Introduction and Basics
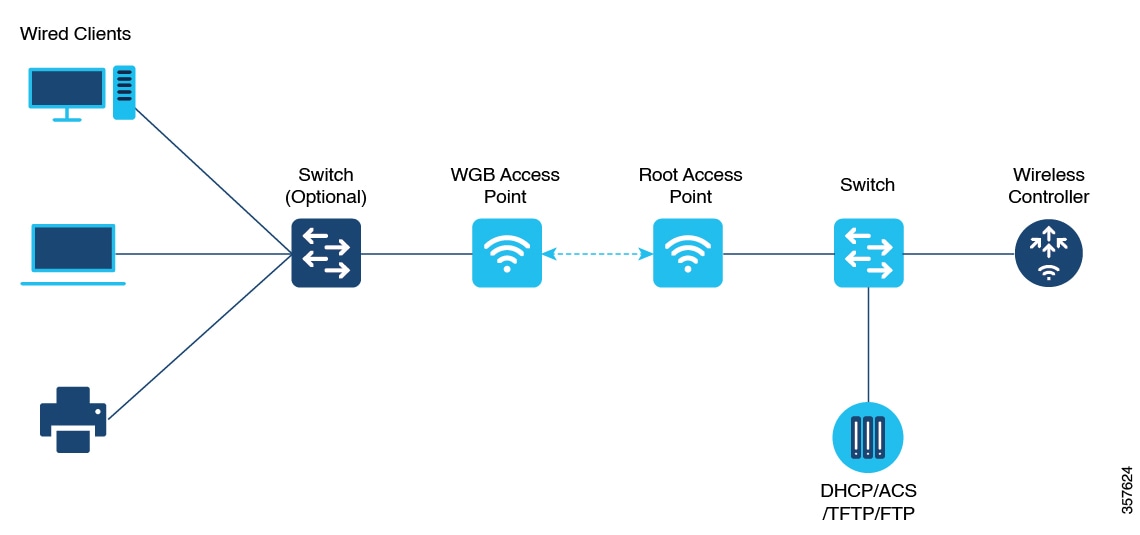
Workgroup Bridge
A Workgroup Bridge (WGB) is a feature in wireless networking that allows a wired device or a group of wired devices to connect to a wireless network.
Both Workgroup Bridge (WGB) and Universal Workgroup Bridge (uWGB) modes are part of WGB and that enable seamless connectivity between wired and wireless networks.
From Unified Industrial Wireless (UIW) Release 17.13.1, both of these modes are supported on the Cisco Catalyst IW9165E Rugged Access Point (AP) and wireless client.
WGB mode
WGB mode provides wireless connectivity to wired clients connected to the Ethernet port of the WGB.
-
Bridges the wired network to a wireless segment.
-
Learns the MAC addresses of connected Ethernet-wired clients and shares these identifiers with the Controller. This is done through an AP infrastructure using Internet Access Point Protocol (IAPP) messaging.
-
Establishes a single wireless connection to the root AP, which treats the WGB as a wireless client.
This mode is ideal for environments requiring wireless connectivity for wired devices that lack native wireless capabilities.
Use case of WGB mode
A factory floor uses wired devices such as sensors and PLCs, which lack built-in wireless connectivity. These devices connect to the WGB using Ethernet, and it bridges them to the wireless infrastructure through a single connection to the root AP.
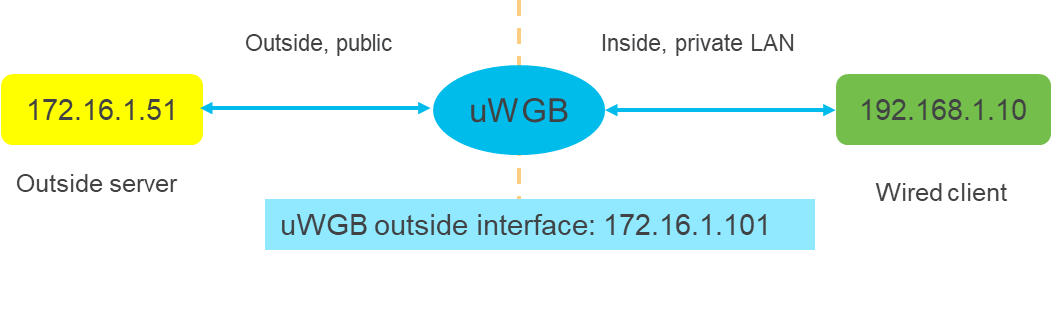
uWGB mode
uWGB mode is a complementary category to the WGB mode, designed to act as a wireless bridge between wired clients and wireless infrastructure.
