Call Agents and Feature Servers
Revised: July 2010, OL-23040-01
Introduction
This chapter describes how to provision BTS Call Agents (CAs) and Feature Servers (FSs).
Call Agents
The CA provides signaling and call processing (call setup and teardown) for the BTS. This section describes adding the CA and associated office tables to the BTS. The following table provides example steps to provision the CA and lists examples of CLI commands with mandatory tokens. For all available tokens, see the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch CLI Database.
|
|
|
Description and CLI Command
|
Step 1 |
Adding CAs. |
The Call Agent (call-agent) table has the domain name and tsap addresses of the CA as well as the primary and secondary IP addresses of the EMS.
add call-agent id=CA101;
tsap-addr=sim-SYS04CA146.ipclab.cisco.com:9146;
|
Step 2 |
Adding CA profiles. |
The Call Agent Profile (ca-agent-profile) table defines the properties (functionality) of the CA. The CA reads this table once every 20 calls. This means that when the CA processes 20 calls per second, changes to this table take effect in one second.
add call-agent-profile id=CA146; cms-id=12345; mgc-supp=y;
mgc-id=12345; feid=financial-entity-id1;
cdb-billing-supp=y; em-billing-supp=n;
|
Step 3 |
Changing CA configurations. |
The Call Agent Configuration (ca-config) table defines the defaults for each CA. The defaults are prepopulated at installation. Only change and show commands are valid.
show ca-config type=susp-tmr;
change ca-config type=susp-tmr; datatype=integer;value=300
Note  The add command is used during installation but additional parameters cannot be added. The add command is used during installation but additional parameters cannot be added. The Call Agent Configuration Base (ca-config-base) table is a static table in the EMS to perform constraint checks. This table is not provisionable. Only the show command is allowed. Information in the Call Agent Configuration Base table must match the information in the Call Agent Configuration table. |
Step 4 |
Adding home area codes. |
The National Destination Code (ndc-code) table defines the home area codes supported by the CA.
add ndc digit-string=469;
|
Step 5 |
Adding exchange codes. |
The Exchange Code (exchange-code) table specifies the exchange codes assigned to a particular CA.
add exchange-code ndc=469; ec=255;
|
Step 6 |
Adding office codes. |
The Office Code (office-code) table specifies the office codes assigned to a particular CA. The office codes defined in this table normally terminate to a subscriber. This table defines the office-code-index (normalized office code) that is used as an index in the DN2Subscriber table.
add office-code call-agent-id=CA146; ndc=469; ec=255;
dn-group=xxxx;
|
Step 7 |
Adding digit maps. |
The Digit Map (digit-map) table tells a media gateway (MGW) how to collect and report dialed digits. The CA uses a default digit map ID for normal digit collection unless a specific digit map ID is assigned to the subscriber. POTS subscribers use a public dialing plan. Centrex subscribers use a customized dialing plan. add digit-map id=default; digit-pattern=0T|00|[2-9]11|[2-9]xx[2-9]xxxxxx|1[2-9]xx[2-9]xxxxxx|0[2-9]xx[2-9]xxxxxx|011xxxxxxxxxxxxx.T|101xxxx|#|*[4-9]x|*[2-3]xx|11xx|[2-9]# |[2-4]x#|[2-9]T|[2-4]xT|01xxxxxxxxxxx; Note  This digit pattern permits the creation of both 2- and 3-digit VSCs. If the first digit is 2 or 3, the length is 3 digits. If first digit is 4-9, the length is 2 digits. For example: This digit pattern permits the creation of both 2- and 3-digit VSCs. If the first digit is 2 or 3, the length is 3 digits. If first digit is 4-9, the length is 2 digits. For example:
*2-3xxx
*4-9xx |
Step 8 |
Adding points of presence. |
The CA can serve several geographical regions or Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs) simultaneously. Each geographical region is referred to as a point of presence (POP). Each POP has its own unique dialing and routing characteristics. The Point of Presence (pop) table contains a default dialing and routing characteristics. Each originating entity (subscriber or trunk group) is assigned to a POP. The POP also performs policy routing, for example, it routes the call to the nearest announcement server in the POP or to the nearest interLATA carrier location within a POP. add pop id=1; state=tx; country=usa; timezone=CST; |
Feature Servers
The FS provides access to features through a well-defined interface, Feature Control Protocol (FCP). BTS FS architecture separates feature control from call control with a clear interface defined between them. The CA uses FCP to provide an effective environment for interfacing with multiple FSs. This provides AIN, POTS, Centrex, and 800 services as required during call processing.
A FS is invoked from a detection point (DP). At the DP, the CA checks if any triggers are armed. If they are, the CA checks if the trigger applies to a subscriber, group, or office, in the order specified. If the trigger is applicable, the CA invokes the feature associated with that trigger.
The following table lists the steps for provisioning a BTS FS and provides commands with mandatory tokens.
For all available tokens, see the Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch CLI Database.
Note  When adding an FS, add the entries to the CA as well as the FS tables in the respective FSs. The POTS FS has the Feature Server table, but the AIN FS does not.
When adding an FS, add the entries to the CA as well as the FS tables in the respective FSs. The POTS FS has the Feature Server table, but the AIN FS does not.
| |
|
Description and CLI Command
|
Step 1 |
Adding FSs. |
The Feature Server (feature-server) table identifies the location and type of FS (POTS or AIN). It also identifies the IP address of the primary and secondary EMS and MGWs used by the FS. It is updated at both the CA and the applicable FS. The FS can be prepopulated during installation using a script, and it is used to automatically provision the Service Trigger table.
add feature-server id=FSAIN201; tsap-addr-sidea=
trn1AIN.trnglab.cisco.com:11205; type=AIN;
|
Step 2 |
Adding features. |
The Feature (feature) table defines characteristics for the features supported by the BTS. Repeat this step for each feature you want to add to the system.
