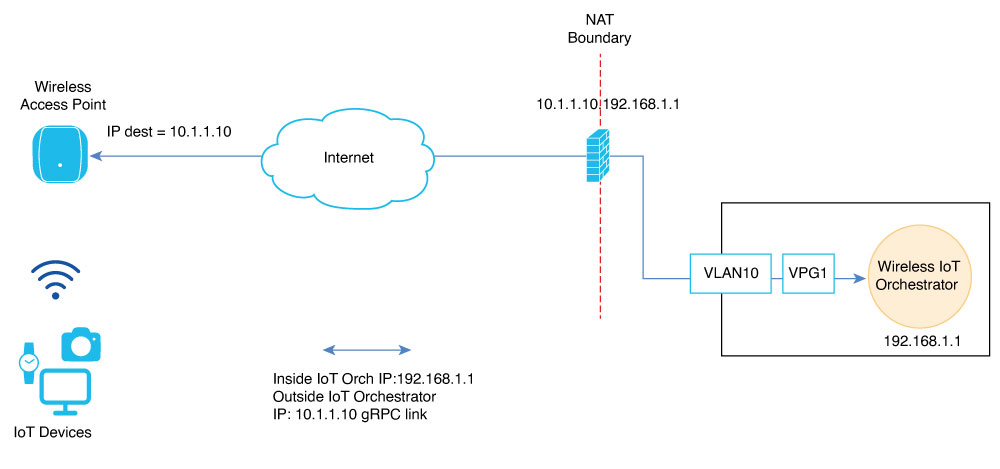
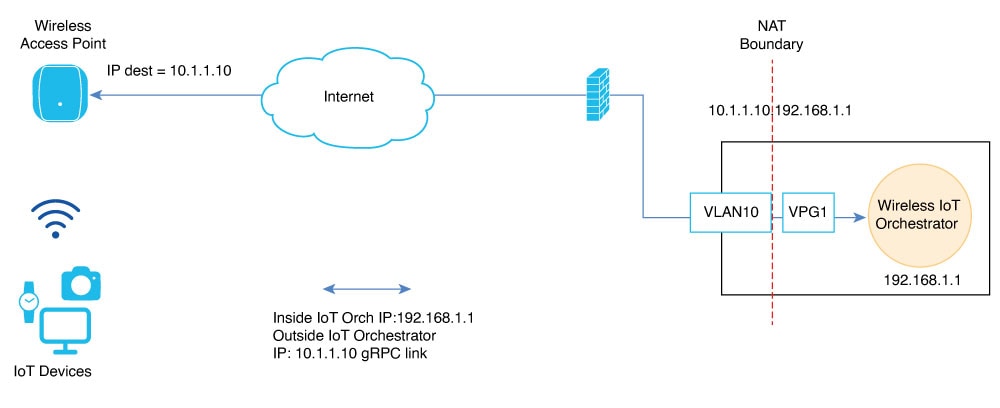
Overview of NAT Configuration
The Cisco Sensor Connect for IoT Services (Wireless IoT Orchestrator) requires Cisco Access Points to establish a TLS connection using GRPC. The default destination target IP address is the Wireless IoT Orchestrator IP address. This IP address is embedded in a JWT token that is passed to APs using AP profile configuration.
In cloud deployments, the IP address configured on Cisco Access Points differs from the IP address configured in the Wireless IoT Orchestrator. This deployment involves NAT to provide reachability over the internet. The NAT IP address field indicates to the Wireless IoT Orchestrator container which destination IP address the Cisco APs can use for GRPC connection.
The NAT IP address field is necessary when the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller is configured to use CAPWAP discovery with a public IP. For more information on CAPWAP discovery with a public IP, see the Wireless Management Interface documentation.
This chapter describes how to use the NAT IP address field in the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller Web UI (Configuration > Services > IoT Services) and configure NAT on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 Wireless Controller for IoT Orchestrator use cases.

 Feedback
Feedback