Feature Description - Location Services
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
MT-LR Location Services |
2024.02.0 |
AMF supports the MT-LR location services using the Location Management Function (LMF) to determine the accurate position and location of the UE. AMF supports the MT-LR location services for regulatory requirements. Command introduced: location lmf-positioning mt-lr — Used to to enable MT-LR for location services. Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration Required |
|
Feature Name |
Release Information |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Network Induced Location Request (NI-LR) |
2025.02.0 |
AMF now includes functionality to facilitate location services for Network Induced Location Requests, ensuring compliance and improving service capabilities. Command introduced: location lmf-positioning ni-lr — Used to to enable NI-LR for location services. Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration Required |
|
Location Services - Compliance to 3GPP Specification Revision 18 |
2025.02.0 |
MT-LR and NI-LR supports revision 18.6 of the 3GPP specification. This update with the latest revision ensures compliance with the most current regulatory requirements. Command introduced: profile compliance compliance_profile_name { service service_name { version spec 3gpp_spec_version } } — Used to configure the 3gpp spec compliance version for namf-loc and nlmf-loc. Default Setting: Disabled – Configuration Required |
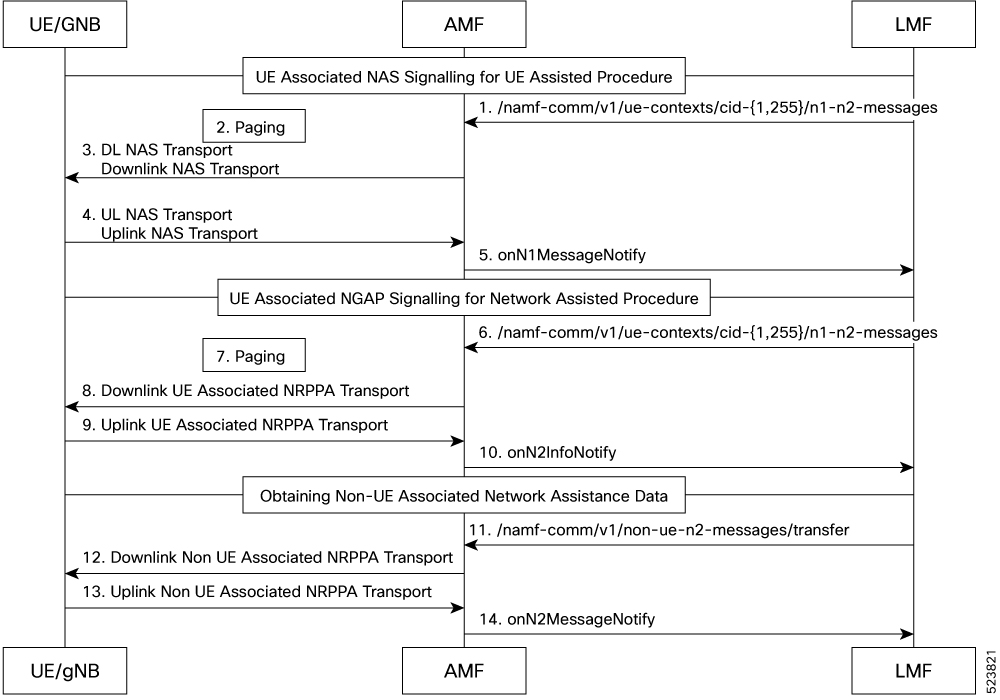
Supported Location Request Types
AMF supports various types of location requests to accurately determine the location of UE. These include:
-
Network Induced Location Request (NI-LR)
-
Mobile-Terminated Location Request (MT-LR)
Network Induced Location Request (NI-LR)
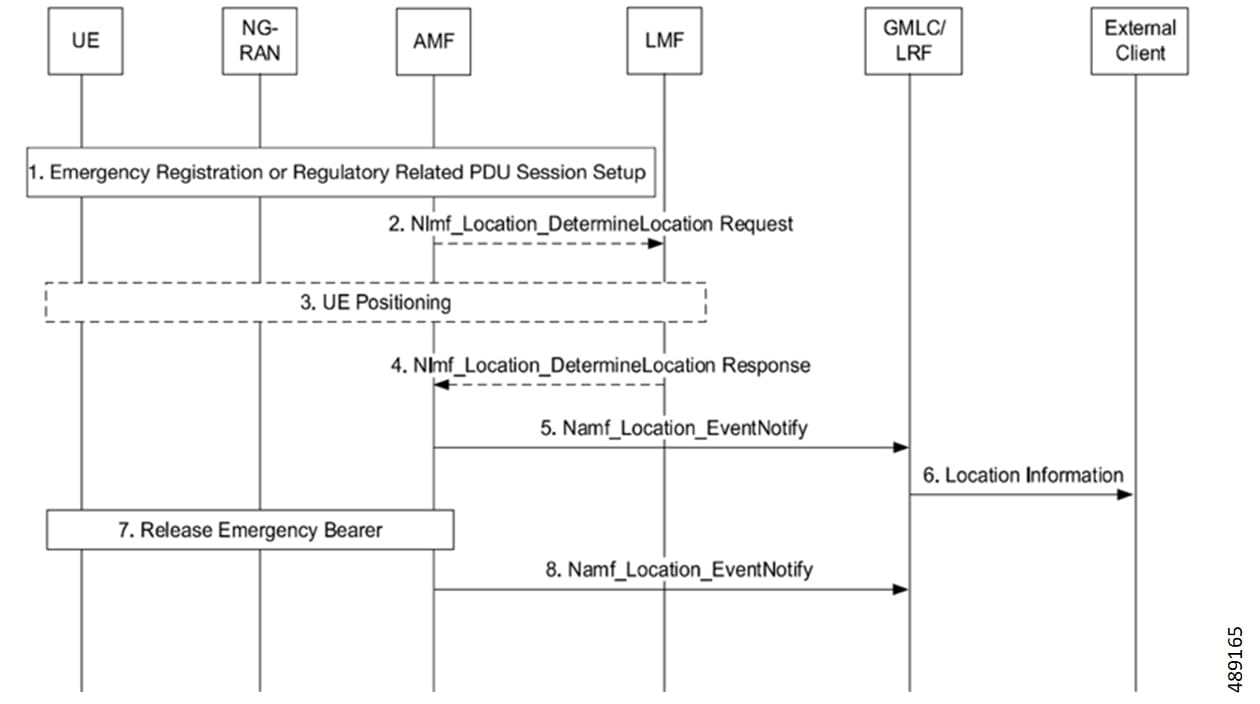
In NI-LR, when an emergency call goes to AMF, the serving AMF initiates the process to determine the location of the UE. This type of request is typically triggered by network operations or regulatory requirements, where the AMF actively seeks location information to ensure compliance with legal obligations. AMF coordinates with the LMF to accurately ascertain and update the location details of the UE to GMLC.
NI-LR-based location services are supported for both emergency-registered subscribers and normal subscribers with emergency PDU. This ensures that location information is readily available in critical situations to support emergency services.
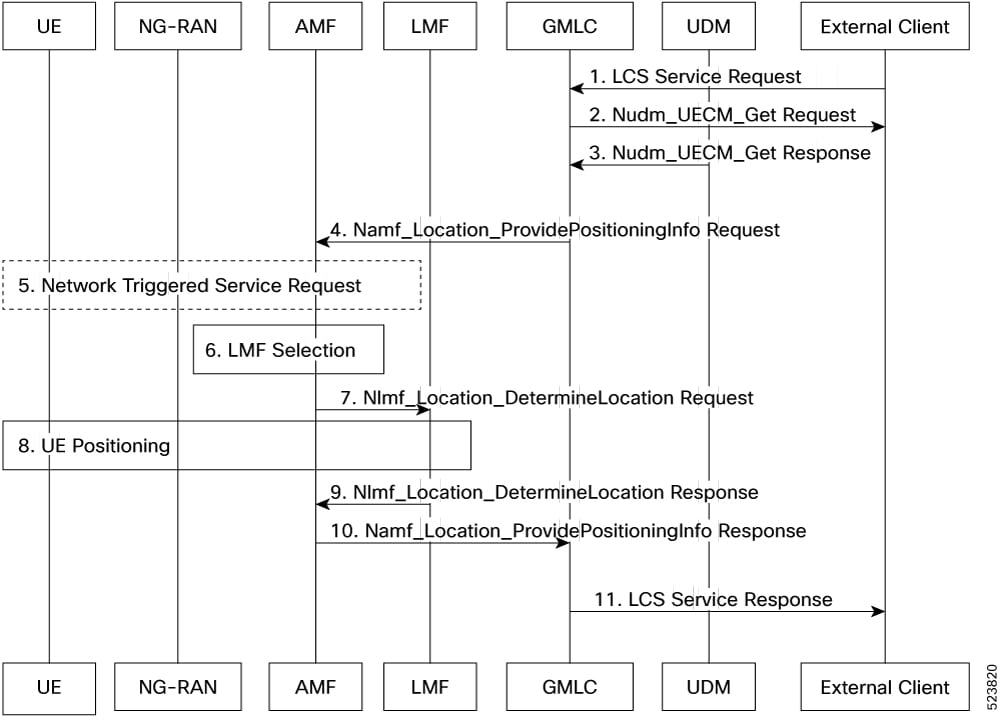
Mobile-Terminated Location Request (MT-LR)
AMF supports location services to fulfill regulatory requirements, such as emergency calls and lawful intercepts.
