- About CMR Hybrid
- Planning
- Deployment Options
- Requirements
- Set Up the Solution Components
- Connect Cisco TelePresence Conductor to Call Control
- Configure Bridge Scheduling
- Configure Cisco MCU and TelePresence Server
- Configure Call Control
- Configure Certificates on Cisco Expressway-E and Cisco VCS Expressway
- Configure Cisco TelePresence Management Suite
- Configure Cisco TelePresence Management Suite Extension for Microsoft Exchange
- Configure TelePresence Management Suite Provisioning Extension
- Configure Audio
- Integrate Cisco TelePresence with a Cisco WebEx Site Administration Account
- Manage CMR Hybrid Meetings
- Troubleshoot CMR Hybrid
- Add Cisco Unified Communications Manager Normalization Scripts
- Migration Paths
- Set Up Cascading for Large-Scale or Critical Meetings
- Index
Cisco Collaboration Meeting Rooms (CMR) Hybrid Configuration Guide (TMS 15.0 - WebEx Meeting Center WBS30)
Bias-Free Language
The documentation set for this product strives to use bias-free language. For the purposes of this documentation set, bias-free is defined as language that does not imply discrimination based on age, disability, gender, racial identity, ethnic identity, sexual orientation, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality. Exceptions may be present in the documentation due to language that is hardcoded in the user interfaces of the product software, language used based on RFP documentation, or language that is used by a referenced third-party product. Learn more about how Cisco is using Inclusive Language.
- Updated:
- May 12, 2016
Chapter: Planning
Planning
Understanding How CMR Hybrid is Deployed
The core elements of CMR Hybrid are:
The TelePresence Conductor manages the conference bridges. SIP trunks connect the bridges to the TelePresence Conductor, which in turn is trunked to one or more call controllers. All XML RPC connections also route via the TelePresence Conductor. Cisco TMS provides conference management, including scheduling, provisioning and monitoring of conferences. XML RPC connections link Cisco TMS to the TelePresence Conductor.
The solution architecture is exclusively SIP. Conferencing with H.323 endpoints requires interworking by a
Cisco VCS Control or Cisco Expressway-C.
CMR Hybrid can be deployed in either of the following networks:
The supported deployment models are described in the section: Deployment Options.
Cisco TMS Scheduling Role
Cisco TMS provides a control link to the Cisco WebEx site. This interface allows Cisco TMS to book a WebEx-enabled meeting on behalf of the WebEx Host, and to obtain Cisco WebEx meeting information that is distributed to meeting participants.Cisco TMS then pushes Cisco WebEx meeting details to the TelePresence Server/MCU.
TelePresence Server and MCU Roles
Cisco TelePresence Server/MCU will send/receive two-way main video with up to 720p30 between WebEx Meeting Center clients and TelePresence endpoints. The MCU/TS sends a single transcoded video stream to the WebEx Meeting Center client.
The MCU/TS will send a single mixed audio stream of the TelePresence meeting participants to the WebEx cloud. Likewise, the MCU/TS will receive a single mixed audio stream from all WebEx participants, including WebEx Meeting Center participants joined over PSTN or VoIP.
Support for two-way content share XGA (1024 x 768) resolution between telepresence endpoints and WebEx clients.
Each meeting creates its own SIP connection to avoid Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) congestion and potential TCP windowing issues.
MCU/Cisco TelePresence Server connects automatically at the meeting's scheduled start time.
Ports and Protocols Used in CMR Hybrid
The following ports and protocols are used between different components of the CMR Hybrid solution.
|
WebEx and TelePresence Integration to Outlook to Cisco TMSXE |
|||
|
Set in accordance with the traversal subzone media port range configured on the Expressway. For more information, refer to the Inbound (Internet > DMZ) requirements in Appendix 3: Firewall and NAT Settings on page 52 of Cisco VCS Basic Configuration Control with Expressway Deployment Guide X8-5 if using Expressway 8.5. If using an earlier supported Expressway version, refer to the same section in the appropriate version of the guide on Cisco.com.
|
|||
*For a complete list of WebEx IP subnets, refer to article WBX264, in the WebEx Knowledge Base.
Note: On WebEx clients using UDP vs TCP, and customers should check their firewall setting to prevent UDP from being blocked.
Firewalls, ports and protocols that do deep packet inspection should not be used. Specifically, the stateful packet inspection used in Check Point Software Technologies, Inc. firewalls is incompatible with Cisco VCS Expressway and Expressway-E.