-
Supports both Cisco and non-Cisco wireless networks.
-
Uses a wireless interface to connect with the AP, employing the radio MAC address for association.
-
Ensures that wired clients connected to the uWGB can access wireless networks seamlessly.
Use case of uWGB mode
A retail store employs a point-of-sale (POS) system with wired devices that require connectivity to a wireless network. uWGB connects these devices to the store's wireless infrastructure, supporting both Cisco and non-Cisco wireless networks. The uWGB uses its wireless interface to associate with the AP, enabling seamless communication between the wired POS devices and the wireless network.
Use both of these modes to efficiently extend wireless capabilities to wired devices to enhance both network scalability and flexibility.
Comparison of key features of WGB and uWGB modes
This table outlines the differences between these two modes.
|
Feature |
WGB mode |
uWGB mode |
|---|---|---|
|
Connectivity |
Cisco wireless networks only |
Cisco and non-Cisco wireless networks |
|
Interface usage |
Learns MAC addresses using Ethernet ports |
Uses radio MAC address for association |
WGB mode recommendations
Understand the limitations and restrictions of both WGB and uWGB modes to ensure optimal performance and avoid potential network issues.
-
The WGB can associate only with Cisco lightweight APs.
-
Speed and duplex settings are automatically negotiated based on the locally connected endpoint's capabilities. These settings cannot be manually configured on the AP’s wired 0 and wired 1 interfaces.
-
When the WGB roams to a foreign controller, a wired client can connect to the WGB network. In this case, the anchor controller shows the wired client’s IP address, but the foreign controller does not.
-
Deauthenticating a WGB record from a controller clears all entries of wired clients connected to that WGB.
-
Wired clients connected to a WGB do not support:
-
MAC filtering,
-
link tests,
-
idle timeout, and
-
web authentication.
-
-
A WGB cannot associate with a WLAN configured with adaptive 802.11r.
IPv6 and IPv4 support
-
The WGB supports IPv6 traffic exclusively for wired clients, even though IPv4 is enabled.
-
IPv6 management for the WGB does not function properly, even if the WGB successfully associates with an uplink. IPv6 pings and SSH to the WGB management IPv6 address do not work.
 Note |
Re-enable IPv6 on the WGB, even if it is already enabled and an IPv6 address has been assigned. |
Channel bandwidth issue
If the infrastructure AP operates on a non-dynamic frequency selection (non-DFS) channel and changes its channel bandwidth, the WGB continues to use the original channel bandwidth.
 Note |
Confirm that the WGB connects to the AP using the correct channel bandwidth. |
uWGB mode recommendations
-
TFTP and SFTP are not supported in uWGB mode. Perform software upgrades in WGB mode only. For more information, see uWGB Image Upgrade.
-
uWGB mode supports wired clients connected to the wired0 interface. However, it doesn't support wired clients connected to the wired1 interface.
-
You should configure an arbitrary non-routable IP address for uWGB. Using a static or dynamic IP address in the same range as the end device can result in unexpected behavior.
-
From UIW Release 17.13.1, an AP in uWGB mode is managed using SSH. Image upgrade can be performed when no wired clients are connected to the AP.
-
When a wired client is detected, the AP in uWGB mode remains in the same uWGB mode. You cannot upgrade the image of the AP.
-
When a wired client is not detected, the AP in uWGB mode switches to WGB mode. You can manage as well as upgrade the image of the AP.
