Release Notes for StarOS™ Software Version, Release 2025.04.gh0
Available Languages
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- US/Canada 800-553-2447
- Worldwide Support Phone Numbers
- All Tools
 Feedback
Feedback
StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
The key highlights of this release include:
● Additional KPI Counters in ePDG:Introduction of new and enhanced KPI counters for improved operational analytics and troubleshooting.
● Configure increased Pilot packet server limits: Network operators can nowconfigure maximum number of 8 pilot packet servers.
● IPv6 address pool utilization visibility: Administrators can now view used and free IPv6 address pool values through Show CLI commands.
● MME Validation on Supermicro Servers with CNDP: MME functionality tested and validated for deployment on Supermicro servers.
● Increased Access Control List (ACL) Capacity on ASR5500: Maximum rules per ACL increased from 128 to 256.
● Monitor subscriber enhancement for Non-VPP PGW-service: This feature enables comprehensive tracing and capture of subscriber control and user plane traffic on non-VPP PGW-Service nodes, generating detailed PCAP files for analysis.
● MME Emergency Profile selection based on IMSI range and service PLMN ID: MME supports handling network outages by enabling inter-operator roaming for emergency calls.
Qualified products and platforms
Table 1. Products and platforms qualified in this release
| Component |
Qualified? |
| Products |
|
| CUPS |
No |
| MME |
Yes |
| ePDG |
Yes |
| P-GW |
Yes |
| SAEGW |
Yes |
| SGSN |
Yes |
| Platforms |
|
| ASR 5500 |
No |
| VPC-DI |
Yes |
| VPC-SI |
Yes |
The following table provides EoL milestones for Cisco StarOS software:
Table 2. EoL milestone information for StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Milestone |
Date |
| First Customer Ship (FCS) |
31-Oct-2025 |
| End of Life (EoL) |
31-Oct-2025 |
| End of Software Maintenance (EoSM) |
01-May-2027 |
| End of Vulnerability and Security Support (EoVSS) |
01-May-2027 |
| Last Date of Support (LDoS) |
30-Apr-2028 |
This section provides a brief description of the new software features introduced in this release.
Table 3. New software features for StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Product impact |
Feature |
Description |
| Software reliability |
This release introduces new and enhanced KPI counters in ePDG for improved operational troubleshooting. Key features include:
● New bulkstat counters for Delete/Modify Bearer Response failure reasons,
● New bulkstat variables for counting number of idle sessions, with the idle duration configurable via CLI
● Extended Diameter Authentication KPI counters with detailed Error codes.
The feature supports 4G/5G segregation based on either N1 mode capability of UE or the type of GW (PGW or PGW-C+SMF) the session is latched. |
|
| Software reliability |
This feature allows network administrators to view the used and free IPv6 address pool values using show CLI commands, even when the Address Hold Timer (AHT) is disabled for those pools. |
|
| Software reliability |
MME Validation of Super Micro Server |
MME has been tested and validated for deployment on Supermicro servers, with CNDP serving as the underlying platform. |
| Software reliability |
Increases the maximum number of rules per Access Control List (ACL) from 128 to 256, supporting up to 2048 ACLs per context on ASR5500 platforms. |
|
| Upgrade |
This feature enables comprehensive tracing and capture of subscriber control and user plane traffic on non-VPP PGW-Service nodes, generating detailed PCAP files for analysis. It extends the Monitor Subscriber functionality by introducing a new CLI option to activate this capability. The system monitors multiple subscribers, capturing traffic and creating separate PCAP files with configurable naming conventions and storage locations, enhancing troubleshooting. CLI modified: monitor-subscriber-poll-timeout poll_timer_val_milliseconds monitor-subscriber-file-name {none | imsi | username | call_id} |
|
| Ease of use |
MME Emergency Profile Selection based on IMSI Range and Service PLMN ID |
This feature enhances MME capabilities to handle network outages by enabling inter-operator roaming for emergency calls. You can now configure LTE Emergency Profiles based on specific IMSI ranges and service PLMN IDs, ensuring communication services during disasters. It allows only authenticated emergency calls while rejecting other attach requests. This is achieved by associating LTE Emergency Profiles with operator policies, selected via IMSI and PLMN ID. Commands introduced:
●
enable-imsi-based-lte-emergency-profile
(under mme-service)
●
associate lte-emergency-profile
Commands updated:
●
attach restrict access-type eps [allow-emergency-auth ]
[ emm-cause-code <code>] (under call-control profile
●
show operator-policy full name
●
show operator-policy full all
●
show mme-service all
|
| Hardware reliability |
This feature allows you to configure maximum number of 8 pilot packet servers. Gateways can now send pilot packets to up to 8 IPv4 destination servers. Note: You cannot configure IPv6 address as pilot packet servers. |
This section provides a brief description of the behavior changes introduced in this release.