Understanding Scheduling Flow
This section describes what takes place when a CMR Hybrid is scheduled using the following:
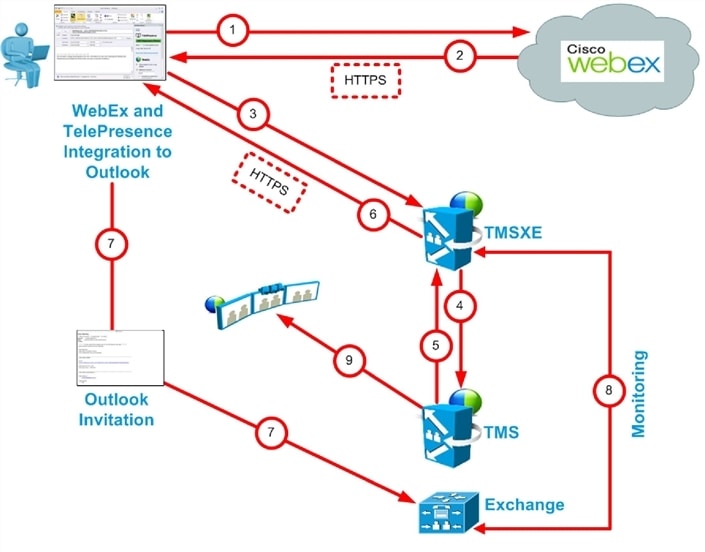
Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx and TelePresence Integration to Outlook
Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx Scheduling Mailbox
- Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx and TelePresence Integration to Outlook
- Scheduling with the Cisco Smart Scheduler
- Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx Scheduling Mailbox
- Differences When Scheduling TelePresence Conductor-Managed Bridges
Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx and TelePresence Integration to Outlook
Cisco WebEx and TelePresence Integration to Outlook Scheduling Flow
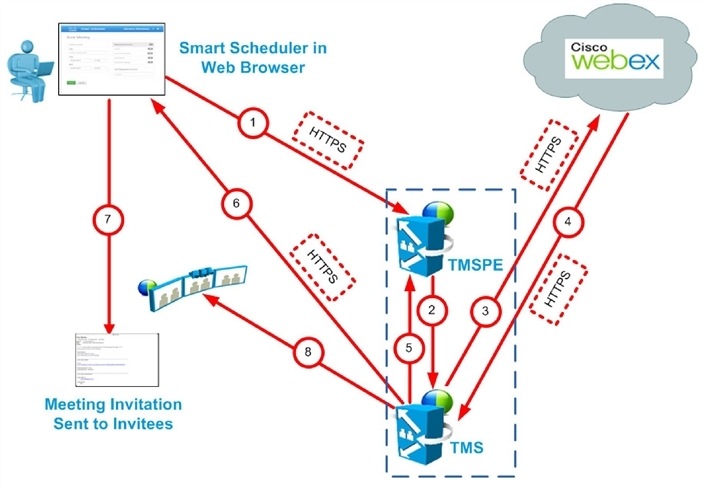
Scheduling with the Cisco Smart Scheduler
Cisco WebEx Smart Scheduler Scheduling Flow
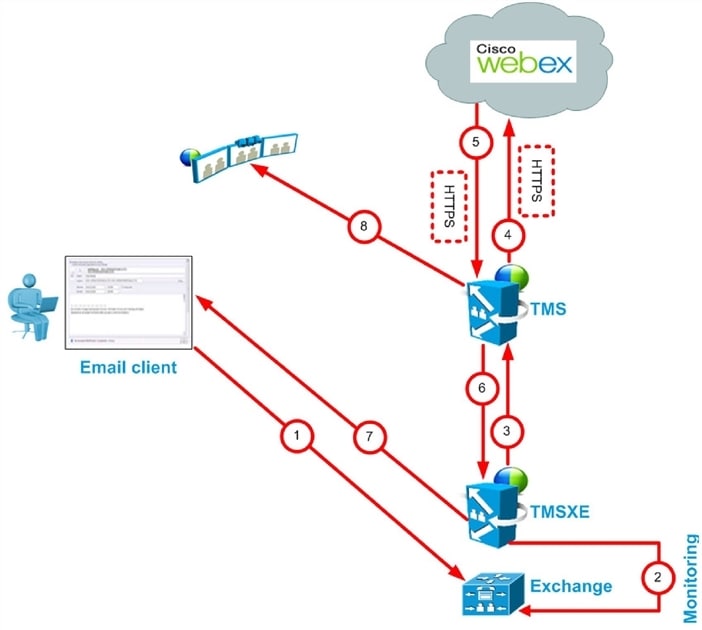
Scheduling with the Cisco WebEx Scheduling Mailbox
Cisco WebEx Scheduling Mailbox Scheduling Flow
Differences When Scheduling TelePresence Conductor-Managed Bridges
Before moving to a TelePresence Conductor scheduling deployment, note the following differences between scheduling direct-managed bridges and bridges managed by TelePresence Conductor.
