Overview
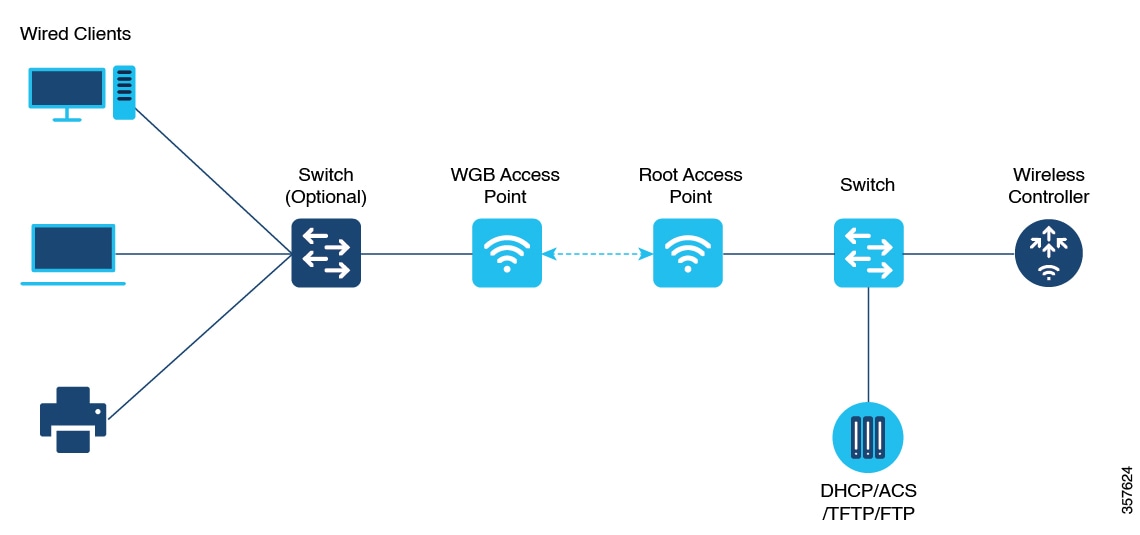
A workgroup bridge (WGB) is an Access Point (AP) mode to provide wireless connectivity to wired clients that are connected to the Ethernet port of the WGB AP. A WGB connects a wired network over a single wireless segment by learning the MAC addresses of its wired clients on the Ethernet interface and reporting them to the WLC through infrastructure AP using Internet Access Point Protocol (IAPP) messaging. The WGB establishes a single wireless connection to the root AP, which in turn, treats the WGB as a wireless client.
Universal WGB (uWGB) is a complementary mode of WGB feature that acts as a wireless bridge between the wired client connected to uWGB and wireless infrastructure including Cisco and non-Cisco wireless network. One of the wireless interface is used to connect with the access point. The radio MAC is used to associate AP.
Starting from Cisco IOS XE Dublin 17.11.1, WGB is supported on the Cisco Catalyst IW9167E Heavy Duty Access Points.

 Feedback
Feedback