Restrictions for Dynamic ARP Inspection
-
Dynamic ARP inspection is an ingress security feature; it does not perform any egress checking.
-
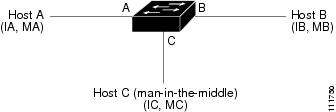
Dynamic ARP inspection is not effective for hosts connected to switches that do not support dynamic ARP inspection or that do not have this feature enabled. Because man-in-the-middle attacks are limited to a single Layer 2 broadcast domain, separate the domain with dynamic ARP inspection checks from the one with no checking. This action secures the ARP caches of hosts in the domain enabled for dynamic ARP inspection.
-
Dynamic ARP inspection depends on the entries in the DHCP snooping binding database to verify IP-to-MAC address bindings in incoming ARP requests and ARP responses. Make sure to enable DHCP snooping to permit ARP packets that have dynamically assigned IP addresses.
When DHCP snooping is disabled or in non-DHCP environments, use ARP ACLs to permit or to deny packets.
-
Dynamic ARP inspection is supported on access ports, trunk ports, and EtherChannel ports.

Note
Do not enable Dynamic ARP inspection on RSPAN VLANs. If Dynamic ARP inspection is enabled on RSPAN VLANs, Dynamic ARP inspection packets might not reach the RSPAN destination port.
-
A physical port can join an EtherChannel port channel only when the trust state of the physical port and the channel port match. Otherwise, the physical port remains suspended in the port channel. A port channel inherits its trust state from the first physical port that joins the channel. Consequently, the trust state of the first physical port need not match the trust state of the channel.
Conversely, when you change the trust state on the port channel, the switch configures a new trust state on all the physical ports that comprise the channel.
-
The rate limit is calculated separately on each switch in a switch stack. For a cross-stack EtherChannel, this means that the actual rate limit might be higher than the configured value. For example, if you set the rate limit to 30 pps on an EtherChannel that has one port on switch 1 and one port on switch 2, each port can receive packets at 29 pps without causing the EtherChannel to become error-disabled.
-
The operating rate for the port channel is cumulative across all the physical ports within the channel. For example, if you configure the port channel with an ARP rate-limit of 400 pps, all the interfaces combined on the channel receive an aggregate 400 pps. The rate of incoming ARP packets on EtherChannel ports is equal to the sum of the incoming rate of packets from all the channel members. Configure the rate limit for EtherChannel ports only after examining the rate of incoming ARP packets on the channel-port members.
The rate of incoming packets on a physical port is checked against the port-channel configuration rather than the physical-ports configuration. The rate-limit configuration on a port channel is independent of the configuration on its physical ports.
If the EtherChannel receives more ARP packets than the configured rate, the channel (including all physical ports) is placed in the error-disabled state.
-
Make sure to limit the rate of ARP packets on incoming trunk ports. Configure trunk ports with higher rates to reflect their aggregation and to handle packets across multiple dynamic ARP inspection-enabled VLANs. You also can use the ip arp inspection limit none interface configuration command to make the rate unlimited. A high rate-limit on one VLAN can cause a denial-of-service attack to other VLANs when the software places the port in the error-disabled state.
-
When you enable dynamic ARP inspection on the switch, policers that were configured to police ARP traffic are no longer effective. The result is that all ARP traffic is sent to the CPU.

 Feedback
Feedback