Table 4. Behavior changes for StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Description |
Behavior changes |
| Consistent SGW Downlink FAR Buffering in CSFB Suspend/Resume [CSCwq94647] |
Previous behavior: In the Circuit-Switched Fallback (CSFB) scenario, when a Radio Access Bearer (RAB) Release Request was received along with suspend and resume notifications, the system did not set the SGW downlink Forwarding Action Rule (FAR) to BUFFER due to a specific check. When only suspend and resume notifications were received (without the RAB Release Request), the SGW downlink FAR was moved to BUFFER, resulting in buffering of downlink data. New behavior: The check preventing the FAR action from moving to BUFFER when the RAB Release Request is present has been removed. This change ensures that the SGW consistently moves the downlink FAR to BUFFER during both scenarios—whether the RAB Release Request is received or not—providing uniform buffering behavior. Customer Impact: Customers will experience consistent buffering of downlink data during CSFB suspend and resume procedures regardless of the presence of a RAB Release Request. This leads to improved handling of downlink data buffering, avoiding discrepancies and potential data loss or forwarding inconsistencies during CSFB suspend and resume operations. |
| Improved Collision Handling for Bearer Requests [CSCwq79531] |
Previous Behavior: When a Pure S/Collapsed call was in progress and the system received an Update Bearer Request while the user equipment (UE) was transitioning from Idle to Active, and the SGW was already processing a Modify Bearer Request for the same transition, the Update Bearer Request was rejected with a "No Resource Available" message. New behavior: Now, if an Update Bearer Request arrives while the SGW is already processing a Modify Bearer Request for the same transition (Idle to Active), the SGW will silently drop the Update Bearer Request. The PGW will automatically retry, and the request will be processed successfully. Customer Impact: With this change, Update Bearer Requests in these scenarios are now retried and processed. |
| Allow N26 traffic over the S10 interface [CSCwr18465] |
Previous behavior: Interworking procedures that use the N26 interface enable the exchange of Mobility Management (MM) and Session Management (SM) states between the source and target network. The default eGTP service is supported on the N26 interface. However, N26 traffic is not allowed over the S10 interface in MME. New behavior: To allow N26 traffic over the S10 interface, enable the combine-n26-s10-interface command in the MME service configuration mode. Command changes: configure context context_name mme-service service_name [ no ] combine-n26-s10-interface exit combine-n26-s10-interface: This option lets N26 traffic over the S10 interface. If S10/S3-S11 Interface Separation is not enabled, N26 and S10 use the default EGTP-C instance or service. If S10/S3-S11 Interface Separation is enabled, N26 uses a separate EGTP-C instance or service linked to S10. S10 uses its own EGTP-C instance or service. no: The no option disables N26 traffic over the S10 interface. |
| Emergency Session Timer Handling Change [CSCwr06145] |
Previous behavior: For emergency sessions with MS network feature support enabled, if the T3412_extended timer was configured to either zero or a non-zero value in mme-service, the system considered the T3412_extended timer as the mobile reachability timer when moving to idle mode. New behavior: For emergency sessions with MS network feature support enabled, if the T3412_extended timer is configured to 0 in mme-service, the system now considers the standard T3412 timer as the mobile reachability timer when moving to idle mode, instead of the T3412_extended timer. |
This table lists the resolved issues in this specific software release.
Note: This software release may contain bug fixes first introduced in other releases. To see additional information, click the bug ID to access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. To search for a documented Cisco product issue, type in the browser: <bug number> site:cisco.com.