In MT-LR, the Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC) initiates a request for location services. It forwards this request to the AMF, which utilizes the Location Management Function (LMF) to determine the location of the UE. Once the location is identified, the information is sent back to the GMLC.
AMF also supports queries from GMLC using the Generic Public Subscription Identifier (GPSI) to obtain location information.
AMF supports, "current location" and "current or last known location" for MT-LR. In case of "current or last known location" if the paging for UE fails or positioning fails due to any of the associated nodes, such as: LMF, UE, or gNB, then AMF returns the last known saved location if available.
 Note |
AMF does not support concurrent location request for the same UE. AMF aborts the processing of previous request and continues with the new request. |
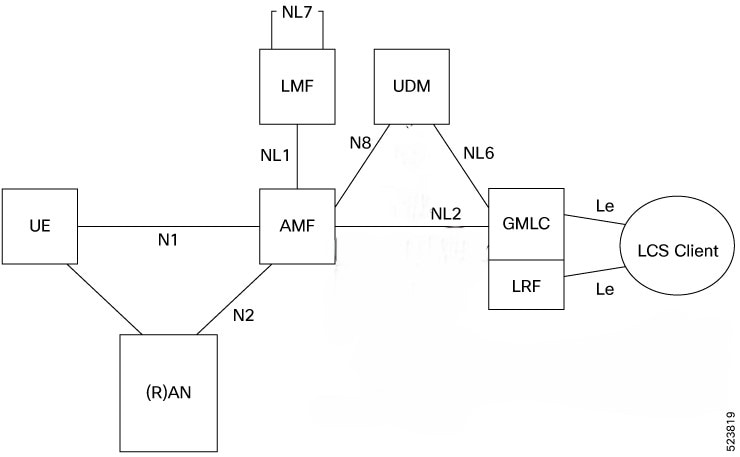
Architecture
Location Service consists of the following layers as part of the non-roaming location services architecture:
-
UE: The UE represents end-user devices, such as smart phones, tablets, or IoT devices. These devices interact with the network.
-
GMLC: GMLC provides the location information services related to mobile devices.
-
LCS Client: The LCS client is an external entity or application that requests location information for a specific mobile device.
-
LRF: The LRF is a component within the Location Services (LCS) architecture in cellular networks. LRF retrieves and provides the location information for mobile devices or user equipment (UE).
-
LMF: The LMF determines the geographical location of the UE.
-
AMF: The AMF is a key component in 5G networks. It manages mobility, session management, and security for user devices.
-
UDM: The UDM handles user-related data, including authentication, authorization, and subscription information.
-
RAN: The RAN connects user devices to the core network. It includes base stations and antennas.
-
N1 Interface: The N1 interface connects the UE and the RAN. It carries user data and control signaling.
-
N2 Interface: The N2 interface connects the AMF and the RAN. It handles signaling and data transfer between the core network and the RAN.
-
NL1 Interface: NL1 interface connects the LMF to the UE.
-
NL2 Interface: NL2 interface connects the AMF to the GMLC.
The following diagram describes the high level architecture for location services.
 Feedback
Feedback