add feature fname=CFU;
tdp1=termination-attempt-authorized;
tid1=termination-attempt-authorized; ttype1=r;
tdp2=collected-information; tid2=vertical-service-code;
ttype2=r; feature-server-id=FSPTC231; fname1=CFUA;
fname2=CFUD;
|
Step 3 |
Adding VSCs. |
The Vertical Service Code (vsc) table translates a vertical service code, also known as a star code (*XX), to a feature name. This table is preprovisioned, based on the Feature table customer records, during installation.
add vsc digit-string=*72; fname=CFUA;
|
Step 4 |
Adding services. |
A service is a collection of one or more features that are invoked when a trigger is reached. Each feature within a service can have one or more triggers. Services can be dynamically created within the BTS 10200. The service provider defines a service and the features associated with it. Up to 10 commonly used features can be grouped into a service, and up to 50 services can be provisioned per subscriber. The subscriber is then provisioned with a service-id instead of individual features.
add service id=1; fname1=CFU; fname2=CFB; fname3=CFNA;
fname4=CW;
|
The following table lists the service types and features available on a POTS or Centrex or Tandem FS.
|
|
|
Class of Service Restrictions |
900 Blocking Directory Assistance Blocking International Blocking 976 Blocking National Black/White List International Black/White List Casual Black/White List Account Codes Authorization Codes |
Screening |
Selective Call Forwarding Selective Call Acceptance Selective Call Rejection, Call Block Distinctive Ringing/Call Waiting |
|
POTS |
Analog Direct Inward Dial (DID) for PBX (FXO) Direct Outward Dial (DOD) for PBX Multiple Directory Numbers (Teen Service) |
|
Common
(POTS and Centrex) |
Call Forwarding Unconditional Remote Activation of Call Forwarding Remote Call Forwarding Call Forwarding On Busy Call Forwarding No Answer Call Forwarding Redirection Calling Number Delivery Blocking Calling Name Delivery Blocking Calling Identity Delivery and Suppression Calling Number Delivery Calling Name Delivery (No External Query) Calling Identity Delivery on Call Waiting Anonymous Call Rejection Automatic Callback (Repeat Dialing) Automatic Recall (Call Return) Call Block (Reject Caller) Call Waiting Cancel Call Waiting Customer-Originated Trace Do Not Disturb Hotline Service Warmline Service Interactive Voice Response Functions Multiline Hunt Group (MLHG) Speed Call (1-digit and 2-digit) Three-Way Calling Usage-Sensitive Three-Way Calling Visual Message Waiting Indicator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic Centrex |
Customized Dialing Plan Intercom Dialing Semi/Fully Restricted Lines DID Distinctive Alerting/Call Waiting Indication on DID DOD Incoming/Outgoing Simulated Facility Group Call Transfer Call Hold Call Park and Call Retrieve Directed Call Pickup (With and Without Barge-in) Group Speed Call |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tandem |
ANI Screening |
Timezones
Table 2-1 lists the various world timezones that the BTS currently supports. Valid time zone values and their associated descriptions are also given.
Table 2-1 Supported Timezones
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LOCAL |
Local System Time (BDMS) |
0 |
|
|
|
|
NWE |
Northwestern Europe |
1 |
+0 |
0 |
03-28-01-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
WA |
Western Africa |
2 |
+0 |
0 |
|
|
WE |
Western Europe |
3 |
+1 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
WCA |
West Central Africa |
4 |
+1 |
0 |
|
|
MAL |
Malta |
5 |
+1 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
NAM |
Namibia |
6 |
+1 |
0 |
09-05-02-00 |
04-04-02-00 |
CE |
Central Europe |
7 |
+1 |
0 |
03-28-03-00 |
10-31-04-00 |
ECA |
East Central Africa |
8 |
+2 |
0 |
|
|
ECE |
East Central Europe |
9 |
+2 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
EGY |
Egypt |
10 |
+2 |
0 |
04-30-00-00 |
10-01-00-00 |
GAZ |
Gaza |
11 |
+2 |
0 |
04-16-00-00 |
10-15-00-00 |
ISR |
Israel |
12 |
+2 |
0 |
04-07-01-00 |
09-22-01-00 |
JOR |
Jordan |
13 |
+2 |
0 |
03-25-00-00 |
10-22-01-00 |
LEB |
Lebanon |
14 |
+2 |
0 |
03-28-00-00 |
10-31-00-00 |
SYR |
Syria |
15 |
+2 |
0 |
04-01-00-00 |
10-01-00-00 |
WB |
West Bank |
16 |
+2 |
0 |
04-07-01-00 |
09-22-01-00 |
EA |
Eastern Africa |
17 |
+3 |
0 |
|
|
PG |
Persian Gulf |
18 |
+3 |
0 |
|
|
GEO |
Georgia |
19 |
+3 |
0 |
03-28-00-00 |
10-31-00-00 |
IRQ |
Iraq |
20 |
+3 |
0 |
04-01-03-00 |
10-01-04-00 |
RUS2 |
Russia Zone 2 |
21 |
+3 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
IRA |
Iran |
22 |
+3 |
30 |
03-21-00-00 |
09-21-00-00 |
AZE |
Azerbaijan |
23 |
+4 |
0 |
03-28-01-00 |
10-31-01-00 |
WIO |
Western Indian Ocean |
24 |
+4 |
0 |