-
Guidelines to reset the login credentials
Credential requirements
Reset your login credentials in day 0 to ensure the security of your network device. Follow these guidelines to configure new login credentials after the first login.
|
Rule type |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Username length |
must be between 1 and 32 characters |
|
Password length |
must be between 8 and 120 characters |
|
Password must include |
|
|
Password can include |
|
|
Password must exclude |
|
|
Password cannot |
|
|
Password must contain |
A new password that must have at least four characters different from the current password. |
Default credentials example:
Username: Cisco
Password: Cisco
Enable Password: Cisco
User credentials example:
Current Password:Cisco
Current Enable Password:Cisco
New User Name:demouser
New Password:DemoP@ssw0rd
Confirm New Password:DemoP@ssw0rd
New Enable Password:DemoE^aP@ssw0rd
Confirm New Enable Password:DemoE^aP@ssw0rd
 Note |
In the provided example, passwords are displayed in plain text for clarity. In real-world scenarios, passwords are masked with asterisks (*). |
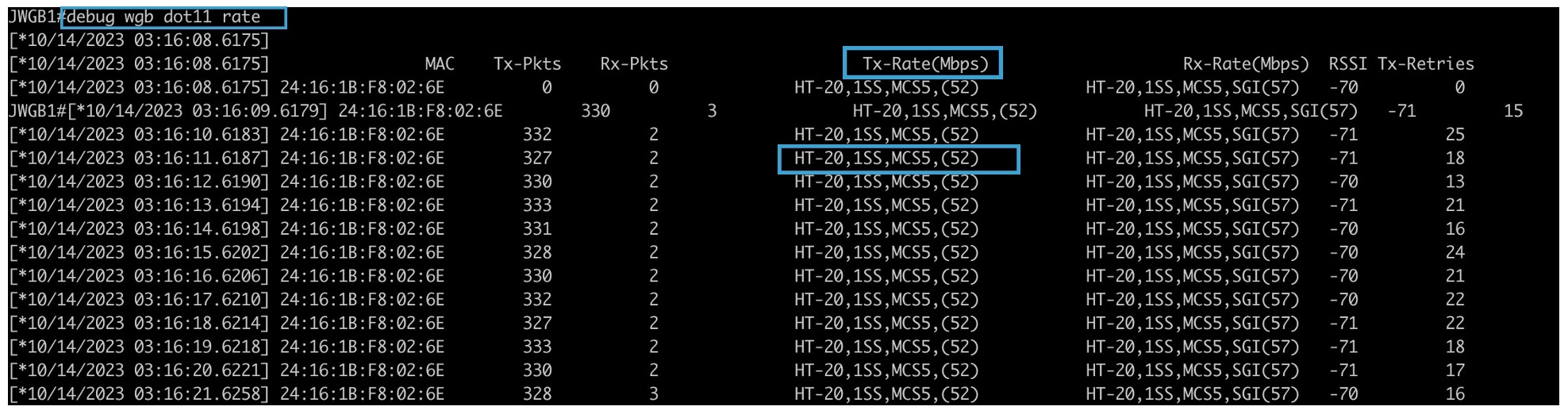
Know your AP status using LED indicators
LED patterns are indicator light sequences that display the operational status and signal strength of a device.
These patterns use visual cues, such as blinking or solid lights, to convey specific conditions or performance metrics. In the context of the IW9165E device, LED patterns help identify system status and signal quality.
IW9165E LED Indicators
The IW9165E device features two LEDs located on the front panel:
-
System Status LED
-
RSSI Status LED
|
LED |
Color or Pattern |
Indication |
|---|---|---|
|
System Status LED |
Blinking Red |
WGB is disassociated. |
|
Solid Green |
WGB is associated with the parent AP. |
|
| RSSI Status LED |
Solid Green |
RSSI ≥ -71 dBm. |
|
Blinking Green |
RSSI between -81 dBm and -70 dBm. |
|
|
Solid Yellow |
RSSI between -95 dBm and -81 dBm. |
|
|
Off |
RSSI outside specified ranges. |


 Feedback
Feedback