- New and Changed Information
- Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices Overview
- Prepare Your Environment
- Deploy Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices
- Troubleshoot Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices
- Known Issues with Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices
- Important Items for Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices Deployments
- Partner Information for Cisco Spark Calling Organizations
Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices Overview
Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices
Cisco Spark Calling for Branch Offices is an evolutionary step in adding cloud collaboration services to your on-premises deployment. You may have sites that are too small to deploy on-premises environments at each site. Use this integrated solution if you have several smaller satellite offices (small store fronts or regional offices, spread throughout the country) that you want to be served from the cloud with messaging, meeting, and calling.
This solution lets you maintain your existing on-premises infrastructure and helps you extend it with cloud-delivered services. The tasks in this document help you integrate your Cisco Unified Communications Manager call control environment with Cisco Spark Calling.
With this cloud and on-premises deployment, you can:
-
Use your current carrier for long distance calling and other features.
-
Maintain control of your dial plan: have a common multisite dial plan that works across the premises and the Cisco Spark Calling cloud.
-
Use a pay-per-user per-month model through the Cisco Collaboration Flex subscription.
-
Extend your solution through the cloud, instead of deploying more hardware.
For reference, see the following illustration:
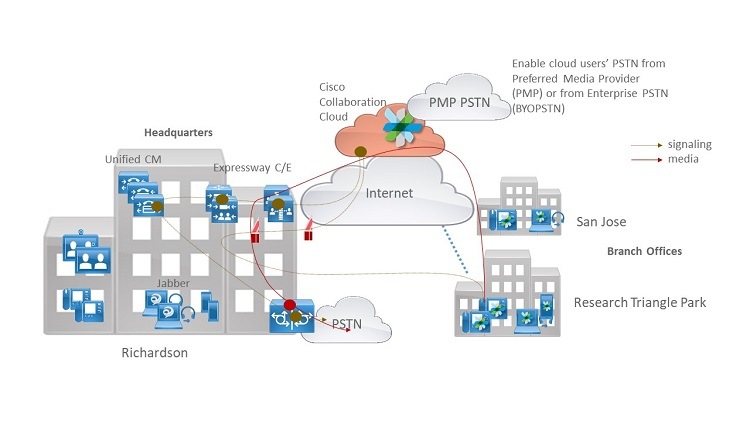
-
When users dial digits, calls are routed to and from Cisco Spark Calling phones and enterprise phones. Some features are not leveraged across the cloud and enterprise—For example, speed dial monitoring, call park, call pickup, voicemail, and so on.
-
The connection between the enterprise and Cisco Collaboration Cloud has the same functionality as a normal trunk.
-
This integration helps you add cloud-connected users in Cisco Spark Calling who are located on a separate site from the premises-based Unified Communications Manager (also known as multisite). This integration supports the following features: -
Unified Directory brings together enterprise and Cisco Spark Calling contacts in one space. It provides Cisco Spark users the ability to search for enterprise contacts in the directory on their Cisco Spark devices and make calls to enterprise contacts in addition to Cisco Spark Calling contacts. Calling functionality behaves the same for both types of users. This feature also provides edit dial functionality for contacts with only phone numbers.
In the contacts search result:
-
If contacts have a dialable URI (Cisco Spark SIP address) and phone number, the URI assocoiated with the contact is displayed.
-
If contacts do not have a diabable URI but do have a phone number, the phone number is shown. They also have an edit dial softkey.
-
If contacts have neither, they are not shown in the directory.
For your enterprise contacts to show up in search results, use the Directory Connector software to perform a directory synchronization.
-
-
This document builds upon the recommendations in the Cisco Preferred Architecture for Enterprise Collaboration. In the Dial Plan Configuration section, we provide a centralized call processing deployment that serves three main sites in the US (San Jose, Richardson, and Research Triangle Park).
-
In the diagram, the on-premises customer has other phone numbers (DIDs) that they already purchased; they wanted to use those numbers for the cloud users. Those numbers are configured on Cisco Spark Calling, but all calls route to enterprise destinations or to PSTN destinations (in case of bring your own PSTN).
-
To call between the on-premises site and the extended users in Cisco Spark Calling, an 8-digit enterprise significant number (ESN) dialing is required. An ESN is the abbreviated intersite dialing equivalent of a directory number.
Your extension lengths depend on your site-specific dial plan (abbreviated dialing) . The preferred architecture example uses 4 as the extension length. If you use 5 as the extension length, then you can use a two-digit routing prefix in your Unified Communications Manager enterprise configuration. While this example uses a routing prefix, it is not required.
| Site | +E.164 Range | Routing Prefix | ESN Range for DIDs | ESN Range for non-DIDs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Jose | +1 408 555 4XXX | 140 | 8-140-4XXX | 8-140-5XXX |
| Research Triangle Park | +1 919 555 1XXX | 140 | 8-140-1XXX | 8-140-2XXX |
| Richardson | +1 972 555 5XXX | 140 | 8-140-5XXX | 8-140-6XXX |
 Feedback
Feedback