|
|
ME |
Middle East |
25 |
+4 |
0 |
|
|
WAS |
Western Asia |
26 |
+4 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
AFG |
Afghanistan |
27 |
+4 |
30 |
|
|
KYR |
Kyrgystan (also Kyrgyzstan) |
28 |
+5 |
0 |
03-28-02-30 |
10-31-02-30 |
ECAS |
Eastern Central Asia |
29 |
+5 |
0 |
|
|
IO |
Indian Ocean |
30 |
+5 |
0 |
|
|
WCAS |
West Central Asia |
31 |
+5 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
IND |
India |
32 |
+5 |
30 |
|
|
NEP |
Nepal |
33 |
+5 |
45 |
|
|
CAS |
Central Asia |
34 |
+6 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
SAS |
Southern Asia |
35 |
+6 |
0 |
|
|
BC |
Burma - Cocos |
36 |
+6 |
30 |
|
|
RUS6 |
Russia Zone 6 |
37 |
+7 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
SEAS |
South Eastern Asia |
38 |
+7 |
0 |
|
|
EAS |
Eastern Asia |
39 |
+8 |
0 |
|
|
MON |
Mongolia |
40 |
+8 |
0 |
03-27-02-00 |
09-25-03-00 |
RUS7 |
Russia Zone 7 |
41 |
+8 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
WAU |
Western Australia |
42 |
+8 |
0 |
|
|
FEAS |
Far Eastern Asia |
43 |
+9 |
0 |
|
|
RUS8 |
Russia Zone 8 |
44 |
+9 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
NAU |
Northern Australia |
45 |
+9 |
30 |
|
|
SAU |
Southern Australia |
46 |
+9 |
30 |
10-31-02-00 |
03-28-03-00 |
EAU |
Eastern Australia |
47 |
+10 |
0 |
10-31-02-00 |
03-28-03-00 |
QUE |
Queensland Australia |
48 |
+10 |
0 |
|
|
RUS9 |
Russia Zone 9 |
49 |
+10 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
TAS |
Tasmania |
50 |
+10 |
0 |
10-03-02-00 |
03-28-03-00 |
WP |
Western Pacific |
51 |
+10 |
0 |
|
|
LAU |
Lord Howe Island - Australia |
52 |
+10 |
30 |
10-31-02-00 |
03-28-02-00 |
RUS10 |
Russia Zone 10 |
53 |
+11 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
WCP |
Western Central Pacific |
54 |
+11 |
0 |
|
|
NOR |
Norfolk Island |
55 |
+11 |
30 |
|
|
NZ |
New Zealand |
56 |
+12 |
0 |
10-03-02-00 |
03-21-03-00 |
RUS11 |
Russia Zone 11 |
57 |
+12 |
0 |
03-28-02-00 |
10-31-03-00 |
SPO |
Southern Pacific Ocean |
58 |
+12 |
0 |
|
|
CI |
Chatham Island |
59 |
+12 |
45 |
10-03-02-45 |
03-21-03-45 |
SEPO |
South Eastern Pacific Ocean |
60 |
+13 |
0 |
|
|
LI |
Line Islands |
61 |
+14 |
0 |
|
|
SMO |
Samoa |
62 |
-11 |
0 |
|
|
HAW |
Hawaii |
63 |
-10 |
0 |
|
|
AI |
Aleutian Islands |
64 |
-10 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
GI |
Gambier Islands |
65 |
-9 |
0 |
|
|
MI |
Marquesas Islands |
66 |
-9 |
30 |
|
|
ALA |
Alaska |
67 |
9 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
SON |
Sonora Mexico |
68 |
-8 |
0 |
|
|
PI |
Pitcairn Islands |
69 |
-8 |
0 |
|
|
PAC |
North American Pacific |
70 |
-8 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
EBC |
Eastern British Columbia |
71 |
-8 |
0 |
|
|
MNT |
North American Mountain |
72 |
-7 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
ARI |
Arizona |
73 |
-7 |
0 |
|
|
SASK |
Saskatechewan |
74 |
-6 |
0 |
|
|
GAL |
Galapagos Islands |
75 |
-6 |
0 |
|
|
EI |
Easter Island |
76 |
-6 |
0 |
10-09-10-00 |
03-13-10-00 |
CA |
Central America |
77 |
-6 |
0 |
|
|
CEN |
North American Central |
78 |
-6 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
WSAM |
Western South America |
79 |
-5 |
0 |
|
|
WCAR |
Western Caribbean |
80 |
-5 |
0 |
|
|
SOU |
Southampton Canada |
81 |
-5 |
0 |
|
|
IDA |
Indiana |
82 |
-5 |
0 |
|
|
EST |
North American Eastern |
83 |
-5 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
CUB |
Cuba |
84 |
-5 |
0 |
03-28-00-00 |
10-31-01-00 |
BAH |
Bahamas |
85 |
-5 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
ACR |
Acre Brazil |
86 |
-5 |
0 |
|
|
SAM |
Central South America |
87 |
-4 |
0 |
|
|
PAR |
Paraguay |
88 |
-4 |
0 |
09-05-00-00 |
04-04-00-00 |
FI |
Falkland Islands |
89 |
-4 |
0 |
09-05-02-00 |
04-18-02-00 |
CHI |
Chile |
90 |
-4 |
0 |
10-10-00-00 |
03-14-00-00 |
CG |
Central Greenland |
91 |
-4 |
0 |
|
|
CAR |
Caribbean |
92 |
-4 |
0 |
|
|
ATL |
North American Atlantic |
93 |
-4 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
NWF |
Newfoundland Canada |
94 |
-3 |
30 |
04-04-12-01 |
10-31-12-01 |
ELAB |
Eastern Labrador Canada |
95 |
-3 |
30 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
SPM |
St.Pierre and Miquelon |
96 |
-3 |
0 |
04-04-02-00 |
10-31-02-00 |
SBRZ |
Southern Brazil |
97 |
-3 |
0 |
10-17-00-00 |
02-15-00-00 |
ESAM |
Eastern South America |
98 |
-3 |
0 |
|
|
EG |
Eastern Greenland |
99 |
-3 |
0 |
|
|
EBRZ |
Eastern Brazil |
100 |
-2 |
0 |
|
|
FEG |
Far Eastern Greenland |
101 |
-1 |
0 |
|
|
CV |
Cape Verde |
102 |
-1 |
0 |
|
|
AZO |
Azores |
103 |
-1 |
0 |
03-28-00-00 |
10-31-01-00 |
ICE |
Iceland |
104 |
+0 |
0 |
|
|
Timezone Localities
Table 2-2 describes the localities covered by the various world timezones that the BTS supports.
