
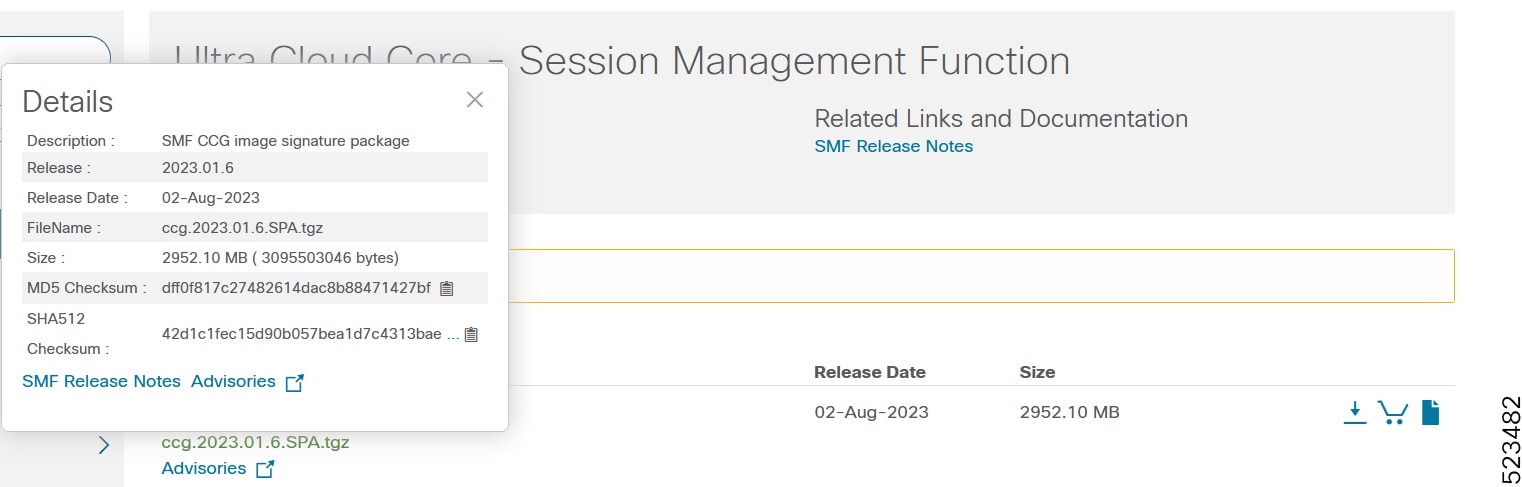
To validate the information, calculate a SHA512 checksum using the information in the following table and verify that it matches the one provided on the software download page.
To calculate a SHA512 checksum on your local desktop, see this table.
Table 7. Checksum calculations per operating system
| Operating System |
SHA512 checksum calculation command examples |
| Microsoft Windows |
Open a command line window and type the following command: > certutil.exe -hashfile <filename.extension> SHA512 |
| Apple MAC |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ shasum -a 512 <filename.extension> |
| Linux |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ sha512sum <filename.extension> OR $ shasum -a 512 <filename.extension> |
| Note: <filename> is the name of the file. <extension> is the file type extension (for example, .zip or .tgz). |
|
If the SHA512 checksum does not match, we advise you not to attempt upgrading any systems with the corrupted software image. Download the software again and verify the SHA512 checksum again. If there is a constant mismatch, please open a case with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center.
This table provides key resources and links to the support information and essential documentation for SMF and other Ultra Cloud Core (UCC) products.
Table 8. Related resources and additional information
| Resource |
Link |
| SMF documentation |
|
| cnSGWc documentation |
|
| SMI documentation |
|
| UPF documentation |
|
| Service request and additional information |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2025 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback