- Index
- Preface
- Cisco Analog Telephone Adaptor Overview
- Installing the Cisco ATA
- Configuring the Cisco ATA for SCCP
- Adding the Cisco ATA to the Cisco CallManager
- Parameters and Defaults
- Configuring and Debugging Fax Services
- Upgrading the Cisco ATA Signaling Image
- Troubleshooting
- How to Use Pre-Call and Mid-Call Services
- Voice Menu Codes
- Cisco ATA Specifications
- Performing a Cross-Protocol Upgrade
- Recommended Cisco ATA Tone Parameter Values by Country
- Glossary
- Default Boot Load Behavior
- Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation
- Steps Needed to Configure the Cisco ATA
- Configuring the Cisco ATA Using a TFTP Server
Configuring the Cisco ATA for SCCP
This section describes how to configure the Cisco ATA to operate with the Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) signaling image and how the Cisco ATA obtains the latest signaling image.
You can configure the Cisco ATA for use with SCCP with any of the following methods:
•![]() By using the Cisco CallManager TFTP server—This is the Cisco-recommended method for deploying a large number of Cisco ATAs. This method allows you to set up a default configuration file for all Cisco ATAs in the network. Additionally, you can set up a configuration file that is unique to a specific Cisco ATA. When the Cisco ATA powers up or boots up from a reset, it automatically downloads its configuration file from the Cisco CallManager TFTP server and updates its configuration parameters.
By using the Cisco CallManager TFTP server—This is the Cisco-recommended method for deploying a large number of Cisco ATAs. This method allows you to set up a default configuration file for all Cisco ATAs in the network. Additionally, you can set up a configuration file that is unique to a specific Cisco ATA. When the Cisco ATA powers up or boots up from a reset, it automatically downloads its configuration file from the Cisco CallManager TFTP server and updates its configuration parameters.
•![]() By using manual configuration:
By using manual configuration:
–![]() Voice configuration menu—This is the method you must use if the process of establishing IP connectivity for the Cisco ATA requires changing the default network configuration settings. These settings are CDP, VLAN, and DHCP. You also can use the voice configuration menu to review all IP connectivity settings. The voice configuration menu can also be used when Web access is not available.
Voice configuration menu—This is the method you must use if the process of establishing IP connectivity for the Cisco ATA requires changing the default network configuration settings. These settings are CDP, VLAN, and DHCP. You also can use the voice configuration menu to review all IP connectivity settings. The voice configuration menu can also be used when Web access is not available.
–![]() Web-based configuration—This method is convenient if you plan to deploy a small number of Cisco ATAs in your network. To use this method, the Cisco ATA must first obtain IP connectivity, either through the use of a DHCP server or by using the voice configuration menu to statically configure IP addresses.
Web-based configuration—This method is convenient if you plan to deploy a small number of Cisco ATAs in your network. To use this method, the Cisco ATA must first obtain IP connectivity, either through the use of a DHCP server or by using the voice configuration menu to statically configure IP addresses.
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Default Boot Load Behavior—This section describes the process that the Cisco ATA follows by default when it boots up. It is very important to understand this process because, if your network environment is not set up to follow this default behavior, you need to make the applicable configuration changes. For example, by default, the Cisco ATA attempts to contact a DHCP server for the necessary IP addresses to achieve network connectivity. However, if your network does not use a DHCP server, you must manually configure various IP settings as described in this section.
Default Boot Load Behavior—This section describes the process that the Cisco ATA follows by default when it boots up. It is very important to understand this process because, if your network environment is not set up to follow this default behavior, you need to make the applicable configuration changes. For example, by default, the Cisco ATA attempts to contact a DHCP server for the necessary IP addresses to achieve network connectivity. However, if your network does not use a DHCP server, you must manually configure various IP settings as described in this section.
•![]() Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation—This section includes a table of the parameters you can configure for VLAN and CDP settings.
Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation—This section includes a table of the parameters you can configure for VLAN and CDP settings.
•![]() Steps Needed to Configure the Cisco ATA—This section provides tables that summarize the general configuration steps you must follow to configure the Cisco ATA.
Steps Needed to Configure the Cisco ATA—This section provides tables that summarize the general configuration steps you must follow to configure the Cisco ATA.
•![]() Configuring the Cisco ATA Using a TFTP Server—This section describes procedures for configuring the Cisco ATA by using a Cisco CallManager TFTP server, which is the recommended configuration method for the deployment of a large number of Cisco ATAs.
Configuring the Cisco ATA Using a TFTP Server—This section describes procedures for configuring the Cisco ATA by using a Cisco CallManager TFTP server, which is the recommended configuration method for the deployment of a large number of Cisco ATAs.
•![]() Voice Configuration Menu—This section includes information on how to obtain basic network connectivity for the Cisco ATA and how to perform a factory reset if necessary.
Voice Configuration Menu—This section includes information on how to obtain basic network connectivity for the Cisco ATA and how to perform a factory reset if necessary.
•![]() Cisco ATA Web Configuration Page—This section shows the Cisco ATA Web configuration page and contains a procedure for how to configure Cisco ATA parameters using this interface.
Cisco ATA Web Configuration Page—This section shows the Cisco ATA Web configuration page and contains a procedure for how to configure Cisco ATA parameters using this interface.
•![]() Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager—This section gives the procedure (via the Cisco CallManager administration web pages) for resetting the Cisco ATA so that your configuration changes take effect.
Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager—This section gives the procedure (via the Cisco CallManager administration web pages) for resetting the Cisco ATA so that your configuration changes take effect.
•![]() Upgrading the SCCP Signaling Image—This section provides references to the various means of upgrading your Cisco ATA signaling image.
Upgrading the SCCP Signaling Image—This section provides references to the various means of upgrading your Cisco ATA signaling image.

Note ![]() The term Cisco ATA is used throughout this manual to refer to both the Cisco ATA 186 and the Cisco ATA 188, unless differences between the Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 are explicitly stated.
The term Cisco ATA is used throughout this manual to refer to both the Cisco ATA 186 and the Cisco ATA 188, unless differences between the Cisco ATA 186 and Cisco ATA 188 are explicitly stated.
Default Boot Load Behavior
Before configuring the Cisco ATA, you need to know how the default Cisco ATA boot load process works. Once you understand this process, you will be able to configure the Cisco ATA by following the instructions provided in this section and in the sections that follow.
All Cisco ATAs are shipped with a boot load signaling-protocol image. However, because this image is not a fully functional Cisco ATA image, the Cisco ATA seeks to obtain the image-load information from the Cisco CallManager and perform a software upgrade. In addition, the Cisco ATA obtains the necessary SCCP-specific configuration files for Cisco CallManager communication and the Cisco ATA configuration file during the boot load process.
The following list summarizes the default Cisco ATA behavior during its boot-up process:
1. ![]() The Cisco ATA uses the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to discover which VLAN to enter. If the Cisco ATA receives a VLAN ID response from the network switch, the Cisco ATA enters that VLAN and adds 802.1Q VLAN tags to its IP packets. If the Cisco ATA does not receive a response with a VLAN ID from the network switch, then the Cisco ATA assumes it is not operating in a VLAN environment and does not perform VLAN tagging on its packets.
The Cisco ATA uses the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to discover which VLAN to enter. If the Cisco ATA receives a VLAN ID response from the network switch, the Cisco ATA enters that VLAN and adds 802.1Q VLAN tags to its IP packets. If the Cisco ATA does not receive a response with a VLAN ID from the network switch, then the Cisco ATA assumes it is not operating in a VLAN environment and does not perform VLAN tagging on its packets.

Note ![]() If your network environment is not set up to handle this default behavior, make the necessary configuration changes by referring to the "Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation" section.
If your network environment is not set up to handle this default behavior, make the necessary configuration changes by referring to the "Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation" section.
2. ![]() The Cisco ATA contacts the DHCP server to request its own IP address.
The Cisco ATA contacts the DHCP server to request its own IP address.

Note ![]() If your network environment does not contain a DHCP server, you need to statically configure various IP addresses so that the Cisco ATA can obtain network connectivity. For a list of parameters that you must configure to obtain network connectivity, see Table 3-7. For instructions on how to use the voice configuration menu, which you must use to perform this configuration, see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section.
If your network environment does not contain a DHCP server, you need to statically configure various IP addresses so that the Cisco ATA can obtain network connectivity. For a list of parameters that you must configure to obtain network connectivity, see Table 3-7. For instructions on how to use the voice configuration menu, which you must use to perform this configuration, see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section.
3. ![]() Also from the DHCP server, the Cisco ATA requests the IP address of the Cisco CallManager TFTP server.
Also from the DHCP server, the Cisco ATA requests the IP address of the Cisco CallManager TFTP server.
4. ![]() The Cisco ATA contacts the Cisco CallManager TFTP server and downloads the appropriate .xml or .cnf configuration file that allows the Cisco ATA to communicate with the correct Cisco CallManager.
The Cisco ATA contacts the Cisco CallManager TFTP server and downloads the appropriate .xml or .cnf configuration file that allows the Cisco ATA to communicate with the correct Cisco CallManager.
5. ![]() The .xml or .cnf file that the Cisco ATA downloads includes information about which signaling image the Cisco ATA needs to function properly. The Cisco ATA finds that image on the TFTP server and automatically downloads this image along with the corresponding version of Cisco ATA release software.
The .xml or .cnf file that the Cisco ATA downloads includes information about which signaling image the Cisco ATA needs to function properly. The Cisco ATA finds that image on the TFTP server and automatically downloads this image along with the corresponding version of Cisco ATA release software.

Note ![]() If you are not using a Cisco CallManager TFTP server, you need to manually upgrade the Cisco ATA to the correct signaling image. For information on this procedure, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Manually" section on page 7-4.
If you are not using a Cisco CallManager TFTP server, you need to manually upgrade the Cisco ATA to the correct signaling image. For information on this procedure, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Manually" section on page 7-4.
6. ![]() The Cisco ATA looks for a Cisco ATA-specific configuration file (designated by the MAC address of the Cisco ATA and named ata<macaddress> with a possible extension) on the TFTP server and downloads this file if it exists. For information about possible configuration file names, see the "Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates" section.
The Cisco ATA looks for a Cisco ATA-specific configuration file (designated by the MAC address of the Cisco ATA and named ata<macaddress> with a possible extension) on the TFTP server and downloads this file if it exists. For information about possible configuration file names, see the "Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates" section.
7. ![]() If the Cisco ATA does not find the MAC-address configuration file, it looks for an atadefault.cfg configuration file and downloads this file if it exists. This file can contain default values for the Cisco ATA to use.
If the Cisco ATA does not find the MAC-address configuration file, it looks for an atadefault.cfg configuration file and downloads this file if it exists. This file can contain default values for the Cisco ATA to use.

Note ![]() When the Cisco ATA is downloading its DHCP configuration, the function button on the top panel blinks.
When the Cisco ATA is downloading its DHCP configuration, the function button on the top panel blinks.
Specifying a Preconfigured VLAN ID or Disabling VLAN IP Encapsulation
If you want the Cisco ATA to use a preconfigured VLAN ID instead of using the Cisco Discovery Protocol to locate a VLAN, or if you want to disable VLAN IP encapsulation, refer to Table 3-1 for a reference to the parameters and bits you may need to configure. Use the voice configuration menu to configure these parameters. (See the "Voice Configuration Menu" section for instructions on using this menu.) Also, refer to Table 3-2 for a matrix that indicates which VLAN-related parameters and bits to configure depending on your network environment.

Note ![]() Bits are numbered from right to left, starting with bit 0.
Bits are numbered from right to left, starting with bit 0.
N/A indicates that the variable is not applicable to the feature and the setting of this variable does not affect the feature.
Example
The following procedure shows you how to configure the OpFlags and VLANSetting parameters to allow the Cisco ATA to use a user-specified VLAN ID. In this example, the voice VLAN ID is 115 (in decimal format).
Step 1 ![]() Set bits 4-6 of the OpFlags parameter to 1, 0, and 1, respectively. This setting translates to the following bitmap:
Set bits 4-6 of the OpFlags parameter to 1, 0, and 1, respectively. This setting translates to the following bitmap:
xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx x101 xxxx
The remaining bits of the OpFlags parameter, using all default values, make up the following bitmap representation:
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0xxx 0010
Therefore, the resulting value of the OpFlags parameter becomes the following bitmap representation:
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101 0010
In hexadecimal format, this value is 0x00000052.
Step 2 ![]() Set bits 18-29 of the VLANSetting parameter to voice VLAN ID 115. This setting translates to the following bitmap
Set bits 18-29 of the VLANSetting parameter to voice VLAN ID 115. This setting translates to the following bitmap
xx00 0001 1100 11xx xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx
where 000001110011 is the binary representation of the decimal value 115.
The remaining bits of the VLANSetting parameter, using all default values, make up the following representation:
00xx xxxx xxxx xx00 0000 0000 0010 1011
Therefore, the resulting value of the VLANSetting parameter becomes the following bitmap representation:
0000 0001 1100 1100 0000 0000 0010 1011
In hexadecimal format, this value is 0x01cc002b.

Note ![]() If you are using the voice configuration menu to set the parameters, you must convert hexadecimal values to decimal values. For example, the OpFlags setting of 0x00000052 is equivalent to 82 in decimal format, and the VLANSetting of 0x01cc002b is equivalent to 30146603 in decimal format.
If you are using the voice configuration menu to set the parameters, you must convert hexadecimal values to decimal values. For example, the OpFlags setting of 0x00000052 is equivalent to 82 in decimal format, and the VLANSetting of 0x01cc002b is equivalent to 30146603 in decimal format.
Steps Needed to Configure the Cisco ATA
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Basic Configuration Steps in a Cisco CallManager TFTP Server Environment
Basic Configuration Steps in a Cisco CallManager TFTP Server Environment
•![]() Basic Configuration Steps in a Non-TFTP Server Environment
Basic Configuration Steps in a Non-TFTP Server Environment
Basic Configuration Steps in a Cisco CallManager TFTP Server Environment
Table 3-3 shows the basic steps for configuring the Cisco ATA and making it operational in a typical SCCP environment, which includes a Cisco CallManager TFTP server.
|
|
|
|---|---|
1. |
|
2. Note |
|
3. |
Configuring the Cisco ATA to Obtain its Configuration File from the TFTP Server |
4. |
|
5. |
|
6. |
|
7. |
Basic Configuration Steps in a Non-TFTP Server Environment
Table 3-4 shows the basic steps for configuring the Cisco ATA without using the TFTP server method.
|
|
|
|---|---|
1. a. b. c. 
Note |
|
2. |
|
3. |
|
4. |
|
5. |
Configuring the Cisco ATA Using a TFTP Server
The TFTP method of configuration is useful when you have many Cisco ATA because you can use a TFTP server for remote, batch configuration of Cisco ATAs. A TFTP server can host one unique configuration file for each Cisco ATA.
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Setting Up the TFTP Server with Cisco ATA Software
Setting Up the TFTP Server with Cisco ATA Software
•![]() Configurable Features and Related Parameters
Configurable Features and Related Parameters
•![]() Creating a Cisco ATA Default Configuration File
Creating a Cisco ATA Default Configuration File
•![]() Creating a Configuration File for a Specific Cisco ATA
Creating a Configuration File for a Specific Cisco ATA
•![]() Configuring the Cisco ATA to Obtain its Configuration File from the TFTP Server
Configuring the Cisco ATA to Obtain its Configuration File from the TFTP Server
Setting Up the TFTP Server with Cisco ATA Software
This section provides the procedure for the Cisco ATA administrator to obtain the correct Cisco ATA software and set up the Cisco CallManager TFTP server with this software.
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() If you are a registered CCO user. go to the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ata186
If you are a registered CCO user. go to the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ata186
Step 2 ![]() Download the zip file that contains the software for the applicable release and signaling image you are using. The contents of each file are described next to the file name. Save the zip file onto a floppy disc.
Download the zip file that contains the software for the applicable release and signaling image you are using. The contents of each file are described next to the file name. Save the zip file onto a floppy disc.

Note ![]() The file that contains the protocol signaling image has an extension of .zup.
The file that contains the protocol signaling image has an extension of .zup.
Step 3 ![]() Insert the floppy disc into the Cisco CallManager disc drive.
Insert the floppy disc into the Cisco CallManager disc drive.
Step 4 ![]() From your computer, navigate to Start > Programs > Terminal Services > Client. The Terminal Services Client screen appears.
From your computer, navigate to Start > Programs > Terminal Services > Client. The Terminal Services Client screen appears.
Step 5 ![]() In the Services field of the Terminal Services Client screen, enter the IP address of the Cisco CallManager that contains the disc you inserted. Then, click the Connect button. The Login screen appears.
In the Services field of the Terminal Services Client screen, enter the IP address of the Cisco CallManager that contains the disc you inserted. Then, click the Connect button. The Login screen appears.
Step 6 ![]() Enter your login information, then click OK. The TFTP Path screen appears.
Enter your login information, then click OK. The TFTP Path screen appears.
Step 7 ![]() Click on the My Computer icon that is located within the Terminal Services Client screen, then navigate to the A: drive.
Click on the My Computer icon that is located within the Terminal Services Client screen, then navigate to the A: drive.
Step 8 ![]() From the A: drive, drag the zip file to the TFTP Path screen. This will extract all the files and place them onto the Cisco CallManager TFTP server.
From the A: drive, drag the zip file to the TFTP Path screen. This will extract all the files and place them onto the Cisco CallManager TFTP server.
Configurable Features and Related Parameters
Table 3-5 lists, in alphabetical order, various features that you can configure for the Cisco ATA. Table 3-5 also includes links to the related parameter that allows you to configure each of these features. Each link takes you to a detailed description of the parameter that includes its default values.
For an example of how to configure parameters for the TFTP Server configuration method, see the "Creating a Cisco ATA Default Configuration File" section.
|
|
|
|---|---|
Audio Media Features • • • • |
Audio Media Parameters |
Caller ID format |
|
Debug and Diagnostics |
NPrintf, page 5-37, TraceFlags, page 5-38, SyslogIP, page 5-38, SyslogCtrl, page 5-39 |
Fax Services Features • • |
Fax Services Parameters • |
Hook-flash detection timing configuration |
|
Mid-call service format—Bellcore, Cisco VG248 or Cisco ATA |
|
Network-related Features • • • • • • |
Network-related Parameters • • • |
SCCP Terminal-related Features • • • • • |
SCCP Terminal-related Parameters • |
User Interface and TFTP Features • • • • |
User Interface and TFTP Parameters • • |
Packet Precedence Features • • |
Packet Precedence Parameters |
Polarity settings for FXS ports |
|
Tone format: BusyTone, CallWaitTone |
|
Tone parameters—Using Network Locale option versus using Cisco ATA tone parameters |
ConnectMode, page 5-21—Bit 0 |
Version control of Cisco ATA configuration file |
CFGID—Version Parameter for Cisco ATA Configuration File, page 5-40 |
Creating a Cisco ATA Default Configuration File
The Cisco ATA release-software zip files includes a file called atadefault.cfg, which is a binary file that contains all the default parameters for the Cisco ATA. However, you likely will need to create your own atadefault.cfg file to contain the default settings that you want Cisco ATAs in your environment to use. For information on each configuration parameter, including all default values, see Chapter 5, "Parameters and Defaults."
Use the text file called sk_example.txt as a basis for creating your default file. The sk_example.txt file is included in the software-release zip file and contains all default values. This file is shown without its annotations in the "Configuration Text File Template" section on page 5-2.
The following procedure illustrates how to create the Cisco ATA default configuration file, convert it to the required binary format that the Cisco ATA can read, and store it on the TFTP server so that the Cisco ATA will download it during the boot-up process:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Make a copy of the sk_example.txt file and rename it atadefault.txt.
Make a copy of the sk_example.txt file and rename it atadefault.txt.
Step 2 ![]() Make the desired configuration changes by editing the atadefault.txt file, then save the file.
Make the desired configuration changes by editing the atadefault.txt file, then save the file.
Step 3 ![]() Convert the atadefault.txt file to a binary file by running the cfgfmt.exe tool, which is bundled with the Cisco ATA software.
Convert the atadefault.txt file to a binary file by running the cfgfmt.exe tool, which is bundled with the Cisco ATA software.

Note ![]() If you wish to encrypt the binary file for security reasons, see the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section. If you encrypt the file using the EncryptKeyEx parameter, the resulting binary file will be called atadefault.cfg.x; if not encrypted with the EncryptKeyEx parameter the resulting binary file name will be atadefault.cfg.
If you wish to encrypt the binary file for security reasons, see the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section. If you encrypt the file using the EncryptKeyEx parameter, the resulting binary file will be called atadefault.cfg.x; if not encrypted with the EncryptKeyEx parameter the resulting binary file name will be atadefault.cfg.
The syntax of the cfgfmt program follows:
Syntax
cfgfmt [Encryption options] -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
–![]() Encryption options are described in the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
Encryption options are described in the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
–![]() sccp is the protocol you are using, which you must specify so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the applicable protocol in the converted output binary file.
sccp is the protocol you are using, which you must specify so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the applicable protocol in the converted output binary file.
–![]() The ptag.dat file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by cfgfmt.exe to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
The ptag.dat file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by cfgfmt.exe to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
–![]() input-text-file is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
input-text-file is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
–![]() output-binary-file is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
output-binary-file is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
Example
cfgfmt -sccp -tptag.dat atadefault.txt atadefault
Step 4 ![]() Store the binary configuration file in the TFTP server root directory, overwriting the atadefault.cfg file that came bundled with the release-software download.
Store the binary configuration file in the TFTP server root directory, overwriting the atadefault.cfg file that came bundled with the release-software download.
During the boot-up process, the Cisco ATA will download the output file as its configuration file unless it first finds a Cisco ATA-specific configuration file named for the MAC address of the Cisco ATA. (If you want to create a MAC-address configuration file for a specific Cisco ATA, see the "Creating a Configuration File for a Specific Cisco ATA" section.)

Note ![]() If you want to make configuration changes after boot up, repeat the process of creating or editing the text file containing the desired parameters, then converting the text file to the binary file and storing the binary file on the TFTP server. For the configuration changes to take effect, reset the Cisco ATA. (See the "Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager" section.)
If you want to make configuration changes after boot up, repeat the process of creating or editing the text file containing the desired parameters, then converting the text file to the binary file and storing the binary file on the TFTP server. For the configuration changes to take effect, reset the Cisco ATA. (See the "Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager" section.)
Creating a Configuration File for a Specific Cisco ATA
Once you have booted up the Cisco ATA, you may decide that you want to create a configuration file that is specific to one Cisco ATA.
The following procedure illustrates how to create a Cisco ATA-specific configuration file, convert it to the required binary format that the Cisco ATA can read, and store it on the TFTP server so that the Cisco ATA will download it as soon as you reset the Cisco ATA.
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Open the atadefault.txt file that you created when you developed your own default file. Find the parameters whose values you want to change for this specific Cisco ATA. Copy only these parameters into a new text file. Save the new text file with the following name:
Open the atadefault.txt file that you created when you developed your own default file. Find the parameters whose values you want to change for this specific Cisco ATA. Copy only these parameters into a new text file. Save the new text file with the following name:
ata<macaddress>.txt
where macaddress is the non-dotted hexadecimal version of the MAC address of the Cisco ATA you are configuring. This non-dotted hexadecimal MAC address is labeled on the bottom of most Cisco ATAs next to the word "MAC." The file name must be exactly 15 characters long. (However, if this filename is supplied by the DHCP server, the name can be as long as 31 characters and can be any name with printable ASCII characters.)
If necessary, you can obtain the non-dotted hexadecimal MAC address by using the atapname.exe command. For information on using the atapname.exe command, see the "Using atapname.exe Tool to Obtain MAC Address" section. That section includes an example of a dotted decimal MAC address and its corresponding non-dotted hexadecimal address.

Note ![]() The ata<macaddress>.txt file should contain only those parameters whose values you are changing from their defaults. Parameter values in the ata<macaddress> configuration file will overwrite any manually configured values (values configured through the web or voice configuration menu) when the Cisco ATA powers up or resets.
The ata<macaddress>.txt file should contain only those parameters whose values you are changing from their defaults. Parameter values in the ata<macaddress> configuration file will overwrite any manually configured values (values configured through the web or voice configuration menu) when the Cisco ATA powers up or resets.
Example
You might want to change the values of the following parameters, whose default values are shown first:
LBRCodec:3
AudioMode:0x00350035
You could change the values as follows:
LBRCodec:0
AudioMode:0x00350034
Step 2 ![]() Save your changes.
Save your changes.
Step 3 ![]() Run the cfgfmt.exe tool, which is bundled with the Cisco ATA software, on the ata<macaddress>.txt text file to generate the binary configuration file. If you wish to encrypt the binary file, see the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
Run the cfgfmt.exe tool, which is bundled with the Cisco ATA software, on the ata<macaddress>.txt text file to generate the binary configuration file. If you wish to encrypt the binary file, see the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
The syntax of the cfgfmt program follows:
Syntax
cfgfmt [Encryption options] -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
–![]() Encryption options are described in the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
Encryption options are described in the "Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool" section.
–![]() sccp is the protocol you are using, which you must specify so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the applicable protocol in the converted output binary file.
sccp is the protocol you are using, which you must specify so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the applicable protocol in the converted output binary file.
–![]() The ptag.dat file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by cfgfmt.exe to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
The ptag.dat file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by cfgfmt.exe to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
–![]() input-text-file is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
input-text-file is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
–![]() output-binary-file is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
output-binary-file is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
Example
cfgfmt -sccp -tptag.dat ata0a141e28323c.txt ata0a141e28323c
This example is based on a Cisco ATA MAC address of 10.20.30.40.50.60, which converts to the two-digit, lower-case hexadecimal representation of each integer as 0a141e28323c.
Step 4 ![]() Store all binary configuration file(s) in the TFTP server root directory. For information about possible configuration file names, see the "Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates" section.
Store all binary configuration file(s) in the TFTP server root directory. For information about possible configuration file names, see the "Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates" section.
Step 5 ![]() Reset the Cisco ATA using the Cisco CallManager. (See the "Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager" section on page 3-23.)
Reset the Cisco ATA using the Cisco CallManager. (See the "Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager" section on page 3-23.)
After being reset, the Cisco ATA will download this ata<macaddress> binary configuration file as its unique configuration file. This file takes precedence over the atadefault.cfg file. If the Cisco ATA finds an ata<macaddress> file on the TFTP server, the Cisco ATA does not look for the atadefault.cfg file.
Using atapname.exe Tool to Obtain MAC Address
This bundled tool is useful for converting the dotted decimal version of the Cisco ATA MAC address (available on the Cisco ATA Web configuration page or from the voice configuration menu code 24#) to its default Cisco ATA profile name. This name has the following format:
ataxxxxxxxxxxxx
where each xx is the two-digit, lower-case hexadecimal representation of each integer in the dotted, decimal version of the Cisco ATA MAC address. This is the name you use for the unique Cisco ATA binary configuration file.
The following command and output show an example of this command.
Command Example
atapname.exe 10.20.30.40.50.60
Command Output
ata0a141e28323c

Note ![]() The same functionality is available from the voice configuration menu (voice menu code 84#), which will announce the Cisco ATA profile name.
The same functionality is available from the voice configuration menu (voice menu code 84#), which will announce the Cisco ATA profile name.
Using Encryption With the cfgfmt Tool
The EncryptKey or EncryptKeyEx parameter can be used to encrypt binary files that are transferred over TFTP. You can change encryption keys for each Cisco ATA so that only one specific Cisco ATA can decode the information.
Cisco strongly recommends using the EncryptKeyEx parameter for encryption because this parameter provides a stronger encryption than the EncryptKey parameter that was used in Cisco ATA software releases prior to release 2.16.
You must use version 2.3 of the cfgfmt configuration-file generation tool to use the new EncryptKeyEx parameter. This tools comes bundled with Cisco ATA software version 3.0. To verify that you have version 2.3 of the cfgfmt tool type the following command:
cfgfmt
The version number of the cfgfmt tool will be returned.
You can configure the EncryptKeyEx parameter by using the Cisco ATA Web configuration page or by using the TFTP configuration method. (For more information, see the "EncryptKeyEx" section on page 5-7.)
You can configure the EncryptKey parameter by using the Cisco ATA Web configuration page, the voice configuration menu, or by using the TFTP configuration method. (For more information, see the "EncryptKey" section on page 5-6.)
By default, the Cisco ATA-specific ata<macaddress> configuration file(s) are not encrypted. If encryption is required, however, you must manually configure the EncryptKeyEx or EncryptKey parameter before you boot up the Cisco ATA so that the TFTP method is secure. The Cisco ATA uses the RC4 cipher algorithm for encryption.

Note ![]() Because the factory-fresh ATA cannot accept encrypted configuration files, the first unencrypted file, if intercepted, can easily be read. (You would still have to know the data structure format in order to decode the binary information from the unencrypted file.) Therefore, the new encryption key in the unencrypted file can be compromised.
Because the factory-fresh ATA cannot accept encrypted configuration files, the first unencrypted file, if intercepted, can easily be read. (You would still have to know the data structure format in order to decode the binary information from the unencrypted file.) Therefore, the new encryption key in the unencrypted file can be compromised.

Note ![]() For security reasons, Cisco recommends that you set the UIPassword parameter (if desired) in the configuration file and not by using one of the manual configuration methods.
For security reasons, Cisco recommends that you set the UIPassword parameter (if desired) in the configuration file and not by using one of the manual configuration methods.
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates
Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates
•![]() cfgfmt Tool Syntax and Examples
cfgfmt Tool Syntax and Examples
Configuration Files that the cfgfmt Tool Creates
The number of output binary configuration files that the Cisco ATA produces is dependent on two factors:
•![]() Which encryption key parameter is used—EncryptKey or EncryptKeyEx
Which encryption key parameter is used—EncryptKey or EncryptKeyEx
•![]() The total size of the binary output
The total size of the binary output
Table 3-6 shows the names of the binary files that can be generated. One, two or four files can be generated.

Note ![]() <macaddress> in Table 3-6 is the MAC address of the Cisco ATA.
<macaddress> in Table 3-6 is the MAC address of the Cisco ATA.

Note ![]() If you are creating an atadefault configuration file, the generated binary file name will be atadefault.cfg.x if you encrypt the text file with the EncryptKeyEx parameter; the binary file name will be atadefault.cfg if you do not use the EncryptKeyEx parameter to encrypt the text file.
If you are creating an atadefault configuration file, the generated binary file name will be atadefault.cfg.x if you encrypt the text file with the EncryptKeyEx parameter; the binary file name will be atadefault.cfg if you do not use the EncryptKeyEx parameter to encrypt the text file.

Note ![]() Place all generated binary configuration files onto the TFTP server.
Place all generated binary configuration files onto the TFTP server.
cfgfmt Tool Syntax and Examples
The syntax of the cfgfmt tool follows:
Syntax
cfgfmt [options] input output
Syntax Definitions—Options
•![]() -eRc4Passwd—This option directs the Cisco ATA to use Rc4Passwd as the key (up to eight hexadecimal characters) to encrypt or decrypt the input text file. However, if the Cisco ATA EncryptKey parameter in the input text file is not 0, then the value of that parameter is used to encrypt the output binary file, and Rc4Passwd is ignored. The -e portion of this option means that the Cisco ATA will use the weaker encryption method.
-eRc4Passwd—This option directs the Cisco ATA to use Rc4Passwd as the key (up to eight hexadecimal characters) to encrypt or decrypt the input text file. However, if the Cisco ATA EncryptKey parameter in the input text file is not 0, then the value of that parameter is used to encrypt the output binary file, and Rc4Passwd is ignored. The -e portion of this option means that the Cisco ATA will use the weaker encryption method.
•![]() -E—This option directs the Cisco ATA to not use the value of the EncryptKey parameter, as set in the input text file, to encrypt the output binary configuration file.
-E—This option directs the Cisco ATA to not use the value of the EncryptKey parameter, as set in the input text file, to encrypt the output binary configuration file.
•![]() -xRc4Passwd—This option directs the Cisco ATA to use Rc4Passwd, which must be a hexadecimal string of as many as 64 characters, as the key to encrypt or decrypt the input text file. However, if the Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx parameter in the input text file is not 0, then the value of that parameter is used to encrypt the output binary file, and Rc4Passwd is ignored. The -x portion of this option means that the Cisco ATA will use the stronger encryption method.
-xRc4Passwd—This option directs the Cisco ATA to use Rc4Passwd, which must be a hexadecimal string of as many as 64 characters, as the key to encrypt or decrypt the input text file. However, if the Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx parameter in the input text file is not 0, then the value of that parameter is used to encrypt the output binary file, and Rc4Passwd is ignored. The -x portion of this option means that the Cisco ATA will use the stronger encryption method.
•![]() -X—This option directs the Cisco ATA to not use the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter, as set in the input text file, to encrypt the output binary configuration file.
-X—This option directs the Cisco ATA to not use the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter, as set in the input text file, to encrypt the output binary configuration file.
•![]() -tPtag.dat—This file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by the cfgfmt tool to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
-tPtag.dat—This file, provided with the Cisco ATA software version you are running, is used by the cfgfmt tool to format a text input representation of the parameter/value pairs to its output binary representation. Be sure this file resides in the same directory from which you are running the cfgfmt program.
•![]() -sip—Specify this tag if you are using the SIP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the SIP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
-sip—Specify this tag if you are using the SIP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the SIP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
•![]() -h323—Specify this tag if you are using the H.323 protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the H.323 protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
-h323—Specify this tag if you are using the H.323 protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the H.323 protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
•![]() -mgcp—Specify this tag if you are using the MGCP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the MGCP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
-mgcp—Specify this tag if you are using the MGCP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the MGCP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
•![]() -sccp—Specify this tag if you are using the SCCP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the SCCP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
-sccp—Specify this tag if you are using the SCCP protocol so that the cfgfmt tool will include only the SCCP protocol parameters in the converted output binary file.
•![]() -g—This tag omits sensitive parameters in an ata<macaddress> file that was created with a version of the cfgfmt tool prior to version 2.3.
-g—This tag omits sensitive parameters in an ata<macaddress> file that was created with a version of the cfgfmt tool prior to version 2.3.
Some parameters, specified in the ptag.dat file used by the cfgfmt tool, are marked as sensitive information (these parameters could include UIPassword, UID, PWD0). These parameters are not included in the output binary file if the -g switch is specified in the cfgfmt syntax.
Syntax Definitions—Required Parameters
•![]() Input—This is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
Input—This is the input text file representation of the Cisco ATA configuration file.
•![]() Output—This is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
Output—This is the final output binary file that Cisco ATA uses as the TFTP configuration file.
Syntax examples
The cfgfmt.exe syntax affects how the EncryptKeyEx or EncryptKey parameters are used, as shown in the following examples. In these examples, input-text-file is the ata<macaddress>.txt file that you will convert to binary to create the ata<macaddress> configuration file(s) for the Cisco ATA; output-binary-file is that binary ata<macaddress> file, and Secret is the encryption key.
•![]() cfgfmt -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
cfgfmt -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
If input-text-file sets the Cisco ATA EncryptKey parameter to 0, then output-binary-file is not encrypted. If the input-text-file sets EncryptKey to a non-zero value, then output-binary-file is encrypted with that value.
•![]() cfgfmt -X -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
cfgfmt -X -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
This is an example of how you might perform encryption on a first-time Cisco ATA.
The -X (uppercase) option means that any value specified for the Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx parameter in input-text-file is ignored. However, because Secret is not specified in this example, output-binary-file is not encrypted. Nevertheless, the EncryptKeyEx parameter and its value, if specified in input-file-text, will be included in output-binary-file for possible encryption at a later time. The next time the Cisco ATA fetches the configuration file from the TFTP server, the file will be encrypted with Secret.
•![]() cfgfmt -X -xSecret -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
cfgfmt -X -xSecret -sccp -tptag.dat input-text-file output-binary-file
This is an example of changing the encryption key from one key to another key.
The -X (uppercase) option means that any value specified for the Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx parameter in input-text-file is ignored and the output-binary-file is encrypted with the Secret key. However, the EncryptKeyEx parameter and its value, if specified in input-text-file, will be included in output-binary-file.
Examples of Upgrading to Stronger Encryption Key
This section contains two examples of how you would upgrade your Cisco ATA configuration to use the stronger encyrption method if the current Cisco ATA firmware version was a version earlier than version 2.16.2. Versions earlier than 2.16.2 do not support the stronger EncryptKeyEx parameter.
Example 1
In this example, the Cisco ATA has not yet been deployed, but its firmware version is earlier than 2.16.2. Therefore, the Cisco ATA will upgrade to to firmware version 3.0 to use the EncryptKeyEx parameter as its encryption key.
The Cisco ATA in this example has a MAC address of 102030405060.
Perform the following steps:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Create a file called ata102030405060.txt by using the applicable example.txt file provided with the Cisco ATA software. (For example, for SCCP, the example.txt file is called sk_example.txt.)
Create a file called ata102030405060.txt by using the applicable example.txt file provided with the Cisco ATA software. (For example, for SCCP, the example.txt file is called sk_example.txt.)
Step 2 ![]() Modify the ata102030405060.txt file with desired parameter values. The value of the EncryptKey parameter should be 0.
Modify the ata102030405060.txt file with desired parameter values. The value of the EncryptKey parameter should be 0.
Step 3 ![]() Set the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter to the chosen encryption key with which you want the output binary file to be encrypted. In the EncryptKeyEx parameter specified in the configuration file, you can also restrict the EncryptKeyEx value to apply only to the Cisco ATA with a particular MAC address. For example, if the chosen key value is 231e2a7f10bd7fe, you can specify EncryptKeyEx as:
Set the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter to the chosen encryption key with which you want the output binary file to be encrypted. In the EncryptKeyEx parameter specified in the configuration file, you can also restrict the EncryptKeyEx value to apply only to the Cisco ATA with a particular MAC address. For example, if the chosen key value is 231e2a7f10bd7fe, you can specify EncryptKeyEx as:
EncryptKeyEx:231e2a7f10bd7fe/102030405060
This means that only the Cisco ATA with the MAC address 102030405060 will be allowed to apply this EncryptKeyEx value to its internal configuration.
Step 4 ![]() Update the upgradecode parameter to instruct the Cisco ATA to upgrade to firmware version 3.0 by means of TFTP configuration. The upgradecode parameter is described in Chapter 7, "Upgrading the Cisco ATA Signaling Image."
Update the upgradecode parameter to instruct the Cisco ATA to upgrade to firmware version 3.0 by means of TFTP configuration. The upgradecode parameter is described in Chapter 7, "Upgrading the Cisco ATA Signaling Image."
Step 5 ![]() Run the cfgfmt tool as follows:
Run the cfgfmt tool as follows:
cfgfmt -g ata102030405060.txt ata102030405060
This will generate the following two binary configuration files:
•![]() ata102030405060
ata102030405060
•![]() ata102030405060.x
ata102030405060.x
ata102030405060 is unencrypted.
ata102030405060.x is encrypted with EncryptKeyEx value.
Step 6 ![]() Place these two files on the TFTP server that the Cisco ATA will contact for its configuration files.
Place these two files on the TFTP server that the Cisco ATA will contact for its configuration files.
When the Cisco ATA powers up, it will obtain its IP address from the DHCP server. If the DHCP server specifies the TFTP server address, the Cisco ATA will contact the TFTP server obtained from DHCP because the Cisco ATA is not preconfigured with a TFTP server address. The boot process is as follows:
a. ![]() The Cisco ATA downloads the configuration file ata102030405060 from the TFTP server.
The Cisco ATA downloads the configuration file ata102030405060 from the TFTP server.
b. ![]() The Cisco ATA applies parameter values in the file ata102030405060 to its internal configuration while ignoring the EncryptKeyEx parameter (because the older version of the Cisco ATA does not yet recognize the EncryptKeyEx parameter).
The Cisco ATA applies parameter values in the file ata102030405060 to its internal configuration while ignoring the EncryptKeyEx parameter (because the older version of the Cisco ATA does not yet recognize the EncryptKeyEx parameter).
c. ![]() The Cisco ATA upgrades to the 3.0 firmware load.
The Cisco ATA upgrades to the 3.0 firmware load.
d. ![]() The Cisco ATA reboots.
The Cisco ATA reboots.
e. ![]() The Cisco ATA again downloads the configuration file ata102030405060.
The Cisco ATA again downloads the configuration file ata102030405060.
f. ![]() The Cisco ATA applies the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter to its internal configuration.
The Cisco ATA applies the value of the EncryptKeyEx parameter to its internal configuration.
g. ![]() The Cisco ATA reboots.
The Cisco ATA reboots.
h. ![]() The Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx value is in effect, so from this point forward the Cisco ATA will download the ata102030405060.x file at each reboot and each time the value configured in the CfgInterval parameter expires.
The Cisco ATA EncryptKeyEx value is in effect, so from this point forward the Cisco ATA will download the ata102030405060.x file at each reboot and each time the value configured in the CfgInterval parameter expires.

Note ![]() Although EncryptKeyEx is encrypted in the ata<macaddress> file, and the ata<macaddress> file does not contain other sensitive information, Cisco recommends that for absolute security you pre-configure the Cisco ATA as described in this example for a private network. Alternatively, you should remove ata<macaddress> once EncryptKeyEx takes effect.
Although EncryptKeyEx is encrypted in the ata<macaddress> file, and the ata<macaddress> file does not contain other sensitive information, Cisco recommends that for absolute security you pre-configure the Cisco ATA as described in this example for a private network. Alternatively, you should remove ata<macaddress> once EncryptKeyEx takes effect.
Example 2
In this example, a new Cisco ATA has already been deployed (with the EncryptKey value set) with a firmware version earlier than 2.16.2. The Cisco ATA needs to be upgraded to version 2.16.2 firmware or greater to use EncryptKeyEx parameter to encrypt its configuration file.
In this scenario, you would follow the same procedure as in Example 1, except that you would need to set the EncryptKey value to the previously configured EncryptKey value. The difference is that the ata<macaddress> file is now encrypted with EncryptKey because the Cisco ATA expects the ata<macaddress> file to be encrypted with EncryptKey. The Cisco ATA can then begin using the ata<macaddress>.x file that is encrypted with the EncryptKeyEx parameter.
Configuring the Cisco ATA to Obtain its Configuration File from the TFTP Server
This section describes three methods from which to choose how the Cisco ATA contacts the TFTP server to obtain its configuration file:
–![]() The Cisco ATA contacts the DHCP server, which provides the IP address of the TFTP server
The Cisco ATA contacts the DHCP server, which provides the IP address of the TFTP server
–![]() The Cisco ATA uses the DHCP server but the DHCP server does not know about TFTP server
The Cisco ATA uses the DHCP server but the DHCP server does not know about TFTP server

Note ![]() In the rare instance where no TFTP server is used, you must manually configure the CA0orCM0 parameter to instruct the Cisco ATA about how to register with Cisco CallManager. For this scenario, see the "CA0orCM0 and CA1orCM1" section on page 5-12.
In the rare instance where no TFTP server is used, you must manually configure the CA0orCM0 parameter to instruct the Cisco ATA about how to register with Cisco CallManager. For this scenario, see the "CA0orCM0 and CA1orCM1" section on page 5-12.
Using a DHCP Server
When using a DHCP server, configuration settings vary depending on whether or not the DHCP server is under the control of the Cisco ATA system administrator or the service provider. The simplest configuration is when the DHCP server is under the control of the Cisco ATA administrator, in which case the DHCP server provides the IP address of the TFTP server. Depending on who controls the DHCP server, follow the applicable configuration procedure:
•![]() Procedure if DHCP Server is Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
Procedure if DHCP Server is Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
•![]() Procedure if DHCP Server is not Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
Procedure if DHCP Server is not Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
This section also includes the topic:
•![]() Other DHCP Options You Can Set
Other DHCP Options You Can Set

Note ![]() If no DHCP server is found and the Cisco ATA is programmed to find one, the function button continues to blink.
If no DHCP server is found and the Cisco ATA is programmed to find one, the function button continues to blink.
Procedure if DHCP Server is Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() On the DHCP server, set one of the following three options:
On the DHCP server, set one of the following three options:
•![]() DHCP option 150 (TFTP server IP address and, if applicable, IP address of alternate TFTP server).
DHCP option 150 (TFTP server IP address and, if applicable, IP address of alternate TFTP server).
•![]() DHCP field siaddr (TFTP server IP address). This field can be used by systems such as Cisco Integrated Communications Services (ICS).
DHCP field siaddr (TFTP server IP address). This field can be used by systems such as Cisco Integrated Communications Services (ICS).
•![]() Standard DHCP option 66 (TFTP server name and, if applicable, name of alternate TFTP server).
Standard DHCP option 66 (TFTP server name and, if applicable, name of alternate TFTP server).
If you use DHCP option 150, the Cisco ATA will ignore the DHCP siaddr field and DHCP option 66. If DHCP option 150 is not used, the Cisco ATA next looks for the DHCP field siaddr. If neither DHCP option 150 nor the siaddr field are available, the Cisco ATA looks for DHCP option 66. If you use DHCP option 66 or the DHCP siaddr field, you must turn off DHCP option 150 or set its value to 0.

Note ![]() You can turn off the DHCP option 150 request by using the Cisco ATA OpFlags parameter (see the "OpFlags" section on page 5-24).
You can turn off the DHCP option 150 request by using the Cisco ATA OpFlags parameter (see the "OpFlags" section on page 5-24).
Step 2 ![]() Make sure to use default values for the following Cisco ATA parameters:
Make sure to use default values for the following Cisco ATA parameters:
•![]() TftpUrl=0
TftpUrl=0
•![]() AlttftpURL=0
AlttftpURL=0
•![]() UseTftp=1
UseTftp=1
•![]() DHCP=1
DHCP=1
•![]() CA0orCM0=0
CA0orCM0=0
This completes the parameter settings and DHCP options you need to configure for this procedure. The Cisco ATA will contact the DHCP server for the IP address of the TFTP server that contains the Cisco ATA configuration file.

Note ![]() If you are configuring an alternate TFTP server, you can choose to configure its IP address or URL with the AlttftpURL parameter (see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5) instead of with DHCP option 150. In this situation, the AlttftpURL will not be 0, as indicated in Step 2 of this procedure.
If you are configuring an alternate TFTP server, you can choose to configure its IP address or URL with the AlttftpURL parameter (see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5) instead of with DHCP option 150. In this situation, the AlttftpURL will not be 0, as indicated in Step 2 of this procedure.
Procedure if DHCP Server is not Under Control of Cisco ATA Administrator
This is the procedure to use if the DHCP server is not under the control of the Cisco ATA administrator, which means that the URL of the TFTP server must be manually configured.
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Using the voice configuration menu, set the parameter TftpURL to the IP address or URL of the TFTP server. For more information on setting the TftpURL parameter, see the "TftpURL" section on page 5-4. For information about using the Cisco ATA voice configuration menu, see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section.
Using the voice configuration menu, set the parameter TftpURL to the IP address or URL of the TFTP server. For more information on setting the TftpURL parameter, see the "TftpURL" section on page 5-4. For information about using the Cisco ATA voice configuration menu, see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section.

Note ![]() If you are not using a DHCP server to provide the TFTP server location, you must manually configure the TftfURL. You can do this by using the voice configuration menu without first obtaining network connectivity for the Cisco ATA. If you want to configure this value using the Web configuration page, you first must obtain network connectivity by using the voice configuration menu to statically configure IP address information (see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section).
If you are not using a DHCP server to provide the TFTP server location, you must manually configure the TftfURL. You can do this by using the voice configuration menu without first obtaining network connectivity for the Cisco ATA. If you want to configure this value using the Web configuration page, you first must obtain network connectivity by using the voice configuration menu to statically configure IP address information (see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section).
Step 2 ![]() If you have an alternate TFTP server that you also want to configure with the Cisco ATA configuration process, set the AlttftpURL parameter to the IP address or URL of the alternate TFTP server. For more information about the AlttftpURL parameter, see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5.
If you have an alternate TFTP server that you also want to configure with the Cisco ATA configuration process, set the AlttftpURL parameter to the IP address or URL of the alternate TFTP server. For more information about the AlttftpURL parameter, see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5.
Step 3 ![]() Use the default value of 1 for the Cisco ATA parameter DHCP.
Use the default value of 1 for the Cisco ATA parameter DHCP.
Step 4 ![]() Use the default value of 1 for the Cisco ATA parameter UseTftp.
Use the default value of 1 for the Cisco ATA parameter UseTftp.
Step 5 ![]() Use the default value of 0 for the Cisco ATA parameter CA0orCM0.
Use the default value of 0 for the Cisco ATA parameter CA0orCM0.
This completes the parameter settings you need to configure for this procedure. The Cisco ATA will contact the manually configured TFTP server that contains the Cisco ATA configuration file.
Other DHCP Options You Can Set
The following parameters can also be configured with DHCP:
•![]() Boot file name of DHCP header—The ata<macaddress> binary Cisco ATA configuration file, which can have a maximum of 31 characters and can be any name with printable ASCII characters
Boot file name of DHCP header—The ata<macaddress> binary Cisco ATA configuration file, which can have a maximum of 31 characters and can be any name with printable ASCII characters
•![]() Client PC address
Client PC address
•![]() DHCP option 1—Client Subnet Mask
DHCP option 1—Client Subnet Mask
•![]() DHCP option 3—Routers on the client's subnet
DHCP option 3—Routers on the client's subnet
•![]() DHCP option 6—One or two Domain Name servers
DHCP option 6—One or two Domain Name servers

Note ![]() DHCP options 43 and 60 are set by the Cisco ATA. Option 43 specifies the protocol and option 60 identifies the vendor class of the Cisco ATA box.
DHCP options 43 and 60 are set by the Cisco ATA. Option 43 specifies the protocol and option 60 identifies the vendor class of the Cisco ATA box.
Without Using a DHCP Server
Use the following procedure if you are not using a DHCP server in your environment but are still using a TFTP server to obtain the Cisco ATA configuration file:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Set the DHCP parameter to 0.
Set the DHCP parameter to 0.
Step 2 ![]() Set the UseTftp parameter to 1.
Set the UseTftp parameter to 1.
Step 3 ![]() Set the Cisco ATA parameter TftpURL to the IP address or URL of the TFTP server. For more information on setting the TftpURL parameter, see the "TftpURL" section on page 5-4.
Set the Cisco ATA parameter TftpURL to the IP address or URL of the TFTP server. For more information on setting the TftpURL parameter, see the "TftpURL" section on page 5-4.

Note ![]() If you are not using a DHCP server to provide the TFTP server location, you must manually enter the TftpURL using either the voice configuration menu or the web configuration page.
If you are not using a DHCP server to provide the TFTP server location, you must manually enter the TftpURL using either the voice configuration menu or the web configuration page.
Step 4 ![]() If applicable, set the Cisco ATA parameter AlttftpURL to the IP address or URL of the alternate TFTP server. For more information about the AlttftpURL parameter, see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5.
If applicable, set the Cisco ATA parameter AlttftpURL to the IP address or URL of the alternate TFTP server. For more information about the AlttftpURL parameter, see the "AlttftpURL" section on page 5-5.
Step 5 ![]() If you have not already done so, statically configure the following parameters using the voice configuration menu (see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section). These are the parameters you need to configure for the Cisco ATA to obtain network connectivity:
If you have not already done so, statically configure the following parameters using the voice configuration menu (see the "Voice Configuration Menu" section). These are the parameters you need to configure for the Cisco ATA to obtain network connectivity:
•![]() StaticIP
StaticIP
•![]() StaticRoute
StaticRoute
•![]() StaticNetMask
StaticNetMask
Other parameters that are normally supplied by DHCP may be provided statically by configuring their values. These parameters are:
•![]() DNS1IP
DNS1IP
•![]() DNS2IP
DNS2IP
•![]() Domain
Domain
This completes the parameter settings you need to configure in order for the Cisco ATA to contact the TFTP server (without using DHCP) that will contain the configuration file for the Cisco ATA.
Voice Configuration Menu
The main reasons to use the voice configuration menu are to establish IP connectivity for the Cisco ATA if a DHCP server is not being used in your network environment, and to reset the Cisco ATA to its factory values if necessary. You can also use the voice configuration menu if you need to configure a small number of parameters or if the web interface and TFTP configuration are not available.

Note ![]() Do not use the voice configuration menu to attempt to change any values that you configured by means of the TFTP configuration file method. Whenever the Cisco ATA resets, it downloads its ata<macaddress> configuration file or atadefault.cfg default configuration file from the TFTP server, and the values in either of these files will overwrite the values of any corresponding parameters configured with the voice configuration menu.
Do not use the voice configuration menu to attempt to change any values that you configured by means of the TFTP configuration file method. Whenever the Cisco ATA resets, it downloads its ata<macaddress> configuration file or atadefault.cfg default configuration file from the TFTP server, and the values in either of these files will overwrite the values of any corresponding parameters configured with the voice configuration menu.
See Chapter 5, "Parameters and Defaults," for a complete list of parameters and their definitions. Also see Table 3-5 for an alphabetical listing of configurable features and references to their corresponding parameters.
This section contains the following topics:
•![]() Using the Voice Configuration Menu
Using the Voice Configuration Menu
•![]() Resetting the Cisco ATA to Factory Default Values
Resetting the Cisco ATA to Factory Default Values
Using the Voice Configuration Menu
To manually configure the Cisco ATA by using the voice configuration menu and the telephone keypad, perform the following steps:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Connect an analog touch-tone phone to the port labeled Phone 1 on the back of the Cisco ATA.
Connect an analog touch-tone phone to the port labeled Phone 1 on the back of the Cisco ATA.
Step 2 ![]() Lift the handset and press the function button located on the top of the Cisco ATA. You should receive the initial voice configuration menu voice prompt.
Lift the handset and press the function button located on the top of the Cisco ATA. You should receive the initial voice configuration menu voice prompt.
Step 3 ![]() Using the telephone keypad, enter the voice menu code for the parameter that you want to configure or the command that you want to execute, then press #. For a list of voice menu codes, see Appendix B, "Voice Menu Codes."
Using the telephone keypad, enter the voice menu code for the parameter that you want to configure or the command that you want to execute, then press #. For a list of voice menu codes, see Appendix B, "Voice Menu Codes."
Table 3-7 lists the menu options that you need to configure basic IP connectivity for the Cisco ATA, after which you can use the Cisco ATA web configuration page to configure additional parameters.

Note ![]() If you are using the voice configuration menu to statically configure the Cisco ATA IP address, you must disable DHCP by setting its value to 0.
If you are using the voice configuration menu to statically configure the Cisco ATA IP address, you must disable DHCP by setting its value to 0.
Step 4 ![]() Follow the voice prompts and enter the appropriate values, then press the # key.
Follow the voice prompts and enter the appropriate values, then press the # key.

Note ![]() Use the * key to indicate a delimiter (dot). For example, to enter an IP address of 192.168.3.1, you would enter 192*168*3*1 on your telephone keypad.
Use the * key to indicate a delimiter (dot). For example, to enter an IP address of 192.168.3.1, you would enter 192*168*3*1 on your telephone keypad.

Note ![]() When entering values for a field that contains a hexadecimal value, you must convert the hexadecimal value to a decimal value in order to enter it into the voice configuration menu system. For example, to enter the hexadecimal value 0x6A, you would enter the number 106 on the telephone keypad.
When entering values for a field that contains a hexadecimal value, you must convert the hexadecimal value to a decimal value in order to enter it into the voice configuration menu system. For example, to enter the hexadecimal value 0x6A, you would enter the number 106 on the telephone keypad.
The voice configuration menu repeats the value you entered, then prompts you to press one of the following keys:
•![]() 1=Change your entered value
1=Change your entered value
•![]() 2=Review your entered value
2=Review your entered value
•![]() 3=Save your entered value
3=Save your entered value
•![]() 4=Review the current saved value
4=Review the current saved value
Step 5 ![]() Cisco strongly recommends that you set a password. Use the voice menu code 7387277 (SETPASS) to configure a password through the voice configuration menu, after which you are prompted for the password whenever you attempt to change a parameter value.
Cisco strongly recommends that you set a password. Use the voice menu code 7387277 (SETPASS) to configure a password through the voice configuration menu, after which you are prompted for the password whenever you attempt to change a parameter value.
Step 6 ![]() After completing the configuration through the voice configuration menu, press the # key to exit.
After completing the configuration through the voice configuration menu, press the # key to exit.
Step 7 ![]() Hang up the telephone. The Cisco ATA configuration refreshes. The function button fast-blinks when the refresh is completed.
Hang up the telephone. The Cisco ATA configuration refreshes. The function button fast-blinks when the refresh is completed.
Entering Alphanumeric Values
Some voice configuration menu options require you to enter alphanumeric characters. Alphanumeric entry differs from numeric entry because you must press # after each character selected.
If you need to enter an alphanumeric value, the voice prompt tells you to enter an alphanumeric value; otherwise, enter a numeric value (0 to 9).
Table 3-8 lists the keys on a telephone keypad and their respective alphanumeric characters.
Using Table 3-8 as a guide, enter the appropriate number key on the telephone keypad as many times as needed to select the number, letter, or symbol required. For example, to enter 58sQ, you would enter:
5 # 8 # 7 7 7 7 7 # 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 # #
Resetting the Cisco ATA to Factory Default Values
It is possible that you may, under some circumstances, want to reset the Cisco ATA to its factory default values. For example, this is the only way to recover a forgotten password without contacting your Cisco representative.
To perform a factory reset, you must use the voice configuration menu and follow these steps:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Press the function button on the Cisco ATA.
Press the function button on the Cisco ATA.
Step 2 ![]() Press the digits 322873738 (FACTRESET) then press # on the telephone keypad.
Press the digits 322873738 (FACTRESET) then press # on the telephone keypad.
Step 3 ![]() Press * on your telephone keypad to confirm that you want to reset the Cisco ATA, then hang up the phone.
Press * on your telephone keypad to confirm that you want to reset the Cisco ATA, then hang up the phone.
Cisco ATA Web Configuration Page
You can use the Cisco ATA web configuration page in a non-TFTP configuration environment, or in a TFTP configuration environment as a read-only record of individual customer parameters.
Figure 3-1 shows an example of the Cisco ATA web configuration page, which displays all configurable parameters.

Note ![]() Do not use the web configuration page to attempt to change any values that you configured by means of the TFTP configuration file method. Whenever the Cisco ATA resets, it downloads its ata<macaddress> configuration file or atadefault.cfg default configuration file from the TFTP server, and the values in either of these files will overwrite the values of any corresponding parameters configured with the Web configuration method.
Do not use the web configuration page to attempt to change any values that you configured by means of the TFTP configuration file method. Whenever the Cisco ATA resets, it downloads its ata<macaddress> configuration file or atadefault.cfg default configuration file from the TFTP server, and the values in either of these files will overwrite the values of any corresponding parameters configured with the Web configuration method.
Figure 3-1 Cisco ATA Web Configuration Page
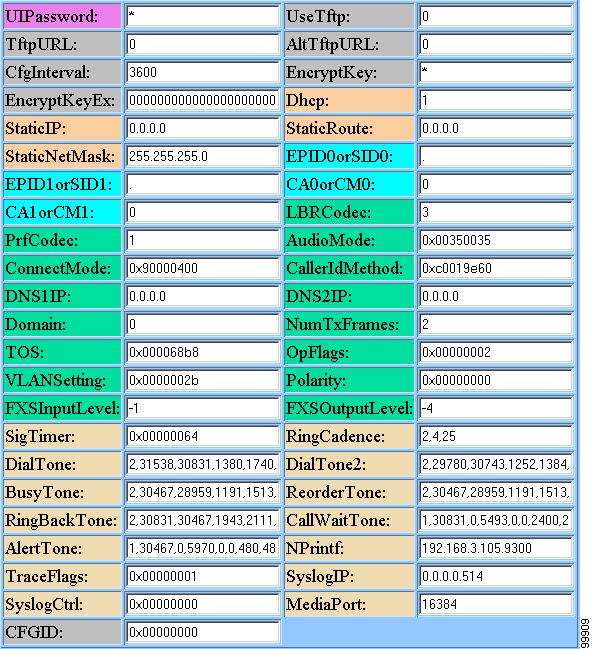
You can access the web configuration page from any graphics-capable browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape. This provides easy initial access to the Cisco ATA configuration within the administrator's private network.
Follow these steps to set parameters using the web configuration page:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Make sure that your PC and the Cisco ATA are already networked and visible to each another.
Make sure that your PC and the Cisco ATA are already networked and visible to each another.
Step 2 ![]() Open your web browser.
Open your web browser.
Step 3 ![]() Enter the URL for your configuration page. The default URL for the web server is:
Enter the URL for your configuration page. The default URL for the web server is:
http://IP Address/dev
For example, the configuration page for a Cisco ATA with the IP address 192.168.3.225 is:
http://192.168.3.225/dev
Step 4 ![]() Select the values for the items that you want to configure. See Chapter 5, "Parameters and Defaults," for a complete list of parameters and their definitions. Also see Table 3-5 for an alphabetical listing of configurable features and references to their corresponding parameters.
Select the values for the items that you want to configure. See Chapter 5, "Parameters and Defaults," for a complete list of parameters and their definitions. Also see Table 3-5 for an alphabetical listing of configurable features and references to their corresponding parameters.

Note ![]() Cisco strongly recommends that you set a password. Use the UIPassword parameter to configure a password, after which you are prompted for the password whenever you attempt to change a parameter value. Configuration parameters cannot be accessed through the voice configuration menu if the password contains one or more letters and can be changed only by using the web interface or the TFTP configuration method.
Cisco strongly recommends that you set a password. Use the UIPassword parameter to configure a password, after which you are prompted for the password whenever you attempt to change a parameter value. Configuration parameters cannot be accessed through the voice configuration menu if the password contains one or more letters and can be changed only by using the web interface or the TFTP configuration method.
Step 5 ![]() Click apply to save your changes.
Click apply to save your changes.
The Cisco ATA automatically refreshes its configuration.
Step 6 ![]() Close your web browser.
Close your web browser.
Resetting the Cisco ATA Using Cisco CallManager
Whenever you make configuration changes to the Cisco ATA, you must reset the Cisco ATA using the Cisco CallManager for these configuration changes to take effect. To reset the Cisco ATA, use the following procedure:
Procedure
Step 1 ![]() Go to the main Cisco CallManager Administration screen.
Go to the main Cisco CallManager Administration screen.
Step 2 ![]() Using voice configuration menu code 21, review the Cisco ATA IP address.
Using voice configuration menu code 21, review the Cisco ATA IP address.
Step 3 ![]() From the Device pull-down menu, select Phone. The Find and List Phones screen appears.
From the Device pull-down menu, select Phone. The Find and List Phones screen appears.
Step 4 ![]() In the area next to the Find button, enter a portion or all of the Cisco ATA MAC address, then press Find. The Find and List Phones screen reappears, and now contains the Cisco ATAs that match the find criteria you entered in the previous screen.
In the area next to the Find button, enter a portion or all of the Cisco ATA MAC address, then press Find. The Find and List Phones screen reappears, and now contains the Cisco ATAs that match the find criteria you entered in the previous screen.
Step 5 ![]() Click the icon of the Cisco ATA that you would like to reset. The Phone Configuration screen appears.
Click the icon of the Cisco ATA that you would like to reset. The Phone Configuration screen appears.
Step 6 ![]() Click the Reset Phone button on the Phone Configuration screen. The Reset Device pop-up window appears.
Click the Reset Phone button on the Phone Configuration screen. The Reset Device pop-up window appears.
Step 7 ![]() Click Reset.
Click Reset.
Step 8 ![]() A confirmation box appears. Click OK.
A confirmation box appears. Click OK.
Upgrading the SCCP Signaling Image
For instructions on how to upgrade the Cisco ATA to the most recent SCCP signaling image, refer to the following list:
•![]() To use the recommended Cisco CallManager TFTP method of upgrading any or all Cisco ATAs at one time, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Via Cisco CallManager" section on page 7-2.
To use the recommended Cisco CallManager TFTP method of upgrading any or all Cisco ATAs at one time, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Via Cisco CallManager" section on page 7-2.
•![]() In the rare instance that you are not using the Cisco CallManager TFTP to configure the Cisco ATA and to obtain software upgrades, you must manually upgrade to the latest signaling image immediately after the Cisco ATA boots up. In this case, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Manually" section on page 7-4.
In the rare instance that you are not using the Cisco CallManager TFTP to configure the Cisco ATA and to obtain software upgrades, you must manually upgrade to the latest signaling image immediately after the Cisco ATA boots up. In this case, see the "Upgrading the Signaling Image Manually" section on page 7-4.
 Feedback
Feedback