Table 2-2 Time zone Localities
|
|
|
|
LOCAL |
Local System Time |
|
NWE |
Northwestern Europe |
Faroe Islands, Guernsey, Ireland, Isle of Man, Portugal, Canary Islands, United Kingdom |
WA |
Western Africa |
Burkina Faso, Cote d'Ivore, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, St.Helena, Togo, Western Sahara |
WE |
Western Europe |
Albania, Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Gibraltar, Hungary, Italy, Lichtenstein, Luxembourg, Macedonia, Monaco, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, San Marino, Serbia, Montenegro, Kosovo, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Vatican City |
WCA |
West Central Africa |
Algeria, Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo (west), Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Niger, Nigeria, Tunisia |
MAL |
Malta |
Malta |
NAM |
Namibia |
Namibia |
CE |
Central Europe |
Bulgaria, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Romania, Turkey, Ukraine |
ECA |
East Central Africa |
Botswana, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo (east), Lesotho, Libya, Malawi, Mozambique, Rwanda, South Africa, Swaziland, Zambia, Zimbabwe |
ECE |
East Central Europe |
Belarus, Greece, Russia (Zone1) |
EGY |
Egypt |
Egypt |
GAZ |
Gaza |
Gaza Strip |
ISR |
Israel |
Israel |
JOR |
Jordan |
Jordan |
LEB |
Lebanon |
Lebanon |
SYR |
Syria |
Syria |
WB |
West Bank |
West Bank |
EA |
Eastern Africa |
Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Mayotte, Somalia, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda |
PG |
Persian Gulf |
Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
GEO |
Georgia |
Georgia |
IRQ |
Iraq |
Iraq |
RUS2 |
Russia Zone 2 |
Russia (Zone2) |
IRA |
Iran |
Iran |
AZE |
Azerbaijan |
Azerbaijan |
WIO |
Western Indian Ocean |
Mauritius, Reunion, Seychelles |
ME |
Middle East |
Oman, United Arab Emirates |
WAS |
Western Asia |
Armenia, Kazakhstan (West), Russia (Zone3) |
AFG |
Afghanistan |
Afghanistan |
KYR |
Kyrgystan |
Kyrgystan |
ECAS |
Eastern Central Asia |
Pakistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan |
IO |
Indian Ocean |
Kerguelen, Maldives |
WCAS |
West Central Asia |
Kazakhstan (Central), Russia (Zone4) |
IND |
India |
India |
NEP |
Nepal |
Nepal |
CAS |
Central Asia |
Kazakhstan (East), Russia (Zone5) |
SAS |
Southern Asia |
Bangladesh, Bhutan, Sri Lanka |
BC |
Burma - Cocos |
Burma, Cocos (Keeling) Islands |
RUS6 |
Russia Zone 6 |
Russia (Zone6) |
SEAS |
South Eastern Asia |
Christmas Island, Cambodia, Indonesia (West), Laos, Thailand, Vietnam |
EAS |
Eastern Asia |
Brunei Darussalem, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia (Central), Macau, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan |
MON |
Mongolia |
Mongolia |
RUS7 |
Russia Zone 7 |
Russia (Zone7) |
WAU |
Western Australia |
Australia (Western Australia) |
FEAS |
Far Eastern Asia |
Indonesia (East), Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Palau, Timor-Leste |
RUS8 |
Russia Zone 8 |
Russia (Zone8) |
NAU |
Northern Australia |
Australia (Northern Territory) |
SAU |
Southern Australia |
Australia (South Australia) |
EAU |
Eastern Australia |
Australia (New South Wales, Victoria, Capital Territory) |
QUE |
Queensland Australia |
Australia (Queensland) |
RUS9 |
Russia Zone 9 |
Russia (Zone9) |
TAS |
Tasmania |
Australia (Tasmania) |
WP |
Western Pacific |
Guam, Micronesia (Chuuk Islands), Northern Mariana Islands, Papua New Guinea |
LAU |
Lord Howe Island - Australia |
Australia (Lord Howe Island) |
RUS10 |
Russia Zone 10 |
Russia (Zone10) |
WCP |
Western Central Pacific |
Micronesia (Senyavin Islands), New Caledonia, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu |
NOR |
Norfolk Island |
Norfolk Island |
NZ |
New Zealand |
New Zealand |
RUS11 |
Russia Zone 11 |
Russia (Zone11) |
SPO |
Southern Pacific Ocean |
Fiji, Kiribati (Gilbert Islands), Marshall Islands, Nauru, Tuvalu, Wallis and Futuna |
CI |
Chatham Island |
Chatham Island |
SEPO |
South Eastern Pacific Ocean |
Kiribati (Phoenix Islands), Tonga |
LI |
Line Islands |
Kiribati (Line Islands) |
SMO |
Samoa |
American Samoa, Niue, Samoa |
HAW |
Hawaii |
Cook Islands, French Polynesia (Society Archipelago, Tuamotu Archipelago, Tubuai Islands), US (Hawaii) |
AI |
Aleutian Islands |
US (Aleutian Islands) |
GI |
Gambier Islands |
French Polynesia (Gambier Islands) |
MI |
Marquesas Islands |
French Polynesia (Marquesas Islands) |
ALA |
Alaska |
US (Alaska) |
SON |
Sonora Mexico |
Mexico (Sonora) |
PI |
Pitcairn Islands |
Pitcairn Islands |
PAC |
North American Pacific |
Canada (Yukon, British Columbia), Mexico (Baja California), US (Washington, Oregon, Idaho-Northern, California, Nevada) |
EBC |
Eastern British Columbia |
Canada (Eastern British Columbia) |
MNT |
North American Mountain |
Canada (Northwest Territory, Nunavut-Western, British Columbia-Southeast, Alberta, Saskatchewan-West), Mexico (Baja California Sur, Chihuahua, Sinaloa, Nayarit), US (Oregon-East, Idaho-Southern, Montana, Wyoming, North Dakota-Southwest, South Dakota-West, Nebraska-West, Kansas-West, Utah, Arizona-Navajo Reservation, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas-Far West) |
ARI |
Arizona |
Arizona |
SASK |
Saskatchewan |
Canada (Saskatchewan) |
GAL |
Galapagos Islands |