Understanding Call Flow
This section describes the call flow of the following CMR Hybrid Meetings:
- SIP Audio Call Flow
- TSP Audio Call Flow with API Command to Unlock Waiting Room
- TSP Audio Call Flow with Waiting Room and MCU/TelePresence Server as Host
- WebEx Audio (PSTN) Call Flow
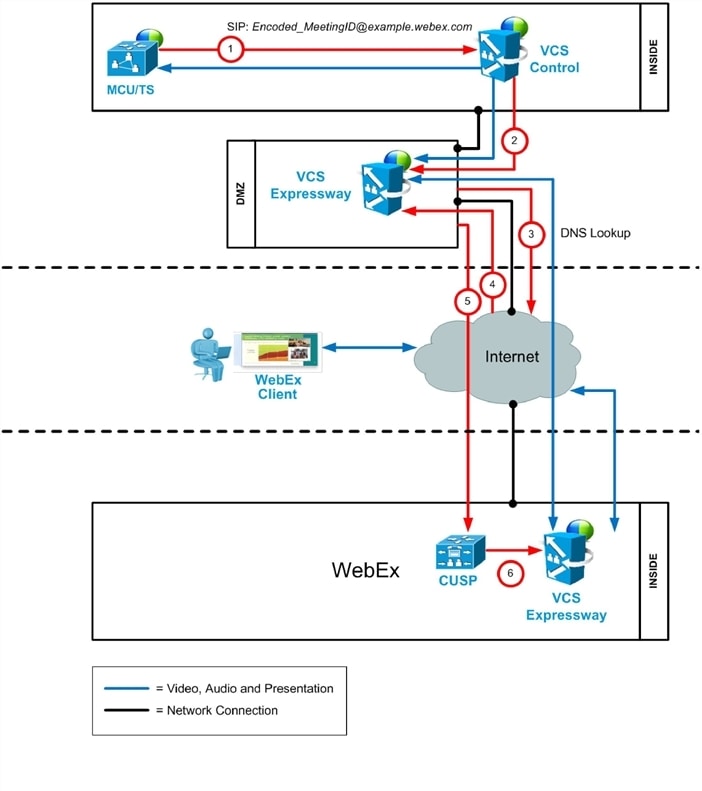
SIP Audio Call Flow
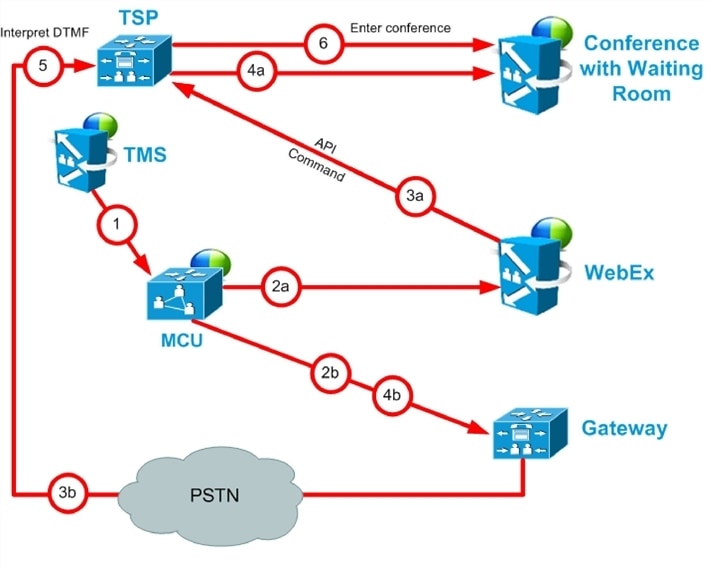
TSP Audio Call Flow with API Command to Unlock Waiting Room
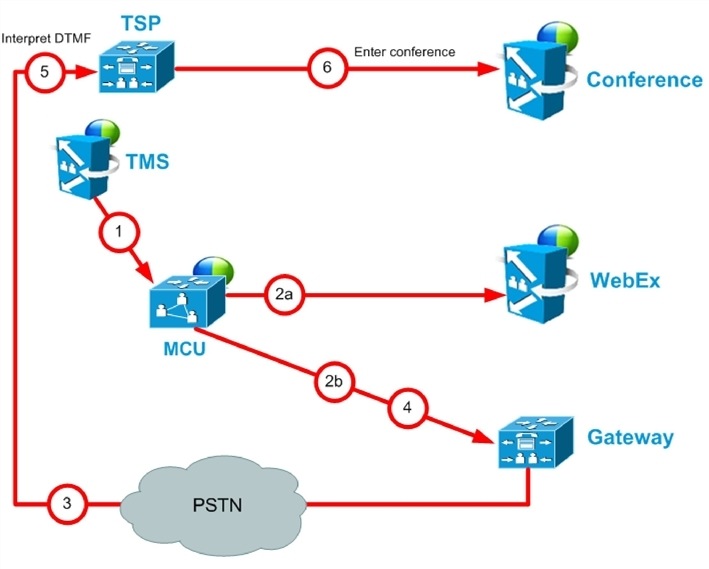
TSP Audio Call Flow with Waiting Room and MCU/TelePresence Server as Host
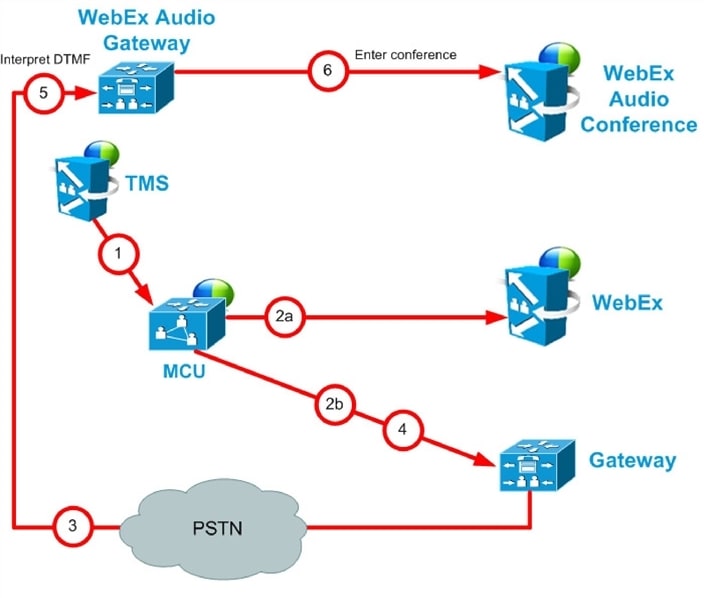
WebEx Audio (PSTN) Call Flow
Server and Site Access Checklist
Done |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Provided by the Cisco WebEx Account Team. Example: https://example.webex.com/example See Configuring the Cisco WebEx Feature in Cisco TMS for instructions. |
||
|
Hostname of WebEx site used by the customer. Provided by the Cisco WebEx Account Team. See Configure Cisco TelePresence Management Suite for instructions. |
||
|