Table 5. Resolved issues for StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Bug ID |
Description |
Product Found |
| ePDG VPC-SI : dhmgr mem warn |
epdg |
|
| sessmgr reload in egtpc_get_pdn_rcvry_info() with rtt enabled |
epdg |
|
| Emergency Call Incorrect Implicit Detach |
mme |
|
| MME Collision Handling between E-RAB Release Indication and E-RAB Modification Indication |
mme |
|
| MME is sending Forward Relocation Response with incorrect local IPv6 address |
mme |
|
| sessmgr failure in Function: mme_emm_registered_idle_handle_im_exit_trigger() |
mme |
|
| UE detaches after 60 secs post MME handover to other MME |
mme |
|
| N26/S10 interface separation - allow N26 traffic over S10 interface |
mme |
|
| During X2 handover MME modifies NR UE Security Capabilities received in Path Switch Request prior returning it to eNB |
mme |
|
| Sessmgr restarts after SGW relocation with dedicated Bearers Deletion for MB Response delay with "context not found" scenarios. |
pdn-gw |
|
| Fatal Signal 11: failures observed due to sessmgr_dhcpv6app_api_release_address |
pdn-gw |
|
| Updates to a Group of Ruledefs triggers an mtree data structure rebuild, the configuration under the GOR retains old hash causing packet mismatches |
pdn-gw |
|
| sessmgr crash when using certain RG acsmgr_dcca_get_cca_n_premptive_request_rating_groups() |
pdn-gw |
|
| Add support for generating the pcap file from the hexdump for a monsub session of a PGW service |
pdn-gw |
|
| Legacy-GW ATT: ASR5500 chassis hwctrl process shows warn state in show task resources |
pdn-gw |
|
| PGW sending wrong ipv6 address format in IpAddress for starSRPIPAddress OID |
pdn-gw |
|
| Discrepancy observed while modification of 'cdr transfer-mode push' CLI |
pdn-gw |
|
| Sessmgr restarts after enabling VoLTE for specific inroamer IMSIs ranges |
pdn-gw |
|
| Sessmgr task restart at function sessmgr_get_ipv6_end_user_address() |
pdn-gw |
|
| 'disable rapid-commit-dhcpv6' command causing SRP Peer Checksum failure error during the image upgrade in Legacy |
pdn-gw |
|
| SGW calls are not getting created due to sessmgr assertion |
pdn-gw |
|
| NPU flow usage for L2TP increased on ICSR standby |
pdn-gw |
|
| session manager crash with an unknown signature time encoding data at smgr_gr_encode_uplane_call_info_uchckpt_cmd |
sae-gw |
|
| Assertion failure at midplane/libsn_midplane.c in SPGW |
sae-gw |
|
| Legacy-GW: Standby Sessmgr process restarts at while upgrading from 21.28.mh25 to 21.28.mh28 |
sae-gw |
|
| sessmgr reload at Function: is_dhcp_server_down() |
staros |
|
| Legacy-GW: kernel panic with sessmgr checkpointing issue observed in osp16 and osp17 setup |
staros |
|
| Unplanned SF migration caused diamproxy instance # out of range |
staros |
This table lists the open issues in this specific software release.
Note: This software release may contain open bugs first identified in other releases. To see additional information, click the bug ID to access the Cisco Bug Search Tool. To search for a documented Cisco product issue, type in the browser: <bug number> site:cisco.com.
Table 6. Open issues for StarOS™ Software, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Bug ID |
Description |
Product Found |
| Emergency call-garbage value seen in bulkstat and show mme-ser statistics lte-emergency-profile profile-name lte1 |
mme |
|
| Unexpected DeleteSessionRequest after UEContextReleaseRequest |
mme |
|
| CUTO Ctrl and VPP library version is not displaying |
sae-gw |
This section describes the known issue that may occur during the upgrade of the StarOS image.
Install and Upgrade Notes
This Release Note does not contain general installation and upgrade instructions. Refer to the existing installation documentation for specific installation and upgrade considerations.
When upgrading the StarOS image from a previous version to the latest version, issues may arise if there is a problem with the Cisco SSH/SSL upgrade. To avoid such issues, ensure that the boot file for Service Function (SF) cards is properly synchronized.
To synchronize the boot file for all the Service Function (SF) VPC-DI non-management cards, use the following CLI command:
[local] host_name# system synchronize boot
This ensures that the changes in boot file are identically maintained across the SF cards.
Note: Execute the system synchronize boot command before reloading for version upgrade from any version earlier than 21.28.mh14 to version 21.28.mh14 or versions higher than 21.28.mh14.
Upgrade the confd version
This section explains upgrading third-party software. Upgrade the confd software to ensure system compatibility and performance.
Note: During July 2025.03.0 release, confd is upgraded to 8.1.16.2 version.
Prerequisites
● Ensureyouhaveappropriatepermissionstoperformthisupgrade.
● Backupallnecessarydataandconfigurationstoavoidpermanentlossduringfiledeletion.
Perform these steps to upgrade the confd version on the system.
1. Enter the debug shell using debug shell command.
2. Navigate to the confd directory.
3. Run the command: cd /mnt/hd-raid/meta/confd/ to access the directory.
4. Remove existing files with the command; rm -rf *
All files and subdirectories are deleted, preparing the system for a fresh installation. To preserve data across the Method of Procedure, users with ConfD configured must contact their Cisco representative.
Method of Procedure (MOP): Upgrade/Downgrade Between Non-Hermes and Hermes Builds
CSCwr80301: HD-RAID Not Ready During Upgrade from Non-Hermes to Hermes
Issue: When upgrading from a non-Hermes (202x.0x.gx) to a Hermes (202x.0x.ghx) build on both Virtualized Packet Core—Distributed Instance (VPC-DI) and Virtualized Packet Core—Single Instance (VPC-SI) platforms, the HD-RAID may not come up as expected.
Workaround: To avoid this hd-raid failure, follow the steps below during the upgrade and downgrade (for example, from 2025.03.g0 to 2025.04.gh0):
1. Pre-requisite: Back up all files stored in /hd-raid before upgrading from the .mx to .mhx build.
Note: All data in /hd-raid will be lost during recovery.
2. Before the upgrade: On the .mx build, run the hd raid clear command.
3. Reboot and upgrade: Reboot the node to upgrade to the .mhx build.
4. Perform the CF card migration in case of VPC-DI or Reload the chassis on VPC-SI. Wait for the HD-RAID to recover.
Note: It is recommended to use this Method of Procedure (MOP) for both upgrading and downgrading between Hermes and Non-Hermes StarOS builds.
This section provides compatibility information about the StarOS package version, and the hardware and software requirements for the Legacy Gateway software release.
Compatible StarOS package version
Table 7. Release package version information
| StarOS packages |
Version |
Build number |
| StarOS package |
2025.04.gh0 |
21.28.mh31.99203 |
Compatible software and hardware components
This table lists only the verified basic software and hardware versions. For more information on the verified software versions for the products qualified in this release contact the Cisco account representative.
Table 8. Compatibility software and hardware information, Release 2025.04.gh0
| Product |
Version |
| ADC P2P Plugin |
2.74.gh0.2727 |
| ESC |
6.0.0.54 |
| CVIM |
5.0.4 |
| Host OS |
Ubuntu 22.04 / RHEL 8.4 |
| RedHat OpenStack |
RHOSP 16.2 |
| E810C NIC Version |
Driver version: ice 1.12.6 Firmware: 4.20 0x80018f67 0.387.18 |
| CIMC |
4.0 (4) |
| NED Package |
ncs-6.1.11.2-nso-mob-fp-3.5.2 -ad74d4f-2024-10-18T1052/ncs-6.1.11.2 -nso-mob-fp-3.5.2-ad74d4f-2024-10- 18T1052.tar.gz |
| NSO |
nso-mob-fp-3.5.2 |
This section provides information about the release packages associated with StarOS Classic Gateway, software.
Table 9. Software packages for Release 2025.04.gh0
| Description |
|
| NSO |
|
| nso-mob-fp-3.5.2-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the signed NSO software image, the signature file, a verification script, the x509 certificate, and a README file containing information on how to use the script to validate the certificate. |
| VPC companion package |
|
| companion-vpc-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains numerous files pertaining to this version of the VPC including SNMP MIBs, RADIUS dictionaries, ORBEM clients. These files pertain to both VPC-DI and VPC-SI, and for trusted and non-trusted build variants. |
| VPC-DI |
|
| qvpc-di-2025.04.gh0.bin.zip |
Contains the VPC-DI binary software image that is used to replace a previously deployed image on the flash disk in existing installations. |
| qvpc-di_T-2025.04.gh0.bin.zip |
Contains the trusted VPC-DI binary software image that is used to replace a previously deployed image on the flash disk in existing installations. |
| qvpc-di-2025.04.gh0.iso.zip |
Contains the VPC-DI ISO used for new deployments; a new virtual machine is manually created and configured to boot from a CD image. |
| qvpc-di_T-2025.04.gh0.iso.zip |
Contains the trusted VPC-DI ISO used for new deployments, a new virtual machine is manually created and configured to boot from a CD image. |
| qvpc-di-template-vmware-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the VPC-DI binary software image that is used to on-board the software directly into VMware. |
| qvpc-di-template-vmware_T-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the trusted VPC-DI binary software image that is used to on- board the software directly into VMware. |
| qvpc-di-template-libvirt-kvm-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the same VPC-DI ISO identified above and additional installation files for using it on KVM. |
| qvpc-di-template-libvirt-kvm_T-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the same trusted VPC-DI ISO identified above and additional installation files for using it on KVM. |
| qvpc-di-2025.04.gh0.qcow2.zip |
Contains the VPC-DI binary software image in a format that can be loaded directly with KVM using an XML definition file, or with OpenStack. |
| VPC-SI |
|
| intelligent_onboarding-2025.02.gh2.zip |
Contains the VPC-SI onboarding signature package that is used to replace a previously deployed image on the flash disk in existing installations. |
| qvpc-si-2025.04.gh0.bin.zip |
Contains the VPC-SI binary software image that is used to replace a previously deployed image on the flash disk in existing installations. |
| qvpc-si-2025.04.gh0.iso.zip |
Contains the VPC-SI ISO used for new deployment. A new virtual machine is manually created and configured to boot from a CD image. |
| qvpc-si-template-vmware-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the VPC-SI binary software image that is used to on-board the software directly into VMware. |
| qvpc-si-template-libvirt-kvm-2025.04.gh0.zip |
Contains the same VPC-SI ISO identified above and additional installation files for using it on KVM. |
| qvpc-si-2025.04.gh0.qcow2.zip |
Contains the VPC-SI binary software image in a format that can be loaded directly with KVM using an XML definition file, or with OpenStack. |
StarOS product version numbering system
The output of the show version command displays detailed information about the version of StarOS currently running on the ASR 5500 or Cisco Virtualized Packet Core platform.