Ecuador (Galapagos Islands) |
EI |
Easter Island |
Easter Island |
CA |
Central America |
Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua |
CEN |
North American Central |
Canada (Nunavut-Central, Ontario-Western, Saskatchewan-East, Manitoba), Mexico (Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, Tamaulipas, Zacatecas, Jalisco, San Luis Potosi, Guanajuato, Aquascalientes, Queretara, Yucatan, Quintana Roo, Campeche, Tabasco, Chiapas, Oaxaca, Veracruz, Guerrero, Michoacan, Colima, Morelos, Tlaxacala, Durango, Edo de Mexico, Hidalgo, Puebla, Federal District), US (North Dakota, South Dakota-Eastern, Nebraska-Eastern, Kansas-Eastern, Minnesota, Iowa, Missouri, Wisconsin, Illinois, Michigan-Western Upper Peninsula, Oklahoma, Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Indiana-Southwestern, Indiana-Northwestern, Kentucky-Western, Tennessee-Western, Mississippi, Florida-Far Western) |
WSAM |
Western South America |
Columbia, Ecuador, Peru |
WCAR |
Western Caribbean |
Cayman Islands, Grand Cayman, Haiti, Jamaica, Panama |
SOU |
Southampton Canada |
Canada (Nunavut-Southampton) |
IDA |
Indiana |
US (Indiana) |
EST |
North American Eastern |
Canada (Nunavut-Eastern, Quebec, Ontario-Eastern), Turks and Caicos Islands, US (Michigan, New York, Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Indiana-Southeastern, Kentucky-Eastern, Tennessee-Eastern, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Virginia, North Carolina, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Washington DC, West Virginia, Alabama, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida) |
CUB |
Cuba |
Cuba |
BAH |
Bahamas |
Bahamas |
ACR |
Acre Brazil |
Brazil (Acre) |
SAM |
Central South America |
Argentina (Mendoza, San Juan), Bolivia, Brazil (Amazonas, Rondonia, Roraima, Mato Grosso, Para-West, Mato Grosso Do Sul), Guyana, Venezuela |
PAR |
Paraguay |
Paraguay |
FI |
Falkland Islands |
UK (Falkland Islands) |
CHI |
Chile |
Chile |
CG |
Central Greenland |
Denmark (Central Greenland) |
CAR |
Caribbean |
Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, Barbados, British Virgin Islands, Dominican Republic, Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Montserrat, Netherlands Antilles, Puerto Rico, St.Kitts and Nevis, St. Lucia, St Vincent and The Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, US Virgin Islands |
ATL |
North American Atlantic |
Bermuda, Canada (Labrador, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island) |
NWF |
Newfoundland Canada |
Canada (Newfoundland) |
ELAB |
Eastern Labrador Canada |
Canada (Labrador-Far Eastern) |
SPM |
St Pierre and Miquelon |
France (St Pierre and Miquelon) |
SBRZ |
Southern Brazil |
Brazil (Minas Gerais, Goias, Distrito Federal, Parana, Espirito Santo, Rio De Janeiro, Sao Paulo, Rio Grande Do Sul, Santa Catarina) |
ESAM |
Eastern South America |
French Guiana, Suriname, Uruguay, Brazil (Para-Eastern, Amapa, Maranhao, Tocantins, Piaui, Ceara, Rio Grande Do Norte, Paraiba, Alagoas, Sergipe, Bahia), Argentina (Buenos Aires, Catamarca, Chaco, Chubut, Cordoba, Corrientes, Entre Rios, Formosa, Jujuy, La Pampa, La Rioja, Misiones, Neuquen, Rio Negro, Salta, San Luis, Santa Cruz, Santa Fe, Santiago del Estero, Tierra del Fuego, Tucuman) |
EG |
Eastern Greenland |
Denmark (Greenland-Eastern) |
EBRZ |
Eastern Brazil |
Brazil (Pernambuco, Fernando de Noronha) |
FEG |
Far Eastern Greenland |
Denmark (Greenland-Far Eastern) |
CV |
Cape Verde |
Cape Verde |
AZO |
Azores |
Portugal (Azores) |
ICE |
Iceland |
Iceland |
Timezone Recommendations
Table 2-2 lists recommended timezones per region.
Caution
 Do not use settings like GMT_MINUS5 or GMT_PLUS5.
Do not use settings like GMT_MINUS5 or GMT_PLUS5.
If your timezone is not listed, please contact your Cisco representative.
Table 2-3 Timezone Recommendations
|
|
|
US_ALASKA |
US/Alaska |
US_ALEUTIAN |
US/Aleutian |
US_ARIZONA |
US/Arizona |
US_CENTRAL |
US/Central Use this instead of CST or CDT. |
US_EAST_INDIANA |
US/East-Indiana |
US_EASTERN |
US/Eastern Use this instead of EST or EDT. |
US_HAWAII |
US/Hawaii |
US_MICHIGAN |
US/Michigan |
US_MOUNTAIN |
US/Mountain Use this instead of MST or MDT. |
US_PACIFIC |
US/Pacific Use this instead of PST or PDT. |
US_SAMOA |
US/Samoa |
|
|
CANADA_ATLANTIC |
Canada/Atlantic Use this instead of AST or ADT. |
CANADA_EAST_SASKATCHEWAN |
Canada/East-Saskatchewan |
CANADA_MOUNTAIN |
Canada/Mountain |
CANADA_PACIFIC |
Canada/Pacific |
CANADA_CENTRAL |
Canada/Central |
CANADA_EASTERN |
Canada/Eastern |
CANADA_NEWFOUNDLAND |
Canada/Newfoundland |
CANADA_YUKON |
Canada/Yukon |
TOS, DSCP, and PHB
This section describes how BTS supports Type of Service (TOS), Differentiated Services Codepoint (DSCP), and Per-Hop Behavior (PHB). For more information, see the following IETF documents:
• TOS—RFC 791, Internet Protocol
TOS—RFC 791, Internet Protocol
• DSCP—RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
DSCP—RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
• PHB—RFC 2597, Assured Forwarding PHB Group, and RFC 3246, An Expedited Forwarding PHB (Per-Hop Behavior)
PHB—RFC 2597, Assured Forwarding PHB Group, and RFC 3246, An Expedited Forwarding PHB (Per-Hop Behavior)
Figure 2-1 shows how the TOS, DSCP, and PHB standards are related.