Your unique address for accessing the Cisco WebEx Site Administration interface where you complete your initial Cisco WebEx setup configuration and manage and maintain your account after initial setup. This URL takes you directly to the WebEx Administration site. Provided by the Cisco WebEx Account Team. Example: https://example.webex.com/admin See Integrate Cisco TelePresence with a Cisco WebEx Site Administration Account for instructions. |
||
|
Cisco WebEx Site Administrator account username. Provided by the Cisco WebEx Account Team. See Integrate Cisco TelePresence with a Cisco WebEx Site Administration Account for instructions. |
||
|
(Optional) Certificate pair, including public certificate and private key from TMS |
Used to authenticate Cisco TMS to the WebEx cloud for meetings booked by users with WebEx accounts when Single Sign On (SSO) is enabled on TMS. When SSO is configured and a user schedules a WebEx-enabled meeting, the WebEx username in their Cisco TMS user profile is passed to the WebEx site to complete the booking. See Configuring Single Sign On in Cisco TMS for instructions. |
|
|
Because the call leg between the Cisco VCS Expressway and the WebEx cloud must be encrypted, . See Cisco Expressway and TelePresence Configuration Tasks and Configure Certificates on Cisco Expressway-E and Cisco VCS Expressway for instructions. |

 Feedback
Feedback