Starting 2024.01.0 release (January 2024), Cisco is transitioning to a new release versioning scheme. The release version is based on the current year and product. Refer to the figure for more details.
Note: During the transition phase, some file names will reflect the new versioning whereas others will refer to the 21.28.x- based naming convention. With the next release, StarOS-related packages will be completely migrated to the new versioning scheme.
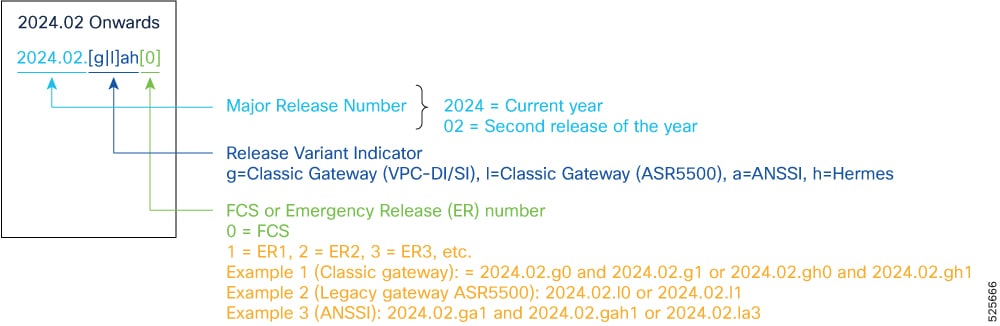
Note: For any clarification, contact your Cisco account representative.
Software integrity verification
To verify the integrity of the software image you have from Cisco, you can validate the SHA512 checksum information against the checksum identified by Cisco for the software. Image checksum information is available through Cisco.com Software Download details. Click Linux and then choose the Software Image Release Version.
To find the checksum, hover the mouse pointer over the software image you have downloaded. At the bottom you find the SHA512 checksum, if you do not see the whole checksum, you can expand it by pressing the "..." at the end.
To validate the information, calculate a SHA512 checksum using the information in the table and verify that it matches the one provided on the software download page. To calculate a SHA512 checksum on your local desktop see the table.
Table 10. Checksum calculations per operating system
| Operating system |
SHA512 checksum calculation command examples |
| Microsoft Windows |
Open a command line window and type the following command: > certutil.exe -hashfile <filename>.<extension> SHA512 |
| Apple MAC |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ shasum -a 512 filename.extension |
| Linux |
Open a terminal window and type the following command: $ sha512sum filename.extension OR $ shasum -a 512 filename.extension |
| Note: filename is the name of the file. extension is the file extension (for example, .zip or .tgz). |
|
If the SHA512 checksum matches, you can be sure that no one has tampered with the software image or the image has not been corrupted during download.
If the SHA512 checksum does not match, we advise you to not attempt upgrading any systems with the corrupted software image. Download the software again and verify the SHA512 checksum again. If there is a constant mismatch, please open a case with the Cisco Technical Assistance Center.
Certificate validation
In 2024.01 and later releases, software images for StarOS, VPC-DI, and VPC-SI, and the companion software packages for StarOS and VPC are signed via x509 certificates. USP ISO images are signed with a GPG key. For more information and instructions on how to validate the certificates, refer to the README file available with the respective software packages.
This table provides key resources and links to the support information and essential documentation for StarOS products.
Table 11. Related resources and additional information
| Resource |
Link |
| Cisco ASR 5500 documentation |
|
| Cisco Ultra Packet Core documentation |
|
| Service request and additional information |
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
© 2025 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Feedback
Feedback