Figure 2-1 Relationship of TOS, DSCP, and PHB Standards
On the BTS, the parameters for TOS, DSCP, and PHB are provisioned differently depending on the token.
Caution
 Restart or swtichover the CA to effect changes you make in the ca-config table.
Restart or swtichover the CA to effect changes you make in the ca-config table.
TOS
If the BTS requires TOS parameters as precedence strings, provision tokens as follows:
• PRECEDENCE = NETCONTROL, INTERNETCONTROL, CRITICAL, FLASHOVERRIDE, FLASH, IMMEDIATE, PRIORITY, or ROUTINE
PRECEDENCE = NETCONTROL, INTERNETCONTROL, CRITICAL, FLASHOVERRIDE, FLASH, IMMEDIATE, PRIORITY, or ROUTINE
• LOWDELAY = Y or N
LOWDELAY = Y or N
• THROUGHPUT = Y or N
THROUGHPUT = Y or N
• RELIABILITY = Y or N
RELIABILITY = Y or N
Diffserv
If the BTS requires Diffserv parameters as bytes, provision a single token as an integer, 0 - 255. The Diffserv byte is based on 8 bits, 2 more bits than the DSCP value. For example, if you want a DSCP value of 24, provision it with 96.
DSCP
If the system requires parameters to be provisioned in the DSCP value format, provision a single token as an integer between 0 and 63. The DSCP value is the decimal equivalent of the first 6 bits of the Diffserv byte.
PHB
If the system requires parameters to be provisioned in the PHB format, provision a single token as one of the following values: CS0, CS1, CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6, CS7, AF11, AF12, AF13, AF21, AF22, AF23, AF31, AF32, AF33, AF41, AF42, AF43, EF, DEFAULT.
Note  Entering the value "DEFAULT" has the same effect as entering "CS0." These values are included in Table 2-5.
Entering the value "DEFAULT" has the same effect as entering "CS0." These values are included in Table 2-5.
Combined PHB/DSCP Format
Some tokens can be provisioned in either the alphanumeric PHB format or the numeric DSCP value format. In this case provision the token as one of the following values: an integer between 0 and 63, CS0, CS1, CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6, CS7, AF11, AF12, AF13, AF21, AF22, AF23, AF31, AF32, AF33, AF41, AF42, AF43, EF, DEFAULT.
Refer to RFC 791 for additional information on the PRECEDENCE values. The relationship between PRECEDENCE and CSx values is as follows: NETCONTROL=CS7, INTERNETCONTROL=CS6, CRITICAL=CS5, FLASHOVERRIDE=CS4, FLASH=CS3, IMMEDIATE=CS2, PRIORITY=CS1, ROUTINE=CS0/DEFAULT.
Allowed and Default Values
This section lists the provisionable TOS, DSCP, and PHB tokens applicable to each protocol.
Caution
 Cisco recommends against using any value other than the default. Changing these values from their defaults can significantly impact network performance. Contact Cisco TAC for further information.
Cisco recommends against using any value other than the default. Changing these values from their defaults can significantly impact network performance. Contact Cisco TAC for further information.
Caution
 If you change any parameters in the ca-config table, these changes do not take effect until the CA platform switches over or restarts.
If you change any parameters in the ca-config table, these changes do not take effect until the CA platform switches over or restarts.
MGCP Signaling
The MGCP-SIG-DSCP parameter from the CA_CONFIG table is used for signaling between the BTS 10200 and MGWs.
SIP Signaling
The SIA-TRUNK-GRP-LEVEL-SIG-TOS parameter from the CA_CONFIG table applies to SIP signaling. For its changes to take effect, you must performa switchover.
• Y: Use the value provisioned for SIP-SIG-DSCP in the SIP-ELEMENT table for the applicable SIP trunk group.
Y: Use the value provisioned for SIP-SIG-DSCP in the SIP-ELEMENT table for the applicable SIP trunk group.
• N: Use the value provisioned for the system-wide parameter SIA-SIG-DSCP in the CA-CONFIG table.
N: Use the value provisioned for the system-wide parameter SIA-SIG-DSCP in the CA-CONFIG table.
The SIA-SIG-DSCP parameter from the CA_CONFIG table defines system-level DSCP for SIP calls.
The SIP-SIG-DSCP parameter in the SIP_ELEMENT table applies to trunk-level SIP signaling.
CA to FS Signaling
TheSIM-SIG-DSCP parameter from the CA_CONFIG table applies.
FS to CA Signaling
The following values from the CA_CONFIG table apply:
• The FSAIN-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal AIN Feature Server (FSAIN) to CA signaling.
The FSAIN-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal AIN Feature Server (FSAIN) to CA signaling.
• The FSPTC-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal POTS/Tandem/Centrex Feature Server (FSPTC) to CA signaling.
The FSPTC-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal POTS/Tandem/Centrex Feature Server (FSPTC) to CA signaling.
DQoS Signaling
DQoS signaling uses the Common Open Policy Service (COPS) protocol. The RTP-DSCP from the QOS table applies.
H.323 Signaling
The SIG-DSCP parameter from the H323_GATEWAY table applies.
COPS and RADIUS Signaling
This section lists the tokens used in provisioning COPS and RADIUS signaling from the QOS and CA_CONFIG tables.
Tip  The tokens in this section are provisioned using values between 0 and 255. For an explanation of how to calculate these values, see the "Diffserv" section.
The tokens in this section are provisioned using values between 0 and 255. For an explanation of how to calculate these values, see the "Diffserv" section.
The QOS table contains the following token (applicable to voice traffic):
• DQOS-CMTS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the packets about to enter a provider backbone from the CMTS.
DQOS-CMTS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the packets about to enter a provider backbone from the CMTS.
• DQOS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token specifies particular bits within the IPv4 DSCP/TOS byte.
DQOS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token specifies particular bits within the IPv4 DSCP/TOS byte.
• DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS—Identifies the DSCP/TOS value that must be matched for packets to be classified onto the IP flow.
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS—Identifies the DSCP/TOS value that must be matched for packets to be classified onto the IP flow.
• DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token determines what bits in the DSCP/TOS byte are to be used as filters in classifying packets.
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token determines what bits in the DSCP/TOS byte are to be used as filters in classifying packets.
Table 2-4 lists the allowed values and default value for each of these tokens.
Table 2-4 COPS Signaling Parameters (from QoS Table)
|
|
|
|
DQOS-CMTS-DSCP-TOS |
0-255 |
160 |
DQOS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK |
0-255 |
224 |
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS |
0-255 |
160 |
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK |
0-255 |
224 |
The following parameters from the CA_CONFIG table apply:
• COPS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on COPS interfaces between the CMS and the CMTS.
COPS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on COPS interfaces between the CMS and the CMTS.
• RADIUS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on RADIUS interfaces between the CMS and the RKS, and the CMS and the DF server.
RADIUS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on RADIUS interfaces between the CMS and the RKS, and the CMS and the DF server.
Table 2-5 lists the allowed value and default value for each of these tokens.
Table 2-5 COPS and RADIUS Signaling Parameters (from CA-CONFIG Table)
|
|
|
|
COPS-DSCP-TOS |
0-255 |
96 |
RADIUS-DSCP-TOS |
0-255 |
96 |
Stream Control Transmission Protocol Signaling
The SCTP-DSCP parameter from the CA_CONFIG table applies. Table 2-6 lists the allowed values and default value for this token.
Table 2-6 SCTP-DSCP Signaling Parameters (from CA-CONFIG Table)
|
|
|
|
SCTP-DSCP |
DEFAULT, CS1, CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6, CS7, AF11, AF12, AF13, AF21, AF22, AF23, AF31, AF32 AF33, AF41, AF42, AF43, EF |
CS3 |
Note  The value "DEFAULT" is mapped to a value of "CS0" as shown in Table 2-5.
The value "DEFAULT" is mapped to a value of "CS0" as shown in Table 2-5.
ISDN Signaling
The following parameters from the BACKHAUL_SET table apply:
• SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY
SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY
• SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE
SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE
• SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY
SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY
• SIG-TOS-SUPP—Allowed values are Y/N; default is N.
SIG-TOS-SUPP—Allowed values are Y/N; default is N.
• SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT
SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT
Table 2-7 lists the allowed values and default value for the -PRECEDENCE, -LOWDELAY, -THROUGHPUT, and -RELIABILITY tokens.
Table 2-7 SIG-TOS Values (from BACKHAUL-SET Table)
|
|
|
|
SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY |
Y/N |
N |
SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE |
NETCONTROL INTERNETCONTROL CRITICAL FLASHOVERRIDE FLASH IMMEDIATE PRIORITY ROUTINE |
CRITICAL |
SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY |
Y/N |
N |
SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT |
Y/N |
N |
Mapping of Provisionable TOS, DSCP, and PHB Values
Table 2-8 shows how the provisionable values in the PHB format are mapped to the values in TOS and DSCP formats.
Caution
 Cisco recommends using the combinations of values in the table. BTS accepts other combinations, depending on format; however, the combinations shown have been tested by Cisco.
Cisco recommends using the combinations of values in the table. BTS accepts other combinations, depending on format; however, the combinations shown have been tested by Cisco.
Note  Binary and Hex values are informational and not used for provisioning.
Binary and Hex values are informational and not used for provisioning.
Table 2-8 Mapping of Provisionable Values in PHB Format to TOS and DSCP Formats1
|
|
Value of TOS PRECEDENCE Bits
|
Other Provisionable TOS Bits
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOS String Format, Based On RFC 791
|
|
|
|
|
CS0
or
DEFAULT |
000 |
ROUTINE |
0 |
N |
N |
N |
000 000 00 |
0 |
0 |
0x0 |
CS1 |
001 |
PRIORITY |
1 |
N |
N |
N |
001 000 00 |
8 |
32 |
0x20 |
AF11 |
N |
Y |
N |
001 010 00 |
10 |
40 |
0x28 |
AF12 |
Y |
N |
N |
001 100 00 |
12 |
48 |
0x30 |
AF13 |
Y |
Y |
N |
001 110 00 |
14 |
56 |
0x38 |
CS2 |
010 |
IMMEDIATE |
2 |
N |
N |
N |
010 000 00 |
16 |
64 |
0x40 |
AF21 |
N |
Y |
N |
010 010 00 |
18 |
72 |
0x48 |
AF22 |
Y |
N |
N |
010 100 00 |
20 |
80 |
0x50 |
AF23 |
Y |
Y |
N |
010 110 00 |
22 |
88 |
0x58 |
CS3 |
011 |
FLASH |
3 |
N |
N |
N |
011 000 00 |
24 |
96 |
0x60 |
AF31 |
N |
Y |
N |
011 010 00 |
26 |
104 |
0x68 |
AF32 |
Y |
N |
N |
011 100 00 |
28 |
112 |
0x70 |
AF33 |
Y |
Y |
N |
011 110 00 |
30 |
120 |
0x78 |
CS4 |
100 |
FLASHOVERRIDE |
4 |
N |
N |
N |
100 000 00 |
32 |
128 |
0x80 |
AF41 |
N |
Y |
N |
100 010 00 |
34 |
136 |
0x88 |
AF42 |
Y |
N |
N |
100 100 00 |
36 |
144 |
0x90 |
AF43 |
Y |
Y |
N |
100 110 00 |
38 |
152 |
0x98 |
CS5 |
101 |
CRITICAL |
5 |
N |
N |
N |
101 000 00 |
40 |
160 |
0xA0 |
EF |
Y |
Y |
N |
101 110 00 |
46 |
184 |
0xB8 |
CS6 |
110 |
INTERNETWORK
CONTROL |
6 |
N |
N |
N |
110 000 00 |
48 |
192 |
0xC0 |
CS7 |
111 |
NETWORK
CONTROL |
7 |
N |
N |
N |
111 000 00 |
56 |
224 |
0xE0 |
|
1 Cisco recommends that you use the combinations of values shown in the table. The system will accept certain other combinations of values, depending on the format; however, the combinations shown in the table have been tested by Cisco for proper behavior.
2 Hexadecimal equivalent. This value is listed for convenience. It is not used in provisioning the BTS.
3 Binary equivalent. This value is listed for convenience. It is not used in provisioning the BTS.
4 D = Delay, T = Throughput, R = Reliability. To provision these tokens, enter N for 0 or Y for 1.
|

![]() When adding an FS, add the entries to the CA as well as the FS tables in the respective FSs. The POTS FS has the Feature Server table, but the AIN FS does not.
When adding an FS, add the entries to the CA as well as the FS tables in the respective FSs. The POTS FS has the Feature Server table, but the AIN FS does not. 
![]() TOS—RFC 791, Internet Protocol
TOS—RFC 791, Internet Protocol ![]() DSCP—RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers
DSCP—RFC 2474, Definition of the Differentiated Services Field (DS Field) in the IPv4 and IPv6 Headers ![]() PHB—RFC 2597, Assured Forwarding PHB Group, and RFC 3246, An Expedited Forwarding PHB (Per-Hop Behavior)
PHB—RFC 2597, Assured Forwarding PHB Group, and RFC 3246, An Expedited Forwarding PHB (Per-Hop Behavior) 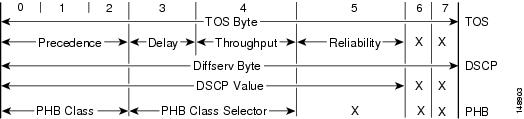

![]() PRECEDENCE = NETCONTROL, INTERNETCONTROL, CRITICAL, FLASHOVERRIDE, FLASH, IMMEDIATE, PRIORITY, or ROUTINE
PRECEDENCE = NETCONTROL, INTERNETCONTROL, CRITICAL, FLASHOVERRIDE, FLASH, IMMEDIATE, PRIORITY, or ROUTINE ![]() LOWDELAY = Y or N
LOWDELAY = Y or N ![]() THROUGHPUT = Y or N
THROUGHPUT = Y or N ![]() RELIABILITY = Y or N
RELIABILITY = Y or N 
![]() Entering the value "DEFAULT" has the same effect as entering "CS0." These values are included in Table 2-5.
Entering the value "DEFAULT" has the same effect as entering "CS0." These values are included in Table 2-5. 

![]() Y: Use the value provisioned for SIP-SIG-DSCP in the SIP-ELEMENT table for the applicable SIP trunk group.
Y: Use the value provisioned for SIP-SIG-DSCP in the SIP-ELEMENT table for the applicable SIP trunk group. ![]() N: Use the value provisioned for the system-wide parameter SIA-SIG-DSCP in the CA-CONFIG table.
N: Use the value provisioned for the system-wide parameter SIA-SIG-DSCP in the CA-CONFIG table. ![]() The FSAIN-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal AIN Feature Server (FSAIN) to CA signaling.
The FSAIN-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal AIN Feature Server (FSAIN) to CA signaling. ![]() The FSPTC-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal POTS/Tandem/Centrex Feature Server (FSPTC) to CA signaling.
The FSPTC-SIG-DSCP value is used for internal POTS/Tandem/Centrex Feature Server (FSPTC) to CA signaling. 
![]() The tokens in this section are provisioned using values between 0 and 255. For an explanation of how to calculate these values, see the "Diffserv" section.
The tokens in this section are provisioned using values between 0 and 255. For an explanation of how to calculate these values, see the "Diffserv" section. ![]() DQOS-CMTS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the packets about to enter a provider backbone from the CMTS.
DQOS-CMTS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the packets about to enter a provider backbone from the CMTS. ![]() DQOS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token specifies particular bits within the IPv4 DSCP/TOS byte.
DQOS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token specifies particular bits within the IPv4 DSCP/TOS byte. ![]() DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS—Identifies the DSCP/TOS value that must be matched for packets to be classified onto the IP flow.
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS—Identifies the DSCP/TOS value that must be matched for packets to be classified onto the IP flow. ![]() DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token determines what bits in the DSCP/TOS byte are to be used as filters in classifying packets.
DOCSIS-DSCP-TOS-BITMASK—This token determines what bits in the DSCP/TOS byte are to be used as filters in classifying packets. ![]() COPS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on COPS interfaces between the CMS and the CMTS.
COPS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on COPS interfaces between the CMS and the CMTS. ![]() RADIUS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on RADIUS interfaces between the CMS and the RKS, and the CMS and the DF server.
RADIUS-DSCP-TOS—This value is used for the signaling packets on RADIUS interfaces between the CMS and the RKS, and the CMS and the DF server. 
![]() The value "DEFAULT" is mapped to a value of "CS0" as shown in Table 2-5.
The value "DEFAULT" is mapped to a value of "CS0" as shown in Table 2-5. ![]() SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY
SIG-TOS-LOWDELAY ![]() SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE
SIG-TOS-PRECEDENCE ![]() SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY
SIG-TOS-RELIABILITY ![]() SIG-TOS-SUPP—Allowed values are Y/N; default is N.
SIG-TOS-SUPP—Allowed values are Y/N; default is N. ![]() SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT
SIG-TOS-THROUGHPUT 

![]() Binary and Hex values are informational and not used for provisioning.
Binary and Hex values are informational and not used for provisioning.  Feedback
Feedback